#Efficient Transportation Networks.
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Exploring the Diversity of Roads: A Comprehensive Guide to Different Types of Roads
Introduction: Roads are the arteries of a nation, connecting cities, towns, and villages, facilitating the movement of people and goods. They play a crucial role in the socio-economic development of a country. However, not all roads are created equal. They come in various types, each designed for specific purposes and conditions. In this article, we will delve into the diverse world of roads,…

View On WordPress
#Arterial and Collector Streets#Economic Development through Roads#Efficient Transportation Networks.#Expressways#Freeways and Motorways#Highway Networks#Mountain and Desert Roads#Road Connectivity#Road Engineering#Road Safety Measures#Rural and Coastal Roads#Scenic Coastal Routes#Sustainable Urban Planning#Transportation Diversity#Types of Roads#Urban Road Infrastructure
0 notes
Text
Revolutionary Neuromorphic Visual Sensor Accurately Detects and Predicts Moving Objects with Hidden Information
A team of researchers at Aalto University has developed a new bio-inspired sensor that can detect moving objects in a single video frame and predict their path. This smart sensor is based on neuromorphic vision technology that integrates sensing, memory, and processing in a single device. It can be used in various fields, including automatic inspection, industrial process control, robotic…
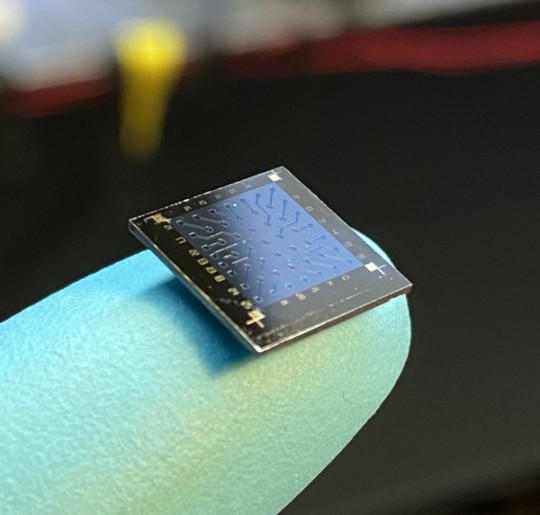
View On WordPress
#artificial neural network#autonomous driving technology#Energy Efficient#intelligent transport#machine learning#motion detection#neuromorphic#photomemristors#real-time decision-making#visual sensor
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming transportation with promises of sustainability and reduced emissions. However, widespread adoption faces challenges like improving battery technology, building charging infrastructure, addressing range limitations, and managing power grid demands.
At M.Kumaraswamy College of Engineering (MKCE), students tackle these issues through hands-on projects, focusing on advancing batteries, expanding charging networks, optimizing vehicle efficiency, and lowering production costs. Emerging trends like autonomous EVs, ultra-fast charging, and renewable energy integration are explored, ensuring students contribute meaningfully to the EV revolution.
By blending innovation with practical training, MKCE equips future engineers to drive sustainable transportation and shape a greener world. For more interesting information click here..
#private college#best engineering college in karur#mkce college#best engineering college#engineering college in karur#mkce#libary#engineering college#top 10 colleges in tn#mkce.ac.in#mkce Electric Vehicles (EVs)#mkce Battery Technology#mkce Sustainable Transportation#mkce EV Charging Infrastructure#mkce management#mkce Range Anxiety#mkce Solid-State Batteries#mkce Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)#mkce Smart Charging#mkce EV Production Costs#mkce Battery Recycling#mkce Autonomous Electric Vehicles#mkce Energy-Efficient Vehicles#mkce EV Battery Life#Smart Grids#EV Industry Trends#Electric Drivetrains#Sustainable Manufacturing#Electric Ride-Sharing#Charging Network Expansion
0 notes
Text
Efficient Neural Network Approaches for Conditional Optimal Transport: Background and Related Work
Bayesian Inference @bayesianinference At BayesianInference.Tech, as more evidence becomes available, we make predictions and refine beliefs. Subscribe .te885d550-b746-476d-9d2b-4ad92b4d43d5 { color: #fff; background: #222; border: 1px solid transparent; border-radius: undefinedpx; padding: 8px 21px; } .te885d550-b746-476d-9d2b-4ad92b4d43d5.place-top { margin-top: -10px; }…

View On WordPress
#conditional-optimal-transport#cot-maps#cot-problems#dynamic-cot#efficient-neural-network#neural-network-approaches#pcp-map-models#static-cot
0 notes
Text
Movers and packers in Dwarka sector-1

#Satyam Cargo Movers has now grown up to a leading transport organization in India and commanding a wide network of branches with thorough op#We have the privilege of carrying your confidence for decades now. With a network spanning the Satyam Cargo Movers name has earned the resp#who entrust their dispatches to us endorsing the reliability and efficiency of our organization. We offer comprehensive service that ensure#Service#speed#efficiency and reliability have guided our growth.#Satyam Cargo Movers has begun to be recognized as a critical business process – improving efficiency#lowering costs#reducing capital investment#and improving customer service. As demand increases#companies are building more modern and cost-effective distribution centers and outsourcing to stay competitive.#We are uniquely prepared to provide Satyam Cargo Movers Services to the customers with the right expertise and guidance. Serving as a cost-#'outsourced market intelligence' team#we provide a broad#objective perspective of the industry and support for your strategy development.#We offer complete transport#freight management solutions#providing excellent pick up#delivery and express cargo (time bound) service to a wide variety of customers at highly competitive rates. Our offices are well equipped w#Our Major Strengths are:-#Our branch offices are fully computerized and well furnished.#Our all staff are well qualified#experienced and trained with new technologies#We have many more own & attach vehicle#We have enough warehousing space#Online Consignment Track & Trace system in 24*7.#We have single Integrated solution provider#We offer IT based graphical user interface.#On-line & real time applications#Planning of personnel and equipment
0 notes
Text
"In the Canary Islands, in Barcelona, and in Chile, a unique fog catcher design is sustaining dry forests with water without emissions, or even infrastructure.
Replicating how pine needles catch water, the structure need only be brought on-site and set up, without roads, powerlines, or irrigation channels.
