#Cluster sampling challenges
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Cluster Sampling: Types, Advantages, Limitations, and Examples
Explore the various types, advantages, limitations, and real-world examples of cluster sampling in our informative blog. Learn how this sampling method can help researchers gather data efficiently and effectively for insightful analysis.
#Cluster sampling#Sampling techniques#Cluster sampling definition#Cluster sampling steps#Types of cluster sampling#Advantages of cluster sampling#Limitations of cluster sampling#Cluster sampling comparison#Cluster sampling examples#Cluster sampling applications#Cluster sampling process#Cluster sampling methodology#Cluster sampling in research#Cluster sampling in surveys#Cluster sampling in statistics#Cluster sampling design#Cluster sampling procedure#Cluster sampling considerations#Cluster sampling analysis#Cluster sampling benefits#Cluster sampling challenges#Cluster sampling vs other methods#Cluster sampling vs stratified sampling#Cluster sampling vs random sampling#Cluster sampling vs systematic sampling#Cluster sampling vs convenience sampling#Cluster sampling vs multistage sampling#Cluster sampling vs quota sampling#Cluster sampling vs snowball sampling#Cluster sampling steps explained
0 notes
Text

Nakarkos is such an interesting creature, so I opted on another monstie sharing its theme. - KARAKAGAU Title - Fulgurite dragon Monster class - Elder dragon Known locales - Deserts Element/ailment - Paralysis Elemental weakness - Water (3), Dragon (2), Ice (1), Thunder (0), Fire (0) Ailment weakness - Paralysis (3), Poison (2), Blast (2), Stun (1), Sleep (1) Karakagau is an elder dragon endemic to desert regions. Contrary to most of its clade, it has an invertebrate form with a multitude of tentacles and a huge soft body. The relation to Nakarkos is obvious, as is its unique placement among elder dragons. Camouflaged by its brown and gold colours, Karakagau excels at burrowing, its rear tendrils digging out pits whilst breathing tubes and motion-sensitive fins protrude above the sand. Though known to sample fruits from time to time, Karakagau is primarily a lurking predator, creating large pits in the sand and waiting patiently for prey to stumble into its grasp, most of its body hidden save for its breathing tubes and fins. To potentially increases its chances of success, Karakagau will wriggle a tentacle around in the pit, mimicking the motions of a trapped animal to lure in other carnivores. For this reason, field workers are advised to pay extremely close attention to their surroundings when working in desert environments, as Karakagau will not hesitate to take humans as prey. Fortunately, there are subtle clues to indicate Karakagau's presence. The elder dragon exudes a strange paralytic chemical from the spines on its body and tentacles. This chemical will react with sand molecules to create an interesting crystalline form similar to fulgurite, which is often seen surrounding the pits it makes. These crystals are how Karakagau mark their territory against others of their kind, and they may even use larger clusters as weapons, either like knives or throwing them at enemies. Otherwise, if its ambush is foiled, Karakagau relies principally on its lashing limbs. It can also spit the chemical from its beak, paralyzing prey and rivals from a distance. Unlike most elder dragons, Karakagau does not display the capacity to meaningfully influence natural phenomena. It controls no elements nor alters its environment in any significant way. It is not even known to drive out neighbouring monsters through occupation, beyond those directly aware of its presence. Karakagau rarely ventures from the pits it creates, usually only leaving when it wishes to travel to an oasis to gather fruit. The elder dragon also relies on oases to reproduce; while the adult is terrestrial, the eggs its lays and the young that emerge are dependant on water. Interestingly, Karakagau are never seen to gather to mate, implying the species is asexual or parthenogenetic. While certainly a cunning ambush predator, Karakagau's comparative lack of power and influences ranks it lower than most elder dragons (Low Rank - 5, High/Master Rank - 5). The real challenge lies in exposing its ambush site. Sonic bombs are highly recommended to disorientate the elder dragon, and water weapons are useful for diluting and nullifying its paralyzing chemicals. Given its dependance on its environment to be an effective threat, the Guild believes Karakagau could be subject to capture, lacking logistical concerns of significant influence. Only accomplished hunters who have proven their worth in higher ranks should attempt such a feat. As ambush predators, Karakagau rarely directly contends with other monsters in combat, opting to simply paralyze and drag under the sand. It can be concerned by the likes of Monoblos and Diablos, whose armoured bodies and sharp horns can threaten it. As with many elder dragons, Karakagau is terrified of Nergigante and burrows as deep as it can should it sense the presence of the predator. - Thank you for reading and take care.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Story Ideas (TW: long post incoming but there's poll at the end and every participant gets a sticker)
As was decided by about 100 people: here are some ideas I had for IFs (all in different degrees of "worked-out" and at the end, you can vote on which ones you find the most interesting.
1
The first one basically makes the MC a teacher at a prestigious high school (although they might make you do classes at the also very prestigious elementary school) and it involves planning lessons and dealing with usual teenage shenanigans. The ROs would be other teachers, the odd parent maybe, and perhaps someone from maintenance? Who knows... It's meant to be a cute slice-of-life thing because I eat that shit up.
2
For this one, I pretty much only wrote down "It was a beautiful day at court and you are a horrible jester". ROs would be Prince/Princess, maybe a foreign visitor with Oberyn Martell vibe.
3
The MC is part of a big mafia family but is mostly trying to live a somewhat normal life. Now, you are acquainted with the family business but you don't play an active part in it. But if someone was to mess with you, well, your family would do anything for you. This one is inspired by the song "Bust Your Kneecaps" by Pomplamoose.
Now to my three favorites:
4
Are you familiar with the novel "Krabat"? We've read it in school and I thought it was really cool, even though it is a little dark, to be honest. It's based on a cluster of Sorbian legends and follows the story of Krabat, a poor orphan boy becoming an apprentice at a mill, where the miller is also practicing and teaching black magic to his twelve apprentices and every year one boy dies in mysterious circumstances. The title I'd give this would probably be "Rapaki", which is Sorbian for ravens, which play a role in the story as well. It could prove to be a challenge to make this historical setting as inclusive as I want it to be (and also since there's a specific character I'd love to have as a RO, but he's an adult and the apprentices are pretty much all teenagers).
5
You were kidnapped by aliens. Now, it's been a couple of months since you arrived at the space station. They don't really seem to want to do anything with you except study humans and you happen to be one of the subjects. You are given spacious living quarters, activities for enrichment, food (they sometimes test things by giving you weird stuff and see if you eat it or not) and even many opportunities for socialization with the other human subjects. Honestly, it's not bad. Beats scrambling for money to pay rent. The newest addition to the human sample group though seems to be very discontent with their new abode. Are you helping them to escape, are you just tagging along for the ride, or are determined to stay in your cozy lab?
6
You are perfect nobility. Your family is hosting a ball to which all the most important members of the ton are invited. There's good food and drink, entertainment and music. You socialize and dance. You even go for a secret midnight swim in the deep fountain in the gardens. Many days are like this and you enjoy it. But one day something very peculiar happens: The ball is in full swing when you notice a person in very strange clothes just striding through the dance hall, never acknowledging the guest or the music but looking at a strange... device in their hands. When they aim to go upstairs towards your private living spaces you decide to follow them but they simply disappear. Were they a ghost? Are you hallucinating? For several days you see more strange figures, some of them in strange clothing, some of them in garments from the past. They never seem as ... corporal as the first one and at this point you fear you have lost your mind. Then the first intruder comes back and you can confront them. They seem awfully aghast when you politely ask them to leave.
Turns out, you are a ghost, reliving the last day of your life, and they are a ghost hunter from the future. The whole manor as you know it seems to crumble, polished floors become broken wood, the furniture disappears and the big chandelier lies demolished on the ground. You learn that the other figures are ghosts, like yourself, former inhabitants of the manor before and after you. And you meet them. They are as flabbergasted by this revelation as you were. The ghost hunter explains that they've been chasing a haunting spirit for some time now and they actually weren't intending to call forward you or the others. Do you all help them catch the evil ghost?
Inspired a little by the bbc chow "Ghosts".
#story ideas#another thing I thought of that would be better as a novel or movie probably is something about Fredericka “Marm” Mandelbaum#You should definitely read the wikipedia article about her#that's girlpower if you ask me
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Astronomers discover striking evidence of 'unusual' stellar evolution
“Astronomers have found evidence that some stars boast unexpectedly strong surface magnetic fields, a discovery that challenges current models of how they evolve.
In stars like our sun, surface magnetism is linked to stellar spin, a process similar to the inner workings of a hand-cranked flashlight. Strong magnetic fields are seen in the hearts of magnetic sunspot regions, and cause a variety of space weather phenomena. Until now, low-mass stars—celestial bodies of lower mass than our sun that can rotate either very rapidly or relatively slowly—were thought to exhibit very low levels of magnetic activity, an assumption which has primed them as ideal host stars for potentially habitable planets.
In a new study, published today in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, researchers from The Ohio State University argue that a new internal mechanism called core-envelope decoupling—when the surface and core of the star start out spinning at the same rate, then drift apart—might be responsible for enhancing magnetic fields on cool stars, a process which could intensify their radiation for billions of years and impact the habitability of their nearby exoplanets.

The research was made possible due to a technique that Lyra Cao, lead author of the study and a graduate student in astronomy at Ohio State, and co-author Marc Pinsonneault, a professor of astronomy at Ohio State, developed earlier this year to make and characterize starspot and magnetic field measurements.
