#Epidemiology and Communicable Diseases
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
do you think the covid situation will ever get any better or do you think it will be a few generations before high risk people can go outside without risking death again (unless climate change unleashes some more new deadly pathogens)
prior to covid, at-risk and disabled people were already being excluded from most public spaces by lack of accommodations, including lack of basic protection from communicable diseases. this is not just an epidemiological problem, but a design issue: as long as we remain a capitalist society that not only discounts but actively attempts to exclude and eliminate disabled people, we are going to see this type of hostile public space continue to proliferate, regardless of what happens with covid specifically. there are absolutely things we can do on a political level to mitigate the risk of disease transmission, which would allow many more disabled and at-risk people to exist in more public spaces; these are things we should have been doing prior to covid as well.
i'm not sure what the prospects are at this point in terms of controlling covid specifically. certainly ventilation, testing, masks, vaccines, &c should all be in wide use, but once something is endemic like this i'm honestly not well-researched enough on this to know what degree of disease control we could institute. i do think it's highly likely that we will see more pandemics within the next century, partly because pathogens always exist and partly because of factors like climate disruptions, poor sanitation, poverty, &c. which is all the more reason that, regardless of how covid continues to play out, we should not just sit around accepting the existence of public spaces that are inherently inaccessible to disabled and otherwise vulnerable people.
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
The funniest thing about the "covid is a hoax designed to control the masses" conservative conspiracy theory is that objectively it didn't control shit. 60% of the population obeyed health measures for about a year and then stopped bothering while the other half decided the government was lying to them and staged often violent protests over something as simple as being asked to wear a mask in public and stand six feet away from other people, the president of the United States at the time dismantled the previous administration's anti-pandemic countermeasures and actively encouraged the spread of the disease in the hopes that it would disproportionately affect the people most likely to vote against him, every measure intended to control the spread of covid received immediate and severe pushback from big business interests and people who thought getting a haircut was more important than preventing the spread of a deadly and highly-communicable disease that has killed millions worldwide, and a large percentage of the public took horse dewormer and attacked the medical doctors and scientists who have spent their entire careers studying epidemiology while at the same time insisting that getting vaccinated was somehow going to let Bill Gates control them through a 5G microchip or some shit. How, exactly, did covid allow the worldwide Illuminati government or whatever the fuck to further its control over the people?
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was reading a fic abt a hunter & a doctor trying to find a cure to an illnesses spreading during like the 17th century or smthing & the doctor was relying on epidemiology principles to solve the case in a time where ppl believed in witchcraft & nonsense. then the next day I walk into college & I get so fucking excited abt new communicable diseases course i felt so giddy & stupid oh my god
#AND THE PROF IS SO PASSIONATE & NICE TOO#sometimes medicine is tolerable . fun even#it makes u feel so human.#𝐏𝐄𝐀𝐂𝐇 ; ooc.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
the Standpoint of being "Chosen"
It is a journey into distortion to understand the positionality of Evangelicals and Zionists, and their ideological siblings in MAGA under Trump and Hindutva under Modi.
This is a positionality not often discussed in Standpoint Theory™️, which posits that all knowledge of the self and the world is informed by social position.
Black feminists like Patricia Hill Collins describe Standpoint™️ as the place where one finds themselves within a 'matrix of oppression'—an individual's standpoint is located at a unique nexus of the intersecting systems of race, gender, and class. When this standpoint is located outside of hegemony, you have a clearer vantage point of the cogs in the greater machine and the contours of these intersecting oppressive systems. From these standpoints, we can better see the violent churn of bureaucracy down to the interpersonal mechanisms of violence.
What happens, then, when the 'matrix of oppression' is replaced with a 'matrix of exceptionalism'? A matrix where entities believe that they sit at the centermost nexus of race, gender, and class systems, a standpoint nestled within hegemony rather than one thrown to a distal area from it. A matrix where the resulting standpoint is one of being "chosen."
Not just exceptional by ordinary standards, but "chosen": singularly "chosen" by God and Nation. Now that is a data validation conundrum.
How does this standpoint of being "chosen" understand equality, equity, or justice? Human rights or humanness itself?
When trying to understand this, I think to a scene from the miniseries Midnight Mass. The series follows a congregation "chosen" by an angel (sorta vampire?) that is now tasked to decide which church members should survive to see the New World Order. A show 100% about epidemiological investigation (ie new incidence of vampires), featuring communicable and zoonotic diseases.
The scene is Annie (neighborhood mom) speaking to Bev ("chosen" church leader, vampire) after much of the town has been sacrificed for the New World Order. Annie to Bev: God doesn't love you more than anyone else. You aren't a hero. And you certainly, certainly aren't a victim. Bev: I wouldn't lecture Annie Flynn. [...] (Gives a bitchy read of Annie's parenting skills because her sacrificed* son killed a child during a DUI.) Annie: And God loves him. Just as much as He loves you, Bev. Why does that upset you so much? Just the idea that God loves everyone just as much as you. (Get her Jade!)
In the 'matrix of exceptionalism,' how does one conceptualize love from God and Nation? God and Nation can certainly love beings that aren't equal to the "chosen." God and Nation can certainly love them less. The love itself does not have to be equal.
Meanwhile, in the 'matrix of oppression':


*see above
All this to say: those of us scattered across the 'matrix of oppression' can look at hegemony and have an outside vantage point of the Master's House™️ per se (coined by Audre Lorde).
I believe that those inside the Master's House are scattered across the 'matrix of exceptionalism.' Nestled within hegemony, they have a proximity to something else.
And perhaps through a keyhole, a crack in the door, a few inches between the window pane and sill, we on the outside see what it is:
The Cuckoo Clock in Hell™️
This is how Kurt Vonnegut describes the innermost mind of the far-right in his 1961 book Mother Night. This mind is a machine so fundamentally broken, random, and pointless, that it functions only enough to simply keep its shoddy machinery operating and whirling.
Ostensibly able to 'make the trains run on time,' but always in a super fucked up way.*
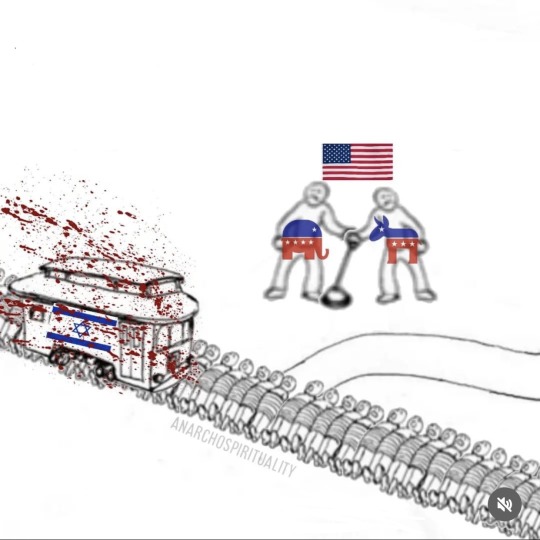
*see above
In Vonnegut's words:
I have never seen a more sublime demonstration of the totalitarian mind, a mind which might be linked unto a system of gears where teeth have been filed off at random. Such snaggle-toothed thought machine, driven by a standard or even by a substandard libido, whirls with the jerky, noisy, gaudy pointlessness of a cuckoo clock in Hell. [...] [The far-right] wasn't completely crazy. The dismaying thing about classic totalitarian mind is that any given gear, thought mutilated, will have at its circumference unbroken sequences of teeth that are immaculately maintained, that are exquisitely machined. Hence the cuckoo clock in Hell - keeping perfect time for eight minutes and twenty-three seconds, jumping ahead fourteen minutes, keeping perfect time for six seconds, jumping ahead two seconds, keeping perfect time for two hours and one second, then jumping ahead a year. The missing teeth, of course, are simple, obvious truths, truths available and comprehensible even to ten-year-olds, in most cases. The willful filing off of gear teeth, the willful doing without certain obvious pieces of information - [...] That was how my father-in-law could contain in one mind an indifference toward slave women and love for a blue vase - That was how Rudolf Hess, Commandant of Auschwitz, could alternate over the loudspeakers of Auschwitz great music and calls for corpse-carriers - That was how Nazi Germany could sense no important difference between civilization and hydrophobia - That is the closest I can come to explaining the legions, the nations of lunatics I've seen in my time.”

