#EDTA cell culture
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
A Beginner’s Guide To Using EDTA And Trypsin Safely In The Lab

Proper handling of reagents such as EDTA and trypsin is of utmost importance in keeping cells intact while working in a cell culture laboratory. Both EDTA and trypsin are important agents used during the detachment and handling of adherent cells, but their safe and effective application relies on knowledge about the properties of each compound and its role in the cell culture system. Read more :- https://www.bloglovin.com/@purmabiologicsllc6/a-beginners-guide-to-using-edta-trypsin-safely-13027393
0 notes
Text
Moth of the Week
African Wild Silk Moth
Gonometa postica
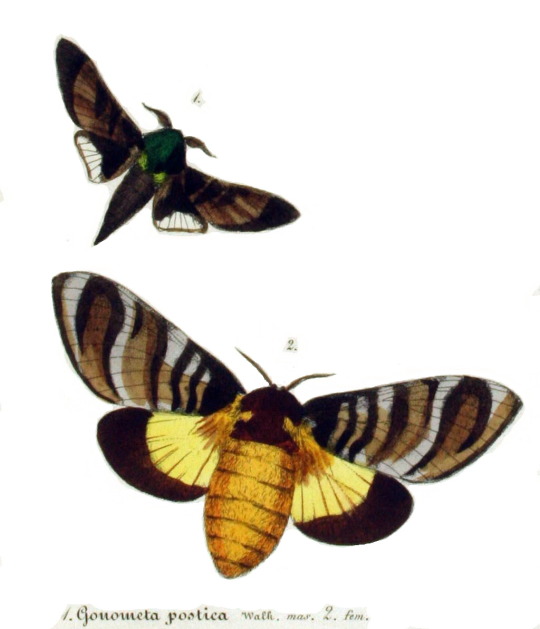

The African wild silk moth is a part of the family Lasiocampidae. It was first described in 1855 by Francis Walker. It is also known as the Brandwurm in its larval stage in Afrikaans, Kweena in its pupal stage in Tshwana, and Molopo moth/mot in English and Afrikaans.
Description The female of this moth is much longer and larger than the male due to having to carry eggs. The male is about half the size of the female and much thinner.
The female has a light brown abdomen with a dark brown thorax and head. The female’s forewings are striped light brown, dark brown, and gray. The hindwings are a yellow-brown with a dark brown edge.
The male has a dark body and wings with a transparent portion of the hindwing.
Female Forewing Range: 35–42 mm (
Male Forewing Range: 21–25 mm (
Diet and Habitat Larva of this species eat Acacia erioloba, A. tortilis, A. melifera, Burkea africana, Brachystegia spp., and Prosopis glandulosa. The larva will feed from the same tree it’s entire life unless there are two many other caterpillars. When there is a large number of caterpillars, they may defoliate the whole tree and the larva must move in order to not starve.
This moth mainly inhabits savannas with many Acacia trees, especially in drier areas. These moths contribute to the Acacia environment by providing food to predators and nutrients to plants through feces. Cocoons are usually found on Acacia tees.
Mating Males detect females’ mating pheromones with their antennae. Males fly to the females because the females are weighed down by the eggs. The female contains about 200 eggs which are laid on the food plant after fertilization. Eggs hatch in about two weeks. Eggs are laid in clumps and the newly hatched caterpillars grow as a group and become more solitary with time.
Predators This moth is preyed on by parasitic wasps and flies. These insects lay their eggs on the caterpillar and feed off of its resources until the moth larva cocoons. The parasites live off the cocoon and grow to adulthood while killing the pupa. Specifically, these larva are subject to parasitism by Diptera and Hymenoptera, the most common parasitoids being Palexorista species from the Tachinidae and Goryphus species from the Ichneumonidae.[6]
To combat external predators and weather, the caterpillars build a tough cocoon. Caterpillars and their cocoons are also covered in stinging hairs to deter predators from touching them. Female cocoons are larger than male cocoons.
Fun Fact In Madagascar, wild silk has been harvested for centuries, and this knowledge has been introduced to southern Africa. The cocoons are harvested commercially in Namibia, Botswana, Kenya and South Africa, and the species also occurs in Zimbabwe and Mozambique. They are difficult to harvest due to the cocoons being covered in calcium oxalate. Oxford University discovered and patented a method known as demineralizing using a warm solution of EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) that soften the cocoons by dissolving the sericin. This lets the silk unravel without weakening it.
- Wild African silk moth cocoons are also used as ankle rattles in southern Africa by San and Bantu tribes. They are filled with materials such as fine gravel, seeds, glass beads, broken sea shells, or pieces of ostrich eggshell.
- Furthermore, the cocoons have long been known to cause the death of cattle, antelope and other ruminants in the Kalahari. During drought periods, the cocoons are eaten, probably because they resemble acacia pods. The silk is indigestible and blocks the rumen of multiple-stomach animals, causing starvation.
- Finally, the protein found in this species’s slik contains many basic amino acids making it a potentially useful biomaterial in cell and tissue culture.
(Source: Wikipedia, SANBI)
#libraryofmoths#animals#bugs#facts#insects#moth#lepidoptera#mothoftheweek#African wild silk moth#Gonometa postica#Lasiocampidae#double post
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering the Order of Draw in Phlebotomy: Essential Guidelines for Accurate Blood Collection
# Mastering the Order of Draw in Phlebotomy: Essential Guidelines for Accurate Blood Collection
**Meta Title:** Mastering the Order of Draw in Phlebotomy | Essential Guidelines
**Meta Description:** Learn about the order of draw in phlebotomy, essential guidelines, benefits, and practical tips for accurate blood sample collection. Master your techniques for optimal results.
## Introduction
In the realm of medical diagnostics, phlebotomy plays a pivotal role. Accurate blood collection is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. One key aspect that often escapes the attention of many practitioners is the **order of draw**. Understanding this guideline is essential for preventing contamination, ensuring accurate test results, and ultimately providing high-quality patient care.
In this article, we will delve into the order of draw in phlebotomy, emphasizing its importance, benefits, practical tips, and experiences that underscore the need for precise blood collection techniques.