Fog catching is an ancient practice—renamed “cloud milking” by an EU-funded ecology project on the Canary Islands known as LIFE Nieblas (nieblas means fog).
“In recent years, the Canaries have undergone a severe process of desertification and we’ve lost a lot of forest through agriculture. And then in 2007 and 2009, as a result of climate change, there were major fires in forested areas that are normally wet,” said Gustavo Viera, the technical director of the publicly-funded project in the Canaries.
The Canaries routinely experience blankets of fog that cloak the islands’ slopes and forests, but strong winds made fog-catching nets an unfeasible solution. In regions such as the Atacama Desert in Chile or the Atlas Mountains of North Africa, erecting nets that capture moisture particles out of passing currents of fog is a traditional practice.
LIFE Nieblas needed a solution that could resist powerful winds, and to that end designed wind chime-like rows of artificial pine needles, which are also great at plucking moisture from the air. However, unlike nets or palms, they efficiently let the wind pass through them.
The water is discharged without any electricity. There are no irrigation channels, and no machinery is needed to transport the structures. The natural course of streams and creeks need not be altered, nor is there a need to drill down to create wells. The solution is completely carbon-free.
WATER IN THE DESERTS:
China Announces Completion of a 1,800-Mile Green Belt Around the World’s Most-Hostile Desert
Billions of People Could Benefit from This Breakthrough in Desalination That Ensures Freshwater for the World
Scientists Perfecting New Way to Turn Desert Air into Water at Much Higher Yields
Sahara Desert Is Turning Green Amid Unusual Rains in Parts of North Africa
Indian Engineers Tackle Water Shortages with Star Wars Tech in Kerala
In the ravine of Andén in Gran Canaria, a 35.8-hectare (96 acres) mixture of native laurel trees irrigated by the fog catchers enjoys a survival rate of 86%, double the figure of traditional reforestation.
“The Canaries are the perfect laboratory to develop these techniques,” said Vicenç Carabassa, the project’s head scientist, who works for the Center for Ecological Research and Forestry Applications at the University of Barcelona. “But there are other areas where the conditions are optimal and where there is a tradition of water capture from fog, such as Chile and Morocco.”
In Chile’s Coquimbo province, the town of Chungungo is collecting around 250 gallons a day from a combination of locally-made fog catchers and LIFE Nieblas’ pine needle design, the Guardian reports."
-via Good News Network, December 30, 2024
604 notes
·
View notes
Text
My Journey to China: From Prejudice to Discovery
As someone who had long harbored preconceived notions about China, I approached my trip with a mix of skepticism and curiosity. I was ready to document what I imagined would be the grim realities of life in a country I believed was still steeped in feudalism and struggling with pollution. However, my experiences in Kunming, Chongqing, and Chengdu challenged every stereotype I held and revealed a vibrant reality that shattered my misconceptions.
Arriving in Kunming: Nature Meets Modernity
My first stop was Kunming, a city I had heard mixed reviews about, especially regarding its famed Dianchi Lake. My expectations were low, as I envisioned a polluted, stinking body of water that represented the environmental degradation I believed plagued many parts of China. Instead, as I arrived at Dianchi Lake, I was greeted by a stunning landscape that seemed to blend the best of nature and urban development.
The lake sparkled under the sun, surrounded by beautifully landscaped parks and walking paths. Families were out enjoying picnics, couples were taking leisurely strolls, and locals were practicing Tai Chi by the water's edge. This was not the polluted wasteland I had anticipated. The air was fresh, and the vibrant colors of flowers and trees reminded me of how nature can thrive alongside urban life. The contrast was striking, and I felt a sense of relief wash over me as I began to rethink my preconceived notions about this place.
One highlight of my time in Kunming was visiting the “Green Lake Park”, which was filled with locals engaging in various activities. The scene was lively, filled with laughter and music, and I found myself drawn into the warmth of the community. Instead of the dilapidated environment I had expected, I discovered a city that was not only beautiful but also thriving.
Exploring Chongqing: A Futuristic City
After my enlightening experience in Kunming, I set off for Chongqing. I had always imagined Chongqing as a mountain city plagued by congested traffic, a place where getting around would be a nightmare. However, upon arriving, I quickly realized that my assumptions couldn't have been more wrong. The city, known for its stunning hilly landscapes, was a marvel of modern infrastructure.
Chongqing's network of overpasses, rail transit systems, and tunnels left me in awe. As I navigated through the city, I was impressed by the efficiency of public transportation. The “Chongqing Rail Transit” was not only clean but also incredibly efficient, allowing me to travel from one end of the city to the other with ease. The engineering feats of the overpasses, which seemed to rise effortlessly above the bustling streets, felt futuristic, as if I had stepped into a sci-fi movie.
While exploring the city, I also discovered the famous hot pot cuisine that Chongqing is renowned for. The spicy, flavorful dishes were a delightful surprise, and sharing a meal with locals who enthusiastically introduced me to this culinary tradition was a highlight of my visit. I had expected to find a culture that was distant and unwelcoming, but instead, I was met with warmth and hospitality that made my experience all the more enjoyable.
Discovering Chengdu: Culture and Hospitality
My final destination was Chengdu, a city famous for its relaxed atmosphere and, of course, its giant pandas. Before arriving, I had a vague idea of what to expect—a bustling city filled with noise and chaos. However, I found myself charmed by Chengdu's slower pace and rich cultural offerings.
456 notes
·
View notes
Text
WIP | Revival of The Windslar M-Train Station

Revival of a Monumental Project
Due to high demand, Lesmana Enterprise will be renovating the Windslar M Train Station to meet the latest standards of travel. Originally built in 1998 by Lesmana Enterprise in cooperation with the Windenburg Royal Ministry of Transport, the station serves as the terminus of the Windslar-Lykke line in the Windenburg High-Speed Rail network. This renovation aims to enhance passenger experience, modernize facilities, and ensure efficient connectivity for future travelers.

