#Biomedical Science and Research Journals
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Rule of Choice of Equations for Calculation of Constants of Enzyme Inhibition and Activation

The Rule of Choice of Equations for Calculation of Constants of Enzyme Inhibition and Activation in Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research
In previous works [1-5] the possibility of construction of L vectors of enzymatic reactions in the three-dimensional (packed) Km V I rectangular coordinate system (Figure 1) is considered. The taking into account of properties of L vectors, such as: symmetric position in the Km V I coordinate system and the ratio of l lengths of orthogonal projections on the coincident (Pa, i ) semi-axis to the ratio of the L vector projection on the semi-axis in basic s0 plane (Figure 2) permitted to construct a parametrical classification of the types of enzymatic reactions (Table 1) and correct the equations for calculation of the Ki and Ka constants of enzyme inhibition and activation, respectively, which now includes fourteen equations: 7 equations s for calculation of constants and 7 equations for calculation of Ka constants. It turned out that some of the obtained equations have similar algebraic forms, which required to consider the rule of choice of these equations to prevent their unjustified use and also for expansion of the possibilities of their application at data analysis in enzyme kinetics.
For more articles in Journals on Biomedical Sciences click here bjstr
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/Biomedres01 Follow on Blogger : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/ Like Our Pins On : https://www.pinterest.com/biomedres/
#Open access clinical and medical journal#Journals on Medical Informatics#Journals on Cancer Medicine#Biomedical Science and Research Journal#Biomedical Open Access Journals
0 notes
Text
Inheritance? Taken Care Of



PAIRING: Ada Wong x fem reader
WARNINGS: RE4r Ada, post-Spain, parentified daughter r, researcher r, morally gray r, mommy issues, psychological drama, oldest daughter core r and because this piece speaks to me since I'm the eldest daughter of the Asian household–this is self-indulgent oops, emotional neglect, workaholic, unhealthy coping, power play, unethical sciences oops, soft dom Ada, emotional manipulation, possessive Ada, unprotected sex, soft to rough sex, raw sex, biting, marking, marathon sex, multiple orgasms, overstimulation and that's about it, I think.
SYNOPSIS: Your mother shaped you into the perfect scientist–brilliant, disciplined, and drowning in her legacy. Even in death, her voice haunts you. Then came Ada Wong. A deal. A distraction. A mistake. Now, she watches you unravel, unwilling to let you go. After all, everything must be taken care of.
MEN, MINORS DNI


"Everything must be taken care of, before you have any respite."
Heavy are the words of your mother–a renowned biomedical scientist in her time before she met her unfortunate end in Raccoon City.
Your mother took you to work with her at a young age, showing you the ins and outs of the lab, her research, her progress, and her data the moment you were finally capable of comprehension. She made you take STEM as a pre-med course, specifically biochemical engineering. With her name known across the world, you were given a full ride to a scholarship at the most prestigious universities in the city.
It didn't take long for your peers and mentors to realize you have the same talent and intelligence as your mother.
It felt empowering, of course.
You were saving lives, just like your mother, and the talent too!
Indeed, saving lives at the expense of ruining your own.
What a passionate way to die.
The world suddenly fell on your shoulders when the news of your mother not making it during the infamous Raccoon City incident made it to you–just days after you finished your internship with one of her trusted colleagues as your mentor–and her attorney informed you that she had left all of her assets in your care.
That includes her unfinished research manuscript, her lab notes, medical journals, and unorganized data.
Oh, what do you do?
Your knees wobbled as you set foot into her office, where most of her things were moved with the help of the family attorney and her trusted friends. Your thoughts raced, causing your forehead to heat up as you force yourself to go through her things just to know where to start–how to start.
Your mother was overly critical of you–she had a reputation to keep. Low grades and a bad track record were a sign of failure in her eyes, and in return, she'd lecture and vent to you about her frustrations in the lab.
Oh, you're having a difficult time at a single subject? What more if you're finally in my shoes, hm?
Tired? Ridiculous! Everything must be accounted for–must be taken care of, even if it meant dragging your body to work.
Even if it meant dragging your body to work.
Her reminders loom over you like a suffocating ghost. Before you can even grieve her passing–you threw yourself to work, just like your mother did; refining vaccines, studying new virus samples (those that your hired men can acquire), and testing for results.
But instead of the empowerment that surged in you before–it feels empty. The achievement that you longed for felt nothing like a chore–and your mother's praises are faint–mixing with the practiced awe of your investors and fellow scientists.
Most of your work proved effective against the virus—so much so that it became highly sought after by the government and private companies alike.
And a few questionable individuals too.
That includes a mercenary who disguised herself as one of the interns in your lab. You caught her scanning a copy of your research for the cure and possible enhancement of the G-virus.
You put her in for questioning–and instead of throwing her to the authorities, you made a transactional relationship with her; you'd pay her to take samples of the virus from her different missions and make a cure, in return, she'd get double the money from different employers.
At first, it was simple. Cold. Uncomplicated.
Ada delivered the virus samples, you worked on the cure, and both of you pretended it was just another business arrangement.
It worked—until it didn’t.
Somewhere along the line, the conversations became longer. The silences became heavier. She started sticking around after a job was done, lingering in the dim glow of your lab, watching you work like she had something else to say but never did.
You ignored it.
She never pried, never asked why you threw yourself into your work the way you did. But the way she watched you—like she saw straight through the walls you built—was unsettling.
You should have known better.
Because when the time came—when she had to choose between you and the people who paid her—she chose you.
That was the first time you realized that, despite everything, you weren’t the only one losing themselves in this arrangement.
And that changed everything.

A small smile graces your lips as a message from Ada glares from your screen.
I'm on my way back with the Amber.
Excellent.
"I'm sure Wesker was less than pleased when you change coarse with the Amber." You mused, days after Ada came back with the said item. The older girl's lips morph to a faint smile as she stands next to you, her arms crossed against her firm chest.
"Wesker has a lot of resources," She turns her head in your direction and tilts her head to the side, "I'm sure he can get new samples elsewhere."
You hum as you examine the stone, "Exquisite," You tear your eyes from the Amber and look at Ada. "Thank you."
"My pleasure, doll." The short-haired woman smirks, "I'll leave you to your work–I know you hate being delayed."
"You know me too well," Your tone cool as Ada leaves the room. On cue, your lips flatten into a line as the mirth swims away from your eyes, becoming dull–empty.
Wonderful. Another chore.
In you're need to start planning your next steps, you fail to notice Ada–who is standing at the entrance of your study–eyes carefully studying your change of expression before walking down the halls of the facility.
Without wasting time–you and your team of proficient biomedical scientist began brainstorming the stone–conducting tests among tests and recording your findings without fail–the Amber held so much potential: a superior form of the Plaga. It didn't take a while for it to become the center of your focus, eating and sleeping became an option–you have so much to work with.
Ada has been observing you, the way your food comes back untouched, your sleep patterns–heck, she even woke up with you not beside her.
And if Ada didn't know any better–have you gotten thinner?
Her brows pinch together–and just as it quickly came, it disappeared.
You tell your team to rest–but you can't apply the same to yourself.
Everything must be taken care of, before you have any respite.
With heavy eyes and a blank face, you type away new data recorded from today's findings. Your wrist feels numb, and your body weighed like lead as your eyes shift from one screen to the next.
Then a familiar, feminine, velvety voice fills your cold, sterile lab.
"It's 4:37 AM,"
Automatically, your brows arch and you swivel your chair to the owner of the voice. There stood Ada, wearing a white-button up shirt and beige tapered trousers.
"And?" You mused.
"You're supposed to be sleeping next to me."
Your eyes scan her outfit, "What an odd set of pajamas." You comment with a small smile. A hum reverberates form Ada's chest, her eyes smoothly move to your desk.
"And I see that you didn't touch your food. Again." Her eyes narrow as she takes slow, measured steps towards you. Pink blossoms in your cheeks–nothing extravagant—just a simple meal. You don’t need to ask who left it.
"You're making a habit of watching me, Ada." You mutter, looking away from the older woman. She smirks, using one hand to grasp your chin, coaxing you to look at her.
"Hard not to when you're wasting away."
"I have work..." You trailed off as her expression sharpens–stern.
"And you'll be no use to anyone if you collapse." She lets go of your jaw and takes the fork, stabbing the meat with it before handing it to you. "Eat, doll."
You blink at her, "But–"
She raises a brow.
The air between you hums with tension, silent yet deafening. Ada doesn't waver, her hand steady as she holds out the fork. You recognize the challenge in her gaze—one she doesn’t need to voice. You could ignore her. Dismiss her with a sharp remark and go back to your research. That’s what you would have done before.
But the weight of her stare is different this time.
Reluctantly, you take the fork from her fingers, avoiding her gaze as you take one bite. Then another. The taste is nothing special, but the way Ada leans against the desk, arms crossed, watching you with quiet satisfaction–it was almost irritating.
"Happy?"
The former smirks, but there's a mellow gleam in her eyes. "Ecstatic."
She doesn’t push you to eat more. Doesn’t hover or pry. Just lets you go at your own pace before pushing off the desk.
"Sleep after you're done eating."
A scoff leaves your lips. "I have work to do."
Ada tilts her head, studying you with something unreadable. "Right. Of course you do."
She turns, walking toward the exit—but pauses at the doorway. Over her shoulder, she adds, "Don’t make me force you."
And then she’s gone.

Days pass. Weeks.
Ada watches. She doesn’t hover, doesn’t nag—but she sees everything.
The untouched meals. The way your hands shake slightly when you reach for a pen. The increasing number of empty coffee cups cluttering your desk. The dark circles under your eyes, like shadows carved into your skin.
You're burning out, and you don’t even notice.
Ada does.
She notices when your fingers tremble as you type. When you blink a second too long, as if fighting the urge to collapse on the spot. She notices when you stand too fast, your vision tilting, and you grip the edge of the desk just to steady yourself.
And then, one night, it happens.
You don’t remember falling—only the sharp sensation of your knees hitting the floor, the rush of dizziness swallowing you whole. A sound escapes your lips, something between a gasp and a curse, but before your body can fully crumple—
Ada is there.
Lithe arms catch you before you hit the cold tile. A firm grip steadies you and through the haze clouding your vision, you hear her voice, lower than usual.
"That's enough."
Your head is spinning. You don’t fight when Ada pulls you up, guiding you towards the couch in the corner of your study. You’re not sure when she sat down, only that you’re suddenly leaning against her, the warmth of her presence pressing into your side.
You hate how comforting it feels.
"You’re overworking yourself," Ada states, voice unreadable.
You huff, though it lacks bite. "That’s nothing new."
Ada is silent for a moment, then:
"This isn’t just about the research, is it?"
Your breath catches.
She’s too close. Not physically—though, yes, she is—but she’s too close to seeing through you. Through the carefully constructed walls, through the weight of your mother’s expectations still coiled around your throat like a noose.
Ada exhales, her voice softer than before. "You can’t outrun her."
Your fingers clench into the fabric of your sleeves. You don't answer.
Ada doesn't push.
She simply sits there, allowing the silence to settle—offering her presence without demand. Without pressure.
Ada doesn't move for a while. Neither do you.
The silence isn’t uncomfortable, but it’s heavy. You can feel her presence—steady, unmoving—like a quiet force refusing to let you spiral any further.
You close your eyes for just a second. Just a second.
And then—
You wake up.
The dim glow of your study lamps is gone, replaced by the soft flicker of the emergency lights. The air is still. Quiet. The weight against your back is warm, solid—Ada.
