#Blood clot in cerebral artery blocks blood flow
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
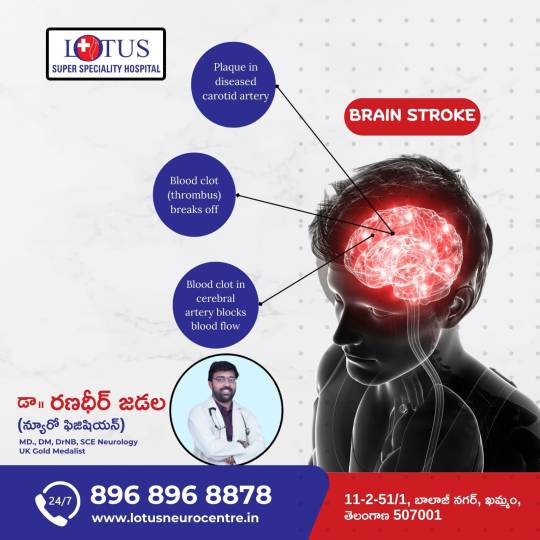
#Understanding Brain Stroke:#Plaque in diseased carotid artery#Blood clot (thrombus) breaks off#Blood clot in cerebral artery blocks blood flow#For expert care and consultation#contact Dr. Randeep Jadal (Neurologist) at Lotus Super Speciality Hospital. Call us 24/7 at 896 896 8878 or visit www.lotusneurocentre.in.
0 notes
Text
“Twila Roe” (USA 1974-1975)
“Twila” underwent a legal first-trimester abortion in either 1974 or 1975. Her death was counted by the CDC.
Twila was at greater risk than most women because of an unspecified congenital heart disease. This may have played a role in the reasoning behind the abortion as well as surgical sterilization by laparotomy. She may have mistakenly believed that the abortion would save her life instead of ending it.
At 11 weeks pregnant, Twila underwent the surgical abortion in a hospital under general anesthesia. She did not survive.
Despite Twila’s lifelong cardiac condition, it was not any pre-existing disease that killed her. She died of a suspected cerebral embolism. This horrifying injury occurred when air, amniotic fluid, blood clots, particles of placenta or even tiny shreds of her dead child’s body entered her bloodstream and blocked an artery to the head, depriving her brain of blood and oxygen.
Twila’s death is similar to the death of “Ana Roe” in Croatia years later. Both women had pre-existing conditions but died of abortion injury instead. In Ana’s case, pieces of placenta in her blood vessels blocked the blood flow to her brain.
Others with cardiac conditions who died after legal abortions include Barbara May Hoppert, Carmen Rodriguez, Christine Mora, Shirley Hollis, “Evie” Roe, “Teresa” Roe, “Valerie” Roe, “Bree” Roe, “Georgia” Roe and “Blaire” Roe. Some of them died because the abortion facility failed to detect their condition beforehand, and others were told to have abortions allegedly for their health only to lose their lives instead.



#tw abortion#victims of roe#pro life#unsafe yet legal#unidentified victim#abortion is not healthcare#tw ab*rtion#tw murder#abortion#abortion debate#death from legal abortion
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blood Clot in Brain: Types, Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
A blood clot in the brain, known as cerebral thrombosis or cerebral embolism, is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. Blood clots can restrict or block blood flow to essential areas of the brain, leading to strokes and other complications. At GS Hospital, one of the best neuro hospital in Ghaziabad and among the top 10 private hospitals in Uttar Pradesh, we have a dedicated team specializing in the treatment and management of neurological conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the types, symptoms, causes, and treatments for brain clots, offering insights into how early diagnosis and prompt care can make all the difference.

Understanding a Blood Clot in the Brain:
A blood clot in the brain occurs when a blockage forms in a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of oxygen-rich blood to brain tissue. This interruption in blood supply causes brain cells to quickly become deprived of oxygen and nutrients, leading to cell death and severe neurological symptoms. Blood clots in the brain are a leading cause of stroke, which is a critical medical emergency that can result in lasting brain damage or even be fatal if not treated promptly.
Key Points on Blood Clots in the Brain:
What Happens: The blockage restricts oxygen and nutrient flow to the brain, leading to cell death.
Symptoms: Patients may experience sudden headaches, vision changes, confusion, dizziness, and weakness, often on one side of the body.
Stroke Risk: Blood clots are a major cause of ischemic stroke, which requires immediate medical attention to prevent severe consequences.
Types of Clots: Clots may develop within the brain’s arteries or can travel from other parts of the body, like the heart or legs, to lodge in brain vessels.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Health Conditions: High blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, and high cholesterol increase clot risks.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to clot formation.
Genetics and Age: Family history and advanced age also raise the likelihood of blood clots in the brain.
Immediate Medical Attention Needed:
If you suspect a blood clot in the brain, seek medical care urgently. Early intervention can prevent further brain damage and improve recovery outcomes.
Types of Blood Clots in the Brain:
Blood clots in the brain can lead to serious medical emergencies, primarily taking the form of two main types of stroke: Ischemic Stroke and Hemorrhagic Stroke. Each has distinct causes, mechanisms, and treatment approaches.
1. Ischemic Stroke: Blockage of Blood Flow:
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms within a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain, obstructing blood flow and depriving brain cells of oxygen.
Causes:
Atherosclerosis: The buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) within the blood vessels narrows the arteries, increasing the risk of a clot forming.
Blood Clot Formation: Blood clots can develop in narrowed areas or as a result of other health issues such as irregular heart rhythms (atrial fibrillation).
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can contribute to the buildup of plaque and increase ischemic stroke risk.
2. Hemorrhagic Stroke: Bleeding in the Brain:
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding and pressure buildup that can damage brain tissue.
Causes:
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension puts stress on blood vessel walls, increasing the risk of rupture.
Aneurysms: Weak spots in blood vessels can balloon and burst under pressure.
Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): Abnormal connections between arteries and veins can lead to vessel rupture.
Trauma or Injury: Physical impact can also lead to bleeding within the brain.
Recognizing Symptoms of a Blood Clot in the Brain:
Blood clots in the brain, often associated with strokes, present symptoms that vary based on the clot’s location and severity. These symptoms can be sudden and life-threatening, so recognizing them quickly is crucial for timely medical intervention. Here are common signs to watch for and what they may indicate:
1. Sudden Weakness or Numbness:
One-Sided Symptoms: Often, blood clots in the brain affect one side of the body, causing weakness or numbness in areas such as the face, arm, or leg.
Facial Drooping: This can manifest as an uneven smile or difficulty moving one side of the face.
Arm Weakness: Affected individuals may find it challenging to raise one arm or keep it lifted without it drifting downwards.
Leg Numbness: Walking or standing may become difficult or unsteady.
2. Speech Difficulties:
Slurred Speech: People with a blood clot in the brain may struggle to pronounce words, resulting in slurred or garbled speech.
Inability to Form Words: Clots impacting certain brain areas can interfere with the ability to form coherent sentences.
Difficulty Understanding Speech: Beyond speaking issues, some may find it hard to comprehend what others are saying, leading to confusion in conversation.
3. Vision Problems:
Sudden Vision Loss: This may occur in one or both eyes, often described as a "curtain" falling over the vision.
Blurred or Double Vision: Blood clots can disrupt normal eye coordination, causing double vision or blurriness.
Partial Vision Loss: Some individuals may lose vision in part of their visual field, often without realizing it immediately.
4. Severe Headache:
Thunderclap Headache: Described as a sudden and extremely painful headache, this symptom can signal a hemorrhagic stroke, where bleeding in the brain increases intracranial pressure.
Unusual or Unfamiliar Pain: Unlike common headaches, these may feel sharp, intense, and escalate quickly.
Accompanying Symptoms: These headaches are often accompanied by other signs like neck stiffness, nausea, or vomiting, especially if bleeding is involved.
5. Dizziness or Loss of Balance:
Sudden Dizziness: Blood clots may disrupt blood flow to areas responsible for balance, leading to sudden and unexplained dizziness.
Loss of Coordination: People may find it challenging to walk straight or stay upright.
