#100 known causes of liver disease
Text
YH23-39. Dee Lippingwell and Your Liver Care
Your Health is Your Choice with Sara Troy and her guest Dee Lippingwell, on air from September 25th
The Real Truth is there are over 100 known causes of liver disease that affect everyone from infants to seniors. One in 10 people will suffer from it. Liver disease is not just with Rock and Roll stars, but anyone can have it. Have you had the blood test that can save your life? Do not delay, it…

View On WordPress
#100 known causes of liver disease#Dee Lippingwell#Sara Troy#www.orchardofwisdom.org#www.selfdiscoverywisdom.com#Your Health is Your Choice show#Your Liver Health
1 note
·
View note
Text

‘Curse’ Behind King Tutankhamun’s Tomb Mysterious Deaths Finally Solved
The unsettling curse of King Tutankhamun’s tomb in Egypt has bewildered archaeologists since it’s been feared to be linked to the mysterious deaths of multiple excavators who discovered it in 1922.
However, a scientist now claims to have solved the mysteries of the infamous “Pharaoh’s Curse” more than 100 years later.
Toxic levels of radiation emanating from uranium and poisonous waste are believed to have lingered inside the tomb since it was sealed over 3,000 years ago, Ross Fellowes wrote last month in the Journal of Scientific Exploration (JSE).

The burial chamber in the tomb of Tutankhamun, near Luxor, Egypt.
The radiation level inside Tutankhamun’s tomb is so high that anyone who comes in contact with it could very likely develop a fatal dose of radiation sickness and cancer.
“Both contemporary and ancient Egypt populations are characterized by unusually high incidences of hematopoietic cancers, of bone/blood/lymph, for which a primary known cause is radiation exposure,” Fellowes wrote in his study.
However, this radioactivity isn’t isolated to Tutankhamun’s tomb.
Fellowes revealed that “unusually high radiation levels have been documented in Old Kingdom tomb ruins” and spread throughout sites in Egypt.
“Radiation has been detected by the Geiger counter at two sites at Giza adjacent to the pyramids,” he wrote, adding that radon — a radioactive gas — has also been detected in “several underground tombs at Saqqara.”
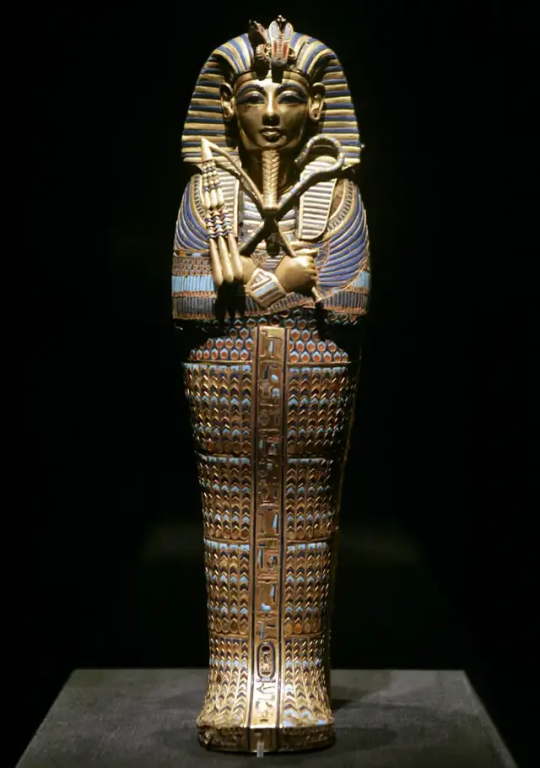

The “Coffinette for the Viscera of Tutankhamun,” which contained the king’s mummified liver, depicts him as Osiris, holding a crook and flail.

