#District executive Constituted
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
एनयूजे के विवेक खुराना जिलाध्यक्ष और राहुल सक्सेना महामंत्री निर्वाचित
बदायूं में शक्ति टेंट हाउस पर हुई बैठक में नेशनल यूनियन जर्नलिस्ट्स की जिला कार्यकारिणी का गठन सर्व-सम्मत्ति से किया गया। उत्तर प्रदेश इकाई के संरक्षक प्रमोद गोस्वामी और प्रदेश अध्यक्ष पूर्व मुख्य सूचना आयुक्त वीरेंद्र सक्सेना के निर्देश पर प्रदेश मंत्री एवं सचिव सचिन भारद्वाज “यशोधन” के निर्देशन में सर्वप्रथम सर्वसम्मति से सुशील धीगड़ा और आशु बंसल को संरक्षक चुना गया। तत्पश्चात जिलाध्यक्ष पद पर…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Federal District Court in Florida Holds FCA’s Qui Tam Provisions Unconstitutional
In the Supreme Court’s 2022 decision in United States ex rel. Polansky v. Executive Health Resources, Inc., three justices expressed concern that the False Claims Act’s qui tam provisions violate Article II of the Constitution and called for a case presenting that question. Justice Clarence Thomas penned a dissent explaining that private relators wield significant executive authority yet are not…
#Anti-Fraud Coalition#Article II#Chamber of Commerce#Constitution#False Claims Act#Middle District of Florida#qui tam#SCOTUS#supreme court#United States ex rel Polansky v Executive Health Resources Inc
0 notes
Text















Post 1341
The inmate was able to smuggle the stolen firearm into the police station after his arrest. Video showed the inmate shifting his legs and even maneuvering the weapon while sitting in the back of the police vehicle.
Hollis Daniels 3rd, Texas inmate 02436813, born 1998, incarceration intake February 2023 at age 24, sentenced to life without parole
Capital Murder of LEO
In February 2023, Jurors in the capital murder trial of 24-year-old Hollis Reid Daniels returned to the Court with a verdict sentencing the Seguin Texas native to life in prison without parole for the Oct. 9, 2017 deadly shooting of Texas Tech University police officer Floyd East Jr.
East, 48, had been a certified police officer for five months before he was killed. A native of El Paso, East was in the midst of completing his training at the Texas Tech University Campus in Lubbock and was slated to serve at the El Paso campus when he was done.
Sighs of relief escaped the from the gallery, where Daniels' family sat as the sentence was announced.
The trial began in October 2022, nearly five years to the day of the shooting. For almost three months, from November to about late January, attorneys worked to pare down a pool of hundreds of potential jurors to a 12-person jury panel with four alternates.
Before jurors heard any testimony and opening statements on February 6, 2023, Daniels entered an open plea of guilty to a count of capital murder of a police officer. However, since Daniels' plea did not arise from a negotiation with the District Attorney, he faced the full range of punishment.
From that point on, the trial focused on what Daniels, who testified in his trial, deserved for his actions the night he shot killed East.
To find Daniels deserved the death penalty, jurors had to answer two questions: Whether the evidence showed a probability that Daniels would commit criminal acts of violence that constituted a continuing threat to the prison population in which he will spend the rest of his life and whether there was proof of mitigating circumstances that should spare him the death sentence.
For Daniels to get a life sentence without parole, at least 10 jurors would have to agree that he wasn't a future danger and 10 had to agree that there was sufficient mitigating circumstances to spare him the death sentence. However, all 12 jurors had to be unanimous to send Daniels to death row.
Attorneys on both sides were given four hours to present their closing arguments during which jurors were given two versions of the defendant.
Prosecutors argued that the evidence portrayed the defendant as a cold, manipulative and deceitful killer, who fooled everyone in his life to keep living a drug-fueled, criminal lifestyle. They said Daniels executed East because the officer was on the wrong side of his moral world view.
They said Daniels' actions the night he shot East clearly showed he posed a future danger and that any change he's displayed in the five years of his incarceration at the Lubbock County Detention Center was just another form of manipulation to escape the death penalty.
However, defense attorneys argued Daniels killed the officer in the fog of a 30-hour mental health crisis stemming from drug abuse, unaddressed mental health issues and grief from the loss of a family member the summer before the shooting.
They argued to jurors that their client's clean disciplinary record in his five-years at the jail showed Daniels does not pose a threat to the prison community in which he will spend the rest of his life.
They called on jail volunteers and employees who described Daniels as a model inmate they've seen help others in class or even ease tensions among other inmates. They told jurors they believe Daniels would act the same way in a prison setting.
Chip Lewis, who led Daniels defense, told jurors that he believed the death penalty was a necessary tool to ride society of evil. But it was meant for the worst circumstances, which his client's case did not meet.
He said outside of the 30-hours leading up to the fatal shooting, there was no record his client engaged in violent criminal behavior.
Defense attorney Lauren Byrne told jurors that testimony from Daniels' friends and family showed that for years his parents missed, ignored or misinterpreted signs their son was on a path of self-destruction.
Evidence at the trial showed that East arrested Daniels after responding to his dorm room to investigate a report the then sophomore's roommates made after hearing a gunshot from his room. The investigation shifted when officers found drugs and drug paraphernalia strewn about Daniels' room.
Evidence at the trial included hours of video from police body worn cameras that not only caught Daniels' interactions with police but also East's shooting.
Daniels could be seen speaking with officers coherently and appeared to have no trouble with his coordination. Friends of Daniels told jurors that they knew the defendant was intoxicated on Xanax because he was often lethargic, forgetful, incoherent and uncoordinated.
The trial shed light on how Daniels was able to smuggle the stolen firearm to the Texas Tech police station after his arrest. Video showed Daniels shifting his legs and even maneuvering the weapon while sitting in the back of East's police vehicle.
For a little more than a half-hour Daniels sat with the officer alone in the station's briefing room. Moments before the shooting, Daniels' asked the officer about his family before pressing the weapon against his head and shooting him.
Daniels told jurors that when he encountered the officers in his dorm room, his immediate thoughts were about getting rid of the gun without the officers seeing it, but failed at every attempt.
He said he remembers shooting East but couldn't offer a reason for it.
"I thought I was stuck," he said. "I thought it was all over. I thought this was an opportunity to go out, to commit suicide ... This was me going out in a flash, in a splash, this is how I can go out without doing it to my self."
He told jurors that before shooting East, he asked the officer about his family and his children. He said East's answer might have determined whether he would pull the trigger. However, he said at the same time, he wanted the officer to think about something pleasant before he killed him.
In the end, Jurors found that Daniels was a future danger but more than 10 of them believed there were mitigating circumstances to spare him the death sentence.
Daniels spent approximately five years in the Lubbock County Detention Center as he awaited trial.
4o
49 notes
·
View notes
Text


In mid-August, a three year-old lawsuit charging that environmentalist groups were religious extremists comparable to some of the more violent, intolerant, ultra-orthodox Islamic sects collapsed when the attorney failed to meet a re-filing deadline with the U.S. Supreme Court.
The suit had been brought against the Forest Guardians, the Superior Wilderness Action Network, and the U.S. Forest Service by the 125 companies that make up the Associated Contract Loggers (A.C.L.) of northern Minnesota. The loggers were asking for $600,000 in damages and permission to plunder timber from the Superior National Forest.
Lawyers for the A.C.L. argued that deep ecology was actually a religion, and so by extension, environmental groups that espoused its philosophies were cults, and by outlawing timber cutting on so-called “federal land,” the Forest Service was favoring a particular set of religious doctrines and was therefore violating the guarantee of neutrality in matters of religion purportedly vouchsafed in the U.S. Constitution.
According to theological scholars at the logging company syndicate like former executive director, Larry Jones, Deep Ecology is an “earth-centered religion,” a “belief system” that holds that “trees and Man [sic] are equal.” Anti-logging activists who extol the virtues of forested spaces over industry profit and environmental degradation are spiritual zealots, and the government functionaries who are swayed by their proselytizing may turn out to be fanatical closet druids themselves.
Stephen Young, the A.C.L. lawyer and a former Republican Party senatorial candidate, explained his legal action on such esteemed venues as Rush Limbaugh’s radio show by saying that clear-cutting in national forests had been restricted by the Forest Service for no reason other than reverebce for some fringe New Age religion.
A U.S. District Court judge in Minnesota dismissed the case as “frivolous” in February 2000, but the A.C.L. petitioned the Supreme Court last year after reports that Wahabi Islamic extremists were responsible for the blitzkrieg attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon.
“The doctrine of Deep Ecology is the very worldview that gave rise to eco-terrorism. We feel that after the events of September 11, it’s an obligation of the Supreme Court to keep religious fanaticism in check,” Young said. “Just as devout faith in the literal words of various Hadith of Mohammad gave the Taliban license to impose through state power harsh conditions on the women of Afghanistan, so Deep Ecology gives license to its adherents to take extreme actions against those who would live by different beliefs.”
Perhaps the less said about this sleazy episode the better, which is just as well, since it is so hard to get a firm analytic grasp on it because it is sad and sick on so many different levels. For instance, likening the plight of women in Afghanistan to that of lumber barons in northern Minnesota is staggering in its shamelessness, as it has been my experience that women living near industrial logging camps are subjected to at least the same sort of abuse, derision, and masculinist domination as women who had been living in Taliban-controlled Kandahar.
And we all know that if the U.S. government was serious about keeping homicidal religious terrorism in check, then John Ashcroft and the Army of God anti-abortionists would be in the Guantanamo Bay gulag. It was all obviously just a miserable attempt to slander and jam up anti-logging activists with legal action, and it failed.
