#1800 - 1945
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Me: [listening to Armenian jazz to focus on my set model for Charrington’s Shop with a very confused expression on my face as I try to determine whether or not the room Winston rented in the second story has a water closet up there]
#Like the two of them were sleeping up there overnight and getting freaky and it’s implied it was Mr. Weeks’ living quarters#It would only make sense#But the water closet could be downstairs too#??????????#calling it a water closet because the building is implied to have been built in the late 1800s or early 1900s because of the steep stairs#and the fact that the living quarters are above the shop#as well as all the antiques#and Winston would have been born in 1945 ish and by then there was already a war#And for Charrington and his imaginary wife to have believably lived there for 27 years before her death#it would have been built AT THE VERY NEWEST in 1930 before the war was afoot
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Austrian-Jewish author Franz Werfel
#Franz Werfel#Werfel#Austrian-Jewish#Austria#Jewish#Austrian#1890#189's#1800's#author#novelist#1945#1940's#1900's#Cisleithanien#Beverly Hills#California#Los Angeles
1 note
·
View note
Note
What moment in ttte made you shocked?
Idk man ttte isn't a very shocking show. It's incredibly down to earth, if a bit real with some of its stories. While yes some of the earlier episodes and especially the books can branch onto more serious and arguably darker content its nothing that would really shock me per se.
Nothing really shocks me, it just makes me think. Maybe be a bit sad or feel for the characters. But that's what any good story does.
#idk really know what you want me to say here#im not super into talking about the quote on quote darker elements of ttte. i like my fluff#people act like its this secretly dark and fucked up kids show. shocking people. constantly bringing up Henry’s tunnel and what not#and they dont take into account not only rhe full context. but the messages themes and time period that the stories were written.#these “darker” storylines were written in the 40s. where a punishment like this would seem normal.#obviously now in 2023 these views have changed#its like the old children's parlor game Snapdragon. played in 1800s.#where children would eat raisins out of a burning dish of brandy while it was still on fire#times change and its important to take the context into consideration. does it make the action or plot point any less unsettling? no.#like i said perceptions have changed. but i dont think its fair to call it a fucked up oooo dark and egdy not what you think show#dont act like it was written in today's time when it wasnt. the authors didnt write that show for Children's television in the 80s to shock-#-and scare kids. it was written in 1945 by Awdry as an allegory for being a brat. you get put on the naughty step or go to your room#like how henry was shut in thr tunnel. granted today the wording and time spent in the tunnel seems overly harsh. which it is.#but it also might be hyperbole. also henry was let out the very next story and everyone fucking misses that fact and i fucking hate it#HE WAS LET OUT OF THR TUNNEL THE VERY NEXT EPISODE#sorry sorry i went on a bit of a rant in the tags. anyways nothing in ttte shocks me cause theres nothing really shocking about it#red answers
1 note
·
View note
Text
Izzy in the 1700s singing a song written in 1945 🤝 Crowley in the 1800s singing a song written in 1965
#ofmd#ofmd 2#ofmd spoilers#our flag means death#good omens#our flag means death 2#good omens 2#our flag means death spoilers#calypso's birthday#izzy hands#con o'neill#crowley#anthony j crowley#david tennant#gomens#la vie en rose#flower of scotland#the accepted canon for good omens is that crowley composed it so i'm going to assume izzy wrote la vie en rose#with frenchie's help maybe#gos2#ourgoodshadows#sort of#mine
962 notes
·
View notes
Text





























portrayals of bats in the 19th century:
Yashô (Japanese , 1782-1825) - Bat in Flight - ink on paper - early 1800s
Nicolas Huet the Younger (French, 1770–1830) - Bat - 1809
Joseph Severn (English, 1793–1879) - Ariel Riding on a Bat - oil on panel - 1820
Yamada Hōgyoku (Japanese, active c.1804-1844) - Bat and Moon - c.1830
Hiroshige (Japanese, 1797-1858) - Bats and Branch
Hōraku (Japanese, active early to mid-19th century) - Owl and Bat -netsuke (two views)
Hōraku (Japanese, active early to mid-19th century) - Bat on Roof Tile - netsuke
Greater Javelin Bat - from Grand Illustrated Encyclopedia of Animated Nature - 1856
Bat fitting - bronze - China - Qing dynasty (1644-1911)
F.W. Key - Bats - illustration from Links in the Chain; Or, Popular Chapters on the Curiosities of Animal Life by George Kearley - 1862
Bowl with bat - Japan - 1870
Isshō (Japanese) - A Bat Flying Near a Pine Tree - painting