Medical imagery of Tutankhamun is shown above a replica of King Tut’s skull on display during the “Tutankhamun And The Golden Age Of The Pharaohs” at the Los Angeles County Museum of Art in California.
These readings were all found to be “intensely radioactive.”
“Modern studies confirm very high levels of radiation in ancient Egyptian tombs, in the order of 10x accepted safety standards,” the study shared.
It’s also theorized that those who built the ancient tombs were aware of the toxins based on the eerie warnings carved on the walls.
“The nature of the curse was explicitly inscribed on some tombs, with one translated presciently as, ‘they that break this tomb shall meet death by a disease that no doctor can diagnose,’” Fellowes wrote.
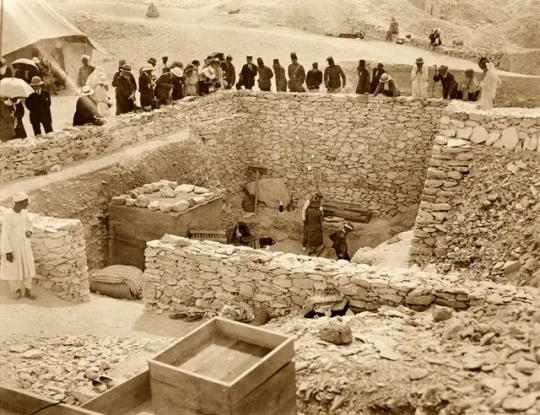

Outside the tomb of Tutankhamun during the 1922 excavation in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt.
Other ominous translations like “forbidden” because of “evil spirits” may have significantly fueled the fear that supernatural curses lingered in the ancient sites.
Those fears intensified with the mysterious deaths of Lord Carnarvon, who funded the excavation in 1922 and reportedly walked through the treasured filled rooms — and multiple others after they unsealed the tomb.
“Carnarvon was dead within a few weeks of the uncertain diagnosis of blood poisoning and pneumonia,” Fellowes wrote.
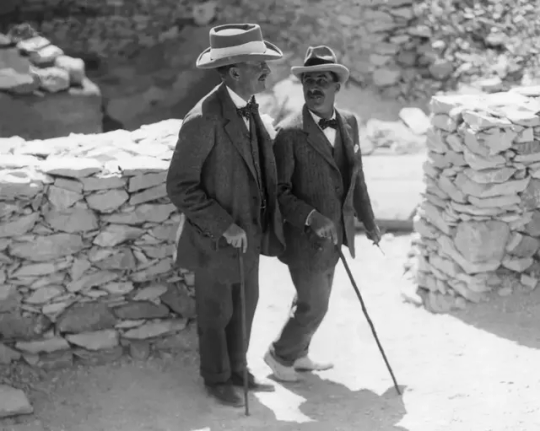

Egyptologist Howard Carter (R) walks with archaeologist Lord Carnarvon, the patron of his research, outside the tomb of King Tutankhamun in 1922.
Egyptologist Arthur Weigall allegedly told colleagues that Carnarvon would “be dead within six weeks” upon entering, the study claimed.
Howard Carter, the first person to walk inside Tutankhamun’s tomb with Carnarvon, died in 1939 after a long battle with Hodgkin’s lymphoma, which was suspected to be caused by radiation poisoning.
British Egyptologist and independent excavator Arthur Weigall was present at the opening of Tut’s Tomb and is also credited with starting the ‘myth’ of the curse.
He died of cancer at 54 years old in 1934.
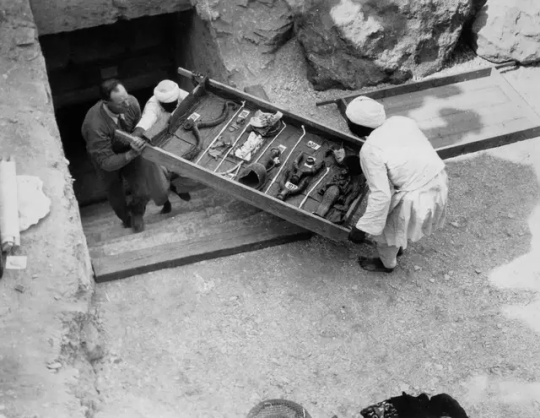