^^ a cuckoo clock, not pictured in hell
In respect to Black Lives Matter, Trans Rights, and Palestine, those of us glimpsing inside the Master's House through a keyhole or opening have seen the faces of friends, family, and community members in there.
More often than not, I see white queers speaking Zionist rhetoric while staring directly into the Cuckoo Clock in Hell™️ --
They agree with it. On the same day pro-Palestine protestors shut down the Brooklyn Bridge, Manhattan Bridge, Williamsburg Bridge, and Holland Tunnel using ACT UP's 1995 "bridges and tunnels" protest techniques. On the same day over 400 persons were arrested for this act of defiance. On the same day ACT UP NY announced fully-funding bus tickets for the ACT UP block going to the January 13th March on Washington.
I see white queers agree with the Cuckoo Clock in Hell™️ and listen to its dissonant whirling. To them, I want to ask: Why do you feel so safe inside the Master's House? You will eventually be evicted, displaced, and discarded. Do you actually believe you are "chosen," a credit to your kind?
When I think of Palestine as a Standpoint™️, I think of what the Castro district of San Francisco, CA has come to mean for queers across the nation (and even globally).
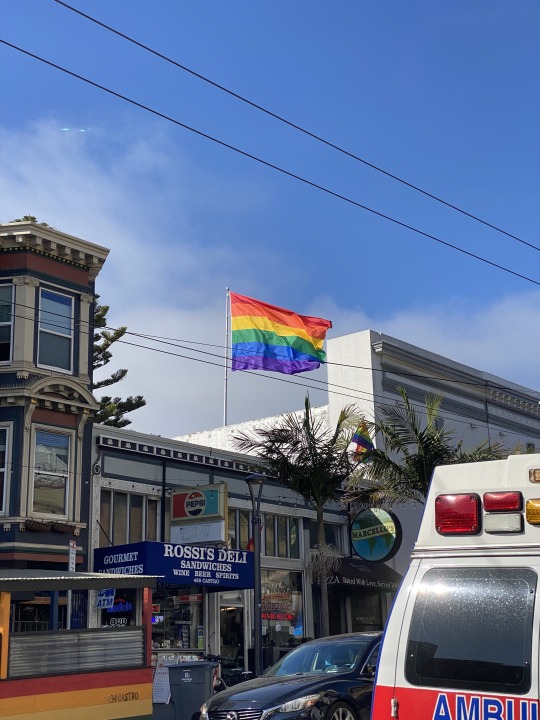
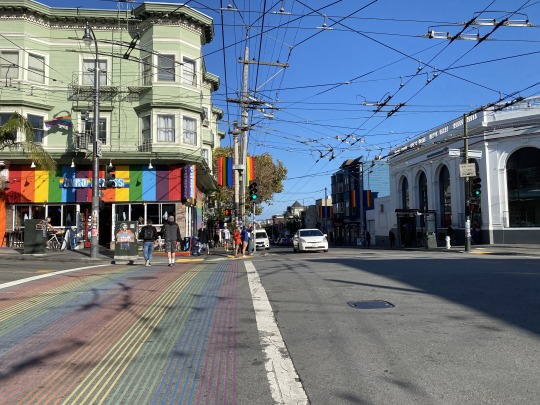


^^ photos taken by me, 2023
When you're in the Castro, you know you're in Castro-- Rainbow crosswalks, rainbow banners on lampposts, a historic 'rainbow walk' with plaques dedicated to famous LGBTQ+ figures, and a giant rainbow flag (20ft x 30ft) flying over Harvey Milk Plaza.
The SF AIDS Foundation has a beautiful multi-story wellness center serving the community. The historic Twink Peaks Tavern sits atop Castro St.; its large panoramic windows were uncovered in 1973, making it the first gay bar to stop hiding its patrons from the public.
The graffiti says 'Protect Trans Kids' and 'Dykes Hate Techies.' There is an ease around queer public displays of affection and sexuality. The Castro 'Welcome Center' plays Kim Petras' album Slut Pop over the sound system.
youtube
The historic Castro theatre visually distinguishes the neighborhood's main drag from anywhere else.
Harvey Milk's old photo shop is now an art space called Queer AF.
Dildos are in a fair amount of store windows. And you will probably pass a nudist on your morning coffee run.
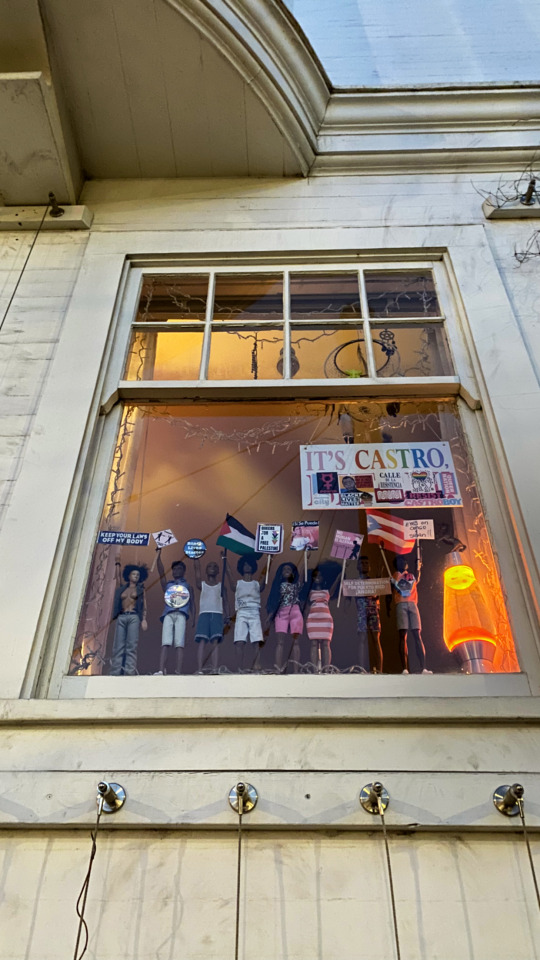
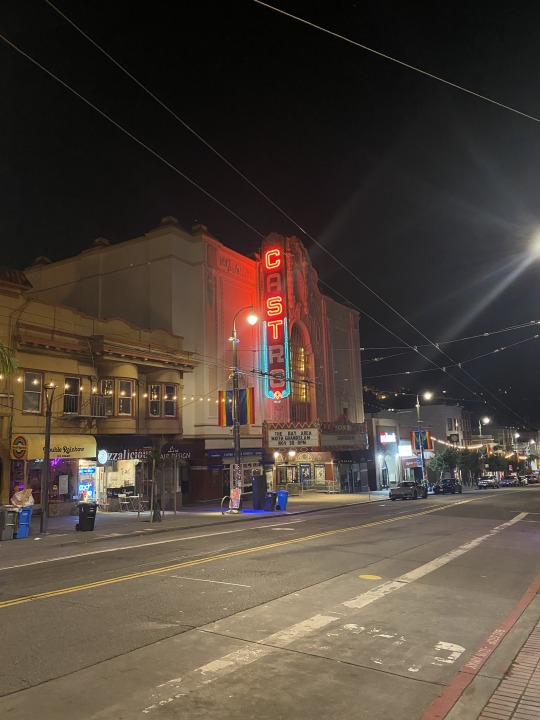


^^ photos taken by me, 2023
The Castro's response to Palestine was immediate and visible.
After Israel's retaliation to Hamas' October 7th attack had begun, Palestinian flags went up in storefronts. Sandwich boards said 'Free Gaza' and 'Let Gaza Live.' Messages of solidarity were written on printer paper and taped to windows. Residents hung Palestinian flags out of their apartment windows. We marched to the Civic Center.
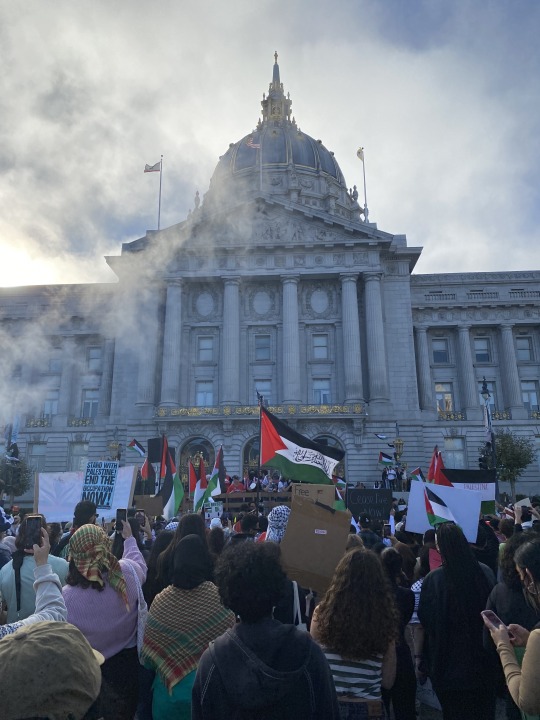