Although low-mass stars are the most common stars in the Milky Way and are often hosts to exoplanets, scientists know comparatively little about them, said Cao.
For decades, it was assumed that the physical processes of lower mass stars followed those of solar-type stars. Because stars gradually lose their angular momentum as they spin down, astronomers can use stellar spins as a device to understand the nature of a star's physical processes, and how they interact with their companions and their surroundings. However, there are times where the stellar rotation clock appears to stop in place, Cao said.
Using public data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey to study a sample of 136 stars in M44, a star crib also known as Praesepe, or the Beehive cluster, the team found that the magnetic fields of the low-mass stars in the region appeared much stronger than current models could explain.”
continue article
#astronomy#cosmology#universe#space#evolution#magnetism#electromagnetism#magnetic fields#energy#spinning#oscillation#vortex#stars#planets#sun#rotation#counter rotation#scaling#science
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering Data Science Using Python
Data Science is not just a buzzword; it's the backbone of modern decision-making and innovation. If you're looking to step into this exciting field, Data Science using Python is a fantastic place to start. Python, with its simplicity and vast libraries, has become the go-to programming language for aspiring data scientists. Let’s explore everything you need to know to get started with Data Science using Python and take your skills to the next level.
What is Data Science?
In simple terms, Data Science is all about extracting meaningful insights from data. These insights help businesses make smarter decisions, predict trends, and even shape new innovations. Data Science involves various stages, including:
Data Collection
Data Cleaning
Data Analysis
Data Visualization
Machine Learning
Why Choose Python for Data Science?
Python is the heart of Data Science for several compelling reasons:
Ease of Learning: Python’s syntax is intuitive and beginner-friendly, making it ideal for those new to programming.
Versatile Libraries: Libraries like Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, and Scikit-learn make Python a powerhouse for data manipulation, analysis, and machine learning.
Community Support: With a vast and active community, you’ll always find solutions to challenges you face.
Integration: Python integrates seamlessly with other technologies, enabling smooth workflows.
Getting Started with Data Science Using Python
1. Set Up Your Python Environment
To begin, install Python on your system. Use tools like Anaconda, which comes preloaded with essential libraries for Data Science.
Once installed, launch Jupyter Notebook, an interactive environment for coding and visualizing data.
2. Learn the Basics of Python
Before diving into Data Science, get comfortable with Python basics:
Variables and Data Types
Control Structures (loops and conditionals)
Functions and Modules
File Handling
You can explore free resources or take a Python for Beginners course to grasp these fundamentals.
3. Libraries Essential for Data Science
Python’s true power lies in its libraries. Here are the must-know ones:
a) NumPy
NumPy is your go-to for numerical computations. It handles large datasets and supports multi-dimensional arrays.
Common Use Cases: Mathematical operations, linear algebra, random sampling.
Keywords to Highlight: NumPy for Data Science, NumPy Arrays, Data Manipulation in Python.
b) Pandas
Pandas simplifies working with structured data like tables. It’s perfect for data manipulation and analysis.
Key Features: DataFrames, filtering, and merging datasets.
Top Keywords: Pandas for Beginners, DataFrame Operations, Pandas Tutorial.
c) Matplotlib and Seaborn
For data visualization, Matplotlib and Seaborn are unbeatable.
Matplotlib: For creating static, animated, or interactive visualizations.
Seaborn: For aesthetically pleasing statistical plots.
Keywords to Use: Data Visualization with Python, Seaborn vs. Matplotlib, Python Graphs.
d) Scikit-learn
Scikit-learn is the go-to library for machine learning, offering tools for classification, regression, and clustering.
Steps to Implement Data Science Projects
Step 1: Data Collection
You can collect data from sources like web APIs, web scraping, or public datasets available on platforms like Kaggle.
Step 2: Data Cleaning
Raw data is often messy. Use Python to clean and preprocess it.
Remove duplicates and missing values using Pandas.
Normalize or scale data for analysis.
Step 3: Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
EDA involves understanding the dataset and finding patterns.
Use Pandas for descriptive statistics.
Visualize data using Matplotlib or Seaborn.
Step 4: Build Machine Learning Models
With Scikit-learn, you can train machine learning models to make predictions. Start with simple algorithms like:
Linear Regression
Logistic Regression
Decision Trees
Step 5: Data Visualization
Communicating results is critical in Data Science. Create impactful visuals that tell a story.
Use Case: Visualizing sales trends over time.
Best Practices for Data Science Using Python
1. Document Your Code
Always write comments and document your work to ensure your code is understandable.
2. Practice Regularly
Consistent practice on platforms like Kaggle or HackerRank helps sharpen your skills.
3. Stay Updated
Follow Python communities and blogs to stay updated on the latest tools and trends.
Top Resources to Learn Data Science Using Python
1. Online Courses
Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and edX offer excellent Data Science courses.
Recommended Course: "Data Science with Python - Beginner to Pro" on Udemy.
2. Books
Books like "Python for Data Analysis" by Wes McKinney are excellent resources.
Keywords: Best Books for Data Science, Python Analysis Books, Data Science Guides.
3. Practice Platforms
Kaggle for hands-on projects.
HackerRank for Python coding challenges.
Career Opportunities in Data Science
Data Science offers lucrative career options, including roles like:
Data Analyst
Machine Learning Engineer
Business Intelligence Analyst
Data Scientist
How to Stand Out in Data Science
1. Build a Portfolio
Showcase projects on platforms like GitHub to demonstrate your skills.
2. Earn Certifications
Certifications like Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate or IBM Data Science Professional Certificate add credibility to your resume.
Conclusion
Learning Data Science using Python can open doors to exciting opportunities and career growth. Python's simplicity and powerful libraries make it an ideal choice for beginners and professionals alike. With consistent effort and the right resources, you can master this skill and stand out in the competitive field of Data Science.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking IoT Anomaly Detection with Clustering Techniques
Understanding Clustering for Anomaly Detection in IoT Sensor Data Introduction IoT sensor data is often characterized by high dimensionality, noise, and irregular sampling patterns, making it challenging to detect anomalies. Clustering is a powerful technique to identify patterns and anomalies in IoT sensor data. In this tutorial, we will explore how to apply clustering for anomaly detection in…
0 notes
Text
Guide to Retrieve the Secret Value Using AWS Secret Manager

App developers are hunting all possible means to find a secure way to store their data in the database or Redis. (Redis is an open-source in-memory Data Structure Store, used as a database and a caching layer or a message broker.) One of the challenging tasks with the database is the storage and retrieval, the process is hard to code. And AWS Secret Manager is a problem solver. The AWS Secret Manager focuses to keep your data in secret. The secrets may be your database credentials, passwords or third party API.
Let us walk you through the process of how to keep the Secret a secret using the AWS Secret Manager.
1.Log into your AWS account, search and select the Secret Manager. Afterwards, enter into the Secret Manager Console and click on the “Store a new secret”.
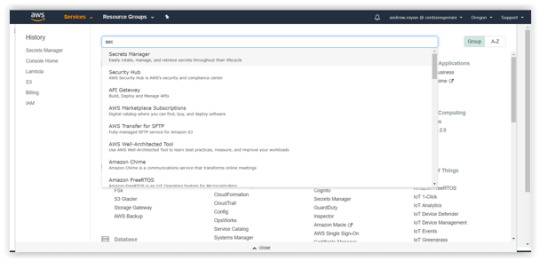
2. In the “Store a new secret” option, you will find the options to select a Secret type.
Credentials for RDS database
Credentials for Redshift Cluster
Credentials for Document database
Credentials for Other database
Other type of secrets
If you do not have a definite value, go with “Other type of secrets”. Then enter the appropriate key name and hit Next.
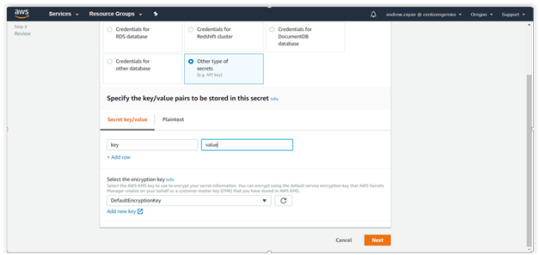
Specify the “Secret name and its description” in the particular fields and other options (optional). Just hit Next.
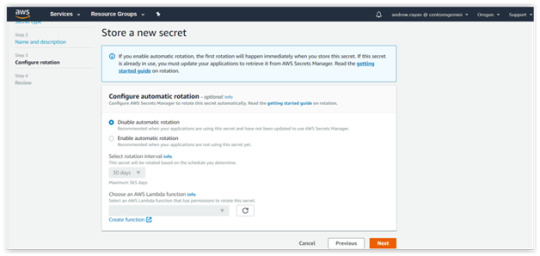
3. After completing Steps 1 and 2, you will be taken to the “Configure Automatic Rotation”. There is an available option to “Disable or Enable the automatic rotation” of the keys via lambda function. Select “Disable” and follow to the next level.
4. You can “Review”, your data in the previous steps and click “Store” button. Then, you’ll get the sample snippets of Java.