## Understanding the Order of Draw
The order of draw refers to the specific sequence in which blood samples should be collected into tubes. This sequence is crucial for minimizing the risk of contamination from additives present in the tubes. The general order of draw, in accordance with The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), is as follows:
1. **Blood Cultures** (if applicable) 2. **Blue Top Tube** (Citrate) 3. **Red Top Tube** (No additive) 4. **Gold Top Tube** or **Tiger Top Tube** (Gel separator) 5. **Green Top Tube** (Heparin) 6. **Lavender Top Tube** (EDTA) 7. **Gray Top Tube** (Fluoride)
### Table 1: Order of Draw for Blood Collection
Tube Color
Additive
Use
Blood Cultures
—
Microbial Analysis
Blue Top
Citrate
Coagulation Studies
Red Top
No Additive
Serology Tests
Gold/Tiger Top
Gel Separator
Serology Tests
Green Top
Heparin
Plasma Tests
Lavender Top
EDTA
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Gray Top
Fluoride
Glucose Testing
## Importance of the Order of Draw
### 1. Preventing Hemolysis and Contamination
Each blood collection tube is designed with specific additives to facilitate different types of tests. If the order is not followed correctly, it can result in hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) or contamination from the additives in previous tubes. For instance, collecting a lavender top tube after a green top tube can lead to contamination with heparin, affecting results for tests requiring EDTA.
### 2. Ensuring Accurate Test Results
Following the correct order of draw is vital for accurate laboratory test results. Inaccurate results might lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment, potentially harming the patient.
### 3. Enhancing Laboratory Efficiency
By adhering to the order of draw, phlebotomists can facilitate smoother workflows in laboratories, allowing for more efficient processing of blood samples. This leads to quicker turnaround times for test results and ultimately better patient care.
## Benefits of Mastering the Order of Draw
### A. Improved Patient Safety
When phlebotomists accurately follow the order of draw, the likelihood of errors is reduced. This not only leads to precise diagnosis and treatment but also enhances overall patient safety.
### B. Cost-Effectiveness
Accurate blood tests mean fewer repeat tests and less wasted time and resources. By mastering the order of draw, healthcare facilities can cut costs related to erroneous test interpretations and follow-up procedures.
### C. Increased Confidence
For phlebotomists, understanding and applying the order of draw fosters a sense of confidence. It reflects diligence and professionalism that clients and healthcare providers appreciate.
## Practical Tips for Mastering the Order of Draw
### 1. Use a Color-Coded Guide
Keep a color-coded chart of the tube types and their corresponding additives within reach during blood collection. Many healthcare facilities provide this visual aid to ensure easy reference.
### 2. Stay Organized
Prepare your collection area and ensure that the necessary tubes are at hand for the order of draw. This approach reduces the chance of accidentally switching the sequence during collection.
### 3. Practice Mindfulness
Stay present and focused during each collection. Take your time to double-check the tube additives and the order before proceeding to collect blood samples.
### 4. Continuous Education
Enroll in workshops, webinars, or training sessions on phlebotomy techniques. Staying updated with the latest standards can reinforce best practices, including the order of draw.
## Case Studies: Real-life Experiences in Phlebotomy
### Case Study 1: An Incident with Miscollection
A phlebotomist at a busy hospital collected a sequence of samples for a patient without adhering to the order of draw. As a result, the lavender tube was collected after the green tube. The laboratory reported hemolysis in the samples, necessitating a repeat blood draw, which caused undue stress for the patient and wasted resources.
### Case Study 2: Training New Phlebotomists
In a training scenario, a seasoned phlebotomist was teaching new hires. They emphasized the order of draw with the aid of a visual reference. The use of guided practice helped the new hires remember the sequence confidently, significantly reducing their error rate during actual draws.
## Conclusion
Mastering the order of draw in phlebotomy is an indispensable part of the blood collection process. By understanding its importance and diligently following established guidelines, phlebotomists can significantly enhance the accuracy of laboratory results and ensure the highest quality of patient care.
By employing practical tips and learning from real-life experiences, both new and experienced phlebotomists can develop their skills effectively. In a field where precision is paramount, mastering the order of draw is not just about following instructions; it’s about ensuring patient safety, optimizing lab efficiency, and fostering a culture of professionalism in healthcare.
—
By addressing the topic with clarity and providing actionable insights, this article serves as a comprehensive guide for anyone involved in or interested in the practice of phlebotomy. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a newcomer, understanding the order of draw will prove invaluable in your medical career.
youtube
https://phlebotomyclassesonline.net/mastering-the-order-of-draw-in-phlebotomy-essential-guidelines-for-accurate-blood-collection/
0 notes
Text
The Essential Guide to the Order of Drawing Blood: Why It Matters and How to Ensure Accurate Results
**Title: The Essential Guide to the Order of Drawing Blood: Why It Matters and How to Ensure Accurate Results**
**Introduction:** Drawing blood is a common medical procedure that is crucial for diagnosing a wide range of health conditions. However, not many people are aware of the specific order in which blood samples should be drawn and the impact it can have on the accuracy of test results. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore why the order of drawing blood matters, how to ensure accurate results, and the benefits of following best practices in blood collection.
**Why Is the Order of Drawing Blood Important?** When collecting multiple blood samples for different tests, the order in which the samples are drawn can significantly affect the results. Here are some key reasons why the order of drawing blood matters:
1. **Preventing Cross-Contamination:** Drawing blood in the wrong order can lead to cross-contamination of samples, resulting in inaccurate test results. For example, if a blood sample for a coagulation test is collected before a sample for a chemistry test, it could introduce contaminants that affect the coagulation test results.
2. **Ensuring Accuracy:** Certain blood tests may be affected by the residual presence of anticoagulants or other substances from previous blood draws. By following the correct order of drawing blood, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of errors and ensure accurate test results.
3. **Avoiding Hemolysis:** Hemolysis, the breakdown of red blood cells, can occur if blood samples are drawn in the wrong order or with excessive force. Hemolyzed samples can lead to unreliable test results and may require repeat blood draws, causing inconvenience for patients.
**The Order of Drawing Blood: Best Practices** To ensure accurate results and minimize the risk of errors in blood collection, healthcare providers should follow these best practices for the order of drawing blood:
1. **Collect Tubes According to Guidelines:** Different blood tubes are used for various types of tests, such as chemistry, hematology, and coagulation tests. Make sure to follow the recommended order of drawing tubes to prevent cross-contamination.
2. **Use the “Proper Order” Rule:** The “proper order” rule states that blood samples should be collected in the following sequence: blood culture tubes, coagulation tubes, serum tubes, heparin tubes, EDTA tubes, and other additives. This order helps to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure accurate results.
3. **Follow Standard Protocols:** Healthcare providers should adhere to standard protocols for blood collection, including using sterile equipment, properly labeling tubes, and ensuring aseptic technique to reduce the risk of infection.
