#3D-bioprinting
Text
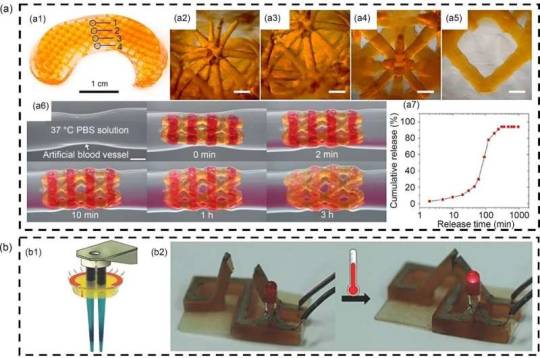
From lab to life: 3D bioprinting unveils new horizons in biomedical applications
With the development of intelligent biomedical engineering, the application of three-dimensional (3D) printing technology has become increasingly widespread. However, existing 3D printing technologies mainly focus on inorganic or polymer materials, limiting their applications in biocompatibility and biodegradability. Due to these challenges, there is a need for in-depth research on biocompatible and functional materials.
This review, conducted by institutions such as China University of Petroleum (East China), Zhejiang University, and Tel Aviv University, was published in Bio-Design and Manufacturing, on 29 April 2024. The research team explored the combination of peptide self-assembly technology with 3D printing for developing complex biological structures and organs. This breakthrough lays the foundation for future biomedical applications.
The study provides an in-depth analysis of recent progress in 3D bioprinting in Israel, focusing on scientific studies on printable components, soft devices, and tissue engineering. It highlights the potential of peptide self-assembly technology as a bioinspired ink for constructing complex 3D structures.
Read more.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
3D Printing Inside Organs Unveils a Surgery Breakthrough!
In a groundbreaking leap toward the future of medicine, researchers at Duke University and Harvard Medical School are rewriting the rules of surgery.
Imagine a world where medical procedures can be performed without a single incision—a reality that may be closer than we think. Junjie Yao, a bioengineer at Duke University, and his co-primary investigator, Yu Shrike Zhang, are at the forefront of…

View On WordPress
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
From 3D Printing to Bioprinting: The Future of Manufacturing
In recent years, the world of manufacturing has experienced significant transformations, with 3D printing and bioprinting technologies emerging as key drivers of change. These advanced manufacturing methods have the potential to revolutionize how products are created, impacting various industries and potentially reshaping the global supply chain. In this article, we will delve into the world of…

View On WordPress
#3D printing#additive manufacturing#bioprinting#decentralized production#future of manufacturing#on-demand manufacturing#personalized medicine#rapid prototyping#sustainability#tissue engineering
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
21yo catgirl gf who doesnt know what 'campfire' is: i just dont get it…. i think you're trying to 'gas light' me….
me: we don't HAVE a fucking gas lighter that's why you need to rub these sticks together so we can have a fire and stay warm until rescue arrives..
spore creature i 3d bioprinted from the workshop that looks like Jeb Bush: (mistaking me for a high tier creature stage species that will make a powerful ally and allow it to advance evolutionarily) 🎶 AR AR AR 🎶 😃
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
The 3D Bioprinting Market in 2023 is US$ 1.57 billion, and is expected to reach US$ 7.24 billion by 2031 at a CAGR of 21.00%.
0 notes
Link
#market research future#3d bioprinting market#3d bioprinting companies#biofabrication market#3d bioprinting market size
0 notes
Text
#life science#medical equipment#health#biopharma#pharmaindustry#biotech and pharmaceuticals#biology#nutrition#pharmacy#3d bioprinting
0 notes
Text
#3D Bioprinting Market#3D Bioprinting Size#3D Bioprinting Growth#3D Bioprinting Trend#3D Bioprinting segment#3D Bioprinting Opportunity#3D Bioprinting Analysis 2024#3D Bioprinting Forecast
0 notes
Link
Welcome to Astronomy Daily, your go-to podcast for the latest updates in the universe. I'm Anna, your host for today. In today's episode, we'll explore a wealth of exciting topics. We'll be delving into the recent scrubbing of a Firefly Aerospace mission that aims to send educational cubesats into space. We'll also discuss groundbreaking research at the intersection of space medicine and human longevity. And finally, we'll look at the fascinating potential of using Martian lava caves as habitats for future astronauts. Today's episode promises to be both engaging and informative, covering the latest developments that push the boundaries of our understanding of the cosmos. So let's dive into our stellar lineup of stories.
Thank you for tuning into Astronomy Daily. I'm Anna, and I hope you enjoyed today's journey through some of the most exciting news and discoveries in astronomy and space exploration. Remember to visit our website at astronomydaily.io for back episodes, our daily newsletter, and the latest news in space and astronomy.
Astronomy Daily is available on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, YouTube Music, and iHeartRadio. Please subscribe, rate, and review.
Special thanks to our sponsors NordPass, NordVPN, ProtonMail, and Amazon. Links to their offers are available on our website. Until next time, keep looking up.
www.astronomydaily.io
www.bitesz.com
#3d#aerospace#autonomous#bioprinting#caves#cubesats#firefly#habitats#human#lava#longevity#martian#medicine#millisecond#nasa#pulsar#pulsars#space#spacecraft#tourism
0 notes
Text