But I can’t help thinking about the broader philosophical implications of who supported it. I have no idea as to whether or not there are Deep Ecologists involved in Forest Guardians or the Superior Wilderness Action Network (and I suspect that none are to be found among the Forest Service feds), but in demonizing Deep Ecology as an alien fanatical religious practice in this lawsuit, we can see once again how tighly Christianity is bound to capitalist exploitation and ecological destruction.
Deep ecology is not a single doctrine, but rather an ethical sensibility informed by a variety of perspectives on the relationship of hummankind to the whole of nature’s systems. We can oversimplifydeep ecology by saying that its fundamentals include a belief in the intrinsic value of all forms of life as well as the holistic diversity of those life forms. The economic, technological, and ideological beliefs that prop up Western civilization antagonistically threaten the existence and diversity of natural life systems.
Individuals who adhere to the ideas of Deep Ecology are obligated to work towards radically changing those deadly attitudes and social structures. Deep ecology challenges the long-held anthropocentrist notion which entitles humans to take advantage of and destroy wilderness at will and for private profit, a view obviously held sacred by the A.C.L. timber industrialists.
Anthropocentrism derives from core Judeo-Christian values that have been part of the settler-capitalist catechism on this continent since the early seventeenth-century. Consider, for example, the preaching of Puritan minister, John Cotton. In his popular pamphlet of the 1630’s, “God’s Promise to His Plantation,” Cotton claimed that God desired colonists to “take possesion” of land in New England, saying that whosoever “bestoweth culture and husbandry upon it” has an inviolable divine right to it.
The Native Americans, dying in large numbers from exposure to European diseases was proff that God wanted to wipe the slate clean for the Puritans and thereby better facilitate His decree in the Book of Genesis that humans aggresively “subdue” the earth. Christians were the center of the universe, exclusively licensed by Almighty God to dominate the land, eradicate wild nature, and replace it with the purity of civilization. “All the world out of the Church is as wilderness, or at best, a wild field where all manner of unclean and wild beasts live and feed,” Cotton proclaimed in 1642.
There were many others during the period who were at least as enthusiastic about Christ, colonization, and commercial cultivation as Cotton was, and these ideas, linked to distinctly Judeo-Christian models of linear (rather than seasonally cyclical) time, became ingrained in the settler psyche, especially during the era of westward expansion some two centuries later. Justified by the Calvinist capitalism of Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations — complete with its fallacious notions about the ennobling “civilizing” powers of wealth, marlets, and economic growth — the implications of Puritan repugnance for the wilderness and wildness on the North American continent becomes depressingly clear.
As inheritors of Puritan fanaticism that have erected the violent, intolerant faith of capitalism, it is individuals and organizations like the A.C.L. who hold a worldview that advances a five hundred year-old campaign of terrorism against entire bioregions and “empowers its adherents to take extreme action against those who would live by different beliefs.”
#deep ecology#environment#Fifth Estate#359#Green Scare#legal system#religion#anarchism#revolution#climate crisis#ecology#climate change#resistance#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you're considering not voting or casting a pointless 3rd party vote in the upcoming US elections*, I'd urge you to read about Project 2025, which is the Republican transition plan for if they win the 2024 election (link is for the wiki page, not the actual website).
A short summary:
Project 2025, also known as the Presidential Transition Project, is a collection of policy proposals to fundamentally reshape the U.S. federal government in the event of a Republican victory in the 2024 U.S. presidential election. Established in 2022, the project aims to recruit tens of thousands of conservatives to the District of Columbia to replace existing federal civil servants—whom Republicans characterize as part of the "deep state"—and to further the objectives of the next Republican president. It adopts a maximalist version of the unitary executive theory, a widely disputed interpretation of Article II of the Constitution of the United States, which asserts that the president has absolute power over the executive branch upon inauguration.
Among the many horrifying and notable points:
Abolishing the Department of Education, whose programs would be either transferred to other government agencies, or terminated. Basic research would only be funded if it suits conservative principles.
Promotes the ideal that the government should "maintain a biblically based, social-science-reinforced definition of marriage and family."
Proposed recognition of only heterosexual men and women, the removal of protection against discrimination on the basis of sexual or gender identity, and the elimination of provisions pertaining to diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) from federal legislation.
Individuals who have participated in DEI programs or any initiatives involving critical race theory might be fired.
Explicitly reject abortion as health care
Revive provisions of the Comstock Act of the 1870s that banned mail delivery of any "instrument, substance, drug, medicine, or thing" that could be used for an abortion.
Restrict access to contraception.
Infuse the government with elements of Christianity, and its contributors believe that "freedom is defined by God, not man."
Criminalizing pornography
Combat "affirmative discrimination" or "anti-white racism," citing the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
Deploy the military for domestic law enforcement and to direct the DOJ to pursue Donald Trump's adversaries by invoking the Insurrection Act of 1807.
Recommend the arrest, detention, and deportation of undocumented immigrants across the country.
Promotes capital punishment and the speedy "finality" of such sentences.
Reform the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) so that the nuclear household structure is emphasized.
Give state governments the authority impose stricter work requirements for beneficiaries of Medicaid
Mandate that federal healthcare providers should deny gender-affirming care to transgender people
Eliminate insurance coverage of the morning-after-pill Ella (required by the Affordable Care Act of 2010).
Remove Medicare's ability to negotiate drug prices.
These are just a few things and I'm sure lots of people will be like lol this will never happen but lots of people said this about overturning Roe, as well.
*FWIW - I think it is absolutely valid to be angry, discouraged, and disappointed in our current administration.
Be mad at Biden! (though I would encourage looking into some of the actually positive things his administration has achieved).
But also consider what's at stake for a huge population of this country if we wind up with a GOP win.
#us politics#politics#don't boo vote#there's a reason people say#vote blue no matter who#it's cause the other side actively wants to kill you
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anna Spoerre at Missouri Independent:
A campaign to enshrine abortion rights in Missouri’s constitution said Friday that it collected more than 380,000 signatures in just three months, more than twice the likely total needed to qualify for this year’s statewide ballot. The coalition, called Missourians for Constitutional Freedom, is hoping to put on the November ballot a measure that would legalize abortion up to the point of fetal viability. Since June 2022, nearly every abortion has been illegal in the state with the exception of medical emergencies.
In order to put a citizen-led constitutional amendment before voters, the campaign had to collect signatures from 8% of voters in six of Missouri’s eight congressional districts. That total equates to more than 171,000 signatures. The campaign on Friday morning announced they officially turned in 380,159 signatures to the Missouri Secretary of State’s office. A breakdown of how many signatures came from each district, which will ultimately determine if they met the threshold needed to qualify, was not provided. But the coalition said they collected signatures from each of Missouri’s counties and congressional districts. “Hundreds of thousands of Missourians are now having conversations about abortion and reproductive freedom; some are sharing their own abortion stories for the very first time; and all are ready to do whatever it takes to win at the ballot box this year,” Mallory Schwarz, executive director of Abortion Action Missouri and spokesperson for Missourians for Constitutional Freedom, said in a statement. “Together, we are going to end Missouri’s abortion ban.”
The effort kicked off 90 days ago, requiring a massive undertaking to reach the May 5 signature deadline. The coalition is led by Abortion Action Missouri, the ACLU of Missouri and Planned Parenthood affiliates in Kansas City and St. Louis. [...] Around the same time the abortion campaign was announced, a separate coalition organized to oppose them. That group, called Missouri Stands with Women, spent the past few months leading a “decline to sign” campaign, urging people not to sign the initiative petition. So far, they’ve been vastly out-fundraised by Missourians for Constitutional Freedom. “Out-of-state Big Abortion supporters think the fight is over,” Stephanie Bell, with Missouri Stands With Women, said in a statement Friday. “They could not be more wrong when it comes to standing up for life in Missouri.”
With more than 380,000 signatures across the state of Missouri submitted, despite harassment from anti-abortion extremists with their "decline to sign" intimidation campaign, the pro-abortion rights Missourians for Constitutional Freedom group is highly confident that their ballot measure will qualify for the November ballot.
#Missourians For Constitutional Freedom#Missouri#2024 Ballot Measures and Referendums#2024 Elections#2024 Missouri Elections#Abortion Rights#Abortion#Reproductive Health#Missouri Stands With Women#ACLU of Missouri#Planned Parenthood#Abortion Action Missouri
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
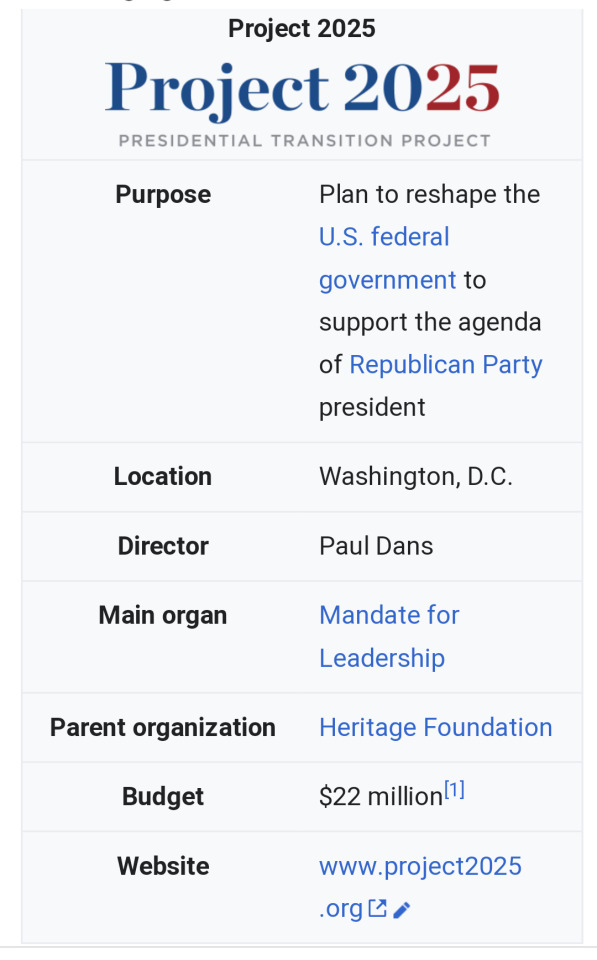
****†** EVERYONE SHOULD READ THIS BEFORE YOU VOTE. ****Project 2025, also known as the Presidential Transition Project, is a collection of policy proposals to thoroughly reshape the U.S. federal government in the event of a Republican victory in the 2024 U.S. presidential election. Established in 2022, the project aims to recruit tens of thousands of conservatives to the District of Columbia to replace existing federal civil servants—whom Republicans characterize as part of the "deep state"—and to further the objectives of the next Republican president. It adopts a maximalist version of the unitary executive theory—which asserts that the president has absolute power over the executive branch upon inauguration. Unitary executive theory is a disputed interpretation of Article II of the Constitution of the United States. Project 2025 envisions widespread changes across the entire government, particularly with regard to economic and social policies and the role of the federal government and its agencies. The plan proposes slashing funding for the Department of Justice (DOJ), dismantling the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), sharply reducing environmental and climate change regulations to favor of fossil fuel production, eliminating the Department of Commerce, and ending the independence of various federal agencies such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The blueprint seeks to institute tax cuts, though its writers disagree on the wisdom of protectionism. .
