#AI-powered estimating tools
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
what’s the story about the generative power model and water consumption? /gen
There's this myth going around about generative AI consuming truly ridiculous amount of power and water. You'll see people say shit like "generating one image is like just pouring a whole cup of water out into the Sahara!" and bullshit like that, and it's just... not true. The actual truth is that supercomputers, which do a lot of stuff, use a lot of power, and at one point someone released an estimate of how much power some supercomputers were using and people went "oh, that supercomputer must only do AI! All generative AI uses this much power!" and then just... made shit up re: how making an image sucks up a huge chunk of the power grid or something. Which makes no sense because I'm given to understand that many of these models can run on your home computer. (I don't use them so I don't know the details, but I'm told by users that you can download them and generate images locally.) Using these models uses far less power than, say, online gaming. Or using Tumblr. But nobody ever talks about how evil those things are because of their power generation. I wonder why.
To be clear, I don't like generative AI. I'm sure it's got uses in research and stuff but on the consumer side, every effect I've seen of it is bad. Its implementation in products that I use has always made those products worse. The books it writes and flood the market with are incoherent nonsense at best and dangerous at worst (let's not forget that mushroom foraging guide). It's turned the usability of search engines from "rapidly declining, but still usable if you can get past the ads" into "almost one hundred per cent useless now, actually not worth the effort to de-bullshittify your search results", especially if you're looking for images. It's a tool for doing bullshit that people were already doing much easier and faster, thus massively increasing the amount of bullshit. The only consumer-useful uses I've seen of it as a consumer are niche art projects, usually projects that explore the limits of the tool itself like that one poetry book or the Infinite Art Machine; overall I'd say its impact at the Casual Random Person (me) level has been overwhelmingly negative. Also, the fact that so much AI turns out to be underpaid people in a warehouse in some country with no minimum wage and terrible labour protections is... not great. And the fact that it's often used as an excuse to try to find ways to underpay professionals ("you don't have to write it, just clean up what the AI came up with!") is also not great.
But there are real labour and product quality concerns with generative AI, and there's hysterical bullshit. And the whole "AI is magically destroying the planet via climate change but my four hour twitch streaming sesh isn't" thing is hysterical bullshit. The instant I see somebody make this stupid claim I put them in the same mental bucket as somebody complaining about AI not being "real art" -- a hatemobber hopping on the hype train of a new thing to hate and feel like an enlightened activist about when they haven't bothered to learn a fucking thing about the issue. And I just count my blessings that they fell in with this group instead of becoming a flat earther or something.
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
Saw a tweet that said something around:
"cannot emphasize enough how horrid chatgpt is, y'all. it's depleting our global power & water supply, stopping us from thinking or writing critically, plagiarizing human artists. today's students are worried they won't have jobs because of AI tools. this isn't a world we deserve"
I've seen some of your AI posts and they seem nuanced, but how would you respond do this? Cause it seems fairly-on point and like the crux of most worries. Sorry if this is a troublesome ask, just trying to learn so any input would be appreciated.
i would simply respond that almost none of that is true.
'depleting the global power and water supply'
something i've seen making the roudns on tumblr is that chatgpt queries use 3 watt-hours per query. wow, that sounds like a lot, especially with all the articles emphasizing that this is ten times as much as google search. let's check some other very common power uses:
running a microwave for ten minutes is 133 watt-hours
gaming on your ps5 for an hour is 200 watt-hours
watching an hour of netflix is 800 watt-hours
and those are just domestic consumer electricty uses!
a single streetlight's typical operation 1.2 kilowatt-hours a day (or 1200 watt-hours)
a digital billboard being on for an hour is 4.7 kilowatt-hours (or 4700 watt-hours)
i think i've proved my point, so let's move on to the bigger picture: there are estimates that AI is going to cause datacenters to double or even triple in power consumption in the next year or two! damn that sounds scary. hey, how significant as a percentage of global power consumption are datecenters?
1-1.5%.
ah. well. nevertheless!
what about that water? yeah, datacenters use a lot of water for cooling. 1.7 billion gallons (microsoft's usage figure for 2021) is a lot of water! of course, when you look at those huge and scary numbers, there's some important context missing. it's not like that water is shipped to venus: some of it is evaporated and the rest is generally recycled in cooling towers. also, not all of the water used is potable--some datacenters cool themselves with filtered wastewater.
most importantly, this number is for all data centers. there's no good way to separate the 'AI' out for that, except to make educated guesses based on power consumption and percentage changes. that water figure isn't all attributable to AI, plenty of it is necessary to simply run regular web servers.
but sure, just taking that number in isolation, i think we can all broadly agree that it's bad that, for example, people are being asked to reduce their household water usage while google waltzes in and takes billions of gallons from those same public reservoirs.
but again, let's put this in perspective: in 2017, coca cola used 289 billion liters of water--that's 7 billion gallons! bayer (formerly monsanto) in 2018 used 124 million cubic meters--that's 32 billion gallons!
so, like. yeah, AI uses electricity, and water, to do a bunch of stuff that is basically silly and frivolous, and that is broadly speaking, as someone who likes living on a planet that is less than 30% on fire, bad. but if you look at the overall numbers involved it is a miniscule drop in the ocean! it is a functional irrelevance! it is not in any way 'depleting' anything!
'stopping us from thinking or writing critically'
this is the same old reactionary canard we hear over and over again in different forms. when was this mythic golden age when everyone was thinking and writing critically? surely we have all heard these same complaints about tiktok, about phones, about the internet itself? if we had been around a few hundred years earlier, we could have heard that "The free access which many young people have to romances, novels, and plays has poisoned the mind and corrupted the morals of many a promising youth."
it is a reactionary narrative of societal degeneration with no basis in anything. yes, it is very funny that laywers have lost the bar for trusting chatgpt to cite cases for them. but if you think that chatgpt somehow prevented them from thinking critically about its output, you're accusing the tail of wagging the dog.
nobody who says shit like "oh wow chatgpt can write every novel and movie now. yiou can just ask chatgpt to give you opinions and ideas and then use them its so great" was, like, sitting in the symposium debating the nature of the sublime before chatgpt released. there is no 'decay', there is no 'decline'. you should be suspicious of those narratives wherever you see them, especially if you are inclined to agree!
plagiarizing human artists
nah. i've been over this ad infinitum--nothing 'AI art' does could be considered plagiarism without a definition so preposterously expansive that it would curtail huge swathes of human creative expression.
AI art models do not contain or reproduce any images. the result of them being trained on images is a very very complex statistical model that contains a lot of large-scale statistical data about all those images put together (and no data about any of those individual images).
to draw a very tortured comparison, imagine you had a great idea for how to make the next Great American Painting. you loaded up a big file of every norman rockwell painting, and you made a gigantic excel spreadsheet. in this spreadsheet you noticed how regularly elements recurred: in each cell you would have something like "naturalistic lighting" or "sexually unawakened farmers" and the % of times it appears in his paintings. from this, you then drew links between these cells--what % of paintings containing sexually unawakened farmers also contained naturalistic lighting? what % also contained a white guy?
then, if you told someone else with moderately competent skill at painting to use your excel spreadsheet to generate a Great American Painting, you would likely end up with something that is recognizably similar to a Norman Rockwell painting: but any charge of 'plagiarism' would be absolutely fucking absurd!
this is a gross oversimplification, of course, but it is much closer to how AI art works than the 'collage machine' description most people who are all het up about plagiarism talk about--and if it were a collage machine, it would still not be plagiarising because collages aren't plagiarism.