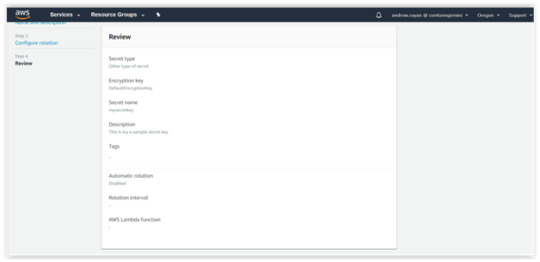
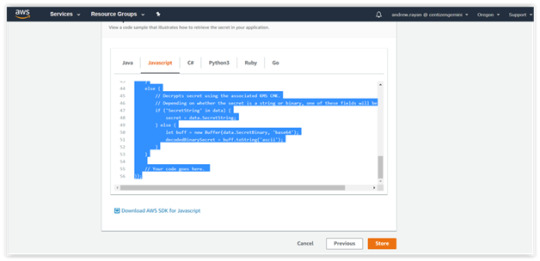
This is the generated Snippet code sample:</.h2
// Use this code snippet in your app.
// If you need more information about configurations or implementing the sample code, visit the AWS docs: // https://aws.amazon.com/developers/getting-started/nodejs/ // Load the AWS SDK var AWS = require(‘aws-sdk’), region = “us-west-2”, secretName = “mysecretkey”, secret, decodedBinarySecret; // Create a Secrets Manager client var client = new AWS.SecretsManager({ region: region }); // In this sample we only handle the specific exceptions for the ‘GetSecretValue’ API. // See https://docs.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/latest/apireference/API_GetSecretValue.html // We rethrow the exception by default. client.getSecretValue({SecretId: secretName}, function(err, data) { if (err) { if (err.code === ‘DecryptionFailureException’) // Secrets Manager can’t decrypt the protected secret text using the provided KMS key. // Deal with the exception here, and/or rethrow at your discretion. throw err; else if (err.code === ‘InternalServiceErrorException’) // An error occurred on the server side. // Deal with the exception here, and/or rethrow at your discretion. throw err; else if (err.code === ‘InvalidParameterException’) // You provided an invalid value for a parameter. // Deal with the exception here, and/or rethrow at your discretion. throw err; else if (err.code === ‘InvalidRequestException’) // You provided a parameter value that is not valid for the current state of the resource. // Deal with the exception here, and/or rethrow at your discretion. throw err; else if (err.code === ‘ResourceNotFoundException’) // We can’t find the resource that you asked for. // Deal with the exception here, and/or rethrow at your discretion. throw err; } else { // Decrypts secret using the associated KMS CMK. // Depending on whether the secret is a string or binary, one of these fields will be populated. if (‘SecretString’ in data) { secret = data.SecretString; } else { let buff = new Buffer(data.SecretBinary, ‘base64’); decodedBinarySecret = buff.toString(‘ascii’); } } // Your code goes here. });
Hope this helped you learn a way to secure your content.
0 notes
Text
Should You Worry About Bird Flu? Experts Explain the Current Risks and Precautions

Should You Worry About Bird Flu? Experts Explain the Current Risks and Precautions The bird flu, specifically the H5N1 strain, has recently been spreading among dairy cows in California, Idaho, and Utah. While the virus primarily infects wild birds, it began impacting commercial poultry in 2022 and has now been detected in cattle since March 2024. Although there have been a few human cases linked to exposure to sick animals, experts emphasize that the situation is currently contained. Current Situation with Bird Flu The H5N1 outbreak was first identified in wild birds in January 2022 and quickly made its way to commercial poultry, affecting turkeys shortly after. Since then, the virus has been detected in various animals, including cattle, goats, alpacas, and even a pig. According to Dr. Amesh Adalja, an infectious disease expert, the ongoing outbreak is largely due to an increase in avian influenza activity among wild birds that has spilled over into livestock. Notably, this is the first time dairy cattle have been infected with H5N1, which raises concerns because there is no flu vaccine for cattle, and the dairy industry has never faced such a challenge before. The detection of H5N1 in pigs is particularly alarming since pigs can be infected by both human and avian viruses, potentially leading to the creation of new influenza strains that could infect humans. Can Humans Contract Bird Flu? As more animals become infected, the likelihood of human exposure increases. In April 2024, a person tested positive for H5N1 after exposure to infected cows, marking the first known case of cow-to-human transmission. By May, several additional cases were reported among individuals who had contact with infected dairy cows. In total, 46 people in the U.S. have been diagnosed with bird flu this year due to exposure to infected animals. A July 2024 study suggested that the actual number of infections might be higher than reported, indicating that approximately 14.3% of farm workers tested had antibodies for H5N1, suggesting prior exposure to the virus. Public Health Threat Assessment According to the CDC, all cases documented in the current outbreak have been classified as sporadic instances of animal-to-human transmission. The risk to the general public remains low since there has been no evidence of human-to-human spread. For the virus to start spreading among humans, significant genetic changes would be necessary, allowing it to bind more effectively to human receptors. For those concerned about food safety, it’s important to note that pasteurized milk is safe, and properly cooking meat should eliminate any risk of the flu virus. Most reported symptoms in infected individuals have been mild, primarily respiratory issues and conjunctivitis. So far, no farmworkers diagnosed with HPAI have required hospitalization. Preparedness for a Larger Outbreak Experts warn that surveillance and testing efforts have not kept pace with the virus’s spread, which could allow it to adapt to humans. The U.S. Department of Agriculture has announced plans to enhance testing, collaborating with state veterinarians to bulk-test milk samples to understand where H5N1 is spreading. Dr. Richard Martinello stresses the importance of monitoring infections in animals, particularly pigs, as each new infection presents an opportunity for the virus to evolve. If clusters of human infections begin to emerge, it may indicate that the virus has gained the ability to spread among people. Vaccination and Prevention While vaccines for H5N1 have been developed, they are not yet publicly available. Experts recommend focusing on seasonal influenza vaccination as a more immediate protective measure, as seasonal flu poses a greater threat to public health than H5N1 at this time. Dr. Martinello emphasizes that getting vaccinated against seasonal influenza is a crucial step for personal protection. Conclusion While the current situation regarding bird flu is concerning, experts believe the risk to the general public remains low. Close monitoring of animal infections and enhanced testing will be vital in preventing the virus from adapting to humans. For now, staying informed and getting vaccinated against seasonal influenza are the best ways to protect yourself. Thank you for taking the time to read this article! Your thoughts and feedback are incredibly valuable to me. What do you think about the topics discussed? Please share your insights in the comments section below, as your input helps me create even better content. I’m also eager to hear your stories! If you have a special experience, a unique story, or interesting anecdotes from your life or surroundings, please send them to me at [email protected]. Your stories could inspire others and add depth to our discussions. If you enjoyed this post and want to stay updated with more informative and engaging articles, don’t forget to hit the subscribe button! I’m committed to bringing you the latest insights and trends, so stay tuned for upcoming posts. Wishing you a wonderful day ahead, and I look forward to connecting with you in the comments and reading your stories! Read the full article
0 notes
Text
From Cassandra To Bigtable Migration At Palo Alto Networks

Palo Alto Networks’ suggestions on database conversion from Cassandra to Bigtable
In this blog post, we look at how Palo Alto Networks, a leading cybersecurity company worldwide, solved its scalability and performance issues by switching from Apache Cassandra to Bigtable, Google Cloud’s enterprise-grade, low-latency NoSQL database service. This allowed them to achieve 5x lower latency and cut their total cost of ownership in half. Please continue reading if you want to find out how they approached this migration.
Bigtable has been supporting both internal systems and external clients at Google. Google Cloud wants to tackle the most challenging use cases in the business and reach more developers with Bigtable. Significant progress has been made in that approach with recent Bigtable features:
High-performance, workload-isolated, on-demand analytical processing of transactional data is made possible by the innovative Bigtable Data Boost technology. Without interfering with your operational workloads, it enables you to run queries, ETL tasks, and train machine learning models directly and as often as necessary on your transactional data.
Several teams can safely use the same tables and exchange data from your databases thanks to the authorized views feature, which promotes cooperation and effective data use.
Distributed counters: This feature continuously and scalablely provides real-time operation metrics and machine learning features by aggregating data at write time to assist you in processing high-frequency event data, such as clickstreams, directly in your database.
SQL support: With more than 100 SQL functions now included into Bigtable, developers may use their current knowledge to take advantage of Bigtable’s scalability and performance.
For a number of business-critical workloads, including Advanced WildFire, Bigtable is the database of choice because to these improvements and its current features.
From Cassandra to Bigtable at Palo Alto Networks
Advanced WildFire from Palo Alto Networks is the biggest cloud-based malware protection engine in the business, evaluating more than 1 billion samples per month to shield enterprises from complex and cunning attacks. It leverages more than 22 distinct Google Cloud services in 21 different regions to do this. A NoSQL database is essential to processing massive volumes of data for Palo Alto Networks’ Global Verdict Service (GVS), a key component of WildFire, which must be highly available for service uptime. When creating Wildfire, Apache Cassandra first appeared to be a good fit. But when performance requirements and data volumes increased, a number of restrictions surfaced:
Performance bottlenecks: Usually caused by compaction procedures, high latency, frequent timeouts, and excessive CPU utilization affected user experience and performance.
Operational difficulty: Managing a sizable Cassandra cluster required a high level of overhead and specialized knowledge, which raised management expenses and complexity.