Project 2025 recommends abolishing the Department of Education, whose programs would be either transferred to other government agencies, or terminated. Scientific research would receive federal funding only if it suits conservative principles. The Project urges the government to explicitly reject abortion as health care and to restrict access to contraception. The Heritage Foundation, an American conservative think tank that leads the development of Project 2025, asserted in April 2024 that "the radical Left hates families" and "wants to eliminate the family and replace it with the state" while driving the country to emulate totalitarian nations, such as North Korea. The Project seeks to infuse the government with elements of Christianity, stating in its Mandate that "freedom is defined by God, not man." Project 2025 proposes criminalizing pornography, removing protections against discrimination based on sexual or gender identity, and terminating diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs, as well as affirmative action. The Project advises the future president to immediately deploy the military for domestic law enforcement and to direct the DOJ to pursue Donald Trump's adversaries by invoking the Insurrection Act of 1807. It recommends the arrest, detention, and deportation of undocumented immigrants across the country. It promotes capital punishment and the speedy "finality" of such sentences. Project director Paul Dans, a former Trump administration official, explained that Project 2025 is "systematically preparing to march into office and bring a new army, aligned, trained, and essentially weaponized conservatives ready to do battle against the deep state." Dans admitted that it was "counterintuitive" to recruit so many people to join the government in order to shrink it, but pointed out the need for a future President to "regain control" of the federal government. Although the project does not promote a specific presidential candidate, many contributors have close ties to Donald Trump and his presidential campaign. The Heritage Foundation has developed Project 2025 in collaboration with over 100 partners including Turning Point USA, led by its executive director Charlie Kirk; the Conservative Partnership Institute including former Trump Chief of Staff Mark Meadows as senior partner; the Center for Renewing America, led by former Trump Office of Management and Budget Director Russell Vought; and America First Legal, led by former Trump Senior Advisor Stephen Miller. The Project is detailed in Mandate for Leadership: The Conservative Promise, a version of which Heritage has written as transition plans for each prospective Republican president since 1980. Critics of Project 2025 have described it as an authoritarian Christian nationalist movement and a path for the United States to become an autocracy. Several experts in law have indicated that it would undermine the rule of law and the separation of powers. Some conservatives and Republicans also criticized the plan, for example in the contexts of centralizing power, climate change, and foreign trade.
#black tumblr#black literature#black community#black americans#civil rights#mexican american#asian american#black colleges#black lives matter#project 2025#americans
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
CNN | Judge dismisses Trump classified documents case
A federal judge on Monday dismissed the classified documents case against Donald Trump, a shock ruling that clears away one of the major legal challenges facing the former president. In a 93-page ruling, District Judge Aileen Cannon said the appointment of special counsel Jack Smith violated the Constitution. She did not rule on whether Trump’s alleged mishandling of classified documents was proper or not. “In the end, it seems the Executive’s growing comfort in appointing ‘regulatory’ special counsels in the more recent era has followed an ad hoc pattern with little judicial scrutiny,” Cannon wrote.
Sigh.
So much for justice.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Project 2025, also known as the Presidential Transition Project, is a collection of conservative policy proposals from The Heritage Foundation to reshape the U.S. federal government in the event of a Republican victory in the 2024 U.S. presidential election.
Established in 2022, the project aims to recruit tens of thousands of conservatives to the District of Columbia to replace existing federal civil servants—whom Republicans characterize as part of the "deep state"—and to further the objectives of the next Republican president.It adopts a maximalist version of the unitary executive theory, a disputed interpretation of Article II of the Constitution of the United States, which asserts that the president has absolute power over the executive branch upon inauguration.
Republicans openly want to supplant the entire executive branch in the same way they have already wrecked the judiciary. Voting in this election for Biden is not optional. If you do not vote for him over Trump, you may never have another vote that matters ever again.
#us politics#politics#trump#biden#us elections#if you are advocating not voting you are either a psyop or an idiot#and if you’re an idiot that’s okay we all are#but question why you think you have the privilege of deciding to abstain from the election of a wannabe facist dictator with a party and a#plan to give him those powers#and then ask yourself again why you’re not voting and what you’re hoping the outcome of that will be. because it will be nothing good.
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is long, but it’s well worth your time.
This might piss some of you off. To that matter, I don’t care. This should make you angry, though it should make you angry at our government and not me. I’m just pointing out the truth and some relating history.
https://www.archives.gov/founding-docs/constitution-transcript
Article 1, Section 8
The Congress shall have Power To lay and collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises, to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defence and general Welfare of the United States; but all Duties, Imposts and Excises shall be uniform throughout the United States;
To borrow Money on the credit of the United States;
To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes;
To establish an uniform Rule of Naturalization, and uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States;
To coin Money, regulate the Value thereof, and of foreign Coin, and fix the Standard of Weights and Measures;
To provide for the Punishment of counterfeiting the Securities and current Coin of the United States;
To establish Post Offices and post Roads;
To promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited Times to Authors and Inventors the exclusive Right to their respective Writings and Discoveries;
To constitute Tribunals inferior to the supreme Court;
To define and punish Piracies and Felonies committed on the high Seas, and Offences against the Law of Nations;
To declare War, grant Letters of Marque and Reprisal, and make Rules concerning Captures on Land and Water;
To raise and support Armies, but no Appropriation of Money to that Use shall be for a longer Term than two Years;
To provide and maintain a Navy;
To make Rules for the Government and Regulation of the land and naval Forces;
To provide for calling forth the Militia to execute the Laws of the Union, suppress Insurrections and repel Invasions;
To provide for organizing, arming, and disciplining, the Militia, and for governing such Part of them as may be employed in the Service of the United States, reserving to the States respectively, the Appointment of the Officers, and the Authority of training the Militia according to the discipline prescribed by Congress;
To exercise exclusive Legislation in all Cases whatsoever, over such District (not exceeding ten Miles square) as may, by Cession of particular States, and the Acceptance of Congress, become the Seat of the Government of the United States, and to exercise like Authority over all Places purchased by the Consent of the Legislature of the State in which the Same shall be, for the Erection of Forts, Magazines, Arsenals, dock-Yards, and other needful Buildings;—And
To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other Powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the United States, or in any Department or Officer thereof.
--
Note: The duties of Congress do not entail any gift giving or foreign donations.
--
Story Time
https://fee.org/resources/not-your-to-give/
[The following story about the famed American icon Davy Crockett was published in Harper’s Magazine in 1867, as written by James J. Bethune, a pseudonym used by Edward S. Ellis. The events that are recounted here are true, including Crockett’s opposition to the bill in question, though the precise rendering and some of the detail are fictional.]
One day in the House of Representatives, a bill was taken up appropriating money for the benefit of a widow of a distinguished naval officer. Several beautiful speeches had been made in its support. The Speaker was just about to put the question when Davy Crockett arose:
“Mr. Speaker–I have as much respect for the memory of the deceased, and as much sympathy for the sufferings of the living, if suffering there be, as any man in this House, but we must not permit our respect for the dead or our sympathy for a part of the living to lead us into an act of injustice to the balance of the living. I will not go into an argument to prove that Congress has no power to appropriate this money as an act of charity. Every member upon this floor knows it. We have the right, as individuals, to give away as much of our own money as we please in charity; but as members of Congress we have no right so to appropriate a dollar of the public money. Some eloquent appeals have been made to us upon the ground that it is a debt due the deceased. Mr. Speaker, the deceased lived long after the close of the war; he was in office to the day of his death, and I have never heard that the government was in arrears to him.
Every man in this House knows it is not a debt. We cannot, without the grossest corruption, appropriate this money as the payment of a debt. We have not the semblance of authority to appropriate it as a charity. Mr. Speaker, I have said we have the right to give as much money of our own as we please. I am the poorest man on this floor. I cannot vote for this bill, but I will give one week’s pay to the object, and if every member of Congress will do the same, it will amount to more than the bill asks.”
He took his seat. Nobody replied. The bill was put upon its passage, and, instead of passing unanimously, as was generally supposed, and as, no doubt, it would, but for that speech, it received but few votes, and, of course, was lost.