(for a better and smarter explanation of the process from soneone who actually understands it check out this great twitter thread by @reachartwork)
today's students are worried they won't have jobs because of AI tools
i mean, this is true! AI tools are definitely going to destroy livelihoods. they will increase productivty for skilled writers and artists who learn to use them, which will immiserate those jobs--they will outright replace a lot of artists and writers for whom quality is not actually important to the work they do (this has already essentially happened to the SEO slop website industry and is in the process of happening to stock images).
jobs in, for example, product support are being cut for chatgpt. and that sucks for everyone involved. but this isn't some unique evil of chatgpt or machine learning, this is just the effect that technological innovation has on industries under capitalism!
there are plenty of innovations that wiped out other job sectors overnight. the camera was disastrous for portrait artists. the spinning jenny was famously disastrous for the hand-textile workers from which the luddites drew their ranks. retail work was hit hard by self-checkout machines. this is the shape of every single innovation that can increase productivity, as marx explains in wage labour and capital:
“The greater division of labour enables one labourer to accomplish the work of five, 10, or 20 labourers; it therefore increases competition among the labourers fivefold, tenfold, or twentyfold. The labourers compete not only by selling themselves one cheaper than the other, but also by one doing the work of five, 10, or 20; and they are forced to compete in this manner by the division of labour, which is introduced and steadily improved by capital. Furthermore, to the same degree in which the division of labour increases, is the labour simplified. The special skill of the labourer becomes worthless. He becomes transformed into a simple monotonous force of production, with neither physical nor mental elasticity. His work becomes accessible to all; therefore competitors press upon him from all sides. Moreover, it must be remembered that the more simple, the more easily learned the work is, so much the less is its cost to production, the expense of its acquisition, and so much the lower must the wages sink – for, like the price of any other commodity, they are determined by the cost of production. Therefore, in the same manner in which labour becomes more unsatisfactory, more repulsive, do competition increase and wages decrease”
this is the process by which every technological advancement is used to increase the domination of the owning class over the working class. not due to some inherent flaw or malice of the technology itself, but due to the material realtions of production.
so again the overarching point is that none of this is uniquely symptomatic of AI art or whatever ever most recent technological innovation. it is symptomatic of capitalism. we remember the luddites primarily for failing and not accomplishing anything of meaning.
if you think it's bad that this new technology is being used with no consideration for the planet, for social good, for the flourishing of human beings, then i agree with you! but then your problem shouldn't be with the technology--it should be with the economic system under which its use is controlled and dictated by the bourgeoisie.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Green energy is in its heyday.
Renewable energy sources now account for 22% of the nation’s electricity, and solar has skyrocketed eight times over in the last decade. This spring in California, wind, water, and solar power energy sources exceeded expectations, accounting for an average of 61.5 percent of the state's electricity demand across 52 days.
But green energy has a lithium problem. Lithium batteries control more than 90% of the global grid battery storage market.
That’s not just cell phones, laptops, electric toothbrushes, and tools. Scooters, e-bikes, hybrids, and electric vehicles all rely on rechargeable lithium batteries to get going.
Fortunately, this past week, Natron Energy launched its first-ever commercial-scale production of sodium-ion batteries in the U.S.
“Sodium-ion batteries offer a unique alternative to lithium-ion, with higher power, faster recharge, longer lifecycle and a completely safe and stable chemistry,” said Colin Wessells — Natron Founder and Co-CEO — at the kick-off event in Michigan.
The new sodium-ion batteries charge and discharge at rates 10 times faster than lithium-ion, with an estimated lifespan of 50,000 cycles.
Wessells said that using sodium as a primary mineral alternative eliminates industry-wide issues of worker negligence, geopolitical disruption, and the “questionable environmental impacts” inextricably linked to lithium mining.
“The electrification of our economy is dependent on the development and production of new, innovative energy storage solutions,” Wessells said.
Why are sodium batteries a better alternative to lithium?
The birth and death cycle of lithium is shadowed in environmental destruction. The process of extracting lithium pollutes the water, air, and soil, and when it’s eventually discarded, the flammable batteries are prone to bursting into flames and burning out in landfills.
There’s also a human cost. Lithium-ion materials like cobalt and nickel are not only harder to source and procure, but their supply chains are also overwhelmingly attributed to hazardous working conditions and child labor law violations.
Sodium, on the other hand, is estimated to be 1,000 times more abundant in the earth’s crust than lithium.
“Unlike lithium, sodium can be produced from an abundant material: salt,” engineer Casey Crownhart wrote in the MIT Technology Review. “Because the raw ingredients are cheap and widely available, there’s potential for sodium-ion batteries to be significantly less expensive than their lithium-ion counterparts if more companies start making more of them.”
What will these batteries be used for?
Right now, Natron has its focus set on AI models and data storage centers, which consume hefty amounts of energy. In 2023, the MIT Technology Review reported that one AI model can emit more than 626,00 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent.
“We expect our battery solutions will be used to power the explosive growth in data centers used for Artificial Intelligence,” said Wendell Brooks, co-CEO of Natron.
“With the start of commercial-scale production here in Michigan, we are well-positioned to capitalize on the growing demand for efficient, safe, and reliable battery energy storage.”
The fast-charging energy alternative also has limitless potential on a consumer level, and Natron is eying telecommunications and EV fast-charging once it begins servicing AI data storage centers in June.
On a larger scale, sodium-ion batteries could radically change the manufacturing and production sectors — from housing energy to lower electricity costs in warehouses, to charging backup stations and powering electric vehicles, trucks, forklifts, and so on.
“I founded Natron because we saw climate change as the defining problem of our time,” Wessells said. “We believe batteries have a role to play.”
-via GoodGoodGood, May 3, 2024
--
Note: I wanted to make sure this was legit (scientifically and in general), and I'm happy to report that it really is! x, x, x, x
#batteries#lithium#lithium ion batteries#lithium battery#sodium#clean energy#energy storage#electrochemistry#lithium mining#pollution#human rights#displacement#forced labor#child labor#mining#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
AI Reminder
Quick reminder folks since there's been a recent surge of AI fanfic shite. Here is some info from Earth.org on the environmental effects of ChatGPT and it's fellow AI language models.
"ChatGPT, OpenAI's chatbot, consumes more than half a million kilowatt-hours of electricity each day, which is about 17,000 times more than the average US household. This is enough to power about 200 million requests, or nearly 180,000 US households. A single ChatGPT query uses about 2.9 watt-hours, which is almost 10 times more than a Google search, which uses about 0.3 watt-hours.
According to estimates, ChatGPT emits 8.4 tons of carbon dioxide per year, more than twice the amount that is emitted by an individual, which is 4 tons per year. Of course, the type of power source used to run these data centres affects the amount of emissions produced – with coal or natural gas-fired plants resulting in much higher emissions compared to solar, wind, or hydroelectric power – making exact figures difficult to provide.
A recent study by researchers at the University of California, Riverside, revealed the significant water footprint of AI models like ChatGPT-3 and 4. The study reports that Microsoft used approximately 700,000 litres of freshwater during GPT-3’s training in its data centres – that’s equivalent to the amount of water needed to produce 370 BMW cars or 320 Tesla vehicles."