Challenges with replication: Low-latency replication across geographically separated regions was challenging to achieve, necessitating a sophisticated mesh architecture to reduce lag.
Scaling challenges: Node updates required a lot of work and downtime, and scaling Cassandra horizontally proved challenging and time-consuming.
To overcome these constraints, Palo Alto Networks made the decision to switch from GVS to Bigtable. Bigtable’s assurance of the following influenced this choice:
High availability: Bigtable guarantees nearly continuous operation and maximum uptime with an availability SLA of 99.999%.
Scalability: It can easily handle Palo Alto Networks’ constantly increasing data needs because to its horizontally scalable architecture, which offers nearly unlimited scalability.
Performance: Bigtable provides read and write latency of only a few milliseconds, which greatly enhances user experience and application responsiveness.
Cost-effectiveness: Bigtable’s completely managed solution lowers operating expenses in comparison to overseeing a sizable, intricate Cassandra cluster.
For Palo Alto Networks, the switch to Bigtable produced outstanding outcomes:
Five times less latency: The Bigtable migration resulted in a five times reduced latency, which significantly enhanced application responsiveness and user experience.
50% cheaper: Palo Alto Networks was able to cut costs by 50% because of Bigtable’s effective managed service strategy.
Improved availability: The availability increased from 99.95% to a remarkable 99.999%, guaranteeing almost continuous uptime and reducing interruptions to services.
Infrastructure became simpler and easier to manage as a result of the removal of the intricate mesh architecture needed for Cassandra replication.
Production problems were reduced by an astounding 95% as a result of the move, which led to more seamless operations and fewer interruptions.
Improved scalability: Bigtable offered 20 times the scale that their prior Cassandra configuration could accommodate, giving them plenty of space to expand.
Fortunately, switching from Cassandra to Bigtable can be a simple procedure. Continue reading to find out how.
The Cassandra to Bigtable migration
Palo Alto wanted to maintain business continuity and data integrity during the Cassandra to Bigtable migration. An outline of the several-month-long migration process’s steps is provided below:
The first data migration
To begin receiving the transferred data, create a Bigtable instance, clusters, and tables.
Data should be extracted from Cassandra and loaded into Bigtable for each table using the data migration tool. It is important to consider read requests while designing the row keys. It is generally accepted that a table’s Cassandra primary key and its Bigtable row key should match.
Make sure that the column families, data types, and columns in Bigtable correspond to those in Cassandra.
Write more data to the Cassandra cluster during this phase.
Verification of data integrity:
Using data validation tools or custom scripts, compare the Cassandra and Bigtable data to confirm that the migration was successful. Resolve any disparities or contradictions found in the data.
Enable dual writes:
Use Cassandra and dual writes to Bigtable for every table.
To route write requests to both databases, use application code.
Live checks for data integrity:
Using continuous scheduled scripts, do routine data integrity checks on live data to make sure that the data in Bigtable and Cassandra stays consistent.
Track the outcomes of the data integrity checks and look into any anomalies or problems found.
Redirect reads:
Switch read operations from Cassandra to Bigtable gradually by adding new endpoints to load balancers and/or changing the current application code.
Keep an eye on read operations’ performance and latency.
Cut off dual writes:
After redirecting all read operations to Bigtable, stop writing to Cassandra and make sure that Bigtable receives all write requests.
Decommission Cassandra:
Following the migration of all data and the redirection of read activities to Bigtable, safely terminate the Cassandra cluster.
Tools for migrating current data
The following tools were employed by Palo Alto Networks throughout the migration process:
‘dsbulk’ is a utility for dumping data. Data can be exported from Cassandra into CSV files using the ‘dsbulk’ tool. Cloud Storage buckets are filled with these files for later use.
To load data into Bigtable, create dataflow pipelines: The CSV files were loaded into Bigtable in a test environment using dataflow pipelines.
At the same time, Palo Alto decided to take a two-step method because data transfer is crucial: first, a dry-run migration, and then the final migration. This tactic assisted in risk reduction and process improvement.
A dry-run migration’s causes include:
Test impact: Determine how the ‘dsbulk’ tool affects the live Cassandra cluster, particularly when it is under load, and modify parameters as necessary.
Issue identification: Find and fix any possible problems related to the enormous amount of data (terabytes).
Calculate the estimated time needed for the migration in order to schedule live traffic handling for the final migration.
It then proceeded to the last migration when it was prepared.
Steps in the final migration:
Set up pipeline services:
Reading data from all MySQL servers and publishing it to a Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic is the function of the reader service.
Writer service: Converts a Pub/Sub topic into data that is written to Bigtable.
Cut-off time: Establish a cut-off time and carry out the data migration procedure once more.
Start services: Get the writer and reader services up and running.
Complete final checks: Verify accuracy and completeness by conducting thorough data integrity checks.
This methodical technique guarantees a seamless Cassandra to Bigtable migration, preserving data integrity and reducing interference with ongoing business processes. Palo Alto Networks was able to guarantee an efficient and dependable migration at every stage through careful planning.
Best procedures for migrations
Database system migrations are complicated processes that need to be carefully planned and carried out. Palo Alto used the following best practices for their Cassandra to Bigtable migration:
Data model mapping: Examine and convert your current Cassandra data model to a Bigtable schema that makes sense. Bigtable allows for efficient data representation by providing flexibility in schema construction.
Instruments for data migration: Reduce downtime and expedite the data transfer process by using data migration solutions such as the open-source “Bigtable cbt” tool.
Adjusting performance: To take full advantage of Bigtable’s capabilities and optimize performance, optimize your Bigtable schema and application code.
Modification of application code: Utilize the special features of Bigtable by modifying your application code to communicate with its API.
However, there are a few possible dangers to be aware of:
Schema mismatch: Verify that your Cassandra data model’s data structures and relationships are appropriately reflected in the Bigtable schema.
Consistency of data: To prevent data loss and guarantee consistency of data, carefully plan and oversee the data migration procedure.
Prepare for the Bigtable migration
Are you prepared to see for yourself the advantages of Bigtable? A smooth transition from Cassandra to Bigtable is now possible with Google Cloud, which uses Dataflow as the main dual-write tool. Your data replication pipeline’s setup and operation are made easier with this Apache Cassandra to Bigtable template. Begin your adventure now to realize the possibilities of an extremely scalable, efficient, and reasonably priced database system.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#Cassandra#BigtableMigration#PaloAltoNetworks#SQL#meachinelearning#databases#Networks#PaloAlto#Pub/Sub#datamodel#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, Volume 32, Issue 10, October 2024
1) Context-Aware Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement Based on Neuro-Fuzzy Modeling and User Preference Learning
Author(s): Song Chen, Jasper Kirton-Wingate, Faiyaz Doctor, Usama Arshad, Kia Dashtipour, Mandar Gogate, Zahid Halim, Ahmed Al-Dubai, Tughrul Arslan, Amir Hussain
Pages: 5400 - 5412
2) Deep Fuzzy Multiteacher Distillation Network for Medical Visual Question Answering
Author(s): Yishu Liu, Bingzhi Chen, Shuihua Wang, Guangming Lu, Zheng Zhang
Pages: 5413 - 5427
3) Explainable Fuzzy Deep Learning for Prediction of Epileptic Seizures Using EEG
Author(s): Faiq Ahmad Khan, Zainab Umar, Alireza Jolfaei, Muhammad Tariq
Pages: 5428 - 5437
4) FJA-Net: A Fuzzy Joint Attention Guided Network for Classification of Glaucoma Stages
Author(s): Dipankar Das, Deepak Ranjan Nayak
Pages: 5438 - 5448
5) FSCNN: Fuzzy Channel Filter-Based Separable Convolution Neural Networks for Medical Imaging Recognition
Author(s): Hao Huang, Sung-Kwun Oh, Zunwei Fu, Chuan-Kun Wu, Witold Pedrycz, Jin-Yul Kim