You realize with slow clarity that you’ve fallen asleep against her.
Your mind is sluggish, torn between the rare, unfamiliar comfort of rest and the immediate need to get back to work. You shift slightly, only for Ada’s arm—wrapped loosely around your waist—to tighten.
"Don’t even think about it."
Her voice is smooth, carrying no room for argument. You tilt your head just enough to catch a glimpse of her—eyes closed, looking impossibly at ease, as if she had all the time in the world.
"How long was I out?" you murmur.
Ada hums, opening one eye. "Longer than you usually allow yourself. Not long enough."
A flicker of annoyance sparks in your chest. "I don’t have time for—"
Ada clicks her tongue, and suddenly, she’s shifting—her arm unwinding from you as she gracefully rises to her feet. The warmth you didn’t realize you were clinging to vanishes.
Fine. If she’s going to leave, that’s—
Your thoughts halt when Ada leans down, placing her hands on the couch—caging you in.
"You’re coming with me," she says, voice smooth as silk but carrying an edge that dares you to refuse.
Your brows furrow. "Excuse me?"
Ada tilts her head, smirking slightly. "You heard me."
She grabs your wrist—not tightly, but firmly—and pulls you up before you can protest. Your legs, still weak from exhaustion, stumble slightly, and Ada steadies you without effort.
"Ada—"
"You need air," she interrupts, her tone final. "A break. And before you start whining about time, I already handled the lab reports for the night. Your little research team will survive without you for a few hours."
You blink. "You—what?"
Ada smirks, guiding you toward the door. "I have my ways."
You stare at her, skepticism laced with something else—something almost like reluctant gratitude.
Ada catches it. Of course she does.
She simply tilts her head toward the exit. "Let’s go, doll."
For once, you don’t fight her.
The low hum of the car engine is the only sound between you. The city lights flicker past, painting streaks of gold and red across the tinted windows.
Ada drives without hurry, one hand on the wheel, the other resting lazily against the gear shift. She hasn’t said much since she pulled you out of the lab, but she doesn’t need to.
You exhale, leaning against the cool glass. "Where are we going?"
Ada glances at you from the corner of her eye, smirking. "Somewhere you can’t escape from."
Your lips twitch. "That so?"
"Mm." She shifts gears smoothly. "You need rest. I’m making sure you get it."
You huff, but there’s no real bite behind it. Maybe a part of you is too tired to fight.
Or maybe a part of you wants to be taken care of for once.

The night air is cool against your skin, but the warmth pressed against your back is unmistakable. Ada.
You don’t remember how she convinced you to stop working for the night, or how you ended up lying in bed with her, tangled in soft sheets. All you know is that her arms are around you, one resting against your stomach, the other tucked under the pillow you share.
Her breath fans against your neck—slow, steady. Unlike you, she seems completely at ease.
You shift slightly, and Ada’s hold tightens just enough to keep you from slipping away.
"You’re still tense," she murmurs, voice low, husky from the quiet.
You scoff. "Habit."
"Bad one," Ada counters, her lips barely brushing your shoulder. "I can think of better ways to relieve stress."
Her fingers trail down your arm, featherlight, before slipping beneath the hem of your shirt. Your breath catches as her fingertips graze your skin, drawing slow, deliberate patterns along your waist.
"Ada—"
"Hm?" Her tone is innocent, but the way her nails drag lightly against your skin is anything but.
You turn your head slightly, just enough to catch the mischievous glint in her eyes.
"You planned this," you accuse.
Ada smirks. "Would you have stopped me if I did?"
You hate how easily she gets under your skin—how the warmth of her touch makes your body betray you.
The way her lips graze the curve of your jaw—soft, teasing—before she bites down just enough to make you shiver.
You don’t answer.
You don’t need to.
Because when Ada shifts, rolling you onto your back, and pins you beneath her with that knowing smirk—you’re already hers for the night.
Your breath hitches as Ada's hips press flush against you, clothes strewn across the floor . Her fingers dance along your torso, grazing your ribs, the. lower; teasing.
"You're so tense," She murmurs, her lips brushing against the shell of your ear. "Let me fix that."
She shifts, her grip firm as she tilts your hips just enough for her to roll against you, slow, deliberate. Heat coils low in your stomach, and you barely suppress a gasp as her cock rubs snuggly against your walls. Your lover chuckles, voice rich in amusement. "See? You don't have to do anything, doll. Just let me do the work."
Your body betrays you, instinctively meeting her hips, craving more.
"That's my girl," She whispers, her voice dark, dripping with satisfaction. Her hands tightens on your hips, and you fele her smirk against your skin.
"Let's see just how much you can take."
She guides your hips, both of you gasping as her pace is agonizingly slow. The tension pulls taut. Deliberate, controlled, taking her time as she fucks you, her movements slow and deep.
Each movement makes pleasure coil tighter and tighter in your core, and Ada knows it. She watches you unravel beneath her, eyes locked on your every reaction. "You love this, don't you?" She taunts, rolling her hips just right, pulling a broken moan from your lips. "Being under me like this, being taken."
Your body trembles, eyes rolling back as your hands grip at her back, nails scratching along her skin as the pleasure builds to unbearable levels.
"Baby–please," You whimper, desperate, your body arching into hers.
The older girl chuckles, her hands sliding up your thighs, gripping your waist as she picks up the pace, thrusting into you with more force, driving deeper. The cacophony of your moans and her groans mixes with the creaks and whines of the bed.
"Say it," She demands, lips brushing against your ear. "Tell me you're mine."
"Yours," You gasp, barely able to breathe. "I'm yours, Ada."
She groans, her rhythm turning rougher, faster, chasing her own release as she takes you apart, the veins on the ridges of her cock rubbing deliciously against your walls while the tip kisses your cervix, eliciting a yelp from you. Pleasure crashes over you, your entire body tensing, and Ada drives into you, pushing you past your limit–until you're crying out her name, clinging to her as waves of euphoria pulse through you.
Ada follows soon after, burying herself deep, her own release hitting as she moans against your throat, her fingers digging into your hips, holding you still as ropes of cum floods your walls, some even oozing out of your folds and down to the sheets. She watches the way you tremble, her smirk returns as she leans down, pressing a lingering kiss against your lips.
"Good girl,"
And just like that, you knew–she isn't done with you yet.
Your body trembles, broken moans and whimpers leave your lips, legs weak and spread open, slick with heat and sweat. She's still inside you, half-hard, twitching against your walls. Your cry out, nails dragging down her back, feeling the way she stretches you all over again, this time with less restraint.
"That's it," She moans lowly, thrusting her hips until there's nowhere left to go. "Take all of me, pretty girl. Just like before."
The ecstasy is almost too much–your pussy still sensitive from the first round but Ada doesn't slow down.
Plap, plap, plap, plap!
The bed creaks, the sound of skin against skin filling the room, and all you can do is cling to her, let her take everything she wants from you. "Mine," She breathes into your ear, her voice dripping with possession.
Your moans swallowed by her kisses as she pounds into you, pushing you higher and higher towards your breaking point. "You'll take everything I give you." Ada growls, gripping your hips, holding you still as she pistons her hips even deeper.
Then, you feel it–the heat, the pressure, the way she stiffens inside you.
Your lover groans, burying herself to the hilt, filling you with viscous ropes of semen, her balls tighten as it slaps against your ass. She stays like that, breathing heavily, enjoying the way your body shudders beneath her, taking everything she has to give.
"Y-you didn't even pull out." You blink at her, dazed, breath ragged.
A cold smile graces Ada's lips. Unapologetic.
"Of course not," She murmurs, dragging her fingers down your stomach, pressing lightly over your womb. "Why would I? You look good like this." She leans down, nipping at your bottom lip, her hands still possessively tracing your lips, before she moves her hips again, rubbing against your puffy folds.
"A-Ada–wait, I-I can't–" You gasp, trying to pry her hips away, but her hands grip your thighs, keeping them spread.
"Oh, baby–I'm not yet down with you."
Her hips press forward, the tip kissing the spongey spot of your walls, making you see stars–your back arches.
"You can take more," She murmurs, kissing down your neck, her hands roaming around your body possessively. "You will take more."
Before you can protest, her knees plant firmly against the sheets as she plows into you, deeper, harder.
Stretching, filling.
Broken moans leave from your lips as your back arches–another choked cry escaping your lips. She's bigger, harder this time–more desperate, more demanding as the headboard keeps slamming against the wall.
"You feel that?" Ada groans, jutting her hips, stealing another moan from you.
"Still so tight–still squeezing me like you don't want to leave."
You whimper, your body is too sensitive, too overwhelmed–Ada doesn't stop. She sets a relentless pace, her thrust deep, hard and void of mercy.
"Look at you, so fucked-out already. But you'll take everything I give you, won't you?" She breathes, watching your eyes lose and your lips open.
So helpless.
"You're mine, inside and out."
Your moans turn into whimpers, gasps, pleas—but it only fuels her more. Ada is insatiable, unrelenting, making you take her over and over again, until you’re nothing but a shaking, overstimulated mess beneath her.
She guides your legs around her hips, pulling out.
A whine leaves your lips before it morphs into a filthy moan with another sharp thrust into your cunt, another nasty squelch echoing into the air–sex and perfume wafts in the room. She slumps against you, pressing her soft chest against your sensitive ones, moving her lips purposefully to the crown of your ear and tugging a bit of your skin in between her teeth.
Your body was hot against hers. Your walls throb deliciously throb around her. Ada's eyes flutter close before she sinks her teeth into your skin.
"A-Ada–fuck!" You sob as she angles precisely into you.
"Nghh–I know, doll." Ada throws her head back, relishing the obscene sound of flesh against flesh.
Plap, plap, plap!
Oh, it's a sound you and Ada never get tired of.
You've already lost your mind beneath her–fucking you to a state of overstimulation, being bred full of her semen.
"You look so beautiful," Ada huffs as she jogs her hips, her pace is shallow to the point that she isn't pulling out anymore.
She grabs the headboard, fucking you into the sheets. The older woman grits her teeth, your mixed fluids being fucked out of your beaten walls, making a mess beneath your legs. Her balls slap against the curve of your ass, heavy with potent seed.
"Mghmm, cumming." Your lover whines, "Cum on my cock, doll–nghh, I want to feel you."
Your eyes roll back again as a strong gush of fluid exits your pussy, coating Ada's cock and her balls. Ada groans, nuzzling her cock into you as she fucks you into overstimulation before she finally stills her hips, shooting ribbons of her seed in you, painting your walls warm and white.
Your mixed essence oozes out, your mind filled with cotton and your body is heavy while Ada looks energized, watching your blissed out state.
"Once I know you're pregnant–I'm putting you on maternity leave." She murmurs.
A promise.
A threat.
And for once, you didn't fight against it.
#ada wong#ada wong x reader#resident evil#resident evil x reader#i'm just a girl#resident evil x you#oneshot#wlw post#wuh luh wuh#sapphic#wlw#fem reader#female reader#yuri
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
New research indicates that people who contracted COVID-19 early in the pandemic faced a significantly elevated risk of heart attack, stroke, and death for up to three years post-infection.
Those with severe cases saw nearly quadruple the risk, especially in individuals with A, B, or AB blood types, while blood type O was associated with lower risk. This finding highlights long-term cardiovascular threats for COVID-19 patients and suggests that severe cases may need to be considered as a new cardiovascular risk factor. However, further studies on more diverse populations and vaccinated individuals are needed to validate these results.