Unsteady Gait: An uncoordinated or “staggering” walk may signal a clot impacting brain regions that control motor skills.
6. Confusion and Cognitive Issues:
Trouble Understanding: Patients might appear confused, struggle with comprehension, or have difficulty following simple instructions.
Disorientation: This includes being unsure of time, place, or identity, especially if the clot affects areas related to memory and cognition.
Sudden Memory Lapses: Clots that affect the brain’s memory centers can cause sudden forgetfulness or confusion about familiar people or surroundings.
Urgency of Seeking Medical Attention:
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is critical to seek medical help immediately. Blood clots in the brain require rapid response to minimize brain damage and increase the chances of recovery. Swift treatment, including clot-dissolving medications and other interventions, can be lifesaving.
Diagnosis of Blood Clots in the Brain:
Accurate and rapid diagnosis is essential when a blood clot is suspected in the brain. Proper identification of a clot can prevent further complications and facilitate timely, targeted treatment. The Top 10 private hospitals in Uttar Pradesh like GS Hospital, our specialists employ advanced diagnostic techniques to detect brain clots with precision and efficiency. Here are the primary methods used:
1. CT Scan:
Rapid Imaging: CT scans are often the first step, as they can quickly reveal bleeding, blockages, or abnormalities within the brain.
Stroke Detection: This scan helps determine if the stroke is ischemic (caused by a clot) or hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding).
Guides Initial Treatment: The results can help doctors make immediate decisions about initial treatment steps.
2. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
Detailed Visualization: MRIs produce high-resolution images, allowing for a closer look at smaller clots or damaged areas.
Distinguishes Between Tissues: MRI can reveal more subtle signs of injury, making it useful for understanding the extent of brain tissue damage.
Ideal for Complex Cases: MRI is often used when CT scans are inconclusive or when further detail is needed.
3. Doppler Ultrasound:
Blood Flow Assessment: This non-invasive test measures blood flow through the arteries in the neck and brain.
Detects Blockages: Doppler ultrasound can indicate blockages or narrowed arteries, which are risk factors for clots.
Portable Option: It is especially valuable for ongoing monitoring or when quick bedside assessments are needed.
4. Angiography:
Blood Vessel Visualization: Angiography involves injecting a contrast dye to make blood vessels visible on X-ray images.
Identifies Precise Blockage Location: It provides a clear map of the arteries and pinpoints the clot’s exact location.
Useful in Planning Surgery: Angiography helps neurosurgeons plan procedures by giving a clear view of the vascular structure.
Treatment Options for Blood Clots in the Brain:
Treating brain clots depends on the type of stroke and the severity of the condition. The top 10 Best Neurology Hospitals in Uttar Pradesh like GS Hospital offers a range of treatment options to manage blood clots effectively:
1. Medications:
Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): Medications such as warfarin or heparin prevent further clot formation and help reduce the risk of additional strokes.
Thrombolytics (Clot-Busting Drugs): These medications dissolve existing clots and are highly effective if administered within hours of symptom onset.
Anti-Platelet Drugs: Medications like aspirin may be prescribed to prevent platelets from sticking together and forming new clots.
2. Surgical Intervention:
Mechanical Thrombectomy: In this minimally invasive procedure, a catheter is used to physically remove the clot from the blocked blood vessel, often through a tiny incision.
Craniotomy: For hemorrhagic strokes, a craniotomy may be necessary to relieve pressure caused by bleeding in the brain.
Endovascular Procedures: These involve inserting devices to treat blood vessel issues, such as stents to keep arteries open.
3. Physical Rehabilitation:
Physical Therapy: Helps patients rebuild strength and mobility that may be lost due to stroke-related damage.
Occupational Therapy: Assists patients in relearning daily activities and improving fine motor skills.
Speech and Cognitive Therapy: Restores language and cognitive abilities affected by the clot’s impact on brain function.
Preventing Blood Clots in the Brain:
Preventing brain clots involves lifestyle adjustments and medical management to reduce the risk of clots forming. Here are some effective steps:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet:
Focus on Heart-Healthy Foods: A diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins supports cardiovascular health.
Limit Saturated Fats and Sugars: Reducing these can help lower cholesterol and blood pressure, both of which are risk factors for clots.
Increase Fiber Intake: Fiber helps manage cholesterol, which can reduce plaque buildup in blood vessels.
2. Engage in Regular Exercise:
Boost Circulation: Physical activity improves blood flow and reduces the risk of clots.
Promotes Heart Health: Regular exercise supports a healthy heart and vascular system.
Reduces Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce strain on blood vessels and lower clot risk.
3. Quit Smoking:
Improves Vascular Health: Smoking damages blood vessels and raises the risk of clot formation.
Reduces Stroke Risk: Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to lower the likelihood of both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
Improves Overall Health: Reducing or eliminating tobacco use has numerous long-term health benefits.
4. Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol:
Monitor Regularly: Regular check-ups allow for early detection and management of high blood pressure and cholesterol.
Medication Adherence: If prescribed, take blood pressure or cholesterol medications as directed to maintain optimal levels.
Diet and Lifestyle Support: Reducing salt intake and exercising regularly are also effective in managing blood pressure.
5. Control Diabetes:
Maintain Stable Blood Sugar Levels: Managing blood sugar through diet, exercise, and medication can help protect blood vessels.
Regular Monitoring: Consistent monitoring of glucose levels helps prevent complications that may increase clot risk.
Healthy Diet and Exercise: Lifestyle adjustments that support blood sugar control can also improve overall vascular health.
Conclusion:
A blood clot in the brain is a critical medical condition requiring immediate care. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this health risk. At GS Hospital, we pride ourselves on being among the best Neurosurgery Hospitals in UP, providing top-tier care with a dedicated team of neuro specialists ready to assist in emergencies.
For any concerns or if you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, reach out to GS Hospital a trusted choice in neurology and neurosurgery care. With our expert team and state-of-the-art technology, we’re committed to helping you on your path to recovery and health.
#BloodClotInBrain#Neurology#NeuroSurgery#DepartmentOfNeurology#GSHospital#Ghaziabad#UttarPradesh#Best Neuro Hospital in Ghaziabad#Top 10 private hospitals in Uttar Pradesh#10 Best Neurology Hospitals in Uttar Pradesh#Best Neurosurgery Hospitals in UP
0 notes
Text
Stroke: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Types
A stroke is a potentially fatal medical illness that arises when there is an interruption in the blood flow to a specific area of the brain, either because of an ischemic stroke or a hemorrhagic stroke. If treatment is delayed, the death of brain cells brought on by this oxygen and food shortage may result in permanent impairment or even death. Improving outcomes and lowering complications depend on identifying the warning signals of a stroke and getting immediate medical intervention.
Access to quality medical care is critical for stroke patients, and for residents of Jaipur, seeking treatment at the Best Neurology Hospital in Jaipur can provide the advanced care necessary to address such emergencies. In this article, we will delve into what a stroke is, its causes, symptoms, types, and available treatment options.

What is a Stroke?
A cerebral blood vessel bursts or a blockage stops blood flow to the brain, resulting in a stroke. Without blood flow, brain cells begin to die within minutes, which can damage physical, cognitive, and emotional processes. Different portions of the body may lose feeling or control, depending on whatever area of the brain is impacted.
There are two main types of strokes:
Ischemic Stroke - This makes up around 87% of all strokes, making it the most prevalent form. It happens when a blood clot narrows or plugs an artery, preventing blood flow to the brain.
Hemorrhagic Stroke – This happens when a cerebral blood artery rupture, resulting in bleeding inside the brain or surrounding it. Although less frequent, hemorrhagic strokes are more fatal.
When there is a brief interruption in blood supply to the brain, a third ailment known as a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or "mini-stroke" takes place. Even though TIAs don't result in permanent damage, they are a severe indicator that a stroke may occur in the future.
Causes of Stroke
The causes of strokes vary depending on the type:
Ischemic Stroke:
Atherosclerosis: The buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the arteries leads to narrowing and hardening of the arteries, reducing blood flow.
Blood Clots (Thrombosis): Clots can form in arteries and block blood flow to the brain.
