#Armstrong Economics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The link between warfare and technological innovation has been well documented [...]. World War II was a particularly intense crucible of technological change, and the repurposing of military technologies and industries in the forging of a new post-war consumer [economy] is crucial [...]. Processes of technological bricolage turned the machines of war onto the natural world as global powers competed to cement their economic and imperial hegemony. In Great Britain’s post-war “groundnut scheme” in its East African territories (1946-51), this collision of nature, military hardware, and technical expertise was part of efforts to both produce more fats for the British diet and to demonstrate to the world (most importantly the United States) that, through a newly energized science-led developmentalism, British colonialism still had a “progressive” role to play in the postwar world.

The aim was to produce millions of tons of peanuts across Tanganyika using the latest methods of advanced scientific agriculture. The environmental conditions in the north, where the scheme was to begin, were known to be especially trying, not least the dry climate [...]. But faith in the power of mechanized agriculture was such that any natural limits were thought to be readily surmountable.
The groundnut scheme was to be, as its Director put it in an interview with the Tanganyika Standard, a “war” with nature, and an “economic Battle of Alamein” waged over some three million acres by an army of colonial technicians - many recruited from military ranks - and local laborers, for many of whom the scheme represented their first entry into the wage labor market.
But it wasn’t just the rhetoric of war that was repurposed.
Lancaster bombers were kitted out to survey and discover “new country” in East Africa for agricultural development. [...] [T]ractors and bulldozers from military surplus stores in Egypt proved unable to tackle the hard ground and tough vegetation, so the planners turned to a novel solution: repurposing surplus Sherman M4A2 tanks. The Vickers-Armstrong factory in Newcastle-Upon-Tyne set about rearranging key elements of the tanks’ construction [...]. The tractors, christened “Shervicks” for their hybrid origins, were [...] thought to be particularly suited to large-scale earth-moving and to the kind of heavy duty “bush clearing” that was required in Tanganyika.


Officials sought to dismiss concerns that large-scale bush clearing would have wider environmental consequences, using the well-worn colonial trope that any observed changes in local climate or erosion patterns were due to the “primitive” agricultural practices of the locals, not to the earth-moving practices of the colonists. [...] As the plants continued to wilt in the sun, [...] [t]he stakes were high. As [J.R.] of the Colonial Development Corporation put it in a letter: “Our standing as an Imperial power in Africa is to a substantial extent bound up with the future of this scheme. To abandon it would be a humiliating blow to our prestige everywhere.” The only option left was to try and bend the weather itself to the scheme’s will, by seeding the clouds for rain. [...] “Balloon bombs” (photographic film canisters tethered to weather balloons) and a repurposed Royal Navy flare gun were used to target individual clouds [...]. The scheme itself has survived as a cautionary tale of governmental hubris, but it is instructive too as a case study of how technologies of war have been turned against other foes.
---
All text above by: Martin Mahony. “The Enemy is Nature: Military Machines and Technological Bricolage in Britain’s ‘Great Agricultural Experiment.’“ Environment and Society Portal, Arcadia (Spring 2021), no. 11. Rachel Carson Center for Environment and Society. doi:10.5282/rcc/9191. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Images and their captions are shown unaltered as they originally appear in Mahony's article. Public Domain Mark 1.0 License for images: creativecommons dot org/publicdomain/mark/1.0/]
195 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have been warning that our Computer has projected that war will continue and that the Neocons are traitors to the people of the United States and a threat to the entire world. Biden, the senile one, will sign anything put in front of him, and he is incompetent to be president. For that matter, so is Kamala. Both threaten the National Security of our nation and the world. Putin is justified to start attacking the United States directly. Since he knows Trump is coming, he will try to sit on his hands. God help us if the Russian Neocons overthrow Putin. There will be no stopping this.
The Russian Foreign Ministry recently came out reminding the collective West that allowing Ukraine to use west-supplied, long-range missiles to attack deep into the interior Russia would make the collective West “parties to the conflict” because those long-range missiles require satellites to guide them to target. The Foreign Ministry reminded everyone that Ukraine does not HAVE any satellites. This is precisely what the Neocons are hoping for. Zelensky has abandoned defending the Donbas and switched to invade Russia on orders from the Neocons. They hoped Putin would attack anything in NATO. Now that Trump is president-elect and he has rejected all Neocons from his cabinet, they are desperate, and this is their next step to force Putin to attack anything so they can claim he started World War III when it has been the West under their control.
The Neocon propaganda is that Biden has authorized the first use of U.S.-supplied long-range missiles by Ukraine to strike inside Russia and then claim it will only be for short-range in defense of Ukrainian forces in the Kursk region of western Russia, the officials said. Let’s face the truth. Ukraine cannot defeat Russia, and this is all a ploy to weaken Russia for the NATO invasion.
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Not enough discussion yet of the Logan-Colin scene. The man who has spent 3 seasons adamantly refusing to acknowledge his own mortality suddenly wants to talk about the afterlife. It's not real, but if IS real then he has some fucking theories.
Logan spends this entire episode wanting someone to tell him he's not that bad a person. Since the beginning of the show, he's used various shields to hold the allegations of moral rot at bay. Everything he's ever done, he's done for his children. This is nothing but cultural blowback, he's being punished for the sins of others. He's a good Catholic boy who couldn't even take off his undershirt in front of his wife. He just knows things about the world, that's how he makes a buck. Each excuse is flimsier than the last. And now, finally, he's out of excuses. The season 3 finale was the moment of truth where he was forced to reveal the kind of man he truly was. He's a man who wants to keep his children close even when it hurts them. He's a man who mocks love and fosters betrayal and whose only goal is to add more billions to his pile. He's a man who poisons everything around him.
And so now here he is, 81, only sycophants at his party. His children aren't here, revealing that he's not the loving father he presented himself as. Mencken isn't here, revealing that he's not as powerful or influential as he used to be (the Raisin would NEVER have snubbed a birthday invite). The Cardinal isn't here, so he can't point to the presence of a churchman as an endorsement of his own righteousness. (Why isn't the Cardinal here? Is it just because he doesn't care, or is there an unsaid moral condemnation involved in that decision?) So he leaves, and he goes to a diner with his "best friend" Colin, a man he pays to be by his side every hour of every day.
On the Succession podcast, Jesse Armstrong talks about Logan's perception of humans as something fundamentally childish. He doesn't know how to exist in the world. He doesn't have the vocabulary to relate to other people. We've spent 3 seasons debating what he considers to be a "real person", and here he reveals that he himself doesn't even know. The only way he can understand other people, the only way he can relate to them, is in economic and business terms. A person is an economic unit, moving through markets. It (and notice he says "it", not "he" or "she" or "they") has dreams and values and goals, but those simply serve to dictate how it moves through those markets. That's true for the random person on the street, but it's also true for himself and his children and everyone at Waystar. The difference is not that other people are economic units and he and his family are not. The difference is that he and his family are much bigger economic units, that make a bigger impact on the markets. They're 100 feet tall, and everyone else is pygmies, and yet being 100 feet tall doesn't make his tuna sandwich taste any better.
(And it's worth noting that when Tom and Shiv finally encounter each other, they use the same kind of economic language to discuss the state of their marriage. Shiv doesn't want to rake up a bunch of bullshit for no profit. Tom asks if she really wants to take a full accounting of all the pain in their marriage. They don't even realize that somewhere along the way they began perceiving each other and their marriage through the same lens that Logan perceives the world. They don't even recognize that they've reduced each other to economic units, moving through various markets searching for some shred of happiness or fulfillment.)
And then finally we come to the question of the afterlife. Logan doesn't believe there is an afterlife. Or does he? Maybe he genuinely doesn't. Maybe he's looked at the world and decided that heaven and hell don't fit into his market-centric worldview. Or maybe, the self-professed "good little Catholic boy" who's upset the Cardinal didn't come to his birthday party knows deep down that if there is an afterlife, he's not going to a good place. Maybe the only shield he has left to defend himself is the idea that there is no heaven and there is no hell, said with all the conviction of a man who fears his own damnation but doesn't see any way to avoid that fate.
And then he comes back to the party and he wants someone to roast him. He's staring down the gun barrel of his own impending death and he needs other people to join him in his glib assessment of his moral failings, to confirm that it's not a big deal, it's just business, his kids just suck and he's a pretty good guy and they all love him. And not a single one of them can. Karl and Frank and Gerri are too afraid of him to try and make light of his faults (in itself a somewhat damning statement). The only person even willing to try is Greg, and sure he has no comedic timing, but the deeper issue is that what's wrong with Logan is simply not funny. It's not lighthearted and glib. It's miserable and sad and lonely, and everyone is afraid of him, and there's no love or camaraderie in anything Greg says. Greg asks him where his children are and the only thing he can do is remind Greg that he, too, has been abandoned by the people who should care about him, that Greg is just as lonely and pathetic and desperately scrambling for connection as he is.
And then finally, we see Logan on the couch, in the middle of the night, watching ATN. Two men are left with life-threatening injuries after a brawl that went too far. A stupid pointless fight from which emerged no victors. Two men far younger than Logan, dying in a hospital. We know nothing about these men. We don't know what kind of legacy they might leave behind. We do know that whatever else they did will be overshadowed by the futility of their deaths. And that's when Logan calls Cyd to tell her that he doesn't like what he sees. It is the truth, but I don't think the root cause is something Cyd can fix.
260 notes
·
View notes
Photo
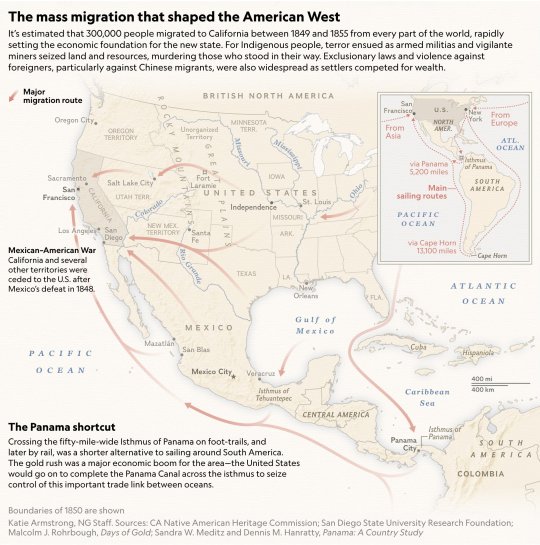
The mass migration that shaped the American West
It's estimated that 300,000 people migrated to California between 1849 and 1855 from every part of the world, rapidly setting the economic foundation for the new state. For Indigenous people, terror ensued as armed militias and vigilante miners seized land and resources, murdering those who stood in their way. Exclusionary laws and violence against foreigners, particularly against Chinese migrants, were also widespread as settlers competed for wealth.
Map by Katie Armstrong.
via RosemaryWardley
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay I Could do work but instead I'm going to write about the time shostakovich had the worst time in america
(So, despite the clickbaity title, this will be more of a serious post. I wrote about the topic a few years ago on Reddit , and I'll be citing a lot of the same sources as I cited there, because there are some good ones, along with some new information I've gathered over the years. This was going to be a video essay on my youtube channel, but I sort of kept putting it off.)
The Scientific and Cultural Congress for World Peace, held in New York in 1949, is a particularly fascinating event to study when it comes to researching Shostakovich because of just how divisive it was. True, the event itself, which only lasted a few days, doesn’t get as much spotlight as the Lady Macbeth scandal or the posthumous “Shostakovich Wars,” but you’ll find that when reading about the Peace Conference, as I’ll be referring to it here for the sake of brevity, many of the primary accounts of it never quite tell the full story. The Peace Conference was held during a volatile time, both in Soviet and American politics, as Cold War tensions were on the rise and an ideological debate between capitalism and communism gradually extended to become the focus of seemingly every factor of life- not just politics and economics, but also the sciences, culture, and the arts.
While artists on both sides were frequently cast in different roles in order to create or destroy the image of Soviet or American cultural and ideological superiority, the image either government sought to cast was sometimes contradictory with the sentiments of the artists themselves. For instance, while the CIA-founded Congress of Cultural Freedom (CCF) sent African American jazz musician Louis Armstrong on various tours around the world to promote jazz as American culture and dispel perceptions of racism in America, Armstrong canceled a trip to the Soviet Union in order to protest the use of armed guards against the integration of Black students at Central High School in Little Rock, Arkansas, in 1957. Meanwhile, the Soviet government’s use of international diplomatic missions by artists as cultural warfare also reflected a desire to portray themselves as the dominant culture, despite the tensions and complications that existed for artists at home. When the Soviet Union sent Dmitri Shostakovich to New York in March 1949 for the Peace Conference, such cultural contradictions are why the conference occurred the way it did, and why Shostakovich’s image has received so much controversy, both in Russia and in the west.
If you’re familiar with Soviet history, you may be familiar with the term Zhdanovshchina, which refers to a period of time between 1946 and 1948 in which Andrei Zhdanov, the Central Committee Secretary of the Soviet Union, headed a number of denunciations against prominent figures in the arts and sciences. Among musicians, Shostakovich was one of the most heavily attacked, likely due to his cultural standing, with many of his pieces censored and referred to as “formalist,” along with his expulsion from his teaching positions at the Moscow and Leningrad conservatories. During this time, Shostakovich often resorted to writing film and ideological music in order to make an income.