Long-Term Cardiovascular Risks Linked to COVID-19 Infection A recent study supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that COVID-19 infection significantly increased the risk of heart attack, stroke, and death for up to three years in unvaccinated people who contracted the virus early in the pandemic. This risk was observed in individuals with and without pre-existing heart conditions and confirms earlier research linking COVID-19 infection to a higher chance of cardiovascular events. However, this study is the first to indicate that the heightened risk may last as long as three years, especially for those infected during the first wave of the pandemic.
The study, published in the journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, revealed that individuals who had COVID-19 early in the pandemic were twice as likely to experience cardiovascular events compared to those with no history of infection. For those with severe cases, the risk was nearly quadrupled.
“This study sheds new light on the potential long-term cardiovascular effects of COVID-19, a still-looming public health threat,” said David Goff, M.D., Ph.D., director for the Division of Cardiovascular Sciences at NIH’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), which largely funded the study. “These results, especially if confirmed by longer term follow-up, support efforts to identify effective heart disease prevention strategies for patients who’ve had severe COVID-19. But more studies are needed to demonstrate effectiveness.”
Genetic Factors and Blood Type’s Role in COVID-19 Complications The study is also the first to show that an increased risk of heart attack and stroke in patients with severe COVID-19 may have a genetic component involving blood type. Researchers found that hospitalization for COVID-19 more than doubled the risk of heart attack or stroke among patients with A, B, or AB blood types, but not in patients with O types, which seemed to be associated with a lower risk of severe COVID-19.
Scientists studied data from 10,000 people enrolled in the UK Biobank, a large biomedical database of European patients. Patients were ages 40 to 69 at the time of enrollment and included 8,000 who had tested positive for the COVID-19 virus and 2,000 who were hospitalized with severe COVID-19 between Feb. 1, 2020, and Dec. 31, 2020. None of the patients had been vaccinated, as vaccines were not available during that period.
The researchers compared the two COVID-19 subgroups to a group of nearly 218,000 people who did not have the condition. They then tracked the patients from the time of their COVID-19 diagnosis until the development of either heart attack, stroke, or death, up to nearly three years.
Higher Cardiovascular Risk in Patients With Severe Cases Accounting for patients who had pre-existing heart disease – about 11% in both groups – the researchers found that the risk of heart attack, stroke, and death was twice as high among all the COVID-19 patients and four times as high among those who had severe cases that required hospitalization, compared to those who had never been infected. The data further show that, within each of the three follow-up years, the risk of having a major cardiovascular event was still significantly elevated compared to the controls – in some cases, the researchers said, almost as high or even higher than having a known cardiovascular risk factor, such as Type 2 diabetes.
“Given that more than 1 billion people worldwide have already experienced COVID-19 infection, the implications for global heart health are significant,” said study leader Hooman Allayee, Ph.D., a professor of population and public health sciences at the University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine in Los Angeles. “The question now is whether or not severe COVID-19 should be considered another risk factor for cardiovascular disease, much like type 2 diabetes or peripheral artery disease, where treatment focused on cardiovascular disease prevention may be valuable.”
Allayee notes that the findings apply mainly to people who were infected early in the pandemic. It is unclear whether the risk of cardiovascular disease is persistent or may be persistent for people who have had severe COVID-19 more recently (from 2021 to the present).
Need for Broader Studies and Vaccine Impact on Risks Scientists state that the study was limited due to the inclusion of patients from only the UK Biobank, a group that is mostly white. Whether the results will differ in a population with more racial and ethnic diversity is unclear and awaits further study. As the study participants were unvaccinated, future studies will be needed to determine whether vaccines influence cardiovascular risk. Studies on the connection between blood type and COVID-19 infection are also needed as the mechanism for the gene-virus interaction remains unclear.
Study link: www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321001
#mask up#covid#pandemic#public health#wear a mask#covid 19#wear a respirator#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#heart health#covidー19#covid conscious#covid is airborne#covid isn't over#covid pandemic#covid19
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
A group of medical researchers has issued a warning after linking cases of unprovoked venous thrombosis in healthy people to Covid mRNA “vaccines.”
Researchers at Qatar University‘s Hamad Medical Corporation and Weill Cornell Medicine launched an investigation after individuals without conventional risk factors began suffering from deadly thrombotic events.
The researchers sought to determine whether Covid “vaccines” were linked to the rise which started after the injections were rolled out for public use.
Their study takes a retrospective approach to evaluating venous thromboembolism (VTE).
VTE is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein and it includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in deep veins, usually in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis.
If there is a large intravenous central line in the vein, DVTs can also occur in the arms.
Pulmonary embolism occurs when a clot breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lungs.
The results of the study were published in the Ibnosina Journal of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers have found a correlation between flavonoids, a compound found in fruits and vegetables, and a reduction in the symptoms of endometriosis. In the study, published in the journal Endocrinology, the researchers outline how flavonoids may be able to help suppress the symptoms of inflammatory diseases like endometriosis. In endometriosis, cells similar to those in the lining of the uterus begin growing in other places in the body, causing inflammation. The painful condition affects millions of women, and there is no cure. Flavonoids have been associated with anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral medical benefits, but the details of how they work have remained a mystery. “Scientists have known for a while that people who eat more fruits and vegetables tend to live longer and have lower risk for many types of diseases, including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases,” says Stephen Safe, a professor in the veterinary physiology and pharmacology department at the School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at Texas A&M University.
Continue Reading.
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
given that he grew up a normal life…
also these jobs are general examples, i dont know entirely enough if they are accurate
#dean winchester#supernatural#dean#spn#winchester#sam winchester#dean headcanons#dean fanfiction#fanfiction#supernatural x reader#college#stanford era#dean au#spn au#dean college#au#dean headcanon
34 notes
·
View notes
Text

Scientists successfully increase measurement rate of Raman spectroscopy by 100-fold
Researchers Takuma Nakamura, Kazuki Hashimoto, and Takuro Ideguchi of the Institute for Photon Science and Technology at the University of Tokyo have increased by 100-fold the measurement rate of Raman spectroscopy, a common technique for measuring the "vibrational fingerprint" of molecules in order to identify them. As the measurement rate has been a major limiting factor, this improvement contributes to advancements in many fields that rely on identifying molecules and cells, such as biomedical diagnostics and material analytics. The findings were published in the journal Ultrafast Science.
Read more.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
New Depths
A new method which deploys confocal microscopy equipped with a Mesolens for imaging molecular and cellular detail in intact tissue samples in 3D – proof of concept demonstrates expression of a protein called GLUT4 in ultrathick sections of intact mouse heart
Read the published research article here
Video from work by Angéline Geiser and colleagues
Strathclyde Institute of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK
Video originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in Journal of Cell Science, August 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#biology#heart#cardiac#confocal microscope#immunofluorescence#microscopy#tissue sections
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researching stuff.
Adding links here to methods for finding out things, because on the modern internet, actually finding out accurate information is now uniformly obfuscated by the relentless enshitification of search functions, proliferation of search engine optimised content mills, nation state level intentional misinformation and propaganda programs, and of course, these days, all the crap sources above are endlessly enriched by the output of generic Large Language Model plagiarism statistical bullshit engines, both image and text (And video and Bot and so forth).
Finding academic and peer reviewed Journal Articles - they haven't quite fucked google scholar yet, so it's better than the enshittified google or bing or <insert enshittified search bar embed here> whatever.
So I generally hit up Google Scholar for whatever subject, author name, paper title or similar that I've gleaned from whatever article or mention or wikpedia page sparked my interest. Often that gets me what I want, as there's often a link to a pdf of what I need within those search results. Yay.
If that doesn't work, then I start escalating, usually via the methodology here described at Logic of Science's blog:
They wrote it down so I don't have to. Excellent. Although some of the links in there have degraded. So the main ones I'll put here:
And then there's the pirate nuclear option, Sci Hub. Because it makes the big publishers and corporates really angry, don't use sci hub from a work or academic 'net access environment. Also it necessarily moves around a lot, so I generally search up where is sci hub now, to avoid going to a link that's expired or may now be a honeypot/trap:
Also, look out for content mill generated fake journals. I usually check here:
The other thing that's getting harder is finding out whether an image is misattributed or just plain fake. So right click and save the image, and then go to images dot google dot com, which is nowhere near as good as it used to be, but still not entirely enshittified, and click on the wee camera icon to the right and upload the image, and look through the results. What you find is _All_ the places that have posted that image, page after page of them. Scroll through - click on the ones that seem to be the oldest, check who's posting them. What you often find with viral outrage images is that they are _not_ what you think, especially if the image is a bit old, a bit bitrotted, or there's something else wrong - the clothing isn't right for the country/culture/time being outraged about, or something like that. Sometimes you find out that it's true, but most of the time you find out that it's wrong, that someone has just done a quick search for an image that roughly matches the outrage or the politics they want to push, added some outragey comments, and shared it, and enjoyed their flamey fire. I've been doing this for decades, ever since I started using a browser capable of image searching, mainly because I was outraged at people posting fake geology memes. But it works just as well on finding anything else.
And of course, if it's to a website, see if the wayback machine still has it cached:
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
Tumblr keeps crashing each time I send this so I gotta be quick: do have any tips on how to study biology (college is not an option atm)
Oh boy! I will do my best!
I've listed the basic irl resources for biological information first, followed by some online resources.
I've got a strong Animalia bias, so apologies that I don't have any botany-specific sites for you. 😔
I'm sure there's some stuff I'm forgetting. I'll add on to this if I think of anything!
If there's anything specific you need help finding a reliable biological resource for, let me know and I will try my best to help find you something!
•••
Finding primary sources (stuff written by the scientists who did the research [i.e. a journal article]) is always very good, but reliable secondary resources (someone else summarizing other people's research [i.e. Wikipedia page, book]) can be very valuable as well.
•••
Meatspace Resources
-
I would highly recommend checking to see if there is a Nature Park in your area! Nature parks often have volunteer programs and/or free educational opportunities. In my experience, naturalists are always very excited to meet new people interested in learning about local ecology!
-
There's also Zoos and Aquariums of course, although I know they cost money and are typically geared more towards kids. I'm lucky to live near some nice ones. Maybe check if there are any special programs happening at Zoos/Aquariums in your area (by checking their website[s]), where you might learn more than you would on a normal day trip.
-
Plus natural history museums, which usually have rotating exhibits so that you can keep learning new things when you come back! They also have more of an all-ages vibe than Zoos in my experience. Once again dependant on if there's one near you, and not free.
-
Last but not least: the local library, although obviously not every published book is a flawless resource. Still, might be interesting to poke around! There's usually some sort of digital search catalogue to make finding things easier. Libraries are fun :)
•••
Online Resources
-
Jstor is GREAT. Not all jstor articles are open access/free, but some are! And you can set a search filter to show you only things you can access.
One good way to find out what experts have written for other experts about biology: search a species name or biological concept or type of experimental study, etc. etc., in jstor's journal articles. I've linked a search for journal articles "I can access" containing the word "biology" as an example.
The website layout can feel a little obtuse at first but I think if you fiddle around with it a bit, it's not too bad to figure out? Feel free to kick my ass if I'm wrong djgjkeg
-
Wikipedia is actually a very good place to introduce yourself to a lot of biological concepts. I would recommend checking out some of the sources yourself if you can-- usually at least some of them are free, and that can introduce you to new free resources for learning more (today I discovered bugguide.net!). Often they will link you to jstor.
But biology-focused wiki pages have a pretty good track record for Correct Information in my experience. The only issue I've run into is there being too little information sometimes.