Embolism: A blood clot or debris from elsewhere in the body (such as the heart) travels through the bloodstream and blocks an artery in the brain.
Cardiovascular Conditions: Heart diseases such as atrial fibrillation can cause blood clots that travel to the brain, leading to a stroke.
Hemorrhagic Stroke:
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Chronic high blood pressure can weaken blood vessels and lead to their rupture.
Aneurysms: Weak spots in blood vessels can bulge and burst, causing bleeding in the brain.
Head Trauma: Physical injury to the head can result in brain hemorrhage.
Blood Thinning Medications: Overuse of anticoagulants or clot-busting medications can lead to an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): TIAs are often caused by temporary clots or other small blockages that reduce blood flow to the brain for a short period.
Symptoms of Stroke
Recognizing the symptoms of a stroke is crucial for getting immediate medical help. The symptoms may include:
Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
Confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech.
Vision problems in one or both eyes.
Severe headache without a known cause.
Dizziness, loss of balance, or trouble walking.
The acronym FAST is often used to quickly identify stroke symptoms:
Face drooping: Is one side of the face numb or drooping?
Arm weakness: Is one arm weak or numb?
Speech difficulty: Is speech slurred or hard to understand?
Time to call emergency services: If any of these symptoms are present, immediate medical help is critical.
Types of Stroke
Ischemic StrokeThis type occurs when blood vessels in the brain become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow. There are two subtypes:
Thrombotic Stroke: Caused by a blood clot that forms in an artery supplying blood to the brain.
Embolic Stroke: Caused by a blood clot or debris that forms elsewhere and travels through the bloodstream to block an artery in the brain.
Hemorrhagic StrokeHemorrhagic strokes occur when blood vessels in the brain rupture. There are two main types:
Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A blood vessel bursts within the brain, causing blood to leak into the surrounding tissue.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Bleeding occurs in the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering it, often due to a burst aneurysm.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)Sometimes referred to as a "mini-stroke," a TIA is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. TIAs do not cause permanent damage but are serious warning signs of future strokes.
Treatment Options
The treatment for stroke depends on the type and severity of the stroke:
Ischemic Stroke:
Clot-busting medications (tPA): Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a medication that can dissolve the clot causing the stroke if administered within 3-4.5 hours of symptom onset.
Mechanical thrombectomy: In some cases, doctors may use a catheter to physically remove the clot from the blocked artery.
Anticoagulants: Blood-thinning medications like aspirin may be prescribed to prevent future strokes.
Hemorrhagic Stroke:
Surgical intervention: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged blood vessels, stop the bleeding, or relieve pressure on the brain.
Medication management: Blood pressure-lowering drugs or medications to reduce the risk of seizures or bleeding may be used.
Rehabilitation: After a stroke, rehabilitation is often necessary to help regain lost functions such as speech, movement, and cognitive abilities. Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy are commonly used.
Conclusion
A stroke is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. The causes, symptoms, and treatments vary depending on the type of stroke, but early intervention can greatly improve the chances of recovery. Understanding the risks and recognizing the symptoms are vital to preventing serious long-term damage. For comprehensive care, seeking treatment at the best hospital in Jaipur can provide patients with the support and expertise needed for a better prognosis and recovery.
0 notes
Text
Exploring Neurovascular Intervention Options
Exploring Neurovascular Intervention Options
Neurovascular interventions represent a vital frontier in modern medicine, offering innovative treatments for conditions affecting the blood vessels of the brain and spinal cord. These interventions are crucial for managing complex disorders such as strokes, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and more. In this blog, we delve into the various neurovascular intervention options available today, highlighting their significance, benefits, and how they contribute to improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Neurovascular Conditions
Neurovascular conditions involve abnormalities or disorders affecting the blood vessels within the central nervous system. These conditions can range from ischemic strokes caused by blood clots to hemorrhagic strokes resulting from ruptured blood vessels, as well as structural anomalies like aneurysms and AVMs. Effective treatment requires precise diagnosis and intervention to prevent further damage and promote recovery.
Key Neurovascular Intervention Options
Mechanical Thrombectomy
Description: Mechanical thrombectomy is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat acute ischemic strokes caused by large artery blockages.
Procedure: A catheter is guided through the blood vessels to the site of the clot in the brain. A stent retriever or aspiration device is then used to physically remove the clot, restoring blood flow and reducing neurological damage.
Benefits: Rapid restoration of blood flow to the brain tissue can significantly improve outcomes, reducing disability and improving recovery rates for stroke patients.
Endovascular Coiling and Clipping for Aneurysms
Description: Endovascular coiling and surgical clipping are techniques used to treat cerebral aneurysms, which are weak spots in blood vessel walls that can bulge and potentially rupture.
Coiling: A catheter is inserted into the aneurysm, and soft platinum coils are deployed to fill the aneurysm sac. This promotes blood clotting within the aneurysm, reducing the risk of rupture.
Clipping: Involves surgically placing a metal clip at the base of the aneurysm to isolate it from the main blood vessel, preventing further expansion or rupture.
Benefits: Both techniques are minimally invasive compared to traditional open surgery, offering quicker recovery times and reduced risk of complications.
Embolization for Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
Description: Embolization is a procedure used to treat AVMs, which are abnormal tangles of blood vessels connecting arteries and veins.
Procedure: A catheter is guided into the abnormal blood vessels supplying the AVM. Embolic agents such as glue, coils, or particles are then injected to block blood flow to the AVM, reducing the risk of rupture or bleeding.
Benefits: Embolization can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with surgery or radiosurgery to shrink or eliminate the AVM, depending on its size, location, and complexity.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Description: Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a non-invasive technique that delivers precisely targeted radiation to treat vascular abnormalities or tumors in the brain.
Procedure: Unlike traditional surgery, SRS uses highly focused radiation beams to target specific areas with minimal impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
Benefits: SRS is effective for treating small to medium-sized AVMs or residual AVMs after embolization, providing an alternative or adjunct to surgical intervention with reduced risk of complications.
Advancements and Future Directions
Robotics and Navigation Systems: Advances in robotic-assisted surgery and advanced imaging-based navigation tools enhance precision and safety during neurovascular interventions.
Genetic and Molecular Therapies: Ongoing research explores therapies targeting genetic factors contributing to neurovascular diseases, potentially offering personalized treatment approaches in the future.
Conclusion
Neurovascular interventions play a critical role in managing complex conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord's blood vessels. By leveraging advanced techniques such as mechanical thrombectomy, endovascular coiling, embolization, and stereotactic radiosurgery, healthcare providers can deliver targeted, effective treatments with reduced risks and improved outcomes for patients. Continued research and technological innovations promise further advancements in neurovascular care, offering hope for enhanced treatment options and better quality of life for individuals facing neurovascular challenges.
0 notes
Text
Thromboembolism - Symptoms, Types, Causes, Complications & Prevention
Thromboembolism is a vascular disorder characterised by obstruction of blood vessels (arteries or veins) due to the formation of an embolus (movement of blood clot from one place to another place), which originates from a blood clot (thrombus). Based on the location of blood clot formation, they are classified into venous thromboembolism (which occurs in veins) or arterial thromboembolism (which arises in arteries). Haematologists lead the healthcare team which diagnoses and treats thromboembolic disorders.

Types of thromboembolism
While there are various types of thromboembolism derived from the location of a blood clot, the major types of thromboembolic disorders include:
Venous Thromboembolism Deep Venous Thrombosis Pulmonary thromboembolism Arterial Thromboembolism Ischemic Stroke Myocardial infarction Other thromboembolism Systemic thromboembolism Cerebral thromboembolism Coronary thromboembolism Massive thromboembolism Thromboembolism in spleen Thromboembolism after muscle injury Thromboembolic coagulopathy Cancer-associated thromboembolism Postpartum thromboembolism Thromboembolic renal disease
Venous thromboembolism :
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) refers to the formation of blood clots in the veins. This is a gradually developing disorder which is often underdiagnosed but can have serious consequences, such as disability and death. Nevertheless, it is a preventable medical condition if diagnosed accurately and early.