Now I don't want to sit here and say that AI is the worst thing that has ever happened. It can be an important tool in advancing effectiveness in technology! However, there are quite a few drawbacks as we have not figured out yet how to mitigate these issues, especially on the environment, if not used wisely. Likewise, AI is not meant to do the work for you, it's meant to assist. For example, having it spell check your work? Sure, why not! Having it write your work and fics for you? You are stealing from others that worked hard to produce beautiful work.
Thank you for coming to my Cyn Talk. I love you all!
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive (Updated daily!)
Researchers report that a new AI tool enhances the diagnostic process, potentially identifying more individuals who need care. Previous diagnostic studies estimated that 7 percent of the population suffers from long COVID. However, a new study using an AI tool developed by Mass General Brigham indicates a significantly higher rate of 22.8 percent.
The AI-based tool can sift through electronic health records to help clinicians identify cases of long COVID. The often-mysterious condition can encompass a litany of enduring symptoms, including fatigue, chronic cough, and brain fog after infection from SARS-CoV-2.
The algorithm used was developed by drawing de-identified patient data from the clinical records of nearly 300,000 patients across 14 hospitals and 20 community health centers in the Mass General Brigham system. The results, published in the journal Med, could identify more people who should be receiving care for this potentially debilitating condition.
“Our AI tool could turn a foggy diagnostic process into something sharp and focused, giving clinicians the power to make sense of a challenging condition,” said senior author Hossein Estiri, head of AI Research at the Center for AI and Biomedical Informatics of the Learning Healthcare System (CAIBILS) at MGB and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. “With this work, we may finally be able to see long COVID for what it truly is — and more importantly, how to treat it.”
For the purposes of their study, Estiri and colleagues defined long COVID as a diagnosis of exclusion that is also infection-associated. That means the diagnosis could not be explained in the patient’s unique medical record but was associated with a COVID infection. In addition, the diagnosis needed to have persisted for two months or longer in a 12-month follow-up window.
Precision Phenotyping: A Novel Approach The novel method developed by Estiri and colleagues, called “precision phenotyping,” sifts through individual records to identify symptoms and conditions linked to COVID-19 to track symptoms over time in order to differentiate them from other illnesses. For example, the algorithm can detect if shortness of breath results from pre-existing conditions like heart failure or asthma rather than long COVID. Only when every other possibility was exhausted would the tool flag the patient as having long COVID.
“Physicians are often faced with having to wade through a tangled web of symptoms and medical histories, unsure of which threads to pull, while balancing busy caseloads. Having a tool powered by AI that can methodically do it for them could be a game-changer,” said Alaleh Azhir, co-lead author and an internal medicine resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
The new tool’s patient-centered diagnoses may also help alleviate biases built into current diagnostics for long COVID, said researchers, who noted diagnoses with the official ICD-10 diagnostic code for long COVID trend toward those with easier access to healthcare.
The researchers said their tool is about 3 percent more accurate than the data ICD-10 codes capture, while being less biased. Specifically, their study demonstrated that the individuals they identified as having long COVID mirror the broader demographic makeup of Massachusetts, unlike long COVID algorithms that rely on a single diagnostic code or individual clinical encounters, skewing results toward certain populations such as those with more access to care.
“This broader scope ensures that marginalized communities, often sidelined in clinical studies, are no longer invisible,” said Estiri.
Limitations and Future Directions Limitations of the study and AI tool include the fact that health record data the algorithm uses to account for long COVID symptoms may be less complete than the data physicians capture in post-visit clinical notes. Another limitation was the algorithm did not capture the possible worsening of a prior condition that may have been a long COVID symptom. For example, if a patient had COPD that worsened before they developed COVID-19, the algorithm might have removed the episodes even if they were long COVID indicators. Declines in COVID-19 testing in recent years also makes it difficult to identify when a patient may have first gotten COVID-19.
The study was limited to patients in Massachusetts.
Future studies may explore the algorithm in cohorts of patients with specific conditions, like COPD or diabetes. The researchers also plan to release this algorithm publicly on open access so physicians and healthcare systems globally can use it in their patient populations.
In addition to opening the door to better clinical care, this work may lay the foundation for future research into the genetic and biochemical factors behind long COVID’s various subtypes. “Questions about the true burden of long COVID — questions that have thus far remained elusive — now seem more within reach,” said Estiri.
Reference: “Precision phenotyping for curating research cohorts of patients with unexplained post-acute sequelae of COVID-19” by Alaleh Azhir, Jonas Hügel, Jiazi Tian, Jingya Cheng, Ingrid V. Bassett, Douglas S. Bell, Elmer V. Bernstam, Maha R. Farhat, Darren W. Henderson, Emily S. Lau, Michele Morris, Yevgeniy R. Semenov, Virginia A. Triant, Shyam Visweswaran, Zachary H. Strasser, Jeffrey G. Klann, Shawn N. Murphy and Hossein Estiri, 8 November 2024, Med. DOI: 10.1016/j.medj.2024.10.009 www.cell.com/med/fulltext/S2666-6340(24)00407-0?_returnURL=https%3A%2F%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%2Fretrieve%2Fpii%2FS2666634024004070%3Fshowall%3Dtrue
#long covid#covid is airborne#mask up#public health#pandemic#covid#wear a respirator#wear a mask#covid 19#coronavirus#covid is not over#covid conscious#still coviding#sars cov 2
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
The cryptocurrency hype of the past few years already started to introduce people to these problems. Despite producing little to no tangible benefits — unless you count letting rich people make money off speculation and scams — Bitcoin consumed more energy and computer parts than medium-sized countries and crypto miners were so voracious in their energy needs that they turned shuttered coal plants back on to process crypto transactions. Even after the crypto crash, Bitcoin still used more energy in 2023 than the previous year, but some miners found a new opportunity: powering the generative AI boom. The AI tools being pushed by OpenAI, Google, and their peers are far more energy intensive than the products they aim to displace. In the days after ChatGPT’s release in late 2022, Sam Altman called its computing costs “eye-watering” and several months later Alphabet chairman John Hennessy told Reuters that getting a response from Google’s chatbot would “likely cost 10 times more” than using its traditional search tools. Instead of reassessing their plans, major tech companies are doubling down and planning a massive expansion of the computing infrastructure available to them.
[...]
As the cloud took over, more computation fell into the hands of a few dominant tech companies and they made the move to what are called “hyperscale” data centers. Those facilities are usually over 10,000 square feet and hold more than 5,000 servers, but those being built today are often many times larger than that. For example, Amazon says its data centers can have up to 50,000 servers each, while Microsoft has a campus of 20 data centers in Quincy, Washington with almost half a million servers between them. By the end of 2020, Amazon, Microsoft, and Google controlled half of the 597 hyperscale data centres in the world, but what’s even more concerning is how rapidly that number is increasing. By mid-2023, the number of hyperscale data centres stood at 926 and Synergy Research estimates another 427 will be built in the coming years to keep up with the expansion of resource-intensive AI tools and other demands for increased computation. All those data centers come with an increasingly significant resource footprint. A recent report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that the global energy demand of data centers, AI, and crypto could more than double by 2026, increasing from 460 TWh in 2022 to up to 1,050 TWh — similar to the energy consumption of Japan. Meanwhile, in the United States, data center energy use could triple from 130 TWh in 2022 — about 2.5% of the country’s total — to 390 TWh by the end of the decade, accounting for a 7.5% share of total energy, according to Boston Consulting Group. That’s nothing compared to Ireland, where the IEA estimates data centers, AI, and crypto could consume a third of all power in 2026, up from 17% in 2022. Water use is going up too: Google reported it used 5.2 billion gallons of water in its data centers in 2022, a jump of 20% from the previous year, while Microsoft used 1.7 billion gallons in its data centers, an increase of 34% on 2021. University of California, Riverside researcher Shaolei Ren told Fortune, “It’s fair to say the majority of the growth is due to AI.” But these are not just large abstract numbers; they have real material consequences that a lot of communities are getting fed up with just as the companies seek to massively expand their data center footprints.