Meanwhile, in the United States, as fears of nuclear war began accumulating, peace movements between the two superpowers were regarded more and more as pro-Communist, an opinion backed by the House Committee of Un-American Activities (HUAC). The Waldorf-Astoria Peace Conference, to be held from March 25-27th 1949, was organized by the National Council of Arts, Sciences, and Professions, a progressive American organization, and was to feature speeches held by representatives of both American and Soviet science and culture. Harlow Shapely, one of the conference’s organizers, stated that he intended for the conference to be “non-partisan” and focused on American and Soviet cooperation.
On the 16th of February, 1949, Shostakovich was chosen to be one of the six Soviet delegates to speak at the conference. This was largely due to his fame in the west, where both his Seventh and Eighth Symphonies met a mostly positive reception. Shostakovich initially did not want to go to the conference, stating in a letter to the Agitprop leader Leonid Ilichev that he was suffering from poor health at the time and wasn’t feeling up to international travel and performances. He also said that if he were to go, he wanted his wife Nina to be able to accompany him, but he ended up being sent to New York without any members of his family- perhaps to quell concerns of defection (recall the amount of artists who defected around the time of the 1917 revolution, including notable names such as Rachmaninov and Heifetz).
Stalin famously called Shostakovich on the phone that same day to address the conference, and again, Shostakovich told him he couldn’t go, as he was feeling unwell. Sofia Khentova’s biography even states that Shostakovich actually did undergo medical examinations and was found to be sick at the time, but Stalin's personal secretary refused to relay this information. Shostakovich's close friend Yuri Levitin recalls that when Stalin called Shostakovich on the phone to ask him to go to the conference (despite the fact he had been chosen to go in advance), Shostakovich offered two reasons as to why he couldn't go- in addition to his health, Levitin claims that Shostakovich also cited the fact that his works were currently banned in the Soviet Union due to the Zhdanov decree, and that he could not represent the USSR to the west if his works were banned. While accounts of the phone call vary, the ban on Shostakovich's works was indeed lifted by the time he went to New York for the conference.
When Shostakovich arrived in New York, general anti-Communist sentiment from both Americans and Soviet expatriates, as well as media excitement, resulted in a series of protests in front of the Waldorf Astoria hotel where the conference was to be held, with some of the protesters directly referencing Shostakovich himself, as he was the most well-known Soviet delegate on the trip. In 1942, Shostakovich's 7th ("Leningrad") Symphony was performed in the United States under Toscanini and the NBC Symphony Orchestra to high acclaim, helping to promote the idea of allyship with the Soviet Union in the US during the war, and Americans were aware of the Zhdanov denunciations in 1948, as well as the previous denunciations that Shostakovich had suffered in 1936 as a result of the scandal surrounding his opera "Lady Macbeth of the Mtsensk District." So by 1949, many people in American artistic circles had a sympathetic, if not completely understanding, view of Shostakovich during the birth of the Cold War. They viewed him as a victim of Communism and the Soviet state, who was forced to appease it in order to stay in favor, and as a result, could potentially voice his dissent with the system once in the west. Pickets visible in footage from the protests outside the Waldorf Astoria carried slogans such as "Shostakovich, jump thru [sic] the window," a likely reference to Oksana Kosyankina, a Soviet schoolteacher who had reportedly jumped out of a window in protest (although the details of this story would be found to be highly dubious). Meanwhile, another sign read "Shostakovich, we understand!," a statement that would prove to be deeply ironic. At the conference itself, Shostakovich did not jump through the window, nor did he attempt any form of dissent. Instead, an interpreter read through a prepared speech as he sat on stage in front of a crowd of about 800. The speech praised Soviet music, denounced American "warmongering," and claimed that Shostakovich had accepted the criticism of 1948, saying it "brought his music forward." Many in the audience could see that Shostakovich was visibly nervous- he was "painfully ill at ease," and Nicholas Nabokov (brother of the writer Vladimir Nabokov) remarked that he looked like a "trapped man." Arthur Miller recalled he appeared "so scared." As they noticed how nervous he looked, some of those in attendance sought to make a demonstration of him in order to illustrate Soviet oppression in contrast to the freedoms supposedly enjoyed by American artists, asking him intentionally provocative questions that they knew he would not be able to answer truthfully. From Nicholas Nabokov:
After his speech I felt I had to ask him publicly a few questions. I had to do it, not in order to embarrass a wretched human being who had just given me the most flagrant example of what it is to be a composer in the Soviet Union, but because of the several thousand people that sat in the hall, because of those that perhaps still could not or did not wish to understand the sinister game that was being played before their eyes. I asked him simple factual questions concerning modern music, questions that should be of interest to all musicians. I asked him whether he, personally, the composer Shostakovich, not the delegate of Stalin’s Government, subscribed to the wholesale condemnation of Western music as it had been expounded daily by the Soviet Press and as it appeared in the official pronouncements of the Soviet Government. I asked him whether he, personally, agreed with the condemnation of the music of Stravinsky, Schoenberg, and Hindemith. To these questions he acquiesced: ‘Yes,’ he said, ‘I completely subscribe to the views as expressed by … etc….’ When he finished answering my questions the dupes in the audience gave him a new and prolonged ovation.
During the discussion panel on March 26th, music critic Olin Downes delivered yet another provocative statement towards Shostakovich:
I found both of your works [the 7th and 8th Symphonies] too long, and I strongly suspected in them the presence of a subversive influence—that of the music of Gustav Mahler.
For Shostakovich, and anyone knowledgeable of Soviet politics and music at the time, it's not hard to see why Downes had explicitly mentioned Mahler. Gustav Mahler (1860-1911) was a highly influential composer when it came to 20th century western music, particularly with regards to the avant-garde movement pioneered by the Second Viennese School- Arnold Schoenberg, Anton Webern, and Alban Berg. Shostakovich was also heavily influenced by Mahler, but such influences were frowned upon in the mid-30s to 50s Soviet Union. Mahler's style was decidedly more "western," and it's potentially for this reason that Shostakovich's 4th Symphony- perhaps his most "Mahlerian," was withdrawn from performance before its premiere in 1936, having followed the "Lady Macbeth" denunciations. To tie Shostakovich to Mahler would be to point out his direct western influences, while he was being made to issue statements that rejected them. During his speech, Shostakovich made statements criticizing Stravinsky and Prokofiev- two composers who had emigrated and adopted western-inspired neoclassical styles (although Prokofiev returned to the Soviet Union in 1936). Stravinsky had taken insult to Shostakovich's comments against him, and carried an animosity towards Shostakovich that appeared once again in their meeting in 1962, according to the composer Karen Khachaturian.
On the last day of the conference, March 27th, Shostakovich performed the second movement of his Fifth Symphony on piano at Madison Square Garden to an audience of about 18,000, and had received a massive ovation, as well as a declaration of friendship signed by American composers such as Bernstein, Copland, Koussevitzky, and Ormandy. He returned to the Soviet Union on April 3.
In addition to the 1948 denunciations, in which Shostakovich was pressured to make public statements against his own works, the likely humiliation he endured at the 1949 conference played a role in cementing his dual "public" and "private" personas. For the rest of his life, Shostakovich displayed mannerisms and characteristics at official events that were reportedly much different from those he displayed among friends and family. For the public, and for researchers after his death, it became difficult to determine which statements from him reflected his genuine sentiments, and which ones were made to appease a wider political or social system.
Both the Soviet Union and the west had treated Shostakovich as a means of legitimizing their respective ideologies against one another, a trend that continued long after his death in 1975 and the fall of the USSR in 1991. The publication of his purported memoirs, "Testimony," allegedly transcribed by Solomon Volkov, fueled this debate among academics and artists, becoming known as the "Shostakovich wars." The feud over the legitimacy of "Testimony," however, stood for something much larger than the credibility of an alleged historical document- as historians and musicologists debated whether or not it was comprised of Shostakovich's own words and sentiments towards the Soviet Union, its political systems, and its artistic spheres, they were largely seeking to prove the credibility of their stances for or against Soviet or western superiority. "Testimony" helped evolve the popular western view of Shostakovich as well, from a talented but helpless puppet at the hands of the regime, to a secret dissident bravely rebelling against the system from inside.
Modern Shostakovich scholars, however, will argue that neither of these views are quite true- as more correspondence and documents come to light, and more research is conducted, a more complete view of Shostakovich has been coming into focus over the past decade or so. Today, many academics tend to view Shostakovich and the debate over his ideology with far more nuance- not as a cowardly government mouthpiece or as an embittered undercover rebel, but as a multifaceted person who made difficult decisions, shaped by the varying time periods he lived in, whose actions were often determined by the shifting cultural atmospheres of those time periods, along with his own relationships with others and the evolution of his art. We can be certain Shostakovich did not approve of Stalin's restrictions on the arts- his posthumous work "Antiformalist Rayok," among other pieces of evidence from people he knew, makes that very clear- but many nuances of his beliefs are still very much debated. There has also been a shift away from judging Shostakovich's music based on its merit as evidence in the ideological dispute, and rather for its quality as artwork (something I'm sure he would appreciate!). As expansive as Shostakovich research has become, one thing has become abundantly clear- none of us can hope to truthfully make the statement, "Shostakovich, we understand."
Sources for further reading:
Articles:
Shostakovich and the Peace Conference (umich.edu)
Louis Armstrong Plays Historic Cold War Concerts in East Berlin & Budapest (1965) | Open Culture
Biographical and Primary Sources:
Laurel Fay, "Shostakovich, a Life"
Pauline Fairclough, "Critical Lives: Dmitry Shostakovich"
Elizabeth Wilson, "Shostakovich, a Life Remembered"
Mikhail Ardov, "Memories of Shostakovich"
HUAC Report on Peace Conference
Video Sources and Historic Footage:
Arthur Miller on the Conference
"New York Greets Mr. Bevin and Peace Conference Delegates"
"Shostakovich at the Waldorf"
"1949 Anti Communism Protest"
"Battle of the Pickets"
#shostakovich#dmitri shostakovich#long post#history#soviet history#classical music#music history#1940s history#new york#russian history#cold war#composers#classical composer#my god this feels good to get out of my drafts
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Great article to read.
God, please protect this man because if everyone is after him, maybe it's not him they're really after - he's just in the way!!
24 notes
·
View notes
Note
ok i apologise if this is a bad question because i don’t know anything about politics but i liked your bourgeois failpolitics post and would love it if you could expand further especially on how their ideological horse blinders lead them to justifying/reproducing what’s trapping them in the first place especially given how some of them, in theory, have “principles” & i guess how the show explores politics in general. again sorry if this is poorly formed i know nothing!!
hmm, not a bad question, but many directions to go in here.
first of all, none of them claims to be anti-capitalist ideologically. shiv wants to be a moral capitalist, kendall wants to be a coolguy capitalist, connor wants to be a virtuous capitalist (different from shiv's morality), and roman wouldn't identify with any ideological term but thinks capitalism is inescapable and omnipotent, and therefore not worth objecting to in any way. so even aside from their class interests, there's no ideological inconsistency between any of their political positions and the actions they take to preserve or strengthen waystar.
since shiv and connor are the ones with political principles, i think they're a good place to start.
shiv is a liberal, meaning she believes in individual liberty, private property, and equality under the law. her line "what if a good person ran waystar" is telling: she doesn't want to alter the fundamental structure of the economy or waystar, but she thinks someone with (her own) principles should be running the propaganda machine. she's being genuine when she talks about reform and wanting the company to be better, but this should not be mistaken for any kind of opposition to the economic structure.
connor self-identifies as a libertarian, so he's in the liberal tradition but with an increased emphasis on individual liberty. by this, he means private property rights, so his politics broadly oppose government intervention (regulation, social welfare policies, labour protections) except where the police / military state and the carceral apparatus are concerned (these are necessary to protect property). connor never had any real hope of inheriting waystar, but his politics are still broadly in support of it, insofar as it's a corporate interest and connor sees 'creating wealth' as a political virtue.
roman and kendall are simpler in this respect. as i've written before and many people have pointed out, kendall wants to kill dad and wants to be a 'good person,' but has no concrete sense of what that means and therefore no principled opposition to anything about waystar or its economic functioning. roman sees capitalism as totalising and inevitable, so it's not something he would ever bother taking a stance against, plus taking any kind of stance is lame anyway. fundamentally he wants daddy's love (kendall is motivated more by daddy's respect, which is why he needs to become a killer).
so the siblings' tendency to reproduce and reinforce their own oppression basically comes from the fact that none of them has the ideological or epistemological creativity to espouse any kind of anti-capitalist critique. there are nuances here (shiv places more value on the idea of market competition, like when she opposes the move to buy pierce in s2; connor sees flows of capital and flows of reproduction as part of the same political economy, hence his usury and onanism line), but at the end of the day they all accede to logan's economic worldview. in their minds, there's no reasonable or viable alternative. they have extremely limited understandings of political ideology, as evidenced by them all thinking that shiv's liberalism is, like, radically different from logan's. in many ways the intra-familial ideological disputes are a smokescreen distracting from the underlying economic convictions they all share.
as to the show's handling of politics in general: it's strange to me that more people don't point out that jesse armstrong has at least a passing familiarity with marx and has referenced him in discussing the show. the main narrative drive for the show is psychological, not ideological; nevertheless, it rests on a view of politics that basically builds off marx's base-superstructure distinction, with politics as an ideoological superstructure determined by the economic base. this doesn't mean people with the same class interest will have exactly the same ideology (obviously, the sibs don't; idt armstrong goes in for that type of crude determinism), but capitalism has a tendency to narrow the field of envisioned possibilities, hence the way that all four sibs fail to see any other economic arrangement as viable or even worth considering.