Workers remove a tray of chariot parts from the Tomb of Tutankhamun in the Valley of the Kings, Egypt, in 1922.
In total, six of the 26 people present when the tomb was opened died within a decade from asphyxia, stroke, diabetes, heart failure, pneumonia, poisoning, malaria and X-ray exposure.
While the deaths can be seen as odd, the curse theory was also likely fueled by the oddities that happened when it opened.
Carnarvon had reportedly suffered a mosquito bite that became severely infected.
Around the time excavators opened the tomb, Cairo reportedly suffered a bizarre power outage and a freak sandstorm, according to National Geographic.’
At one point during the excavation, Carnarvon’s favorite dog allegedly let out a chilling howl and suddenly dropped dead.
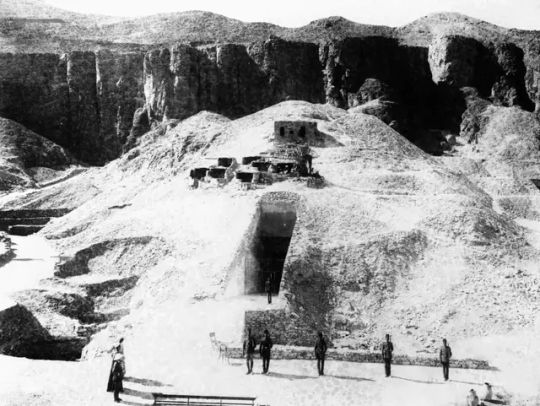

A photograph showing guards standing outside the tomb of Tutankhamun in Egypt in 1922.

A sacred cow being removed from Tomb of Tutankhamun in 1922.
From a historical perspective, the discovery of the tomb in the Valley of Kings is considered one of the most fascinating finds that gave modern society a glimpse into the Egyptian royalty voyage into the afterlife.
Five thousand items, including solid gold funeral shoes, statues, games, and strange animals, were discovered inside Tutankhamun’s tombs.
It would take the excavators ten years to clear the tomb of its treasure.