Deep vein thrombosis:
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT or venous thrombosis) is a medical condition referring to blood clot formation in the veins where the thrombus formation could occur due to either injured veins or the blood's hypercoagulability (increased coagulation affinity). Usually found in the lower extremities, such as the lower leg, thigh, etc. Deep vein thrombosis could cause partial or complete blockage to the blood flow to the respective organs.
Pulmonary thromboembolism:
This is also known as pulmonary embolism, a medical condition that disrupts (blocks) the pulmonary arterial blood flow due to the embolus either in the pulmonary artery or its branches. Here, the thrombus is formed elsewhere in the circulatory system but gets detached and passes through the pulmonary artery or its capillaries.
The combination of disrupted pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis is collectively called venous thromboembolism (VTE). Pulmonary emboli originate from deep venous thrombus and are responsible for the most common form of pulmonary thromboembolic disease. Based on the severity of the disease, the pulmonary embolism is of two types:
Acute pulmonary embolism: In acute embolism, the increased diameter of the pulmonary artery is observed. Chronic pulmonary embolism: In chronic embolism, narrowing of distal blood vessels is observed.
Thromboembolic disease causes :
The thromboembolism depends on the formation of thrombus or blood clot in arteries or veins.
Etiology of venous thromboembolism (venous thromboembolism causes) Injury of the deep vein leads to the formation of a blood clot. Limited movement in physical activity, so there is a deficient supply of blood circulation in blood vessels, leads to the formation of a blood clot. Heavy usage of oestrogen leads to the formation of a blood clot.
Etiology of arterial thromboembolism (arterial thromboembolism causes)
Increased age Smoking Increased fibrinogen levels
Thromboembolic disease symptoms :
Thromboembolic disorder's signs and symptoms may vary depending upon thrombus formation in the venous and arteries.
Venous thromboembolism Symptoms
The following are the venous thromboembolic disease symptoms.
Tenderness along the veins: Tenderness along the veins, which are sensitive to touch Aching pain: An unpleasant sensitised pain and emotional experience associated with potential tissue damage Swelling occurs whenever the organs, skin, or other parts of your body enlarge. It leads to inflammation or a buildup of fluid. Swelling can occur internally, or it can affect your outer skin and muscles.
Thromboembolic complications :
Thromboembolic complications are serious medical conditions that occur when a blood clot breaks off from its original location and travels through the bloodstream to another part of the body, where it can block blood flow and cause damage. These complications can be life-threatening and require prompt medical attention.
Thromboembolic aneurysm: Thromboembolism rarely occurs in large aneurysms where decreased blood flow within the aneurysm leads to blood clots, which are considered thromboembolic aneurysms.
Pulmonary venous thromboembolism: This is a rare form of venous thromboembolism complications, that is observed in veins of the pulmonary blood vessels. The pulmonary veins are the most common source of arterial thromboembolism. Pulmonary vein thrombosis (PVT) is a rare but potentially lethal disease which could occur due to the direct extension of the tumour into the vein, thus compressing the vein and causing epithelial damage and a hypercoagulable state.
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH): Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) is one of the complications of venous thromboembolic disease; specifically, CTEPH, due to pulmonary embolism, is a significant cause of chronic pulmonary hypertension, leading to right heart failure and death.
PACE Hospitals: Your Partner in Clot Care:
Our team of expert vascular surgeons, cardiologists, and hematologists are dedicated to providing comprehensive care for thromboembolism patients. We offer advanced diagnostic tools, minimally invasive treatment options, and personalized rehabilitation programs to ensure optimal recovery and prevent future clots. Remember, thromboembolism is a serious condition, but with knowledge and prompt action, you can overcome the clot challenge. Choose PACE Hospitals as your partner in proactive prevention and compassionate care. Together, let's keep the blood flowing freely and your health blooming!
0 notes
Text
An Overview of Neurology
Neurology is a branch of medicine used by specialists to diagnose and treat disorders of the nervous system. The nervous system is a complicated and precise system that controls all the activities of the body. The two major focuses are:
Central Nervous System: The CNS refers to the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System: The PNS involves all other neural elements like eyes, ears, skin, and other "sensory receptors."
Originally, neurology was a diagnostic specialty as it was dependent on correctly evaluating the symptoms presented and treated with limited drugs available. However, in the past couple of decades, this has completely changed due to the tremendous advancements made in neuroimaging and also in neuropharmacology.
Interventional Neurology
This subspecialty of neurology comprises various disorders affecting the nervous system. It employs tools like catheters and radiology to diagnose and treat the neurological condition with minimally invasive neurosurgical techniques. Through this method, our specialists pass certain tools through the blood to pinpoint the condition and treat it instead of open surgery.
Our doctors who practice interventional neurology use advanced radiology imaging and 3D technology to assist them in visualizing and treating the disorder. As a super specialty neuro hospital in Nagercoil, our team of board-certified neurologists is committed to providing each patient with customized and individual care.
We treat and help recover patients suffering from common yet serious neurological ailments like strokes, epilepsy (seizures), headaches, dementia (Alzheimer's disease), multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, etc.
Diseases Treated By Interventional Neurology
Some of the major conditions treated by physicians in interventional neurology include:
Cerebral Aneurysm: Swelling and weakening of a blood-carrying artery to the brain
Extracranial & Intracranial Atherosclerosis: Arteries supplying blood to the head and neck harden over time
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH): Blood vessel bursts in the brain
Brain and Spinal Vascular Malformations
Head and Neck Tumours
Neck Lesions
Extreme Nosebleeds
Stroke/Blood Clot in the Brain
Techniques of Interventional Neurology
As one of the best neuro hospitals in Nagercoil, we are invested in newer and advanced technology to treat our patients with the highest level of accuracy. Some of the techniques employed by our skilled staff are:
Angioplasty: Assessing blood flow to the neck and brain to learn of any irregularities like diseased, narrowed, enlarged, or blocked vessels
Coil Embolisation: A thin wire or coil is inserted to block blood flow to an area
Embolectomy: Stroke-causing blood clot is removed by this procedure
Stenting: A tiny balloon and/or stent is inserted to open a narrow vessel
Thrombectomy: In this procedure, a catheter is threaded through an artery in the patient’s groin to the blocked artery in the brain.
Interventional neurology gives doctors the ability to diagnose a disorder of the nervous system even before the onset of the disease. It has also opened up varied avenues of treatment in precision medicine. As a result, we are excited to offer you our services as an interventional neurology hospital in Nagercoil for the betterment of the community and humankind.
0 notes
Text
Can an Interventional Radiologist Help with Brain-Related Disorders?
Interventional radiologists primarily specialize in using minimally invasive image-guided procedures to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions, often related to blood vessels and internal organs. While their expertise is not typically focused on brain-related disorders, there are some specific scenarios where an interventional radiology Phoenix clinic may play a role in addressing certain brain conditions. Most interventional radiologists can perform cerebral angiography, a diagnostic procedure used to visualize blood vessels in the brain. It helps in the assessment of conditions like aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and stenosis of brain arteries. If there is a need to deal with problems involving abnormal blood flow, radiologists can perform embolization procedures to block or reduce blood flow to abnormal blood vessels in the brain. This is often used for treating AVMs or certain types of brain tumors. In some cases, these experts are also involved in the management of acute stroke. They may perform procedures like intra-arterial thrombolysis or mechanical thrombectomy to remove blood clots in the brain’s blood vessels. While not directly related to brain disorders, the management of chronic pain conditions could also be related to their expertise, including primarily diseases that are either directly or indirectly associated with neurological disorders. Procedures like nerve blocks or neurolysis may be used to alleviate pain. The post Can an Interventional Radiologist Help with Brain-Related Disorders? appeared first on blog.vipinterventional.com. Originally published here: https://blog.vipinterventional.com/can-an-interventional-radiologist-help-with-brain-related-disorders/
0 notes
Text
Primary Angioplasty

Primary angioplasty is a treatment to reopen a blocked coronary artery. When angioplasty is used to reopen a coronary artery when someone is having an acute myocardial infarction, it is called a primary angioplasty.