^^ photo taken by me, 2023
And so, when I see white queers parroting the Cuckoo Clock in Hell™️, I want to ask: What would it mean for the queers of Castro to become forcibly displaced?
Would it be a stretch of the imagination for windows to be broken, residents to be threatened, stores to be trashed, or pedestrians to be beaten? Would it be a stretch of the imagination for the few franchises among the queer-owned local businesses to pull out of the neighborhood with enough political pressure?
What if you heard that queer residents on the outer blocks of Castro had their homes bricked. They left in fear. The city quickly seized the property. Squatters and developers moved in. The violence may move inwards towards the heart of the neighborhood.
Now more people want these dykes, fags, trannies, groomers, pedophiles, and perverts out of here.
And they found a system for doing so.


^^ graphic design is their passion
So let's just stop here. This is the most benign level of forced displacement. This will not create refugees or a humanitarian crisis. This isn't even on par with raiding gay bars like in the good ol' days.
This isn't police beating up queers in the street or arresting them for now being 'unwanted traffic' in public space. This isn't vigilantes telling "the queers" to get out of their homes and businesses at gunpoint. This isn't throwing all of your belongings out of the window and into the street.
This isn't making flying the LGBT flag illegal.
This isn't tearing down the sign for Harvey Milk Plaza.
This isn't defacing the Castro Theatre.
This isn't even a loss of life.
This isn't even war.
I want to posit this to all the white queers fixated on the Cuckoo Clock in Hell™️. I want to ask why they feel safe from state violence that, given the current anti-LGBTQ+ landscape, is only one move of the needle away.
When you are no longer "chosen," how will you return to and face your community again? And better yet: can you? We protect us, after all.
This article is dedicated to you.

#kurt vonnegut#mother night#anti war#anti zionisim#antisemitic#antisemitism#colonization#ethics#free gaza#lgbt#lgbtq rights#lgbtq community#lgbt pride#lgbtq#castro district#san francisco#refugees#displacement#fuck maga#trump indictment#fuck modi#fuck trump#fuck israel#fuck evangelicals#midnight mass#rahul kohli#larry kramer#act up#activism#human rights
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Cultural Capital of AngloWest Africa - Ghana 🇬🇭
Ghana in 2021, the estimated population of Ghana is approximately 31.4 million people. The country has a relatively young population, with approximately 57% of the population under the age of 25. The population is also growing rapidly, with an annual population growth rate of 2.15%.

The ethnic composition of Ghana is diverse, with over 100 different ethnic groups. The largest ethnic group is the Akan, who make up around 47% of the population. Other significant ethnic groups include the Mole-Dagbon, Ewe, Ga-Adangbe, and Gurma.
The official language of Ghana is English, but there are many other languages spoken throughout the country, including Akan, Ewe, and Twi. The majority of the population is Christian, with approximately 71% of Ghanaians identifying as Christian. There is also a significant Muslim population, making up around 18% of the population, and a smaller population of traditional African religion practitioners.
Ghana has a relatively high urbanization rate, with approximately 56% of the population living in urban areas. The capital city, Accra, is the largest city in Ghana, with a population of over 2.2 million people. Other major cities in Ghana include Kumasi, Tamale, and Sekondi-Takoradi.

The median age in Ghana is approximately 21 years, and the life expectancy at birth is around 65 years. The literacy rate in Ghana is relatively high, with approximately 76% of the population over the age of 15 being able to read and write.
Major Health Conditions
Most prevalent health conditions in Ghana include:
Malaria: Malaria is a major public health problem in Ghana, accounting for approximately 29% of all outpatient visits, 25% of all admissions, and 22% of all deaths.
Acute Respiratory Infections (ARI): ARI is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in Ghana, particularly among children under five years old.
Diarrheal Diseases: Diarrheal diseases are common in Ghana, with an estimated 13% of deaths in children under five years old attributed to diarrhea.
Tuberculosis (TB): TB is a major health problem in Ghana, with an estimated 14,000 new cases reported in 2020.
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs): NTDs, including schistosomiasis, lymphatic filariasis, and onchocerciasis, are endemic in Ghana and affect millions of people.
Non-communicable Diseases (NCDs): NCDs, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer, are on the rise in Ghana due to changing lifestyles and increasing urbanization.
Acne or Pimple or Blemish
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, including those living in Ghana. However, there is limited research available on the prevalence and epidemiology of acne and pimples in Ghana specifically.
One study conducted in Ghana in 2019 examined the prevalence of acne and associated risk factors among students at a tertiary institution. The study found that the overall prevalence of acne was 59.5%, with females being more affected than males. The study also identified several risk factors for acne, including stress, family history, and certain dietary habits.
Another study conducted in 2017 investigated the prevalence of acne and its impact on the quality of life of Ghanaian students. The study found that 67.9% of the participants had acne, and that acne significantly impacted their quality of life in terms of social interactions and self-esteem.
Overall, while limited research exists on the prevalence and epidemiology of acne and pimples in Ghana, available studies suggest that acne is a relatively common skin condition among Ghanaians, particularly among young people. Further research is needed to better understand the epidemiology and impact of acne in Ghana and to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.

Acid Reflux - The sour fluid
Studies have reported a high burden of gastrointestinal (GI) diseases in sub-Saharan Africa, including Ghana. According to a systematic review published in 2016, the most common GI disorders in sub-Saharan Africa are infectious diarrhea, helminth infections, and viral hepatitis, among others.
Furthermore, a study published in the West African Journal of Medicine in 2010 reported that upper GI symptoms, including heartburn and acid regurgitation, were prevalent among Ghanaians. The study also found that the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) was a significant risk factor for upper GI symptoms.
Another study published in the Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Research in 2018 reported a high prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) among Ghanaians. The study found that IBS affected 20.7% of the study participants and that females were more affected than males.
Studies suggest that digestive problems are prevalent in Ghana. The most common GI disorders in Ghana are infectious diarrhea, helminth infections, and viral hepatitis. Upper GI symptoms and IBS are also prevalent in Ghana.

Loving thyself is paramount
Male libido problems are not unique to Ghana, as they affect men all over the world. However, there are certain factors specific to Ghana that may contribute to male libido problems, including cultural and societal norms, access to healthcare, and lifestyle factors.
In Ghana, there is a cultural emphasis on masculinity and sexual prowess, which can lead to feelings of shame or inadequacy for men who struggle with low libido. This can make it difficult for men to seek help or talk openly about their issues.
Access to healthcare can also be a barrier for men in Ghana who are experiencing libido problems. Some men may not have access to medical facilities or trained healthcare professionals who can provide appropriate treatment.
Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and high levels of stress can also contribute to male libido problems in Ghana. These factors can lead to issues such as obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure, which are all risk factors for low libido.
To address male libido problems in Ghana, it is important to address these underlying factors. This may involve promoting a more open and accepting attitude towards male sexual health, increasing access to healthcare services, and encouraging healthy lifestyle behaviors. Additionally, healthcare providers can offer treatments such as counseling, medication, and lifestyle interventions to help men overcome their libido problems.