#in re: the last paragraph i obviously mean the presentation of Politics Proper#which is distinct from the way the show explores the internal functioning of liberal capitalism as articulated via the family#sorry this is kind of rambly it's hard to deal with 4 fully nuanced characters in any depth without like.... just going insanely long lol#tripping the light fantastic
68 notes
·
View notes
Text

Bibliography for FAQ
Non-Anarchist Works
Adams, Arthur E., Bolsheviks in the Ukraine: the second campaign, 1918–1919, Yale University Press, New Haven, 1963
Anderson, Terry L. and Leal, Donald R., Free Market Environmentalism, Pacific Research Institute for Public Policy,San Francisco, 1991.
Anweiler, Oskar, The Soviets: The Russian Workers, Peasants, and Soldiers Councils 1905–1921, Random House, New York, 1974.
Archer, Abraham (ed.), The Mensheviks in the Russian Revolution, Thames and Hudson Ltd, London, 1976.
Arestis, Philip, The Post-Keynesian Approach to Economics: An Alternative Analysis of Economic Theory and Policy, Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd., Aldershot, 1992.
Armstrong, Philip, Glyn, Andrew and Harrison, John, Capitalism Since World War II: The making and breakup of the great boom, Fontana, London, 1984.
Capitalism Since 1945, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1991.
Arrow, Kenneth, “Economic Welfare and the Allocation of Resources for Inventiveness,” in National Bureau of Economic Research, The Rate and Direction of Inventive Activity, Princeton University Press, 1962.
Aves, Jonathan, Workers Against Lenin: Labour Protest and the Bolshevik Dictatorship, Tauris Academic Studies, London, 1996.
Bain, J.S., Barriers in New Competition: Their Character and Consequences in Manufacturing Industries, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, 1967.
Bakan, Joel, The Corporation: The Pathological Pursuit of Profit and Power, Constable, London, 2004.
Bakunin, Michael, The Confession of Mikhail Bakunin, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, N.Y., 1977.
Bukharin, Nikolai, Economy Theory of the Leisure Class, Monthly PressReview, New York/London, 1972.
Bagdikian, Ben H., The New Media Monopoly, Beacon Press, Boston, 2004.
Baldwin, William L., Market Power, Competition and Anti-Trust Policy, Irwin, Homewood, Illinois, 1987.
Balogh, Thomas, The Irrelevance of Conventional Economics,Weidenfield and Nicolson, London, 1982.
Baran, Paul A. and Sweezy, Paul M., Monopoly Capital, Monthly Press Review, New York, 1966.
Baron, Samuel H., Plekhanov: the Father of Russian Marxism, Routledge & K. Paul, London, 1963
Barry, Brian, “The Continuing Relevance of Socialism”, in Thatcherism, Robert Skidelsky (ed.), Chatto & Windus, London, 1988.
Beder, Sharon, Global Spin: The Corporate Assault on Environmentalism, Green Books, Dartington, 1997.
Beevor, Antony, The Spanish Civil War, Cassell, London, 1999.
The Battle for Spain: The Spanish Civil War 1936–1939, Phoenix, London, 2006.
Berghahn, V. R., Modern Germany: society, economy and politics in the twentieth century, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987.
Berlin, Isaiah, Four Essays on Liberty, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1969.
Bernstein, Michael A., The Great Depression: Delayed recovery and Economic Change in America, 1929–1939, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1987.
Beynon, Huw, Working for Ford, Penguin Education, London, 1973.
Binns, Peter, Cliff, Tony, and Harman, Chris, Russia: From Workers’ State to State Capitalism, Bookmarks, London, 1987.
Blanchflower, David and Oswald, Andrew, The Wage Curve, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass., 1994.
Blinder, Alan S. (ed.), Paying for productivity: a look at the evidence, Brookings Institution, Washington, D.C, 1990.
Blum, William, Killing Hope: US Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II, 2nd edition, Zed Books, London, 2003.
Rogue State: A Guide to the World’s Only Superpower, 3rd edition, Zed Books, London, 2006.
Böhm-Bawerk, Eugen, Capital and Interest, Libertarian Press, South Holland,Ill., 1959.
Bolloten, Burnett, The Spanish Civil War: Revolution and Counter Revolution, Harvester-Wheatsheaf, New York, 1991.
Boucher, Douglas H. (ed.), The Biology of Mutualism: Biology and Evolution, Croom Helm , London, 1985.
Bourne, Randolph, Untimely Papers, B.W. Huebsch, New York, 1919.
War and the Intellectuals: Essays by Randolph S. Bourne 1915–1919, Harper Torchbooks, New York, 1964.
Bowles, Samuel and Edwards, Richard (Eds.), Radical Political Economy, (two volumes), Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd., Aldershot, 1990.
Bowles, Samuel and Gintis, Hebert, Schooling in Capitalist America: Education Reform and the Contradictions of Economic Life, Routledge & Kegan Paul, London, 1976.
Braverman, Harry, Labour and Monopoly Capital: The Degradation of Work in theTwentieth Century, Monthly Review Press, New York, 1974.
Brecher, Jeremy, Strike!, South End Press, Boston, 1972.
Brecher, Jeremy and Costello, Tim, Common Sense for Hard Times, Black Rose Books, Montreal, 1979.
Brenan, Gerald, The Spanish Labyrinth: An Account of the Social and Political of the Spanish Civil War, 2nd Edition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1976.
Broido, Vera, Lenin and the Mensheviks: The Persecution of Socialists under Bolshevism, Gower Publishing Company Limited, Aldershot, 1987.
Brovkin, Vladimir N., From Behind the Front Lines of the Civil War: political parties and social movements in Russia, 1918–1922, Princeton University Press, Princeton, N.J, 1994.
The Mensheviks After October: Socialist Opposition and the Rise of the Bolshevik Dictatorship, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, 1987. Russia after Lenin : politics, culture and society, 1921–1929, Routledge, London/New York, 1998
Brovkin, Vladimir N. (ed.), The Bolsheviks in Russian Society: The Revolution and Civil Wars, Yale University Press, New Haven and London, 1997.
Bunyan, James, The Origin of Forced Labor in the Soviet State, 1917–1921: Documents and Materials, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 1967.
Byock, Jesse, Viking Age Iceland, Penguin Books, London, 2001
C.P.S.U. (B), History of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (Bolsheviks), International Publishers, New York, 1939.
Cahm, Eric and Fisera, Vladimir Claude (eds), Socialism and Nationalism, Spokesman, Nottingham, 1978–80.
Carr, Edward Hallett, The Bolshevik Revolution: 1917–1923, in three volumes, Pelican Books, 1966.
The Interregnum 1923–1924, Penguin, Harmondsworth, 1969.
Carr, Raymond, Spain: 1808–1975, 2nd Edition, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1982.
Carrier, James G. (ed.), Meanings of the market: the free market in western culture, Berg, Oxford, 1997.
Chandler, Lester V., America’s Greatest Depression, 1929–1941, Harper & Row, New York/London, 1970.
Chang, Ha-Joon, Kicking Away the Ladder: Development Strategy in Historic Perspective, Anthem Press, London, 2002.
Bad samaritans: rich nations, poor policies and the threat to the developing world, Random House Business, London, 2007
Clark, J.B., The Distribution of Wealth: A theory of wages, interest and profits, Macmillan, New York, 1927
Cliff, Tony, Lenin: The Revolution Besieged, vol. 3, Pluto Press, London,1978.
Lenin: All Power to the Soviets, vol. 2, Pluto Press, London,1976. State Capitalism in Russia, Bookmarks, London, 1988. “Trotsky on Substitutionism”, contained in Tony Cliff, Duncan Hallas, Chris Harman and Leon Trotsky, Party and Class,Bookmarks, London, 1996. Trotsky, vol. 3, Bookmarks, London, 1991. Revolution Besieged: Lenin 1917–1923, Bookmarks, London, 1987.
Cohen, Stephan F., Bukharin and the Bolshevik Revolution, Oxford University Press, London, 1980.
“In Praise of War Communism: Bukharin’s The Economics of the Transition Period”, pp. 192–203, Revolution and politics in Russia: essays in memory of B.I. Nicolaevsky, Alexander and Janet Rabinowitch with Ladis K.D. Kristof (eds.).
Collins, Joseph and Lear, John, Chile’s Free-Market Miracle: A Second Look,Institute for Food and Development Policy, Oakland, 1995.
Communist International, Proceedings and Documents of the Second Congress1920, (in two volumes), Pathfinder, New York, 1991.
Confino, Michael (ed.), Daughter of a Revolutionary: Natalie Herzen and the Bakunin-Nechayev Circle, Library Press, LaSalle Illinois, 1973.
Cowen, Tyler, “Law as a Public Good: The Economics of Anarchy”,Economics and Philosophy, no. 8 (1992), pp. 249–267.
“Rejoinder to David Friedman on the Economics of Anarchy”, Economics and Philosophy, no. 10 (1994), pp. 329–332.
Cowling, Keith, Monopoly Capitalism, MacMillian, London, 1982.
Cowling, Keith and Sugden, Roger, Transnational Monopoly Capitalism,Wheatshelf Books, Sussez, 1987.
Beyond Capitalism: Towards a New World Economic Order, Pinter, London, 1994.
Curry, Richard O. (ed.), Freedom at Risk: Secrecy, Censorship, and Repression in the 1980s, Temple University Press, 1988.
Curtis, Mark, Web of Deceit: Britain’s real role in the world,Vintage, London, 2003.
Unpeople: Britain’s Secret Human Rights Abuses,Vintage, London, 2004.
Daniels, Robert V., The Conscience of the Revolution: Communist Opposition in Soviet Russia, Harvard UniversityPress, Cambridge, 1960.
Daniels, Robert V. (ed.), A Documentary History of Communism, vol. 1,Vintage Books, New York, 1960.
Davidson, Paul, Controversies in Post-Keynesian Economics, E. Elgar, Brookfield, Vt., USA, 1991.
John Maynard Keynes, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke, 2007
Davis, Mike, Late Victorian Holocausts: El Niño Famines and the Making of the Third World, Verso, London, 2002.
Denikin, General A., The White Armies, Jonathan Cape, London, 1930.
DeShazo, Peter, Urban Workers and Labor Unions in Chile 1902–1927,University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, 1983.
Deutscher, Isaac, The prophet unarmed : Trotsky 1921–1929, Oxford University Press, 1959.
Devine, Pat, Democracy and Economic Planning, Polity, Cambridge, 1988.
Dobbs, Maurice, Studies in Capitalist Development, Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd., London, 1963.
Dobson, Ross V. G., Bringing the Economy Home from the Market, Black Rose Books, Montreal, 1993.
Domhoff, G. William, Who Rules America Now? A view from the ‘80s, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1983.
Donaldson, Peter, A Question of Economics, Penguin Books, London, 1985.
Economics of the Real World, 3rd edition, Penguin books, London, 1984.
Dorril, Stephen and Ramsay, Robin, Smear! Wilson and the Secret State, Fourth Estate Ltd., London, 1991.
Douglass, Frederick, The Life and Writings of Frederick Douglass, vol. 2, Philip S. Foner (ed.) International Publishers, New York, 1975.
Draper, Hal, The ‘dictatorship of the proletariat’ from Marx to Lenin, Monthly Review Press, New York, 1987.
The Myth of Lenin’s “Concept of The Party”, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/draper/works/1990/myth/myth.htm
Du Boff, Richard B., Accumulation and Power: an economic history of the United States, M.E. Sharpe, London, 1989.
Dubois, Pierre, Sabotage in Industry, Penguin Books, London, 1979.
Eastman, Max, Since Lenin Died, Boni and Liveright, New York, 1925.
Eatwell, Roger and Wright, Anthony (eds.), Contemporary political ideologies, Pinter, London, 1993.
Edwards, Stewart, The Paris Commune 1871, Victorian (& Modern History) Book Club, Newton Abbot, 1972.
Edwards, Stewart (ed.), The Communards of Paris, 1871, Thames and Hudson, London, 1973.
Eisler, Rianne, Sacred Pleasure,
Ellerman, David P., Property and Contract in Economics: The Case forEconomic Democracy, Blackwell, Oxford, 1992.
The Democratic Worker-Owned Firm: A New Model for Eastand West, Unwin Hyman, Boston, 1990. as “J. Philmore”, The Libertarian Case for Slavery, available at: http://cog.kent.edu/lib/Philmore1/Philmore1.htm
Elliot, Larry and Atkinson, Dan, The Age of Insecurity, Verso, London, 1998.