Later, when asked by a friend why he had opposed the appropriation, Crockett gave this explanation:
“Several years ago I was one evening standing on the steps of the Capitol with some other members of Congress, when our attention was attracted by a great light over in Georgetown . It was evidently a large fire. We jumped into a hack and drove over as fast as we could. In spite of all that could be done, many houses were burned and many families made homeless, and, besides, some of them had lost all but the clothes they had on. The weather was very cold, and when I saw so many women and children suffering, I felt that something ought to be done for them. The next morning a bill was introduced appropriating $20,000 for their relief. We put aside all other business and rushed it through as soon as it could be done.
“The next summer, when it began to be time to think about the election, I concluded I would take a scout around among the boys of my district. I had no opposition there, but, as the election was some time off, I did not know what might turn up. When riding one day in a part of my district in which I was more of a stranger than any other, I saw a man in a field plowing and coming toward the road. I gauged my gait so that we should meet as he came to the fence. As he came up, I spoke to the man. He replied politely, but, as I thought, rather coldly.
“I began: ‘Well, friend, I am one of those unfortunate beings called candidates, and–’
“‘Yes, I know you; you are Colonel Crockett, I have seen you once before, and voted for you the last time you were elected. I suppose you are out electioneering now, but you had better not waste your time or mine. I shall not vote for you again.’
“This was a sockdolager . . . I begged him to tell me what was the matter.
“‘Well, Colonel, it is hardly worth-while to waste time or words upon it. I do not see how it can be mended, but you gave a vote last winter which shows that either you have not capacity to understand the Constitution, or that you are wanting in the honesty and firmness to be guided by it. In either case you are not the man to represent me. But I beg your pardon for expressing it in that way. I did not intend to avail myself of the privilege of the constituent to speak plainly to a candidate for the purpose of insulting or wounding you. I intend by it only to say that your understanding of the Constitution is very different from mine; and I will say to you what, but for my rudeness, I should not have said, that I believe you to be honest. . . . But an understanding of the Constitution different from mine I cannot overlook, because the Constitution, to be worth anything, must be held sacred, and rigidly observed in all its provisions. The man who wields power and misinterprets it is the more dangerous the more honest he is.’
“‘I admit the truth of all you say, but there must be some mistake about it, for I do not remember that I gave any vote last winter upon any constitutional question.’
“‘No, Colonel, there’s no mistake. Though I live here in the backwoods and seldom go from home, I take the papers from Washington and read very carefully all the proceedings of Congress. My papers say that last winter you voted for a bill to appropriate $20,000 to some sufferers by a fire in Georgetown . Is that true?’
“‘Well, my friend; I may as well own up. You have got me there. But certainly nobody will complain that a great and rich country like ours should give the insignificant sum of $20,000 to relieve its suffering women and children, particularly with a full and overflowing Treasury, and I am sure, if you had been there, you would have done just as I did.’
“‘It is not the amount, Colonel, that I complain of; it is the principle. In the first place, the government ought to have in the Treasury no more than enough for its legitimate purposes. But that has nothing to do with the question. The power of collecting and disbursing money at pleasure is the most dangerous power that can be intrusted to man, particularly under our system of collecting revenue by a tariff, which reaches every man in the country, no matter how poor he may be, and the poorer he is the more he pays in proportion to his means. What is worse, it presses upon him without his knowledge where the weight centers, for there is not a man in the United States who can ever guess how much he pays to the government. So you see, that while you are contributing to relieve one, you are drawing it from thousands who are even worse off than he. If you had the right to give anything, the amount was simply a matter of discretion with you, and you had as much right to give $20,000,000 as $20,000. If you have the right to give to one, you have the right to give to all; and, as the Constitution neither defines charity nor stipulates the amount, you are at liberty to give to any and everything which you may believe, or profess to believe, is a charity, and to any amount you may think proper. You will very easily perceive what a wide door this would open for fraud and corruption and favoritism, on the one hand, and for robbing the people on the other. No, Colonel, Congress has no right to give charity. Individual members may give as much of their own money as they please, but they have no right to touch a dollar of the public money for that purpose. If twice as many houses had been burned in this county as in Georgetown , neither you nor any other member of Congress would have thought of appropriating a dollar for our relief. There are about two hundred and forty members of Congress. If they had shown their sympathy for the sufferers by contributing each one week’s pay, it would have made over $13,000. There are plenty of wealthy men in and around Washington who could have given $20,000 without depriving themselves of even a luxury of life. The congressmen chose to keep their own money, which, if reports be true, some of them spend not very creditably; and the people about Washington , no doubt, applauded you for relieving them from the necessity of giving by giving what was not yours to give. The people have delegated to Congress, by the Constitution, the power to do certain things. To do these, it is authorized to collect and pay moneys, and for nothing else. Everything beyond this is usurpation, and a violation of the Constitution.
“‘So you see, Colonel, you have violated the Constitution in what I consider a vital point. It is a precedent fraught with danger to the country, for when Congress once begins to stretch its power beyond the limits of the Constitution, there is no limit to it, and no security for the people. I have no doubt you acted honestly, but that does not make it any better, except as far as you are personally concerned, and you see that I cannot vote for you.’
“I tell you I felt streaked. I saw if I should have opposition, and this man should go to talking, he would set others to talking, and in that district I was a gone fawn-skin. I could not answer him, and the fact is, I was so fully convinced that he was right, I did not want to. But I must satisfy him, and I said to him:
“‘Well, my friend, you hit the nail upon the head when you said I had not sense enough to understand the Constitution. I intended to be guided by it, and thought I had studied it fully. I have heard many speeches in Congress about the powers of Congress, but what you have said here at your plow has got more hard, sound sense in it than all the fine speeches I ever heard. If I had ever taken the view of it that you have, I would have put my head into the fire before I would have given that vote; and if you will forgive me and vote for me again, if I ever vote for another unconstitutional law I wish I may be shot.’
“He laughingly replied: ‘Yes, Colonel, you have sworn to that once before, but I will trust you again upon one condition. You say that you are convinced that your vote was wrong. Your acknowledgment of it will do more good than beating you for it. If, as you go around the district, you will tell people about this vote, and that you are satisfied it was wrong, I will not only vote for you, but will do what I can to keep down opposition, and, perhaps, I may exert some little influence in that way.’
“‘If I don’t,’ said I, ‘I wish I may be shot; and to convince you that I am in earnest in what I say I will come back this way in a week or ten days, and if you will get up a gathering of the people, I will make a speech to them. Get up a barbecue, and I will pay for it.’
“‘No, Colonel, we are not rich people in this section, but we have plenty of provisions to contribute for a barbecue, and some to spare for those who have none. The push of crops will be over in a few days, and we can then afford a day for a barbecue. This is Thursday; I will see to getting it up on Saturday week. Come to my house on Friday, and we will go together, and I promise you a very respectable crowd to see and hear you.’
“‘Well, I will be here. But one thing more before I say good-by. I must know your name.’
“‘My name is Bunce.’
“‘Not Horatio Bunce?’
“‘Yes.’
“‘Well, Mr. Bunce, I never saw you before, though you say you have seen me, but I know you very well. I am glad I have met you, and very proud that I may hope to have you for my friend.’
“It was one of the luckiest hits of my life that I met him. He mingled but little with the public, but was widely known for his remarkable intelligence and incorruptible integrity, and for a heart brimful and running over with kindness and benevolence, which showed themselves not only in words but in acts. He was the oracle of the whole country around him, and his fame had extended far beyond the circle of his immediate acquaintance. Though I had never met him before, I had heard much of him, and but for this meeting it is very likely I should have had opposition, and had been beaten. One thing is very certain, no man could now stand up in that district under such a vote.
“At the appointed time I was at his house, having told our conversation to every crowd I had met, and to every man I stayed all night with, and I found that it gave the people an interest and a confidence in me stronger than I had every seen manifested before.
“Though I was considerably fatigued when I reached his house, and, under ordinary circumstances, should have gone early to bed, I kept him up until midnight, talking about the principles and affairs of government, and got more real, true knowledge of them than I had got all my life before.
“I have known and seen much of him since, for I respect him–no, that is not the word–I reverence and love him more than any living man, and I go to see him two or three times every year; and I will tell you, sir, if every one who professes to be a Christian lived and acted and enjoyed it as he does, the religion of Christ would take the world by storm.
“But to return to my story. The next morning we went to the barbecue, and, to my surprise, found about a thousand men there. I met a good many whom I had not known before, and they and my friend introduced me around until I had got pretty well acquainted–at least, they all knew me.
“In due time notice was given that I would speak to them. They gathered up around a stand that had been erected. I opened my speech by saying:
“‘Fellow-citizens–I present myself before you today feeling like a new man. My eyes have lately been opened to truths which ignorance or prejudice, or both, had heretofore hidden from my view. I feel that I can today offer you the ability to render you more valuable service than I have ever been able to render before. I am here today more for the purpose of acknowledging my error than to seek your votes. That I should make this acknowledgment is due to myself as well as to you. Whether you will vote for me is a matter for your consideration only.’
“I went on to tell them about the fire and my vote for the appropriation and then told them why I was satisfied it was wrong. I closed by saying:
“‘And now, fellow-citizens, it remains only for me to tell you that the most of the speech you have listened to with so much interest was simply a repetition of the arguments by which your neighbor, Mr. Bunce, convinced me of my error.
“‘It is the best speech I ever made in my life, but he is entitled to the credit for it. And now I hope he is satisfied with his convert and that he will get up here and tell you so.’
“He came upon the stand and said:
“‘Fellow-citizens–It affords me great pleasure to comply with the request of Colonel Crockett. I have always considered him a thoroughly honest man, and I am satisfied that he will faithfully perform all that he has promised you today.’
“He went down, and there went up from that crowd such a shout for Davy Crockett as his name never called forth before.