Pages: 5449 - 5461
6) Fuzzy Attention-Based Border Rendering Orthogonal Network for Lung Organ Segmentation
Author(s): Sheng Zhang, Yingying Fang, Yang Nan, Shiyi Wang, Weiping Ding, Yew-Soon Ong, Alejandro F. Frangi, Witold Pedrycz, Simon Walsh, Guang Yang
Pages: 5462 - 5476
7) Fuzzy Deep Learning for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease: Approaches and Challenges
Author(s): M. Tanveer, M. Sajid, M. Akhtar, A. Quadir, T. Goel, A. Aimen, S. Mitra, Y-D Zhang, C. T. Lin, J. Del Ser
Pages: 5477 - 5492
8) Fuzzy Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Detection of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
Author(s): Xiaotong Wu, Yan Ding, Xiaokang Zhou, Yanwei Xu, Shoujin Wang, Xiaolong Xu, Lianyong Qi
Pages: 5493 - 5507
9) Fuzzy-Centric Fog–Cloud Inspired Deep Interval Bi-LSTM Healthcare Framework for Predicting Yellow Fever Outbreak
Author(s): Prabal Verma, Tawseef A. Shaikh, Sandeep K. Sood, Harkiran Kaur, Mohit Kumar, Huaming Wu, Sukhpal Singh Gill
Pages: 5508 - 5519
10) Fuzzy Multiview Graph Learning on Sparse Electronic Health Records
Author(s): Tao Tang, Zhuoyang Han, Shuo Yu, Adil Bagirov, Qiang Zhang
Pages: 5520 - 5532
11) Hybrid Parallel Fuzzy CNN Paradigm: Unmasking Intricacies for Accurate Brain MRI Insights
Author(s): Saeed Iqbal, Adnan N. Qureshi, Khursheed Aurangzeb, Musaed Alhussein, Shuihua Wang, Muhammad Shahid Anwar, Faheem Khan
Pages: 5533 - 5544
12) MFISN: Modality Fuzzy Information Separation Network for Disease Classification
Author(s): Fengtao Nan, Bin Pu, Jiayi Pan, Yingchun Fan, Jiewen Yang, Xingbo Dong, Zhaozhao Xu, Shuihua Wang
Pages: 5545 - 5556
13) SLIDE-Net: A Sequential Modeling Approach With Adaptive Fuzzy C-Mean Empowered Data Balancing Policy for IDC Detection
Author(s): Abhinav Kumar, Harshit Tiwari, Rishav Singh, Amit Kumar Singh, Sanjay Kumar Singh
Pages: 5557 - 5570
14) ViTH-RFG: Vision Transformer Hashing With Residual Fuzzy Generation for Targeted Attack in Medical Image Retrieval
Author(s): Weiping Ding, Chuansheng Liu, Jiashuang Huang, Chun Cheng, Hengrong Ju
Pages: 5571 - 5584
15) TDEC: Evidential Clustering Based on Transfer Learning and Deep Autoencoder
Author(s): Lianmeng Jiao, Feng Wang, Zhun-Ga Liu, Quan Pan
Pages: 5585 - 5597
16) Dialectic Feature-Based Fuzzy Graph Learning for Label Propagation Assisting Text Classification
Author(s): Cherukula Madhu, Sudhakar M S
Pages: 5598 - 5612
17) Stochastic Sampled-Data Model Predictive Control for T-S Fuzzy Systems With Unknown Stochastic Sampling Probability
Author(s): Hong-Gui Han, Shi-Jia Fu, Hao-Yuan Sun, Zheng Liu
Pages: 5613 - 5624
18) Fuzzy Shared Representation Learning for Multistream Classification
Author(s): En Yu, Jie Lu, Guangquan Zhang
Pages: 5625 - 5637
19) Adaptive Event-Triggered Saturation-Tolerant Control for Multiagent Systems Based on Finite-Time Fuzzy Learning
Author(s): Xiaohui Yue, Huaguang Zhang, Jiayue Sun, Lei Wan
Pages: 5638 - 5647
20) Bounded and Saturation Control-Based Fixed-Time Synchronization of Discontinuous Fuzzy Competitive Networks With State-Dependent Switching
Author(s): Honglin Ni, Fanchao Kong, Quanxin Zhu, Chaoxu Mu
Pages: 5648 - 5659
21) Internal Purity: A Differential Entropy-Based Internal Validation Index for Crisp and Fuzzy Clustering Validation
Author(s): Bin Cao, Chen Yang, Kaibo He, Jing Fan, Honghao Gao, Pengjiang Qian
Pages: 5660 - 5673
22) Reinforced Fuzzy-Rule-Based Neural Networks Realized Through Streamlined Feature Selection Strategy and Fuzzy Clustering With Distance Variation
Author(s): Zheng Wang, Eun-Hu Kim, Sung-Kwun Oh, Witold Pedrycz, Zunwei Fu, Jin Hee Yoon
Pages: 5674 - 5686
23) A Robust Pseudo Fuzzy Rough Feature Selection Using Linear Reconstruction Measure
Author(s): Lin Qiu, Xingwei Wang, Yanpeng Qu, Kaimin Zhang, Fei Gao, Bo Yi, Keqin Li
Pages: 5687 - 5701
24) A Bayesian Network Inference Approach for Dynamic Risk Assessment Using Multisource-Based Information Fusion in an Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Set Environment
Author(s): Jintao Xu, Yang Sui, Tao Dai
Pages: 5702 - 5713
25) Fuzzy Neural Tangent Kernel Model for Identifying DNA N4-Methylcytosine Sites
Author(s): Yijie Ding, Prayag Tiwari, Fei Guo, Quan Zou, Weiping Ding
Pages: 5714 - 5727
26) Impulsive Formation Tracking of Nonlinear Fuzzy Multiagent Systems With Input Saturation Constraints
Author(s): Xiaowei Jiang, Le You, Ni Zhang, Ming Chi, Huaicheng Yan
Pages: 5728 - 5736
27) Data-Driven Decentralized Learning Regulation for Networked Interconnected Systems Using Generalized Fuzzy Hyperbolic Models
Author(s): Jian Liu, Jiachen Ke, Jinliang Liu, Xiangpeng Xie, Engang Tian, Jie Cao
Pages: 5737 - 5749
28) Observer-Based Fuzzy Control for Nonlinear Networked Systems Under Multichannel Attacks With Indirectly Accessible Mode Information
Author(s): Shiyu Jiao, Shengyuan Xu, Ju H. Park, Jun Chen
Pages: 5750 - 5761
29) A Fuzzy Multigranularity Convolutional Neural Network With Double Attention Mechanisms for Measuring Semantic Textual Similarity
Author(s): Butian Zhao, Runtong Zhang, Kaiyuan Bai
Pages: 5762 - 5776
30) FuSVC: A New Labeling Rule for Support Vector Clustering Using Fuzzy Sets
Author(s): Ramiro Saltos, Richard Weber, Dayana Saltos
Pages: 5777 - 5790
31) Inverse Compensation-Based Global Fast Terminal Integral Sliding Mode Control With Lumped Uncertainty Fuzzy Estimation for Dielectric Electro-Active Polymer Actuator
Author(s): Yue Zhang, Yawu Wang, Jundong Wu, Chun-Yi Su
Pages: 5791 - 5801
32) Fuzzy-Based Control for Multiple Tasks With Human–Robot Interaction
Author(s): Yuwei Yang, Zhijun Li, Peng Shi, Guoxin Li
Pages: 5802 - 5814
33) Decentralized Periodic Dynamic Event-Triggering Fuzzy Load Frequency Control for Multiarea Nonlinear Power Systems Based on IT2 Fuzzy Model
Author(s): Shanling Dong, Genyuan Yang, Yougang Bian, Zheng-Guang Wu, Meiqin Liu
Pages: 5815 - 5826
34) Event-Based Adaptive Fuzzy Constrained Control for Nonlinear Multiagent Systems via State-Error Unified Barrier Function Approach
Author(s): Xiyue Guo, Huaguang Zhang, Xin Liu, Xiaohui Yue
Pages: 5827 - 5835
35) Command Filter-Based Finite-Time Constraint Control for Flexible Joint Robots Stochastic System With Unknown Dead Zones
Author(s): Yuanbao Dong, Hak-Keung Lam, Jiapeng Liu, Jinpeng Yu
Pages: 5836 - 5844
36) A Tree-Shaped Fuzzy Clustering Answer Retrieval Model Based on Question Alignment
Author(s): Qi Lang, Witold Pedrycz, Xiaodong Liu, Yan Fang
Pages: 5845 - 5857
37) Local Fuzzy-Basis-Dependent Stabilization of Interval Type-2 T–S Fuzzy Systems via an Improved Adaptive Memory-Based Event-Triggered Mechanism
Author(s): Gia Bao Hong, Sung Hyun Kim
Pages: 5858 - 5871
38) Fuzzy Boundary Sampled-Data Control for Nonlinear DPSs With Random Time-Varying Delays
Author(s): Zi-Peng Wang, Bo-Ming Chen, Junfei Qiao, Huai-Ning Wu, Tingwen Huang
Pages: 5872 - 5885
39) A Multimodal Sentiment Analysis Method Based on Fuzzy Attention Fusion
Author(s): Yuxing Zhi, Junhuai Li, Huaijun Wang, Jing Chen, Wei Wei
Pages: 5886 - 5898
40) Adaptive Fuzzy Resilient Decentralized Control for Nonlinear Large-Scale CPSs Under DoS Attacks
Author(s): Zhihong Zhao, Tong Wang, Feng Peng, Jinyong Yu
Pages: 5899 - 5909
41) Synergizing Two Types of Fuzzy Information Granules for Accurate and Interpretable Multistep Forecasting of Time Series
Author(s): Yuqing Tang, Fusheng Yu, Witold Pedrycz
Pages: 5910 - 5923
42) Robust Discriminant Embedding Projection Fuzzy Clustering With Optimal Mean
Author(s): Jingyu Wang, Xinru Zhang, Feiping Nie, Xuelong Li
Pages: 5924 - 5938
43) Tensor-Based Possibilistic C-Means Clustering
Author(s): Josephine Bernadette M. Benjamin, Miin-Shen Yang
Pages: 5939 - 5950
44) Physics-Informed Spatial Fuzzy System and Its Applications in Modeling
Author(s): Hai-Peng Deng, Bing-Chuan Wang, Han-Xiong Li
Pages: 5951 - 5962
45) Three-Way Approximations Fusion With Granular-Ball Computing to Guide Multigranularity Fuzzy Entropy for Feature Selection
Author(s): Deyou Xia, Guoyin Wang, Qinghua Zhang, Jie Yang, Shuyin Xia
Pages: 5963 - 5977
46) Adaptive Fuzzy Predefined-Time Tracking Control Design for Nonstrict-Feedback High-Order Nonlinear Systems With Input Quantization
Author(s): Shuai Sui, Lin Zhao, C. L. Philip Chen
Pages: 5978 - 5990
47) Bumpless Tracking Switching Control for Interval Type-2 Switched Positive T–S Fuzzy Systems
Author(s): Ying Zhao, Zhe Feng, Ben Niu
Pages: 5991 - 5996
0 notes
Text
How AI is improving simulations with smarter sampling techniques
New Post has been published on https://sunalei.org/news/how-ai-is-improving-simulations-with-smarter-sampling-techniques/
How AI is improving simulations with smarter sampling techniques

Imagine you’re tasked with sending a team of football players onto a field to assess the condition of the grass (a likely task for them, of course). If you pick their positions randomly, they might cluster together in some areas while completely neglecting others. But if you give them a strategy, like spreading out uniformly across the field, you might get a far more accurate picture of the grass condition.