Fantasy Island: Waking Up to the Incredible Economic, Political and Social Illusions of the Blair Legacy, Constable, London, 2007. The Gods That Failed: Now the Financial Elite have Gambled Away our Futures, Vintage Books, London, 2009.
Engler, Allan, Apostles of Greed: Capitalism and the myth of the individual in the market, Pluto Press, London, 1995.
Evans Jr., Alfred B., Soviet Marxism-Leninism: The Decline of an Ideology, Praeger, London, 1993.
Faiwel, G. R., The Intellectual Capital of Michal Kalecki: A study ineconomic theory and policy, University of Tennessee Press, 1975.
Farber, Samuel, Before Stalinism: The Rise and Fall of Soviet Democracy, Polity Press, Oxford, 1990.
Fedotoff-White, D., The Growth of the Red Army, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1944.
Ferguson, C. E., The Neo-classical Theory of Production and Distribution, Cambridge University Press, London, 1969.
Ferro, Marc, October 1917: A social history of the Russian Revolution, Routledge & Kegan Paul, London, 1980.
Figes, Orlando, A People’s Tragedy: The Russian Revolution 1891–1924, Jonathan Cape, London, 1996.
Peasant Russia, Civil War: the Volga countryside in revolution 1917–1921, Phoenix Press, London, 2001.
Flamm, Kenneth, Creating the Computer: Government, Industry, and High Technology, The Brookings Institution, Washington D.C., 1988.
Forgacs, David (ed.), Rethinking Italian fascism: capitalism, populismand culture, Lawrence and Wishart, London, 1986.
Fraser, Ronald, Blood of Spain: the experience of civil war, 1936–1939, Allen Lane, London, 1979.
French, Marilyn, Beyond Power: On Women, Men, and Morals , Summit Books, 1985.
Frenkel-Brunswick, Else, The Authoritarian Personality,
Friedman, David, The Machinery of Freedom, Harper and Row, New York, 1973.
Friedman, Milton, Capitalism and Freedom, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 2002.
Economic Freedom, Human Freedom, Political Freedom,available at: http://www.cbe.csueastbay.edu/~sbesc/frlect.html The Hong Kong Experiment, available at: http://www.hoover.org/publications/digest/3532186.html
Funnell, Warrick, Jupe, Robert and Andrew, Jane, In Government we Trust:Market Failure and the delusionsof privatisation, Pluto Press, London,2009.
Gaffney, Mason and Harrison, Mason, The Corruption of Economics, Shepheard-Walwyn (Publishers) Ltd., London, 1994.
Galbraith, James K., Created Unequal: The Crisis in American Pay, The Free Press, New York, 1999.
Galbraith, John Kenneth, The Essential Galbraith, Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, 2001.
The New Industrial State, 4th edition, Princeton University Press, Princeton and Oxford, 2007.
Gemie, Sharif, French Revolutions, 1815–1914, Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh, 1999.
Getzler, Israel, Kronstadt 1917–1921: The Fate of a Soviet Democracy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1983.
Martov: A Political Biography of a Russian Social Democrat, Melbourne University Press, Carlton, 1967. “Soviets as Agents of Democratisation”, in Revolution in Russia: reassessments of 1917, Edith Rogovin Frankel, Jonathan Frankel, Baruch Knei-Paz (eds.), Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/New York, 1991. “Marxist Revolutionaries and the Dilemma of Power”, pp. 88–112, Revolution and Politics in Russia, Alexander and Janet Rabinowitch with Ladis K.D. Kristof (eds.)
Gilmour, Ian, Dancing with Dogma, Britain Under Thatcherism, Simon and Schuster, London, 1992.
Glennerster, Howard and Midgley, James (eds.), The Radical Right and the Welfare State:an international assessment, Harvester Wheatsheaf,1991.
Gluckstein, Donny, The Tragedy of Bukharin, Pluto Press, London, 1994
The Paris Commune: A Revolutionary Democracy, Bookmarks,London, 2006
Glyn, Andrew, Capitalism Unleashed: Finance Globalisation and Welfare,Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2006.
Glyn, Andrew and Miliband, David (eds.), Paying for Inequality: The Economic Costs of Social Injustice, IPPR/Rivers Oram Press, London, 1994.
Goodstein, Phil H., The Theory of the General Strike from the French Revolution to Poland, East European Monographs, Boulder, 1984.
Gould, Stephan Jay, Ever Since Darwin: Reflections in Natural History,Penguin Books, London, 1991.
Bully for Brontosaurus: Reflections in Natural History, Hutchinson Radius, London, 1991.
Gramsci, Antonio, Selections from Political Writings (1921–1926), Lawrence and Wishart, London, 1978.
Grant, Ted, The Unbroken Thread: The Development of Trotskyism over 40 Years, Fortress Publications, London, 1989.
Russia from revolution to counter-revolution available at https://www.marxist.com/russia-from-revolution-to-counter-revolution.htm
Gray, John, False Dawn: The Delusions of Global Capitalism, Granta Books, London, 1998.
Green, Duncan, Silent Revolution: The Rise of Market Economics in Latin America, Cassell, London, 1995.
Greider, William, One World, Ready or Not: The Manic Logic of Global Capitalism, Penguin Books, London, 1997.
Gross, Bertram, Friendly Fascism, South End Press, Boston, 1989.
Gunn, Christopher Eaton, Workers’ Self-Management in the United States, Cornell University Press, Ithaca and London, 1984.
Gunson, P., Thompson, A. and Chamberlain, G., The Dictionary of Contemporary Politics of South America, Routledge, 1989.
Hahnel, Robin and Albert, Michael, The Quiet Revolution in Welfare Economics, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1990.
The Political Economu of Participatory Economics, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1991. Looking Forward: Participatory Economics for the Twenty First Century, South End Press, Boston, 1991.
Hallas, Duncan, The Comintern, Bookmarks, London, 1985.
“Towards a revolutionary socialist party”, contained inTony Cliff, Duncan Hallas, Chris Harman and Leon Trotsky,Party and Class, Bookmarks, London, 1996.
Harding, Neil, Leninism, MacMillan Press, London, 1996.
Lenin’s political thought, vol. 1, Macmillan, London, 1977.
Harman, Chris, Bureaucracy and Revolution in Eastern Europe, Pluto Press, London, 1974.
“Party and Class”, contained in Tony Cliff, Duncan Hallas, Chris Harman and Leon Trotsky, Party and Class,Bookmarks, London, 1996, How the revolution was lost available at: http://www.marxists.de/statecap/harman/revlost.htm
Hastrup, Kirsten, Culture and History in Medieval Iceland, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1985.
Hatch, John B., “Labour Conflict in Moscow, 1921–1925” contained in Russia in the Era of NEP: explorations in Soviet society and culture, Fitzpatrick, Sheila, Rabinowitch, Alexander and Stites, Richard (eds.), Indiana University Press, Bloomington, 1991.
Hawkins, Howard, “Community Control, Workers’ Control and the Co-operative Commonwealth”, Society and Nature, no. 3, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 55–85.
Haworth, Alan, Anti-Libertarianism: Markets, Philosophy and Myth, Routledge, London, 1994.
Hayek, F. A. von, The Essence of Hayek, Chiaki Nishiyama and Kurt Leube (Eds.), Hoover Institution Press, Stanford, 1984
Individualism and Economic Order, Henry Regnery Company, Chicago, 1948 “1980s Unemployment and the Unions” contained in Coates, David and Hillard, John (Eds.), The Economic Decline of Modern Britain: The Debate between Left and Right, Wheatsheaf Books Ltd., 1986. New Studies in Philosophy, Politics, Economics and the History of Ideas, Routledge & Kegan Paul. London/Henley, 1978. Law, Legislation and Liberty, Routledge and Kegan Paul, London, 1982.
Hayek, F. A. von (ed.), Collectivist Economic Planning, Routledge and Kegan Paul, London, 1935.
Hayward, Jack, After the French Revolution: Six critics of Democracy and Nationalism, Harvester Wheatsheaf, Hemel Hempstead, 1991.
Heider, Ulrike, Anarchism: left, right, and green, City Lights Books, San Francisco, 1994.
Hein, Eckhard and Schulten, Thorsten, Unemployment, Wages and Collective Bargaining in the European Union, WSI_Discussion Paper No. 128, Witschafts- und Sozialwissenschaftliches Institut, Dusseldorf, 2004.
Henwood, Doug, Wall Street: How it works and for whom, Verso, London, 1998.
“Booming, Borrowing, and Consuming: The US Economy in 1999”, Monthly Review, vol. 51, no. 3, July-August 1999, pp.120–33. After the New Economy, The New Press, New York, 2003. Wall Street: Class Racket, available at http://www.panix.com/~dhenwood/WS_Brecht.html
Herbert, Auberon, “Essay X: The Principles Of Voluntaryism And Free Life”, The Right And Wrong Of Compulsion By The State, And Other Essays, available at: http://oll.libertyfund.org/Texts/LFBooks/Herbert0120/CompulsionByState/HTMLs/0146_Pt11_Principles.html
“Essay III: A Politician In Sight Of Haven”, The Right And Wrong Of Compulsion By The State, And Other Essays, available at: http://oll.libertyfund.org/Texts/LFBooks/Herbert0120/CompulsionByState/HTMLs/0146_Pt04_Politician.html
Herman, Edward S., Beyond Hypocrisy, South End Press, Boston, 1992.
Corporate Control, Corporate Power, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1981. “Immiserating Growth: The First World”, Z Magazine, January, 1994. “The Economics of the Rich”, Z Magazine, July, 1997
Herman, Edward S. and Chomsky, Noam, Manufacturing Consent: the politicaleconomy of the mass media, Pantheon Books,New York, 1988.
Heywood, Paul, Marxism and the Failure of Organised Socialism in Spain 1879–1936, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1990.
Hicks, J. R., Value and capital: an inquiry into some fundamental principles of economic theory, 2nd edition, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1975.
Hills, John, Inequality and the State, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2004.
Hobsbawm, Eric, Primitive Rebels: Studies in Archaic Forms of Social Movements in the 19th and 20th Centuries, 2nd Edition, W. W. Norton and Co., New Yprk, 1965.
Revolutionaries, rev. ed., Abacus, London, 2007.
Hodgskin, Thomas, Labour Defended against the Claims of Capital, available at: http://socserv2.socsci.mcmaster.ca/~econ/ugcm/3ll3/hodgskin/labdef.txt
Hollis, Martin and Edward Nell, Rational Economic Man: A Philosophical Critique of Neo-classic Economics, Cambridge University Press, London, 1975.
Hodgson, Geoffrey Martin, Economics and Utopia: why the learning economy is not the end of history, Routledge, London/New York, 1999.
Hoppe, Hans-Hermann, Democracy: The God That Failed: The Economics andPolitics of Monarchy, Democracy, and Natural Order,Transaction, 2001.
Anarcho-Capitalism: An Annotated Bibliography, available at: http://www.lewrockwell.com/hoppe/hoppe5.html
Holt, Richard P. F. and Pressman, Steven (eds.), A New Guide to Post KeynesianEconomics, Routledge, London, 2001.
Howell, David R. (ed.), Fighting Unemployment: The Limits of Free MarketOrthodoxy, Oxford University Press, New York, 2005.
Hutton, Will, The State We’re In, Vintage, London, 1996.
The World We’re In, Little, Brown, London, 2002.
Hutton, Will and Giddens, Anthony (eds.), On The Edge: living with global capitalism,Jonathan Cape, London, 2000.
ISG, Discussion Document of Ex-SWP Comrades, available at: http://www.angelfire.com/journal/iso/isg.html
Lenin vs. the SWP: Bureaucratic Centralism Or Democratic Centralism?, available at: http://www.angelfire.com/journal/iso/swp.html
Jackson, Gabriel, The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1965.
Jackson, J. Hampden, Marx, Proudhon and European Socialism, English Universities Press, London, 1957.
Johnson, Martin Phillip, The Paradise of Association: Political Culture and Popular Organisation in the Paris Commune of 1871, University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, 1996
Kaldor, Nicholas, Further Essays on Applied Economics, Duckworth, London, 1978.
The Essential Kaldor, F. Targetti and A.P. Thirlwall (eds.), Holmes & Meier, New York, 1989. The Economic Consequences of Mrs Thatcher, Gerald Duckworth and Co. Ltd, London, 1983.
Kaplan, Frederick I., Bolshevik Ideology and the Ethics of Soviet Labour,1917–1920: The Formative Years, Peter Owen, London, 1969.
Kaplan, Temma, Anarchists of Andalusia: 1868–1903, Princeton University Press, Princeton, N.J., 1965.
Katouzian, Homa, Ideology and Method in Economics, MacMillian Press Ltd., London, 1980.
Kautsky, Karl, The road to power: political reflections on growing intothe revolution, Humanities Press, Atlantic Highlands, 1996.
Keen, Steve, Debunking Economics: The Naked Emperor of the social sciences, Pluto Press Australia, Annandale, 2001.
Keynes, John Maynard, The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, MacMillan Press, London, 1974.
Kerhohan, Andrew, “Capitalism and Self-Ownership”, from Capitalism, pp. 60–76, Paul, Ellen Frankel, Fred D. Miller Jr., Jeffrey Paul and John Ahrens (eds.), Basil Blackwood, Oxford, 1989.