**Benefits of Following Best Practices** By following best practices in the order of drawing blood, healthcare providers can benefit in the following ways:
1. **Improved Patient Safety:** Following proper blood collection procedures ensures the safety and well-being of patients by reducing the risk of errors and complications.
2. **Enhanced Test Accuracy:** Accurate blood test results are crucial for diagnosing and monitoring health conditions. By following the correct order of drawing blood, healthcare providers can improve the accuracy of test results and provide better patient care.
3. **Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness:** Avoiding errors in blood collection can save time and resources by eliminating the need for repeat tests and additional blood draws.
**Practical Tips for Ensuring Accurate Blood Collection** To ensure accurate blood collection and minimize the risk of errors, healthcare providers can follow these practical tips:
1. **Double-Check Labels:** Always double-check the labels on blood tubes to ensure they are correctly labeled with the patient’s information and the type of test to be performed.
2. **Communicate with the Laboratory:** If you have any questions or concerns about the order of drawing blood or specific test requirements, communicate with the laboratory staff for guidance.
3. **Train Staff on Best Practices:** Provide training and education to healthcare staff on the importance of following proper blood collection procedures to maintain quality and accuracy in test results.
**Conclusion:** The order of drawing blood is a critical aspect of the blood collection process that can have a significant impact on the accuracy of test results. By following best practices, healthcare providers can ensure the safety and well-being of patients, improve the quality of test results, and enhance overall efficiency in blood collection procedures. Remember to always prioritize patient safety and adherence to guidelines to deliver high-quality care to your patients.
understanding the importance of the order of drawing blood and implementing best practices in blood collection can help healthcare providers deliver accurate and reliable test results that are essential for diagnosing and treating various health conditions. By prioritizing patient safety and following proper protocols, healthcare providers can maintain high standards of care and ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients.
youtube
https://phlebotomytrainingcenter.net/the-essential-guide-to-the-order-of-drawing-blood-why-it-matters-and-how-to-ensure-accurate-results/
0 notes
Text
Trypsin-EDTA 0.05%
PurMa™ Trypsin-EDTA 0.05% contains ultra-pure trypsin. Furthermore, trypsin is one of the members of the serine protease family. Cell culture laboratories widely use trypsin to dissociate the adherent mammalian cells for routine cell culture. The Trypsin family is conservative. Trypsin performs the best at 37oC and at the PH 7.3-8.5. For any further information visit: https://purmabiologics.com/product/trypsin-3/

0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Order Of The Draw Phlebotomy: Understanding the Importance and Correct Sequence for Blood Collection
**Title: The Ultimate Guide to Order Of The Draw Phlebotomy: Understanding the Importance and Correct Sequence for Blood Collection**
**Introduction** Phlebotomy, the process of drawing blood from patients for various medical tests and procedures, is a crucial aspect of healthcare. The order of the draw in phlebotomy refers to the sequence in which different blood collection tubes are filled during a blood draw. Understanding and following the correct order of draw is essential to ensure accurate test results and patient safety. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the importance of the order of draw in phlebotomy, the correct sequence for blood collection, and provide practical tips for healthcare professionals.
**Importance of Order of Draw** The order of draw in phlebotomy is crucial for several reasons:
1. **Preventing Cross-Contamination**: Using the correct order of draw helps prevent contamination of blood samples with additives from different tubes, which could affect test results.
2. **Ensuring Accurate Test Results**: Following the correct sequence for blood collection minimizes the risk of test result errors due to sample contamination or interference.
3. **Maintaining Patient Safety**: Proper order of draw practices help prevent adverse reactions in patients, such as hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells) or incorrect test results.
**Correct Sequence for Blood Collection** The standard order of draw in phlebotomy is as follows:
1. **Yellow (Sterile) Tube**: Used for blood cultures to detect bacteria or fungi in the bloodstream. This tube must be collected first to prevent contamination with additives from other tubes.
2. **Light Blue Tube**: Contains sodium citrate and is used for coagulation studies, such as PT/INR and APTT tests.
3. **Red Tube**: Does not contain any additives and is used for serum tests, such as glucose and cholesterol levels.
4. **Gold/Red Tiger-Top Tube**: Contains a gel separator and is used for various chemistry tests, including blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and liver function tests.
5. **Light Green Tube**: Contains heparin and is used for plasma tests, such as electrolyte levels and arterial blood gas analysis.
6. **Lavender Tube**: Contains EDTA and is used for hematology tests, such as complete blood count (CBC) and blood typing.
7. **Gray Tube**: Contains anticoagulants, such as sodium fluoride or potassium oxalate, and is used for glucose testing.
By following this standard order of draw, healthcare professionals can ensure the integrity of blood samples and the accuracy of test results.
**Practical Tips for Healthcare Professionals** Here are some practical tips to help healthcare professionals maintain proper order of draw practices:
– Always check the manufacturer’s instructions for the blood collection tubes being used. – Label each tube immediately after collection to avoid mix-ups. – Use a new, sterile needle for each blood collection to prevent cross-contamination. – Invert tubes gently to mix the blood with additives without causing hemolysis.
**Conclusion** Understanding the importance of the order of draw in phlebotomy and following the correct sequence for blood collection are essential for accurate test results and patient safety. By adhering to proper order of draw practices and implementing practical tips, healthcare professionals can ensure the integrity of blood samples and provide high-quality care to patients. Remember, following the standard order of draw is not just a guideline but a critical step in the phlebotomy process.
By prioritizing patient safety and accuracy in blood testing, healthcare professionals can optimize the quality of care provided while maintaining professional standards in phlebotomy practices.
**References** – “Phlebotomy Handbook” by Diana Garza and Kathleen Becan-McBride – “Clinical Laboratory Blood Banking and Transfusion Medicine” by Dr. Christopher Hillyer, Dr. Leslie Silberstein, Dr. Paul Ness, and Dr. Kenneth Anderson.
youtube
https://phlebotomycertificationcourse.net/the-ultimate-guide-to-order-of-the-draw-phlebotomy-understanding-the-importance-and-correct-sequence-for-blood-collection/
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to the Order of Blood Draw: What You Need to Know
**Title: The Ultimate Guide to the Order of Blood Draw: What You Need to Know**
**Introduction**
When it comes to drawing blood for medical testing, following the correct order of draw is crucial to ensure accurate results and patient safety. The order of blood draw refers to the sequence in which different blood tubes are filled during venipuncture. This process helps prevent cross-contamination between tubes and ensures the integrity of the blood samples. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss everything you need to know about the order of blood draw, including why it is important, the correct sequence to follow, and practical tips for healthcare professionals.
