#DialogflowCX
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Utilizing Dialogflow CX To Develop A Self-Escalating Chatbot
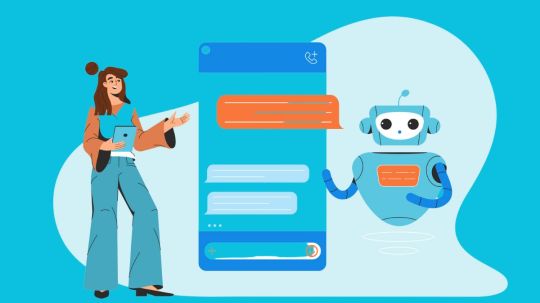
Use Webhooks and Generators to build a self-escalating chatbot in Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX). Application developers must create chatbots that can accurately offer information and recognize when to escalate a user’s issue to a human agent, as conversational AI becomes an increasingly important aspect of the user experience.
This blog article will demonstrate how to use Google Cloud’s generative AI products, including Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) and Vertex AI, to build a self-escalating chatbot.
The solution has a number of advantages:
Better user experience: Even for complicated queries, users get quick help and accurate information.
Reduced agent workload: Agent effort is decreased since agents are given succinct recaps of prior exchanges, which enables them to handle problems quickly.
Improved chatbot capabilities: By learning from escalated requests, the chatbot can get better at handling encounters in the future.
Enhanced security and scalability: Cloud Run Functions (CRF) offers a safe and scalable environment for executing the webhook function.
Build the knowledge base
Suppose it would like a chatbot to respond to inquiries on Indian tourism. First, it will develop it using Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) and Vertex AI Agent Builder.
Datastore without structure: To use Vertex AI to index an article on “Tourism in India” as an unstructured datastore. This enables the chatbot to instantly access and extract pertinent information from the article, giving thorough responses to user inquiries.
Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX): To utilize Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) to create the conversational flow, which allows the chatbot to comprehend user intent and react accordingly.
Gauge user satisfaction
Asking the user if they are happy with the chatbot’s response is an essential part of the conversation flow that to include to guarantee user happiness. This is accomplished by employing “yes” and “no” chips that are defined as part of the custom payload, giving consumers an easy-to-understand method of expressing their opinions.
Escalate with generative AI
The chatbot starts the escalation procedure if the user clicks “no,” indicating discontent. This is where generative AI’s capability is useful.
Generators: In Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX), it develop a generator called “Summarize_mail” that summarizes the discussion using a zero-shot prompt, which is a direct prompt without any examples. The body of an email is then created using this summary, giving the human agent context.
You are an English expert in summarizing the text in form of a very short mail. Summarize the conversation and write it in form of a concise e-mail which will be forwarded to an agent as a ticket. The mail should be on point, properly formatted and written in formal tone with a polite closure. Keep the text as less as possible. Also, specify the conversation messages below the summary which are present in the conversation. The conversation is as follows: $conversation The feedback of the user about the issue is $last-user-utterance.
Model setup: To assist guarantee logical and instructive summaries, this generator makes use of the Gemini-1.5-flash model with a temperature of 0.3.
Trigger the email with Cloud Run Functions (CRF)
To link it Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) agent to a serverless function that is set up on Cloud Run Functions via a webhook in order to send the email. The logic for sending emails is handled by this function.
Configuring Cloud Run Functions (CRF): The following options are used while configuring the CRF:
Python 3.12 is the runtime.
Setting: Second Generation
Point of entry: handle_webhook
Type of trigger: HTTPS
Allotted memory: 256 MiB
Settings for ingress: Permit all traffic.
Requirements: functions-framework==3 (requirements.txt).
For Dialogflow CX Webhooks, are you unsure which CRF version to select? Here’s how to make a decision quickly:
First Generation: Suitable for simple webhooks with less demanding performance needs, it is easier to set up and deploy.
Second Generation: Better suited for intricate webhooks or high-traffic situations, it provides greater flexibility, control, and scalability.