The Size of Prize
The pharmaceutical industry in Ghana has been growing steadily over the years. According to a report by the Ghana Investment Promotion Centre (GIPC), the industry's value was estimated to be around $630 million in 2019, with an annual growth rate of 6.8%. The government of Ghana has been implementing policies to promote the development of the pharmaceutical industry, with the aim of achieving self-sufficiency in drug production.
The pharmaceutical industry in Ghana can be categorized into the following products:
Generic drugs: These are drugs that are not branded and are marketed under their chemical names. They are cheaper than branded drugs and are essential in providing affordable healthcare.
Branded drugs: These are drugs marketed under a brand name and are usually more expensive than generic drugs. They are protected by patents, which give the manufacturer exclusive rights to produce and market them.
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs: These are drugs that can be bought without a prescription from a healthcare provider. They are usually used to treat common ailments such as headaches, colds, and coughs.
Medical devices: These are instruments, machines, and apparatus used to diagnose, treat, or prevent disease.
The Ghanaian pharmaceutical industry is dominated by local manufacturers who produce generic drugs, with only a few multinational companies operating in the country. The government of Ghana has been implementing policies to promote the development of the pharmaceutical industry, including tax exemptions and incentives for local manufacturers. The industry is also regulated by the Food and Drugs Authority (FDA).
Nature Offers More
The herbal over-the-counter (OTC) products market in Ghana is a significant segment of the country's healthcare industry. Ghana has a rich tradition of herbal medicine, and many Ghanaians rely on traditional herbal remedies to treat various health conditions. The demand for herbal OTC products has been increasing in recent years due to a growing interest in natural and alternative medicine.
Some of the commonly used herbal OTC products in Ghana include herbal teas, capsules, powders, and creams. These products are made from a variety of herbs and plants, such as aloe vera, ginger, neem, moringa, and turmeric. They are marketed as remedies for a range of ailments, including digestive disorders, skin conditions, and respiratory problems.
The herbal OTC products market in Ghana is largely unregulated, and many of these products are sold without proper quality control or safety testing. However, the Ghana Standards Authority has established guidelines for the manufacture, labeling, and packaging of herbal products to ensure quality and safety.

The market for herbal OTC products in Ghana is highly competitive, with many small-scale producers and distributors. However, some larger companies have entered the market, such as Phyto-Riker Pharmaceuticals and Ernest Chemists Limited, which have established themselves as leading manufacturers and distributors of herbal products in Ghana.
Overall, the herbal OTC products market in Ghana is growing, driven by a strong demand for natural and traditional remedies.
The Access Points
There are various distribution channels for over-the-counter (OTC) and fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) products. Some of these distribution channels include:
Traditional Trade: This involves the use of small independent retailers such as mom-and-pop stores, kiosks, and corner shops. They are typically located in residential areas and are convenient for consumers to access.
Supermarkets/Hypermarkets: These are larger stores that offer a wider range of products and are typically located in commercial areas or shopping malls.

Pharmacies and Drug Stores: These are stores that specialize in the sale of pharmaceutical and healthcare products. They are typically located in urban areas and are often frequented by consumers seeking OTC products.

Direct Selling: This involves the use of a network of independent distributors who sell products directly to consumers. This method is commonly used for products such as cosmetics and personal care items.

Online Retail: With the rise of e-commerce, online retail has become an increasingly popular channel for the distribution of OTC and FMCG products. Online marketplaces such as Jumia, Konga, and Jiji have become prominent players in the Ghanaian retail market.
Wholesalers and Distributors: These are companies that buy products in bulk from manufacturers and sell them to retailers. They are often used by manufacturers to reach a wider market.
The distribution channels for OTC and FMCG products in Ghana are diverse, ranging from traditional trade to online retail. Manufacturers often use a combination of these channels to ensure their products are widely available to consumers.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The projected burden of non-communicable diseases attributable to overweight in Brazil from 2021 to 2030

Although studies have quantified the current burden of diseases attributable to overweight and obesity in Brazil, none have estimated its burden in the future. The study aimed to estimate the potential impact of different scenarios of changes in the prevalence of overweight on non-communicable diseases (NCD) in the Brazilian adult population until 2030. We developed a multistate life table model including 11 body mass index (BMI) related diseases to estimate attributable NCDs cases and deaths under the following scenarios of changes in overweight over a 10-year simulation: (1) the continuity of the current trajectory of BMI increases, (2) reducing the rate of increase by half, (3) stopping future BMI increases, and (4) the reduction of the prevalence of overweight by 6.7%. In Brazil, if the current trends of BMI increase are maintained from 2021 to 2030, approximately 5.26 million incident cases and 808.6 thousand deaths from NCDs may occur due to overweight. If the annual increase in overweight was reduced by half until 2030, 1.1% of new NCD cases and 0.2% of deaths could be prevented (respectively, 29,600 cases and 1900 deaths). Alternatively, if the current prevalence of overweight is maintained, as set as a national goal in Brazil until 2030, the incident NCD cases and the deaths could be reduced by respectively 3.3% (92,900) and 1.5% (12,100) compared to continuation of current trends. If the prevalence of overweight is reduced by 6.7% until 2030, 6.5% (182,200) of NCD cases and 4.2% (33,900) of deaths could be prevented. The epidemiologic burden of overweight in Brazil tends to increase if bold policy interventions are not adopted in Brazil.
Read the paper.
#brazil#science#epidemiology#brazilian politics#politics#mod nise da silveira#image description in alt
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
SkepTalk: Origins of the COVID-19 Pandemic
If we don’t understand the origins of SARS-CoV-2 and the COVID-19 pandemic, we won’t understand the risks that could lead to future viral emergence events and pandemics. I will discuss the multitude of scientific lines of evidence relevant to this topic, including epidemiological and evolutionary data. Analyses of these data reveal overwhelming evidence of a zoonotic origin. About the Speaker: Michael Worobey is a Professor and the Head of the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of Arizona. Originally from British Columbia, he received his Ph.D. from the Department of Zoölogy at the University of Oxford, in 2001, where he was a Rhodes Scholar. He uses the genomes of viruses to trace the evolution of major communicable diseases and to understand their origins, emergence and control. He has made seminal discoveries pinpointing where, when and how HIV originated and spread worldwide, and how pandemics like the 1918 ‘Spanish flu’ and COVID-19 have emerged and killed large numbers of people. His work is regularly published in respected journals such as Nature and Science and is the subject of multiple books and films, including Spillover and Rise of the Killer Virus.
1 note
·
View note
Text

The course aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of communicable diseases, their prevention, diagnosis, and management. It covers epidemiology, transmission patterns, control measures, and public health policies.Readmore
#docthub#communicablediseases#infectiousdiseases#publichealth#healthcare#certificate#course#training#epidemiology#diseasecontrol
0 notes
Text
Nigerian Science: Nurturing Innovation and Advancement