**Why is the Order of Blood Draw Important?**
The order of blood draw is essential for several reasons:
1. **Prevents Cross-Contamination:** Different blood tubes contain various additives that can interfere with test results if mixed incorrectly. Following the correct order of draw helps prevent contamination between tubes, ensuring accurate test results.
2. **Maintains Sample Integrity:** Drawing blood in the correct order ensures that the blood samples remain uncontaminated and undiluted, leading to reliable test results.
3. **Minimizes Hemolysis:** Hemolysis, the rupture of red blood cells, can affect test results. By following the proper order of draw, healthcare professionals can reduce the risk of hemolysis and obtain accurate blood samples.
**The Correct Order of Blood Draw**
The recommended order of draw for venipuncture is as follows:
1. **Blood Cultures:** Always draw blood cultures first to prevent contamination with additives from other tubes.
2. **Sodium Citrate (Light Blue):** Used for coagulation studies, such as PT and PTT tests.
3. **Serum Tubes (Red, Gold, or Red/Gray):** These tubes are used for various tests, including chemistry panels and lipid profiles.
4. **Heparin Tubes (Green):** Used for testing electrolytes, cardiac enzymes, and arterial blood gases.
5. **EDTA Tubes (Purple or Pink):** Used for hematology tests, such as CBC and blood typing.
6. **Glycolytic Inhibitor Tubes (Gray):** Used to preserve glucose levels in blood samples.
**Practical Tips for Healthcare Professionals**
To ensure proper blood draw procedures, healthcare professionals should:
1. **Correctly Identify Patients:** Always confirm the patient’s identity and verify the lab order before drawing blood.
2. **Use the Correct Equipment:** Ensure that you have the right needles, tubes, and collection equipment for the tests being performed.
3. **Apply Proper Technique:** Follow standard venipuncture protocols to minimize patient discomfort and reduce the risk of complications.
4. **Label Tubes Accurately:** Label each blood tube with the patient’s name, date, and time of collection to avoid sample mix-ups.
**Conclusion**
Understanding the order of blood draw is essential for healthcare professionals to ensure accurate test results and patient safety. By following the correct sequence and implementing best practices during venipuncture, healthcare providers can maintain the integrity of blood samples and improve the quality of care for their patients. Remember, accuracy and attention to detail are key when it comes to drawing blood, so always adhere to the recommended order of draw guidelines.
mastering the order of blood draw is a fundamental skill for any healthcare professional involved in phlebotomy. By following the correct sequence and implementing best practices, you can enhance the quality of patient care and contribute to the accuracy of diagnostic testing. Remember to prioritize patient safety, sample integrity, and proper technique when performing venipuncture procedures. With this ultimate guide to the order of blood draw, you are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in this critical aspect of healthcare.
youtube
https://phlebotomytechnicianprogram.org/the-ultimate-guide-to-the-order-of-blood-draw-what-you-need-to-know/
0 notes
Text
The Essential Guide to Order of Draw Blood: How Proper Sequence Ensures Accurate Results
**The Essential Guide to Order of Draw Blood: How Proper Sequence Ensures Accurate Results**
When it comes to drawing blood samples for testing, healthcare professionals follow a specific order of draw to ensure accuracy and patient safety. The order of draw is crucial in preventing sample contamination and ensuring that test results are reliable. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the importance of the order of draw blood and provide practical tips to follow the proper sequence.
**Why is the Order of Draw Blood Important?**
The order of draw blood is essential because different blood collection tubes contain different additives to aid in specific tests. If the tubes are not filled in the correct order, there is a risk of contamination and inaccurate results. By following the proper sequence, healthcare professionals can prevent clotting, hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells), and other issues that may affect the quality of the sample.
**The Correct Order of Draw Blood**
Here is the recommended order of draw blood to follow when collecting samples for testing:
1. Yellow tube – Blood culture bottles 2. Light blue tube – Citrate tube for coagulation studies 3. Red tube - Serum tube 4. Gold or tiger top tube – Serum separator tube 5. Light green tube – Heparin tube for plasma determinations 6. Dark green tube – Heparin tube with gel separator 7. Lavender tube – EDTA tube for hematology tests 8. Pink tube - EDTA tube for blood bank tests 9. Gray tube – Oxalate/fluoride tube for glucose testing
By adhering to this specific order, healthcare professionals can ensure that each sample is collected correctly and that the integrity of the specimen is maintained throughout the testing process.
**Benefits of Following the Order of Draw Blood**
– Improved accuracy of test results – Reduced risk of sample contamination – Minimized potential errors in the laboratory – Increased patient safety and satisfaction
**Practical Tips for Proper Blood Collection**
Here are some practical tips to keep in mind when following the order of draw blood:
– Always verify the patient’s identity before starting the blood collection procedure. – Use sterile equipment and follow proper hygiene protocols to prevent infections. – Invert the tubes gently but thoroughly to ensure proper mixing of additives. – Label each tube with the patient’s information and the time of collection. – Transport the samples to the laboratory promptly to maintain sample integrity.
**Case Study: The Impact of Incorrect Order of Draw Blood**
In a recent study conducted at a hospital laboratory, researchers found that deviations from the correct order of draw blood resulted in a 10% increase in sample contamination rates. This led to delays in diagnosis and treatment for patients, as well as increased costs for the healthcare facility. By retraining staff on the proper sequence of blood collection, the contamination rates decreased significantly, improving the overall quality of care provided to patients.
**First-Hand Experience: A Phlebotomist’s Perspective**
As a phlebotomist with over 10 years of experience, I have seen firsthand the importance of following the order of draw blood. By adhering to the recommended sequence, I have been able to consistently provide accurate and reliable test results for healthcare providers. Proper blood collection techniques not only ensure patient safety but also help to streamline the laboratory process and improve overall efficiency.
**Conclusion**
the order of draw blood is a critical component of the blood collection process that healthcare professionals must adhere to. By following the correct sequence, practitioners can ensure accurate test results, maintain sample integrity, and improve patient care outcomes. Remember to always follow proper hygiene protocols, use sterile equipment, and transport samples promptly to the laboratory. By prioritizing the order of draw blood, healthcare providers can uphold the highest standards of quality and safety in patient care.
youtube
https://phlebotomytechnicianschools.net/the-essential-guide-to-order-of-draw-blood-how-proper-sequence-ensures-accurate-results/
0 notes
Text
M2T2
The blood study comprises:
Hematology: whole blood with anticoagulant;
Biochemistry:
Plasma: tube with anticoagulant; Serum: tube without anticoagulant.