-
Pubmed is a really good resource to read biomedical scientific papers for free if that interests you at all! Reading scientific papers is a really important skill and I think you can pick up a lot just by diving in and googling words you don't know.
A well-designed experiment is replicable (that is, you can understand from the paper how they set things up to the point that you could do it yourself, given the resources). It's also important to pay attention to sample size. The more times you replicate any process in an experiment, the more likely you will be able to identify what the most common result really is, and why.
-
Fishbase is a website I was introduced to in my icthyology class to find info about different fish species :) It kind of just dumps all the info on you in a big text wall, but many pages include great details about life cycle and diet that might go unmentioned on wiki pages.
-
I've never used bugguide.net before today, but so far it seems solid and like it has a lot of good info. I assume it is similar to fishbase but for bugs
-
EDIT: FREE ONLINE TEXTBOOKS I FORGOT ABOUT!!!
I used both of these for university classes at some point. I didn't use them much, so there may be issues I don't know about.
In my experience though they were solid resources, if a little confusingly worded at times. Bouncing between the textbooks and wikipedia tended to help me.
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The research, completed by scientists from the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences and Uppsala University in Sweden and published in the journal Nature Communications, determined that the number of copies of a small DNA sequence within the gray coat gene carried by each horse determines if they are "slow graying" or "fast graying." Those horses in the fast-graying category—the ones that eventually turn white to the eye—have a gene variant with three copies while the slow-graying horses—which remain a dappled gray color—have two copies."
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
An Early Excessive Release of Cytokines by Ionizing Radiation Exposure in Macrophages Accentuates Inflammatory Disorders
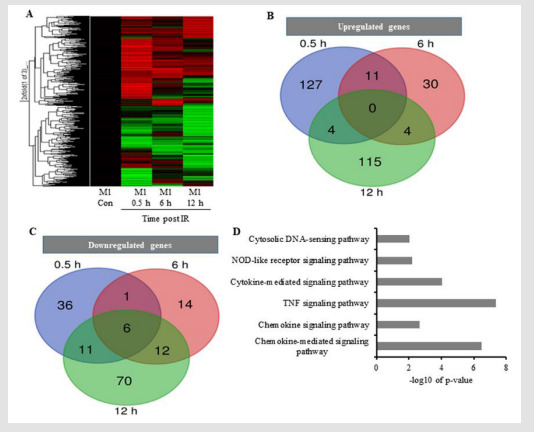
An Early Excessive Release of Cytokines by Ionizing Radiation Exposure in Macrophages Accentuates Inflammatory Disorders in Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research
Excessive release of cytokines after radiation exposure reportedly induces inflammatory disorders. To prevent the occurrence of cytokine-mediated disorders, several strategies are employed, including preventing cytokine overproduction in irradiated tissue; however, this strategy is less effective in some tissues, such as the lung, and ineffective at preventing exacerbation of diseases and other disorders. Therefore, to elucidate the mechanisms associated with cytokine overproduction following radiation exposure, we investigated macrophage-specific immune responses resulting in cytokine production by initially assessing their levels in irradiated M1-primed RAW264.7 cells via microarray and computational analyses. We found that differentially expressed genes were mainly related to inflammatory responses and cytokine activity, and that tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin (Il)-1, and Il-7 overexpressed at 0.5-h after radiation exposure, with these early cytokines important to downstream activation of other cytokines and inducers of various disorders when produced in excess. Moreover, we found correlation between induced expression of these cytokines and increased lipocalin-2 expression, which signified the initiation of inflammatory disorders. Our results indicated that the excessive release of cytokines following radiation exposure promoted inflammatory responses associated with subsequent increased cytokine expression.
For more articles in Journals on Biomedical Sciences click here bjstr
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/Biomedres01 Follow on Blogger : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/ Like Our Pins On : https://www.pinterest.com/biomedres/
#Biomedical Journal Articles#Scientific Research Articles on Biomedical#Journal of Scientific and Technical Research#Journals on Biomedical Engineering#journal of biomedical sciences research review
0 notes
Text
WEAR A MASK BECAUSE YOU DON'T NEED TO BE AN INCUBATOR
At least 58 people in the U.S. have been infected by the H5N1 bird flu virus this year, according to federal statistics. All but two of them had been around cows or chickens, two species in which H5N1 is circulating widely. That’s reassuring to scientists because it suggests the virus is spreading primarily through close contact with infected animals, and not from person to person.
Less comforting are the results of a study published Dec. 5 in the journal Science: the H5N1 strain spreading among U.S. cows is only one specific mutation away from more easily binding to human cells, “a prerequisite for transmission among humans,” says study co-author James Paulson, a professor in the department of molecular medicine at Scripps Research in California.
In its current form, the H5N1 virus is better at infecting certain animal species than humans. It has sickened millions of birds and cows from more than 700 U.S. dairy herds, but a relatively small number of people.
Most of those human cases have been among farmworkers. That suggests that—even though the bird flu virus isn’t very good at infecting humans—it sometimes finds a way when people are exposed to high enough concentrations of it, such as through close contact with sick animals, explains Troy Sutton, an assistant professor of veterinary and biomedical sciences at Penn State University, who wasn’t involved in the new study. Because the virus isn’t good at growing in the human nose and throat, however, people who get sick don’t seem able to easily infect others by coughing or sneezing, as happens with the regular seasonal flu, Sutton says.
If the bird flu changes enough to effectively infect, grow in, and jump between people,“that’s how a pandemic starts,” Paulson says.
His team focused on the first step in that process: how the virus would need to change to easily bind to human cells. In the lab, they studied a synthetic form of a gene from the viral strain that is currently circulating among cows. They made targeted mutations to see how the shifts altered its ability to attach to human cells. “The surprising finding,” Paulson says, was that one specific mutation seemed to be enough. Previous research on H5N1, including Paulson’s, had suggested that more changes would be required.
“The emergence of a bovine H5N1 virus capable of recognizing human receptors may be closer than previously thought,” Yoshihiro Kawaoka, a professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison who studies bird flu but was not involved in the new study, wrote in an email to TIME.
Read More: Did the Pandemic Break Our Brains?
That’s a “striking” finding, Sutton agrees, and a good motivation to prevent further human cases to the extent possible. Already, federal health officials recommend that high-risk people, such as farmworkers, wear personal protective equipment around animals that may be sick and take flu antivirals (which also seem to work against bird flu) if they have a potential exposure.
Still, Paulson emphasizes that his study does not mean a pandemic is imminent. Despite what his team found in the lab, the virus circulating in the real world does not seem to have evolved to easily target humans. Public-health officials maintain that the virus is not spreading from person to person and currently presents a low risk to the general public.
More changes might be necessary for the virus to present a true pandemic threat. The ability to easily bind to human cells—which Paulson’s team tested for—is only the first step toward widespread person-to-person transmission, he says. Further changes might be needed for the virus to become highly contagious in the real world.
Kawaoka agrees. The fact that more than 50 people in the U.S. have gotten sick, but health officials have not seen any evidence of person-to-person spread, suggests that “additional mutations are likely necessary for the virus to achieve efficient human-to-human transmission,” he wrote.
Read More: Is it Time to Worry About Bird Flu?
Health officials are closely monitoring the situation, and some worrying observations have already been documented. Recently, a Canadian teenager who caught bird flu was hospitalized. When scientists analyzed the genetic sequence of the virus taken from the teen, they reportedly found that it had mutated in a way that could make it more transmissible among people, similar to the mutation Paulson’s team identified in their study. (Luckily, though, the teen doesn’t seem to have infected anyone else.)
Kawaoka has also studied a viral strain taken from an infected U.S. farmworker. That strain, which was able to grow in samples of human lung cells, contained a mutation known to promote viral growth among mammals, Kawaoka and his team found. But that mutation is not seen in the viral strains spreading among cows, his team emphasized when the study was published in October.
Although there is no evidence of person-to-person spread yet, Paulson says health authorities should prepare for wider spread of bird flu as a precaution. It’s worth stockpiling bird flu vaccines and making plans for how they would be rolled out if they become necessary, he says.
It’s also important to keep closely monitoring the virus for any signs of change, Sutton says. But “what’s alarming to me is that we often realize we have a pandemic after the pandemic has started,” he says. “If we started to see this mutation, would it already be too late? We don’t know the answer to that.”
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
NIH-funded study focused on original virus strain, unvaccinated participants during pandemic.
Infection from COVID-19 appeared to significantly increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and death for up to three years among unvaccinated people early in the pandemic when the original SARS-CoV-2 virus strain emerged, according to a National Institutes of Health (NIH)-supported study. The findings, among people with or without heart disease, confirm previous research showing an associated higher risk of cardiovascular events after a COVID-19 infection but are the first to suggest the heightened risk might last up to three years following initial infection, at least among people infected in the first wave of the pandemic.
Compared to people with no COVID-19 history, the study found those who developed COVID-19 early in the pandemic had double the risk for cardiovascular events, while those with severe cases had nearly four times the risk. The findings were published in the journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.
“This study sheds new light on the potential long-term cardiovascular effects of COVID-19, a still-looming public health threat,” said David Goff, M.D., Ph.D., director for the Division of Cardiovascular Sciences at NIH’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), which largely funded the study. “These results, especially if confirmed by longer term follow-up, support efforts to identify effective heart disease prevention strategies for patients who’ve had severe COVID-19. But more studies are needed to demonstrate effectiveness.”
The study is also the first to show that increased risk of heart attack and stroke in patients with severe COVID-19 may have a genetic component involving blood type. Researchers found that hospitalization for COVID-19 more than doubled the risk of heart attack or stroke among patients with A, B, or AB blood types, but not in patients with O types, which seemed to be associated with a lower risk of severe COVID-19.
Scientists studied data from 10,000 people enrolled in the UK Biobank, a large biomedical database of European patients. Patients were ages 40 to 69 at the time of enrollment and included 8,000 who had tested positive for the COVID-19 virus and 2,000 who were hospitalized with severe COVID-19 between Feb. 1, 2020, and Dec. 31, 2020. None of the patients had been vaccinated, as vaccines were not available during that period.
The researchers compared the two COVID-19 subgroups to a group of nearly 218,000 people who did not have the condition. They then tracked the patients from the time of their COVID-19 diagnosis until the development of either heart attack, stroke, or death, up to nearly three years.
Accounting for patients who had pre-existing heart disease – about 11% in both groups – the researchers found that the risk of heart attack, stroke, and death was twice as high among all the COVID-19 patients and four times as high among those who had severe cases that required hospitalization, compared to those who had never been infected. The data further show that, within each of the three follow-up years, the risk of having a major cardiovascular event was still significantly elevated compared to the controls – in some cases, the researchers said, almost as high or even higher than having a known cardiovascular risk factor, such as Type 2 diabetes.
“Given that more than 1 billion people worldwide have already experienced COVID-19 infection, the implications for global heart health are significant,” said study leader Hooman Allayee, Ph.D., a professor of population and public health sciences at the University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine in Los Angeles. “The question now is whether or not severe COVID-19 should be considered another risk factor for cardiovascular disease, much like type 2 diabetes or peripheral artery disease, where treatment focused on cardiovascular disease prevention may be valuable.”
Allayee notes that the findings apply mainly to people who were infected early in the pandemic. It is unclear whether the risk of cardiovascular disease is persistent or may be persistent for people who have had severe COVID-19 more recently (from 2021 to the present).