Now, imagine needing to spread out not just in two dimensions, but across tens or even hundreds. That’s the challenge MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) researchers are getting ahead of. They’ve developed an AI-driven approach to “low-discrepancy sampling,” a method that improves simulation accuracy by distributing data points more uniformly across space.
A key novelty lies in using graph neural networks (GNNs), which allow points to ���communicate” and self-optimize for better uniformity. Their approach marks a pivotal enhancement for simulations in fields like robotics, finance, and computational science, particularly in handling complex, multidimensional problems critical for accurate simulations and numerical computations.
“In many problems, the more uniformly you can spread out points, the more accurately you can simulate complex systems,” says T. Konstantin Rusch, lead author of the new paper and MIT CSAIL postdoc. “We’ve developed a method called Message-Passing Monte Carlo (MPMC) to generate uniformly spaced points, using geometric deep learning techniques. This further allows us to generate points that emphasize dimensions which are particularly important for a problem at hand, a property that is highly important in many applications. The model’s underlying graph neural networks lets the points ‘talk’ with each other, achieving far better uniformity than previous methods.”
Their work was published in the September issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Take me to Monte Carlo
The idea of Monte Carlo methods is to learn about a system by simulating it with random sampling. Sampling is the selection of a subset of a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. Historically, it was already used in the 18th century, when mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace employed it to estimate the population of France without having to count each individual.
Low-discrepancy sequences, which are sequences with low discrepancy, i.e., high uniformity, such as Sobol’, Halton, and Niederreiter, have long been the gold standard for quasi-random sampling, which exchanges random sampling with low-discrepancy sampling. They are widely used in fields like computer graphics and computational finance, for everything from pricing options to risk assessment, where uniformly filling spaces with points can lead to more accurate results.
The MPMC framework suggested by the team transforms random samples into points with high uniformity. This is done by processing the random samples with a GNN that minimizes a specific discrepancy measure.
One big challenge of using AI for generating highly uniform points is that the usual way to measure point uniformity is very slow to compute and hard to work with. To solve this, the team switched to a quicker and more flexible uniformity measure called L2-discrepancy. For high-dimensional problems, where this method isn’t enough on its own, they use a novel technique that focuses on important lower-dimensional projections of the points. This way, they can create point sets that are better suited for specific applications.
The implications extend far beyond academia, the team says. In computational finance, for example, simulations rely heavily on the quality of the sampling points. “With these types of methods, random points are often inefficient, but our GNN-generated low-discrepancy points lead to higher precision,” says Rusch. “For instance, we considered a classical problem from computational finance in 32 dimensions, where our MPMC points beat previous state-of-the-art quasi-random sampling methods by a factor of four to 24.”
Robots in Monte Carlo
In robotics, path and motion planning often rely on sampling-based algorithms, which guide robots through real-time decision-making processes. The improved uniformity of MPMC could lead to more efficient robotic navigation and real-time adaptations for things like autonomous driving or drone technology. “In fact, in a recent preprint, we demonstrated that our MPMC points achieve a fourfold improvement over previous low-discrepancy methods when applied to real-world robotics motion planning problems,” says Rusch.
“Traditional low-discrepancy sequences were a major advancement in their time, but the world has become more complex, and the problems we’re solving now often exist in 10, 20, or even 100-dimensional spaces,” says Daniela Rus, CSAIL director and MIT professor of electrical engineering and computer science. “We needed something smarter, something that adapts as the dimensionality grows. GNNs are a paradigm shift in how we generate low-discrepancy point sets. Unlike traditional methods, where points are generated independently, GNNs allow points to ‘chat’ with one another so the network learns to place points in a way that reduces clustering and gaps — common issues with typical approaches.”
Going forward, the team plans to make MPMC points even more accessible to everyone, addressing the current limitation of training a new GNN for every fixed number of points and dimensions.
“Much of applied mathematics uses continuously varying quantities, but computation typically allows us to only use a finite number of points,” says Art B. Owen, Stanford University professor of statistics, who wasn’t involved in the research. “The century-plus-old field of discrepancy uses abstract algebra and number theory to define effective sampling points. This paper uses graph neural networks to find input points with low discrepancy compared to a continuous distribution. That approach already comes very close to the best-known low-discrepancy point sets in small problems and is showing great promise for a 32-dimensional integral from computational finance. We can expect this to be the first of many efforts to use neural methods to find good input points for numerical computation.”
Rusch and Rus wrote the paper with University of Waterloo researcher Nathan Kirk, Oxford University’s DeepMind Professor of AI and former CSAIL affiliate Michael Bronstein, and University of Waterloo Statistics and Actuarial Science Professor Christiane Lemieux. Their research was supported, in part, by the AI2050 program at Schmidt Futures, Boeing, the United States Air Force Research Laboratory and the United States Air Force Artificial Intelligence Accelerator, the Swiss National Science Foundation, Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and an EPSRC Turing AI World-Leading Research Fellowship.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How AI is improving simulations with smarter sampling techniques
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/how-ai-is-improving-simulations-with-smarter-sampling-techniques/
How AI is improving simulations with smarter sampling techniques

Imagine you’re tasked with sending a team of football players onto a field to assess the condition of the grass (a likely task for them, of course). If you pick their positions randomly, they might cluster together in some areas while completely neglecting others. But if you give them a strategy, like spreading out uniformly across the field, you might get a far more accurate picture of the grass condition.
Now, imagine needing to spread out not just in two dimensions, but across tens or even hundreds. That’s the challenge MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) researchers are getting ahead of. They’ve developed an AI-driven approach to “low-discrepancy sampling,” a method that improves simulation accuracy by distributing data points more uniformly across space.
A key novelty lies in using graph neural networks (GNNs), which allow points to “communicate” and self-optimize for better uniformity. Their approach marks a pivotal enhancement for simulations in fields like robotics, finance, and computational science, particularly in handling complex, multidimensional problems critical for accurate simulations and numerical computations.
“In many problems, the more uniformly you can spread out points, the more accurately you can simulate complex systems,” says T. Konstantin Rusch, lead author of the new paper and MIT CSAIL postdoc. “We’ve developed a method called Message-Passing Monte Carlo (MPMC) to generate uniformly spaced points, using geometric deep learning techniques. This further allows us to generate points that emphasize dimensions which are particularly important for a problem at hand, a property that is highly important in many applications. The model’s underlying graph neural networks lets the points ‘talk’ with each other, achieving far better uniformity than previous methods.”
Their work was published in the September issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Take me to Monte Carlo
The idea of Monte Carlo methods is to learn about a system by simulating it with random sampling. Sampling is the selection of a subset of a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. Historically, it was already used in the 18th century, when mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace employed it to estimate the population of France without having to count each individual.
Low-discrepancy sequences, which are sequences with low discrepancy, i.e., high uniformity, such as Sobol’, Halton, and Niederreiter, have long been the gold standard for quasi-random sampling, which exchanges random sampling with low-discrepancy sampling. They are widely used in fields like computer graphics and computational finance, for everything from pricing options to risk assessment, where uniformly filling spaces with points can lead to more accurate results.
The MPMC framework suggested by the team transforms random samples into points with high uniformity. This is done by processing the random samples with a GNN that minimizes a specific discrepancy measure.
One big challenge of using AI for generating highly uniform points is that the usual way to measure point uniformity is very slow to compute and hard to work with. To solve this, the team switched to a quicker and more flexible uniformity measure called L2-discrepancy. For high-dimensional problems, where this method isn’t enough on its own, they use a novel technique that focuses on important lower-dimensional projections of the points. This way, they can create point sets that are better suited for specific applications.
The implications extend far beyond academia, the team says. In computational finance, for example, simulations rely heavily on the quality of the sampling points. “With these types of methods, random points are often inefficient, but our GNN-generated low-discrepancy points lead to higher precision,” says Rusch. “For instance, we considered a classical problem from computational finance in 32 dimensions, where our MPMC points beat previous state-of-the-art quasi-random sampling methods by a factor of four to 24.”
Robots in Monte Carlo
In robotics, path and motion planning often rely on sampling-based algorithms, which guide robots through real-time decision-making processes. The improved uniformity of MPMC could lead to more efficient robotic navigation and real-time adaptations for things like autonomous driving or drone technology. “In fact, in a recent preprint, we demonstrated that our MPMC points achieve a fourfold improvement over previous low-discrepancy methods when applied to real-world robotics motion planning problems,” says Rusch.