Vincent Van Gogh (Dutch, 1853-1890) - De Vleermuiz (The Bat) - (portraying a taxidermied flying fox) - 1886
Design for a Japanese Window - Catalog from Belcher Mosaic Glass Co.; New York - 1886
Hyakunen Suzuki (Japanese, 1825–1891) - Bat and Willow Tree - fan painting
Bat - sulphide marble - late 19th century
Bat button - silver - Art Nouveau - France - late 19th century
Bat - Ojime bead - ivory - Japan - late 19th century
Peach-Shaped Vessel with Bat - porcelain - China - Qing dynasty
Tonkotsu (tobacco container) with lucky bats - Japan
bookcover for 'Stories and Interludes' by Barry Pain - 1892
Antonio de la Gandara (French, 1861-1917) - illustration for the book 'Les Chauves-Souris' (The Bats) by R. Montesquiou - 1895
Vase with Bats - earthenware ceramic - Art Nouveau - 1896
two illustrations of Bats from Cassell’s Natural History - 1896
Cover of 'Dracula' - 1st Edition - Bram Stoker - 1897
Rene Lalique (French, 1860-1945) - Batgirl pendant - gold with enameled wings & pearl - 1898
Rene Lalique (French, 1860-1945) - bat anklet - 1899
#art by others#other's artwork#sculpture#painting#print#ceramic#book cover#jewelry#container#marble#Rene Lalique#Antonio de la Gandara#ivory#silver#Hyakunen Suzuki#Yashô#Nicolas Huet#Joseph Severn#Hiroshige#Yamada Hōgyoku#netsuke#button#fan painting
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
Donald
1 George Washington 1732-1799 Indépendant 1789-1797
2 John Adams 1735-1826 Parti fédéraliste 1797-1801
3 Thomas Jefferson 1743-1826 Parti républicain-démocrate 1801-1809
4 James Madison 1751-1836 Parti républicain-démocrate 1809-1817
5 James Monroe 1758-1831 Parti républicain-démocrate 1817-1825
6 John Quincy Adams 1767-1848 Parti républicain-démocrate 1825-1829
7 Andrew Jackson 1767-1845 Parti démocrate 1829-1837
8 Martin Van Buren 1782-1862 Parti démocrate 1837-1841
9 William Henry Harrison 1773-1841 Parti whig 1841
10 John Tyler 1790-1862 Parti whig 1841-1845
11 James Knox Polk 1795-1849 Parti démocrate 1845-1849
12 Zachary Taylor 1784-1850 Parti whig 1849-1850
13 Millard Fillmore 1800-1874 Parti whig 1850-1853
14 Franklin Pierce 1804-1869 Parti démocrate 1853-1857
15 James Buchanan 1791-1868 Parti démocrate 1857-1861
16 Abraham Lincoln 1809-1865 Parti républicain 1861-1865
17 Andrew Johnson 1808-1875 Parti démocrate 1865-1869
18 Ulysses Simpson Grant 1822-1885 Parti républicain 1869-1877
19 Rutherford Birchard Hayes 1822-1893 Parti républicain 1877-1881
20 James Abram Garfield 1831-1881 Parti républicain 1881
21 Chester Alan Arthur 1829-1886 Parti républicain 1881-1885
22 Grover Cleveland 1837-1908 Parti démocrate 1885-1889
23 Benjamin Harrison 1833-1901 Parti républicain 1889-1893
24 Grover Cleveland 1837-1908 Parti démocrate 1893-1897
25 William McKinley 1843-1901 Parti républicain 1897-1901
26 Theodore Roosevelt 1858-1919 Parti républicain 1901-1909
27 William Howard Taft 1857-1930 Parti républicain 1909-1913
28 Woodrow Wilson 1856-1924 Parti démocrate 1913-1921
29 Warren Gamaliel Harding 1865-1923 Parti républicain 1921-1923
30 Calvin Coolidge 1872-1933 Parti républicain 1923-1929
31 Herbert Clark Hoover 1874-1964 Parti républicain 1929-1933
32 Franklin Delano Roosevelt 1882-1945 Parti démocrate 1933-1945
33 Harry S. Truman 1884-1972 Parti démocrate 1945-1953
34 Dwight D. Eisenhower 1890-1969 Parti républicain 1953-1961
35 John Fitzgerald Kennedy 1917-1963 Parti démocrate 1961-1963
36 Lyndon Baines Johnson 1908-1973 Parti démocrate 1963-1969
37 Richard Milhous Nixon 1913-1994 Parti républicain 1969-1974
38 Gerald R. Ford 1913-2006 Parti républicain 1974-1977
39 Jimmy Carter 1924-2024 Parti démocrate 1977-1981
40 Ronald Wilson Reagan 1911-2004 Parti républicain 1981-1989
41 George Herbert Walker Bush 1924-2018 Parti républicain 1989-1993
42 Bill Clinton*1946 Parti démocrate 1993-2001
43 George W. Bush*1946 Parti républicain 2001-2009
44 Barack Hussein Obama II.*1961 Parti démocrate 2009-2017
45 Donald John Trump*1946 Parti républicain 2017-2021
46 Joseph “Joe” Robinette Biden, Jr.*1942 Parti démocrate 2021-2025
47 Donald John Trump*1946 Parti républicain 2025-2029
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
just. the way that ghosts so thoroughly shows that people have always been people. they've always been a little bit messy and a little bit silly and they get mad and they laugh and they learn and they grow and they have forever and will continue to forever. and then when you consider the queer aspect of like. gay people have always been here. robin slept with anyone he wanted to and they raised children as a community. fanny's husband was gay in the 1800s. the captain was gay in 1945. sam and clare had their wedding at button house in the 2020s. people have always been here and sometimes they're gay and sometimes they fight and sometimes they grieve and sometimes they love and sometimes they're mean and sometimes they're kind and they apologize and they play games and they organize clubs and they play pretend and they cry and they live. they're dead but they live. they live.