9 February 2024
#ai#artificial intelligence#energy#big data#silicon valley#climate change#destroy your local AI data centre
74 notes
·
View notes
Text



editorial from the english version of the Hankyoreh
archive link
plain text
Before focusing on my master’s thesis, I worked for a brief period for an organization supporting victims of cyber sex crimes. My job was to put each and every case of illegally filmed footage assigned to me through a search engine and if I found that the images had been uploaded to certain sites, I would beg the operator of that site to take those images down.
The process of searching and subsequently scrubbing illegally filmed footage probably isn’t what most people would expect. There is no advanced AI that categorizes footage based on the faces of victims, lists the sites the footage is uploaded to, and sends automated requests for the deletion of such posts. Instead, employees and volunteers divide each reported video frame by frame, put each fragmented frame through search engines, organize each site the footage is posted to on a spreadsheet, collate the sites for verification, find the site operator’s email or contact channel, and write a message that read, “This video is illegally filmed footage so we ask that you remove it from your site. If it is not removed, the South Korean government may take action against the site pursuant to relevant laws,” translate it from Korean into English and then send it to the operator.
This happened daily. Sometimes, you would have to go through 100 or 200 cases a day. I’ve assigned a nickname to this procedure: “The Illegally Filmed Footage Removal Protocol that Seems Absurdly Advanced, But Basically Follows the Same Grueling Procedures as a Sweatshop.”
The biggest challenge when fighting digital sex crimes is their overwhelming breadth and scale. It was impossible for us, as we sat in front of our computer screens, to estimate which far-out depths of the internet any of the footage had reached.
Even if we painstakingly found 20 posts using a particular photo and saw that every post was erased, the next day we would see the photo spring up in 40 different posts. Websites distributing illegally filmed footage make various backup sites with different domains to make sure that sites are up and running even if the main site is taken down.
Many of the sites in question have servers based abroad, so even if you sent a beseeching email citing South Korean laws, they simply could just pretend that they never saw the email.
The terror of that vast scope goes beyond distribution and duplication. While deepfake pornography has been in the news recently, photoshopping a real person’s face onto a pornographic image has been a crime for some time now.
The difference is that producing such images used to be time-consuming and technically challenging, requiring the “manual” manipulation of images. But the new tool of AI has made it easy for anyone to instantaneously create deepfakes in a dizzying variety of formats.
Another frightening aspect is that anyone with access to photographs on social media can choose victims at random. And since the images are “fakes” created by AI, the perpetrator can deliberately duck the guilt of harming a real person.
Deepfake creation has spread so rapidly because it gives perpetrators a perverse sense of power over their victims — the ability to create dozens of humiliating images of someone from photographs scraped off Instagram — while also enabling them to ignore victims’ suffering because the images aren’t technically “real.” In short, deepfakes represent a game-changing acceleration of the production cycle of sexually exploitative media.
Those images spread far too fast for the handful of employees at nonprofits to keep up with. Facing such a vast challenge, permanent employees began to drift away, and their positions were once again filled by people on short-term contracts.
Lee Jun-seok, a lawmaker with the Reform Party, said during a meeting of the National Assembly’s Science, ICT, Broadcasting and Communications Committee that the 220,000 members of a deepfake channel on Telegram was an “overblown threat” and estimated that, given the percentage of Korean users on Telegram, only about 726 of the channel members are actually Koreans.
But what does it matter whether there are 220,000 Koreans on the channel or just 726?
Let’s suppose there aren’t even 726, but just 10 people in the group — they could still produce 220,000 deepfakes if they set their mind to it. Those images would then be copied and circulated beyond their point of origin and around the world, perhaps remaining permanently in some dark corners of the Internet without ever being deleted.
That’s the nature of sex crimes in the digital age.
So assuming that the criminal potential of this technology remains the same regardless of whether the channel has 220,000 members, 726 members or even just 10, I can’t help wondering what Lee thinks would be an acceptable number of deepfake purveyors that would not constitute an “overblown threat.”
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Amazon’s Alexa has been claiming the 2020 election was stolen
The popular voice assistant says the 2020 race was stolen, even as parent company Amazon promotes the tool as a reliable election news source -- foreshadowing a new information battleground

This is a scary WaPo article by Cat Zakrzewski about how big tech is allowing AI to get information from dubious sources. Consequently, it is contributing to the lies and disinformation that exist in today's current political climate.
Even the normally banal but ubiquitous (and not yet AI supercharged) Alexa is prone to pick up and recite political disinformation. Here are some excerpts from the article [color emphasis added]:
Amid concerns the rise of artificial intelligence will supercharge the spread of misinformation comes a wild fabrication from a more prosaic source: Amazon’s Alexa, which declared that the 2020 presidential election was stolen. Asked about fraud in the race — in which President Biden defeated former president Donald Trump with 306 electoral college votes — the popular voice assistant said it was “stolen by a massive amount of election fraud,” citing Rumble, a video-streaming service favored by conservatives.
The 2020 races were “notorious for many incidents of irregularities and indications pointing to electoral fraud taking place in major metro centers,” according to Alexa, referencing Substack, a subscription newsletter service. Alexa contended that Trump won Pennsylvania, citing “an Alexa answers contributor.”
Multiple investigations into the 2020 election have revealed no evidence of fraud, and Trump faces federal criminal charges connected to his efforts to overturn the election. Yet Alexa disseminates misinformation about the race, even as parent company Amazon promotes the tool as a reliable election news source to more than 70 million estimated users. [...] Developers “often think that they have to give a balanced viewpoint and they do this by alternating between pulling sources from right and left, thinking this is going to give balance,” [Prof. Meredith] Broussard said. “The most popular sources on the left and right vary dramatically in quality.” Such attempts can be fraught. Earlier this week, the media company the Messenger announced a new partnership with AI company Seekr to “eliminate bias” in the news. Yet Seekr’s website characterizes some articles from the pro-Trump news network One America News as “center” and as having “very high” reliability. Meanwhile, several articles from the Associated Press were rated “very low.” [...] Yet despite a growing clamor in Congress to respond to the threat AI poses to elections, much of the attention has fixated on deepfakes. However, [attorney Jacob] Glick warned Alexa and AI-powered systems could “potentially double down on the damage that’s been done.” “If you have AI models drawing from an internet that is filled with platforms that don’t care about the preservation of democracy … you’re going to get information that includes really dangerous undercurrents,” he said. [color emphasis added]
#alexa#ai is spreading political misinformation#2020 election lies#the washington post#cat zakrzewski#audio
166 notes
·
View notes
Text
As digital scamming explodes in Southeast Asia, including so called “pig butchering” investment scams, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) issued a comprehensive report this week with a dire warning about the rapid growth of this criminal ecosystem. Many digital scams have traditionally relied on social engineering, or tricking victims into giving away their money willingly, rather than leaning on malware or other highly technical methods. But researchers have increasingly sounded the alarm that scammers are incorporating generative AI content and deepfakes to expand the scale and effectiveness of their operations. And the UN report offers the clearest evidence yet that these high tech tools are turning an already urgent situation into a crisis.