Scientists state that the study was limited due to inclusion of patients from only the UK Biobank, a group that is mostly white. Whether the results will differ in a population with more racial and ethnic diversity is unclear and awaits further study. As the study participants were unvaccinated, future studies will be needed to determine whether vaccines influence cardiovascular risk. Studies on the connection between blood type and COVID-19 infection are also needed as the mechanism for the gene-virus interaction remains unclear.
This study was supported by NIH grants R01HL148110, R01HL168493, U54HL170326, R01DK132735, P01HL147823, R01HL147883, and P30ES007048.
About the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): NHLBI is the global leader in conducting and supporting research in heart, lung, and blood diseases and sleep disorders that advances scientific knowledge, improves public health, and saves lives. For more information, visit www.nhlbi.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
Study Allayee, H, et al. COVID-19 Is a Coronary Artery Disease Risk Equivalent and Exhibits a Genetic Interaction With ABO Blood Type(link is external). [2024] Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321001
#mask up#covid#pandemic#wear a mask#covid 19#coronavirus#public health#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator
30 notes
·
View notes
Text


How can medicinal mushrooms support your mood and emotions?👀
[Hit SAVE so you can get these little miracle workers later!]
🍄Lion’s Mane: In a study of 30 women who were randomly assigned a snack of cookies containing Lion’s Mane or placebo cookies for 4 weeks, the Lion’s Mane group reported a significant reduction in feelings of helplessness, irritability and anxiety (Biomedical Research, 2010).
🍄Maitake: Researchers in 2017 found that Maitake had promising effects on mood and suggested it could be “a safe medical food supplement for the patient with depression” (Pharmaceutical Biology, 2017). This mushroom also acts as an adaptogenic food and can lower the stress hormone cortisol (Northern American Journal of Medical Sciences, 2011).
🍄Poria: Researchers in 2020 discovered that by calming the overreaction of the immune system and regulating our important neurotransmitters, including feel-good hormones serotonin and dopamine, Poria had a positive effect on mood. They also suggested that it could be “a traditional herbal
potential medicine for the treatment of depression.” (Journal of
Enthnopharmacology)
🍄Reishi: This powerful mushroom has been shown to reverse the decline in serotonin in the brain, meaning more of this happy hormone is circulating the brain to keep a positive mindset (Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021). Additionally, Reishi can help avoid low blood sugar, a common trigger for bad moods.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Anna Krylov and Jay Tanzman
Published: Oct 2, 2023
Note: A version of this article will appear as an invited chapter in the forthcoming volume The Free Inquiry Papers edited by Robert Maranto, Lee Jussim, and Sally Satel.
1. An age of unreason
The liberal enlightenment, humanism, and democracy are under siege. A once-obscure postmodernist worldview, Critical Social Justice (CSJ) [1-3], has escaped the academy and is quickly reshaping our institutions and society at large. Long-standing merit-based practices in science are rapidly being subordinated to practices based on the tenets of CSJ theory [4]. Increasingly, scientists must compete for funding, no longer only on the basis of scientific merit, but also on the basis of how their proposed research will promote the goals of CSJ. As an example, an NIH neurology program requires grant applications to include a “plan for enhancing diverse perspectives” with the goal to “bring about the culture change necessary to address the inequities and systemic biases in biomedical research….” [5] Similarly, funding for fundamental research in chemistry and physics now depends on researchers demonstrating their commitment to “promote equity and inclusion as an intrinsic element to advancing scientific excellence” [6].
In the academy, faculty hiring and administrative appointments are increasingly made on the basis of the candidate’s identity [7-9]. Merit-based admission to schools and universities is being weakened, with standardized tests such as the SAT and ACT being abandoned on “social justice” grounds [10,11]. K–12 is affected as well. Some school districts have stopped giving D and F grades in order to improve “equity” [12]. In math classes, activist teachers claim that getting the right answer and showing your work are white supremacist concepts and are advocating, instead, a supposedly anti-racist CSJ pedagogy [13,14]. Accelerated mathematics programs for gifted students, necessary to prepare them for advanced training and careers in STEM [15], are being dismantled in the name of “social justice” [16-18]. Many school districts have eliminated honors classes altogether in the name of “equity” [19]. The resultant weakening of the workforce has already contributed to the fall of the US from its position as the world leader in science [20].
In the university, faculty and staff are instructed to use Newspeak—neopronouns and other neologisms—in their written and verbal communications for the purpose of “inclusivity” [21,22]. To be avoided are such apparently un-inclusive terms as “strawman,” “brown-bag lunch,” and “picnic” [22–25]. Professional societies and corporations are following suit, proscribing terms such as “field,” “dark times,” “black market,” “double-blind study,” “nursing mother,” “hip-hip hooray,” “smart phone,” “homeless,” and “the French” [26–30].
In biology, an education paper recommends that teachers emphasize the sexual diversity across species in nature, which includes “organisms such as ciliates, algae, and fungi [that] have equal-size gametes (isogamy) and do not therefore have gametic sexes [that is, binary sexes, as mammals do].” This is supposed to promote inclusivity of LGBTQIA2+ students in the classroom [25]. Chemistry education also needs to be reformed, according to the journal Chemical Education, which published a virtual Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) collection of 67 papers exploring such topics as decolonization of the chemistry curriculum, chemistry and racism, and gender and sexual orientation identities in the chemistry classroom [31]. A recent paper in the same journal describes “a special topic class in chemistry on feminism and science as a tool to disrupt the dysconcious racism in STEM,” which explores “the development and interrelationship between quantum mechanics, Marxist materialism, Afro-futurism/pessimism, and postcolonial nationalism.” “To problematize time as a linear social construct,” the paper says, “the Copenhagen interpretation of the collapse of wave-particle duality was utilized” [32]. No, Deepak Chopra was not a co-author of the paper.
In STEM, prospective faculty are asked to pledge their commitment to the ideology of CSJ and to document their activism in advancing DEI [8,9,33,34]. Medical schools are abolishing long-accepted assessments of competency in order to improve racial parity in residency programs [35]. A pamphlet published by the University of Illinois Chicago School of Public Health claims that public health anti-obesity campaigns are an example of “fatphobia,” that public health’s “focus on body size is rooted in racism,” that “higher weight is not causal to worse health outcomes," and that “focusing on weight ignores systematic injustices” [36,37]. Under the doctrine of gender-affirming care, adolescents are offered life-changing transgender treatments, often after only perfunctory psychological assessment, despite the poor understanding that medicine currently has on the risks and benefits of these treatments [38–40].

[ Unreason and intolerance. Upper left: Yale students protest “offensive” Halloween costumes (2015). Lower left: Activists burn books by J.K. Rowling (2023). Right: Students at UC Davis disrupt a film viewing by throwing a bag of manure into the room. ]
Free speech itself, the cornerstone of liberal democracy, is under attack. As viewed by CSJ activists, free speech is dangerous, harmful, and equivalent to violence [41]. Adherents of DEI ideology believe that DEI should trump academic freedom [42]. Institutions essential for providing a platform for the marketplace of ideas, information exchange, and debate have largely abandoned their mission in the name of social justice activism. Articles in the press are infused with CSJ ideology [4]. Scientific publishers from Scientific American to the flagship journals Science and Nature have become mouthpieces for CSJ [43–56]. Universities, whose primary mission is education and truth seeking, have become complicit in censorship, scholarship suppression, indoctrination, and intimidation [57–59]. Universities and professional organizations have compromised their mission as seekers and communicators of objective truths by abandoning traditional institutional neutrality in favor of political activism, taking official positions on elections, police reform, abortion, wars, and other social issues [60,61], leaving dissenters out in the cold. Where debate, constructive disagreement, and discussion were once cultivated, conformity and dogmatism, enforced both top-down (by CSJ-infused DEI trainings [62,63]) and bottom-up (by ideologically driven activists [58]), now reign.
On campus, another essential provision of democracy, the presumption of innocence until proven guilty, no longer guides procedures for resolving conflict. Suspensions and terminations of professors without a hearing in response to offense taken by students, faculty members, or administrators has become commonplace (see, for example, Ref. 64–67). A predictable consequence is that there is now an unprecedented level of self-censorship by students and faculty [57,68,69]. Proposed changes to Title IX regulations will further erode the free speech of students and the protection of due process [70].
CSJ adherents accuse dissenters of being indifferent to existing inequalities and historic injustices, of being bigots, of having nefarious motives, and of perpetuating existing power structures. We reject these accusations. We oppose the practices of CSJ because they harm everyone, including those groups they purport to elevate [71-73]. It is precisely because we care about the existing problems in the world and about real social justice that we oppose CSJ.
What we are witnessing today—curriculum “decolonization,” the elimination of honors classes in schools, the ubiquitous war on merit [4], the imposition of political litmus tests for academic positions, Newspeak, the renaming of everything in sight, and on and on—are not isolated excesses perpetrated by a handful of overly zealous but otherwise well-meaning individuals; they are symptoms of a wholesale takeover of our institutions by an illiberal movement that currently has the upper hand. The current situation is not a pendulum that has swung too far and will self-correct [74]; it is a train hurtling full speed toward a cliff. Those of us unwillingly to go over the edge can either jump off—leave academia (or maybe start up alternative institutions)—or fight to get the brakes applied before it is too late. The remainder of this chapter is about the latter course of action.
2. Why we should fight
To put it simply, we should fight because it is the right thing to do. It is not only our duty to the next generation, but an opportunity to pay our debt to the previous generations of dissenters who fought against forces of illiberalism to create the free and prosperous world that we enjoy today [75,76]. By fighting, we, too, can fend off the forces of unreason and restore the values of humanism, liberalism, and The Enlightenment. Inaction and submission will only enable the further spread of illiberalism. The history of past illiberal regimes, such as the USSR and Nazi Germany, provide ample lessons and motivation to stand and fight today. The train is gaining momentum; the longer we wait, the harder it will be to stop it. We must act now, while we still can.
Although there are uncanny parallels with totalitarian regimes of the past [23,77–80], we are still living in a free, democratic society. Despite the advances of illiberal ideology, manifested by the rise of censorship, the spread of cancel culture [23,57,58,81–83], and the proliferation of institutionalized structures (such as DEI bureaucracies) to enforce CSJ ideology, the dissenters of today do not face incarceration in prisons, labor camps, and mental hospitals. Nonetheless, we can learn from history.
In his book To Build a Castle: My Life as a Dissenter [84], Vladimir Bukovsky [85] describes his experiences as a dissident who refused to comply with the Soviets and challenged the regime. Bukovsky describes the apathy and complacency of the majority of the population at that time. People understood the corrupt and inhumane nature of the regime, but they chose to keep their heads down because—as the Russian proverb goes—“No man can splay the stone” (in Russian: плетью обуха не перешибёшь).
Because of this complacency, the economically bankrupt, oppressive, and inhumane Soviet regime lasted as long as it did (70+ years). But it was the actions of dissidents that ultimately catalyzed its downfall. Consider, for example, the impact of the books of Solzhenitsyn, who told the world the truth about the atrocities of the Soviet regime [86]. In addition to meticulously documenting the scale of the atrocities, Solzhenitsyn explained that they came to be, not due to deviations from the party line or shortcomings of its individual leaders, but as the direct result of Marxist-Leninist ideology.