#do you GET IT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!#PEOPLE HAVE ALWAYS BEEN PEOPLE#AND IT'S BEAUTIFUL!!!!!!!!!!!!!#WAHHH!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!#bbc ghosts
398 notes
·
View notes
Text
Want to write a mystery based on history? Check out my blog for posts about the unsolved past, with writing prompts!
Roopkund Lake Skeletons: unexplained remains of at least 300 people found at an isolated lake in the Indian Himalayas, from 800 and 1800 CE
The Beast of Gevaudan: History’s most well-documented werewolf, France, 1764
The Mystery of the Moving Coffins: tales of supposed unexplained movement of heavy coffins in burial vaults, most well-known in Barbados, 1808-19
The Female Stranger: unidentified decedent, Virginia (US), 1816
Spring-Heeled Jack: well-documented apparition or cryptid, England 1837-1904
The ghost ships Mary Celeste (1872) and Carroll A. Deering (1920)
Lizzie Borden: unsolved double murder, Massachusetts (US), 1892
The Flannan Isles Vanishing: disappearance of three lighthouse keepers, Scotland, 1900
Disappearance of Everett Ruess: missing person in the Utah (US) desert, 1934
Planes lost in the Bermuda Triangle: Flight 19 (1945) and The Star Tiger and Star Ariel, (1948-49)
Dyatlov Pass: mysterious deaths of 9 hikers, Ural Mountains, 1959
A werewolf prompt:
Escapist fiction. It’s possible the Beast of Gevaudan was not a wolf or dog, but another large creature, like a hyena or lion. Local zoos would have been private, so who knows what people were keeping? Obviously, once the killing started, the owner would have taken down the lost pet posters, so nobody owned up to owning the beast. People were not expecting to see anything other than local creatures in the woods, and they might not have had much familiarity with lions anyway, so it would probably make sense for them to call it a “wolf.” As for plots, there’s room for a sweeping historical novel starting in the place where the wild beast was captured, on the ship sending it to France, in the private zoo, and then out into the woods to become the Beast. Or what if it was not one lion that escaped, but a breeding pair? How would the locals cope with a growing population of big cats in the woods?
DannyeChase.com ~ AO3 ~ Linktree ~ Weird Wednesday writing prompts blog ~ Resources for Writers
#Dannye writes#writing inspiration#writing prompts#writing#writers on tumblr#writeblr#writeblogging#writing community#Weird Wednesday blog#blogging#scifi prompt#fantasy prompt#horror prompt#unsolved mysteries#historical mysteries#mystery#unsolved#vanishing#bermuda triangle#ghost ship
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
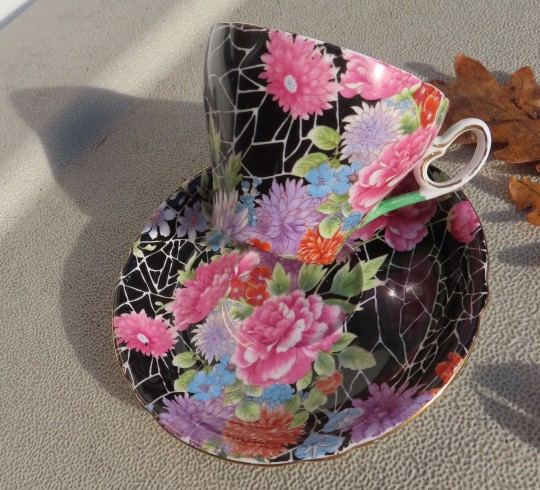
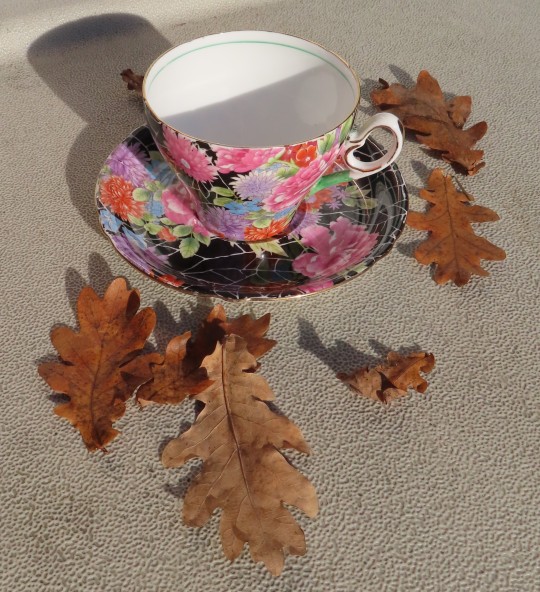



Art Deco
Maybe the rarest tea cup in the collection is this Shelley 'Cloisonne Black Crackle Chintz' pattern made between 1925 and 1945. Shelley Potteries was established in mid-1800s in Staffordshire, England. However, Shelley is probably best known for its fine bone china "Art Deco" ware of the inter-War years.