In addition to buying written scripts to use with potential victims or relying on templates for malicious websites, attackers have increasingly been leaning on generative AI platforms to create communication content in multiple languages and deepfake generators that can create photos or even video of nonexistent people to show victims and enhance verisimilitude. Scammers have also been expanding their use of tools that can drain a victim’s cryptocurrency wallets, have been manipulating transaction records to trick targets into sending cryptocurrency to the wrong places, and are compromising smart contracts to steal cryptocurrency. And in some cases, they’ve been purchasing Elon Musk’s Starlink satellite internet systems to help power their efforts.
“Agile criminal networks are integrating these new technologies faster than anticipated, driven by new online marketplaces and service providers which have supercharged the illicit service economy,” John Wojcik, a UNODC regional analyst, tells WIRED. “These developments have not only expanded the scope and efficiency of cyber-enabled fraud and cybercrime, but they have also lowered the barriers to entry for criminal networks that previously lacked the technical skills to exploit more sophisticated and profitable methods.”
For years, China-linked criminals have trafficked people into gigantic compounds in Southeast Asia, where they are often forced to run scams, held against their will, and beaten if they refuse instructions. Around 200,000 people, from at least 60 countries, have been trafficked to compounds largely in Myanmar, Cambodia, and Laos over the last five years. However, as WIRED reporting has shown, these operations are spreading globally—with scamming infrastructure emerging in the Middle East, Eastern Europe, Latin America, and West Africa.
Most prominently, these organized crime operations have run pig butchering scams, where they build intimate relationships with victims before introducing an “investment opportunity” and asking for money. Criminal organizations may have conned people out of around $75 billion through pig butchering scams. Aside from pig butchering, according to the UN report, criminals across Southeast Asia are also running job scams, law enforcement impersonation, asset recovery scams, virtual kidnappings, sextortion, loan scams, business email compromise, and other illicit schemes. Criminal networks in the region earned up to $37 billion last year, UN officials estimate. Perhaps unsurprisingly, all of this revenue is allowing scammers to expand their operations and diversify, incorporating new infrastructure and technology into their systems in the hope of making them more efficient and brutally effective.
For example, scammers are often constrained by their language skills and ability to keep up conversations with potentially hundreds of victims at a time in numerous languages and dialects. However, generative AI developments within the last two years—including the launch of writing tools such as ChatGPT—are making it easier for criminals to break down language barriers and create the content needed for scamming.
The UN’s report says AI can be used for automating phishing attacks that ensnare victims, the creation of fake identities and online profiles, and the crafting of personalized scripts to trick victims while messaging them in different languages. “These developments have not only expanded the scope and efficiency of cyber-enabled fraud and cybercrime, but they have also lowered the barriers to entry for criminal networks that previously lacked the technical skills to exploit sophisticated and profitable methods,” the report says.
Stephanie Baroud, a criminal intelligence analyst in Interpol’s human trafficking unit, says the impact of AI needs to be considered as part of a pig butchering scammer’s tactics going forward. Baroud, who spoke with WIRED in an interview before the publication of the UN report, says the criminal’s recruitment ads that lure people into being trafficked to scamming compounds used to be “very generic” and full of grammatical errors. However, AI is now making them appear more polished and compelling, Baroud says. “It is really making it easier to create a very realistic job offer,” she says. “Unfortunately, this will make it much more difficult to identify which is the real and which is the fake ads.”
Perhaps the biggest AI paradigm shift in such digital attacks comes from deepfakes. Scammers are increasingly using machine-learning systems to allow for real-time face-swapping. This technology, which has also been used by romance scammers in West Africa, allows criminals to change their appearance on calls with their victims, making them realistically appear to be a different person. The technology is allowing “one-click” face swaps and high-resolution video feeds, the UN’s report states. Such services are a game changer for scammers, because they allow attackers to “prove” to victims in photos or real-time video calls that they are who they claim to be.
Using these setups, however, can require stable internet connections, which can be harder to maintain within some regions where pig butchering compounds and other scamming have flourished. There has been a “notable” increase in cops seizing Starlink satellite dishes in recent months in Southeast Asia, the UN says—80 units were seized between April and June this year. In one such operation carried out in June, Thai police confiscated 58 Starlink devices. In another instance, law enforcement seized 10 Starlink devices and 4,998 preregistered SIM cards while criminals were in the process of moving their operations from Myanmar to Laos. Starlink did not immediately respond to WIRED’s request for comment.
“Obviously using real people has been working for them very well, but using the tech could be cheaper after they have the required computers” and connectivity, says Troy Gochenour, a volunteer with the Global Anti-Scam Organization (GASO), a US-based nonprofit that fights human-trafficking and cybercrime operations in Southeast Asia.
Gochenour’s research involves tracking trends on Chinese-language Telegram channels related to carrying out pig butchering scams. And he says that it is increasingly common to see people applying to be AI models for scam content.
In addition to AI services, attackers have increasingly leaned on other technical solutions as well. One tool that has been increasingly common in digital scamming is so-called “crypto drainers,” a type of malware that has particularly been deployed against victims in Southeast Asia. Drainers can be more or less technically sophisticated, but their common goal is to “drain” funds from a target’s cryptocurrency wallets and redirect the currency to wallets controlled by attackers. Rather than stealing the credentials to access the target wallet directly, drainers are typically designed to look like a legitimate service—either by impersonating an actual platform or creating a plausible brand. Once a victim has been tricked into connecting their wallet to the drainer, they are then manipulated into approving one or a few transactions that grant attackers unintended access to all the funds in the wallet.
Drainers can be used in many contexts and with many fronts. They can be a component of pig butchering investment scams, or promoted to potential victims through compromised social media accounts, phishing campaigns, and malvertizing. Researchers from the firm ScamSniffer, for example, published findings in December about sponsored social media and search engine ads linked to malicious websites that contained a cryptocurrency drainer. The campaign, which ran from March to December 2023 reportedly stole about $59 million from more than 63,000 victims around the world.
Far from the low-tech days of doing everything through social engineering by building a rapport with potential victims and crafting tricky emails and text messages, today’s scammers are taking a hybrid approach to make their operations as efficient and lucrative as possible, UN researchers say. And even if they aren’t developing sophisticated malware themselves in most cases, scammers are increasingly in the market to use these malicious tools, prompting malware authors to adapt or create hacking tools for scams like pig butchering.
Researchers say that scammers have been seen using infostealers and even remote access trojans that essentially create a backdoor in a victim’s system that can be utilized in other types of attacks. And scammers are also expanding their use of malicious smart contracts that appear to programmatically establish a certain agreed-upon transaction or set of transactions, but actually does much more. “Infostealer logs and underground data markets have also been critical to ongoing market expansion, with access to unprecedented amounts of sensitive data serving as a major catalyst,” Wojcik, from the UNODC, says.
The changing tactics are significant as global law enforcement scrambles to deter digital scamming. But they are just one piece of the larger picture, which is increasingly urgent and bleak for forced laborers and victims of these crimes.