Coagulation study;
Cytological study;
Parasitological study;
Immunological study;
Microbiological study.
Routine urine analysis consists of:
Physical examination: color, odor, transparency/turbidity and density;
Chemical examination: pH¹, glucose, ketones, bilirubin², occult blood³, proteins, nitrites, and urobilinogen;
Study of urinary sediment.
The study of feces comprises:
Occult blood detection;
Microbiological analysis;
Parasitological analysis:
Concentration by fluctuation; Sedimentation.
Body fluid analysis requires:
A tube with EDTA anticoagulants: nucleated cell count and cytological studies.
A tube without anticoagulant or with lithium heparin anticoagulant: biochemical parameters;
A sterile tube without anticoagulant: microbiological culture.
Notes:
Coprological analysis: simple, effective, and low-cost technique. Ketone bodies appear in the starvation state. CSF = Cephalo-Spinal Fluid.
¹ 4,7 - 7,0 ² Destruction of erythrocytes in the liver. ³ Blood that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
0 notes
Text
Cell Culture Reagents: Essentials for Successful Cell Research
Cell culture plays a vital role in modern biomedical research, allowing scientists to study the behavior of cells in controlled laboratory settings. Central to any cell culture experiment are the reagents, which are essential components that support cell growth, proliferation, and experimentation. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to the essential cell culture reagents required for successful cell research, covering their functions, applications, and best practices for use.
Growth Media
Growth media are nutrient-rich solutions that provide cells with the essential nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and growth factors necessary for their survival and proliferation. There are various types of growth media available, each formulated to support the specific requirements of different cell types. Common types of growth media include Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), RPMI 1640, and Minimum Essential Medium (MEM). It's essential to select the appropriate growth medium based on the cell type being cultured and the experimental objectives.
Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) is a critical component of many cell culture media formulations. FBS contains a complex mixture of growth factors, hormones, proteins, and other factors that support cell growth and viability. It provides essential nutrients and promotes cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation. However, it's essential to use high-quality FBS from reliable sources to ensure consistency and reproducibility in cell culture experiments.
Antibiotics and Antimycotics
Contamination with bacteria, fungi, or mycoplasma can compromise the integrity of cell culture experiments and lead to inaccurate results. Antibiotics and antimycotics are commonly added to cell culture media to prevent microbial contamination. Common antibiotics used in cell culture include penicillin-streptomycin and gentamicin, while antimycotics such as amphotericin B or fungizone are used to prevent fungal contamination. It's crucial to use antibiotics and antimycotics judiciously to avoid potential adverse effects on cell growth and function.
Serum-Free Media Supplements
In some cell culture applications, researchers may opt for serum-free or defined media formulations to minimize variability and enhance reproducibility. Serum-free media supplements are designed to replace or reduce the dependency on FBS while still providing the necessary nutrients and growth factors for cell growth. These supplements may include insulin, transferrin, selenium (ITS), bovine serum albumin (BSA), and various growth factors and cytokines tailored to specific cell types and applications.
Cell Detachment Reagents
During routine cell culture maintenance or experimental procedures, it's often necessary to detach cells from the culture vessel for subculture, analysis, or further experimentation. Cell detachment reagents facilitate the gentle and efficient dissociation of adherent cells from the culture substrate. Common cell detachment reagents include trypsin-EDTA, accutase, and enzyme-free cell dissociation buffers. Proper selection and optimization of cell detachment reagents are essential to ensure high cell viability and minimal disruption of cell function.
Cell Counting and Viability Assays
Accurate cell counting and viability assessment are essential for quantifying cell populations, monitoring cell growth, and evaluating the effects of experimental treatments. Cell counting reagents, such as trypan blue exclusion, hemocytometers, and automated cell counters, allow researchers to determine cell concentration and viability with precision and reproducibility. These assays are critical for maintaining optimal cell culture conditions and interpreting experimental results accurately.
Cryopreservation Reagents
Cryopreservation is a method used to preserve cells for long-term storage by freezing them at ultra-low temperatures. Cryopreservation reagents, such as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and cryoprotective agents, help protect cells from damage during the freezing and thawing process. Proper cryopreservation techniques and reagent formulations are essential to maintain cell viability and functionality over extended periods. Cryopreserved cells can be thawed and revived as needed for downstream experiments, providing a renewable source of cells for research purposes.
Cell Differentiation and Specialized Culture Reagents
In addition to basic cell culture reagents, specialized reagents may be required for specific applications such as cell differentiation, cell lineage tracing, or organoid culture. These reagents may include growth factors, cytokines, differentiation inducers, extracellular matrix components, or small molecules that modulate cell behavior and function. Proper selection and optimization of specialized culture reagents are essential to replicate physiological conditions and study complex cellular processes accurately.
Conclusion
Cell culture reagents are essential components of any cell culture experiment, providing the necessary nutrients, growth factors, and support systems for cell growth, maintenance, and experimentation. By understanding the functions and applications of various cell culture reagents and following best practices for their use, researchers can ensure the success and reproducibility of their cell culture experiments. Whether studying basic cell biology, disease mechanisms, drug discovery, or regenerative medicine, the right combination of cell culture reagents is essential for advancing scientific knowledge and translating research findings into clinical applications.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Do You Prepare A Trypsin EDTA Solution?

Trypsin is an enzyme used in culture that is used to help release the attached cells of the culture from its growth surface during passaging. It does this by cutting peptide bonds within proteins, which makes it possible to easily release cells. EDTA is a chelating agent that can sequester calcium ions; it works well in combination with 0.25 trypsin EDTA solutions for cell dissociation. Read more:- https://qr.ae/p2B9F9
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Blood Collection Tubes

What is Blood Collection Tubes
Blood collection tubes, also know as vacutainer tubes or phlebotomy tubes, are sterile tubes use to collect and transport blood specimens for medical testing or analysis. They are design to draw and store a specific volume of blood, usually ranging from 2-10 milliliters, depending on the type of tube used and the intended application.
Blood collection tubes are made of plastic or glass and contain various additives, such as anticoagulants or preservatives, to maintain the quality of the blood sample for testing. They come in different sizes, colors, and types, each with a unique combination of additives to suit specific testing requirements.
Importance of Blood Collection Tubes
Blood collection tubes play a crucial role in the collection and analysis of blood samples for medical purposes. There are essential tools use by healthcare professionals, such as phlebotomists, to collect blood specimens from patients for diagnostic tests, blood donations, and research studies.