“I am not much given to tears, but I was taken with a choking then and felt some big drops rolling down my cheeks. And I tell you now that the remembrance of those few words spoken by such a man, and the honest, hearty shout they produced, is worth more to me than all the honors I have received and all the reputation I have ever made, or ever shall make, as a member of Congress.
“Now, sir,” concluded Crockett, “you know why I made that speech yesterday.
“There is one thing now to which I will call your attention. You remember that I proposed to give a week’s pay. There are in that House many very wealthy men–men who think nothing of spending a week’s pay, or a dozen of them, for a dinner or a wine party when they have something to accomplish by it. Some of those same men made beautiful speeches upon the great debt of gratitude which the country owed the deceased–a debt which could not be paid by money–and the insignificance and worthlessness of money, particularly so insignificant a sum as $10,000, when weighted against the honor of the nation. Yet not one of them responded to my proposition. Money with them is nothing but trash when it is to come out of the people. But it is the one great thing for which most of them are striving, and many of them sacrifice honor, integrity, and justice to obtain it.”
Holders of political office are but reflections of the dominant leadership–good or bad–among the electorate.
Horatio Bunce is a striking example of responsible citizenship. Were his kind to multiply, we would see many new faces in public office; or, as in the case of Davy Crockett, a new Crockett.
For either the new faces or the new Crocketts, we must look to the Horatio in ourselves!
--
Why does it matter?
https://foreignassistance.gov/
In 2024 alone, the US has “given” $23 BILLION in US Taxpayer money to 203 countries through 11,000+/- “activities”. The US Constitution does NOT allow for any of this money to be handed out.
Additionally, as much as this might chafe, Congress (and all the departmental budgets) are not supposed to dole out money to natural disaster areas. Those areas are supposed to be handled from a private money or private sector restoration perspective. The US government’s job is the infrastructure (roads, bridges, highways, power, etc) to those impacted areas.
--
If you’re mad as hell about the US government saying all these foreign aid projects are more important than anything related to the protection and safety of our country and its citizenry, then your anger is directed in the right direction. Congress’s job and loyalties are supposed to be directed inward; our country is supposed to be their priority. That our country isn’t their priority is treasonous and grounds for impeachment – the whole lot of them.
BUT, as much as we all want to help our fellow citizens in FL, NC, TN, and HI (Maui fires), that’s not the job of the federal government. They’re not doling out “fed funds”; they’re doling out our Taxes that should be going to any number of things including paying off our debts.
It might sound callous in lieu of the recent hurricane and the one coming, but there’s always a tragedy occurring somewhere whether it’s on the news or not. So, by those events, there’s never a good time. That makes now as good a time as any and maybe better than average since everyone is aware of how corrupt and treasonous our current “leadership” has been. Knowing their allegiance is to anyone not an American, now is the opportune time to turn the light back on Constitutional truth and reeducate people regarding the stated duties of Congress.
#truth#constitution#american history#Dave’s Crockett#congressional duties#foreign aid#appropriation of funds#congressional overstepping#treasonous actions
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Many of you know that I'm a lawyer, retired, but still a member of the bar. I don't practice law (can't), but I still read professional articles and media reports about environmental law and other laws that interest me. From my humble perspective, some of the recent decisions of the US Supreme Court are invalid because the decisions were issued by the Court acting not in its constitutional capacity of a court of appeals, but acting as a court of original jurisdiction. If I'm correct (and I'm sure I can find a slew of right wing lawyers who are laughing at me), then the executive branch of the US government, i.e., the President, is not obligated to enforce those decisions. Plus, the ethical issues of Justice Thomas.......what the fuck is he doing participating in a decision on trump's January 6 sins when Thomas' wife was furiously clicking away on e-mails encouraging the rioting and insurrection? Wishful thinking, but somehow sometime somewhere something dramatic has to happen to smack down the Supreme Court, or at least create some sense of doubt in their tiny little pointed heads.
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
A spate of decisions over the past two years by the Supreme Court has significantly impaired the Environmental Protection Agency’s authority to limit pollution in the air and water, regulate the use of toxic chemicals and reduce the greenhouse gasses that are heating the planet.
This term, the court’s conservative supermajority handed down several rulings that chip away at the power of many federal agencies.
But the environmental agency has been under particular fire, the result of a series of cases brought since 2022 by conservative activists who say that E.P.A. regulations have driven up costs for industries ranging from electric utilities to home building. Those arguments have resonated among justices skeptical of government regulation.
On Friday, the court ended the use of what is known as the Chevron doctrine, a cornerstone of administrative law for 40 years that said that courts should defer to government agencies to interpret unclear laws. That decision threatens the authority of many federal agencies to regulate the environment and also health care, workplace safety, telecommunications, the financial sector and more.
But more remarkable have been several decisions by the court to intervene to stop environmental regulations before they were decided by lower courts or even before they were implemented by the executive branch.
On Thursday, the court said the E.P.A. could not limit smokestack pollution that blows across state borders under a measure known as the “good neighbor rule.” In that case, the court took the surprising step of weighing in while litigation was still pending at the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit.
The court also acted in an unusually preliminary fashion last year when it struck down a proposed E.P.A. rule known as Waters of the United States that was designed to protect millions of acres of wetlands from pollution, acting before the regulation had even been made final.
Similarly, in a 2022 challenge to an E.P.A. climate proposal known as the Clean Power Plan, the court sharply limited the agency’s ability to regulate greenhouse gas emissions from power plants, even though that rule had not yet taken effect.
That kind of intervention has little in the way of precedent. Usually, the Supreme Court is the last venue to hear a case, after arguments have been made and opinions have been rendered by lower courts.
“This court has shown an interest in making law in this area and not having the patience to wait for the cases to first come up through the courts,” said Kevin Minoli, a lawyer who worked in the E.P.A.’s office of general counsel from the Clinton through the Trump administrations. “They’ve been aggressive on ruling. It’s like, we’re going to tell you the answer before you even ask the question.”
Collectively, those decisions now endanger not only many existing environmental rules, but may prevent future administrations from writing new ones, experts say.
“These are among the worst environmental law rulings that the Supreme Court will ever issue,” said Ian Fein, a senior attorney with the Natural Resources Defense Council, an advocacy group. “They all cut sharply against the federal government’s ability to enforce laws that protect us from polluters.”
The march of environmental cases is not over: The court has agreed to hear a case next term that could limit the reach of National Environmental Policy Act, the 1970 law that requires federal agencies to analyze whether their proposed projects have environmental consequences. Businesses and industries have long complained that the reviews can take years, inflate costs and be used by community groups to block projects.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text

Today in North Carolina!
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
September 20, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Sep 21, 2024
On September 16, CNN senior data reporter Harry Enten wrote that while it’s “[p]retty clear that [Democratic candidate Vice President Kamala] Harris is ahead nationally right now… [h]er advantage in the battlegrounds is basically nil. Average it all, Harris’[s] chance of winning the popular vote is 70%. Her chance of winning the electoral college is 50%.” Two days later, on September 18, Senator Lindsey Graham (R-SC) skipped votes in the Senate to travel to Nebraska, where he tried to convince state legislators to switch the state’s system of allotting electoral votes by district to a winner-take-all system. That effort so far appears unsuccessful.
In a country of 50 states and Washington, D.C.—a country of more than 330 million people—presidential elections are decided in just a handful of states, and it is possible for someone who loses the popular vote to become president. We got to this place thanks to the Electoral College, and to two major changes made to it since the ratification of the Constitution.
The men who debated how to elect a president in 1787 worried terribly about making sure there were hedges around the strong executive they were creating so that he could not become a king.
Some of the delegates to the Constitutional Convention wanted Congress to choose the president, but this horrified others who believed that a leader and Congress would collude to take over the government permanently. Others liked the idea of direct election of the president, but this worried delegates from smaller states, who thought that big states would simply be able to name their own favorite sons. It also worried those who pointed out that most voters would have no idea which were the leading men in other states, leaving a national institution, like the organization of Revolutionary War officers called the Society of the Cincinnati, the power to get its members to support their own leader, thus finding a different way to create a dictator.
Ultimately, the framers came up with the election of a president by a group of men well known in their states but not currently office-holders, who would meet somewhere other than the seat of government and would disband as soon as the election was over. Each elector in this so-called Electoral College would cast two votes for president. The man with the most votes would be president, and the man with the second number of votes would be vice president (a system that the Twelfth Amendment ended in 1804). The number of electors would be equal to the number of senators and representatives allotted to each state in Congress. If no candidate earned a majority, the House of Representatives would choose the president, with each state delegation casting a single vote.
In the first two presidential elections—in 1788–1789 and 1792—none of this mattered very much, since the electors cast their ballots unanimously for George Washington. But when Washington stepped down, leaders of the newly formed political parties contended for the presidency. In the election of 1796, Federalist John Adams won, but Thomas Jefferson, who led the Democratic-Republicans (which were not the same as today’s Democrats or Republicans) was keenly aware that had Virginia given him all its electoral votes, rather than splitting them between him and Adams, he would have been president.
On January 12, 1800, Jefferson wrote to the governor of Virginia, James Monroe, urging him to back a winner-take-all system that awarded all Virginia’s electoral votes to the person who won the majority of the vote in the state. He admitted that dividing electoral votes by district “would be more likely to be an exact representation of [voters’] diversified sentiments” but, defending his belief that he was the true popular choice in the country in 1796, said voting by districts “would give a result very different from what would be the sentiment of the whole people of the US. were they assembled together.”
Virginia made the switch. Alarmed, the Federalists in Massachusetts followed suit to make sure Adams got all their votes, and by 1836, every state but South Carolina, where the legislature continued to choose electors until 1860, had switched to winner-take-all.