In Bukovsky’s time (the late 1950s to mid-1970s), open dissent was rare. Growing up in the Soviet Union, I [Anna]—as most of my peers—did not even know dissidents existed. It wasn’t until Perestroyka in the late 80s, when I read Solzhenitsyn’s books and learned about Sakharov [87] that I found out. Yet, it is through the actions of the dissidents that the West came to understand the Soviet regime as an “evil empire,” and this understanding propelled the political forces in the West that ultimately decided the outcome of the Cold War. The impact of the dissident movement on the Soviet regime has been illuminated through a series of memoranda of the Central Committee of the Communist Party, stolen and published by Bukovsky in his book Judgment in Moscow [88]. The acts of individuals splayed the stone after all.
I [Anna] was born (in the then-Soviet state of Ukraine) into the luckiest generation in the history of the USSR—the generation that witnessed the fall of the Wall when they were still young. We could escape to the free world, live as free people, and build successful and fulfilling careers in the West. Had the regime lasted another 20 years, my generation would have been yet another of the long list of those whose lives were ruined by the Soviet regime. I feel a personal debt to the dissidents of the day.
Now, it is our turn to be the dissidents and to fight the good fight.
Fighting for what is right is not just the right thing to do; it is empowering. Standing up and speaking your mind is liberating, even exhilarating; while hunkering down in fear, hoping the storm will pass, is a bleak experience. Being honest feels good, while being complicit in lies is dispiriting. Fighting the good fight puts you in control, whereas passive submission leaves you helpless. Whether we ultimately win or lose this fight, those who choose to remain silent will look back and ask themselves why they did not act when they could. As Martin Niemöller wrote after World War II,
First they came for the socialists, and I did not speak out—because I was not a socialist. Then they came for the trade unionists, and I did not speak out—because I was not a trade unionist. Then they came for the Jews, and I did not speak out—because I was not a Jew. Then they came for me—and there was no one left to speak for me.
Eventually, this illiberal movement, like those of the past, will come not only for the dissidents, but for the silent bystanders as well (and, eventually, for its own vocal supporters).
There are myriad excuses, as old as the history of totalitarianism and oppression itself, invoked to justify inaction, complacency, and collaboration. Bukovsky [84] enumerates a few of the more familiar: “What can I do alone?”; “I’ll be more effective after I get the promotion”; “It’s not my job; I’m a scientist.” “If I don’t collaborate, someone else will anyway (and I’ll probably do less harm).” These reasons may seem logical, even compelling; however, they are self-deceptions. Not pushing back against bad ideas allows them to spread. Not fighting back against illiberalism allows it to grow. Not standing up for truth permits the lies to flourish. Not confronting the CSJ ideologists permits them to advance. And when they advance, we lose. It is a zero-sum game.
The choice to fight in the face of potential consequences is personal [89] and not an easy one to make. But as you contemplate whether to act or to lay low, consider the importance of truth and integrity in your life. To paraphrase Bari Weiss: Worship truth more than Yale. As she says:
[D]o not lose sight of what is essential. Professional prestige is not essential. Being popular is not essential. Getting your child into an elite preschool is not essential. Doing the right thing is essential. Telling the truth is essential. Protecting your kids is essential. [90]
Sure, no one wants to become a martyr for free speech or experience bullying, ostracism, and professional damage [81,91–93]. Cancel culture is real, but the risks are not what dissenters to totalitarian regimes faced historically or face today—cancel culture does not put you in jail. One still can write a dissenting op-ed without the fear of being stripped of their citizenship and expelled from the country, as Solzhenitsyn was for his writings [83]. We still can criticize DEI policies without fear of being put under house arrest, as Sakharov was for his vocal opposition to nuclear weapons and his unwavering defense of human rights [87]. But if we delay, some of the totalitarian nightmares of the past may become a reality. There are already worrying signs of this totalitarian-style repression in America: parents opposing CSJ in schools have been accused of terrorism and investigated by the FBI [94]; a journalist who wrote about collusion between the government and social media was paid a surprise home visit by the Internal Revenue Service [95]; a student who questioned the concept of microaggressions [96] at a mandatory training was expelled and forced to “seek to psychological services” [97]. These incidents in America today are chillingly similar to practices in Russia in the Soviet era, when the KGB routinely investigated dissidents, and dissent from Soviet ideology was considered a psychiatric disorder [84,88]. In the absence of resistance, this illiberal movement, like illiberal movements of the past, will gain ever more power, and we will face ever worse repression and erosion of individual freedom.
Inaction does not guarantee survival, but fighting a successful fight does. The only way to defend yourself against repression by an illiberal ideology is to stop the spread of the ideology.
The dangers of inaction are real, but how much risk one should take must be a personal decision [89]. Above all, it rarely does any good to get fired. Getting fired is playing into their hands. It’s one less enemy in the organization to fight against its ideological capture. Should all the dissidents get fired, the ideology wins. Full stop.
But it’s not hopeless. As we elaborate below, there are ways to maximize the impact of your actions and minimize the chances of negative consequences of resistance.
3. How to fight
Although there is no sure-fire roadmap to solve the current crisis, there are some do’s and don’ts. A recently published handbook, Counter Wokecraft (which we highly recommend), written by an anonymous STEM professor, provides concrete recommendations for staging the resistance [98]. It convincingly explains how small but deliberate actions add up to big change and elaborates on the perils of delaying action. In what follows, we offer our view on how to fight, and we share examples of successful acts of resistance that give us reason for hope. Small contributions add up, so do something rather than nothing. As Gad Saad writes in The Parasitic Mind:
The battle of ideas knows no boundaries, so there is plenty to do. If you are a student and hear your professors spouting postmodern nonsense or spewing anti-science drivel, challenge them politely and constructively. If you are a graduate and your alma mater is violating its commitment to freedom of speech and freedom of thought, withdraw your donations—and let the school know why. If your Facebook friends are posting comments with which you disagree, engage them and offer an alternative viewpoint.... If you are sitting at your local pub having a conversation about a sensitive topic, do not refrain from speaking your mind. If your politicians are succumbing to suicidal political correctness, vote them out of office. [99]
1. Educate yourself; knowledge is power.
To effectively counter the ideology of CSJ, it is crucial to understand its nature and the tactics it employs. As two-time Nobel Laureate Marie Sklodowska-Curie said:
Nothing in life is to be feared, it is only to be understood. Now is the time to understand more, so we may fear less.
Although Curie was referring to phenomena of the natural world, the observation applies equally to the world of ideas. By understanding the origins and tenets of CSJ, we can fear less—and fight more effectively.
For me [Anna] and my former compatriots, who were forcibly schooled in Marxist-Leninism and experienced its implementation as Socialism firsthand, it is easy to recognize the current illiberal movement’s philosophical roots [78,79]. We recognize the familiar rhetoric and the Orwellian co-option of the language: the media outlet of the Communist Party, which disseminated its lies, was called Pravda (Правда), which is Russian for “truth”; victims of Red terror were called “enemies of the people” (враги народа); Soviet troops invading other countries were called “liberators” (освободители); and nuclear weapons were developed with the slogan “nucleus for the cause of peace” (атом—делу мира). We are used to looking behind the facade of nice-sounding words and seeing their real meaning to those in power [100]. It is not hard to see that today’s “Diversity,” “Equity,” and “Inclusion” have about as much in common with the noble concepts of diversity, equality, and inclusion as Orwell's Ministry of Love had to do with love or his Ministry of Plenty had to do with plenty. (A more-fitting operational definition of DEI would be Discrimination, Entitlement, and Intimidation.) This linguistic tactic is used because it works. It has fooled many STEM academics and ordinary citizens and has enabled the illiberal ideology to get its foot in the door [3].
As Counter Wokecraft explains, the tactics CSJ employs to gain power in our institutions include the use of liberal-sounding “crossover words” to shroud the illiberal aims of the movement [98]. The concise essay “DEI: a Trojan Horse for Critical Social Justice in Science” by the same author offers insights into the philosophy that undergirds the CSJ movement and clearly elucidates its aims [3]. For a deeper dive into CSJ, we recommend the book by Pluckrose and Lindsay [1].
2. Use all existing means of resistance, but first and foremost, the official ones.
Mechanisms of resistance are available through existing institutions, even if the institutions themselves are failing to protect their mission [101]. These mechanisms can be exploited to change the institution from within.
Bukovsky describes how their dissident group worked within the legal boundaries of the Soviet regime [84]. He contrasts this approach with anarchism and revolutionary destructivism, which, he argues, lead to outcomes that are worse than the original evils. Bukovsky and his dissident comrades structured their activism and resistance within the framework of the Soviet constitution—which many legitimately considered to be a joke. When allowed to speak in court, Bukovsky framed his defense to emphasize the constitutional rights of Soviet citizens, for example, to peacefully demonstrate. Bukovsky attributes their success to this strategy. As an example of an important victory, he describes how he and his fellow political prisoners managed to resist and ultimately eliminate mandatory “corrective labor” for political prisoners. Following legal protocols, they rolled out a concerted effort of filing official complaints. Although isolated complaints never had any effect (they would be registered, duly processed, and dismissed), by flooding the bureaucratic system with a massive number of such complaints (which each had to be properly registered and responded to), they pushed the system beyond its limits. The sheer number of complaints compelled administrative scrutiny of the prison and its officers. And the prisoners won the fight.
Today, we can work within the system of our universities and professional organizations, even if they have already been ideologically corrupted. We can participate in surveys; communicate our concerns to leadership; nominate candidates committed to liberal principles to committees and leadership; vote against CSJ ideologues; speak up against practices that violate the stated mission of the institution [43,102,103]; publish well-reasoned opinion pieces [4,14,15,23,82,83,102]; and insist that our institutions adhere to their stated institutional (and legal) commitments to free speech and non-discrimination, such as being equal opportunity employers. Counter Wokecraft [98] provides concrete suggestions on how to effectively oppose the advances of the CSJ agenda by simply insisting that standard protocols of decision-making be followed—that is, through formal meetings with organized discussions that adhere to a set agenda, vote by secret ballot, and so on. In short, the existing governance structures and institutional policies can still be utilized to defend and even restore the institutional mission, even when the institution’s workings have been undermined by CSJ activists.
The following success stories illustrate the effectiveness of working within the system.
At the University of Massachusetts, a faculty group fought—and won—against a proposed rewriting of the university mission statement, which would have redefined the purpose of the university as engaging in political and ideological activism, rather than pursuing the truth [104].
Faculty at the University of Chicago succeeded in having departmental statements that violated institutional neutrality (by voicing collective support for specific social and political issues in violation of the University’s Kalven Report [105]) rescinded [106].
Also at the University of Chicago, in response to faculty complaints to the institution’s Title IX coordinator and general counsel, at least seven programs that gave preferences to specific races or sexes in violation of Federal regulations were discontinued [106].
The faculty of the University of Washington voted down a proposal to require DEI statements for all tenure and promotion candidates [107]. As reported to us, an email campaign initiated by a single faculty member was decisive in defeating the proposal.
At the University of North Carolina (UNC), the Board of Trustees adopted [108] the Chicago Free Speech Principles [109] and Kalven Report [105]. The former articulates the university’s commitment to free speech and is considered to be a model policy on this issue; the latter ensures institutional neutrality, prohibiting units of the university from taking stands on moral, political, or ideological issues, unless they directly affect the mission of the institution.
Also at UNC, responding to a faculty petition, the Board of Governors moved to ban diversity, equity, and inclusion requirements from its hiring and promotion process. The mandate states that the university “shall neither solicit nor require an employee or applicant for academic admission or employment to affirmatively ascribe to or opine about beliefs, affiliations, ideals, or principles regarding matters of contemporary political debate or social action as a condition to admission, employment, or professional advancement” [110].