#flowers#photographers on tumblr#Art Deco#Shelley 'Cloisonne Black Crackle Chintz'#tea cups#flores#fiori#fleurs#blumen#bloemen#Vancouver
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dylan Scott at Vox:
Measles, mumps, and polio are supposed to be diseases of the past. In the early to mid-20th century, scientists developed vaccines that effectively eliminated the risk of anyone getting sick or dying from illnesses that had killed millions over millennia of human history. Vaccines, alongside sanitized water and antibiotics, have marked the epoch of modern medicine. The US was at the cutting edge of eliminating these diseases, which helped propel life expectancy and economic growth in the postwar era. Montana native Maurice Hilleman, the so-called father of modern vaccines, developed flu shots, hepatitis shots, and the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine in the 1950s and ’60s, which became virtually universally adopted among Americans.
Smallpox, the most common form of which has a 30 percent fatality rate, has been eradicated. Mitch McConnell, Republican titan of the Senate, may be the last major public figure still afflicted by a childhood case of polio, less than a century after it paralyzed a sitting American president. Measles likely infected millions of people annually in the US in the 1800s, although precise estimates from the era are hard to come by. In the early 1990s, thousands of people died from the disease every year. It was still infecting more than half a million and killing hundreds per year on average in the 1950s and ’60s, before the vaccine debuted. Diphtheria, a deadly respiratory infection, killed more than 1,800 people annually between 1936 and 1945 as the vaccine against it was still being rolled out. It has not killed anybody in the United States in decades. The vaccines that made this possible are among the most important achievements in human history. And yet many Americans appear to be losing faith in them, a worrying trend that could accelerate if President-elect Donald Trump succeeds in handing control of the top US health agency into the hands of Robert F. Kennedy Jr., the country’s foremost vaccine denier.
Kennedy has spent much of his public career pushing the thoroughly debunked theory of a link between autism and childhood vaccines. He has supported an anti-vaccine group in Samoa, where measles vaccination rates have since fallen off; a 2019 outbreak killed 83 people just a few months after Kennedy visited the island and met with anti-vaccine advocates. He has likewise cast doubt on the safety and efficacy of the Covid vaccines, a position that helped nudge the lifelong Democrat toward Trump. After Kennedy dropped his own presidential campaign this year, he became Trump’s most influential health adviser and last week was nominated by the president-elect to lead the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
[...] As long-accepted, lifesaving public health measures increasingly become politically polarized, routine vaccination rates are rapidly declining in much of the US. In the 2019–2020 school year, three states had less than 90 percent of K–12 students vaccinated against measles, mumps, and rubella. By the 2023–2024 school year, 14 states had fallen below that threshold. The number of states with more than 95 percent of schoolchildren vaccinated — the preferred level of coverage to prevent outbreaks — dropped from 20 to 11 during that same period.
Smallpox, measles, and polio, which were thought to be eradicated with mass vaccinations, but the anti-vaxxer extremist movement’s rise in influence in recent years threatens to undo decades worth of progress.
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Add what country you're from in the tags.
#for us it's a book that was printed in 1911 I think#or 1912? 1917?#anyway 1910s#a translation from English of a somewhat sentimental Christian book#(not saying that the things depicted don't happen irl but it becomes sentimental when it's a fictional narrative)#but frankly better than today's Christian fiction#I have no idea how we happen to have it#№2 would be a painting of the Virgin Mary and Child that my great-grandmother picked up upon first coming to Poland right after ww2#(Ukrainian -- met my great-grandfather in Germany -- he was a forced labourer -- she... long story -- moved to Poland with him afterwards)#it's anyones guess how old it is#or what it's history would be... who first owned it...#She found it in an antique shop and - not having any money - traded her boots for it because she liked it that much#therese rambles#polls
205 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think it'd be fun to sort of liveblog looking for countries that haven't abused/exiled Jews
I haven't found a list. So I'm making one.
Let's start with China. China has Jewish communities, and maybe not enough of them to become a target! The perfect amount?
Wow, Jews have lived in China since the 7th century CE. I've heard of the Kaifeng Jews!
Oh, this is ominous: "In the first half of the 20th century, thousands of Jewish refugees escaping from pogroms in the Russian Empire arrived in China. By the time of the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949, only a few Jews were known to have maintained the practice of their religion and culture."
Wow, fun fact:
According to an oral tradition dictated by Xu Xin, Director of the Centre for Judaic Studies at Nanjing University, in his book Legends of the Chinese Jews of Kaifeng, the Kaifeng Jews called Judaism Yīcìlèyè jiào (一賜樂業教), lit. the religion of Israel. Yīcìlèyè is a transliteration and partial translation of "Israel".