This change horrified the so-called Father of the Constitution, James Madison, who worried that the new system would divide the nation geographically and encourage sectional tensions. He wrote in 1823 that voting by district, rather than winner-take-all, “was mostly, if not exclusively in view when the Constitution was framed and adopted.” He proposed a constitutional amendment to end winner-take-all.
But almost immediately, the Electoral College caused a different crisis. In 1824, electors split their votes among four candidates—Andrew Jackson, John Quincy Adams, Henry Clay and William Crawford—and none won a majority in the Electoral College. Although Jackson won the most popular votes and the most electoral votes, when the election went to the House, the state delegations chose Adams, the son of former president John Adams.
Furious Jackson supporters thought a developing elite had stolen the election, and after they elected Jackson outright in 1828, the new president on December 8, 1829, implored Congress to amend the Constitution to elect presidents by popular vote. “To the people belongs the right of electing their Chief Magistrate,” he wrote; “it was never designed that their choice should in any case be defeated, either by the intervention of electoral colleges or…the House of Representatives.”
Jackson warned that an election in the House could be corrupted by money or power or ignorance. He also warned that “under the present mode of election a minority may…elect a President,” and such a president could not claim legitimacy. He urged Congress “to amend our system that the office of Chief Magistrate may not be conferred upon any citizen but in pursuance of a fair expression of the will of the majority.”
But by the 1830s, the population of the North was exploding while the South’s was falling behind. The Constitution counted enslaved Americans as three fifths of a person for the purposes of representation, and direct election of the president would erase that advantage slave states had in the Electoral College. Their leaders were not about to throw that advantage away.
In 1865 the Thirteenth Amendment ended slavery (except as punishment for a crime) and scratched out the three-fifths clause, meaning that after the 1870 census the southern states would have more power in the Electoral College than they did before the war. In 1876, Republicans lost the popular vote by about 250,000 votes out of 8.3 million cast, but kept control of the White House through the Electoral College. As Jackson had warned, furious Democrats threatened rebellion. They never considered Republican Rutherford B. Hayes, whom they called “Rutherfraud,” a legitimate president.
In 1888 it happened again. Incumbent Democratic president Grover Cleveland won the popular vote by about 100,000 votes out of 11 million cast, but Republican candidate Benjamin Harrison took the White House thanks to the 36 electoral votes from New York, a state Harrison won by fewer than 15,000 votes out of more than 1.3 million cast. Once in office, he and his team set out to skew the Electoral College permanently in their favor. Over twelve months in 1889–1890, they added six new, sparsely populated states to the Union, splitting the territory of Dakota in two and adding North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, Washington, Idaho, and Wyoming while cutting out New Mexico and Arizona, whose inhabitants they expected would vote for Democrats.
The twentieth century brought another wrench to the Electoral College. The growth of cities, made possible thanks to modern industry—including the steel that supported skyscrapers—and transportation and sanitation, created increasing population differences among the different states.
The Constitution’s framers worried that individual states might try to grab too much power in the House by creating dozens and dozens of congressional districts, so they specified that a district could not be smaller than 30,000 people. But they put no upper limit on district sizes. After the 1920 census revealed that urban Americans outnumbered rural Americans, the House in 1929 capped its numbers at 435 to keep power away from those urban dwellers, including immigrants, that lawmakers considered dangerous, thus skewing the Electoral College in favor of rural America. Today the average congressional district includes 761,169 individuals—more than the entire population of Wyoming, Vermont, or Alaska—which weakens the power of larger states.
In the twenty-first century the earlier problems with the Electoral College have grown until they threaten to establish permanent minority rule. A Republican president hasn’t won the popular vote since voters reelected George W. Bush in 2004, when his popularity was high in the midst of a war. The last Republican who won the popular vote in a normal election cycle was Bush’s father, George H.W. Bush, in 1988, 36 years and nine cycles ago. And yet, Republicans who lost the popular vote won in the Electoral College in 2000—George W. Bush over Democrat Al Gore, who won the popular vote by about a half a million votes—and in 2016, when Democrat Hillary Clinton won the popular vote by about 3 million votes but lost in the Electoral College to Donald Trump.
In our history, four presidents—all Republicans—have lost the popular vote and won the White House through the Electoral College. Trump’s 2024 campaign strategy appears to be to do it again (or to create such chaos that the election goes to the House of Representatives, where there will likely be more Republican-dominated delegations than Democratic ones).
In the 2024 election, Trump has shown little interest in courting voters. Instead, the campaign has thrown its efforts into legal challenges to voting and, apparently, into eking out a win in the Electoral College. The number of electoral votes equals the number of senators and representatives to which each state is entitled (100 + 435) plus three electoral votes for Washington, D.C., for a total of 538. A winning candidate must get a majority of those votes: 270.
Winner-take-all means that presidential elections are won in so-called swing or battleground states. Those are states with election margins of less than 3 points, so close they could be won by either party. The patterns of 2020 suggest that the states most likely to be in contention in 2024 are Arizona, Georgia, Michigan, Nevada, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin, although the Harris-Walz campaign has opened up the map, suggesting its internal numbers show that states like Florida might also be in contention. Candidates and their political action committees focus on those few swing states—touring, giving speeches and rallies, and pouring money into advertising and ground operations.
But in 2024 there is a new wrinkle. The Constitution’s framers agreed on a census every ten years so that representation in Congress could be reapportioned according to demographic changes. As usual, the 2020 census shifted representation, and so the pathway to 270 electoral votes shifted slightly. Those shifts mean that it is possible the election will come down to one electoral vote. Awarding Trump the one electoral vote Nebraska is expected to deliver to Harris could be enough to keep her from becoming president.
Rather than trying to win a majority of voters, just 49 days before the presidential election, Trump supporters—including Senator Graham—are making a desperate effort to use the Electoral College to keep Harris from reaching the requisite 270 electoral votes to win. It is unusual for a senator from one state to interfere in the election processes in another state, but Graham similarly pressured officials in Georgia to swing the vote there toward Trump in 2020.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Letters From An American#Heather Cox Richardson#Lindsay Graham#electoral college#american history#The Constitution's framers#popular vote
11 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Supreme Court ruled that the Defense of Marriage Act was unconstitutional on June 26, 2013.
In U.S. v Windsor, SCOTUS held that the federal government could not discriminate against same-sex couples.
Record Group 267: Records of the Supreme Court of the United States Series: Appellate Jurisdiction Case Files
Transcription:
[Stamped: " FILE COPY "]
(Bench Opinion) OCTOBER TERM, 2012 1 [Handwritten and circled " 1" in upper right-hand corner]
Syllabus
NOTE: Where it is feasible, a syllabus (headnote) will be released, as is
being done in connection with this case, at the time the opinion is issued.
The syllabus constitutes no part of the opinion of the Court but has been
prepared by the Reporter of Decisions for the convenience of the reader.
See United States v. Detroit Timber & Lumber Co., 200 U.S. 321, 337.
SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES
Syllabus
UNITED STATES v. WINDSOR, EXECUTOR OF THE
ESTATE OF SPYER, ET AL.
CERTIORARI TO THE UNITED STATES COURT OF APPEALS FOR
THE SECOND CIRCUIT
No. 12-307. Argued March 27, 2013---Decided June 26, 2013
The State of New York recognizes the marriage of New York residents
Edith Windsor and Thea Spyer, who wed in Ontario, Canada, in
2007. When Spyer died in 2009, she left her entire estate to Windsor.
Windsor sought to claim the federal estate tax exemption for surviv-
ing spouses, but was barred from doing so by §3 of the federal Defense
of Marriage Act (DOMA), which amended the Dictionary Act---a
law providing rules of construction for over 1,000 federal laws and
the whole realm of federal regulations-to define "marriage" and
"spouse" as excluding same-sex partners. Windsor paid $363,053 in
estate taxes and sought a refund, which the Internal Revenue Service
denied. Windsor brought this refund suit, contending that DOMA vi-
olates the principles of equal protection incorporated in the Fifth
Amendment. While the suit was pending, the Attorney General notified
the Speaker of the House of Representatives that the Department
of Justice would no longer defend §3's constitutionality. In re-
sponse, the Bipartisan Legal Advisory Group (BLAG) of the House of
Representatives voted to intervene in the litigation to defend §3's
constitutionality. The District Court permitted the intervention. On
the merits, the court ruled against the United States, finding §3 un-
constitutional and ordering the Treasury to refund Windsor's tax
with interest. The Second Circuit affirmed. The United States has
not complied with the judgment.
Held:
1. This Court has jurisdiction to consider the merits of the case.
This case clearly presented a concrete disagreement between oppos-
ing parties that was suitable for judicial resolution in the District
Court, but the Executive's decision not to defend §3's constitutionali-
[page 2]
2 UNITED STATES v. WINDSOR
Syllabus
ty in court while continuing to deny refunds and assess deficiencies
introduces a complication. Given the Government's concession, ami-
cus contends, once the District Court ordered the refund, the case
should have ended and the appeal been dismissed. But this argu-
ment elides the distinction between Article Ill's jurisdictional re-
quirements and the prudential limits on its exercise, which are "es-
sentially matters of judicial self-governance." Warth v. Seldin, 422
U. S. 490, 500. Here, the United States retains a stake sufficient to
support Article III jurisdiction on appeal and in this Court. The re-
fund it was ordered to pay Windsor is "a real and immediate econom-
ic injury," Hein v. Freedom From Religion Foundation, Inc., 551 U. S.
587, 599, even if the Executive disagrees with §3 of DOMA. Wind-
sor's ongoing claim for funds that the United States refuses to pay
thus establishes a controversy sufficient for Article III jurisdiction.