“Traditional low-discrepancy sequences were a major advancement in their time, but the world has become more complex, and the problems we’re solving now often exist in 10, 20, or even 100-dimensional spaces,” says Daniela Rus, CSAIL director and MIT professor of electrical engineering and computer science. “We needed something smarter, something that adapts as the dimensionality grows. GNNs are a paradigm shift in how we generate low-discrepancy point sets. Unlike traditional methods, where points are generated independently, GNNs allow points to ‘chat’ with one another so the network learns to place points in a way that reduces clustering and gaps — common issues with typical approaches.”
Going forward, the team plans to make MPMC points even more accessible to everyone, addressing the current limitation of training a new GNN for every fixed number of points and dimensions.
“Much of applied mathematics uses continuously varying quantities, but computation typically allows us to only use a finite number of points,” says Art B. Owen, Stanford University professor of statistics, who wasn’t involved in the research. “The century-plus-old field of discrepancy uses abstract algebra and number theory to define effective sampling points. This paper uses graph neural networks to find input points with low discrepancy compared to a continuous distribution. That approach already comes very close to the best-known low-discrepancy point sets in small problems and is showing great promise for a 32-dimensional integral from computational finance. We can expect this to be the first of many efforts to use neural methods to find good input points for numerical computation.”
Rusch and Rus wrote the paper with University of Waterloo researcher Nathan Kirk, Oxford University’s DeepMind Professor of AI and former CSAIL affiliate Michael Bronstein, and University of Waterloo Statistics and Actuarial Science Professor Christiane Lemieux. Their research was supported, in part, by the AI2050 program at Schmidt Futures, Boeing, the United States Air Force Research Laboratory and the United States Air Force Artificial Intelligence Accelerator, the Swiss National Science Foundation, Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and an EPSRC Turing AI World-Leading Research Fellowship.
#affiliate#ai#AI-powered#air#air force#Algorithms#applications#approach#Art#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#assessment#author#autonomous#autonomous driving#Boeing#Canada#challenge#classical#cluster#computation#computational science#computer#Computer Science#Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)#Computer science and technology#continuous#course#data#Deep Learning
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Philosophy of Natural Kinds
The philosophy of natural kinds deals with the classification and categorization of objects, entities, and phenomena in the natural world. It explores the concept of natural kinds as groups or categories that reflect the structure of reality, rather than arbitrary or human-made classifications. This area of philosophy is central to metaphysics, philosophy of science, and philosophy of language.
Key Concepts in the Philosophy of Natural Kinds:
Definition of Natural Kinds:
Natural vs. Artificial Kinds: Natural kinds are categories that exist independently of human thought or social conventions. They are contrasted with artificial or conventional kinds, which are categories created by humans for practical purposes. For example, "water" and "gold" are considered natural kinds, while "furniture" or "vehicles" are seen as artificial kinds.
Essential Properties: Natural kinds are often thought to have essential properties, which are the characteristics that all members of the kind share and that define what it means to belong to that kind. For instance, the chemical structure H₂O is an essential property of water.
Realism about Natural Kinds:
Metaphysical Realism: Realists about natural kinds argue that these kinds exist independently of human beliefs, language, or practices. According to this view, natural kinds reflect the objective divisions in nature, and science discovers these kinds rather than inventing them.
Essentialism: Some realists hold an essentialist view, which suggests that natural kinds have a set of necessary and sufficient conditions (essential properties) that determine their membership. For example, the essence of a species like "tiger" includes certain genetic and biological traits.
Nominalism and Conventionalism:
Nominalism: Nominalists, on the other hand, deny the existence of natural kinds as objective features of the world. They argue that categories are constructed by humans and do not reflect any inherent divisions in nature.
Conventionalism: Conventionalists believe that the categories we use to classify the world are based on human conventions and practices rather than on any intrinsic structure of reality. According to this view, what counts as a natural kind is largely determined by social or linguistic conventions.
Philosophical Issues:
Inductive Inference: Natural kinds are often linked to the problem of induction in philosophy. The idea is that if natural kinds are real, they can support inductive inferences—generalizing from a sample of observations to broader conclusions. For example, observing that all samples of water boil at 100°C (under standard conditions) allows us to infer that this is a property of the natural kind "water."
Scientific Classification: The philosophy of natural kinds has significant implications for scientific classification. Scientists rely on the notion of natural kinds to group entities in ways that reflect underlying natural structures, which is crucial for forming scientific laws and theories. For example, the periodic table in chemistry is a classification of elements based on their natural kinds.
Challenges to the Concept of Natural Kinds:
Biological Species Problem: One of the major challenges to the idea of natural kinds is the problem of biological species. In biology, species are often seen as fluid and not always fitting neatly into natural kinds because of evolution, gene flow, and hybridization. This challenges the idea that species have essential properties or that they are fixed natural kinds.
Homeostatic Property Cluster (HPC) Theory: In response to such challenges, some philosophers propose the HPC theory, which suggests that natural kinds are not defined by a single essence but by a cluster of properties that tend to co-occur due to a stable underlying mechanism. For example, a species might be defined by a cluster of genetic, morphological, and behavioral traits that are maintained by evolutionary processes.
Natural Kinds in Chemistry and Physics:
Chemical Elements: The concept of natural kinds is perhaps most straightforward in chemistry and physics, where elements and fundamental particles are seen as paradigmatic examples of natural kinds. Each element on the periodic table is classified based on its atomic number, which is considered an essential property of that kind.
Subatomic Particles: In physics, particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons are also treated as natural kinds, with specific properties (e.g., charge, mass) that define their identity.
Natural Kinds in the Social Sciences:
Debate on Social Kinds: The application of the concept of natural kinds to the social sciences is more contentious. Some argue that categories like race, gender, or mental disorders should be treated as natural kinds, while others see them as socially constructed and not reflecting natural divisions in the world.
Social Kinds as Natural Kinds: Some philosophers propose that certain social kinds could be considered natural if they are stable and have causal powers similar to those of natural kinds in the physical sciences. For instance, certain mental health conditions might be seen as natural kinds if they consistently manifest specific symptoms and respond to particular treatments.
The philosophy of natural kinds is an exploration of how we categorize and understand the world around us. It raises important questions about the nature of reality, the basis of scientific classification, and the extent to which our concepts reflect objective divisions in the natural world. Whether natural kinds are real or constructed, essential or cluster-based, the debate continues to shape our understanding of science, language, and reality itself.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#ontology#metaphysics#Philosophy of Science#Essentialism#Realism#Nominalism#Classification#Scientific Taxonomy#Induction#Biological Species Problem#Homeostatic Property Cluster (HPC) Theory#Natural Kinds in Chemistry#Social Kinds#Philosophy of Language#Naturalism
0 notes
Text
Genome Editing Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis 2024-2031
In the rapidly evolving world of biotechnology, genome editing stands out as one of the most transformative and controversial technologies of our time. From its revolutionary applications in medicine to its potential to reshape agriculture, genome editing promises to unlock new possibilities while also raising complex ethical and regulatory questions.
What is Genome Editing?
Genome editing refers to the precise alteration of an organism’s DNA sequence. By making targeted changes to the genetic code, scientists can add, remove, or alter specific genes. This technology holds the potential to address a myriad of challenges, from curing genetic diseases to creating crops that can withstand environmental stresses.
Get Your Global Market Position Here - https://www.skyquestt.com/sample-request/genome-editing-market
The advent of genome editing began with the development of tools like CRISPR-Cas9, a technology derived from bacterial defense mechanisms. CRISPR, short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, has become synonymous with modern genome editing due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Other techniques, such as TALENs (Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases) and ZFNs (Zinc Finger Nucleases), also play crucial roles in this field.
Medical Breakthroughs
In medicine, genome editing is heralded as a potential game-changer. One of its most promising applications is in gene therapy, where faulty genes responsible for genetic disorders are corrected. For instance, conditions like cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and certain types of cancer could be treated by directly editing the genes involved.
A landmark case in genome editing occurred in 2023 when a patient with sickle cell anemia became the first to receive a CRISPR-based treatment. The therapy successfully corrected the mutation responsible for the disease, offering hope to millions affected by this and similar conditions.
Researchers are also exploring the use of genome editing to create personalized medicines tailored to individual genetic profiles, potentially revolutionizing the way diseases are treated and managed.
Genome Editing Market Top Players Company Profiles - Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., CRISPR Therapeutics AG, Editas Medicine, Inc., Intellia Therapeutics, Inc., Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc., Precision Biosciences, Inc., Cellectis S.A., Merck KGaA, Lonza Group AG, Horizon Discovery Group plc, Genscript Biotech Corporation, Agilent Technologies, Inc., New England Biolabs, Inc., Takara Bio, Inc., Synthego Corporation, OriGene Technologies, Inc., Genewiz, Inc., Eurofins Scientific SE, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Qiagen N.V.
Genome Editing Market Analysis
Segments covered
Technology
CRISPR, TALEN, ZFN, Antisense, Other Technologies
Delivery Method
Ex-vivo, In-vivo
Mode
Contract, In-house
End Use
Biotechnology & Pharmaceutical Companies, Academic & Government Research Institutes, Contract Research Organizations
The Future of Genome Editing
Looking ahead, the future of genome editing is filled with both promise and complexity. Advances in precision and efficiency continue to drive research forward, with new techniques like base editing and prime editing offering even greater accuracy and reduced off-target effects.