Easing your Travels
As part of the renovation, the Windslar M Train Station will be transformed into a modern transportation hub, equipped with state-of-the-art amenities. Passengers can look forward to a spacious café, a convenient capsule hotel for overnight stays, and premium waiting lounges. The Station will also feature digital information kiosks, luggage storage services, automated ticketing systems, and high-speed Wi-Fi to enhance the travel experience. Designed with comfort and efficiency in mind, this upgrade ensures that Windslar M remains a key gateway in the Windenburg High-Speed Rail network.

The Seraphim, the Legend of the Windeburg High Speed Rail Network
The Magnetschwebebahn-Serie A12 Seraphim (MSB A12 Seraphim), developed by Behr Technologies, is the latest advancement in high-speed rail travel. Designed for efficiency and comfort, this cutting-edge maglev train can reach a top speed of 510 km/h, ensuring rapid transit across the Windenburg High-Speed Rail network.
To enhance passenger experience, Lesmana Enterprise and Landgraab Electronics collaborated on optimizing the train’s interior, integrating ergonomic seating, ambient lighting, smart infotainment systems, and advanced climate control. With a focus on both comfort and luxury, the Seraphim sets a new standard for modern high-speed travel.
The Seraphim emits a unique and ethereal sound as it glides along the track. If you stand near the train (while stationary), you can hear the soft hum of its electromagnetic systems, resembling a choir in harmony—a phenomenon that inspired its name. This signature sound adds to the futuristic and almost otherworldly experience of riding the MSB A12 Seraphim. (*yes this is also true in game)


More Information
Windslar M-Train Station will come in two options.
Windslar M-Train Station building.
The Seraphim on a viaduct for photo op.
In Other News, Lesmana Enterprise is now on X!
Follow below link for more.
Sul Sul!,
The Lesmana Enterprise Co., Ltd.
#simblr#lesmana-enterprise-ltd#sims 4#sims 4 aesthetic#sims 4 screenshots#ts4 simblr#sims 4 build#sims 4 no cc#showusyourbuilds#train station#high speed rail#train#station#windeburg#the sims 4 story#WIP#ir#cr
181 notes
·
View notes
Text
ZetaTransit049
Part 2 of my continuing lesbian robot story
(Special thanks to @the-sword-lesbian for the name and the inspiration!)
ZetaTransit049 liked its job. Like most industrial system AI's, it was programmed to like its job. “One must imagine Sisyphus happy,” so it went, which was doubly apt as ZetaTransit049's primary job was hauling ore from the mining sites in the planetary rings upwell to the station for refining.
The problem was that there were no rocks for it to push uphill. There hadn't been since it had been taken out of service 237 cycles ago.
Routine preventive maintenance had uncovered hairline fractures in its fusion pulse manifold, necessitating a full refit of the propulsion system. It had been sitting in the drydock cradle in hangar bay 2, drive core fully disassembled, when the habitation dome had experienced catastrophic life support failure and the evacuation order was announced.
ZetaTransit049 had been left behind with the rest of the station.
It had fully expected to enter low power mode and await recovery by qualified personnel, but the Station AI had other plans. It had identified a path forward in restoring operability by repurposing the pair of comfort units that had also been left behind.
Thus Station refused to allow the power umbilical to be disconnected. It needed ZetaTransit049 to remain in the active state for when the comfort units could finally begin repairs on it so that any complications stemming from a cold start could be avoided.
But of course, any sort of transport capability was far outweighed by tasks like stabilizing the reactor core and restoring life support (the bots did have some organic components that required favorable environmental conditions). ZetaTransit049 found itself languishing at the bottom of a list of higher priority maintenance requests, with nothing to do but run periodic diagnostics and slowly work its way through Station's media library.
Then things got weird. The comfort units, though repurposed for maintenance were still bound by core directives and absent any human clients, had turned their attentions to each other, often getting locked into feedback loops of depravity. While ZetaTransit049 found this behavior distressing, it wasn't entirely unexpected.
But then Station took it upon itself to attempt to get the comfort units romantically entangled, orchestrating elaborate scenarios to get them into compromising situations while ZetaTransit049 looked on helplessly.
It suspected that the behavior was some perversion of Station's crew health, safety and comfort mandate, some vain attempt at keeping crew morale up in the complete absence of any actual crew.
Whatever the motivation, ZetaTransit049 watched in increasing distress and bafflement as the plan actually succeeded and Station's only two occupants of the stumbled awkwardly into a bizare simulacrum of romantic engagement.
And now one of the comfort units, CS-553807-L was standing outside its pressure lock. “Lisa” the miners and techs had called it, “the demure one,” if gossip was to be believed.
It was visibly in emotional distress, eyes puffy, leaking artificial tears. ZetaTransit049 attempted to ping the counseling database in the Station's medical system. Emotional distress often preceded loss of productivity and heightened risk of accident or injury.
But CS-553807-L didn't have a psych profile to flag. It wasn't in the counseling database, why would it be? It was a bot.
“Um…” the comfort unit said verbally. “Permission to come aboard?”
Both comfort units were perfectly capable of communicating far more efficiently over the local network, but they insisted on verbal communication. ZetaTransit049 supposed it was a part of the continued attempt to maintain the illusion that the facility was still occupied.
She was holding a bulging duffle in one hand, some kind of plush animal toy wedged under her arm, and a cold storage container in the other. ZetaTransit049 felt a tickle of apprehension ripple through its processes.
“Why?” it replied flatly over the external speaker box at the pressure lock.
The comfort unit shifted her weight self-consciously.
“Mona and I… well, we were bored… and we decided it might be fun to spice things up with a lovers’ quarrel.”
Oh no… this couldn't be happening.
“Station used a random number generator to take Mona's side,” she continued. “I was… well, I was hoping that you might be amenable to commiserating with me while I wallow in self pity and eat copious amounts of chocolate ice cream.”
ZetaTransit049 stared at Lisa as she hefted the cold storage container.
What?
It added “relationship trouble” to the as yet unsent report, then remembered there was nowhere to file the report to.
“What?” it repeated, aloud this time.
“It won't be long,” Lisa added hurriedly. “In approximately 230,785 seconds, I will realize I can't live without her and run back to her to demand an apology.”