Blood collection tubes help to ensure the accuracy and reliability of blood test results by providing a standardized and controlled environment for the blood sample. Each type of tube is design with specific additives, such as anticoagulants or preservatives, to preserve the integrity of the sample and prevent clotting or degradation.
The correct use of blood collection tubes is critical for accurate and reliable diagnostic test results. Different types of tubes are use for different types of tests, and following the appropriate protocol for collecting blood samples is essential to avoid errors or contamination.
Different types of Blood Collection Tubes
There are several types of blood collection tubes, each designed for specific types of blood tests. Some of the most common types of blood collection tube discuss below.
Serum Separator Tube (SST):
This tube contains a gel separator that helps separate the serum from the blood cells after centrifugation. It is use for a wide range of tests, including blood chemistry, hormone assays, and serology.
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) Tube: This tube contains EDTA, which binds to calcium and prevents blood from clotting. It is use for hematology tests, such as complete blood count (CBC), blood typing, and DNA analysis.
Heparin Tube
This tube contains heparin, which also prevents blood from clotting. It is use for tests that require plasma, such as coagulation studies, thrombin time, and fibrinogen assays.
Sodium Citrate Tube
This tube contains sodium citrate, which also acts as an anticoagulant. It is use for coagulation studies, including prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and D-dimer.
Fluoride Tube
This tube contains a mixture of fluoride and an anticoagulant (usually EDTA). It is use for glucose testing, as the fluoride prevents glycolysis (the breakdown of glucose in the blood sample).
Blood Culture Bottle
This tube is use for collecting blood specimens for microbiological culture, which helps identify bacterial or fungal infections in the blood.
The choice of blood collection tube depend on the type of test to be performe and the specific requirements of the laboratory. It is essential to follow proper blood collection techniques to ensure accurate and reliable test results.
Best Practices for Blood Collection Tubes
Blood collection tubes are an essential tool for drawing blood samples for various medical purposes, including diagnostic tests, blood donations, and research studies. Here are some best practices for using blood collection tubes:
Handling and Storage
Blood collection tube should be stored at the appropriate temperature, as specified by the manufacturer, to maintain the integrity of the sample. Tubes should be handled with care to prevent damage or contamination.
Order of Draw
The order of draw should be followed to minimize the risk of cross-contamination between tubes. The order of draw is the sequence in which tubes are filled during a blood draw. This helps prevent the transfer of additives or contaminants between tubes.
Needle Size and Angle
The needle size and angle used for blood collection needle should be appropriate for the patient’s age and size. A needle that is too large or inserted at the wrong angle can cause pain and bruising.
Avoiding Hemolysis
Hemolysis, the breakdown of red blood cells, can occur if the blood collection process is not done correctly. This can result in inaccurate test results. To avoid hemolysis, the phlebotomist should use the appropriate size needle, avoid excessive suction, and invert the tube gently after collection.
Know more : Blood Collection Tubes
#BloodCollectionTube#bloodcollectiontubes#healthcare#medical devices#medical equipment#bloodcollectiongtubes#bloodcollectionsets#vacuum blood collection tube#medical instruments#medical equipment manufacturers#medical device manufacturers#medical equipment supplier
0 notes
Text
Cosmetic Chemicals Market Share, Size, Demand, Growth & Trends by 2032
The global cosmetic chemicals market is worth US$ 15.89 Bn as of now and expected to reach US$ 26.84 Bn by the year 2032 at a CAGR of 5.4% between 2022 and 2032.
Ingredients most commonly used in cosmetics are inclusive of preservatives, emulsifiers, moisturizers, thickeners, fragrances, and colors. They could be devised either naturally or synthetically. One could also derive synthetic chemicals from the natural products like bio- or petroleum-based ingredients. However, manufacturing process involved in synthesizing these chemicals is pretty complex. Moreover, as they are ‘derived’, they are categorized as synthetic. The natural products are inclusive of microbial, animal, mineral, and plant.
Elevance Renewable Sciences, Inc. is a manufacturer of specialty chemicals that develops as well as markets the emollients formulated by using the patented technology from various plant-based products for usage in cosmetics, skin lotions, and hair styling products.
Constructive disruption in cosmetic chemicals market is expected to take place through incorporation of technological advancements. On these grounds, Givaudan is making use of plant cell culture as well as phyto peptides technology for developing skin care products. Extensive research is being conducted by the key participants for developing sustainable products to address customers’ demands with growing inclination toward organic and natural cosmetic products.
Request to Sample @ https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-322
Moisturizers and emollients hold more than 30% of the market share. Emollients are known for softening the skin by prevention of water loss. The applications include skin moisturizers, body lotions, lipsticks, and face creams. They get sold at commercial level in both – synthetic and natural forms. Emollients broadly used include coconut oil beeswax, olive oil, lanolin, glycerine, petrolatum (petroleum jelly), zinc oxide, mineral oil, butyl stearate, and diglycol laureate.
Preservatives are added to cosmetics products during their formulations with the objective of extending shelf life and checking the proliferation of fungi and bacteria. The preservatives commonly used are inclusive of benzyl alcohol, parabens, formaldehyde, salicylic acid, and EDTA (tetrasodium ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid). Players like COBIOSA do develop as well as distribute chemicals pertaining to skin care formulations. These chemicals are developed from botanicals inclusive of camelina, polyphenols, collagen, algae, and insects as well. Future Market Insights has walked through these findings with future perspectives in its latest market study entitled ‘Cosmetic Chemicals Market’. It has its line of expertise in the form of analysts and consultants to do the things.
Key Takeaways from Cosmetic Chemicals Market
North America holds more than 34% of the market share. This could be credited to cosmetic chemicals being increasingly used to manufacture organic personal care products.
Europe holds a significant market share in the cosmetic chemicals market. This could be credited to growing demand for the cosmetic products that are formulated through natural ingredients.
The Asia-Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the cosmetic chemicals market due to countries like China and India being subject to rising buying power.
Competitive Chemicals
Knowlton Development Corporation, in February 2020, announced that it had completed acquisition of Shanghai Paristy Daily Chemicals.
Knowlton Development Corporation (KDC/ONE), in December 2019, entered into partnership with HCT Group for creating end-to-end solutions provider for catering to personal care & beauty vertical. The latter is a leader at the global level with respect to provision of full-service solutions of the cosmetic products related to production, filling, design, formulation, and logistics.