As the technology matures, it will be crucial to address the ethical and societal implications, ensuring that the benefits of genome editing are realized while minimizing potential risks. Collaborative efforts between scientists, ethicists, and regulators will be essential in shaping a future where genome editing is used responsibly to improve human health and well-being.
In conclusion, genome editing stands at the forefront of scientific innovation, offering transformative potential across various fields. Its journey from a groundbreaking concept to a practical tool in medicine and agriculture reflects both the excitement and challenges inherent in pushing the boundaries of science. As we move forward, balancing innovation with ethical considerations will be key to unlocking the full potential of this remarkable technology.
For more information on the latest developments in genome editing, visit - https://www.skyquestt.com/report/genome-editing-market
#GenomeEditing#CRISPR#GeneEditing#GeneticEngineering#BioTech#GeneTherapy#Genomics#GeneticModification#PrecisionMedicine#GeneticResearch#CRISPRCas9#GeneEditingRevolution#SyntheticBiology#GenomeTherapy#EthicalScience#GenomicAdvances#BioInnovation#GeneEditingFuture#HealthTech#AgriculturalBiotech
1 note
·
View note
Text
Discovering Da Nang: Top Things to Do
Da Nang, a bustling coastal city in central Vietnam, is a perfect blend of urban charm, cultural heritage, and natural beauty. Whether you are seeking adventure, relaxation, or a taste of Vietnamese culture, Da Nang has something for everyone. From pristine beaches and delicious cuisine to exhilarating activities and vibrant nightlife, this city offers a wide range of experiences. In this blog, we'll explore the top things to do in Da Nang, making your visit truly memorable.

Da Nang
Nestled between the East Sea and the Annamite Range, Da Nang is Vietnam's fourth-largest city and one of its most important port cities. Known for its friendly locals and laid-back vibe, Da Nang has rapidly transformed into a popular tourist destination. With its stunning beaches, historical sites, and modern amenities, Da Nang offers a unique blend of attractions that cater to all types of travelers.
Adventure Activities in Da Nang
For those with a thirst for adventure, Da Nang is a playground of exciting activities. Trekking in Vietnam is a fantastic way to explore the lush landscapes and scenic trails around the city. The Marble Mountains, a cluster of five marble and limestone hills, offer excellent trekking and Rock Climbing in Vietnam opportunities. These mountains are filled with caves, tunnels, and Buddhist sanctuaries, providing a spiritual and adventurous experience.
If you're visiting during the warmer months, Sandboarding in Vietnam is another thrilling activity to try. The nearby sand dunes in Quang Phu are perfect for this adrenaline-pumping sport. Additionally, the Han River running through the city is ideal for River Rafting in Vietnam, offering both serene and challenging sections for different skill levels.
Beaches in Da Nang
Da Nang is renowned for its beautiful beaches, making it a prime destination for sun-seekers. Beaches in Vietnam are some of the most picturesque in Southeast Asia, and Da Nang’s coastline is no exception. My Khe Beach, also known as China Beach, is one of the most famous beaches in the area. With its golden sands, clear blue waters, and gentle waves, it’s perfect for swimming, sunbathing, and surfing.
Non Nuoc Beach, located at the foot of the Marble Mountains, is another stunning beach known for its tranquil atmosphere and scenic beauty. For a more secluded experience, Bac My An Beach offers a peaceful retreat away from the crowds.
Cultural and Historical Sites
Da Nang is rich in cultural and historical sites that provide a glimpse into Vietnam's past. The ancient town of Hoi An, a short drive from Da Nang, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most romantic Honeymoon Destinations in Vietnam. Its well-preserved architecture, charming lantern-lit streets, and vibrant markets make it a must-visit.
The Dragon Bridge, a modern architectural marvel, is a symbol of Da Nang. Spanning the Han River, it is especially spectacular at night when it is illuminated and breathes fire and water. The Linh Ung Pagoda, located on the Son Tra Peninsula, features the tallest Lady Buddha statue in Vietnam and offers breathtaking views of the city and the sea.
Vietnamese Food and Dining Experiences
Da Nang is a culinary paradise, offering a diverse array of Vietnamese food. From street food stalls to upscale Restaurants in Vietnam, the city caters to all tastes and budgets. Must-try local dishes include Mi Quang (turmeric noodles with pork and shrimp), Bun Thit Nuong (grilled pork with vermicelli noodles), and Banh Xeo (Vietnamese savory pancakes).
For a unique dining experience, visit the Han Market, where you can sample an array of local delicacies. Madame Lan and Quan Com Hue are popular restaurants that offer authentic Vietnamese cuisine in a cozy setting.
Nightlife in Da Nang
The Vietnam Nightlife scene in Da Nang is vibrant and diverse, offering something for everyone. From beachfront bars and nightclubs to quiet cafes and rooftop lounges, the city comes alive after dark. The Sky36 Bar, located on the top floors of the Novotel Hotel, offers stunning panoramic views of the city and the Han River. For a more laid-back experience, head to one of the many beach bars along My Khe Beach.
Best Time to Visit Da Nang
The best time to visit Vietnam and Da Nang, in particular, is from February to May when the weather is warm and dry. During this period, the temperatures are pleasant, making it ideal for outdoor activities and beach excursions. If you prefer a quieter experience, visiting during the shoulder seasons of September to November can also be enjoyable, although you may encounter occasional rain showers.

Conclusion
Da Nang is a destination that promises a rich tapestry of experiences, from its stunning natural beauty and adventurous activities to its cultural treasures and culinary delights. Whether you're basking on the Beaches in Vietnam, exploring historical sites, or indulging in the local cuisine, Da Nang offers an unforgettable journey. So, pack your bags, book your Vietnam tour packages, and get ready to explore the myriad attractions of this dynamic city. Embrace the adventure, savor the flavors, and let Da Nang's charm captivate you.
0 notes
Text
The Complete Guide for Content Creation in 2022
The process of choosing a fresh topic to write about, deciding on the format, developing a strategy for keywords and structure, and then producing the material in compliance with all the requirements may be summed up as content creation. Forming a content creation strategy is not always a cakewalk, there are multiple rounds of edits and revisions need before finalization. In marking customer is your target or your end game so developing a content based on the customer’s view point is one of the most important things. Made an idea about your product or service is the foremost thing, and developing a content strategy based on the audience is secondary.
The stepping stone for any big task to be successful is conducting research. When it comes to content this is also the important thing. You must conduct a rigorous and in-depth research before coming up with any suggestions for highly competitive branded content development. There are two ways to categorize this research, i.e, through SEO research and finding ground topics. When you have a general idea of the themes you want to write about, you should do keyword or SEO research to see how many people are searching for the keywords you’ll be utilizing in your chosen topic. Write out some potential questions that your users might have in relation to their objectives as an excellent method to start your keyword research. Then, you can carry out manual research on these subjects to determine how frequently the same question is raised. Additionally, there is the choice of using external tools for SEO analysis. eWoke is the best SEO Company In Kochican help you build your brand through content strategy.
It’s time to start coming up with content ideas once you have determined the keywords you want to target. Topic clusters are one of the greatest approaches for structuring your material. Here, you can develop a detailed, lengthy pillar page based on a keyword that links to material you’ve written on associated subtopics. You can use the central keyword you choose to construct a pillar content article that thoroughly examines the subject. Shorter articles can then be written to guide your audience into learning more about the subject and focus on long-tail keywords. Once you have your topics and keywords, you can begin your content formation. When you write your content keep this model on your mind i.e, AIDA model, attention, interest, desire and action.
Grab Attention
To grab an attention to a customer you must build a content strategy before that because attention grabbing is one of the most important things. That might be an email subject line or a blog topic headline or any headline topic. Start by considering what matters to your audience or customer persona in order to create attention-grabbing copy. To understand why they could be interested in hearing from you, take into account their background, industry, challenges, motivations, and even seasonality.
Interest
After getting attention from your audience, the challenging part is keeping it. Why should they keep reading your blog post or email? For SEO reasons, this may also encourage people to interact with your content and stay on your page longer. Personalization is a fantastic method to engage readers or potential customers and demonstrate your understanding of them. Give them just enough information to keep them interested without overwhelming them or dumping on pointless talking points. Recall that more is less.
Desire
Once your audience is interested in your topic, tell them what your offer is. Showcase sample work, case studies, or testimonials to boost your reputation and encourage them to move on. You can demonstrates with examples, and can show uniqueness of the products, and keep on your mind this don’t over promote our service/product.
Action
Your end point or the destination is the action right?, which means making an action is the crucial point. Grabing customer’s attention and interest for making them an action, it might be a purchase or a link click to drive traffic on your website.
Content writings can be done for your website, i.e, home page, blog page, contact page, service page, blogs and more. Using new trends and techniques to build a content strategy is the most effective way. Getting top on the search engines is not at all an easy task so before implementing seek advice from the experts. eWoke offers the best Content Writing Services in Kochi to build your effectively and we are always committed to help our clients to grab a top position than their competitors and this will result increase in ROI and more potential customers.
Recent Posts
0 notes