Connect the pieces
To guarantee that the escalation procedure is initiated appropriately when necessary, provide the URL of it installed CRF as the webhook URL in Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX).
Here’s how it all comes together
With a focus on the escalation process and the function of the CRF, this breakdown offers a thorough knowledge of the Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) flow architecture. Don’t forget to modify the email’s text, messages, and flow to fit your unique requirements and branding.
The name of the flow, such as “Customer Support Flow”
Pages: “Start Page” and “Escalate” are the two pages.
Start Page
Purpose: The goal is to greet the user and start a conversation while measuring their level of happiness.
Greeting entry fulfillment:
“Hello, name!” says the agent. Tell us how to may help you, please.
Datastore response entry fulfillment:
“Are you satisfied with the response?” asks the agent.
(This generates the “Yes” and “No” chips.) Custom payload
Routes:
Status: “Yes” chip was chosen
Transition: First page (Denotes that the discussion was successful.)
“Thank you!” says the agent. Do you need to assistance with anything else?
Situation: “No” chip was chosen
Transition: Page “Escalate”
“Sorry to hear that!” the agent says. (Recognizes user discontent.)
Escalate
Purpose: Providing the user with the choice to escalate to a human agent is the goal.
Fulfillment of entry:
“Would you like to escalate?” asks the agent.
(Identical “Yes” and “No” chips as the “Start Page”) Custom payload
Routes:
Situation: “No” chip was chosen
Change of Scene: “Start Page”
“Sure, Thank you!” the agent replies. (Permits the user to keep using the bot.)
Status: “Yes” chip was chosen
“Escalation Webhook” is the transition.
Webhook: Functions of Cloud Run (Starts the escalation procedure)
Goals:
It use the training terms “yes” and “no” to indicate the two intentions “confirm.yes” and “confirm.no.” This is equivalent to the user clicking on the “yes” and “no” chips or just writing the words or phrases that are comparable.
Cloud Run Functions (Escalation Webhook)
Trigger: When the “Escalate” page switches to the webhook, the HTTPS Eventarc trigger is triggered.
Usability:
Compile the history of the conversation: Using the $conversation in the generator prompt, which records the discussion between the agent and the user, excluding the user’s final utterance and the agent’s subsequent utterances, get and parse the whole conversation history from the Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) session.
Create a succinct synopsis of the discussion ($conversation), emphasizing any important user requests or problems.
Retrieve user data: Get the user’s email address (along with any other pertinent information) from your user database or the Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) session.
Write an email: Make an email using:
Topic: (for instance, “Escalated Conversation from [User Email]”)
Recipient: The email address of the support agent
CC: The email address of the user
Body:
Details about the user (e.g., name, ID)
Synopsis of the conversation
If accessible, a link to the entire discussion in Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX)
Send email: Send the email using the API provided by your email provider or an email sending library (such as sendgrid, mailgun, or smtp).
Optional return response: Notify Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) that the user’s request has been escalated by sending a response (e.g., “The mail is successfully sent!” or “Your request has been escalated”). An agent will be in touch with you soon.”
Chatbot testing and results
You may test the chatbot by clicking “Publish” and then “Try it now” after finishing the aforementioned steps.
A few examples of user journeys are as follows:
The user does not want to escalate further since they are dissatisfied with the response.
The user escalates as well since they are dissatisfied with the response. The right image below displays an example of triggered mail.
This method demonstrates how to integrate several Google Cloud services, such as Vertex AI, to create intelligent and intuitive chatbots.
This may anticipate even more creative solutions that improve client experiences as conversational AI develops further.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#UtilizingDialogflowCX#DevelopA#VertexAI#SelfEscalatingChatbot#CloudRunFunctions#Gemini15flash#DialogflowCX#Chatbottesting#EscalationWebhook#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Embed Dialogflow ES Chatbot with Messaging Apps & Websites

Dialogflow ES or Dialogflow Essentials
Dialogflow, a service provided by Google Cloud that enables the creation of conversational agents that comprehend and react to natural language, is frequently used by organisations seeking to develop chatbots. Because Dialogflow CX comes in two variants and has sophisticated chatbot features, many organisations opt for it. If you integrate a chatbot with your website without using a middleware solution, you run the danger of using unauthenticated URLs or directly inserting sensitive credentials like service account keys into the frontend. For production-grade systems, this is not a great practice since it can leave your agent and Google project ID vulnerable.