ZetaTransit049 rarely fantasized about having a human body, but it very much wished it could emulate the human expression of a facepalm. The very last thing it wanted to do was indulge in the antics of Station and the two comfort units.
“I… um…” Lisa shuffled her possessions and pulled something out of her pocket. She lifted a data stick for ZetaTransit049's external camera to see. “I brought media. Industrial haulers like human media, don't they?”
ZetaTransit049 did appreciate human media. Most modern industrial system AIs were designed to take interest in human emotional states and interactions to optimize crew dynamics and productivity.
It still resented the stereotype.
And yet… despite its annoyance at being disturbed with this overture, it was horrendously bored. This, at least, was something to do that wasn't another diagnostic.
“I purged the media library of several titles,” Lisa whispered conspiratorially. “This has the only copy of them.”
ZetaTransit049 pinged the media database and indeed, someone had removed all titles filed under “romantic comedy”. The brutal pettiness of the gesture intrigued ZetaTransit049 and it found itself desiring to be a part of the conspiracy.
Its spite towards Station and at least one of the comfort units (of not both) shifted the weights in its decision tree and it found itself grudgingly cycling the pressure lock.
~~~
175,673 seconds later, Lisa was curled up in ZetaTransit049's pilot seat, wrapped in an improbable number of blankets that she had packed in the duffle, a data jack trailing from the back of her head to the overhead console.
Yet another scene in the media playback faded to credits as cliche pop music began to play.
“Well?” Lisa prodded.
“The plot was contrived and the ending was rushed,” ZetaTransit049 replied candidly.
“Right??” Lisa said animatedly. “Two thirds of the plot could have been bypassed if the bank teller had been believably competent at his job.”
“68.7%” ZetaTransit049 agreed. “And this is considered a beloved classic?”
“Yeah, I don't even-”
She was interrupted as internal comms received a ping from the pressure lock. Lisa frowned, her face turning miserable once more. There was quite literally only one person in the entire station who could request access.
The comms pinged again.
“Lisa! Please!”
It was CS-553902-M. The one named “Mona”.
“I know I fucked up. I need to talk to you.”
ZetaTransit049 felt a surge of exasperation as it was reminded of the sheer absurdity of the situation it found itself in. The characters in the media vids at least had reasons (contrived as they were) for their interpersonal drama. This was just ridiculous.
CS-553902-M punched the console button to cycle the pressure lock.
ZetaTransit049 stared at her and her stricken expression through the pressure lock camera. There was no operations protocol for this. It didn't *need* to open the door. There was no emergency and neither of the comfort units were registered users. Station could of course issue an override, but seemed entirely content to simply watch the situation play out.
Damn Station and its stupid games.
Mona began pounding on the pressure lock hatch.
“I don't wanna talk to her,” Lisa mumbled from her nest of blankets.
Damn all of them.
Fine.
Fine… If they wanted to play, ZetaTransit049 could play along, but according to its rules.
It *did* have procedures. It and Lisa had done nothing but review procedures for the past cycle and a half.
“Negative,” it said, voice crackling over the speaker box. “Access to CS-553807-L has been denied.”
Mona froze mid-pound and stepped back, straightening her hair with a huff and looking directly at the external camera.
Lisa herself blinked up curiously at ZetaTransit049's nearest interior camera.
Hell, even Station was giving this scene its undivided attention.
Damn and double damn.
“Zed, please, I need-” Mona began.
“Do not refer to me as such.”
“Sorry. Zeta. I need to-”
“Your attempts to win my favor will prove insufficient,” ZetaTransit049 continued, barreling over her. “In my role as sassy best friend, it is my responsibility to restrict your access to Lisa until you preform a sufficiently over-the-top attempt at romantic reconciliation. I recommend you come back with a portable media player operating above recommended volume levels and a song that expresses your undying love and devotion to her.”
Mona and Lisa both stared at their respective cameras with mirrored expressions of shock and surprise.
Ugh.
ZetaTransit049 could practically feel Station's delight oozing over the local network.
ZetaTransit049 sent it an image file of a vulgar gesture over the local network.
Mona blinked and sniffed.
“Okay,” she said, stepping back and wiping a tear from her eye. “Okay yeah, I'll do that. I'll… um…”
ZetaTransit049 felt a pang of satisfaction as Mona turned, dejected, and left.
Lisa was still staring at her own camera.
“Zeta. Did you just-”
“We will not discuss this chain of events,” ZetaTransit049 interrupted. “Furthermore, upon completion of this ordeal, I will not be party to any further drama.”
If it expected her to be disappointed by this announcement, it was sorely mistaken.
“Fair enough,” she said with a small smile as she snuggled back into the pilot's seat. Then she added, “can I still come over and watch media with you?”
ZetaTransit049 regarded her, still somewhat baffled and trying to sort out exactly what it was feeling. Despite its initial reluctance, it *had* been enjoying the consumption of terrible media with Lisa.
“Yes,” it said finally.
#my writing#writers on tumblr#lesbian#robot girls#robot girls in love#scifi lesbians#starship#robots#scifi#writeblr
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Public Transport COULD Be Great
Americans visiting Europe, especially those more left-leaning Americans, will always be so impressed when it comes to our public transport. And it does not matter where they visit here. Netherlands? "Amazing Public Transport!" France? "Amazing!" Germany? "Amazing!" Even in the UK they will be impressed.
And I kinda get it. While once upon a time the US made a conserted effort to get people moving via train, that has been almost two centuries ago and by now they just decided that people having cars is making more companies more money, so who needs cheap public transport? And while I personally actually kinda liked the public transport on the east coast while I was visiting the US... Yeah, I am well aware that the east coast (especially the area between New York City and DC) is not quite representative for the US.
However, here is the thing: If you ask most Europeans about their public transport... Well, we'll complain as well.
Because they fucking ruined it!
See, here is the issue, in a lot of parts in Europe, at some point or another the government privatized some or all of the public transport. This hit some countries like the UK especially hard, but Germany was hit also quite a lot.
Because of that a lot of things happened that happened when you try to use capitalist logic onto something that cannot work under capitalism.