Nigeria, a country rich in cultural diversity and natural resources, is also making significant strides in the field of science and technology. Despite facing challenges such as infrastructure limitations and funding constraints, Nigerian scientists, researchers, and innovators are actively contributing to global scientific knowledge and technological advancements. This article explores the landscape of Nigerian science, highlighting key areas of research, notable achievements, challenges faced, and future prospects.
Historical Context and Development
The history of scientific inquiry in Nigeria dates back to pre-colonial times, where indigenous knowledge systems flourished in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and metallurgy. With colonization came the introduction of Western education and scientific practices, laying the groundwork for formal scientific institutions.
Post-independence, Nigeria witnessed the establishment and growth of universities, research institutes, and government agencies dedicated to scientific research. The Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (now known as the Federal Institute of Industrial Research, Oshodi, FIIRO) and the Nigerian Institute for Oil Palm Research (NIFOR) are among the pioneering institutions focused on applied research.
Key Areas of Research
Health and Medicine: Nigerian scientists are actively engaged in research on infectious diseases (such as malaria, HIV/AIDS, and tuberculosis), non-communicable diseases, traditional medicine, and public health interventions. Collaborative efforts with international partners have led to breakthroughs in vaccine development and epidemiological studies.
Agriculture and Food Security: Given Nigeria’s agrarian economy, research in this area focuses on crop improvement, soil fertility, irrigation techniques, and pest management. Institutions like the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) play a crucial role in agricultural research and development.
Energy and Environment: Renewable energy sources, environmental conservation, and climate change adaptation are growing areas of interest. Nigerian scientists are exploring solar, wind, and biomass energy solutions, as well as strategies to mitigate the impact of environmental degradation.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT): With a burgeoning tech industry, Nigeria is becoming a hub for ICT innovation. From mobile app development to cybersecurity and artificial intelligence (AI), Nigerian tech entrepreneurs and researchers are making significant strides.
Notable Achievements
Nigerian scientists have achieved several milestones that have garnered international recognition:
Dr. Philip Emeagwali, a computer scientist and mathematician, is known for his work on the development of the supercomputer.
Prof. Francis Mojica, of Nigerian descent, contributed to the discovery of CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology.
NigeriaSat-1, the first satellite developed by Nigerians, was launched in 2003, marking a significant achievement in space technology.
Challenges
Despite these achievements, Nigerian science faces numerous challenges:
Funding: Insufficient funding for research and development limits the scale and impact of scientific initiatives.
Infrastructure: Inadequate laboratory facilities, unreliable electricity supply, and limited access to high-speed internet hinder research efforts.
Brain Drain: Many talented Nigerian scientists migrate to developed countries in search of better opportunities and resources.
Future Prospects
To address these challenges and capitalize on opportunities, several initiatives are underway:
Government Support: Increased funding allocation to research and development, and policies to support innovation and entrepreneurship.
Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships between universities, research institutions, and industry to foster innovation and knowledge transfer.
Capacity Building: Investing in science education and training programs to develop a skilled workforce.
Conclusion
Nigerian science is on a trajectory of growth and innovation, driven by the dedication and resilience of its scientists and researchers. Despite challenges, the country continues to produce groundbreaking research and technological advancements that contribute to global scientific knowledge and socio-economic development. With strategic investments, supportive policies, and collaboration, Nigeria is poised to further elevate its position in the global scientific community and address pressing societal challenges through science and technology.
0 notes
Text
The Career Guide to Pursuing a Master of Public Health [MPH] Course in 2024
Hey, do you recall any of those maxims we had to live by, including hand washing and social distancing? That is public health in practice. It is about maintaining the health of different communities, minimizing the incidence rates, and ensuring adequate and effective treatment for the people. Professionals in the context of public health may be compared to health superheroes, and the world indeed needs more of those.
Thinking of MPH Course?
So, you want to study public health and help society? Awesome! This article will guide you on how to navigate the world of choices in the Master of Public Health (MPH) course in the calendar year 2024.
Overview of the Importance of Public Health
Public health is a significant area of study that deals with the promotion of health and the prevention of diseases in societies. The significance of public health has attained an all-time high in the current world that is so connected. In addition to informing the communities concerning various diseases such as COVID-19, which is a global pandemic, chronic diseases, and differences throughout the world in relation to health, among others, public health practitioners are critical in shielding society.
Purpose of the Guide
This practical roadmap is designed to equip prospective students and professionals with relevant information on how to pursue a Master of Public Health (MPH) in 2024. This article offers details on the program's information, program admission, the available career opportunities, and the program's future prospects.
Who Should Consider a Master of Public Health (MPH)?
An MPH should be pursued by persons desiring to have a positive influence on the health of communities. This includes postgraduate learners in health-related fields, health care providers who wish to expand their area of practice, and other learners from other disciplines interested in health care.
Understanding the MPH Course
What is a Masters in Public Health (MPH Course)?
An MPH is an academic degree that one attains after acquiring a basic degree; it is a postgraduate degree that prepares students to solve health issues affecting large populations. This consists of several branches: epidemiology, biostatistics, health sector operations research, and environmental health.
History and Evolution of Public Health Education
The history of public health education dates back to the nineteenth century, with an emphasis on sanitation and control of communicable diseases, but today we have a wholesome approach to several health factors. The MPH course has evolved over the years in an attempt to include new threats to health and new technologies.
Core Disciplines within Public Health
Epidemiology
Biostatistics
Environmental Health Sciences
Health Policy and Management
Social and Behavioral Sciences
Benefits of Pursuing an MPH
Career Opportunities and Job Market Trends
An MPH creates opportunities for working with governmental bodies, non-profit organizations, healthcare facilities, and research institutes. Employment opportunities are expected to increase for these professionals in the near future due to advancing interest in health promotion and the worldwide emphasis on disease prevention.
Impact on Community and Global Health
Masters in Public Health enable graduates to change people's lives by practicing and designing health programs, performing research, and influencing the policies that govern entire societies' health.
Personal and Professional Growth
Earning an MPH enhances critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and health systems analysis skills among the students. This also includes client contacts, which enable one to network and the opportunity to be associated with different groups of people, which is personal and professional growth.
Master of Public Health (MPH) Course Details
MPH at SGT University is a two-year full-time postgraduate program designed to teach skills and knowledge on public health research, policy and practice, including core disciplines like epidemiology, biostatistics, health policy and management, environmental health, socio-behavioral sciences and field-based research, while focusing on applied learning through practical or list projects that could address today's public health challenges.
Here, the eligibility criteria is a graduate degree in health sciences or related fields with a minimum 55% marks; the intake capacity is 10 students per year; the fee structure is INR 1,25,000/- per annum; and the course contents include Introduction to Public Health, Epidemiology, Demography, Health Policy, Nutrition and Health, Environmental Health Science and many other subjects.
Why Study Master in Public Health?
Studying an MPH empowers you to help solve some of the world's most pressing health challenges and shape policies that advance the well-being of diverse populations. Thus, it is an appropriate option for people willing to make a greater impact on society.
Who should do a Masters in Public Health?
Medical workers seeking to increase their sphere of influence
Youth with diplomas in health sciences, social sciences or any related qualifications
Health care providers for those who wish to change their career and join the health sector
Those interested in closing the gap of differences existing between the underserved populace and the healthcare they receive.
Masters in Public Health: Admission Procedure
Masters in Public Health: Eligibility Criteria
Ideally, the candidates should have a bachelor's degree in the specific area of operation or related line of work. An applicant with a colorful educational background can be considered for some programs, provided he or she shows a great passion for public health.
Masters in Public Health: Admission 2024
Gives detailed information about the course in public health. Here are the key details about the Masters in Public Health Admissions (MPH) course admission at SGT University Gurgaon, India.
Admission Process: Masters in Public Health
Candidates must have passed a graduate degree in any branch of health science, allied health science, life sciences, statistics, biostatistics, demography, population studies, nutrition, sociology, psychology, anthropology or social work from any university or institute recognized by the university.
The minimum total percentage to graduate for students is 50%.
A student does not have to sit for any entrance exam, as admissions are merit-based. The method of application is online; this can be done through the university website.
Masters in Public Health: Course Details
The MPH course that is offered at SGT University is a two-year full-time degree course.
The fee structure for a year is INR 1,25,000, which is for a two-year' program.
A total of 10 seats are offered.
Masters in Public Health: Career Prospects
The MPH course graduates may seek jobs in government health departments, non-government organizations, international health organizations, research organizations, and health facilities.
Some of the organizations in which MPH graduates from SGT University were placed are Amazon, Amul, Artemis Hospital, Essar Steel, L&T Infotech, Medanta, Microsoft, Nestle, Parle Agro, and others.