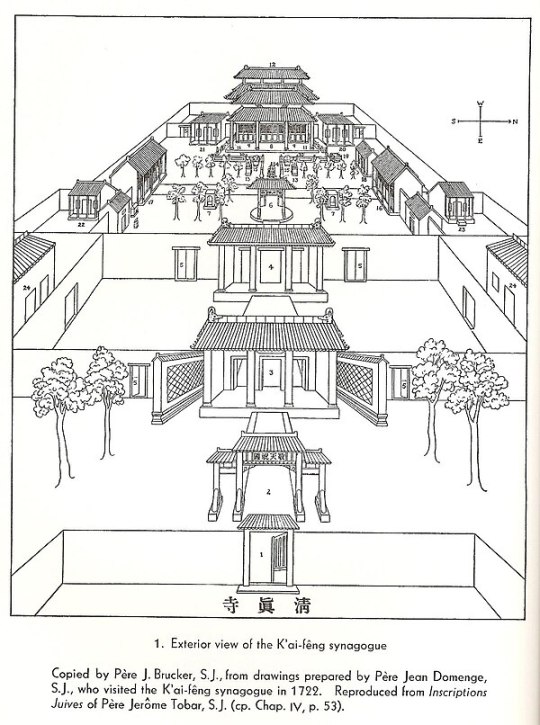
Surprising and cool:
Famous Venetian traveler Marco Polo, who visited China, then under the Yuan dynasty, in the late 13th century, described the prominence of Jewish traders in Beijing.
Neither surprising nor cool:
Genghis Khan called both Jews and Muslims Huihui when he forbade Jews and Muslims from practicing kosher and halal preparation of their food, calling both of them "slaves" and forcing them to eat Mongol food, and banned them from practicing circumcision.
In the late 1800s a lot of Jews emigrated from India and Iraq to China; they "took a considerable part in developing trade in China, and several served on the municipal councils."
In the early 1900s, 20,000 Jewish refugees from Russian pogroms emigrated to Harbin, in northeast China and "and played a key role in the shaping of local politics, economy and international trade."
Surprisingly:
Dr. Sun Yat-sen, founder of the Republic of China, admired the Jewish people and Zionism, and he also saw parallels between the persecution of Jews and the domination of China by the Western powers. He stated, "Though their country was destroyed, the Jewish nation has existed to this day ... [Zionism] is one of the greatest movements of the present time. All lovers of democracy cannot help but support wholeheartedly and welcome with enthusiasm the movement to restore your wonderful and historic nation, which has contributed so much to the civilization of the world and which rightfully deserve [sic] an honorable place in the family of nations."
Wow. It really doesn't go into any more detail about the SMALL gap between "40,000 Jews moved to China from 1845-1945," and "most of these Jews emigrated to Israel or the West... by the time of the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949, only a few Jews were known to have maintained the practice of their religion and culture."
That's four years.
Let's look at other sources.
At first, life in Shanghai was peaceful for its newest residents. The Jewish refugees were welcomed by Shanghai residents and they created a strong community with schools and a vibrant social scene. Some refugees began working as dentists and doctors, while others set up shops, cafes and clubs in the neighbourhood.
What the refugees couldn't foresee was they would travel across the globe only to fall into the clutches of the Nazis' most powerful ally. In 1941, Japan seized Shanghai. Acting under instruction from the Nazis, Japanese troops rounded up all of the city's Jews and confined them in Tilanqiao. Shanghai's Jewish ghetto had been born....
According to [historian Dvir] Bar-Gal, even prior to the Japanese invasion, many Jewish refugees in Tilanqiao lived in poverty compared to their comfortable lifestyles back in Europe. Conditions worsened greatly after Japanese soldiers gathered Jews from across Shanghai and forced them to all live within the borders of this newly formed ghetto. Jews were banned from leaving the area, even for work, unless they received permission from Japanese officers, which rarely happened.
Disease and malnutrition plagued the many heinously overcrowded group homes. "It went from a poor neighbourhood to an extremely poor neighbourhood," Bar-Gal said. "Many people had no jobs and lived in communal housing with many other beds and common bathrooms and kitchens. They had zero privacy and almost no food."
Yet, while six million Jews were murdered during the Holocaust, and up to 14 million Chinese soldiers and civilians were killed during their nation's war with Japan from 1937 to 1945, the majority of Shanghai's Jewish refugees survived. This remarkable feat was described by Holocaust historian David Kranzler as the "Miracle of Shanghai", and according to Bar-Gal, they survived because Jews weren't a primary target of the Japanese forces.
In 1945, when World War Two ended with the defeat of Japan and Nazi Germany, Japanese troops retreated and most of Shanghai's Jews quickly left, relocating to places like the US, Australia and Canada. But had Shanghai not taken these refugees in, many of these more-than-20,000 Jews may have never survived the Nazi death squads....