Why would you need an angioplasty?
treat an abnormal stress test
increase blood flow to the heart
reduce chest pain, or angina
improve blood supply to the heart muscle during or after a heart attack
support more activity for people with chest pain.
Types:
Balloon angioplasty.
Carotid artery angioplasty.
Cerebral angioplasty.
Coronary artery stent.
Laser angioplasty.
PTA of the Femoral Artery.
What are the risk factors for angioplasty?
The most common angioplasty risks include
Re-narrowing of your artery. When angioplasty is combined with drug-eluting stent placement, there’s a small risk the treated artery will become clogged again. …
Blood clots. Blood clots can form within stents even after the procedure. …
Bleeding.
Heart attack.
Stroke.
Injury to the catheterized artery.
Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
Allergic reactions to the dye or medications used during the procedure.
Kidney damage.
Infection.

Accounting for thorough experience and practice, Dr. Aritra Konar is a Consultant Interventional Cardiologist at Apollo Gleneagles Hospital, Kolkata. He has been deemed one of the best cardiologists in Kolkata for his expertise lies in Coronary (femoral & radial routes) angiography, Coronary angioplasty (including primary angioplasty), Peripheral angiography and angioplasty, Permanent pacemaker, ICD, CRT implantation, BMV, BPV, Right heart catheterization and so on, in procedural skills. His guidance is trusted and so are his skills.
0 notes
Text
ISCHEMIC VS. HEMORRHAGIC STROKE: UNRAVELING THE DIFFERENCES IN CAUSES AND TREATMENTS

Strokes are a significant medical emergency characterized by a sudden disruption of blood flow to the brain. They can be broadly categorized into two main types: ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. The primary difference between these two types lies in their underlying causes and subsequent treatments. Let's delve into the details of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, highlighting their differences in causes and treatments.
Ischemic Stroke: Causes: Ischemic strokes are the most common type of stroke, accounting for about 85% of all cases. They occur when there's a blockage in a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain. This blockage is usually caused by a blood clot, which can either form within the blood vessel (thrombus) or travel from elsewhere in the body and lodge in a cerebral artery (embolus).
Risk Factors: Several risk factors contribute to the development of ischemic strokes, including hypertension (high blood pressure), high cholesterol levels, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and a family history of stroke or cardiovascular disease.
Types: Ischemic strokes are further classified into two main subtypes:
1. Thrombotic Stroke: This type occurs when a blood clot forms within an artery that supplies blood to the brain. It's often related to atherosclerosis, a condition in which fatty deposits (plaques) build up on the inner walls of arteries.
2. Embolic Stroke: An embolic stroke occurs when a blood clot or debris travels from another part of the body, such as the heart or neck arteries, and gets lodged in a brain artery, blocking blood flow.
Treatment: The main goal in treating ischemic strokes is to restore blood flow to the brain as quickly as possible. Treatment options include:
Thrombolytic Therapy (tPA): This involves administering tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), a medication that dissolves blood clots. It's most effective when given within a few hours of stroke onset.
Mechanical Thrombectomy: For larger clots, a procedure called mechanical thrombectomy may be performed. This involves using specialized tools to physically remove the clot from the blocked artery.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Causes: Hemorrhagic strokes occur when there's bleeding within or around the brain. The bleeding can result from a ruptured blood vessel, often due to weakened vessel walls or an aneurysm (a ballooning of a blood vessel wall).
Risk Factors: Hypertension is a major risk factor for hemorrhagic strokes, as it can weaken blood vessel walls over time. Other risk factors include a family history of aneurysms, drug use (such as cocaine or amphetamines), and certain medical conditions that affect blood clotting.
Types: Hemorrhagic strokes can be divided into two primary types:
Intracerebral Hemorrhage: This occurs when a blood vessel within the brain ruptures and leaks blood into the surrounding brain tissue.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: This type involves bleeding into the space between the brain and the thin tissues that cover it. It's often caused by the rupture of an aneurysm.
Treatment: Treating hemorrhagic strokes focuses on stopping the bleeding, relieving pressure on the brain, and preventing complications. Treatment options include:
• Surgical Interventions: Surgery may be required to repair a ruptured aneurysm or to remove blood clots or hematomas (collections of blood).
• Medication and Monitoring: Blood pressure may be managed carefully to prevent further bleeding, and other medications may be administered to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Mr. Jayesh Saini says, “Ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes are distinct in terms of their causes, risk factors, and treatments. Ischemic strokes involve blockages in brain arteries, often caused by blood clots, while hemorrhagic strokes result from bleeding within or around the brain.”
He further says that, “Prompt medical attention and accurate diagnosis are crucial in determining the appropriate treatment approach for each type of stroke, with the ultimate goal of minimizing brain damage and maximizing the chances of recovery.”
0 notes
Text
Amplatz Sheath in Neuro Interventions: Expanding the Horizons of Stroke Treatment
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving field of neuro interventions, medical advancements continuously push the boundaries of stroke treatment. One such revolutionary device that has improved patient outcomes is the Amplatz sheath. At Manish Medi Innovations, we are committed to staying at the forefront of medical innovations, and the Amplatz sheath is a testament to our dedication to providing cutting-edge solutions to healthcare professionals. In this blog, we will delve into the significance of the Amplatz sheath in neuro interventions and how it has expanded the horizons of stroke treatment.
Understanding the Amplatz Sheath
The Amplatz sheath, named after its inventor, the renowned interventional radiologist Dr Julio Amplatz, is a specialized catheterization device. It is designed to facilitate the introduction of various medical devices, such as stents, balloons, and embolic agents, into the vascular system with enhanced precision and control.
Key Applications in Neuro Interventions
Mechanical Thrombectomy
Mechanical thrombectomy is a groundbreaking procedure for ischemic stroke treatment. During an ischemic stroke, a blood clot blocks a cerebral artery, leading to a sudden lack of blood flow to the brain. The Amplatz sheath enables interventional neurologists to access the affected blood vessel and deploy specialized devices, like stent retrievers and aspiration catheters, to remove the clot effectively. This minimally invasive procedure has revolutionized stroke care, significantly improving the chances of a full recovery and reducing the risk of disability.

Stent-Assisted Coiling
The Amplatz sheath is also crucial in treating cerebral aneurysms using stent-assisted coiling. This procedure navigates a stent through the Amplatz sheath to the aneurysm site. Once in place, detachable platinum coils are delivered through the stent to promote clotting and prevent rupture. This technique reduces the risk of complications during coiling and enhances the overall safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
Embolization of Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are abnormal tangles of blood vessels that can occur in the brain and spinal cord. AVMs are often treated by embolization, wherein the Amplatz sheath is used to deliver embolic agents, such as glue or particles, to occlude the abnormal vessels. By doing so, blood flow is redirected away from the AVM, reducing the risk of rupture and potential bleeding.
The Advantages of Amplatz Sheath in Neuro Interventions
Enhanced Precision and Control
The Amplatz sheath's design allows for smooth navigation through complex vascular structures, ensuring precise placement of interventional devices. This level of control is critical in delicate neuro interventions, where even the slightest deviation can have significant consequences.
Minimally Invasive Approach
Compared to traditional open surgical procedures, neuro interventions using the Amplatz sheath offer a minimally invasive approach. This means smaller incisions, reduced risk of infection, shorter recovery times, and improved patient comfort.
Real-time Visualization
The Amplatz sheath's radiopaque nature enables real-time visualization during procedures, allowing interventional neurologists to monitor the progress and make adjustments as necessary. This capability enhances procedural safety and ensures the best possible outcomes for patients.
Conclusion
The Amplatz sheath has undoubtedly transformed the landscape of stroke treatment and neuro interventions. Its versatility, precision, and minimally invasive nature have made it an indispensable tool for interventional neurologists. At Manishmedi Innovations, we recognize the immense impact that innovative devices like the Amplatz sheath can have on patient care and outcomes. As we continue to push the boundaries of medical advancements, we remain committed to providing healthcare professionals with the latest and most reliable neuro intervention solutions. With the Amplatz sheath at the forefront of our offerings, we strive to expand stroke treatment horizons and improve patients' lives worldwide.