Kindleberger, Charles P., Manias, Panics, and Crashes: a history of financialcrises, 2nd Edition, Macmillan, London, 1989.
King, J.E., A history of post Keynesian economics since 1936, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham, 2002
Kirzner, Israel M., “Entrepreneurship, Entitlement, and Economic Justice”, pp. 385–413, in Reading Nozick: Essays on Anarchy, State and Utopia, Jeffrey Paul (ed.), Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1982.
Perception, Opportunity, and Profit, University of ChicagoPress, Chicago, 1979.
Klein, Naomi, No Logo, Flamingo, London, 2001.
Fences and Windows: Dispatches from the front lines of theGlobalisation Debate, Flamingo, London, 2002.
Koenker, Diane P., “Labour Relations in Socialist Russia: Class Values and Production Values in the Printers’ Union, 1917–1921,” pp. 159–193, Siegelbaum, Lewis H., and Suny, Ronald Grigor (eds.), Making Workers Soviet: power, class, and identity, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, 1994.
Koenker, Diane P., Rosenberg, William G. and Suny, Ronald Grigor (eds.), Party, State, and Society in the Russian Civil War, Indiana University Press, Indiana, 1989.
Kohn, Alfie, No Contest: The Case Against Competition, Houghton Mufflin Co.,New York, 1992.
Punished by Rewards: The Trouble with Gold Stars, Incentive Plans, A’s, Praise and Other Bribes, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, 1993.
Kollontai, Alexandra, The Workers Opposition, Solidarity, London, date unknown.
Selected Writings of Alexandra Kollontai, Allison and Busby, London, 1977.
Kowalski, Ronald I., The Bolshevik Party in Conflict: the left communist opposition of 1918, Macmillan, Basingstoke, 1990.
Krause, Peter, The Battle for Homestead, 1880–1892: politics, culture, and steel, University of Pittsburgh Press, Pittsburgh/London, 1992
Krugman, Paul, Peddling Prosperity: Economic Sense and Nonsense in the Age of Diminished Expectations, NW Norton & Co., New York/London, 1994.
The Conscience of a Liberal, W.W. Norton & Co., New York/London, 2007.
Krugman, Paul and Wells, Robin, Economics, W. H. Freeman, New York, 2006.
Kuhn, Thomas S., The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, 3rd ed., University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1996.
Kuznets, Simon, Economic Growth and Structure: Selected Essays, Heineman Educational Books, London, 1966.
Capital in the American Economy, Princeton University Press, New York, 1961.
Lange, Oskar and Taylor, Fred M., On the Economic Theory of Socialism, Benjamin Lippincott (ed.), University of Minnesota Press, New York, 1938.
Laqueur, Walter (ed.), Fascism: a Reader’s Guide, Harmondsworth, Penguin, 1979.
Lazonick, William, Business Organisation and the Myth of the Market Economy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1991.
Competitive Advantage on the Shop Floor, Havard University Press, Cambridge, Mass., 1990. Organisation and Technology in Capitalist Development, Edward Elgar, Brookfield, Vt, 1992.
Lea, John and Pilling, Geoff (eds.), The condition of Britain: Essays on Frederick Engels, Pluto Press, London, 1996.
Lear, John, Workers, Neighbors, and Citizens: The Revolution in Mexico City, University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, 2001.
Lee, Frederic S., Post Keynesian Price Theory, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998
Leggett, George, The Cheka: Lenin’s Political Police, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1981.
Lenin, V. I., Essential Works of Lenin, Henry M. Christman (ed.), Bantam Books, New York, 1966.
The Lenin Anthology, Robert C. Tucker (ed.), W.W. Norton & Company, New York, 1975. Will the Bolsheviks Maintain Power?, Sutton Publishing Ltd,Stroud, 1997. Left-wing Communism: An Infantile Disorder, Lawrence & Wishart,London, 1947. The Immediate Tasks of the Soviet Government, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1970. Six Thesis on the Immediate Tasks of the Soviet Government,contained in The Immediate Tasks of the Soviet Government, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1970, pp. 42–45. The Threatening Catastrophe and How to Avoid It, Martin Lawrence Ltd., undated. Selected Works: In Three Volumes, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1975.
Lenin, V. I., and Trotsky, Leon, Kronstadt, Monad Press, New York, 1986.
Levin, Michael, Marx, Engels and Liberal Democracy, MacMillan Press, London, 1989.
Lichtenstein, Nelson and Howell, John Harris (eds.), Industrial Democracy in America: The Ambiguous Promise, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1992
Lichtheim, George, The origins of socialism, Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London, 1969
A short history of socialism, Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London, 1970
Lincoln, W. Bruce, Red Victory: A History of the Russian Civil War, Simon and Schuster, New York, 1989.
List, Friedrich, The Natural System of Political Economy, Frank Cass, London, 1983.
Lovell, David W., From Marx to Lenin: An evaluation of Marx’s responsibility for Soviet authoritarianism, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1984.
Luxemburg, Rosa, Rosa Luxemburg Speaks, Mary-Alice Waters (ed.), Pathfinder Press, New York, 1970.
MacPherson, C.B., The Political Theory of Possessive Individualism: Hobbes to Locke, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1964.
Malle, Silvana, The Economic Organisation of War Communism, 1918–1921, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1985.
Mandel, David, The Petrograd Workers and the Soviet Seizure of Power: from the July days 1917 to July 1918, MacMillan, London, 1984.
Marglin, Steven, “What do Bosses Do?”, Review of Radical Political Economy, Vol. 6, No.2, New York, 1974.
Marshall, Alfred, Principles of Economics: An Introductory Volume, 9th Edition (in 2 volumes), MacMillian, London, 1961.
Martin, Benjamin, The Agony of Modernisation: Labour and Industrialisation in Spain, ICR Press, Cornell University, 1990.
Martov, J., The State and Socialist Revolution, Carl Slienger, London, 1977.
Marx, Karl, Capital: A Critique of Political Economy, vol. 1, Penguin Books, London, 1976.
Capital: A Critique of Political Economy, vol. 3, Penguin Books, London, 1981. Theories of Surplus Value, vol. 3, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1971. A Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1970.
Marx, Karl and Engels, Frederick, Selected Works, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1975.
The Marx-Engels Reader, Second Edition,Robert C. Tucker (ed.), W.W. Norton & Co, London & New York, 1978. The socialist revolution, F. Teplov and V. Davydov (eds.)Progess, Moscow, 1978. Basic Writings on Politics and Philosophy,Lewis S. Feuer (ed.), Fontana/Collins, Aylesbury, 1984. “Manifesto of the Communist Party”, Selected Works, pp. 31–63. Fictitious Splits In The International,available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1864iwma/1872-e.htm
Marx, Karl, Engels, Federick and Lenin, V.I., Anarchism and Anarcho-Syndicalism, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1974.
Matthews, R.C.O. (ed.), Economy and Democracy, MacMillan Press Ltd., London, 1985.
McAuley, Mary, Bread and Justice: State and Society in Petrograd 1917–1922, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1991.
McElroy, Wendy, Anarchism: Two Kinds, available at:http://www.wendymcelroy.com/mises/twoanarchism.html
McLay, Farguhar (ed.), Workers City: The Real Glasgow Stands Up, Clydeside Press, Glasgow, 1988.
McNally, David, Against the Market: Political Economy, Market Socialism and the Marxist Critique, Verso, London, 1993.
Another World Is Possible: Globalization & Anti-Capitalism, Revised Expanded Edition, Merlin, 2006.
Mehring, Franz, Karl Marx: The Story of his life, John Lane, London, 1936.
Miliband, Ralph, Divided societies: class struggle in contemporary capitalism, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1989.
Mill, John Stuart, Principles of Political Economy, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1994.
On Liberty and Other Essays, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1991.
Miller, David, Social Justice, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1976.
Market, State, and community: theoretical foundations of marketsocialism, Clarendon, Oxford, 1989.
Miller, William Ian, Bloodtaking and Peacemaking: Feud, Law and Society in Saga Iceland, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1990.
Mills, C. Wright, The Power Elite, Oxford University Press, London, 1956.
Milne, S., The Enemy Within, Verso, London, 1994.
Minsky, Hyman, Inflation, Recession and Economic Policy, Wheatsheaf Books, Sussex, 1982.
“The Financial Instability Hypothesis” in Post-Keynesian Economic Theory, pp. 24–55, Arestis, Philip and Skouras, Thanos (eds.), Wheatsheaf Books, Sussex, 1985.
Mises, Ludwig von, Liberalism: A Socio-Economic Exposition,Sheed Andres and McMeek Inc., Kansas City, 1978.
Human Action: A Treatise on Economics, William Hodge and Company Ltd., London, 1949. Socialism: an economic and sociological analysis, Cape, London, 1951.
Montagu, Ashley, The Nature of Human Aggression, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1978.
Montgomery, David, Beyond Equality: Labour and the Radical Republicans, 1862–1872, Vintage Books, New York, 1967.
The Fall of the House of Labour: The Workplace, the state, and American labour activism, 1865–1925, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987.
Moore, Michael, Downsize This! Random Threats from an Unarmed America, Boxtree, London, 1997.
Morrow, Felix, Revolution and Counter-Revolution in Spain, Pathfinder Press, New York, 1974.
Mumford, Lewis, The Future of Technics and Civilisation, Freedom Press, London, 1986.
Negri, Antonio, Marx Beyond Marx, Autonomedia, Brooklyn, 1991.
Neill, A.S, Summerhill: a Radical Approach to Child Rearing, Penguin, 1985.
Newman, Stephen L., Liberalism at wit’s end: the libertarian revolt against the modern state, Cornell University Press, 1984.
Noble, David, America by Design: Science, technology, and the rise of corporate capitalism, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1979.
Progress without People: In defense of Luddism, Charles H. Kerr Publishing Ltd., Chicago, 1993. Forces of Production: A Social History of Industrial Automation, Oxford University Press, New York, 1984.
Nove, Alec, An economic history of the USSR: 1917–1991, 3rd ed., Penguin, Harmondsworth, 1992.
Socialism, Economics and Development, Allen & Unwin, London, 1986.
Nozick, Robert, Anarchy, State and Utopia, B. Blackwell, Oxford, 1974.
Oestreicher, Richard Jules, Solidarity and fragmentation: working people and class consciousness in Detroit, 1875–1900, University of Illinois Press, Urbana, 1986.
Ollman, Bertell, Social and Sexual Revolution: Essays on Marx and Reich, Black Rose Books, Montreal, 1978.
Ollman, Bertell (ed.), Market Socialism: The Debate Among Socialists, Routledge, London, 1998.
O’Neill, John, Markets, Deliberation and Environment, Routledge, Oxon, 2007.
The market: ethics, knowledge, and politics, Routledge, London, 1998 Ecology, policy, and politics: human well-being and the natural world, Routledge, London/New York, 1993.
Oppenheimer, Franz, The State, Free Life Editions, New York, 1975.
Ormerod, Paul, The Death of Economics, Faber and Faber Ltd., London, 1994.
Orwell, George, Homage to Catalonia, Penguin, London, 1989.
The Road to Wigan Pier, Penguin, London, 1954. Nineteen Eighty-Four, Penguin, Middlesex, 1982. Orwell in Spain, Penguin Books, London, 2001. Inside the Whale and Other Essays, Penguin Books, Harmondsworth, 1986.
Pagano, U. and Rowthorn, R. E. (eds.), Democracy and Efficiency in Economic Enterprises, Routledge, London, 1996.
Palley, Thomas I., Plenty of Nothing: The Downsizing of the American Dreamand the case for Structural Keynesian, Princeton UniversityPress, Princeton, 1998.
Paul, Ellen Frankel. Miller, Jr., Fred D. Paul, Jeffrey and Greenberg, Dan (eds.), Socialism, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1989.
Perrin, David A., The Socialist Party of Great Britain: Politics, Economics and Britain’s Oldest Socialist Party, Bridge Books, Wrexham, 2000.
Petras, James and Leiva, Fernando Ignacio, Democracy and Poverty in Chile: The Limits to Electoral Politics, Westview Press, Boulder, 1994.
Pipes, R., Russia Under the Bolshevik Regime, 1919–1924, Fontana Press, London, 1995.
Pirani, Simon, The Russian revolution in retreat, 1920–24: Soviet workers and the new Communist elite, Routledge, New York, 2008
Phillips, Kevin, The Politics of Rich and Poor: Wealth and the American Electorate in the Reagan Aftermath, Random House, New York, 1990.
Polanyi, Karl, The Great Transformation: the political and economic origins of our time, Beacon Press, Boston, 1957.
Popper, Karl, Conjectures and Refutations: The Growth of Scientific Knowledge, Basic, New York, 1965.
Preston, Paul, The coming of the Spanish Civil War: reform, reaction, and revolution in the Second Republic, 2nd ed., Routledge, London/New York, 1994.
Preston, Paul (ed.), Revolution and War in Spain 1931–1939, Methuen, London, 1984.
Prychitko, David L., Markets, Planning and Democracy: essays after the collapse of communism, Edward Elgar, Northampton, 2002.
Rabinowitch, Alexander, Prelude to Revolution: The Petrograd Bolsheviks and the July 1917 Uprising, Indiana University Press, Bloomington, 1991.