The program on Master of Public Health being offered at SGT University's Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, which is ranked among the top medical colleges in Haryana and Delhi NCR, will instill in the students a strong base of knowledge on public health and guide them towards the different career paths available for graduates in this field. The admissions procedure is quite selective and the program has the best infrastructural facilities and faculty members.
MPH Subjects and Syllabus
Core Subjects and Specializations
Principles of Epidemiology
Biostatistics
Environmental Health
Health Policy and Management
Social and Behavioral Sciences in Public Health
MPH Specializations
Global Health
Health Policy
Epidemiology
Environmental Health
Health Promotion and Communication
Top Colleges for Master of Public Health in India
SGT University is a top college for pursuing a Master of Public Health (MPH) degree in India.
SGT University, The best university in Haryana, Delhi NCR, Gurugram, and India. The University is one of the Top Colleges for Master of Public Health in India. requires its students to go through a strict curriculum that is handled by experienced faculty and whose emphasis is on practical learning.
Why Choose SGT University?
Choosing SGT University for an MPH course in 2024 offers several compelling reasons, particularly when considering its Faculty of Medical & Health Sciences:
Accomplished staff members with real life field exposure
Modern utility and laboratory services
Internship and training affiliation with the particular industry
Curriculum that aligns with the international standards of public health.
Selecting SGT University is a perfect decision for starting an MPH course in 2024 because the faculty with a great experience, strong material base, and numerous career-related prospects are crucial for students in the constantly evolving sphere of public health and medicine.
Career Paths with an MPH
Government and Public Sector Jobs
Public Health Officer
Health Policy Advisor
Epidemiologist in public health departments
Non-Profit and Non-Governmental Organizations
Program Manager for health initiatives
Community Health Educator
International Health Consultant
Healthcare Administration and Management
Hospital Administrator
Health Services Manager
Quality Improvement Specialist
Research and Academia
Public Health Researcher
University Professor
Health Data Analyst
Corporate and Private Sector Opportunities
Corporate Wellness Program Manager
Pharmaceutical Research Consultant
Health Insurance Analyst
Skills and Competencies Gained from an MPH
Analytical and Research Skills: MPH course establishes abilities in analyzing data, methods of research, and the ability to assess any health intervention.
Communication and Advocacy: In more detail, the learners are able to formulate and disseminate health information, promote balanced health policies, and promote health programs.
Leadership and Management: It comprises MPH Subjects such as leadership development, project management and planning of strategic health activities.
Ethical and Cultural Competency: The acquisition of strong ethical standards and cultural competence is vital when dealing with people.
The Future of Public Health
The future of public health in India holds immense potential for transformative advancement, driven by the adoption of digital technologies and a focus on addressing key challenges:
Emerging Trends and Technologies: Another trend identified for future development of public health is the use of new technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence, and digital health.
Global Health Challenges and Solutions: Global climate change, infectious diseases, those that are newly detected, and other diseases that are not communicable will remain priorities of the public health workers in the future.
The Role of Public Health Professionals in a Post-Pandemic
Public health workers are helpful when it comes to preventing and managing outbreaks of diseases that affect the population, such as the current COVID-19 outbreak. Their key responsibilities include:
Epidemiology and Disease Surveillance
Health Education and Promotion
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Research and Innovation
The events of the COVID-19 pandemic have shown how necessary it is to have a solid and adequately financed public health system. In the future, public health professionals will serve a major role in reconstructing stronger and more capable public health systems in order to deal with future health crises.
Conclusion
The Master of Public Health (MPH) degree at SGT University, the best university in Haryana, Delhi NCR, Gurugram, and India, provides various opportunities to elevate the profession of public health students as graduates. The MPH Subjects are strong, and they include most of the core disciplines of public health. The variety of MPH specializations offered by SGT University guarantees the students and all rounded training in public health.
The MPH admission process of SGT University for session 2024 has been structured to be as simple as possible, where no separate MPH entrance test is to be given and the MPH eligibility criteria are well defined. The SGT University Master of Public Health (MPH) course provides students with a future oriented and more practical-based curriculum that blends academic knowledge with real applications
Key Points of Master of Public Health in 2024
Comprehensive MPH Subjects: Bulk of the Master of Public Health (MPH) program at SGT University includes foundational public health core competencies and concentration areas.
Career-Focused Education: One of the features of the MPH course is that it is focused on the variety of public health professions and the modern issues of the global health.
Flexible Admission Process: The MPH admission process 2024 of SGT University is totally merit-based and there is no entrance examination and students from any field can apply.
Affordable Education: The MPH course fees at SGT University are considered economical, making it an affordable MPH course option.
Industry-Relevant Training: The MPH Syllabus has been developed in such a way that it fits into the trends in the public health job market and post COVID-19 public health jobs.
Global Health Focus: The MPH Subjects focuses on todays and tomorrows leading issues in the sphere of world health to equip students for worldwide professions.
0 notes
Text
"Tracking Health Trends: Insights from the Epidemiology Frontline"
Epidemiology is the study of how diseases and health conditions spread among populations. It involves investigating the causes and effects of health outcomes to improve population health. By analyzing data on demographics, behaviors, environmental factors, and more, epidemiologists can identify risk factors, trends, and patterns that influence public health.
Current Trends in Public Health:
Infectious Disease Outbreaks: From COVID-19 to seasonal flu outbreaks, epidemiologists play a pivotal role in tracking and controlling the spread of infectious diseases. Through surveillance systems and modeling techniques, they assess the impact of outbreaks and recommend strategies for containment and prevention.
Chronic Disease Burden: Non-communicable diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer continue to pose significant challenges globally. Epidemiologists study risk factors like diet, physical activity, genetics, and socio-economic status to develop strategies for prevention and management.
Global Health Disparities: Disparities in health outcomes based on race, ethnicity, income, and geographic location remain a critical focus. Epidemiologists work to identify root causes and advocate for policies that promote health equity and reduce disparities. The Importance of Collaboration:
Public Health Agencies: Collaborations with local, national, and international health agencies strengthen surveillance systems and response efforts.
Academic Research: Partnerships with universities and research institutions drive innovation in epidemiological methods and interventions.
Community Engagement: Engaging communities in research and health initiatives promotes trust, enhances data collection, and improves health outcomes.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the complexities of global health challenges, epidemiologists continue to adapt and innovate. By leveraginghttps://health.universeconferences.com/ data-driven insights and collaborative efforts, we can address emerging health threats, promote health equity, and improve overall well-being. Stay tuned as we explore more topics in epidemiology, from emerging infectious diseases to innovative research methodologies. Together, we can make strides towards a healthier future.
Important Information: Conference Name: 15th American Healthcare, Hospital Management, Nursing, And Patient Safety Summit Patient Safety Conference Short Name: #15AHNPSUCG2025 Dates: May 14-16,2025 Venue|: San Francisco, United States & Virtual Email: [email protected] Visit: https://health.universeconferences.com/ Call for Papers: https://health.universeconferences.com/call-for-paper/Register here: https://health.universeconferences.com/registration/Call/WhatsApp Us: +442033222718
#Epidemiology#PublicHealth#HealthTrends#DataScience#HealthResearch#DiseaseControl#GlobalHealth#HealthEquity#InfectiousDiseases#ChronicDisease#DataAnalytics#HealthPolicy#CommunityHealth#ResearchMethods#HealthInterventions
0 notes
Text
Doctor Prescription Habit Analysis In India: An Overview
The healthcare landscape in India is swiftly evolving, driven by factors like technological advancements, shifting demographics, and changing patient requirements. At the heart of this evolution lies the pivotal role of doctors and their prescription practices, which significantly influence the dynamics of the Indian pharmaceutical market.
Grasping the Doctor Prescription Habit Analysis in Indiaholds paramount importance for pharmaceutical firms aiming to effectively market their products and for policymakers striving to enhance healthcare provision.
Impact of Medical Education and Training
Medical practitioners in India undergo extensive education and training, profoundly shaping their prescription patterns. Their decisions are often guided by their training, clinical experiences, and exposure to medical literature, conferences, as well as interactions with peers and pharmaceutical representatives.
The prevalence of specific diseases and epidemiological patterns significantly influences prescription trends. For instance, in a country like India burdened with communicable diseases such as tuberculosis and vector-borne ailments, doctors may prescribe more antibiotics and antivirals. Conversely, in urban locales witnessing a rise in non-communicable diseases like diabetes and hypertension, there might be an upsurge in prescriptions for chronic medications.
Patient Demographics and Socioeconomic Factors
Patient demographics and socioeconomic elements also wield a significant influence on prescription habits. Doctors often tailor their prescriptions based on factors like patient age, gender, income levels, and access to healthcare facilities. For instance, physicians may opt for more economical generic medications for patients from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
The regulatory framework and pharmaceutical marketing strategies exert substantial sway over doctor prescription habits. Stringent regulations on drug promotion and a growing emphasis on evidence-based medicine are gradually fostering a more rational approach to prescribing. Nevertheless, challenges such as aggressive marketing tactics by pharmaceutical companies and the impact of incentives on prescription behavior persist.