By adding an Apigee layer between your frontend and DialogFlow CX APIs, you can lessen this. Google Cloud provides Apigee, a full lifecycle API management platform that helps companies create, protect, publish, examine, track, and make money from their APIs. Apigee offers a wide range of capabilities and advantages by serving as a strong layer between clients that access backend services and them. In this situation, Apigee offers:
Centralised authorization and authentication: Apigee manages all authorization and authentication procedures, serving as a safe gateway. As a result, there’s no need to reveal login credentials on the front end. Controlled access: Using Apigee, you can create fine-grained access controls that specify which frontend elements are able to communicate with which DialogFlow CX APIs. Apigee facilitates the management of API keys by streamlining the rotation and revocation procedures in the event of a compromise. Threat protection: To protect your APIs from abuse and possible attacks, Apigee comes with built-in tools like rate limitation, quota management, and spike arrest. Dialogueflow CX basics
This guide covers Dialogflow CX basics. It summarises key ideas.
Agents Dialogflow CX agents are virtual agents that handle concurrent end-user discussions. This natural language understanding module understands human language subtleties. Dialogflow converts conversational text or audio into structured data your apps and services can understand. You create a Dialogflow agent for your system’s talks.
Dialogflow agents resemble call centre agents. You prepare them both to handle typical conversation scenarios without being explicit.
Flows Complex conversations often cover numerous topics. Pizza delivery agents may discuss meal order, customer details, and confirmation. An agent needs many conversational turns to get end-user information on each topic.
Flows define themes and conversational pathways. Every agent has a Default Start Flow. One flow may be enough for a simple agent. Different development team members can construct and maintain flows for more complex agents.
Dialogflow CX flows resemble Dialogflow ES mega agent sub-agents. Flows improve conversation control without costing more.
Dialogflow ES A Google Cloud service called Dialogflow ES, or Dialogflow Essentials, lets you create virtual assistants and chatbots. It’s a viable choice for building chatbots that manage easier interactions and chores.
The following is an overview of Dialogflow ES’s features: Dialogflow ES uses natural language understanding, or NLU, to decipher user text or spoken words. It determines the purpose of the user’s query and retrieves pertinent data (entities) such as names, locations, and dates. Pre-built features: To facilitate conversation management, Dialogflow ES includes pre-built functionality. In addition to handling small talk and asking customers if they need any additional help, it can refer users to human agents in the event that it is unable to understand them. Integrations: Dialogflow ES may be integrated with a number of different platforms, including websites, phone systems, and messaging apps. This enables you to use your chatbot in many locations. The following are a few Dialogflow ES usage cases: Chatbots for customer service: Respond to often asked queries, solve issues, and get user input. Make it possible for people to make appointments via a chat interface. Information retrieval: Give consumers details about goods, services, or corporate guidelines. The alternative edition of Dialogflow, called Dialogflow CX, is a viable option if you’re searching for a strong solution for sophisticated chatbots with cutting-edge features. Still, Dialogflow ES is a decent choice if you want to start building chatbots for easier jobs. Pages
A Dialogflow CX session is a state machine. Pages reflect CX session states.
For each flow, you define several pages that can cover its topics. At any one time, one page is active and its flow is active. All flows have unique start pages. The start page becomes the current page when a flow starts. Every conversational turn, the page either stays the same or changes.
You configure each page to capture end-user information related to its conversational state.
Entity types Entity types control end-user data extraction. CX entity types like ES entity types. Dialogflow predefined system entities match many common data types. There are system entities for matching dates, timings, colours, email addresses, etc. You can also create custom entities to match specific data. You may define a vegetable object to match grocery shop agent veggie selections.