The first structure I came across was the imposing old Tilanqiao Prison. During World War Two, the Japanese incarcerated dozens of Jewish refugees and Chinese dissidents behind its thick stone walls. The brutality of the Japanese gave the Jews and the Chinese a common enemy and a shared experience. This connection remains strong, according to Tian.
That still leaves at least another 20,000, though? (I would say almost 20,000, but for the ones who already lived in China.)
Hmm. Here's a paper that says Jews "not only took part in the revolution but had also helped igniting it and then stayed on or joined later. While dealing with this puzzle in my paper, I’ll try to offer a typology of Jewish activists and revolutionaries in China, to explain their motives (by choice or not), and to evaluate their contributions in perspective. It appears that their Jewish identity did not play a direct role in their revolutionary activism, but it did play an indirect role. Included in this study are Grigorii Gershuni, Grigorii Voitinski, Boris Shumiatsky, Michail Borodin, Adolf Joffe, Pavel Mif, David Crook, Sidney Rittenberg, Israel Epstein, Sidney Shapiro, Solomon Adler, Sam Ginsbourg, Michael Shapiro, and more. Their main value to the revolution was mainly writing, translation, communication and publication. Although they were all deeply committed to the Chinese Communist revolution, some of them were jailed – for years – and occasionally more than once. Nonetheless, they continued to believe in, and even to justify, the Chinese Communist Party."
Wait, waaaaait. I was about to try to find the full paper (titled "Combining contradictions: Jewish contributions to the Chinese revolution"), but I ran across this first:
A century ago, the Communist International and the then-Russian Communist Party dispatched several agents to help foment revolution in China, including Russians like Grigori Voitinsky and Vladimir Neiman-Nikolsky and the Dutch Communist Henk Sneevliet. In addition to their shared commitment to Communism, all three were of Jewish heritage.
O rly??
They came with SKILLS!
On the evening of July 30, less than a month after the founding of the Communist Party of China (CPC), members of the CPC’s First National Congress met for a vote on a new party program. Suddenly, an unfamiliar middle-aged man barged into the meeting hall. “Sorry, I’m in the wrong place,” the man declared before hurrying off.
Sneevliet, well-versed in the techniques used by the police around the world to crack down on revolutionary activities, suggested that the meeting be adjourned and urged members to leave. By the time police arrived 10 minutes later, the building was already cleared out.
If you think that's impressive, try this!
Richard Frey... was an Austrian Jew who fled to Shanghai in the late 1930s. He worked for a hospital in the city until 1941, when he moved to a Communist military base in North China to teach medicine. In 1944, Frey was transferred to the central Communist base in Yan’an in China’s northwest Shaanxi province, where he soon succeeded in producing a crude but much-needed form of penicillin.
He just. Made up his own penicillin for them.
What the entire fuck.
HERE we go!
International Journal of China Studies, December 2020. "Combining Contradictions: Jewish Contributions to the Chinese Revolution," by Yitzhak Shichor, University of Haifa and Hebrew University of Jerusalem.

Fun Fact:
Jewish Lithuanian activist Grigory Gershuni emigrated from Russia to China by hiding in a barrel of sauerkraut.
Yeah okay, I think China's number one on the list of Hey, Some Countries Didn't Try That!
Next time: Japan? Or Brazil? Hmmmm.
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
World Events & Hazbin Characters
@shokolandish this is your fault.
1800s
1840s- Sir Pentious is born (approximately maybe)
1841- The word 'dinosaur' is coined.
1861- The American Civil War begins
1869- The Suez Canal is completed
1873- Blue jeans are invented
1879- Thomas Edison invents the lightbulb
1888- Sir Pentious dies
1888- Jack the Ripper murders occur
1890s- Husk is born (approximately maybe)
1890- 1st use of the electric chair
1892- Basketball is invented
1896- The Olympics are revived
1900s
1900s- Alastor is born (approximately maybe)
1910s- Angel Dust & Vox are born (approximately maybe)
1912- The Titanic sinks
1914- Panama Canal opens & WWI begins
1918- WWI ends
1920s- Niffty is born (approximately maybe)
1920- Prohibition begins in the U.S.
1923- Time Magazine is first published & Disney is founded
1927- The first sound film "The Jazz Singer" is released
1929- The Great Depression begins
1933- Alastor dies & U.S. Prohibition ends
1937- The Hindenburg Disaster
1939- WWII begins
1945- WWII ends
1947- Angel Dust dies
1948- Gandhi is assassinated
1950s- Niffty & Vox die
1953- 1st color TV is produced
1954- Rock & Roll hits the American mainstream
1959- 1st documented AIDS cases
1960s- Cherri Bomb is born (approximately maybe)
1960- The Beatles are formed
1967- The New Orleans Saints football team is formed
1968- MLK Jr is assassinated
1969- 1st moon landing
1970s- Husk & Valentino die
1977- Star Wars is released
1980s- Cherri Bomb dies
1982- Michael Jackson's album Thriller is released
1984- Radio Ga Ga by Queen is released
1985- The Macintosh 128K is released
1990- The World Wide Web begins
A few takeaways:
They all died before the the internet as we know it began.