The Bolsheviks Come to Power: The Revolution of 1917 in Petrograd, W.W. Norton & Co., New York, 1976. The Bolsheviks in Power: The first year of Soviet rule in Petrograd, Indiana University Press, Bloomington, 2007. “Early Disenchantment with Bolshevik Rule: New Data form the Archives of the Extraordinary Assembly of Delegates from Petrograd Factories”, Politics and Society under the Bolsheviks, Dermott, Kevin and Morison, John (eds.), Macmillan, Basingstoke, 1999.
Rabinowitch, Alexander and Janet with Kristof, Ladis K.D. (eds.), Revolution and politics in Russia: essays in memory of B.I. Nicolaevsky, Indiana University Press for the International Affairs Center, Bloomington/London, 1973.
Radcliff, Pamela Beth, From mobilization to civil war: the politics of polarizationin the Spanish city of Gijon, 1900–1937, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1996.
Radin, Paul, The World of Primitive Man, Grove Press, New York, 1960.
Radek, Karl, The Kronstadt Uprising available at, https://www.marxists.org/archive/radek/1921/04/kronstadt.htm
Raleigh, Donald J., Experiencing Russia’s Civil War: Politics, Society,and Revolutionary Culture in Saratov, 1917–1921,Princeton University Press, Woodstock, 2002.
Rand, Ayn, Capitalism: The Unknown Ideal, New American Library, New York, 1966.
The Ayn Rand Lexicon: Objectivism from A to Z, Harry Binswanger (ed.), Meridian, New York, 1986. The Virtue of Selfishness, New American Library, New York, 1964.
Ransome, Arthur, The Crisis in Russia 1920, Redwords, London, 1992.
Rayack, Elton, Not So Free To Choose: The Political Economy of MiltonFriedman and Ronald Reagan, Praeger, New York, 1987.
Read, Christopher, From Tsar to Soviets: The Russian people andtheir revolution, 1917–21, UCL Press, London, 1996.
Reed, John, Ten Days that shook the World, Penguin Books, 1982.
Shaking the World: John Reed’s revolutionary journalism,Bookmarks, London, 1998.
Reekie, W. Duncan, Markets, Entrepreneurs and Liberty: An Austrian Viewof Capitalism, Wheatsheaf Books Ltd., Sussex, 1984.
Reich, Wilhelm, The Mass Psychology of Fascism, Condor Book, Souvenir Press (E&A) Ltd., USA, 1991.
Reitzer, George, The McDonaldization of Society: An Investigation into the changing character of contemporary social life, Pine Forge Press, Thousand Oaks, 1993.
Remington, Thomas F., Building Socialism in Bolshevik Russia: Ideology and Industrial Organisation 1917–1921, University of Pittsburgh Press, London, 1984.
Richardson, Al (ed.), In defence of the Russian revolution: a selection of Bolshevik writings, 1917–1923, Porcupine Press, London, 1995.
Ricardo, David, The Principles of Political Economy and Taxation, J.M. Dent & Sons/Charles E. Tuttle Co., London/Vermont, 1992.
Ridgeway, James, Blood in the Face: The Ku Klux Klan, Aryan Nations, Nazi Skinheads, and the Rise of a New White Culture, Thunder’s Mouth Press, 1990.
Roberts, David D., The Syndicalist Tradition and Italian Fascism,University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, 1979.
Robertson, Dennis, “Wage-grumbles”, Economic Fragments, pp. 42–57, in W. Fellner and B. Haley (eds.), Readings in the theoryof income distribution, The Blakiston, Philadephia, 1951.
Robinson, Joan, The Accumulation of Capital (2nd Edition), MacMillan, St. Martin’s Press, 1965.
Contributions to Modern Economics, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1978. Collected Economic Papers, vol. 4, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1973. Collected Economic Papers, vol. 5, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1979.
Rodrik, Dani, Comments on ‘Trade, Growth, and Poverty by D. Dollar and A. Kraay, available at: http://ksghome.harvard.edu/~drodrik/Rodrik%20on%20Dollar-Kraay.PDF
Rollins, L.A., The Myth of Natural Rights, Loompanics Unlimited, Port Townsend, 1983.
Rose, Steven, Lewontin, R.C. and Kamin, Leon J., Not in Our Genes: Biology, Ideology and Human Nature, Penguin Books, London, 1990.
Rosenberg, William G., “Russian Labour and Bolshevik Power, pp. 98–131, The Workers Revolution in Russia: the view from below, D. Kaiser (ed.), Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987.
“Workers’ Control on the Railroads and Some Suggestions Concerning Social Aspects of Labour Politics in the Russian Revolution”, pp. D1181-D1219, The Journal of Modern History, vol. 49, no. 2.
Rosmer, Alfred, Lenin’s Moscow, Bookmarks, London, 1987.
Rosnick, David and Weisbrot, Mark, Are Shorter Work Hours Good for the Environment? A Comparison of U.S. and European Energy Consumption, available at: http://www.cepr.net/documents/publications/energy_2006_12.pdf
Rothbard, Murray N., The Ethics of Liberty, Humanities Press, Atlantic Highlands, N.J., 1982.
For a New Liberty, MacMillan, New York, 1973. “Praxeology: The Methodology of Austrian Economics” in The Foundation of Modern Austrian Economics, pp. 19–39,Dolan, Edwin G. (ed.), Sheed & Ward, Inc., Kansas, 1976. Egalitarianism as a Revolt against Nature and Other Essays, Libertarian Press Review, 1974. “Nations by Consent: Decomposing the Nation-State,”in Secession, State and Liberty, David Gordon (ed.),Transaction Publishers, New Brunswick, 1998. Power and Market, Institute for Humane Studies,Menlo Park, 1970. Man, Economy, and State, with Power and Market, Ludwig von Mises Institute, Auburn, 2004. “Society Without A State”, pp. 191–207, Anarchism: Nomos XIX, J. Roland Pennock and John W. Chapman (eds.), New York University Press, New York, 1978. America’s great depression, Van Nostrand, Princeton/London, 1963. Conceived in Liberty (in four volumes), Arlington House Publishers,New Rochell, 1975. The Logic of Action II: Applications and Criticism from the Austrian School, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham/Lyme, 1997. Classical Economics: An Austrian Perspective on the Historyof Economic Thought, Edward Elgar, Brookfield, 1995. Konkin on Libertarian Strategy, available at:http://www.anthonyflood.com/rothbardkonkin.htm Are Libertarian’s ‘Anarchists’?, available at: http://www.lewrockwell.com/rothbard/rothbard167.html
Rousseau, J-J, The Social Contract and Discourses, Everyman, London, 1996.
Rowbotham, Sheila, Hidden from History: 300 Years of Women’s Oppression and the fight against it, Pluto Press, London, 1977.
“Edward Carpenter: Prophet of the New Life”, Rowbotham, Sheila and Weeks, Jeffrey, Socialism and the New Life: The Personal and Sexual Politics of Edward Carpenter and Havelock Ellis, Pluto Press, London 1977.
RSDLP, Minutes of the Second Congress of the RSDLP, New ParkPublications, London, 1978.
St. Clair, David, The Motorization of American Cities, Praeger, New York, 1986.
Sakwa, Richard, Soviet Communists in Power: a study of Moscow during the Civil War, 1918–21, Macmillan, Basingstoke, 1987.
Sawyer, Malcolm C., The Economics of Michal Kalecki, MacMillan, Basingstoke,1985.
The Economics of Industries and Firms: theories, evidence and policy (2nd ed.), Croom Helm, London, 1985.
Schapiro, Leonard, The Origin of the Communist Autocracy: PoliticalOpposition in the Soviet State: The First Phase, 1917–1922, Frederick A. Praeger, New York, 1965.
Schlosser, Eric, Fast Food Nation: What the all-american meal is doing to the world, Allen Lane, London, 2001.
Schneider, Cathy Lisa, Shantytown protest in Pinochet’s Chile, Temple University Press, Philadelphia, 1995.
Schor, Juliet B., The Overworked American: The Unexpected Decline of Leisure, BasicBooks, New York, 1992.
Schorske, C., German Social Democracy, 1905–1917, Cambridge, Mass., 1955.
Schulkind, Eugene (ed.), The Paris Commune of 1871: The View from the Left, Jonathan Cape, London, 1972.
Schumacher, E.F., Small is Beautiful: A Study of Economics as if people mattered, Vintage, London, 1993.
Schweickart, David Against Capitalism, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1993.
After Capitalism, Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, inc., Lanham, 2002.
Sen, Amartya, Resources, Values and Development, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1984.
Development as Freedom, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1999.
Senior, Nassau, An Outline of the Science of Political Economy, Alan & Unwin, London, 1951
Serge, Victor, Memoirs of a Revolutionary 1901–41, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1963.
Revolution in Danger: Writings from Russia, 1919–1921, Redwords, London, 1997. Year One of the Russian Revolution, Bookmarks, Pluto Press and Writers and Readers, London/New York, 1992. The Serge-Trotsky Papers, D. J. Cotterill (ed.), Pluto Press, London, 1994 Anarchists Never Surrender: Essays, Polemics, and Correspondence on Anarchism, 1908–1938, PM Press, Oakland, 2015. The Life and Death of Leon Trotsky, Haymarket Books, Chicago, 2016
Service, Robert, The Bolshevik Party in Revolution: A Study of Organisational change, Macmillan, London, 1979.
Silk L., and Vogel, D., Ethics and Profits: The Crisis of Confidence in American Business, Simon and Schuster, New York, 1976.
Sirianni, Carmen, Workers’ Control and Socialist Democracy, Verso/NLB, London, 1982.
Shanin, Teodor, The Awkward Class: Political Sociology of Peasantry in a Developing Society: Russia 1910–1925, OxfordUniversity Press, London, 1972.
Skidelsky, Robert (ed.), Thatcherism, Chatto & Windus, London, 1988.
Skidmore, Thomas E. and Smith, Peter H., Modern Latin America, Second Edition, Oxford University Press, 1989.
Smith, Adam, The Wealth of Nations, Everyman’s Library, London, 1991.
The Wealth of Nations, book 5, contained in An Inquiry intothe Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations: A SelectedEdition, Oxford University Press, Oxford/New York, 1998.
Smith, S.A., Red Petrograd: Revolution in the Factories 1917–1918, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1983.
Revolution and the People in Russia and China: A Comparative History, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2008. Russia in Revolution: An Empire in Crisis, 1890–1928, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2017.
Solvason, Birgir T. Runolfsson, Ordered Anarchy, State and Rent-seeking: The Iceland Commonwealth, 930–1262, available at http://www.hag.hi.is/~bthru/ritgerd.htm
Sorel, Georges, Reflections on Violence, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1999.
Sorenson, Jay B., The Life and Death of Soviet Trade Unionism: 1917–1928, Atherton Press, New York, 1969.
Spriano, Paolo, The Occupation of the Factories: Italy 1920, Pluto Press, London, 1975.
Staub, Ervin, The Roots of Evil: The Origins of Genocide and Other Group Violence, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000
Stauber, John, and Sheldon Rampton, Toxic Sludge is good for you! Lies, Damn Lies and the Public Relations Industry, Common Courage Press, Monroe, Maine, 1995.
Steinberg, I., Spiridonova: revolutionary terrorist, Methuen, London, 1935.
Steinbeck, John, The Grapes of Wrath, Mandarin, London, 1990.
Stewart, Michael, Keynes in the 1990s: A Return to Economic Sanity, Penguin Books, London, 1993.
Keynes and After, 3rd edition, Penguin Books, London, 1987.
Stiglitz, Joseph, Globalisation and its Discontents, Penguin Books, London, 2002.
Stretton, Hugh, Economics: A New Introduction, Pluto Press, London, 2000.
Suny, Ronald Grigor (ed.), The Structure of Soviet History: Essays and Documents, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2003
Swain, Geoffrey, The Origins of the Russian Civil War, Longman, London/New York, 1996.
Sweezy, Paul, Theory of Capitalist Development, Monthly Review Press, New York, 1942.
Targetti, Ferdinando, Nicholas Kaldor: The Economics and Politics of Capitalism as a Dynamic System, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1992.
Taylor, M. W., Men versus the state: Herbert Spencer and late Victorian individualism,Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1992.
Taylor, Michael W. (ed.), Herbert Spencer and the Limits of the State: The LateNineteenth-Century Debate Between Individualism andCollectivism, St. Augustine’s Press, 1997.
Thomas, Hugh, The Spanish Civil War, Hamish Hamilton, London, 1986.
Thomas, Paul, Karl Marx and the Anarchists, Routledge & Kegan Paul plc,London, 1985.
Tomlins, Christopher L., Law, Labor, and Ideology in the Early American Republic, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1993.
Thompson, E.P., The Making of the English Working Class, Penguin Books, London, 1991.
Customs in Common, Penguin Books, London, 1993.
Thompson, Noel, The Real Rights of Man: Political Economies for the Working Class, 1775–1850, Pluto Press, London, 1998.
Ticktin, Hillel and Cox, Michael (eds.), The Ideas of Leon Trotsky, Porcupine Press, London, 1995.