Examining doctor prescription habits analysis in India provides valuable insights into the Indian pharmaceutical landscape. Pharmaceutical enterprises can leverage these doctor prescription habit analysis in India insights to devise targeted marketing strategies, innovate new products, and fortify their market presence. Moreover, policymakers can utilize this data to formulate policies promoting rational drug usage, ensuring essential medicine access, and enhancing healthcare delivery.
Comprehending doctor prescription behaviors or Indian pharmaceutical market insights is crucial for navigating the intricate terrain of the Indian pharmaceutical market. By considering factors like medical education, disease burden, patient demographics, regulatory frameworks, and emerging technologies, stakeholders can glean valuable insights to drive informed decision-making and shape the future healthcare landscape in India.
#Doctor Prescription Habit Analysis in India#Strategic Prescription Research in India#Pharma Strategic Brand Management in India
0 notes
Text
A Range of Choices in Educational Excellence at D Y Patil Deemed To Be University

D Y Patil University offers courses that go beyond mere lectures, serving as catalysts for creating tangible impact in the world. The Environmental Studies Course, Bachelor of Public Health Course, and Event Management Course in Mumbai are known for their academic rigor, allowing students to pursue their passions, fulfill their purpose, and make a global impact. Let us have a look at some of the key features of this university:
1)Nurturing the Next Generation of Earth's Guardians
The environmental studies course combines deep ecological knowledge with practical action to train future environmentalists. The study includes wide areas from deforestation, soil erosion to global warming and landfills. Moreover, the course enables candidates to understand the impact and interaction of activities done by humans on nature. Some of the key principles of this course include:
A deep dive into ecological principles and environmental challenges.
Practical experience through projects and internships.
Preparation for careers in environmental policy, conservation, and sustainable development.
The curriculum combines fieldwork, research projects, and interactive lectures. Learning in a university that prioritizes environmental consciousness with its own weather station and PLATINUM LEED-certified buildings inspires students to build a sustainable future.
2)Advocates for Public Health
The Bachelor of public health is not just a program, but a manifestation of the belief that every person is entitled to the utmost level of health. This is a pledge, a dedication to provide upcoming leaders with the necessary resources to mend communities and construct a more prosperous future. Let us look at some of the key features of this course.
A curriculum that covers epidemiology, global health, and health policy.
Opportunities for hands-on experience in public health initiatives.
Pathways to careers in public health administration, policy-making, and nonprofit leadership.
Recognized as the first in India, the group's medical simulation lab is a testament to its commitment to cutting-edge education and practical training in the healthcare domain. The "Most Engaged" simulation facility in Southeast Asia is the high-fidelity Medical Simulation Centre at D Y Patil Deemed To Be University, which opened its doors in 2013. The center works in partnership with Mayo Clinic USA to provide training to students from health sciences colleges and to certify faculty members through more than 525 workshops held each year.
All of the medical facilities, including the 153-bed Ayurvedic Hospital, the 428-chair Dental Hospital, and the 1660-bed super specialty charitable teaching hospital, are accredited by NABH and NABL. Through access to the data of the hospitals which is gathered due to a huge footfall students can study in great depth, various communicable and non-communicable diseases.
3) Creating Meaningful Experiences Through Curated Events
Students can experience immersive learning where the event management course in Mumbai transforms the city's vibrant energy into your educational environment. This programme is not solely focused on event planning; its purpose is to craft remarkable experiences that evoke happiness and foster meaningful connections in people's lives. What are the special features of this course?
Networking opportunities with industry leaders and professionals.
A stepping stone to careers in event management and entertainment industries through internships, projects, case studies, and more.
Identify best practice in the development and delivery of successful conferences and corporate gatherings.
Identify management essentials such as developing budgets, work breakdown structures, risk mitigation and contingency planning.
Bringing Together Aspirations and Obligations
All these programs aim to develop students into professionals, empathetic, and knowledgeable people who can improve the world. D Y Patil University extends an invitation to join a worldwide movement for positive transformation, encompassing green initiatives, advancements in health, and the creation of joyful gatherings.
DY Patil University is not solely focused on academic achievement; it serves as a refuge where aspiring leaders are nurtured and prepared to influence a more promising and diverse world.
Globalization has increased demand for people with extensive knowledge, strong enthusiasm, and unwavering commitment. The university offers educational opportunities to change the world beyond the classroom. Join us in this exploration, as we create a sustainable, thriving, and joyful future together.
#bachelor of public health#Environmental studies course#Event management course in Mumbai#dy patil university navi mumbai#dypu navi mumbai#dypu university navi mumbai
0 notes
Text
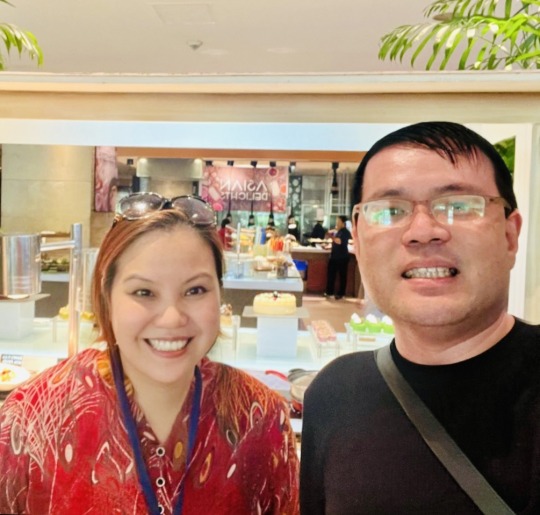

With Thai epidemiologist Dr. Vasoontara Sbirakos Yiengprugsawan. Vas is The Asian Development Bank’s Senior Universal Health Coverage Specialist (Service Delivery with the ADB Health Sector Group).
She focuses on economic and health assessments and lessons learned from COVID-19, supporting health promotion initiatives, and health systems strengthening related projects. Vas has extensive experience working on life-course risk factors for chronic non-communicable diseases, equity in health services, and supporting primary health care in developing Asia.
Before ADB, she held a World Health Organization Fellowship with the Asia Pacific Observatory on Health Systems and Policies, senior research positions on aging and health (The Australian National University and University of New South Wales), and an Endeavour Fellowship at the University College London (UCL). She worked in policy research with the UN Migration Agency, Geneva.
Vas was awarded a Ph.D. in Epidemiology from The ANU, an MA in International Relations from Syracuse University, and a BA in Economics from Thammasat University.
Vas and I were Ph.D. batchmates and housemates at ANU’s University House for three years 🥂
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Panama Canal's Epidemiology