0 notes
Text
Stroke causes and prevention

Stroke is one of the critical factors in the death of people in society, a situation that, in addition to end, can cause the patient to suffer severe complications for a long time, so it is an essential factor for Eliminating the risks caused by stroke is knowing the factors that cause it so that the necessary preventive measures can be taken before the stroke occurs.
Why do strokes occur?
Mild stroke A stroke occurs when the blood flow to a part of your brain is interrupted or severely reduced, and the brain tissue is deprived of oxygen and nutrients. This state can happen due to blockage of brain vessels or due to the rupture of containers; in any case, after that, within a few minutes, brain cells start to die; during this interval, the patient has a golden time for treatment and Prevention has its side effects, the more and longer this time is, the less chance the patient will have, and this is where the patient or his companions should immediately call the emergency room or transfer the patient to appropriate medical centers. Types of stroke About 85% of strokes are ischemic strokes. Ischemic stroke happens when the arteries in your brain are narrowed or blocked and cause a severe reduction in blood flow (ischemia); you should pay attention to the fact that if the patient is diagnosed before reaching the stage of vascular blockage and with the help of methods Currently, including stenting in the brain, the artery will be opened, this patient will not experience a stroke, now with the help of devices such as brain doppler ultrasound, a doctor can quickly check the condition of the brain arteries and if there is a blockage, using Methods such as drug therapy, brain stent guided by the brain angiography device or other methods to treat it. The most common ischemic strokes are: Thrombotic stroke When a blood clot (thrombus) develops in one of the arteries supplying the brain with blood, it causes a thrombotic stroke. Those who are old are among the people who are more prone to blood clots and strokes, the deposition of fats and some other factors in the vein can cause narrowing and clogging of the artery, and if this clogging exceeds the limit, the patient suffers from thrombosis. Became. embolic stroke In cases like varicose veins, where clots form inside the veins, an embolic stroke happens when a blood clot or other lesions form far from your brain and enter the cerebral arteries through the bloodstream, causing their narrowing. Blood pressure can cause a stroke by removing the lump and bringing it to the cerebral arteries; in such a situation, if the patient is immediately transferred to the medical center, there is a high probability of treating the blocked artery, and the doctor can prevent the creation of permanent clots with the help of methods such as tpa injection. And stop it permanently. Transient or mild ischemic stroke A mild stroke has a short period of symptoms similar to those of a stroke. A temporary reduction in blood flow to part of your brain causes a mild stroke, which often lasts less than five minutes. Like an ischemic stroke, a gentle stroke occurs when a clot or other material blocks blood flow to a part of your brain. Research has shown that many people who experience a mild stroke soon and at some point experience a massive stroke, so it is critical that cerebral ischemic patients, even if they have experienced brief symptoms, refer to the doctor and ensure the conditions of their cerebral arteries.
Symptoms before stroke
Some early warning signs of a stroke are difficulty speaking and understanding, numbness in one side of the face, arms or legs, especially in one or both eyes; blurriness or diplopia, Sudden and severe headache with vomiting, dizziness or Loss of consciousness, difficulty walking and imbalance. Stroke symptoms in women The stroke symptoms in women may differ from those in men. These symptoms may include: Nausea or vomiting convulsions hiccups Difficulty breathing the pain Fainting or losing consciousness General weakness Since these symptoms are unique to women, they may not be diagnosed quickly, and treatment may be delayed. Strange behaviors, such as sudden sleepiness, can also indicate a stroke. Doctors call these symptoms altered mental status. These symptoms include: Unresponsive fainting confusion Sudden behavior change Delusion
Prevention of stroke
Numerous heart disease and stroke prevention techniques are similar. In general, healthy lifestyle recommendations include the following: Controlling high blood pressure This is the most important action you can take to reduce your risk of stroke. To control your blood pressure. If you have a history of stroke, lower your blood pressure to prevent ischemic or mild stroke. There are many ways to manage high blood pressure, including exercising, dealing with stress, maintaining a healthy weight, and consuming less sodium and alcohol. Reducing the amount of cholesterol and saturated fat in your diet can reduce plaque in the arteries. Quit smoking Both smokers and non-smokers who are exposed to cigarette smoke have an increased risk of stroke. Control of diabetes You can control diabetes with diet, exercise, weight control, and medication. Maintaining a healthy weight High blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes are stroke risk factors that are exacerbated by obesity. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables Proper nutrition after stroke A diet containing five fruits or vegetables per day may reduce the risk of stroke. Olive oil, nuts, and whole grains can also be helpful. Regular exercise Aerobic exercise reduces the risk of stroke and can lower blood pressure.Exercise increases levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and improves overall vascular and heart health.It can also help you lose weight, manage diabetes, and reduce stress. Avoiding the use of illegal drugs Some street drugs, such as cocaine and methamphetamine, are risk factors for stroke. Cocaine reduces blood flow and constricts arteries. Stroke medications If you have had a history of an ischemic or mild stroke, your doctor may prescribe medications to reduce the risk of another stroke, including: Antiplatelet drugs Antiplatelet drugs reduce the risk of clot formation. The most commonly used antiplatelet drug is aspirin. If aspirin doesn't prevent a stroke or you can't take aspirin, your doctor may prescribe antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel (Plavix). Anticoagulant drugs These drugs include heparin and warfarin (Coumadin), which reduce blood clotting. Heparin works quickly and can be used in a hospital for a short time. Warfarin should be taken long-term. Duration of stroke treatment Once the symptoms of a stroke begin, there is only a short time for treatment to save the person. If a patient comes to the emergency room within four and a half hours of experiencing stroke symptoms, doctors can prescribe a powerful anti-clotting drug and often save brain tissue. But if more than four and a half hours have passed, the medicine should not be used. Complications after stroke A stroke can sometimes cause permanent or permanent disabilities, depending on which part of the brain is affected by the lack of blood flow. Some complications of stroke include: Problems in speaking or swallowing A stroke may cause you to lose control over the muscles in your mouth and throat, which may cause problems in swallowing or speaking. It may also cause problems with the tongue in speaking or understanding speech, reading, or writing, which are usually treatable. Paralysis or Loss of muscle movement You may be paralyzed on one side of your body or lose control of specific muscles on one side of your face or arm. Physical therapy may help you return to activities that prevent Paralysis, such as walking, eating, and dressing. Loss of memory or problems in thinking Many people with stroke may lose their memory. Others may need help in thinking, judging, and understanding concepts. Emotional problems People with stroke may have problems controlling their emotions or become depressed. Pain When a stroke occurs, the body parts affected by the stroke may feel painful, numb, or strange. For example, if a stroke causes Loss of success in the left arm, an uncomfortable burning sensation may develop. A person may be sensitive to temperature changes, especially after a severe stroke. This condition is known as severe stroke pain or central pain syndrome. This condition usually develops a few weeks after the stroke and may improve. Changing behavior and self-care ability People who have had a stroke are sometimes less social or aggressive. These patients may require daily care. As brain damage is different in people, the success of treating these complications also varies from person to person. Physiotherapy after stroke If the stroke affects the part of the brain that controls movement, The patient may have issues moving and carrying out daily tasks, as well as weakness or paralysis on one side of the body. He may also experience other symptoms, such as muscle spasms, balance problems, and joint pain. Physical therapy can help you recover. Caring for stroke patients at home 1- Take prescribed medicines on time and be careful of any side effects caused by them. 2- Be careful of complications after a stroke. 3- Pay attention to supplements; Because they may provoke the next stroke. 4- Evaluate the rate of the patient's recovery and its speed. 5- Be careful so the patient does not fall when standing up and walking. 6- If the patient falls, take it seriously and see a neurologist immediately. 7- Take care of the patient's emotions and mental state, and do not argue with him. 8- Show the patient that you support him. Nutrition of stroke patients Fruits and vegetables contain antioxidants that can reduce damage to blood vessels. They also contain potassium, which is very useful for controlling blood pressure. The fiber in fruits and vegetables can lower cholesterol. Folate, found in green leafy vegetables, may reduce the risk of stroke. Seeds and grains also contain fiber and folate. Dairy products are a source of potassium and calcium and help control blood pressure. Dairy alternatives include calcium-fortified soy milk or rice milk. Other sources of calcium include bony fish, almonds, and tofu. Do not eat these after a stroke! Things that are limited after a stroke include: Salt Too much salt can raise blood pressure. Read food labels and choose low-salt options. Do not add salt while cooking or on the table. Use herbs and spices to enhance flavor. If you reduce your consumption gradually, you will adjust your deficiency within a few weeks. Sugar Too much sugar can damage blood vessels. Read food labels and choose options with lower sugar. Even foods that you may not recognize as sweets have added sugar. Saturated fat This fat increases cholesterol. Consume unsaturated oils. Try peanut or avocado oil. Alcohol Excessive alcohol consumption increases risk factors for stroke, including high blood pressure. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Brain Stroke Treatment in Aundh | Best Stroke Treatment Clinic in Aundh
Tonde's Neuro & Ortho Clinic is one of the successful Best Stroke Treatment Clinic in Aundh, we offer comprehensive Brain Stroke Treatment in Aundh.