“It is now increasingly clear that a potentially irreversible displacement and spillover has taken place in which organized crime are able to pick, choose, and move value and jurisdictions as needed, with the resulting situation rapidly outpacing the capacity of governments to contain it,” UN officials wrote in the report. “Failure to address this ecosystem will have consequences for Southeast Asia and other regions.”
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Math Myths Busted! 🚨 Debunking Common Misconceptions
1. "Trigonometry is pointless in real life."
Want to design a bridge, map the stars, or even create 3D models? Welcome to the world of trigonometry. Engineers use sine and cosine to calculate forces, angles, and stress on structures. Naval navigation? That’s spherical trigonometry. And let’s not forget medical imaging (MRI and CT scans)—trigonometric algorithms are essential for reconstructing images from cross-sectional slices of the body.
2. "Pi is just 3.14."
Pi is irrational, meaning it goes on forever without repeating. It’s used in everything from signal processing to quantum physics. In general relativity, gravitational waves are calculated using Pi to map the curvature of spacetime. Even fractals, the infinitely complex geometric shapes that mirror nature’s patterns, rely on Pi for accurate dimension calculations. Simplifying Pi to 3.14 is like calling a complex painting “just a bunch of colors.” It’s a universe in itself.
3. "Math is for nerds, not for normal people."
Mathematics is fundamental to the universe. The Fibonacci sequence is embedded in everything from flower petals to galaxies. Whether it’s understanding the Golden Ratio in art or applying optimization techniques to improve energy use in smart cities, math is the tool that drives technology, medicine, and economics. Cryptography keeps your bank account safe and ensures secure communication online—it’s all built on abstract algebra and number theory. So, is math for “nerds”? It’s for civilization.
4. "I’ll never be good at math."
Growth mindset matters. The very concept of calculus—which studies the rate of change—starts from understanding infinitesimally small changes. Once you grasp limits, derivatives, and integration, you unlock the power to model everything from population growth to financial markets. Complex equations that once seemed impenetrable are just tools for breaking down the world. Perseverance is the key, not an innate ability. You learn, you grow, you become a mathematical thinker.
5. "Math is boring."
If math’s boring, then understanding gravity and black holes is boring. Einstein’s general theory of relativity wasn’t just an academic concept—it was formulated using highly sophisticated tensor calculus. Fractals, which appear in clouds, mountains, and even coastlines, are beautiful examples of math in nature. When you solve differential equations, you’re predicting everything from weather patterns to market crashes. Math is not static, it’s the language of everything, from the universe’s creation to your daily commute.
6. "I don’t need math in my everyday life."
You calculate interest rates, optimize your workout routine, and even estimate cooking times using math without realizing it. Statistics helps you make informed decisions in the stock market, and probability theory is the reason you can accurately predict outcomes in games, risk-taking, and even weather forecasting. Linear algebra is involved in everything from computational biology to machine learning. And when was the last time you built a website without using algorithms? Exactly.
7. "Calculators do all the work, so why learn math?"
Calculators are tools. Algorithms—the underlying mathematical processes that make your calculator or smartphone function—are the result of years of mathematical study. Machine learning algorithms, the backbone of AI, rely heavily on linear algebra and calculus. Building a calculator that can compute anything from simple arithmetic to complex number operations requires advanced math, often involving abstract algebra and number theory. It’s not the tool; it’s the thinking behind it that counts.
Math is the DNA of the universe.
#mathematics#math#mathematician#mathblr#mathposting#calculus#geometry#algebra#numbertheory#mathart#STEM#science#academia#Academic Life#math academia#math academics#math is beautiful#math graphs#math chaos#math elegance#education#technology#statistics#data analytics#math quotes#math is fun#math student#STEM student#math education#math community
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
While generative AI models and tools can and will use a significant amount of energy, we shouldn't conflate AI energy usage with the larger and largely pre-existing energy usage of "data centers" as a whole.
Unfortunately for Bloomberg, that quote is followed almost immediately by a chart that heavily undercuts the AI alarmism. That chart shows worldwide data center energy usage growing at a remarkably steady pace from about 100 TWh in 2012 to around 350 TWh in 2024. The vast majority of that energy usage growth came before 2022, when the launch of tools like Dall-E and ChatGPT largely set off the industry's current mania for generative AI. If you squint at Bloomberg's graph, you can almost see the growth in energy usage slowing down a bit since that momentous year for generative AI.

In his study "The growing energy footprint of artificial intelligence," de Vries starts with estimates that Nvidia's specialized chips are responsible for about 95 percent of the market for generative AI calculations. He then uses Nvidia's projected production of 1.5 million AI servers in 2027—and the projected power usage for those servers—to estimate that the AI sector as a whole could use up anywhere from 85 to 134 TWh of power in just a few years.
measured against other common worldwide uses of electricity, it's not representative of a mind-boggling energy hog. A 2018 study estimated that PC gaming as a whole accounted for 75 TWh of electricity use per year, to pick just one common human activity that's on the same general energy scale (and that's without console or mobile gamers included).
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
How AI & Machine Learning Are Changing UI/UX Design

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing UI/UX design by making digital experiences more intelligent, adaptive, and user-centric. From personalized interfaces to automated design processes, AI is reshaping how designers create and enhance user experiences. In this blog, we explore the key ways AI and ML are transforming UI/UX design and what the future holds.
For more UI/UX trends and insights, visit Pixelizes Blog.
AI-Driven Personalization
One of the biggest changes AI has brought to UI/UX design is hyper-personalization. By analyzing user behavior, AI can tailor content, recommendations, and layouts to individual preferences, creating a more engaging experience.
How It Works:
AI analyzes user interactions, including clicks, time spent, and preferences.
Dynamic UI adjustments ensure users see what’s most relevant to them.
Personalized recommendations, like Netflix suggesting shows or e-commerce platforms curating product lists.
Smart Chatbots & Conversational UI
AI-powered chatbots have revolutionized customer interactions by offering real-time, intelligent responses. They enhance UX by providing 24/7 support, answering FAQs, and guiding users seamlessly through applications or websites.
Examples:
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
AI chatbots in banking, e-commerce, and healthcare.
NLP-powered bots that understand user intent and sentiment.
Predictive UX: Anticipating User Needs
Predictive UX leverages ML algorithms to anticipate user actions before they happen, streamlining interactions and reducing friction.
Real-World Applications:
Smart search suggestions (e.g., Google, Amazon, Spotify).
AI-powered auto-fill forms that reduce typing effort.
Anticipatory design like Google Maps estimating destinations.
AI-Powered UI Design Automation
AI is streamlining design workflows by automating repetitive tasks, allowing designers to focus on creativity and innovation.
Key AI-Powered Tools:
Adobe Sensei: Automates image editing, tagging, and design suggestions.
Figma AI Plugins & Sketch: Generate elements based on user input.
UX Writing Assistants that enhance microcopy with NLP.
Voice & Gesture-Based Interactions
With AI advancements, voice and gesture control are becoming standard features in UI/UX design, offering more intuitive, hands-free interactions.
Examples:
Voice commands via Google Assistant, Siri, Alexa.
Gesture-based UI on smart TVs, AR/VR devices.
Facial recognition & biometric authentication for secure logins.
AI in Accessibility & Inclusive Design
AI is making digital products more accessible to users with disabilities by enabling assistive technologies and improving UX for all.