Cell-friendly bioprinting at high fidelity enhances its medical applicability
What if organ damage could be repaired by simply growing a new organ in the lab? Improving researchers' ability to print live cells on demand into geometrically well-defined, soft complex 3D architectures is essential to such work, as well as for animal-free toxicological testing.
In a study recently published in ACS Biomaterials Science and Engineering, researchers from Osaka University have overcome prior limitations that have hindered cell growth and the geometrical fidelity of bioprinted architectures. This work might help bring 3D-printed cell constructs closer to mimicking biological tissue and organs.
Ever since bioprinting was first reported in 1988 by using a standard inkjet printer, researchers have explored the potential of this layer-by-layer tissue assembly procedure to regrow damaged body parts and test medical hypotheses. Bioprinting is to eject a cell-containing "ink" from a printing nozzle to form 3D structures. It is usually easier to print hard rather than soft structures. However, soft structures are preferable in terms of cell growth in the printed structures.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Biomaterials#3D printing#Bioprinting#Medical Technology#Cells#Osaka University
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Science Behind 3D Printing and Its Innovations
Introduction
Alternative term for additive manufacturing: in this process, objects are conceptualized in another manner, changing how the objects are thought of by using 3D printing. One such technology is making creation from prototyping to final products more flexible and efficient. At TechtoIO, we deep dive into the science of 3D printing and the innovations that fuel this groundbreaking technology. Read to continue link
#Science Explained#Tags3D printed houses#3D printed prosthetics#3D printing applications#3D printing benefits#3D printing education#3D printing future#3D printing in automotive#3D printing in fashion#3D printing in healthcare#3D printing materials#3D printing prototyping#3D printing science#3D printing technology#additive manufacturing#aerospace 3D printing#bioprinting#construction 3D printing#custom 3D printing#innovations in 3D printing#Technology#Science#business tech#Adobe cloud#Trends#Nvidia Drive#Analysis#Tech news#Science updates#Digital advancements
1 note
·
View note
Text
3D bioprinting has developed as an encouraging new approach for fabricating complex biological constructs in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. It aims to alleviate the hurdles of conventional tissue engineering methods by precise and controlled layer-by-layer assembly of biomaterials in a desired 3D pattern. As per the U.S. government information on Organ donation and Transplantation, 17 people die every year waiting for an organ transplant.
0 notes
Link
#market research future#3d bioprinting market#3d bioprinting market size#3d bioprinting market trends#3d bioprinting market growth
0 notes
Text
Bioprinting Takes Shape: Creating Tissues and Organs for Medical Advancements - By Daniel Reitberg
The world of medicine is witnessing a revolution with the emergence of bioprinting, a technology poised to reshape the future of healthcare. This groundbreaking technique leverages the power of 3D printing to create functional living tissues and even organs. Bioprinting utilizes biocompatible materials and living cells, meticulously arranged layer by layer to mimic natural structures. The potential applications in regenerative medicine are truly transformative. Imagine a future where bioprinted grafts seamlessly repair damaged tissues, restoring function and mobility. Even more remarkable is the possibility of bioprinting transplantable organs, eliminating the agonizing wait for compatible donors and offering a lifeline to countless patients suffering from organ failure. Bioprinting research is rapidly advancing, tackling the complex challenges of replicating intricate vascular networks and ensuring cell viability within the printed structures. While there's still a road ahead, bioprinting holds immense promise for revolutionizing medical treatments and offering a new era of hope for patients worldwide.
#artificial intelligence#machine learning#deep learning#technology#robotics#autonomous vehicles#robots#collaborative robots#business#healthcare#3d bioprinting#medicine
0 notes