The golden funerary mask of Tutankhamun.
The unsealing and studying of the tomb is also credited with launching the modern era of Egyptology.
Tutankhamun took the throne as pharaoh around nine or ten years old and ruled between 1332 BC and 1323 BC.
However, he died by the time he turned 18.
There are no surviving records of Tutankhamun’s death and how the young pharaoh died remains a mystery.
However, Tutankhamun is suspected to have suffered from several health issues — likely linked to his father, Akhenaten, and his mother, Nefertiti, being brother and sister.
By Richard Pollina.
#‘Curse’ Behind King Tutankhamun’s Tomb Mysterious Deaths Finally Solved#King Tutankhamun#Pharaoh’s Curse#Old Kingdom#Valley of the Kings#Lord Carnarvon#Howard Carter#Egyptology#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient egypt#egyptian history#egyptian mythology#egyptian pharaoh#egyptian antiquities#egyptian art
72 notes
·
View notes
Text
Magic Bullets: The Antibiotic Story
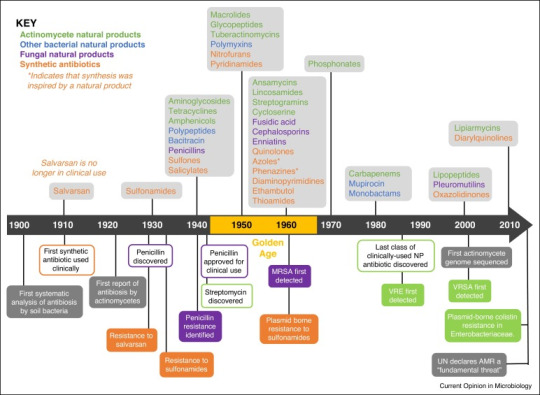
The year was 1907 and a Dr. Alfred Bertheim was trying to make arsenic less toxic to humans.
Why? Because in addition to killing humans, arsenic also kills trypanosomes- single-celled protozoa that cause the life-threatening infection trypanosomiasis. By creating a version of arsenic that still killed the protozoa, but not the human they infected, Dr. Bertheim could create a drug to treat the disease*.
This was not a fully new idea. About 50 years earlier, a drug called Atoxyl had been created in France. About 40 times less toxic than pure arsenic, it had been shown to not only successfully treat trypanosomiasis, but also the equally devastating syphilis infection.
But 40 times less toxic than pure arsenic is still not great. About 2% of people treated even one time with the drug ended up blind, among a myriad of other side effects. It was a start, but not ideal.
And Dr. Bertheim (under the direction of better-known Dr. Paul Ehrlich) was setting out to change that.
And it just so happened that the sixth compound from the sixth group he tried did so. Known as "compound 606", the new Arsphenamine could treat trypanosomiasis, relapsing fever, and syphilis very effectively- and it didn't leave its takers dead or blind.
Most of the time, at least. See, arsphenamine, also known by the brand name salvarsan, was a pain in the ass to administer. It had to be dissolved in several hundred mililiters of water under a nitrogen atmosphere to prepare it for administration. If it touched air, it would rapidly react, causing toxic byproducts that could cause liver failure, severe skin rashes, and even death.
But both trypanosomiasis and syphilis were definitely going to kill you, so it was worth the risk.
And the seed had been planted, so to say. The idea of a chemical able to kill infection-causing agents without killing the host was a true possibility for the future of medicine.
And by 1912, Neosalvarsan, a drug somewhat less effective -but far easier to administer and with significantly fewer side effects- was on the market. Over the next decade, Neosalvarsan would be responsible for a massive drop in syphilis cases worldwide.
But neither of the drugs could treat deadly infections from staph or strep or the hundreds of other bacterial or viral infections that still had no cure in the 1910's and 1920's.
Then came the first of the heavy-hitters. Bayer was a dye company when it started, and in 1932, three and a half decades after switching mostly to pharmaceuticals, chemists at Bayer were testing the company's dyes for anti-infective properties. They went through thousands of trials, finally finding a dye that could kill streptococcal bacteria without killing a mouse host.
Pre-1930s, streptococcal disease was a major problem. It caused strep throat, cellulitis, scarlet fever, childbed (purpural) fever, some forms of toxic shock syndrome, impetigo, necrotizing fasciitis, rheumatic fever, and many others. The skin infections may have been at least somewhat treatable with a hot compress, but the rest were prone to cause blindness, deafness, loss of limbs, and for many, loss of life.
In 1936, sulfonamide antibiotics changed that. Protosil, the first of the sulfonamides, became available to treat many of the infections listed above. These would be used for wound infections throughout WWII. Unfortunately, they would also cause the untimely death of nearly 100 people via the Elixer Sulfanilamide tragedy.
Sulfanilamide was a similar drug to Prontosil and was safe and effective for treating strep infections. However, when mixed with diethylene glycol (now used as standard car antifreeze) to make it into a liquid suspension, it was deadly. See this letter from a doctor who had prescribed the liquid form of the medication, not knowing it was poison:

[to read more about the Elixer Sulfanilamide Disaster, see here]
Despite the sulfanilamide tragedy, the race was on for more antibiotics. Three years before they went on the market, researchers had found evidence of bacterial resistance to sulfonamides. What would happen when these new bacteria, that didn't die when exposed to the new wonder drug, made up so much of the bacterial population?
In 1942, the Cocoanut Grove fire in Boston caused over 492 deaths and 130 injuries. The injured were among the first to receive a remarkable new drug called penicillin. The fire and the fate of the victims were publicized throughout the world, and penicillin became a household name overnight. But once again, even before it went on the market in 1943, just in time for the end of the Second World War, there was evidence of resistance.
But fortunately, the fire had been sparked. Over the next 30 years, many dozens of antibiotics would come into clinical use. If you've taken it, it probably came out between 1940 and 1970. Tetracycline, isoniazid, metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, vancomycin, amoxicillin, and dozens more you've never heard of.
And then? Nothing.
Well, not completely nothing, there were a couple that came out in the 1980s and a few in the early 2000s. But nothing like that 30-year golden age.
But now we're running into problems due to drug resistance. About 1.27 million people die annually directly from antibiotic resistant infection, while antibiotic resistance contributes to about 4.95 million more deaths.
The good news is that the drugs that are being made today are directly targeting those antibiotic resistant infections. In fact, as I'm writing this, a new drug (Zosurabalpin) is being tested for a bacteria called Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, which up until now has had no antibiotic that works against it.
*as you may imagine for the time period, this was not necessarily a benevolent act. See, most of the reason Europeans wanted to treat trypanosomiasis in the first place was because they kept dying of it when they went to colonize Africa. And they wanted something that would give them a leg up on the people who were already there.
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
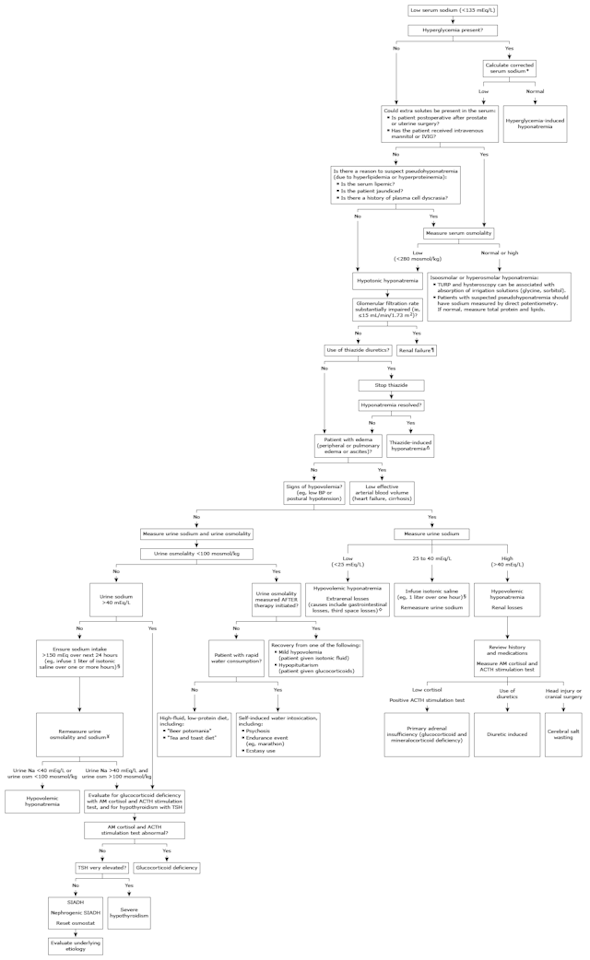
Hyponatremia, defined as a serum sodium concentration below 135 mEq/L, is usually caused by a failure to excrete water normally. In healthy individuals, the ingestion of water does not lead to hyponatremia because suppressed release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also called vasopressin, allows excess water to be excreted in a dilute urine.
●The initial diagnostic approach to the adult patient with hyponatremia consists of a directed history and physical examination as well as selected laboratory tests. When hyponatremia is first discovered, some elements of the history, key features of the physical exam, and the results of several helpful laboratory tests are usually already available, and these guide the subsequent diagnostic approach:
•If hyperglycemia is present, the serum sodium concentration should be corrected for the effect of glucose to exclude hypertonic hyponatremia. To calculate the "corrected" serum sodium, we recommend the use of the following ratio: the sodium concentration will fall by approximately 2 mEq/L for each 100 mg/100 mL (5.5 mmol/L) increase in glucose concentration.
•Patients with lipemic serum, severe obstructive jaundice, or a known plasma cell dyscrasia may have pseudohyponatremia. This laboratory artifact can occur if the sodium is measured with flame photometry or indirect potentiometry using ion-selective electrodes when the solid phase portion of serum or plasma is increased due to severe elevations of triglycerides, lipoprotein-X, or protein. The true concentration of sodium in plasma water can be measured using direct ion-selective electrodes, which are not susceptible to the artifact. Such direct ion-selective electrodes are utilized by most "point of care" bedside analyzers and devices used to measure blood gases. In addition, patients with pseudohyponatremia typically have a normal serum osmolality.
•Patients who have had recent surgery utilizing large volumes of electrolyte-poor irrigation fluid (eg, prostate or intrauterine procedures) and those treated with mannitol, glycerol, or intravenous immune globulin may have isotonic or hypertonic hyponatremia. Measurement of the plasma osmolality is helpful in these settings.
•Patients who do not have hyperglycemia or one of these other features associated with pseudohyponatremia, isotonic hyponatremia, or hypertonic hyponatremia are likely to have hypotonic hyponatremia.
●The serum creatinine concentration, which can be used to estimate glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and the patient's medication history are typically available at the time that hyponatremia is discovered. Both severely reduced GFR and thiazide (or thiazide-type) diuretics are important causes of hypotonic hyponatremia.
●In patients with hypotonic hyponatremia who do not have severely reduced GFR and who are not taking a thiazide diuretic, or in patients suspected of having an additional cause of hyponatremia, the subsequent evaluation depends upon whether or not the patient has clinically apparent edema and/or ascites:
•Patients with hyponatremia due to heart failure or cirrhosis typically have advanced disease and present with clinically apparent peripheral edema and/or ascites along with a previous diagnosis of heart or liver failure.
•Nonedematous patients with hypotonic hyponatremia are either euvolemic or hypovolemic. Most patients with hyponatremia due to true hypovolemia will have obvious signs of volume depletion; however, some hypovolemic patients have more subtle signs and are mistakenly judged to be euvolemic. The evaluation of nonedematous patients usually requires further testing:
-Hyponatremic patients who present with clinical symptoms and signs of hypovolemia may have extrarenal fluid losses or renal fluid losses. Measurement of the urine sodium and chloride concentrations can often distinguish between these two causes.
-Most hyponatremic patients who appear to be euvolemic by physical examination have the syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH). However, such patients may occasionally have hyponatremia due to true volume depletion, primary polydipsia, malnutrition, glucocorticoid deficiency, or severe hypothyroidism. The subsequent evaluation in such patients includes measurement of the urine sodium and urine osmolality as well as levels of cortisol and thyroid-stimulating hormone.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Experts Advise, Offer New Vaccination for Pet Rabbits