Vox died just before color TV came around
They all could have worn blue jeans in life
Angel Dust and Vox lived through both World Wars and they were likely at an age to be drafted into service during WWII. Maybe that's where Angel got so good with Tommy Guns? And MP-40s, come to think of it...
32 notes
·
View notes
Text

A surprisingly consistent thing in history is people coming up with plans involving enormous construction projects that are intended to have a short-term positive impact, which when looked at from both a modern perspective, would have enormously bad environmental impacts globally.
One such proposed plan came from the Soviet Union, where Derek Mead recounts how they at one point wished to melt the Arctic.
In an article for Motherboard, they wrote:
You might laugh, but while Soviet Russia was blessed with the largest land mass of any nation on Earth, much of it resource rich, putting that land to use was stunningly difficult. …Russia was already spending an enormous amount of money combating the ice. Exploiting the vast petroleum reserves of the Arctic and Siberia was crucial to the growth of the Soviet economy, but every well pitted far-flung men against frozen earth and wind.
This meant that in order to exploit the resources they felt they required to properly compete with the USA, they needed to thaw Siberia. This is where a Soviet scientist named Petr Mikhailovich Borisov comes into the picture.
Borisov proposed building a 55-mile long dam that stretched from Russia to Alaska across the Bering Strait, potentially one of the largest, most expensive projects in history, with the intention of blocking the flow of cold water into the Arctic from the Pacific so the warm water from the Atlantic would over time cause the temperature in the Arctic to rise, thus melting the ice cap.
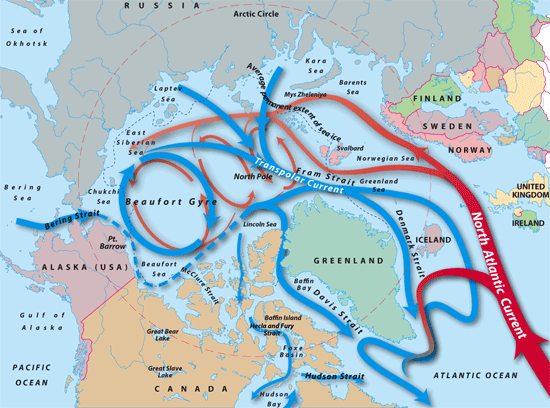
As bananas as this plan is, Mead contends that it nearly had America's support in the project, much the same way that the surprisingly similar plan to do the same in the 1800s did (albeit, that being an American plan to raise the temperature in America and Canada while freezing Europe).
Borisov dreamed of enlisting the US, Canada, Japan, and Northern Europe in the plan, as all would theoretically benefit from a warmer climate. Surprisingly, the US was intrigued by the idea. In fact, in a response to a series of questions sent in 1960 by the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists to presidential candidates Richard Nixon and John F. Kennedy, Senator Kennedy noted, as part of a larger point about the value of innovation in fostering cooperation, that the Siberia-Alaska dam was “certainly worth exploring.”
Amusingly this wasn't the only plan in this period to melt the Arctic as British scientist Julian Huxley, a cofounder of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), spoke at a conference in Madison Square Garden in 1945 about using nuclear bombs as “atomic dynamite [for] landscaping the Earth” (melting the polar ice cap).
Some have commented that considering the then recent bombings of Japan by the US this was in bad taste, but considering there were people who worked in the US government who repeatedly argued for "tactical" nuclear weapons usage (Henry Kissinger being one of them), I think that if there was enough public support behind it someone might have actually considered it.
38 notes
·
View notes
Text

Figaro's Famous Fanfare | 66 Brilliant Baritones Battle OUT NOW!
Gioachino Rossini’s opera Il Barbiere di Siviglia (The Barber of Seville) remains one of the most beloved and enduring works in the operatic repertoire.
Among its many memorable moments, Figaro's entrance aria, "Largo al Factotum," stands out as a tour de force for the baritone voice and a cornerstone for both character development and comedic expression.
The famous "Figaro, Figaro, Figaro" section, performed unaccompanied, exemplifies Rossini's wit, musical humour, and masterful control of operatic timing.
This moment showcases the singer’s vocal precision, agility, and musicianship, while also highlighting their acting skills, characterisation, dramatic flair, and ability to engage the audience.
In this 10-minute video, 66 great operatic baritones bring their own unique interpretations to this iconic a cappella passage.