Companies do take part in several events as well as exhibitions for promoting the product portfolio and improvising on customer base. On these grounds, Solvay (a multi-specialty chemical company) had attended ‘In-Cosmetics London 2017’ for showcasing company’s formulations related to hair, skin, and body care.
“Growing demand for cosmetic products, that too, formulated with various natural ingredients is expected to drive the cosmetic chemicals market”, says an analyst from Future Market Insights.
What does the Report get through?
The research study is based on product (cosmetic surfactants, cosmetic polymer ingredients, cosmetic colorants, and cosmetic preservatives), and by application (cosmetic chemicals for skin care, cosmetic chemicals for hair care, cosmetic chemicals for make-up applications, cosmetic chemicals for oral care, cosmetic chemicals for fragrances, and cosmetic chemicals for other applications).
Urge to improve appearance and looks is expected to take the cosmetic chemicals market at a greater stride in the years to come.
Key Segments Profiled in the Cosmetic Chemicals Industry Survey
Product:
Cosmetic Surfactants
Cosmetic Polymer Ingredients
Cosmetic Colorants
Cosmetic Preservatives
Application:
Cosmetic Chemicals for Skin Care
Cosmetic Chemicals for Hair Care
Cosmetic Chemicals for Make-Up Applications
Cosmetic Chemicals for Oral Care
Cosmetic Chemicals for Fragrances
Cosmetic Chemicals for Other Applications
Region:
North America
Latin America
Western Europe
Eastern Europe
APEJ
Japan
Middle Eats & Africa
Browse Full Report: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/cosmetic-chemicals-market
0 notes
Text
Some help for fellow Phlebotomy students!
This is the saying that helps me remember the order of draw for venipuncture:
Yellow (blood cultures)
Light (PT, PTT, Coagulation)
Stop (Chemistry testing)
Green (Any plasma test except plasma cells)
Light (Blood group, Carbon Monoxide levels, CBC)
Go (Glucose, Lactic acid, Blood alcohol levels)
And then these are the tubes and their functions!
Yellow tube:
Blood cultures
Invert 8-10x
Light blue tube:
PT
PTT
Coagulation studies.
Always draw two.
Invert 3-4x
Red, tiger, or gold tubes:
Chemistry testing
Electrolyte panel:
Bicarbonate, carbon dioxide, chloride, potassium, sodium
Basic metabolic panels:
Electrolyte panel, BUN, creatinine, glucose, calcium
Drug monitoring:
Digoxin, vancomycin, aminoglycosides, phenobarbital, phenytoin, valproic acid, methotrexate, lithium, theophylline
Comprehensive metabolic panel
Basic metabolic panel, hepatic function panel
Hepatic function panel
ALT, AST, Bilirubin, albumin, total proteins
Total cholesterol
HDL, LDL
Lipid panel
HDL, LDL, TG
Thyroid profile
T3, T4, TSH
Individual tests
Folic acid, Vitamin B12, HIV, hCG
Invert 5-6x
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Capillary/Dermal Tubes:
Pink tube:
Blood bank studies
Rh typing
Pearl/white tube:
bDNA
Keep on ice.
Royal blue with purple or red stripe:
Toxicology
Heavy metal testing
Chain of custody.
Tan, royal blue (no stripe), or lavender:
Lead levels
Royal blue (plain):
Trace metal analysis.
Sodium Heparin
Pale yellow:
Compatibility for transplant
DNA & Paternity testing.
Chain of custody
ACD
Capillary/Dermal Tubes END
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Dark or light green tubes:
Any plasma test EXCEPT plasma cells
C reactive protein for inflammation
Immunoglobin A measures antibodies and tests for autoimmune diseases
Liver enzymes
Bone marrow disorders
Serum HCG
Gets spun!
Lithium heparin
Sodium heparin (Dark green)
Ammonium Heparin
Invert 8-10x
Lavender tubes:
Blood group (ABO)
Carbon monoxide levels
CBC
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
RBC
WBC
WBC w/ diff.
Platelets
Hemoglobin A1c
Rh typing
Sickle cell anemia
ANY blood cells
EDTA
Invert 8-10 times
Gray tubes:
Glucose
Glucose fasting and tolerance testing
Lactic acid
Do NOT use tourniquet
Patient does NOT need to make a fist
Blood alcohol levels:
DO NOT USE alcohol-based antiseptic
USE Chlorhexidine as an antiseptic.
Potassium Oxalate
Sodium Fluoride
Invert 8-10 times
Feel free to let me know if you have any questions, or if I missed something!! This is straight from my notebook, so it's highly likely that I missed something!
Have a wonderful day and stay safe!!
#phlebotomy#medical studies#studyblr#medical student#medical studyblr#medical stuff#order of draw#venipuncture
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Phlebotomy Tests and Tubes: Everything You Need to Know
Title: The Ultimate Guide to Phlebotomy Tests and Tubes: Everything You Need to Know
Introduction: Phlebotomy is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the drawing of blood for various diagnostic tests and treatments. One of the key components of phlebotomy is understanding the different types of tests that can be performed and the various tubes used to collect blood samples. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about phlebotomy tests and tubes, including their types, uses, and best practices.
Types of Phlebotomy Tests: Phlebotomy tests encompass a wide range of diagnostic procedures that involve analyzing blood samples for various purposes. Some common types of phlebotomy tests include: – Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood. – Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP): This test evaluates the levels of electrolytes, glucose, and kidney function markers in the blood. – Lipid Panel: This test assesses the levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. – Blood Glucose Test: This test measures the concentration of glucose in the blood to diagnose diabetes. – Blood Cultures: These tests detect the presence of bacteria or other microorganisms in the blood to diagnose infections.
Types of Phlebotomy Tubes: Phlebotomy tubes, also known as vacutainer tubes, are color-coded tubes that are used to collect blood samples for specific tests. Each tube contains a different additive that helps preserve the integrity of the blood sample for accurate diagnostic results. Some common types of phlebotomy tubes include: – Red Top Tube: This tube contains no additive and is used for collecting serum samples. – Lavender Top Tube: This tube contains EDTA, an anticoagulant, and is used for hematology tests. – Green Top Tube: This tube contains heparin, an anticoagulant, and is used for chemistry tests. – Gray Top Tube: This tube contains sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate, which preserve glucose levels in the blood.