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and bleeds, or when there’s a blockage in the blood supply to the brain. The rupture or blockage prevents blood and oxygen from reaching the brain’s tissues. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)Trusted Source, stroke is a leading cause of death. Without oxygen, brain cells and tissue become damaged and begin to die within minutes. There are types of strokes, Transient ischemic attack (TIA) involves a blood clot that typically reverses on its own, Ischemic stroke involves a blockage caused by either a clot or plaque in the artery. The symptoms and complications of ischemic stroke can last longer than those of a TIA, or may become permanent.
Stroke symptoms The loss of blood flow to the brain damages tissues within the brain. Symptoms of a stroke show up in the body parts controlled by the damaged areas of the brain.

The sooner a person having a stroke gets care, the better their outcome is likely to be. For this reason, it’s helpful to know the signs of a stroke so you can act quickly. Stroke symptoms can include
Paralysis
numbness or weakness in the arm, face, and leg, especially on one side of the body
trouble speaking or understanding others
slurred speech
confusion, disorientation, or lack of responsiveness
sudden behavioral changes, especially increased agitation
vision problems, such as trouble seeing in one or both eyes with vision blackened or blurred, or double vision
trouble walking
loss of balance or coordination
dizziness
severe, sudden headache with an unknown cause
seizures
nausea or vomiting
What causes a stroke? The cause of a stroke depends on the type of stroke. Strokes fall into three main categories:
transient ischemic attack (TIA)
ischemic stroke
hemorrhagic stroke
These categories can be further broken down into other types of strokes, including:
embolic stroke
thrombotic stroke
intracerebral stroke
subarachnoid stroke
The type of stroke you have affects your treatment and recovery process.
Ischemic stroke During an ischemic stroke, the arteries supplying blood to the brain narrow or become blocked. Blood clots or severely reduced blow flow to the brain causes these blockages. Pieces of plaque breaking off and blocking a blood vessel can also cause them.
There are two types of blockages Trusted Source that can lead to ischemic stroke: a cerebral embolism and cerebral thrombosis.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) A transient ischemic attack, often called a TIA or ministroke, occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked temporarily. Symptoms are similar to those of a full stroke. However, they’re typically temporary and disappear after a few minutes or hours, when the blockage moves and blood flow is restored. A blood clot usually causes a TIA. While it’s not technically categorized as a full stroke, a TIA
Hemorrhagic stroke A hemorrhagic stroke happens when an artery in the brain breaks open or leaks blood. The blood from that artery creates excess pressure in the skull and swells the brain, damaging brain cells and tissues.
Risk factors for stroke Certain risk factors make you more susceptible to stroke. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Trusted Source, risk factors for stroke include:
Diet An unbalanced diet can increase the risk of stroke. This type of diet is high in:
salt
saturated fats
trans fats
cholesterol
Inactivity
Inactivity, or lack of exercise, can also raise the risk of stroke.
Regular exercise has a number of health benefits. The CDC recommends that adults get at least 2.5 hours Trusted Source of aerobic exercise every week. This can mean simply a brisk walk a few times a week.
Heavy alcohol use The risk of stroke also increases with heavy alcohol use.
If you drink, drink in moderation. This means no more than one drink a day for women, and no more than two drinks a day for men.
Heavy alcohol use can raise blood pressure levels. It can also raise triglyceride levels, which can cause atherosclerosis. This is plaque buildup in the arteries that narrows blood vessels.
Tobacco use Using tobacco in any form also raises the risk of stroke, since it can damage the blood vessels and heart. Nicotine also raises blood pressure.
0 notes
Text
Do you know the causes of a Stroke?

Introduction
Stroke is a common cause of disability and, even worse, death, killing over 400,000 people each year around the world.
What do you know about stroke?
When a person's brain stops functioning, it is a stroke caused by a sudden disturbance in the blood flow to the brain. Anyone can fall prey to it, but it's more common in older people.
A cerebrovascular accident (CVA) happens when an artery supplying blood to your head or neck is blocked or partially blocked by a blood clot, restricting the usual blood flow to your brain tissue. This can lead to the following:
feeling weak or dizzy
pain in your arms and legs
slurred speech
If you have symptoms like these after having CVA, call 112 immediately!
Causes of stroke
The causes of a stroke may vary, but they often cluster into four major categories: atherosclerosis, diabetes, hypertension (high blood pressure), and smoking. Atherosclerosis is the build-up of fatty plaque inside your arteries. High cholesterol and high triglycerides can also cause the narrowing of blood vessels, leading to stroke if not treated properly. Smoking causes inflammation in the brain, which may lead to a greater risk for stroke and other types of dementia, like Alzheimer's disease. All the Best Neuro Hospital in UP also link high blood sugar levels with increased risk for vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis; Type II diabetes tends to increase these risks because it promotes too much insulin production, which leads directly to an increase in blood glucose levels over time!
This article will help you gain in-depth knowledge not only about the cause of a stroke but also educate its types, symptoms, related risk, and essential factors that will aid in preventing a stroke- well... That's because we want you to be aware before something happens!
Its types
Strokes are classified into four main types:
Cerebral infarction (Cerebrovascular accident)- Cerebral infarction is when the blood supply to your brain becomes blocked. While the reason for this condition may vary, it is commonly caused due to atherosclerosis and hypertension. Some of the best neurologist in UP run transcendental meditation and relaxation programs to manage hypertension and high blood pressure effectively.
Subcortical arterial ischemia- Occurs when blood flow to specific brain parts becomes restricted due to the narrowing of arteries or damaged valves in large vessels such as those leading from your heart. A combination of changes in blood pressure and cholesterol levels is often responsible for this type of stroke.
Embolic stroke (Thromboembolism)- An embolus composed primarily of fat globules or clots can travel through arteries and block them, causing a thrombosis which causes damage inside your brain tissue; this condition may be accompanied by inflammation, which causes further complications later on down the road if left untreated appropriately!
Risk factors for stroke
The research carried out in GS Hospital shows that there are several risk factors for stroke, including high blood pressure and diabetes. Other factors that can increase your chances of stroke include family history, smoking, and rising age.
High blood pressure: It's estimated that one in three adults have some form of hypertension—a condition characterized by abnormal increases in blood pressure over time. Still, only one-third of those people are being treated for it.
High cholesterol: This condition puts you at risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) when it's left untreated.
Smoking: Tobacco products contain thousands of chemicals that may increase your risk for heart disease.
Diabetes mellitus type 2: Having diabetes can make you more likely to develop CVD later in life due to reduced circulation throughout the body.
Family history: Your personal history is essential in determining how susceptible you are to developing certain diseases and how well they will respond when they occur.
Symptoms of a stroke
Stroke symptoms include:
Facial droop- This is the most common stroke symptom, and it can affect both or just one side of your face at once. The records from one of the Best Hospital in Hapur show patients may also have difficulty speaking, swallowing, and chewing food properly.
Difficulty walking or being able to move around at all (unable to put on shoes).
One side of your body will feel immense weakness that will gradually affect muscle control (for example, weakness in one leg or arm). This could be mild or severe depending on how long after the stroke occurred, it occurred.