Cf. INS v. Chadha, 462 U. S. 919.
Prudential considerations, however, demand that there be "con-
crete adverseness which sharpens the presentation of issues upon
which the court so largely depends for illumination of difficult consti-
tutional questions." Baker v. Carr, 369 U. S. 186, 204. Unlike Article
III requirements---which must be satisfied by the parties before judi-
cial consideration is appropriate---prudential factors that counsel
against hearing this case are subject to "countervailing considera-
tions [that] may outweigh the concerns underlying the usual reluc-
tance to exert judicial power." Warth, supra, at 500-501. One such
consideration is the extent to which adversarial presentation of the
issues is ensured by the participation of amici curiae prepared to de-
fend with vigor the legislative act's constitutionality. See Chadha,
supra, at 940. Here, BLAG's substantial adversarial argument for
§3's constitutionality satisfies prudential concerns that otherwise
might counsel against hearing an appeal from a decision with which
the principal parties agree. This conclusion does not mean that it is
appropriate for the Executive as a routine exercise to challenge stat-
utes in court instead of making the case to Congress for amendment
or repeal. But this case is not routine, and BLAG's capable defense
ensures that the prudential issues do not cloud the merits question,
which is of immediate importance to the Federal Government and to
hundreds of thousands of persons. Pp. 5-13.
2. DOMA is unconstitutional as a deprivation of the equal liberty of
persons that is protected by the Fifth Amendment. Pp. 13--26.
(a) By history and tradition the definition and regulation of mar-
riage has been treated as being within the authority and realm of the
separate States. Congress has enacted discrete statutes to regulate
the meaning of marriage in order to further federal policy, but
DOMA, with a directive applicable to over 1,000 federal statues and
[NEW PAGE]
Cite as: 570 U.S._ (2013) 3
Syllabus
the whole realm of federal regulations, has a far greater reach. Its
operation is also directed to a class of persons that the laws of New
York, and of 11 other States, have sought to protect. Assessing the
validity of that intervention requires discussing the historical and
traditional extent of state power and authority over marriage.
Subject to certain constitutional guarantees, see, e.g., Loving v.
Virginia, 388 U.S. 1, "regulation of domestic relations" is "an area
that has long been regarded as a virtually exclusive province of the
States," Sosna v. Iowa, 419 U. S. 393, 404. The significance of state
responsibilities for the definition and regulation of marriage dates to
the Nation's beginning; for "when the Constitution was adopted the
common understanding was that the domestic relations of husband
and wife and parent and child were matters reserved to the States,"
Ohio ex rel. Popovici v. Agler, 280 U. S. 379, 383-384. Marriage laws
may vary from State to State, but they are consistent within each
State.
DOMA rejects this long-established precept. The State's decision
to give this class of persons the right to marry conferred upon them a
dignity and status of immense import. But the Federal Government
uses the state-defined class for the opposite purpose---to impose re-
strictions and disabilities. The question is whether the resulting injury
and indignity is a deprivation of an essential part of the liberty
protected by the Fifth Amendment, since what New York treats as
alike the federal law deems unlike by a law designed to injure the
same class the State seeks to protect. New York's actions were a
proper exercise of its sovereign authority. They reflect both the
community's considered perspective on the historical roots of the in-
stitution of marriage and its evolving understanding of the meaning
of equality. Pp. 13--20.
(b) By seeking to injure the very class New York seeks to protect,
DOMA violates basic due process and equal protection principles ap-
plicable to the Federal Government. The Constitution's guarantee of
equality "must at the very least mean that a bare congressional de-
sire to harm a politically unpopular group cannot" justify disparate
treatment of that group. Department of Agriculture v. Moreno, 413
U. S. 528, 534-535. DOMA cannot survive under these principles.
Its unusual deviation from the tradition of recognizing and accepting
state definitions of marriage operates to deprive same-sex couples of
the benefits and responsibilities that come with federal recognition of
their marriages. This is strong evidence of a law having the purpose
and effect of disapproval of a class recognized and protected by state
law. DOMA's avowed purpose and practical effect are to impose a
disadvantage, a separate status, and so a stigma upon all who enter
into same-sex marriages made lawful by the unquestioned authority
[page 3]
4 UNITED STATES v. WINDSOR
Syllabus
of the States.
DOMA's history of enactment and its own text demonstrate that
interference with the equal dignity of same-sex marriages, conferred
by the States in the exercise of their sovereign power, was more than
an incidental effect of the federal statute. It was its essence. BLAG's
arguments are just as candid about the congressional purpose.
DOMA's operation in practice confirms this purpose. It frustrates
New York's objective of eliminating inequality by writing inequality
into the entire United States Code.
DOMA's principal effect is to identify and make unequal a subset of
state-sanctioned marriages. It contrives to deprive some couples
married under the laws of their State, but not others, of both rights
and responsibilities, creating two contradictory marriage regimes
within the same State. It also forces same-sex couples to live as mar-
ried for the purpose of state law but unmarried for the purpose of
federal law, thus diminishing the stability and predictability of basic
personal relations the State has found it proper to acknowledge and
protect. Pp. 20-26.
699 F. 3d 169, affirmed.
KENNEDY, J., delivered the opinion of the Court, in which GINSBURG,
BREYER, SOTOMAYOR, and KAGAN, JJ., joined. ROBERTS, C. J., filed a
dissenting opinion. SCALIA, J., filed a dissenting opinion, in which
THOMAS, J., joined, and in which ROBERTS, C. J., joined as to Part I.
ALITO, J., filed a dissenting opinion, in which THOMAS, J., joined as to
Parts II and III.
[NEW PAGE]
Cite as: 570 U. S. _ (2013) 1
Opinion of the Court
NOTICE: This opinion is subject to formal revision before publication in the
preliminary print of the United States Reports. Readers are requested to
notify the Reporter of Decisions, Supreme Court of the United States, Washington,
D. C. 20543, of any typographical or other formal errors, in order
that corrections may be made before the preliminary print goes to press.
SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES
No. 12-307
UNITED STATES, PETITIONER v. EDITH SCHLAIN
WINDSOR, IN HER CAPACITY AS EXECUTOR OF THE
ESTATE OF THEA CLARA SPYER, ET AL.
ON WRIT OF CERTIORARI TO THE UNITED STATES COURT OF
APPEALS FOR THE SECOND CIRCUIT
[June 26, 2013]
JUSTICE KENNEDY delivered the opinion of the Court.
Two women then resident in New York were married
in a lawful ceremony in Ontario, Canada, in 2007. Edith
Windsor and Thea Spyer returned to their home in New
York City. When Spyer died in 2009, she left her entire
estate to Windsor. Windsor sought to claim the estate tax
exemption for surviving spouses. She was barred from
doing so, however, by a federal law, the Defense of Mar-
riage Act, which excludes a same-sex partner from the
definition of "spouse" as that term is used in federal stat-
utes. Windsor paid the taxes but filed suit to challenge
the constitutionality of this provision. The United States
District Court and the Court of Appeals ruled that this
portion of the statute is unconstitutional and ordered the
United States to pay Windsor a refund. This Court granted
certiorari and now affirms the judgment in Windsor's
favor.
I
In 1996, as some States were beginning to consider the
concept of same-sex marriage, see, e.g., Baehr v. Lewin, 74
#archivesgov#June 26#2013#2010s#Pride#LGBTQ+#LGBTQ+ history#U.S. v Windsor#Defense of Marriage Act#same-sex marriage#Supreme Court#SCOTUS
143 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dedan Kimathi Waciuri (October 31, 1920 – February 18, 1957) born Kimathi wa Waciuri in British Kenya, was the senior military and spiritual leader of the Mau Mau Uprising. Widely regarded as a revolutionary leader, he led the armed military struggle against the British colonial regime in Kenya in the 1950s until his capture in 1956 and execution. He is credited with leading efforts to create formal military structures within the Mau Mau, and convening a war council in 1953. He, along with Musa Mwariama and Muthoni Kirima, was one of three Field Marshals.
Kenyan nationalists viewed him as the heroic figurehead of the Kenyan freedom struggle against British colonial rule, while the British government saw him as a terrorist. Despite being viewed with disdain by the first two presidents of independent Kenya, Jomo Kenyatta, and Daniel Arap Moi, he and his fellow Mau Mau rebels were recognized as heroes in the struggle for Kenyan independence under the Mwai Kibaki administration, culminating in the unveiling of his statue in 2007. This was reinforced by the passage of a new Constitution in 2010 calling for recognition of national heroes.
He was born in Thegenge Village, Tetu division, Nyeri District. His father died in September 1920, a month after he was born. He was raised by his mother, Waibuthi. He had two brothers and two sisters. He was a passionate writer and wrote extensively before and during the Mau Mau uprising. Tumutumu could not contain his rebellious nature. It is alleged he even tried to paralyze learning at the institution by stealing the school bell. His associates said he took the bell and rang it loudly while atop the Tumutumu hill. The missionaries were lenient, his name remains in the preserved school register. In 1940, he enlisted in the British Army but was discharged after a month, allegedly for drunkenness and persistent violence against his fellow recruits.