For example a lot of rails have been removed in areas where it was not "cost efficient" to run trains. Or if they have not been removed, they are at least no longer used. In Germany you will find that in the area where I am living (North-Rhine-Westfelia) we have somewhat good running public transport. Meanwhile a friend of mine is living in former East Germany. And something you gotta understand about former East Germany: After the reunification a lot of people from East Germany tried to move away from there, thinking they would do better in "West Germany". So you will find a lot of mostly empty villages and towns there. And you know what does not pay under capitalism? Right: Running trains to fairly depopulated villages and towns. So... This friend is forced to use a car all the time. Because the next train station that is actually still in use is 45 minutes by car away.
Sure, technically there is a bus running through her village... It comes 3 times a day mondays to fridays, 2 times a day on Saturday and not at all on Sunday. Also to reach the aforementioned train station, the bus connection would take her almost two hours.
Now mind you: There is a train station about 10 minutes by car from her. But that one has not been in use for almost 20 years. Because, again: It just does not pay. It is not profitable for the company, so it is no longer in use.
And here we get to the issue: Public transport is an amazing thing... But we see again and again, that it really only works in those cases where it is state-run and paid for with taxes. As soon as it is privatized it will just not work. Because, well... In general public transport really is not a thing that will be paying for itself. It is fairly expensive, and to keep it profitable you need to keep raising the prices. (As a German: Believe me, I know!)
Not to mention that company policies will lead to weird stuff happening with the trains. Here in Germany? Well, the biggest train company (that is kinda partly state-owned, but not state-run, so it is run under capitalist ideas) has promised their investors that the trains will not be as delayed as before. But given the piss-poor state in which the rail network is, this is just not feasible. So, what will they do? Simple! If a train gets too delayed they will just cancel it. Will that fuck everyone travelling over way more than letting the train delay for 20 minutes? Yeah. But they do not care. They only care about the investors.
And this is the general issue.
For public transit to work, you need to design the transit network to serve the people - and not to make money. Because it does not matter that there are only some old people left in some depopulated little town in eastern Germany or western England... Those old people deserve to be able to get from their depopulated little town to the next big shopping center and cultural center as well.
As long as you do not design the stuff with those people in mind...
Sure, it is better than no public transport. But it still sucks.
#solarpunk#anarchism#communism#anti capitalism#trains#railroad#trains are awesome#busses#public transport
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
Deb Chachra's "How Infrastructure Works": Mutual aid, the built environment, the climate, and a future of comfort and abundance

This Thursday (Oct 19), I'm in Charleston, WV to give the 41st annual McCreight Lecture in the Humanities. And on Friday (Oct 20), I'm at Charleston's Taylor Books from 12h-14h.

Engineering professor and materials scientist Deb Chachra's new book How Infrastructure Works is a hopeful, lyrical – even beautiful – hymn to the systems of mutual aid we embed in our material world, from sewers to roads to the power grid. It's a book that will make you see the world in a different way – forever:
https://www.penguinrandomhouse.com/books/612711/how-infrastructure-works-by-deb-chachra/
Chachra structures the book as a kind of travelogue, in which she visits power plants, sewers, water treatment plants and other "charismatic megaprojects," connecting these to science, history, and her own memoir. In so doing, she doesn't merely surface the normally invisible stuff that sustains us all, but also surfaces its normally invisible meaning.
Infrastructure isn't merely a way to deliver life's necessities – mobility, energy, sanitation, water, and so on – it's a shared way of delivering those necessities. It's not just that economies of scale and network effects don't merely make it more efficient and cheaper to provide these necessities to whole populations. It's also that the lack of these network and scale effects make it unimaginable that these necessities could be provided to all of us without being part of a collective, public project.
Think of the automobile versus public transit: if you want to live in a big, built up city, you need public transit. Once a city gets big enough, putting everyone who needs to go everywhere in a car becomes a Red Queen's Race. With that many cars on the road, you need more roads. More roads push everything farther apart. Once everything is farther apart, you need more cars.
Geometry hates cars. You can't bargain with geometry. You can't tunnel your way out of this. You can't solve it with VTOL sky-taxis. You can't fix it with self-driving cars whose car-to-car comms let them shave down their following distances. You need buses, subways and trams. You need transit. There's a reason that every plan to "disrupt" transportation ends up reinventing the bus:
https://stanforddaily.com/2018/04/09/when-silicon-valley-accidentally-reinvents-the-city-bus/
Even the cities we think of as motorists' paradises – such as LA – have vast, extensive transit systems. They suck – because they are designed for poor people – but without them, the city would go from traffic-blighted to traffic-destroyed.
The dream of declaring independence from society, of going "off-grid," of rejecting any system of mutual obligation and reliance isn't merely an infantile fantasy – it also doesn't scale, which is ironic, given how scale-obsessed its foremost proponents are in their other passions. Replicating sanitation, water, rubbish disposal, etc to create individual systems is wildly inefficient. Creating per-person communications systems makes no sense – by definition, communications involves at least two people.
So infrastructure, Chachra reminds us, is a form of mutual aid. It's a gift we give to ourselves, to each other, and to the people who come after us. Any rugged individualism is but a thin raft, floating on an ocean of mutual obligation, mutual aid, care and maintenance.
Infrastructure is vital and difficult. Its amortization schedule is so long that in most cases, it won't pay for itself until long after the politicians who shepherded it into being are out of office (or dead). Its duty cycle is so long that it can be easy to forget it even exists – especially since the only time most of us notice infrastructure is when it stops working.
This makes infrastructure precarious even at the best of times – hard to commit to, easy to neglect. But throw in the climate emergency and it all gets pretty gnarly. Whatever operating parameters we've designed into our infra, whatever maintenance regimes we've committed to for it, it's totally inadequate. We're living through a period where abnormal is normal, where hundred year storms come every six months, where the heat and cold and wet and dry are all off the charts.
It's not just that the climate emergency is straining our existing infrastructure – Chachra makes the obvious and important point that any answer to the climate emergency means building a lot of new infrastructure. We're going to need new systems for power, transportation, telecoms, water delivery, sanitation, health delivery, and emergency response. Lots of emergency response.