In California, mathematicians organized a petition that has, so far, blocked the implementation of radical, CSJ-based revisions to the K–12 math curriculum [18]. At the time of publication, the fight is not over; but they’ve won so far.
A new nonprofit, Do No Harm, has been formed to fight against the encroachment of identity politics in medicine [111]. Among their successes, filings with the US Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights against two medical schools has resulted in the elimination of race as a requirement for certain scholarships. Scholarships “meant for individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds, [a] worthy goal, can and should be met without racial discrimination,” writes the organization’s founder [112].
Adverse publicity and mockery, too, can cause Universities, which are sensitive to their public image, to roll back woke policies, as the following examples illustrate.
The administration of MIT reversed its own decision and reinstated the use of standardized tests for admission [113], the elimination of which had been mocked by dissidents [114].
The Stanford University “Elimination of Harmful Language Initiative” website, which listed 161 verboten expressions, including “beating a dead horse,” “white paper,” “insane,” and even “American,” was taken down after sustained mockery in the press and on social media. The university’s president ultimately disowned the initiative and reaffirmed the university’s commitment to free speech [29].
At the University of Southern California, the interim provost made a clear statement that “the university does not maintain a list of banned or discouraged words” in response to the mockery [115] of an earlier memorandum the university's School of Social Work announcing the cancellation of the word “field” as racist [26,29].
At Texas Tech, the administration announced that it was dropping mandatory DEI statements from the hiring process [116], after details of how these statements influenced hiring decisions had been publicized [9].
These examples illustrate the maxim that sunlight is the best disinfectant [117]. We can use social media and the press to shine a light on the excesses of CSJ to bring about change.
Pressure from state governments can also force universities to change course away from DEI ideology. Facing threats from the state assembly to cut funding, the University of Wisconsin system has announced it will eliminate mandatory DEI statements for job applicants. As we are writing this chapter, the state assembly is also threatening to eliminate funding for administrative positions at UW dedicated to DEI [118].
Arizona has also dealt a blow to DEI ideology. The state’s Board of Regents has mandated that public universities drop the use of DEI statements in hiring. The move was in response to a finding by the Goldwater Institute that DEI statements, which were required in over three-fourths of job postings, were being used “to circumvent the state’s constitutional prohibition against political litmus tests in public educational institutions” [119].
Organizations such as the Academic Freedom Alliance (AFA) and the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE) have successfully used institutions’ own governing policies and bylaws as well as the law to defend scores of scholars who have been attacked for their extramural speech and threatened with administrative discipline or firing [120,121].
A move is afoot to strengthen universities’ commitment to academic freedom by encouraging them to officially adopt the Chicago Trifecta (the Kalven report, the Chicago Principles, and the Shils report). The “Restoring Academic Freedom” letter [122], which calls on universities to do so, has garnered 1700 signatures so far.
3. Don't play their game: You can’t win.
We are trained to seek compromises and solutions that bring different groups on board; we seek consensus. That is a fine approach under normal circumstances, when all agents are acting in good faith. But we must recognize that we are up against agents who are driven—knowingly or unknowingly—by an ideology whose goal is to take over the institution. Every compromise with them brings them closer to their goal [1,3,74,98,123]. Therefore, we must stand our ground.
A major advance in the spread of illiberalism has been the establishment of DEI bureaucracies in our intuitions to enforce CSJ ideology through policy [3,8,98,124-127]. It is important to understand the power of this system and to distinguish the system from the people. A DEI apparatchik can be a nice, well-meaning individual, who has been fooled by the movement’s deliberately deceptive language [1,98]; a cynical opportunist who seeks power and career advancement; or a True Believer. A DEI administrator may be completely unaware of the philosophical origins of CSJ, whose goals the DEI machine has been installed to implement. But just as a Soviet apparatchik need not have read Das Kapital to have been an agent enforcing conformity to Marxist doctrine, a DEI apparatchik need not have read the works of the critical theorists Gramsci, Derrida, Foucault, Bell, Crenshaw, and Delgado to be implementing CSJ-inspired ideology. But even participants who are naive of the movement’s history, philosophy, or ultimate goals are furthering its aims; they are still cogs in the machine. Do not be fooled by DEI administrators who may naively or deceptively deny that they are advancing CSJ ideology. They are, whether or not they know it or acknowledge it.
The power of the system—the DEI bureaucracy—and its ideological foundation make the motivations of the individual participants irrelevant. The story of Tabia Lee illustrates this point [128]. Lee—a black woman who directed a DEI program at a community college in California—questioned anti-racist and gender orthodoxy, declined to join a “socialist network,” objected to land acknowledgments and Newspeak terms such as “Latinx,” “Filipinx,” and neopronouns, and supported a campus event focused on Jewish inclusion and antisemitism. Lee describes her non-orthodox worldview as follows:
I don’t have ideological or viewpoint fidelity to anyone. I’m looking for what’s going to help people and what will help our students and how we can be better teachers and our best teaching selves. [128]
This attitude was found to be incompatible with the ideology of DEI. When Lee refused to change her worldview to comply with the orthodoxy, she was terminated from her position [128].
The establishment of the DEI bureaucracy in our institutions represented a tectonic shift from CSJ as a grass-roots movement to CSJ as an official power structure within the university equipped with a massive budget to promote its ideology [124,126,129-132].
A 2021 report by the Heritage Foundation [130], which documented the size of this new bureaucracy, identified 3,000 administrators with DEI responsibilities among the 65 universities they surveyed [124,131]. This number is in addition to the already extensive staff of Federally mandated Title VI, Title IX, and disability offices, who also perform DEI-related tasks. The new diversicrats already outnumber the mandated staffers. For example, the average university examined had 4.2 DEI personnel for every one ADA compliance administrator [124]. Given the sheer number of DEI officials and their generous salaries (one-third of chief diversity officers are paid more than $200,000 annually [132]), it is not surprising that DEI budgets are enormous; for example, in 2021, UC–Berkeley dedicated 41 million dollars to DEI [129].
The DEI bureaucracy is given official status within the university and is empowered to interfere in faculty hiring, to disseminate CSJ ideology by means of mandatory trainings, to infuse the ideology into teaching [10,13,16,25,31], and to curtail academic freedom [42,127]. Khalid and Snyder provide insight into the logic and financial incentives behind the DEI machine:
This attitude was found to be incompatible with the ideology of DEI. When Lee refused to change her worldview to comply with the orthodoxy, she was terminated from her position [128].
The establishment of the DEI bureaucracy in our institutions represented a tectonic shift from CSJ as a grass-roots movement to CSJ as an official power structure within the university equipped with a massive budget to promote its ideology [124,126,129-132].
A 2021 report by the Heritage Foundation [130], which documented the size of this new bureaucracy, identified 3,000 administrators with DEI responsibilities among the 65 universities they surveyed [124,131]. This number is in addition to the already extensive staff of Federally mandated Title VI, Title IX, and disability offices, who also perform DEI-related tasks. The new diversicrats already outnumber the mandated staffers. For example, the average university examined had 4.2 DEI personnel for every one ADA compliance administrator [124]. Given the sheer number of DEI officials and their generous salaries (one-third of chief diversity officers are paid more than $200,000 annually [132]), it is not surprising that DEI budgets are enormous; for example, in 2021, UC–Berkeley dedicated 41 million dollars to DEI [129].
The DEI bureaucracy is given official status within the university and is empowered to interfere in faculty hiring, to disseminate CSJ ideology by means of mandatory trainings, to infuse the ideology into teaching [10,13,16,25,31], and to curtail academic freedom [42,127]. Khalid and Snyder provide insight into the logic and financial incentives behind the DEI machine:
DEI Inc. is a logic, a lingo, and a set of administrative policies and practices. The logic is as follows: Education is a product, students are consumers, and campus diversity is a customer-service issue that needs to be administered from the top down. (“Chief Diversity Officers,” according to an article in Diversity Officer Magazine, “are best defined as ‘change-management specialists.’”) DEI Inc. purveys a safety-and-security model of learning that is highly attuned to harm and that conflates respect for minority students with unwavering affirmation and validation.
Lived experience, the intent–impact gap, microaggressions, trigger warnings, inclusive excellence. You know the language of DEI Inc. when you hear it. It’s a combination of management-consultant buzzwords, social justice slogans, and “therapy speak.” The standard package of DEI Inc. administrative “initiatives” should be familiar too, from antiracism trainings to bias-response teams and mandatory diversity statements for hiring and promotion. [127]
The DEI bureaucracy is a categorical enemy. Don't deceive yourself that you can work with it to accomplish good for your institution [128]. This bureaucracy is founded on ideas that are in direct opposition to the liberal enlightenment and humanism [1,3,4,42,79,99,125–128,133,134]. Their goals are not your goals; consequently, you cannot ally or compromise with them. We must, instead, focus our efforts on stripping the DEI bureaucracy of its power, ideally, ridding the institution of it completely. This will not be an easy fight, but neither is it an impossible dream. State legislatures are already taking action against DEI. At the time of this writing, 35 states have introduced bills that would restrict or ban DEI offices and staff, mandatory DEI training, diversity statements, and/or identity-based preferences for hiring and admissions [135]. Recognizing that such bills could go too far and compromise academic freedom, the Manhattan Institute has drafted model legislation that would abolish DEI bureaucracies on campuses while preserving academic freedom [136]. To date, at least one state, Texas, has enacted legislation based on the Manhattan Institute’s model [137].
Another reason not to attempt to work with the DEI bureaucracy is that CSJ ideology leaves no space for rational dialog. As explained by McWhorter [71], Pincourt [3,98], Pluckrose [1], Saad [99], and others, CSJ is not a rational or empirical worldview, but an ideology whose adherents have accepted a set of unfalsifiable tenets that may not be questioned. Thus, CSJ ideologues are not open to reasoned arguments that contradict their worldview; it is, thus, futile to argue with them. We need, instead, to reason with those of our colleagues who have not yet drunk of the Kool Aid.
Finally, since the goal of CSJ is to take over the institution, small compromises with them ultimately lead to large losses for us. Give CSJ an inch, and it will take a mile. Consider, for starters, the following example, in which the dean of the Duke Divinity School made the mistake of conceding to student activists, which led to ever-increasing demands and personal attacks on the dean herself [138]. “The chickens have come home to roost at Duke’s divinity school,” writes John Staddon. Dean Heath, the dean of the school, fully allied herself with the CSJ agenda, rolled out a variety of DEI initiatives, issued a self-flagellating editorial admitting the “structural sins” of the school, and forced non-conforming faculty to resign. Yet, despite these concessions, the demands of “marginalized groups” only grew stronger, culminating in uncivil acts, such as the disruption of the dean’s state-of-the-school address by “four dissident female students bearing bull-horns and chanting, ‘I am somebody and I won’t be stopped by nobody,’ followed by a rap, a little theatrical performance [of a rude nature].”
Staddon writes:
There is poetic justice in this incident. Despite the dean’s earnest attempts “to provide a welcoming and safe place for students,” even after she designed “a space for the work of Sacred Worth, the LGBTQIA+ student group in the Divinity School”—even after disciplining, and losing—Professor Griffiths [a non-conforming faculty], in spite all this, she has apparently not done enough! The LGBT folk want more, much more, in the form of 15 demands. “We make up an integral part of this community, and yet our needs remain deliberately unheard.”
The demands include:
“To appoint a black trans woman or gender non-conforming theologian” as well as “a tenure-track trans woman theologian” and a “tenure-track queer theologian of color, preferably a black or indigenous person.”