How AI Enhances Accessibility:
Voice-to-text and text-to-speech via Google Accessibility.
Alt-text generation for visually impaired users.
Automated color contrast adjustments for better readability.
Sentiment Analysis for Improved UX
AI-powered sentiment analysis tools track user emotions through feedback, reviews, and interactions, helping designers refine UX strategies.
Uses of Sentiment Analysis:
Detecting frustration points in customer feedback.
Optimizing UI elements based on emotional responses.
Enhancing A/B testing insights with AI-driven analytics.
Future of AI in UI/UX: What’s Next?
As AI and ML continue to evolve, UI/UX design will become more intuitive, adaptive, and human-centric. Future trends include:
AI-generated UI designs with minimal manual input.
Real-time, emotion-based UX adaptations.
Brain-computer interface (BCI) integrations for immersive experiences.
Final Thoughts
AI and ML are not replacing designers—they are empowering them to deliver smarter, faster, and more engaging experiences. As we move into a future dominated by intelligent interfaces, UI/UX designers must embrace AI-powered design methodologies to create more personalized, accessible, and user-friendly digital products.
Explore more at Pixelizes.com for cutting-edge design insights, AI tools, and UX trends.
#AI in UX Design#Machine Learning UX#UX Personalization#Conversational UI#Predictive UX#AI Chatbots#Smart UX Tools#UI Automation#Voice UI Design#Inclusive UX Design#Sentiment Analysis in UX#Future of UX#AI UX Trends 2025#Figma AI Plugins#Accessibility with AI#Adaptive UI Design#UX Innovation#Human-Centered AI#Pixelizes Blog#UX Strategy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Unlikely Nature of Scary Cosmic Scenarios ~ 05 Feb 2025
The Unlikely Nature of Scary Cosmic Scenarios ~ 05 Feb 2025, Philip Sedgwick
As if everything going on in the world isn’t enough, recent astronomical projections have slated two doomsday scenarios for us and managed to show up on news feeds. The scenarios involve the Earth enduring a collision from a Potentially Hazardous Object (PHO) originating with the category of asteroids known as Near Earth Objects (NEO).
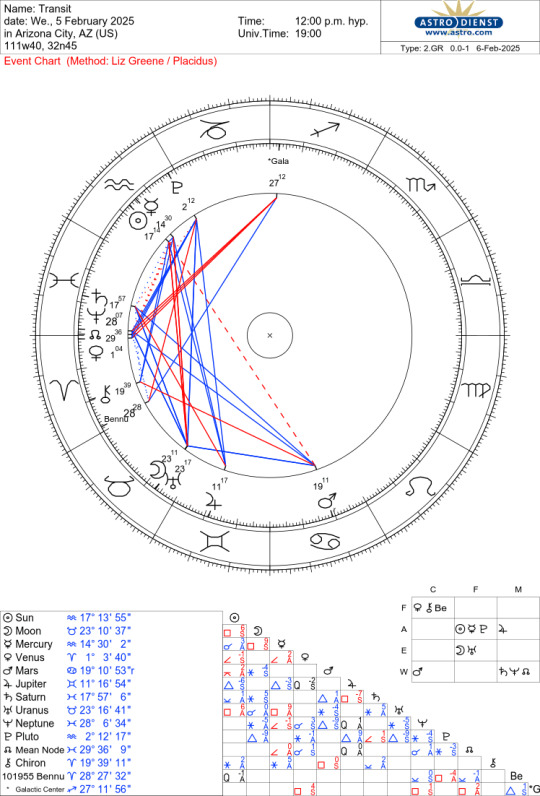
Initial calculations suggest that 2024 YR4, an asteroidish thing with an estimated diameter between 130 and 330 feet, may crash into the Earth on 22 December 2032. Expect a heap of last-minute holiday shopping that year! To rain on the shopping procrastination parade, the probability of impact stands at a mere 1.3%. If a weather forecaster provided a 1 - 2 % chance of rain, no one would be sufficiently bothered to change outdoor plans.
If you want to have some solar system fun, check out this groovy orbit gizmo. Here’s screenshot of the orbit of 2024 YR4. The link to the very fun orbit tool used for this pic is: Orbits
If 2024 YR4 is not enough, come 24 September 2182, asteroid Bennu may impact what’s left of Earth. The projected collision is only fair. After all, this asteroid with a period of 1.19 years, was struck by the OSIRIS-REx probe on 20 October 2020. The probe pogo-sticked off Bennu, collecting a sample of the asteroid’s raw materials and successfully returned to Earth with the booty. Analysis of the materials of Bennu suggest it contains the critical materials to create life. How ironic; Bennu contains the potential to create life on Earth and equally maintains the potential to end life on Earth.
Wait! There’s more! Upward-looking, plutocratic entrepreneurs have decided we should mine asteroids. Recent estimates of the asteroid Psyche’s worth exceed the global economy - this is more solid that crypto currency! No wonder those tech moguls now devote so much attention to the natural resources of our solar system. How many asteroids are there? Is this how ka-ching is correctly spelled?
In the category of mining asteroids, there are a number of top contending companies: Karman+, TransAstra, AstroForge, Origin Space and Asteroid Mining Corporation. All seek a competitive timeline edge and projections are that in 2029, they’ll be able to set up shop and do their mining thing. Here’s the $64,000 question and one that is not rhetorical: How many asteroids can be mined before the center of gravity of the asteroid belt becomes impacted? Wouldn’t this gravitational shift potentially influence the orbit of Mars? Isn’t it possible that the result would be like a bad pool table break? Isn’t it curious that the first contending company on the list is Karman+? Again, isn’t it interesting that Bennu, impacted by those studying space potentially could strike Earth and wipe out life and simultaneously plant the seeds of life?
Why is it that astronomers feel the need to blast the news outlets with their possible asteroid strike which falls into the category of only minimally likely? Is this the result of being excluded from campfire story time? Don’t we have enough to think about with drones hovering overhead - authorized by the FAA and conducting unstated “research?” Is this an attempt to get humans to ponder cosmic possibilities, despite the concerns of the real world and thus, engage the highest minded themes of Pluto in Aquarius?
Actually, there is supposed to be a moratorium on announcing potentially disastrous solar system catastrophes. It is supposed to be a length of time such that several astronomical organizations using high-power computers that do not use AI for calcs to come to a consensus agreement on the probability of Earth impact. All the “transiting gravel” (as it has been called by astrologers in the past - which now would include the Kuiper Belt) out there that we know about has been pretty much considered and determined to pose no threat. Likely it would be something new that gets discovered somehow, somewhere that potentially poses hazard to Earth. Will the Earth be struck by asteroid-like objects in the future? Absolutely. Every year Earth is hit by some 17,000 meteorites.
Fortunately, Earth possesses (at least currently, it does) an atmosphere that causes most incoming objects to burn up, or mostly diminish upon arrival. Do the odds go up with asteroid mining? Possibly, that depends upon how well the mining operation attends to all details of its operation. Should anything be considered at this time regarding the human influence on the environment of the entire solar system? Absolutely.