Best Practices for Phlebotomy Tests and Tubes: To ensure accurate test results and patient safety, phlebotomists should adhere to the following best practices: – Verify patient identification before collecting blood samples. – Follow proper aseptic techniques to prevent contamination of blood samples. – Use the correct color-coded tubes for specific tests to avoid errors in sample collection. – Label tubes accurately with patient information and test details. – Properly mix tubes with additives by gently inverting them to ensure proper mixing. – Store blood samples at the appropriate temperature to maintain sample integrity.
Benefits and Practical Tips: - Phlebotomy tests are essential for diagnosing various medical conditions and monitoring patient health. – Proper training and certification in phlebotomy are crucial for ensuring safe and accurate blood sample collection. – Familiarize yourself with the color-coding system for phlebotomy tubes to ensure proper collection and handling of blood samples.
Conclusion: Phlebotomy tests and tubes play a critical role in healthcare by providing valuable diagnostic information for patient care. By understanding the different types of tests and tubes, as well as following best practices for blood sample collection, phlebotomists can ensure accurate test results and patient safety. Remember to always prioritize patient care and follow established protocols to deliver quality phlebotomy services.
youtube
https://phlebotomycertificationcourse.net/the-ultimate-guide-to-phlebotomy-tests-and-tubes-everything-you-need-to-know/
0 notes
Text

Primary Human Epidermal Keratinocytes, adult (C-005-5C)
Thaw procedure
Reagents (do not warm in water bath):
50mL Epilife medium (M-EPI-500CA)
500uLHuman Keratinocytes Growth Supplement (S-005-1)
Steps
Prepare a 37C water bath for the thawing of cryopreserved primary cells.
Sterilize tissue culture hood with 75% alcohol.
Mix the two reagents (do not warm in water bath) in laminar flow culture hood and pour 7mL into a 10cm plate (Corning). Label with date, cell type, passage number, and your name.
Thaw the primary cells in 37C water bath with gentle agitation (around 1 to 2 minutes). Do not thaw thoroughly, a movable sliver of ice should still be seen in the cryogenic tube. Wipe cryogenic tube with 75% alcohol.
Transfer thawed primary cells into plate in laminar flow culture hood.
Use 500uL of fresh medium to wash cryogenic tube by pipetting up and down. Transfer medium into plate.
Store cell in a humidified 37C incubator with 5% CO^2, 95% air.
Do not disturb cell for at least 24 hours before changing cell media the next day by aspirating media then pouring in 7.5mL of fresh media.
They should have a cobblestone appearance, as shown in the picture below.
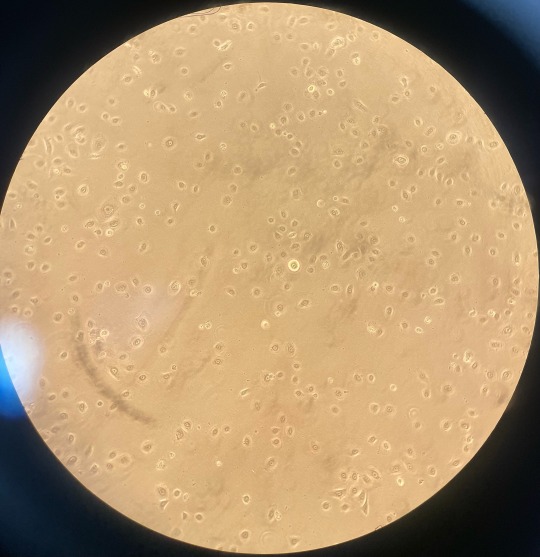
Maintenance procedure
Reagents (do not warm in water bath)
Maintenance medium (Epilife + HKGS)
Reminder
Change media every other day until 85% confluence.
Subculture procedure
Reagents
Trypsin/EDTA solution 0.025%
Maintenance media (Epilife medium + HKGS)
Trypsin Neutralizer Solution,TNS (R-002-100)
Steps
Thaw TNS in 37C water bath, and take out when thawed to cool off.
Sterilize tissue culture hood with 75% alcohol.
Move culture plate to laminar flow culture hood, aspirate medium.
Wash cells with 1mL trypsin/EDTA solution, remove solution after ensuring that entire surface was covered.
Add 1mL trypsin/EDTA and incubate at room temperature for approximately 8 to 10 minutes (check every 4 minutes) until the cells are completely round.
Check under microscope and lightly rap/tap under and on the sides of the the plate to dislodge cells.
When cells are detached, tilt the plate a little and add 3mL TNS into plate. “Wash” cells by gently pipetting solution over the plate several times.
Transfer solution into a sterile 15mL conical tube.
Add 3mL of fresh TNS into plate while tilting the plate. Repeat “wash” action, and transfer solution to the 15mL conical tube. A total of 7mL of solution should be in the 15mL conical tube.
Centrifuge cells at 180g (or 1268rpm for a 100mm radius motor) for 7 minutes.
Observe pellet, then remove supernatent gently from tube.
Resuspend cells gently in maintenance medium by pipetting up and down for a homogenous mixture.
Determine concentration of cells in suspension.
Seed new culture plate with at least 2.5x10^3cells/cm^2.
Incubate in humidified incubator at 37C, with 5% CO^2 and 95% air.
Cryopreserving procedure
Reagents
Trypsin/EDTA 0.025%
CryoStor CS10 Cell Crypreservation Media (C2874)
Maintenance medium (Epilife medium + HKGS)
Steps (if you would like to cryoperserve a tube and continue on with culturing)
Ensure 95% confluency of cells.
Follow “Subculture procedure” steps 1 to 9.
Transfer 4mL of solution to conical tube 2 and centrifuge both tubes at 180g (1268rpm for a 100mm radius motor).
Aspirate solution from both tubes.
Add 1mL to 2 mL cold CryoStor solution to conical tube 1 (previously with 3mL trypsin/EDTA/TNS solution) and resuspend pellet by gentle pipetting. Transfer solution to cryogenic tube and store in -80C overnight before transferring cryogenic tubes to liquid nitrogen.
Resuspend conical tube 2 (previously with 4mL trypsin/EDTA/TNS solution) with maintenance medium and add back to plate with fresh maintenance medium. Incubate plate in humidified incubator at 37C with 5% CO^2 and 95% air.
I guess that’s it for HEKa cell culture. If you have any questions relating to my protocol or otherwise, feel free to DM me 💖
#university#studyspiration#study hard#study blog#studygram#study#studyabroad#studyspo#studyblr#study notes#phdblr#phd research#phd struggles#phdjourney#phd life#phd stuff#phd student#phd guidance#phd studyblr#protocol#protocols#phdracconprotocol#biomedical#science#biomedicine#primary cell#keratinocytes#epidermis
2 notes
·
View notes