Tokes, Rudolf L., Bela Kun and the Hungarian Soviet Republic: The Origins and Role of the Communist Party of Hungary in the Revolutions of 1918–1919, Pall Mall Press, London, 1967.
Trotsky, Leon, History of the Russian Revolution, in three volumes, Gollancz and Sphere Books, London, 1967.
Writings of Leon Trotsky: Supplement (1934–40), Pathfinder Press, New York, 1979. Writings 1936–37, Pathfinder Press, New York, 1978. Writings 1933–34, Pathfinder Press, New York, 2003. Writings 1932, Pathfinder Press, New York, 1999. Writings 1930–31, Pathfinder Press, New York, 2002. Writings 1930, Pathfinder Press, New York, 2003. Terrorism and Communism, Ann Arbor, 1961. The Revolution Betrayed: What is the Soviet Union and where is it going?, Faber and Faber Ltd, London, 1937. Leon Trotsky Speaks, Pathfinder, New York, 1972. How the Revolution Armed: the military writings and speeches of Leon Trotsky, vol. I, New Park Publications, London, 1979. How the Revolution Armed: the military writings and speeches of Leon Trotsky, vol. II, New Park Publications, London, 1979. How the Revolution Armed: the military writings and speeches of Leon Trotsky, vol. IV, New Park Publications, London, 1979. Stalin: An Appraisal of the man and his influence, in two volumes, Panther History, London, 1969. The Death Agony of Capitalism and the Tasks of the Fourth International, contained in How Solidarity can change the world, Alliance for Workers’ Liberty, London, 1998. First Year Years of the Communist International, (in 2 volumes), New Park Publications, London, 1974. The Third International After Lenin, Pioneer Publishers, New York, 1957. The Challenge of the Left Opposition (1923–25), Pathfinder Press, New York, 1975. The Challenge of the Left Opposition (1926–27), Pathfinder, New York, 1980. On Lenin: Notes towards a Biography, George G. Harrap & Co. Ltd., London, 1971. “Lessons of October”, pp. 113–177, The Essential Trotsky, Unwin Books, London, 1963. Leon Trotsky on China, Monad Press, New York, 2002 In Defense of Marxism, Pathfinder, New York, 1995. Platform of the Opposition, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1927-plo/ch01.htm The Lessons of October, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1924-les.htm How Did Stalin Defeat the Opposition?, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1935-sta.htm Work, Discipline, Order, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1918-mil/ch05.htm More Equality! available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1919-mil/ch12.htm The Revolution Betrayed, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1936-rev/index.htm The Class Nature of the Soviet State, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/sovstate.htm The Path of the Red Army, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1918-mil/ch02.htm The Moralists and Sycophants against Marxism, contained in Their Morals and Ours, pp. 53–66, Pathfinder, New York, 1973. The Makhno Movement, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1919-mil/ch49.htm Stalinism and Bolshevism, available at:http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1937/1937-sta.htm
Turner, Adai, Just Capital: The Liberal Economy, Pan Books, London, 2002.
Utton, M. A., The Political Economy of Big Business, Martin Robinson, Oxford, 1982.
van der Linden, Marcel, Western Marxism and the Soviet Union : a survey of critical theories and debates since 1917Brill, Leiden, 2007
Wade, Robert, Governing the Market: Economic Theory and the role of governmentin East Asian Industrialisation, Princeton University Press,Princeton, 1990.
Walford, George, George Walford on Anarcho-Capitalism, available at http://flag.blackened.net/liberty/walford-on-anarcap.html
Wallerstein, Immanuel, Geopolitics and Geoculture, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1991.
The Capitalist World System (vol. 1),
Walras, L, Elements of Pure Political Economy, Allen and Unwin, London, 1954.
Ward, Benjamin, What’s Wrong with Economics?, Basic Books, New York, 1972
Ware, Norman, The Industrial Worker 1840–1860: The Reaction of American IndustrialSociety to the Advance of the Industrial Revolution, Elephant Paperbacks, Chicago, 1924.
Watson, Andrew, From Red to Green: Green Politics and environmentalism cannot save the environment. A socialist politics can,Privately Published, 1990.
Weisbrot, Mark, Globalisation for Whom?, available at: http://www.cepr.net/Globalization.html
Weisbrot, Mark, Baker, Dean, Kraev, Egor and Chen, Judy,The Scorecard on Globalization 1980–2000: Twenty Years of Diminished Progress,available at: http://www.cepr.net/publications/globalization_2001_07_11.htm
Weisbrot, Mark, Baker, Dean, Naiman, Robert and Neta, Gila, Growth May Be Good for the Poor — But are IMF and World Bank Policies Good for Growth? available at: http://www.cepr.net/publications/econ_growth_2001_05.htm
Weisbrot, Mark and Rosnick, David, Another Lost Decade?: Latin America’s Growth Failure Continues into the 21st Century, available at: http://www.cepr.net/publications/latin_america_2003_11.htm
Wilkinson, Richard and Pickett, Kate, The Spirit Level: Why More Equal Societies Almost Always Do Better, Allen Lane, London, 2009.
Williams, Gwyn A., Proletarian Order: Antonio Gramsci, factory councils and the origins of Italian Communism, 1911–1921, Pluto Press, London, 1975.
Artisans and Sans-Culottes: Popular Movements in France and Britain during the French Revolution, Edward Arnold, London, 1981.
Wilson, H., The Labour Government 1964–1970, London, 1971.
Wilkinson, Richard and Pickett, Kate, The Spirit Level: Why More Equal SocietiesAlmost Always Do Better, Allen Lane, London,2009.
Winn, Peter (ed.), Victims of the Chilean Miracle: Workers and Neoliberalism in the Pinochet Era, 1973–2002, Duke University Press, Durham and London, 2004.
Wolff, Edward N., Top Heavy: A Study of Increasing Inequality in America, Twentieth Century Fund, 1995
Wolff, Jonathan, Robert Nozick: Property, Justice and the Minimal State, Polity Press, Oxford, 1991.
Wray, L. Randall, Money and Credit in Capitalist Economies: the endogenousmoney approach, Aldershot, Elgar, 1990.
Zinoviev, Grigorii, History of the Bolshevik Party: A Popular Outline, New Park Publications, London, 1973.
#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#faq#anarchy faq#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate crisis#climate#ecology#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blog Post #10 (Week 12)
1. How have online communities evolved in terms of economic viability, as well as what challenges have emerged from these developments?
Online communities, initially debated for their economic viability, have evolved into major business ventures. As noted by Armstrong & Hagel, these communities, once seen as uncertain investments, have grown into lucrative markets, leading to the creation of products like The Online Community Report, which aids community creators in navigating challenges such as fluctuating venture capital & maintaining user engagement (1997). A key debate in the community sector is how to generate revenue, with some, like Jim Cashel (2000), suggesting the implementation of subscriber fees, while others have even profited by selling online communities for millions (Cashel, 1999). However, this shift toward monetization has led to a dilemma: the balance between profit and genuine community engagement. Janelle Brown (1999) pointed out that the pursuit of financial gain often results in the neglect of community maintenance and development, as seen in the failure of platforms like GeoCities, Xoom, and theglobe.com, which, despite being branded as community hubs, failed to foster meaningful user empowerment or connection.
2. How do ethnic online communities (EOCs) both reinforce & challenge stereotypes?
Ethnic online communities like BlackPlanet.com, MiGente.com, & AsianAvenue.com have provided spaces where users can express their identities in ways that are both reflective of & even resistant to mainstream stereotypes. As described in the text, members of these communities often choose usernames that embody certain cultural or racial stereotypes, such as “FineAssAznGurl” on AsianAvenue.com or *blacklatindiva* on MiGente.com. While these names might seem to perpetuate stereotypical representations, they are also a form of self-expression within a community that is designed to highlight ethnic pride & identity. This dynamic brings to mind Nakamura’s (1999) concept of “identity tourism,” where stereotypes are commodified by outsiders, but in this context, members of these ethnic communities might be reclaiming & reappropriating stereotypes as a form of empowerment. Yet the implications for user empowerment are mixed: on one hand, these communities provide a sense of belonging & the opportunity to challenge dominant narratives. On the other hand, the commercial pressures & the use of stereotypes within these spaces can undermine the deeper purpose of cultural empowerment.
3. What are the benefits and challenges of online communities in empowering marginalized groups, as demonstrated by the activism within AsianAvenue.com, & how do these examples illustrate the potential of online spaces to influence real-world change?
Online communities, like AsianAvenue.com, exhibit cases like the Moy family seeking a bone marrow donor for their daughter & the successful protest against the MSNBC headline during the 1998 Winter Olympics. They illustrate how online spaces can mobilize people for social causes, creating real-world impact. In the Moy family’s case, the community's online organizing helped raise awareness and led to a matching donor in Singapore, even though it was ultimately too late. This story underscores the power of digital solidarity & shows that online communities can serve as platforms for collective action that extend into offline, tangible results.
4. How does the Gamergate movement detail the complexities of online activism, particularly in terms of its stated goals versus its underlying motivations?
The #Gamergate movement provides a case study of how online activism can be driven by contradictory motivations, & how its publicly stated goals often result in more harmful, underlying intentions. On the surface, Gamergate participants framed their movement as a fight for journalistic ethics in video game journalism. They argued that game writers were too close to game developers & that their professional relationships compromised the integrity of the reporting. However, this stance was quickly complicated by the movement's actions & rhetoric. For example, some sought reform in how game journalism was conducted, but the movement's actions suggest the ethics were pushed to the side in favor of personal online attacks. Plenty of the initial energy behind #Gamergate was centered on targeting Zoë Quinn, an indie game developer who became a central figure in the controversy. Chat logs released from various 4chan boards reveal that many early participants focused on harassing her, making comments about her physical appearance, personal life, & even fantasizing about her harm. The rhetoric, which included misogynistic & violent language, highlighted that the movement's primary focus was not on ethical reform but on punishing Quinn, particularly because of her identity as a woman & her status as an underrepresented voice in the gaming industry.
Ayers, M. D., & McCaughey, M. (2014). Cyberactivism: Online activism in theory and Practice. Routledge.
Hathaway, J. (n.d.). What is Gamergate, and why? an explainer for Non-Geeks – Tech mistake. Gawker. https://www.gawkerarchives.com/what-is-gamergate-and-why-an-explainer-for-non-geeks-1642909080
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think, however, while we can talk about how Japanese society sees things differently in the West due to different cultural values, this also ignores the current state of Japan. Or at least, the political state of Japan during the time of Houses' release, when Japan's Prime Minister was Shinzo Abe.
Abe, who was considered a Japanese nationalist with a revisionist view of Japan's history. He wanted to make Japan great again. Who unsuccessfully sought to amend article 9 of Japan's constitution, the part that renounces war, in order to remilitarize. People argue his economic policies were a failure, or that he incited hate towards South Koreans, minorities and people in poverty. He was also involved with the Moonie church, which got him assassinated.
It's not like Japanese media isn't afraid of him either. When Tomino made Reconguista in G, part of it was in response to the administrations attempts to remilitarize, especially considering the reason why Tomino started calling out the mecha genre even before Gundam with Zambot 3. The plot of IBO s1 the following year also saw the protagonists putting a corrupt politician back into office after he was forced to leave due to a corruption scandal, much like Abe's first time as PM, but there's more to it than that as the protagonists end up being seen as the bad guys, their memorial monument defaced by those seeking justice, after they tried to take over the world (with the director's faction of the staff saying they were punished for their crimes). Persona 5 was meant to reflect Japanese social issues, and Shido is often seen as being based on Abe. Likewise, Yakuze Like a Dragon's Ryo Aoki's Bleach Japan movement has a lot of the same energy. Senator Armstrong in Metal Gear Rising wants to reinvigorate the war economy to MAGA.
I mean, when Hopes dropped people in Asia were saying it must have been written by a guy with right-leaning tenancies because of how more pro-Edelgard it came off as. She's the most hated character in the Korean fanbase, the Chinese fanbase treat her supporters as “those fans,” and Japan itself saw her as the villain of Houses. Then you look at Hopes, where the guy in charge of the BE route said he picked them because they looked like they would reunify Fodlan.
So I think there might be something to this theory, but it's a context lost in the West because Abe had a better image over here.
And, look, I'm not going to go so far as to say that the creators of Hopes are on the Japanese right. Hopes is supposed to be a game of bad endings for Fodlan in comparison to Houses, it's a sideshow not the main attraction, only you'd have to be intimately familiar with Houses to get this. Silver Snow is, and always will be, the only good route for the Black Eagles class of the four options. But taken on it's own? In a game that's supposed to be fanservice for Houses' fans? It does come across that way.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Believe it or not, Americans want a fair election. One side is using never-before-seen tactics to secure the vote, such as installing a new nominee without securing a single nomination in the primaries and permitting illegal aliens to vote. A recent poll shows that both Republicans and Democrats want a fair election that includes requiring voter ID.
The latest Gallup poll found that an overwhelming 84% of all Americans believe photo identification should be required to vote. Then, 83% of all Americans believe first-time voters must provide proof of citizenship. Americans want to determine the outcome of their own election, but the government continues to ignore the will of the people.