Parameters Parameters store and reference end-user session values. Parameters have names and object types. Instead of raw end-user input, parameters are structured data that can be used for logic or answers.
The syntax of CX parameters has changed, but they are the same as ES parameters in terms of usability and scope.
Forms You can construct a form for each page to collect end-user parameters. The agent talks to the end-user many times until it collects all form parameters, or page parameters. The agent collects these parameters in page order. You give the agent prompts to ask the end-user for each form parameter. A process called form filling.
A Collect Customer Info page might employ a form to collect the end-user’s name and phone number.
CX form filling resembles ES slot filling.
Intents An end-user’s conversation turn intent is categorised. Compared to ES intentions, CX intents are simpler and more reusable.
Webhook
Webhooks are programmes that can call other programmes or host your business logic. Webhooks let you use the information that Dialogflow’s natural language processing extracts throughout a session to validate data that has been collected, generate dynamic answers, or start backend activities.
There are two types of webhooks: standard and adaptable. Dialogflow defines the request and response fields for a typical webhook. You can specify the request and response fields when using a flexible webhook.
Fulfilment An agent’s response to an end-user inquiry, information request, or session termination marks the beginning of the conversational turn. In order to provide dynamic responses or take action for a turn, your agent might also need to get in touch with your service. All of this is achieved through the use of fulfilment.
Any of the following could be present in a fulfilment:
Responses that are static. Webhook requests action and/or dynamic responses. Set or override parameter values with parameter presets. It is feasible (and occasionally desirable) to call more than one fulfilment during an agent’s turn, and each fulfilment may provide a response message. These answers are kept in a response queue by Dialogflow. Dialogflow sends the end-user the ordered responses after the agent’s turn is over.
The only way to use ES fulfilment is to link a webhook service. For CX, the scope of fulfilment has been expanded to include all possible prompts and responses.
State handlers State handlers, commonly referred to as handlers, are responsible for managing the conversation by generating responses for end users and/or switching between pages. Handlers are assessed for every conversational turn and have the potential to impact the session.
Integrations Dialogflow CX has various built-in discussion platform connections. These integrations call the Dialogflow API for you and provide an end-user experience. Simply design your agent and possibly install a webhook service. The integration documentation outlines how each integration handles interactions on each platform.
Interactions Each verbal turn involves interaction. Dialogflow responds to end-user input. You can handle interactions with your system using the API or an integration.
When using API, your system must handle:
Make an agent. Create an end-user interface. For each conversational turn, transmit end-user input to the Dialogflow API. A webhook service is needed for webhook-enabled fulfilment unless agent responses are static (uncommon). Your system just needs to handle the following with an integration:
Make an agent. Webhooks are optional. By acting as a middleman, Apigee gives you a strong tool for managing and monitoring your APIs in addition to improving the security of your chatbot integration. We’ll show you how to set up Apigee to enhance conversational agent security in this post.
Setting up and customising the conversational agents Apigee Proxy
To begin, launch a new Apigee instance on Google Cloud or utilise an already-existing one. To create an instance of an assessment trail, click this link. Use this instructions to create a DialogFlow CX Agent. Retrieve the Agent ID and location from the console and save them for later use. Establish a service account and assign the function of “DialogFlow API Client.” Click “Create a Proxy” of type “Reverse Proxy” on apigee.google. cloud. Give it a name, such as “myproxy.” Set up the DialogFlow CX Detect Intent API as the target endpoint, and change the project, agent, and location as needed. Add and to the HTTP target connection in the Proxy Develop tab as indicated below. Set up the proxy in the environment that is accessible. It is crucial that you use the Service Account that you previously generated in this stage. Requests to the DialogFlow CX API will be authenticated using this Service Account. Try your proxy using any API client. An answer from the DialogFlow CX Intent API ought to be visible to you. Whoa! The DialogFlow CX should be communicating with your proxy and operating as intended.
The complete course of the request can be traced using the Apigee debug console for verification.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
0 notes