List of Figaros:
Giuseppe Campanari [1855–1927] — Over 200 Met performances Mattia Battistini [1856–1928] — ‘King of Baritones’ Joseph Winogradoff [1866–1936] — Sang Figaro in Yiddish John Forsell [1868–1941] — Debuted as Figaro Mario Sammarco [1868–1930] — Noted for versatility & acting Emilio De Gogorza [1872–1949] — Recorded prodigiously
Riccardo Stracciari [1875–1955] — Figaro a signature role Giuseppe De Luca [1876–1950] — Created Sharpless & Schicchi Titta Ruffo [1877–1953] — ‘Voice of The Lion’ Pasquale Amato [1878–1942] — Sang at the Met 1908–1921 Peter Dawson* [1882–1961] — Bass-baritone. Over 1500 recordings Carlo Galeffi [1882–1961] — One of the finest interwar baritones
Enrico Molinari [1882–1956] — Sang as bass & baritone Armand Crabbé [1883–1947] — A lead in London 1906–1914, 1937 Giuseppe Danise [1883–1963] — Four Met premieres Anafesto Rossi [1883–1933] — Graduated as a bass Enrico De Franceschi [1885–1945] — Figaro in Turin & Honduras Umberto Urbano [1885–1969] — Recorded ‘marvels of lyric beauty’
Apollo Granforte [1886–1975] — c.1800 performances Giulio Fregosi [1887–1951] — Figaro in Paris Luigi Montesanto [1887–1954] — Created Michele Giacomo Rimini [1887–1952] — Sang Figaro with GalliCurci Heinrich Schlusnus [1888–1952] —Top German interwar lyric baritone Mariano Stabile [1888–1968] — Outstanding singing-actor
Richard Bonelli [1889–1980] — Sang Figaro in early sound film Benvenuto Franci [1891–1985] — A top Figaro interpretator John Charles Thomas [1891–1960] — Hollywood Walk of Fame Mario Basiola [1892–1965] — 66 roles. Taught by Cotogni Giovanni Inghilleri [1894–1959] — Sang with Ponselle & Gigli Lawrence Tibbett [1896–1960] — Legendary singer & actor
Iso Golland [1898–1961] — Respected pedagogue Dennis Noble* [1898–1966] — Bristolian [UK]. Prolific broadcaster Carlo Tagliabue [1898–1978] — Sang Wagner, Excelled at Verdi Ivan Petroff [1899–1963] — Debuted as Figaro Igor Gorin [1904–1982] — Cantor fluent in 8 languages Alexander Sved [1906–1979] — Taught by Sammarco & Stracciari
Frank Valentino [1907–1991] — 26 roles in 21 seasons at the Met Leonard Warren [1911–1960] — Met lead. Had a top C Gino Bechi [1913–1993] — Cast in musical films Tito Gobbi [1913–1984] — 136 roles over 44 years Paolo Silveri [1913–2001] — Sang as bass, baritone & tenor Giuseppe Valdengo [1914–2007] — Debuted as Figaro
Josef Metternich [1915–2005] — Created Hindemith’s Kepler Giuseppe Taddei [1916–2010] — Aged 69 at Met debut Robert Merrill [1917–2004] — Met’s principal baritone Manuel Ausensi [1919–2005] — Famous full recording of this opera Sesto Bruscantini [1919–2003] — Also sang Bartolo Aldo Protti [1920–1995] — Student of Basiola
Ettore Bastianini [1922–1967] — Recorded this opera for Decca Cornell MacNeil [1922–2011] — ‘Rivals, but [..] no equals’ Renato Capecchi [1923–1998] — Singer, actor & director Frank Guarrera [1923–2007] — Figaro a signature role Rolando Panerai [1924–2019] — More than 150 roles. Famed for buffo Piero Cappuccilli [1926–2005] — 17 major Verdi roles
Nicolae Herlea [1927–2014] — Sang Figaro c.550 times Peter Glossop [1928–2008] — A lead in London, Europe & USA Hermann Prey [1929–1998] — Figaro in film and live TV Yuri Gulyayev [1930–1986] — Figaro a best role Yuri Mazurok [1931–2006] — People’s Artist of the USSR Stoyan Popov [1933–2017] — ’The Bulgarian Titto Gobbi’
Sherrill Milnes [1935-] — Recorded Figaro under Levine Franco Pagliazzi [1937–2018] — Became dramatic tenor Silvano Carroli [1939–2020] — Taught by Mario Del Monaco Muslim Magomayev [1942–2008] — ’Soviet Sinatra’ Allan Monk [1942-] — Awarded a Golden Jubilee Medal Amartuvshin Enkhbat [1986-] — Numerous international awards
*Recorded 'Largo al Factotum' in the Key of Bb

Please join me for the premiere of this new video and share your thoughts in the comments and in the chat! I’m curious… Who’s YOUR favourite Figaro?! 🎶
There's a 'notify me' option available on the video page
Feel free to invite anyone else who might enjoy it— I look forward to you joining me there! Moodoo Van Spoon
youtube
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
I dance at two main venues. One of them is billed as a "waltz" events, but has lots of swing and Latin dances, and features music from about 1800 onward, weighted heavily toward the last couple decades. The music we dance for swings goes from about 1920 to 2024 (although there's lots of 50s-70s rock).
The other event is swing (Lindy, Charleston, Balboa) only, to music written between about 1920-1945. And they are extremely insistent that you just cannot dance swing to any music after about 1945 (with excepts for music recorded more recently, but is strictly in the style of music from 1920-1945).
Apparently this is standard for Lindy groups. But I have a hard time taking seriously anyone who insists that rock and roll isn't right for swing dancing.
8 notes
·
View notes