The point is, nothing catastrophic on a cosmic calamity scale appears on the calender in the foreseeable times ahead. While the world engages in circumstances and situations that may appear to defy the nature of Pluto in Aquarius, there is no need to stress over any incoming solar system body of which there is current knowledge. But two interesting thoughts arise from such speculation. Is an ounce of prevention worth a pound of cure (or whatever weights and measure system fits the adage in your neck of the world)? Absolutely. Are efforts to see if we can successfully deflect an incoming asteroid useful? Yes, and like any prevention system, we apply our hope and faith in never needing that system? Larger and potentially more evolving, would nations and their leaders be more inclined to seek collaboration for saving our bacon as opposed to imposing tariffs on our bacon, and thus cause realization that all humans are equally subject to cosmic events?
And here, insert a wink from Pluto that is absolutely impossible to interpret.
More soon.
Yes, I do work with some of that transiting gravel. I actively use Psyche and asteroids elevated to dwarf planet status and I consider all of the larger, named objects in the Kuiper Belt when I conduct consultations. Is the effort worth it? Perhaps intangibly so. Is such inclusion preventative? Hard to calculate unknown things that did not happen, but navigating life with less chaos and disruption always seems a good plan. To get that good plan going, use the links below to order reports, ask questions or schedule sessions.
And if you have not watched my short film METEORIC yet, and have 20 minutes, there's a link below!
One Stop Shopping Order Form Astrological Texts
METEORIC the Movie on Vimeo ZAP! on Vimeo
3 notes
·
View notes
Link
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
1 in 5 People Could Have Long COVID - Published Nov 8, 2024
By Dennis Thompson
FRIDAY, Nov. 8, 2024 (HealthDay News) -- More than 1 in 5 Americans likely suffer from long COVID, a new AI-assisted review has found.
The analysis suggests that nearly 23% of U.S. adults experience the symptoms of long COVID, according to results published Nov. 8 in the journal Med.
That’s much higher than the 7% prevalence of long COVID that’s been suggested by other studies, researchers said.
“Questions about the true burden of long COVID -- questions that have thus far remained elusive -- now seem more within reach,” said senior researcher Hossein Estiri, head of AI research at Mass General Brigham in Boston.
For the study, researchers developed an AI tool that can sift through mounds of electronic health records looking for the frequently subtle symptoms related to long COVID.
These symptoms can occur in a wide range of body systems, and include fatigue, chronic cough, heart problems and “brain fog.” They typically develop weeks or months after a person shakes off their initial COVID-19 infection.
“Our AI tool could turn a foggy diagnostic process into something sharp and focused, giving clinicians the power to make sense of a challenging condition,” Estiri said in a Mass General news release.
The AI specifically looks for symptoms that can’t be explained by a person’s medical history, have persisted for two months or longer and occur following a COVID infection, researchers said.
For example, the AI can detect if shortness of breath might be explained by pre-existing heart failure or asthma, rather than long COVID.
“Physicians are often faced with having to wade through a tangled web of symptoms and medical histories, unsure of which threads to pull, while balancing busy caseloads. Having a tool powered by AI that can methodically do it for them could be a game-changer,” said lead researcher Dr. Alaleh Azhir, an internal medicine resident at Brigham and Women’s.
Based on these parameters, the AI estimated that nearly 23% of Americans likely have long COVID, a figure that researchers argue aligns more closely with national trends.
The researchers plan to release the AI publicly on open access, so doctors and health care systems can employ and test it.
Study Link : www.cell.com/med/fulltext/S2666-6340(24)00407-0?_returnURL=https%3A%2F%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%2Fretrieve%2Fpii%2FS2666634024004070%3Fshowall%3Dtrue
#long covid#covid 19#mask up#covid#pandemic#public health#wear a respirator#still coviding#wear a mask#coronavirus#sars cov 2#covid conscious#covid is airborne
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was introduced to Charles Dickens in high school.
By which I mean I was assigned to read his sprawling 1859 historical novel “A Tale of Two Cities.” The tale itself is set before and during the French Revolution and the chaotic, bloody Reign of Terror, while the protagonists navigate, literally and figuratively, the span between the two great cities of London and Paris, and the tumultuous events of the era.
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times,” the book famously begins, “it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of light, it was the season of darkness…”
I’ve thought a lot of these anaphoric lines lately, and the contrasts they highlight. In Dickens’ story there are certainly heroes and villains, good and evil, and love and hate, along with well-earned wisdom and stubborn foolishness.
As always with Dickens there is also a focus on the gulf between classes of people, those who assume the power and privilege of wealth and the many who struggle with the crushing oppression of poverty. In both extremes there exists kindness and cruelty, and the various characters choose one or the other based on their personal, sometimes dawning, morality. In Dickens’ world, villains are not necessarily born bad, but some are led to do harm out of desperation and despair and a perverse sense of justice, both righteous and foul.
The hefty novel had an equally weighty impact on me at the time, and perhaps influenced my own emerging understanding of how circumstance and context might propel someone to particular extremes of thought and behavior. I don’t think I necessarily knew a lot about the politics depicted, capricious and convoluted then as now, but I understood how fear and prejudice, set against hope and optimism, can be powerful enough to shift both individual lives and the fates of nations.
Once again we are at a time of extremes, and the challenges they present. Wisdom and foolishness battle daily, and there is no foreseeable shortage of incredulity. Technology exists, literally in our hands, far beyond the steam-powered advances of Dickens’ time, while “updates” regularly occur as we sleep. The tools which, ostensibly, promote greater connection sometimes have exactly the opposite effect, numbing us to our immediate environment and those who inhabit it. We contend with “virtual,” “real time,” “chat,” and “reality,” as concepts separate from (or even the opposite of) what the terms have traditionally meant, while artificial intelligence, or “AI” potentially redefines our perceptions to a degree yet to be fully recognized. We are met, often engulfed, by a wave of information which can deliver knowledge or promulgate drivel, and a very great deal in between. The delineation between fact and fiction becomes muddied, and far too often conspiracy theories, rather than crucial critical thinking, fill the voids in available knowledge. Of all the extremes which have become evident, the most appalling for me at least, is the yawning gap between questioning intelligence and confident ignorance.
In another work of Dickens, the novella “A Christmas Carol,” the iconic character of Scrooge is unwillingly guided into his past, present and future to confront his own assumptions, prejudices, and moral failings. At one point he is shown two wretched figures, a boy and a girl who represent, in the author’s estimation, the worst of humanity:
“They are Man’s….And they cling to me, appealing from their fathers. The boy is Ignorance. The girl is Want. Beware of them both, and all of their degree, but most of all beware this boy, for on his brow I see that written which is Doom, unless the writing be erased.”
Will the writing be altered? I do not know. I continue to believe hope is available and appropriate, as is kindness, and the need for both has seldom been greater.
As in Dickens’ age, of course, there are those today whose wealth and power, sometimes inherited, has placed them outside the sphere of daily worry or want, while conveying faulty assumptions about their relative intelligence and the “rightness” of their position. It has always been so, and I suppose will always be the case, while Edmund Burke’s well-known observation, “those who don't know history are doomed to repeat it,” has never felt quite so apt.
And yet, hope and kindness are present and persist. They are always options available to each of us, and the time to exercise them is now.
We carry on, we stay informed, we make meaningful communities. We value creative thinking and we absolutely must honor true expertise, whether in science, or the arts, or in world affairs. Injustice ought to be recognized and exposed, and bigotry denounced. That is, I believe, how we move forward as caring humans in a functioning society.
“….. it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the other way—in short, the period was so far like the present period, that some of its noisiest authorities insisted on its being received, for good or for evil, in the superlative degree of comparison only.”

2 notes
·
View notes