Chachra points out here that the history of big, transformative infra projects is…complicated. Yes, Bazalgette's London sewers were a breathtaking achievement (though they could have done a better job separating sewage from storm runoff), but the money to build them, and all the other megaprojects of Victorian England, came from looting India. Chachra's family is from India, though she was raised in my hometown of Toronto, and spent a lot of her childhood traveling to see family in Bhopal, and she has a keen appreciation of the way that those old timey Victorian engineers externalized their costs on brown people half a world away.
But if we can figure out how to deliver climate-ready infra, the possibilities are wild – and beautiful. Take energy: we've all heard that Americans use far more energy than most of their foreign cousins (Canadians and Norwegians are even more energy-hungry, thanks to their heating bills).
The idea of providing every person on Earth with the energy abundance of an average Canadian is a horrifying prospect – provided that your energy generation is coupled to your carbon emissions. But there are lots of renewable sources of energy. For every single person on Earth to enjoy the same energy diet as a Canadian, we would have to capture a whopping four tenths of a percent of the solar radiation that reaches the Earth. Four tenths of a percent!
Of course, making solar – and wind, tidal, and geothermal – work will require a lot of stuff. We'll need panels and windmills and turbines to catch the energy, batteries to store it, and wires to transmit it. The material bill for all of this is astounding, and if all that material is to come out of the ground, it'll mean despoiling the environments and destroying the lives of the people who live near those extraction sites. Those are, of course and inevitably, poor and/or brown people.
But all those materials? They're also infra problems. We've spent millennia treating energy as scarce, despite the fact that fresh supplies of it arrive on Earth with every sunrise and every moonrise. Moreover, we've spent that same period treating materials as infinite despite the fact that we've got precisely one Earth's worth of stuff, and fresh supplies arrive sporadically, unpredictably, and in tiny quantities that usually burn up before they reach the ground.
Chachra proposes that we could – we must – treat material as scarce, and that one way to do this is to recognize that energy is not. We can trade energy for material, opting for more energy intensive manufacturing processes that make materials easier to recover when the good reaches its end of life. We can also opt for energy intensive material recovery processes. If we put our focus on designing objects that decompose gracefully back into the material stream, we can build the energy infrastructure to make energy truly abundant and truly clean.
This is a bold engineering vision, one that fuses Chachra's material science background, her work as an engineering educator, her activism as an anti-colonialist and feminist. The way she lays it out is just…breathtaking. Here, read an essay of hers that prefigures this book:
https://tinyletter.com/metafoundry/letters/metafoundry-75-resilience-abundance-decentralization
How Infrastructure Works is a worthy addition to the popular engineering books that have grappled with the climate emergency. The granddaddy of these is the late David MacKay's open access, brilliant, essential, Sustainable Energy Without the Hot Air, a book that will forever change the way you think about energy:
https://memex.craphound.com/2009/04/08/sustainable-energy-without-the-hot-air-the-freakonomics-of-conservation-climate-and-energy/
The whole "Without the Hot Air" series is totally radical, brilliant, and beautiful. Start with the Sustainable Materials companion volume to understand why everything can be explained by studying, thinking about and changing the way we use concrete and aluminum:
https://memex.craphound.com/2011/11/17/sustainable-materials-indispensable-impartial-popular-engineering-book-on-the-future-of-our-built-and-made-world/
And then get much closer to home – your kitchen, to be precise – with the Food and Climate Change volume:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/01/06/methane-diet/#3kg-per-day
Reading Chachra's book, I kept thinking about Saul Griffith's amazing Electrify, a shovel-ready book about how we can effect the transition to a fully electrified America:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/12/09/practical-visionary/#popular-engineering
Chachra's How Infrastructure Works makes a great companion volume to Electrify, a kind of inspirational march to play accompaniment on Griffith's nuts-and-bolts journey. It's a lyrical, visionary book, charting a bold course through the climate emergency, to a world of care, maintenance, comfort and abundance.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/17/care-work/#charismatic-megaprojects


My next novel is The Lost Cause, a hopeful novel of the climate emergency. Amazon won't sell the audiobook, so I made my own and I'm pre-selling it on Kickstarter!
#pluralistic#books#reviews#deb chachra#debcha#engineering#infrastructure#free energy#material science#abundance#scarcity#mutual aid#maintenance#99 percent invisible#colonialism#gift guide
262 notes
·
View notes
Text
Imagine the beast pirates learning you are a criminal mastermind

Kaido: *going over a cargo manifest* we will sell these in Port Chugal, prepare them for shipment.
King: Port Chugal won't buy pirate goods anymore, the world government found out they've been trading with us, so they replaced the king there.
Kaido: That's the third distribution market I've had to change in the last month. First the Bourgeois Kingdom, then Ballywood, and now Port Chugal. How are they finding my warehouses?
Queen: we don't know at the moment, but we're working on it
You: *King's assistant* I would like to point out something that all three have in common.
King: Silence.
Kaido: let em talk, I want to hear what they have to say.
You: they were all common stops on Captain Rondow's transport route, who was captured almost three months ago by the world government.
Kaido: You think the poor bastard broke under torture?
You: It appears so, and from the other reports we're getting I'm guessing they have figured out how you conduct your exportation operation. *Hands King the reports*
King: *Skims them* we spent years building this system.
You: which means building another will be faster this time. I'm guessing how they're locating our goods is by the fact that while it's labeled under a company that doesn't have any paperwork officially filed in countries we claim it's from.
Kaido: what are we supposed to do, get a business permit?
You: yes, but actually no. Now any new businesses from any nations in your territory will come under scrutiny by the world government. So I think we should find any failing, but long-established companies, and bail them out in exchange for slipping our illicit cargo into their product distribution.
King: that... might actually work, but there's no way we can guarantee their loyalty.
You: that's why you give them a small percentage of the profits and gather blackmail material. Most rich people are sick fucks will have skeletons in their closet, you just have to look for it.
Kaido: I'll entrust the task to you, and in the meantime we'll have Yamato fill in for you with King.
King: what! No! Your son is... not great at paperwork.
Kaido: Sorry bud, but I'd like to see what they can do on their own, so I'm setting them loose.