He was married to Mukami Kimathi. Among their children are two sons and seven daughters. #africanhistory365 #africanexcellence
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trudy Ring at The Advocate:
A federal court ruled Tuesday that New Hampshire’s classroom censorship law is unconstitutional. The law, House Bill 2, passed in 2021, “actively discouraged public school teachers from teaching and talking about race, gender, sexual orientation, disability, and gender identity inside and outside the classroom,” according to the American Civil Liberties Union’s New Hampshire affiliate, which was among the organizations representing the teachers and advocacy groups challenging the statute. It is the first ruling in the nation striking down a classroom censorship law affecting K-12 public schools. HB 2 amended the state’s education and nondiscrimination laws to stipulate that no one could teach that any group of people was superior due to their race, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity, or certain other characteristics, or that any group was inherently racist, sexist, or oppressive, whether consciously or unconsciously. Like other classroom censorship laws passed in states around the nation, it seems to encourage equal treatment of all, but it’s part of a movement to quash any teaching that racism, sexism, homophobia, or other forms of bigotry exist. They are sometimes characterized as "don't say gay" laws. An earlier New Hampshire bill, which did not pass, was based on Donald Trump’s executive order banning the use of federal funds in educational programs to promote so-called divisive concepts relating to race and sex. Joe Biden rescinded that order when he became president, but the primary components of the earlier New Hampshire legislation were wrapped into HB 2.
Teachers and educational advocates argued that the changes made by HB 2 were “unconstitutionally vague,” and U.S. District Court Judge Paul J. Barbadoro agreed. “The Amendments [contained in HB 2] are viewpoint-based restrictions on speech that do not provide either fair warning to educators of what they prohibit or sufficient standards for law enforcement to prevent arbitrary and discriminatory enforcement,” he wrote. “Thus, the Amendments violate the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.” For instance, he noted, one teacher avoided certain topics both in the classroom and in his role as an adviser to his high school’s Model United Nations project “out of fear that he might violate the Amendments by commenting on the sort of ‘controversial topics’ that frequently arise at Model UN competitions.” Another teacher said he shied away from discussions of the legacy of slavery when teaching about Toni Morrison’s novel Beloved. “These examples are only illustrative of the wide-ranging difficulties that teachers face in attempting to conform their behavior to the vague strictures of the Amendments,” Barbadoro wrote.
New Hampshire’s anti-LGBTQ+ Don’t Say Gay or Trans law HB2 got rightly struck down by a federal judge.
#New Hampshire HB2#New Hampshire#Don't Say Gay or Trans#LGBT Schools#LGBTQ+#Anti LGBTQ+ Extremism#Schools#Local 8027 v. Edelblut#New Hampshire HB544
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
The April 10 legislative elections in South Korea loom especially large for President Yoon Suk-yeol. After winning his election in March 2022 by the narrowest margin in the country’s history, the conservative Yoon inherited the National Assembly elected in 2020, in which South Korea’s liberals won a historic landslide thanks to the Moon Jae-in administration’s strong response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Out of the legislature’s 300 seats, the liberal coalition won a 180-seat majority, the largest margin of victory in South Korea’s democratic history.
Two years into his five-year presidential term, Yoon has left a mark in areas that are down to the president alone. Yoon made profligate use of presidential decrees, executive orders that don’t require legislative approval. In his first year, Yoon issued 809 presidential decrees, while his two immediate predecessors, Moon and Park Geun-hye, issued 660 and 653 decrees, respectively, in their first years. Yoon also exerted influence through his appointments—most notably Park Min, the new head of the state-owned broadcaster KBS who sacked popular liberal journalists as soon as he took office. In foreign policy, Yoon capitulated to Japan’s demands to sideline World War II-era Korean forced laborers and release wastewater from the failed Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, paving the way for U.S.-Japan-South Korea trilateral cooperation.
But in areas that require legislative assent, Yoon has been stymied. The South Korean Constitution allows the executive branch to directly propose a bill to the legislature. For the first six months of Yoon’s presidency, the National Assembly refused to pass a single bill proposed by the government. Yoon’s campaign pledge of abolishing the Ministry of Gender Equality and Family, pandering to the toxic misogyny rampant among young Korean men and fueling their conservative turn, has not come to pass because a reorganization of cabinet ministries requires passing a law. (Yoon has responded by simply refusing to appoint a gender equality minister.)
Meanwhile, the opposition Democratic Party has leveraged its commanding majority to pass laws that could have been highly damaging to Yoon, such as providing for special prosecutor investigations of the Itaewon Halloween disaster, in which 159 partygoers died in crushing crowds in Seoul’s popular nightlife district, and the alleged stock pump-and-dump scheme on the part of first lady Kim Keon-hee. Each time, Yoon responded by exercising a presidential veto, quickly racking up nine vetoes in the first two years of his presidency—equal to the total number of vetoes exercised by six of his predecessors combined.
Naturally, the Yoon administration and the ruling People Power Party (PPP) are heavily focused on recapturing the legislative majority in elections this month. Yoon was able to win the presidency by flipping a significant part of Seoul from liberal to conservative between 2020 and 2022, by pandering heavily to grievances over rising property tax. The real estate slump since Yoon’s election—Seoul’s condominium prices dipped by more than 7 percent in the past year—threatened to erode that support, as the lower condo price damaged upper-middle-class Seoul residents’ primary investment while the decreased profits and higher interest rate pushed large construction companies to the brink.
In response, South Korea’s Financial Supervisory Service audited banks for charging what the regulators claimed were overly high interest rates, in a move seen as a tactic to pressure banks to extend loans to companies that posed a credit risk. The government also delayed the publication of major economic indicators such as the previous year’s budget deficit and the rising price of consumer goods until after election day on April 10.
For its interim leader in the run-up to the election, the PPP tapped Han Dong-hoon, Yoon’s justice minister and heir apparent. Because of his patrician air and relative youth at 51 years old, Han has been hailed as representing the next generation of conservatives. In the words of conservative columnist Kim Soon-deok of Dong-A Ilbo, Han stands in contrast to Yoon in three ways: “First, he does not drink. Second, he is not a stinky old man. Third, he dresses well and speaks with refined language.” With Han at the center, the conservative party has been able to distance itself from the deeply unpopular president.
The Yoon administration also enjoyed a bump in popularity with its proposal to increase the number of medical students by 2,000—a significant jump from the current level of around 3,000. South Korea has a very low number of doctors, which has resulted in a lack of access to medical care especially outside the Seoul metropolitan area. At just 2.6 doctors per 1,000 people, it’s as low as in the United States, which also has a significant and artificially created shortage, and less than half of the number of most developed countries. Doctors reacted strongly, with more than 90 percent of interns and residents going on strike. Nevertheless, the Yoon administration effectively painted doctors as money-grubbers who wished to artificially restrict the size of their ranks to protect their bottom line. With all these moves, by late February it appeared that Yoon and the conservatives had put themselves in the pole position.
Meanwhile, South Korean liberals have been mired in a civil war. Lee Jae-myung, the leader of the Democratic Party and a former presidential candidate who opposed Yoon, began as a member of the minority faction within his party. As the Democratic Party finalized its slate of candidates in February, the legislators not aligned with Lee found themselves sidelined from running for their seats again. Many of them—including high-ranking members such as Assembly Deputy Speaker Kim Young-joo—quit the party, casting their lot with the PPP or seeking a third-party bid with former Prime Minister Lee Nak-yeon, who lost a bitter presidential primary against Lee in 2021.
But the campaign landscape changed dramatically in March as a new third party, the Rebuilding Korea Party (RKP), took the scene by storm. The RKP was founded by Cho Kuk, who was widely considered to be the heir apparent to Moon as the liberal president’s justice minister. Instead, Cho’s short time in office fueled the rise of Yoon.
As South Korea’s prosecutor general at the time, Yoon conducted a massive investigation campaign against Cho and his family, eventually putting his wife in prison for forging a service certificate that was included in their daughter’s college applications. Yoon’s prosecution of Cho galvanized the conservatives, who saw Cho as a symbol of liberal hypocrisy. Liberals, on the other hand, saw Cho as a martyr whose family was destroyed for the sake of Yoon’s quest for power.
With Yoon’s unpopularity, the latter narrative began to win out. The RKP’s slogan is not subtle: “Three years is too long,” referring to the remaining term of Yoon’s presidency. The new party quickly became the rallying flag for South Korean liberals critical of Yoon but disappointed with the Democratic Party’s internal squabbling. Even moderates began joining the RKP ranks, attracted by the clear message of punishing the Yoon administration. Within weeks of its launch, the RKP became South Korea’s most popular party with approximately 25 percent support.
A major turning point came on March 18, when Yoon made a highly publicized visit to a supermarket—a photo op to show that the president was tending to the wild increase in food prices. In January and February, the cost of food in South Korea increased by 6.7 percent year over year, with popular items like apples rising by as much as 121.9 percent in the same period, resulting in some supermarkets selling a single apple for 19,800 won (about $15).
At the supermarket, Yoon held up a bundle of scallions and said: “I do a lot of grocery shopping, and 875 won for a bundle seems reasonable.” But in most grocery stores around South Korea, a bundle of scallions typically sells for between 4,000 and 7,000 won; the supermarket that Yoon visited just happened to be running a suspiciously well-timed promotion on scallions.
Yoon’s attempt at Potemkin produce, over a household item whose price is common knowledge, instantly became fodder for viral mockery. Especially in the Seoul metropolitan area, where partisanship is relatively weak and election results tend to alternate, support for the conservatives began crashing. Yoon’s gaffe, and the rise of his nemesis Cho, is threatening to reverse the gain that South Korea’s conservatives have made in Seoul in the past two years.
Seeking to recapture the momentum, Yoon took to the bully pulpit on April 1 to exhort the striking doctors to return to work. But the government’s standoff against doctors is now losing popularity, as the public is facing the consequences of a lack of medical care, such as emergency rooms rejecting ambulances and cancer surgeries being delayed indefinitely. The newly elected head of the Korea Medical Association vowed that the doctors would not negotiate unless Yoon apologized and sacked the health minister.
In his April 1 statement, Yoon offered no compromise—a stance that has done little for conservatives as election day approaches. After the president’s address, one unnamed conservative legislator despaired: “I feel like a dinosaur looking up at the oncoming comet, sensing our extinction.”
14 notes
·
View notes