How is a stroke diagnosed?
When a stroke occurs, many people can help, but the first person to notice that something is wrong will be your family or loved one. The family members must treat this as an emergency and take the patient to the nearest hospital, where an ER physician, nurse practitioner, neurologist, or other medical professionals specially trained in treating strokes will examine them. A state circular forwarded by the 10 Best Neurology Hospitals in Uttar Pradesh stated, "If you think someone has had a stroke and they aren't talking clearly or walking correctly after receiving treatment, this could mean that they haven't been properly diagnosed yet!"
Knowing your risk factors is essential
Knowing your risk factors is vital to managing your health. The more you know about your stroke risk, the better you can handle it. Knowing your risk factors can help you avoid stroke, other health problems, and even death by preventing or controlling high blood pressure and cholesterol levels (a significant risk factor for heart disease) as well as diabetes mellitus (which is associated with cardiovascular disease).
Knowing how likely someone is to have a heart attack or stroke based on age alone isn't enough; it's also essential to understand what lifestyle changes might be able to lower this probability even further. For example: Do they smoke cigarettes? How much do they weigh?
Are they physically active regularly? How often do they eat healthy foods—or not eat at all before bedtime? These questions should be asked periodically so everyone has access when needed!
Conclusion
Stroke is a scary word for some people. It's important to know why you have risks and what you can do about them. Knowing your risk factors is the most effective prevention. Following up with your family or medical history will help you better understand what happens to your body in case of a stroke or heart attack.
0 notes
Text
Cutting-Edge Neurointerventional Procedures
In the realm of neurology, advancements in medical technology have paved the way for cutting-edge neurointerventional procedures. These procedures represent a significant stride forward in the treatment of various neurological disorders, offering patients new hope and improved outcomes.
What are Neurointerventional Procedures?
Neurointerventional procedures refer to minimally invasive techniques used to treat conditions affecting the brain, spine, and peripheral nervous system. Unlike traditional surgical approaches that may require large incisions and longer recovery times, neurointerventional procedures involve using catheters, wires, and advanced imaging techniques to access and treat the affected area with precision.
Key Benefits of Neurointerventional Procedures:
Minimally Invasive: These procedures typically involve smaller incisions or entry points, leading to reduced trauma to surrounding tissues and faster recovery times for patients.
Precision and Accuracy: Advanced imaging technologies such as fluoroscopy and MRI guidance allow neurointerventionalists to precisely navigate and treat even the most delicate structures within the nervous system.
Treatment of Complex Conditions: Neurointerventional procedures are particularly effective in treating complex conditions such as cerebral aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), stroke, and spinal cord disorders.
Reduced Risks: Compared to open surgery, neurointerventional techniques often carry lower risks of complications such as infection and bleeding.
Improved Patient Outcomes: By targeting specific areas of concern with greater accuracy, these procedures can lead to improved clinical outcomes, symptom relief, and enhanced quality of life for patients.
Common Neurointerventional Procedures:
Endovascular Coiling and Embolization: Used to treat cerebral aneurysms and AVMs by blocking blood flow to abnormal vessels.
Thrombectomy: A procedure to remove blood clots from cerebral arteries, often performed in acute stroke cases.
Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Techniques to stabilize vertebral fractures caused by osteoporosis or trauma, reducing pain and restoring spinal alignment.
Neurostimulation: Implantation of devices to modulate nervous system activity, used in conditions like chronic pain and movement disorders.
Future Directions:
As technology continues to advance, the field of neurointerventional procedures is poised for further innovation. Emerging techniques such as robotic-assisted interventions and nanotechnology-based therapies hold promise for enhancing procedural precision and expanding treatment options for a broader range of neurological conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cutting-edge neurointerventional procedures represent a significant advancement in the field of neurology, offering patients less invasive treatment options with improved outcomes. These procedures continue to evolve, driven by ongoing research, technological innovation, and the dedication of healthcare professionals to enhance neurological care worldwide
0 notes
Text
Cerebrovascular Surgery In India by Dr. Vijendra Kumar Jain
Cerebrovascular Surgery
Cerebrovascular surgery is a type of surgery that is used to treat problems with the blood vessels in the brain. These problems can include blocked blood vessels, aneurysms, and strokes. Cerebrovascular surgery can be used to treat these problems by either repairing or removing the damaged blood vessels.
Cerebrovascular surgery is a necessary treatment for many people who have problems with their blood vessels in the brain. Blocked blood vessels can cause a stroke, and aneurysms can burst and cause serious damage. Cerebrovascular surgery can repair these problems and help to prevent further damage.
What kind of conditions are commonly treated by cerebrovascular surgery?
Here are some of the conditions that are treated by cerebrovascular surgery:
Ischemic stroke: Ischemic stroke is a common type of stroke that is caused by a blockage in one of the arteries supplying blood to the brain. This can occur as a result of a blood clot, atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), or another condition that restricts blood flow.
Hemorrhagic stroke: A hemorrhagic stroke, also called a cerebral hemorrhage, is a form of stroke that results from bleeding within the brain. It occurs when an artery in the brain ruptures and leaks blood into the surrounding tissue. Hemorrhagic strokes are less common than ischemic strokes, but they are often more deadly.
Cavernous malformations: Cavernous malformations are congenital, non-cancerous, blood vessel abnormalities. They can occur anywhere in the body but are most commonly found in the brain and spine.
Cerebral aneurysms: A cerebral aneurysm is a bulge or weak spot in the wall of an artery in the brain. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all the parts of our body. When an aneurysm ruptures, it can cause a hemorrhage (a type of bleeding), which can lead to death.
Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: A cerebral arteriovenous malformation, or CAVM, is a congenital defect in the brain where blood vessels are abnormally connected. This can cause blood to flow too quickly and lead to a hemorrhage. Symptoms can include seizures, headaches, and vision problems. Treatment options include medication, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Spinal arteriovenous malformations: Spinal arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are rare lesions that occur when veins and arteries in the spine mix together. This can cause blood to flow abnormally and lead to serious health problems.
Cerebral/spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: A cerebral spinal dural arteriovenous fistula (CVAF) is a rare and serious type of vascular malformation that develops between the arteries and veins in the dura mater, the outermost membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord. C
Moyamoya disease: Moyamoya disease is a rare neurological disorder that leads to the abnormal development of blood vessels in the brain. These new blood vessels are thin and can easily rupture, which can lead to a stroke.
Transient ischemic attacks: A transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke, is a short-term stroke that causes minimal or no permanent damage. TIA symptoms are very similar to those of a full-blown stroke, but they usually last only a few minutes and then disappear.
Trigeminal neuralgia: Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic, stabbing pain in the face that is caused by damage to or irritation of the trigeminal nerve. The trigeminal nerve is one of the main nerves in the head and controls facial sensations and movement.
Hemifacial spasm: Hemifacial spasm is a disorder that affects the muscles on one side of the face. It causes the muscles to contract uncontrollably, which can lead to facial distortion and difficulty speaking. The cause of hemifacial spasm is unknown, but it may be related to a problem with the blood vessels or nerves in the face.
Cerebrovascular Surgery in India
Cerebrovascular surgery is a critical surgical procedure that is used to treat various conditions that affect the blood vessels in the brain. This type of surgery can be very complex, and it is important to find a doctor who is experienced in performing this procedure.There are a few surgeons who offer cerebrovascular surgery in India and Dr. VK Jain is one of them.
Dr. VK Jain is considered as the best neurosurgeon in India for cerebrovascular surgery. He has over 41 years of experience in performing this type of surgery, and he has successfully treated many patients with complex vascular problems. Dr. Jain works at Max Hospital, one of the leading hospitals in India, and he is highly skilled in providing state-of-the-art care for his patients.
TAG- Best spine surgeon in India, Neurologist in India, Cerebrovascular treatment in Delhi, Best brain tumor surgeon in Delhi
#bestspinesurgeonindelhi#bestneurosurgeonindelhi#bestbraintumorsurgeryinindia#neurologistinindia#spinespecialistinindia
0 notes