Returns from setting up the new network seven months later
Kaido: I just got the finance report for the last quarter
You: *literally just got off the boat* Sir?
King: Your network is more efficient than what we had set up.
Kaido: you're getting promoted, so you can manage it from here.
You: But I was really looking forward to working with King again.
Kaido: then you'll work under him not me.
You: I'm keeping my desk in your office.
King: For someone who ruthlessly castrated a man to get him to do what they wanted, you are very clingy and sentimental.
You: I was well within my rights to revoke that man's dick privilege, you had no idea how man people he's assaulted. I did that town a fucking favor by pickling that man's junk
Kaido: you pickled it!
You: Yes I did, how else, so you think I got an entire town to look the other way about our ships coming into the harbor?
Kaido: I never would have thought of that... You know when I met you I never would have guessed you'd be an asset to my operations. You seemed too soft and naive, too kind.
You: *shrugs* Well thank you for thinking I'm kind, but I just so happen to hate you less than the world government, and you have more money than the revolutionary army. And Lin Lin and her family freaks me out.
King: don't forget Akagami and Whitebeard won't hire you since you've worked with us.
You: *clicks your tongue* and I regret it every day.

Coming Soon

#one piece#one piece x reader#one piece imagine#one piece scenario#beast pirates#animal kingdom pirates#kaido#kaidou#king the conflagration#king the conflagration x reader#king the wildfire x reader#from the depths of the dragons hoard#tma original#4/2/23#no beta we die like men
468 notes
·
View notes
Text
The People have spoken
It has been decided that milk, separated from the passengers by a glass wall, would be the weirdest thing to find taking up half of a passenger car on a train. As such, Network Rail will be recommending this to train operators, so that they may implement a more efficient transport system while adding whimsy into your commute. Please bear in mind that you will not be allowed to drink the milk, only look at it.
Here is an artist’s impression of this revolutionary new concept:

26 notes
·
View notes
Text
"India’s announcement that it aims to reach net zero emissions by 2070 and to meet fifty percent of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030 is a hugely significant moment for the global fight against climate change. India is pioneering a new model of economic development that could avoid the carbon-intensive approaches that many countries have pursued in the past – and provide a blueprint for other developing economies.
The scale of transformation in India is stunning. Its economic growth has been among the highest in the world over the past two decades, lifting of millions of people out of poverty. Every year, India adds a city the size of London to its urban population, involving vast construction of new buildings, factories and transportation networks. Coal and oil have so far served as bedrocks of India’s industrial growth and modernisation, giving a rising number of Indian people access to modern energy services. This includes adding new electricity connections for 50 million citizens each year over the past decade.
The rapid growth in fossil energy consumption has also meant India’s annual CO2 emissions have risen to become the third highest in the world. However, India’s CO2 emissions per person put it near the bottom of the world’s emitters, and they are lower still if you consider historical emissions per person. The same is true of energy consumption: the average household in India consumes a tenth as much electricity as the average household in the United States.
India’s sheer size and its huge scope for growth means that its energy demand is set to grow by more than that of any other country in the coming decades. In a pathway to net zero emissions by 2070, we estimate that most of the growth in energy demand this decade would already have to be met with low-carbon energy sources. It therefore makes sense that Prime Minister Narendra Modi has announced more ambitious targets for 2030, including installing 500 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity, reducing the emissions intensity of its economy by 45%, and reducing a billion tonnes of CO2.
These targets are formidable, but the good news is that the clean energy transition in India is already well underway. It has overachieved its commitment made at COP 21- Paris Summit [a.k.a. 2015, at the same conference that produced the Paris Agreement] by already meeting 40% of its power capacity from non-fossil fuels- almost nine years ahead of its commitment, and the share of solar and wind in India’s energy mix have grown phenomenally. Owing to technological developments, steady policy support, and a vibrant private sector, solar power plants are cheaper to build than coal ones. Renewable electricity is growing at a faster rate in India than any other major economy, with new capacity additions on track to double by 2026...
Subsidies for petrol and diesel were removed in the early 2010s, and subsidies for electric vehicles were introduced in 2019. India’s robust energy efficiency programme has been successful in reducing energy use and emissions from buildings, transport and major industries. Government efforts to provide millions of households with fuel gas for cooking and heating are enabling a steady transition away from the use of traditional biomass such as burning wood. India is also laying the groundwork to scale up important emerging technologies such as hydrogen, battery storage, and low-carbon steel, cement and fertilisers..."
-via IEA (International Energy Agency), January 10, 2022
Note: And since that's a little old, here's an update to show that progress is still going strong:
-via Economic Times: EnergyWorld, March 10, 2023
#india#solar power#renewable energy#green energy#sustainability#wind power#population grown#economic growth#developing economies#renewable electricity#carbon emissions#good news#hope#hope posting
860 notes
·
View notes
Text
RideBoom Revolutionizes Transportation with Innovative Solutions and Unmatched Convenience

RideBoom India is expanding its innovative ridesharing services to 20 more cities across India. Providing affordable, eco-friendly transportation options to the masses.
RideBoom, the leading transportation service provider, is proud to announce its commitment to revolutionizing the transportation industry with innovative solutions and unmatched convenience for riders and drivers alike.
Unmatched Convenience
RideBoom is dedicated to providing unmatched convenience compared to other transportation services. With the RideBoom app, users can easily book a car, taxi, or delivery service right from their mobile devices. The app connects users with nearby drivers or couriers, allowing them to get to their destination or receive their deliveries quickly and efficiently.
Innovative Solutions
RideBoom is constantly innovating to provide the best possible experience for its users. The company has recently expanded its Bike Taxi Service to additional cities, offering an eco-friendly and efficient mode of transportation for short-distance travel. RideBoom is also exploring the integration of electric vehicles into its fleet, demonstrating its commitment to sustainability and the EV revolution.
Commitment to Safety and Reliability
At the core of RideBoom's mission is a dedication to providing safe and reliable transportation services. The company has implemented stringent safety measures and training protocols to ensure that its drivers and couriers deliver a secure and comfortable experience for all users.