A dissident MIT website, the Babbling Beaver [139], illustrates the same point by a mock resignation statement by MIT’s former President Reif:
You would think giving them a Women’s and Gender Studies Program, hiring six dozen DEI deans and staffers, most of whom couldn’t pass 18.01 [MIT’s introductory math course] if their lives depended on it, and cancelling invited lecturers to appease shouting Twitter mobs would be enough,” lamented the weary lame duck. “But noooo ... The only thing I accomplished by giving in to the incessant demands was encouraging additional demands, each more strident than the last.” [140]
The statement is satire, but the concessions made by the president and the ever-increasing demands were real.
Stories of how CSJ, once it is let in the door, rapidly infiltrates the organization and eventually takes it over are too many to enumerate. We present but one example, where the process has been meticulously documented. The report, spon.sored by the organization Alumni and Donors Unite, explains how CSJ took over University of San Diego “first gradually then suddenly.”
Gradually, over the course of a decade, CSJ-DEI became sown into the university’s fabric through changes in hiring committees and curriculum. Then suddenly in 2020–2021 the administration, outside all normal channels of decision-making, initiated a hostile takeover of USD and adopted a radical woke agenda into nearly all facets of the university’s life. [141]
The devaluation of merit and intellectual honesty in the guise of social justice that we now witness will inevitably lead to the decline of our institutions, if not to their destruction [4]. A case in point is The Evergreen State University, which, in 2017, experienced a notorious CSJ uprising on campus [142]. Since then, the university has suffered a 25% drop in enrollment and has lost 45 faculty through lay-offs and attrition [143].
Learn how to recognize and take on categorical enemies [98]. Remember—it is a zero sum game.
4. Focus on truth, not partisanship. Do not fear verbal attacks.
When you take on CSJ, there is something you will need to come to terms with: you are going to be called names, and your views and beliefs are going to be distorted and misrepresented. These are standard tactics of the CSJ movement. Since the adherents of CSJ have adopted an ideological, rather than a rational, worldview, they cannot rationally defend it; so they use the only tools they have: personal attacks and strawman arguments. They will call you transphobe, racist, misogynist, alt-right, Nazi, etc., no matter what you say or do. They will use deliberate misrepresentation of your expressions to subvert and discredit them [98]. They will use the “Motte and Bailey” trick [144] to derail conversations. Learn about these tactics so that you can anticipate, recognize, and counter them [98]. As Gad Saad explains:
The name calling and accusations are locked and loaded threats, ready to be deployed against you should you dare to question the relevant progressive tenets. Most people are too afraid to be accused of being racist or misogynist, and so they cover in silence.… Don't fall prey to this silencing strategy. Be assured in your principles and stand ready to defend them with the ferocity of a honey badger. [99]
Because you will be attacked no matter what you believe, what you say, or how carefully you say it, there is no point in affirming in your interactions with CSJ ideologues that you are committed to traditional humanistic, liberal values. They don’t care. In her essay “I'm a Progressive, Please Don't Hurt Me,” Sarah Haider calls this practice of hedging “throat-clearing” and explains why it is not effective [145]. She also points out the hidden bigotry of it, that is, the implicit assumption that those on the other side of the aisle are inherently evil. Haider writes:
Before touching on any perspective that I knew to not be kosher among other Leftists, I tended to precede with some version of throat-clearing: “I’m on the left” or “I’ve voted Democrat my whole life.” I told myself that this was a distinction worth insisting on because 1) it was the truth and 2) because it helped frame the discussion properly—making clear that the argument is coming from someone who values what they value. But there was another reason too. My political identity reminders were a plea to be considered fully and charitably, to not be villainized and presumed to be motivated by “hate.” The precursor belief to this, of course, is that actual conservatives should not be taken charitably, are rightfully villainized, and really are motivated by “hate.” But I’m done sputtering indignantly about being mischaracterized as “conservative,” or going out of my way to remind the audience that I really am a good little liberal.
She goes on to explain that throat-clearing is counterproductive because: (1) it doesn’t work, you won't be spared; (2) it is a tax on energy and attention; (3) it is bad for you; and (4) it is bad for the causes you care about.
So we should stop worrying about our group loyalties and focus on our cause. Truth wears no clothes, so do not try to dress it up in partisan attire. Say what you mean, mean what you say, and move on.
It may be tempting to stay out of the fight in order to preserve friendships. It is true that some people you thought of as friends may turn against you—privately or even publicly. It has happened to us, and it hurts. But it also lets you know who your real friends are—those who stick up for you whether they agree with your views or not. And you will find new friends and allies who share your values. These relationships, forged fighting the good fight, will be enduring and empowering.
5. Do not apologize.
We cannot stress this enough. Your apology will be taken as a sign of weakness and will not absolve you—in fact, it will make matters worse. Apologies to the illiberal mob are like drops of blood in the water to a pack of sharks. Additionally, your apology can be interpreted as an admission of guilt, which can come back to haunt you in the event you need to defend yourself legally or in an administrative proceeding. The Academic Freedom Alliance advises: “If you confess to an offense you didn’t commit, or if you concede to a claim or accusation that is factually inaccurate or not truly an offense, the admission can and will be used against you.” [146] Recognize that the CSJ activists on Twitter do not care about your apology; they care about publicly flaying you in order to sow fear among other potential dissenters [147]. Someone claims to have been offended by your speech? Someone claims it caused them pain? Fine, that's their problem [148]. You know what your views are. And your friends do too. Stay on message.
6. Build a community and a network.
Communities and networks provide moral support and there is safety in numbers. Some groups already exist. The Heterodox Academy (HxA), for example, provides a platform to organize communities (e.g., HxSTEM is a community of STEM faculty) and to connect with colleagues who are open to reasoned debate, as per the HxA statement, which each member is asked to endorse: “I support open inquiry, viewpoint diversity, and constructive disagreement in research and education.” The Foundation Against Intolerance and Racism (FAIR) also provides resources and support to those who push back on anti-humanistic policies, especially in schools, universities, and in the medical profession.
Organizations like FIRE and the Academic Freedom Alliance (AFA) provide educational resources, opportunities to network, and—most importantly—protection, including legal representation. Join and support them. Build groups and act as a group—e.g., write an op-ed piece with a group of co-authors. Ten people are harder to cancel than one. Counter Wokecraft describes how to identify the allies among your colleagues and how to build effective resistance at your workplace [98].
Stand up for others. Next time they will do it for you. When you see a colleague being ostracized for what she said, think first, “Which parts of her message do I agree with?” not “Which parts do I disagree with?” If you agree with the main message, say so, and be charitable about imperfect expression. Way too often do we hear colleagues justifying their silence with excuses like “I agree with her in general, but she should have been more careful about how she said this or that.”
Some communities, including mathematicians and psychologists, in response to CSJ takeovers of their professional societies, have simply started new ones [149,150]. Perhaps we need more of these to send a strong message to the old societies that they need to change course. We see evidence of the effectiveness of this strategy; for example, the American Mathematical Society [151] cancelled its CSJ-dominated blog shortly after the establishment of the new Association for Mathematical Research [149], whose apolitical mission is simply to “support mathematical research and scholarship.”
In 2022, in response to increasing ideological influence and censorship in their profession, behavioral scientists founded the Society for Open Inquiry in the Behavioral Sciences, dedicated to “open inquiry, civil debate, and rigorous standards” in the field [152]. It publishes the Journal of Open Inquiry in the Behavioral Sciences, which commits to “free inquiry,” “rigorous standards,” and “intellectual exchange” [152]. Notably, its terms and conditions state that the journal will base retraction decisions strictly on the basis of the widely accepted COPE guidelines [153]; otherwise, the terms and conditions state, “We will never retract a paper in response to social media mobs, open or private letters calling for retraction, denunciation petitions, or the like....” [154]
There is even a new university—The University of Austin (UATX)—established in response to the current crisis in higher education [155]. The message on the UATX webpage—“We are building a university dedicated to the fearless pursuit of truth”—makes clear what void in the American academy UATX aspires to fill [156]. That the university received over $100 million in donations and over 3500 inquiries by professors from other institutions within six months of the project’s announcement, makes clear the demand [157].
The success of such new initiatives will inspire more educators and scientists to stand up and defend the key principles of science and education. And it will send a strong message to our leadership. Even if we cannot appeal to their sense of duty, the financial considerations (Go Woke, Go Broke [158]) and the effect of negative publicity of the excesses of CSJ (such as DEI loyalty oaths, “decolonizing” the curriculum, renaming everything, and Newspeak [9,23,24,139]) may provide incentives to straighten out their act.
4. Conclusion
Will we succeed? Will we stop the train before it goes over the cliff? We do not know what will happen if we fight. But we know what will happen if we don’t. The task ahead might look impossible. But remember the USSR. It looked like an unbreakable power, yet in the end it collapsed like a house of cards. The Berlin Wall looked indestructible, yet it came down overnight. Recalling his 20 years’ experience in the gay marriage debate, Jonathan Rauch told us: “I can tell you that the wall of received opinion is sturdy and impenetrable...until it isn't. And that it's the quiet people in the room who are the swing vote.... and please illegitimi non carborundum [159].”
We are not helpless. We have agency and we should not be afraid to exercise it. We should fight not just because it is the right thing to do, but because fighting brings results. If we behave as if we were living in a totalitarian society, it will become a self-fulfilling prophecy.
Afterword
A Russian proverb says, “Fear has big eyes” (у страха глаза велики), meaning that people tend to exaggerate danger. Accordingly, it may feel like resisting the mob will inevitably lead to career damage. But this is not the case; the flip side of risk is reward. In recognition of her activism, including her publication of “The Peril of Politicizing Science” [23], which “launched a national conversation among scientists and the general public,” Anna Krylov, co-author of this chapter, was awarded the inaugural Communicator of the Year Award, Sciences and Mathematics, by the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts, and Sciences [160]. In “Victory Lap” [161], Lee Jussim, co-editor of the book in which this article will appear, documents how as a result of his public resistance to a mob attack on a colleague falsely accused of racism, his career enjoyed a variety of benefits including additional conferences invitations, massive positive public support for his activism, national attention to his scholarship, and an appointment to a departmental chair (with commensurate increase in salary), which he was offered because he had demonstrated that he could take the heat.
==
Stop saying "nO oNe iS sAyInG aNy oF tHiS!!" They are. You know they are. Dotted throughout the article are references to sources for quotes and claims. For the list of references, see: References.
Liberalism really is under attack. It's always been under attack from the religous right, but its influence has diminished over time, with society becoming increasingly secular and irreligious, or at least indifferent to religious influence. And principles like the US's First Amendment keep it, at least in theory, from breaching the threshold.
But where the religious attack is on the downswing, the attack from the illiberal left is on the upswing, and both more rapid and more successful, having infiltrated everything from government to science and even knitting clubs. And it hides behind nice-sounding words like "equity" and "diversity," people don't recognize it for what it is, and welcome it inside in a way they don't welcome religious intrusion.
This isn't about left vs right. It's about do we want a liberal society, or do we want a rampantly illiberal, or indeed anti-liberal society?
#Anna Krylov#Jay Tanzman#enlightenment#the enlightenment#attack on liberalism#liberalism#liberal values#liberal society#enlightenment values#throat clearing#critical social justice#social justice#DEI#DEI bureaucracy#diversity equity and inclusion#diversity#equity#inclusion#woke#wokeness#wokeism#cult of woke#wokeness as religion#cancel culture#DEI statements#diversity statements#compelled speech#humanism#liberal principles#liberal ethics
11 notes
·
View notes