Cowards die many times before their deaths; The valiant never taste of death but once. William Shakespeare, Julius Caesar, 1599
Another oversight shunned by Americans but had hampered the French was the latter’s want of disease control claiming 22,000 lives. The Canal’s predecessors seem to have stood idly by as the grim toll of pestilence decimated the ranks of workers. The ubiquity of funeral trains laden with remains ravaged by malaria and yellow fever testified to the illiteracy for epidemiology on the isthmus at the time. The arrival in 1904 of Colonel William Gorgas who helmed the Department of Sanitation would herald a paradigm shift. In a bid to end the miasma of stagnation throttling the Canal’s progress a regimen for prophylaxis displaced the unreconstructed one of therapeutics. In taking stock of this epidemic Gorgas took the offensive with his petition for countermeasures against the blight of mosquitos which bore culpability for the tyranny of death. In a knee-jerk response Chief Engineer John Wallace balked at this cri de coeur and abruptly resigned but his successor John Stevens elected instead to mobilize four thousands engineers against this vector of infirmity. Such a theory of transmission first gained prominence in 1900 when Gorgas and his peer Dr Walter Reed quarterbacked off the scientific corpus of physician Carlos Finlay who fathomed causality between mosquitos and Cuba’s mortality rate.
The capital of Havana was once a necropolis-cum-laboratory writ large for testing the pathogenesis of disease when the dated Miasma Theory had long been medical lore. This established dogma equated illness with fetid air but germ theory began to gain currency over the cognoscenti particularly after physician John Snow mapped London’s cholera outbreak in 1854 to a contaminated water pump. Neither fomites nor foul gasses from decaying matter sickened the population as it was firmly believed. By the dawn of the 20th century a consensus that looked askance at the communicability of polluted air crescendoed into Cuba’s Yellow Fever Commission which defenestrated this relic of a theory for good. Although the idea specific to mosquito-borne transmission languished in obscurity for two decades due to a lack of empirical evidence it was Gorgas and Reed who put the hypothesis under scrutiny anew. Amidst the onslaught of yellow fever besieging Havana in the wake of the Spanish-American War a public health crusade was set loose to pinpoint the cause. At Camp Lazear mosquitos revealed themselves to be the vector for the rogues’ gallery of disease running amok across the archipelago of islands. No longer captured by ignorance a new edict thus spurred proactive measures to spoil the habitat of these winged critters.
Lessons of sanitation from Cuba were exported to Panama three years later so the Canal could be salvaged after the heavy toll exacted upon the French. The intervention by Gorgas and his army of engineers would consume 35 percent of the project’s lucre in its most prolific phase which systematically fumigated buildings, scythed down tall grass and drained standing water (Rogers 2014: 156). The big dike would have come to naught were it not for such mitigation lest panic prompt workers to flee which they initially did. Fear was sown most acutely in the spring of 1905 when three-quarters of expatriates boarded steamers bound for New York (Rogers 2014). In fact Chief Engineer Wallace tendered his resignation amongst this very same cohort to escape the harrowing crisis a mere fifteen months after his appointment. Prior to Gorgas’ breakthrough this pall of phobia put the Canal at risk since the etiology of yellow fever and malaria was little understood and speculation gave rise to hysteria. The psychological trauma borne from this indiscriminate threat spared no one as labourers and administrators alike were prostrate with fear when symptoms between jaundice and hemorrhages gnawed at morale. Salvation against such defeatism came by Gorgas who won credence as the spectre of disease subsided.
By happenstance Roosevelt’s industrial policy on the Isthmus engendered nothing short of a revolution in epidemiology. Many of the remedies to ward off infection would be universally adopted much like how screen windows find themselves in homes today. After Gorgas procured $90k of these copper meshes for structures abutting the Canal this same feature saw prevalence in the abodes of South Florida until it evolved into standard practice for homebuilders (Rogers 2014). Other measures brought to bear included: (1) drainage of pools within a radius of a hundred yards from dwellings; (2) admixtures of oil and kerosene as larvicide that coated swamps; (3) prophylactic daily doses of quinine made available at dispensaries. Statistics fructified these concerted efforts as hospitalization rates from malaria declined sharply between 1905 and 1909 from 9.6 percent of the workforce to 1.6 percent. Where deaths mounted each month from yellow fever by 1906 only one non-fatal case emerged for the entire year. Under Gorgas’ residency the bête noire of pestilence appeared to be all but eradicated. The sea change placated the public relations fiasco ginned up by the fourth estate back home and by 1913 the tide of disease was stemmed insofar as 5.2 deaths per thousand were recorded (Maurer and Yu 2023).

The seminal public health policies on the isthmus curved the bacchanalia of death where once the Canal stood on the precipice of failure. Within the firmament of construction a symbiosis between epidemiology and engineering is seldom seen whose absence in this case would have conduced to a French redux of futility. Whether by machine or microbial mitigation success on the Canal hinged on the mastery of nature that defied human control for millennia. At the dawn of the 20th century President Roosevelt’s industrial policy reversed this longstanding status quo as a testament to America’s preeminence. Akin to a palimpsest the project went on to domesticate the jungle where once this notion bordered on the realm of science fiction. The saga of the Canal therefore bears the hallmarks of engineering just as much as epidemiology. If the lifecycle of the Anopheles and Aedes aegypti mosquito was not disrupted it is dubious if the Canal would have ever seen the light of day. What made matters untenable was how in the incipient stages the Canal became tantamount to a lottery of death. The scare from an invisible foe brought work to a standstill. Were it not for the draconian interventions the flight of workers would have continued unabated. Until and unless Gorgas hedged against disease the Canal could not proceed.
0 notes
Text
Future Directions for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Treatment in Bangladesh

I. Introduction
Future directions for cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment in Bangladesh, consequently contributing to a substantial burden of morbidity and mortality. Moreover, it is a pressing concern as it affects individuals across various age groups and socioeconomic backgrounds. The current state of CVD prevention and treatment in Bangladesh is characterized by challenges such as limited access to healthcare, inadequate awareness, and a lack of infrastructure to support early detection and effective management. This article aims to explore the future directions for CVD prevention and treatment in Bangladesh, focusing on the evolving epidemiology, innovative strategies, and the role of various stakeholders in improving the overall cardiovascular health of the population.
II. Current Landscape of CVD in Bangladesh
Bangladesh faces a high prevalence of CVD, resulting in coronary artery disease, stroke, and hypertension being the most common cardiovascular conditions. Notably, the country is grappling with a growing number of risk factors, including tobacco use, unhealthy diets, physical inactivity, and high blood pressure. Access to healthcare, especially in rural areas, remains a challenge, hindering early diagnosis and timely intervention. Efforts are needed to understand the epidemiological trends and devise effective strategies to mitigate the impact of CVD.
III. The Changing Epidemiology of CVD
Bangladesh is undergoing rapid urbanization, with a significant shift in lifestyle and dietary habits. These changes have contributed to an increasing burden of non-communicable diseases, thus including CVD. The rise in sedentary lifestyles and the consumption of processed and high-sugar foods have fueled the prevalence of risk factors for CVD. Understanding these shifts in epidemiology is crucial for tailoring prevention and treatment efforts to the changing needs of the population.
IV. Future directions for cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment in Bangladesh for CVD Prevention
The future of CVD prevention in Bangladesh lies in comprehensive public health initiatives. These should include awareness campaigns that educate the population about the risk factors and preventive measures. In addition, encouraging a healthier lifestyle by promoting physical activity and a balanced diet is essential. Policies and regulations aimed at reducing tobacco and alcohol consumption, salt, and sugar reduction strategies, and stringent food labeling and marketing restrictions can significantly contribute to CVD prevention. Furthermore, leveraging telemedicine and digital health solutions can help reach underserved populations and improve access to preventive care. Screening and early detection programs that use innovative methods and targeted risk assessments are crucial for identifying at-risk individuals and intervening early.
V. Advances in CVD Treatment
Improving access to quality healthcare is a paramount concern. While prevention is crucial, effective treatment options should be available for those already affected by CVD. Advances in medical technology, such as minimally invasive surgical procedures and innovative pharmaceuticals, offer hope for better treatment outcomes. Simultaneously, building and upgrading healthcare infrastructure to accommodate the increasing number of CVD patients is necessary. Additionally, reducing the overall cost of treatment through government initiatives and collaborations with pharmaceutical companies can make these services more affordable and accessible to the population.
VI. Research and Innovation
Ongoing research projects and studies are vital in understanding the unique challenges and characteristics of CVD in the Bangladeshi context. Collaboration with international organizations, sharing knowledge, and leveraging their expertise can accelerate the progress in CVD prevention and treatment. Moreover, indigenous research initiatives should focus on tailoring strategies to the local culture, needs, and resources.
VII. The Role of Government and NGOs
Government policies and support play a pivotal role in steering CVD prevention and treatment efforts. In this regard, proper funding, healthcare regulation, and coordination among ministries are essential. Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) also make valuable contributions through their outreach programs, community-based healthcare, and awareness campaigns. Additionally, collaborations between government bodies and NGOs can amplify the impact of interventions.
VIII. Challenges and Barriers in Future directions for cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment in Bangladesh
Despite progress, challenges persist. Economic constraints limit the scope and sustainability of prevention programs. A limited healthcare workforce can strain the delivery of healthcare services. In light of this, cultural and societal factors may influence lifestyle choices and adherence to medical advice. Addressing these challenges is essential for effective CVD prevention and treatment.
IX. Success Stories and Case Studies of Future directions for cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment in Bangladesh
Highlighting successful CVD prevention and treatment projects and sharing real-life success stories can inspire further initiatives and encourage collective efforts. These illustratively demonstrate case studies can provide a roadmap for implementing effective strategies in other regions of Bangladesh.
X. Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment in Bangladesh holds promise but requires a concerted effort from various stakeholders. Taking into consideration the preceding discussions, understanding the evolving epidemiology, implementing innovative prevention strategies, improving access to quality healthcare, and conducting research are key components of a comprehensive approach to combat CVD in the country. The role of the government and NGOs in coordinating these efforts is paramount. Ultimately, by addressing the challenges and building on success stories, Bangladesh can strive for a healthier cardiovascular future. Read the full article
0 notes