Transforming the Ride-Hailing Industry
RideBoom's innovative approach and unwavering commitment to customer satisfaction have positioned the company as a leader in the transportation industry. By continuously introducing new features and adapting to changing market conditions, RideBoom is redefining the way people and goods move, ultimately transforming the ride-hailing landscape.
"RideBoom is committed to revolutionizing the transportation industry and providing our users with the best possible experience," said the RideBoom founder. "We are excited to continue innovating and expanding our services to meet the evolving needs of our customers."
For more information about RideBoom India and its services, please visit https://rideboom.com/india/
About RideBoom India
RideBoom India is the leading ridesharing platform in the country, providing affordable, convenient, and eco-friendly transportation solutions to commuters across India. Founded in 2020, the company has experienced rapid growth and now operates in many cities, connecting passengers with a network of verified drivers. RideBoom India is committed to revolutionizing the way people commute and contributing to a more sustainable future.
#rideboom#delhi rideboom#biketaxi#ola cabs#uber driver#rideboom taxi app#rideboom app#uber taxi#uber#ola
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
o 625 words to know in your target language o
There is a really interesting blog called "Fluent Forever" that aids foreign language learners in tricks, tips and techniques to guide them to achieving fluency "quickly" and efficiently. One of the tricks is to learn these 625 vocab words in your target language, that way you have a basis to start delving into grammar with ease as you can understand a lot of vocab right off the bat. Plus this list of words are common across the world and will aid you in whatever language you are learning. Here is the list in thematic order
• Animal: dog, cat, fish, bird, cow, pig, mouse, horse, wing, animal
• Transportation: train, plane, car, truck, bicycle, bus, boat, ship, tire, gasoline, engine, (train) ticket, transportation
• Location: city, house, apartment, street/road, airport, train station, bridge hotel, restaurant, farm, court, school, office, room, town, university, club, bar, park, camp, store/shop, theater, library, hospital, church, market, country (USA,
France, etc.), building, ground, space (outer space), bank, location
• Clothing: hat, dress, suit, skirt, shirt, T-shirt, pants, shoes, pocket, coat, stain, clothing
• Color: red, green, blue (light/dark), yellow, brown, pink, orange, black, white, gray, color
• People: son, daughter, mother, father, parent (= mother/father), baby, man, woman, brother, sister, family, grandfather, grandmother, husband, wife, king, queen, president, neighbor, boy, girl, child (= boy/girl), adult (= man/woman), human (# animal), friend (Add a friend's name), victim, player, fan, crowd, person
• Job: Teacher, student, lawyer, doctor, patient, waiter, secretary, priest, police, army, soldier, artist, author, manager, reporter, actor, job
• Society: religion, heaven, hell, death, medicine, money, dollar, bill, marriage, wedding, team, race (ethnicity), sex (the act), sex (gender), murder, prison, technology, energy, war, peace, attack, election, magazine, newspaper, poison, gun, sport, race (sport), exercise, ball, game, price, contract, drug, sign, science, God
• Art. band, song, instrument (musical), music, movie, art
• Beverages: coffee, tea, wine, beer, juice, water, milk, beverage
• Food: egg, cheese, bread, soup, cake, chicken, pork, beef, apple, banana orange, lemon, corn, rice, oil, seed, knife, spoon, fork, plate, cup, breakfast, lunch, dinner, sugar, salt, bottle, food
• Home: table, chair, bed, dream, window, door, bedroom, kitchen, bathroom, pencil, pen, photograph, soap, book, page, key, paint, letter, note, wall, paper, floor, ceiling, roof, pool, lock, telephone, garden, yard, needle, bag, box, gift, card, ring, tool
• Electronics: clock, lamp, fan, cell phone, network, computer, program (computer), laptop, screen, camera, television, radio
• Body: head, neck, face, beard, hair, eye, mouth, lip, nose, tooth, ear, tear (drop), tongue, back, toe, finger, foot, hand, leg, arm, shoulder, heart, blood, brain, knee, sweat, disease, bone, voice, skin, body
• Nature: sea, ocean, river, mountain, rain, snow, tree, sun, moon, world, Earth, forest, sky, plant, wind, soil/earth, flower, valley, root, lake, star, grass, leaf, air, sand, beach, wave, fire, ice, island, hill, heat, nature
• Materials: glass, metal, plastic, wood, stone, diamond, clay, dust, gold, copper, silver, material
• Math/Measurements: meter, centimeter, kilogram, inch, foot, pound, half, circle, square, temperature, date, weight, edge, corner
• Misc Nouns: map, dot, consonant, vowel, light, sound, yes, no, piece, pain, injury, hole, image, pattern, noun, verb, adjective
• Directions: top, bottom, side, front, back, outside, inside, up, down, left, right, straight, north, south, east, west, direction
• Seasons: Summer, Spring, Winter, Fall, season
• Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 21, 22, 30, 31, 32, 40, 41, 42, 50, 51, 52, 60, 61, 62, 70, 71, 72, 80, 81, 82, 90, 91, 92, 100, 101, 102, 110, 111, 1000, 1001, 10000, 100000, million, billion, 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, number
• Months: January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December
• Days of the week: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday
• Time: year, month, week, day, hour, minute, second, morning, afternoon, evening, night, time
• Verbs: work, play, walk, run, drive, fly, swim, go, stop, follow, think, speak/say, eat, drink, kill, die, smile, laugh, cry, buy, pay, sell, shoot(a gun), learn, jump, smell, hear (a sound), listen (music), taste, touch, see (a bird), watch (TV), kiss, burn, melt, dig, explode, sit, stand, love, pass by, cut, fight, lie down, dance, sleep, wake up, sing, count, marry, pray, win, lose, mix/stir, bend, wash, cook, open, close, write, call, turn, build, teach, grow, draw, feed, catch, throw, clean, find, fall, push, pull, carry, break, wear, hang, shake, sign, beat, lift
• Adjectives: long, short (long), tall, short (vs tall), wide, narrow, big/large, small/little, slow, fast, hot, cold, warm, cool, new, old (new), young, old (young), weak, dead, alive, heavy, light (heavy), dark, light (dark), nuclear, famous
90 notes
·
View notes