Democrats were less likely to demand proof of citizenship, but still, the majority (66%) believe it should be required. The majority of the left (67%) also believe photo identification cannot be overlooked. Republicans naturally see that illegal migrants will vote against their party. Why would anyone vote against the party that has provided them a taxpayer-subsidized life in a new nation where they are not required to assimilate nor are they held to the same legal code as citizens. Of no surprise, 98% of Republicans are demanding proof of citizenship, and 96% want to see a photo ID. About 84% of Independents support both measures.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

By: Brandy Shufutinsky
Published: Jan 23, 2024
Until about 160 years ago Black American labor was used to benefit the few, especially a small group of privileged white landowners. Today, we are still being used. Progressive academics, activists, and political leaders are constantly exploiting Black Americans as living, breathing excuses for policies that benefit progressives and their constituents but fail Black people.
Chicago Mayor Brandon Johnson has set his sights on eliminating high-achieving magnet schools in the name of equity. Currently, academically gifted students from low socioeconomic backgrounds are able to compete for entrance into high-achieving schools. One need not guess why some Black parents welcome this opportunity for their children. After all, only 17% of Black students are proficient in reading and even fewer (7%) demonstrate proficiency in math. Moreover, in 2022, fewer than 10% of Black third-grade students and just under 11% of low-income third-grade students could read at grade level. These dismal figures entail that a great many talented Black students in Chicago must suffer through classes geared not to them but to their illiterate and innumerate peers. Magnet schools offer these talented students a way out. One would think that policy makers committed to providing access to quality education for all students, not just the ones whose parents were able to send them to private schools, would increase the number of high-achieving schools, rather than eliminate them.
So, why would Mayor Johnson want to eliminate one of the few opportunities for gifted but economically disadvantaged students to access quality education? Well, according to Chicago Public Schools Board CEO, Pedro Martinez, allowing gifted students access to quality education causes “stratification and inequity in Chicago Public Schools.” One has to wonder whether this excuse (as incoherent as it is) is sincere or whether it reflects instead a cynical push to discard selective schools that have proven to be top-tier nationally because these schools compete directly with the union-led public school system.
In Portland, Oregon education leaders are planning to roll out a system of equitable grading that calls for teachers to consider “non-academic factors” when grading student work. Portland Public School Chief Academic Officer Kimberlee Armstrong, a supporter of the policy, argues that in order to address “biases” educators must, wait for it, engage in bias themselves, by “considering the diverse backgrounds and needs of students.��� Just how does considering background rather than correct answers and knowledge acquisition reduce bias?
Oregon’s student literacy rates are slightly better than Chicago’s but still fewer than half of students read at grade level, with Black student literacy hovering around 26%. Yet rather than provide students with the necessary resources to achieve basic literacy, Oregon policymakers are simply eliminating any method of measuring student achievement.
We must ask ourselves, who gets lost in educational politicking? Students who desire a quality education are being sacrificed at the altar of progressive policies that do them more harm than good. When I was in the third grade my teacher suggested I be tested for the Gifted and Talented Education (GATE) program. I was attending an under-resourced, high-poverty school where the majority of students qualified for the free-lunch program, including me. My GATE score allowed me access to all of the resources that I would otherwise have missed because my socioeconomic circumstance did not allow for tutors or extracurricular activities, let alone private school tuition. Fast-forward a few decades and instead of providing support for students who find themselves in a situation similar to mine, policy makers are relegating them to mediocrity.
Who benefits from policies that disenfranchise the most vulnerable students? Many organizations that claim to work to improve student achievement by using equity-based practices have sprouted up over recent years. They offer services to school districts, providing teacher training and curricular materials with a stated goal not of teaching students the knowledge and skills they need to succeed but of “building social justice starting in the classroom.” These organizations are very successful in using our public schools to build their client base and sell their obviously political goals of equity and social justice. When it comes to improving student achievement, however, their results are dismal. Policies that eliminate access to quality education, lower standards and reframe what knowledge is will not help Black students, it will harm them. Politicizing education by lowering expectations is a racist endeavor that denies Black Americans the credit they rightly deserve for overcoming obstacles and reaching the highest levels of success. It’s the bigotry of low expectations.

Brandy Shufutinsky is a social worker, writer, researcher, and advocate. She holds her Doctorate in International and Multicultural Education from the University of San Francisco, her MSW from the University of Southern California, and her MA in International Relations from the University of San Diego. Dr. Shufutinsky has worked towards advancing the rights of victims and survivors of domestic violence and sexual assault through practice, education, and research, and is now focusing her advocacy on developing intercultural and academic opportunities to enhance liberal democratic ideals as the director of education and community engagement with the Jewish Institute for Liberal Values. Follow her on Twitter.
==
This is what "equity" does. In order to force everybody to have equal outcomes, it has to eliminate the ability for people to overachieve or exceed others. Because that would make people jealous and would be "unfair." It can't make everybody an Elon Musk, but it can make everybody a Joe Schlub. And so "equity" always results in the lowest of the lowest common denominators. When you inevitably use force to ensure that happens, that's how you get Russia and China.
The people activists who are putting in these policies are the exact same people who put in the policies that caused this illiteracy and innumeracy in the first place.
#Brandy Shufutinsky#Brandon Johnson#equity#magnet school#literacy#numeracy#bigotry of low expectations#corruption of education#education#equitable grading#inequity#racial bias#wokeness#woke#wokeism#cult of woke#wokeness as religion#religion is a mental illness
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
〰️ Lo-Wav Delay 〰️ (LWD for short)
Another Role Swap AU!? The idea initially sparked after seeing @gorochuva 's Vandelay Sibling swap and I wanted to push it further. I know @magmalaz also has a role swap au, but it'd be weird for me not to share mine when I mentioned it in my playlist post. So here we go. 🙃
What's This All About?
Roxanne and Kale lead Vandelay Technologies together, with Kale developing SPECTRA in secret. Unlike in canon, Roxanne discovers it early on and fires Kale on the spot.
The corporate culture at Vandelay is healthier than canon, but there's an undercurrent of unease. Misbehaving employees return from Human Resources listless, robotic. It has not escaped Kale's notice. He looks into it, discovering to his horror that Roxanne revived SPECTRA and that she plans to include it inside Project Armstrong applicants' prosthetics.
Kale and his team has a month to shut down SPECTRA before Project Armstrong launches. Assuming they can get their act together.
The Protagonists
Mimosa, Social Media Account Manager for Vandelay Tech and a former pop star. Assumes Chai's role. She joins the team after an interrupted HR referral. (Girl dodged a bullet.)
Kale Vandelay , disgraced former Vice President. The Peppermint to Mimosa's Chai and 1/2 of Mission control (shared with Roquefort). An important detail to note is that none of his teammates knows he created SPECTRA in the beginning.
Roquefort, retired economic advisor and Kale's business mentor. He hasn't been converted into a robo-werewolf so he is... fragile.
W01F-G4NG, Roquefort's robotic service dog (commissioned by Kale). 100% Certified Good Boy. Like 808, Wolfie acts as Roquefort's eyes and ears on the field in addition to being the squad telephone.
Zanzo, an eccentric engineer evading disciplinary measures by hiding in a storage area he converted into an office. He's in Macaron's role, but with Korsica's mechanics. Zanzo alternates between a walker and wheelchair because of his Cerebral Palsy (headcanon go brr). He doesn't have cybernetics as he can't afford them.
Rekka, a Production supervisor with a near flawless conduct and output records. The Korsica of the team (with similar mechanics to Macaron), as she needs further convincing to go against Vandelay.
Also a secret temporary teammate who I'm not going to name. 🤫
The Antagonists
Roxanne Vandelay, founder and CEO of Vandelay Technologies. Assumes Kale's role. Foils Mimosa in a similar way to Chai and Kale.
Chai, newly hired Brand Ambassador for the pending Project Armstrong. Works closely with the Head Of Marketing. Might still have musical and magnetism powers, only on purpose this time.
808, pretty much the same except she can turn into a panther mech.
Peppermint Vandelay, favored younger Vandelay sibling (according to Kale). Officially on record as a programmer, but her role in the company is closer to VP. Peppermint heads Vandelay Tech's "secret security force" which consists of her, 808, Chai, Macaron, CNMN, and Korsica.
Macaron, Head of Research and Development.
CNMN is considered the co head of R&D. He also helps out in Human Resources.
Korsica, heads Security after the previous head quit without notice. She's still getting used to her position six months on.
Also OC department heads for Production, Marketing, Finance, and Human Resources
The AU Name
Hi-Fi RUSH -> Lo-Wav Delay
Subtle reference to Ultra Low Frequency. Definition: Ultra Low Frequency (ULF) is a low frequency electromagnetic wave band that can penetrate the earth. It's used for communications in mines and might aid in predicting earthquakes in the future.
If LWD were a game, I see its gameplay as being more stealth and social engineering based. Also puzzles and Space Channel Five type rhythm sections (since Mimosa is the player character).
#hi-fi rush#hfr#hfr mimosa#hfr kale#hfr roquefort#hfr zanzo#hfr rekka#role swap au#lo-wav delay#i'm not going to tag all the characters I mentioned for brevity's sake
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
ISLAM 101: WOMEN IN ISLAM: Part 1
Women and the Qur’anic Prescriptions
One of the most sensitive and oft-debated issues with regard to Islam concerns the status and role of women in society. Arguably one of the aspects of social life which the emergence of Islam affected most was the status of women, with “the Qur’an hav[ing] more to say about the position of women than any other social question.”
At the time of its revelation in the seventh century, the Qur’an exacted considerable change in Arabian society regarding the question of women and continued to do so in the centuries that followed. The principles outlined in the Qur’an which determine the lives of Muslim women can be outlined in several distinct terms. These include the social, spiritual and economic status of women. In order to discuss the multiple nature of Islam’s reformations to the position of women, an exploration of pre-Islamic Arabian society, especially its sociopolitical, economic and religious landscape, and a comparison to Qur’anic principles are required.
The social milieu that provided the background for the emergence of Islam in Arabia is described by Muslims in one term: Jahiliyya, or The Age of Ignorance.
Armstrong argues that this term was not used to define a historical era but to illustrate the spirit that pervaded this time of “spiritual and moral crisis,” thus referring “to a state of mind that caused violence and terror in seventh-century Arabia.” Women were not exempt from this violence and social crisis: infanticide, the burying alive of baby girls, was rife; the marriage was not sanctioned; women did not have the right of inheritance and bequest; they were not treated fairly during divorce, and women were not afforded full control of their wealth. It is in placing the Qur’an and its principles against the backdrop of such a setting that the reformist spirit of Islam, which restores the true human character, can be seen.
One of the most important principles detailed in the Qur’an which regulates the lives of Muslim women is the spiritual status assigned to women. Viewed by Muslims as the literal word of God, the Qur’an is taken to be the means through which God makes Himself known and describes His laws.
When Islam emerged in tribal Arabia, religion reflected the tribal nature of society and its social structure. Polytheism and idolatry were dominant, with the Ka‘ba, the shrine revered since the time of Abraham, housing 360 idols. Families banded together to form clans and clans came together to form tribes; tribal allegiance was the most important factor governing an individual’s position in society.
One of the points discussed with reference to women in pre-Islamic society is the level of their participation in religious rites and traditions. Some have argued that, while being seen as improving the rights of women, the advent of Islam, in fact, restricted them.
However, in his discussion of the feminine in Islamic mysticism, Elias locates the chief reason for women’s involvement in soothsaying, Blackmagic and such occupations, as being women’s exclusion from religion. Islam’s emergence drastically altered the spiritual landscape of Arabia for women. One of the most important principles outlined in the Qur’an is the notion of religious, moral and spiritual, obligations being incumbent upon all individuals, regardless of sex.
The Qur’an states, for example: “Those who submit to God and accept the true Faith; who are devout, sincere, patient, humble charitable, and chaste; who fast and are ever mindful of God-on these, both men and women, God will bestow forgiveness and a rich recompense.”
The Qur’an clearly rejects any such notion of the “inherent” evil of woman. It explicitly demands respect for her “inherent” good as potential child-bearer (and primary nurturer). It places her on absolute par with men in terms of the spiritual potential (to know and serve Allah) and the potential to attain Paradise, provided she and he strive to realize such potential.
The Qur’anic principle of spiritual and moral obligation has meant that women, from the very early days of Islam, have played an essential role, not just in practicing the faith and engaging in Islamic mysticism, but also in writing the official history of Islam and compiling foundational works establishing the standards of religious and social practice for Islamic society.
Another essential principle pertaining to women which is woven through the fabric of the Qur’an is that of marriage. The Qur’an defines marriage as a contract between man and woman, with both assuming equal, though not identical, places. It sees the institution and the sexual relations between husband and wife not as shameful, but as commendable:
By another sign, He created for you spouses from among yourselves, that you might live in peace with them, and planted love and kindness in your hearts.
The status of women and the family in Islamic society was thus the product chiefly of Qur’anic prescriptions, which endure in affecting the lives of Muslim women.
#Allah#god#islam#quran#muslim#revert#revert islam#convert#convert islam#converthelp#reverthelp#revert help#revert help team#help#islam help#salah#dua#prayer#pray#reminder#religion#mohammad#muslimah#hijab#new muslim#new revert#new convert#how to convert to islam#convert to islam#welcome to islam
4 notes
·
View notes