COVID-19 hasn’t been the only global pandemic arriving on our shores recently. A new variant of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV), previously common in wild rabbits in Europe, Asia, and Australia, was first detected in the United States in early 2020. It has now spread to multiple states in the U.S., particularly the western states.
How to Get the Vaccine
Vaccination clinics for RHDV will be held
on the following dates at
Veterinary Medicine South Clinic
2100 S Goodwin Ave, Urbana.
Clinic Dates:
* August 18, 2023
* September 15, 2023
* October 13, 2023
Call for an appointment: 217-244-2555
On July 13, 2023, the first case of RHDV was detected in the state of Illinois in a pet rabbit. The case was in Cook County. Prior to this detection, the disease had not been diagnosed in wild or domestic rabbits. This detection raises the level of concern for the health implications of both wild and domestic rabbits within Illinois.
If RHDV is detected or suspected in wild or domestic rabbits, it must be reported to the World Organisation for Animal Health.
Dr. Michelle Borsdorf, a board-certified specialist in zoological medicine at the University of Illinois Veterinary Teaching Hospital in Urbana, recommends that all pet rabbits be vaccinated against this new variant (RHDV2), which is more dangerous than earlier forms of the virus. This variant of RHDV has 70% to 100% mortality rates in pet rabbits.
Its presence in Illinois emphasizes the need to act now to vaccinate and protect against this disease!
What Is RHDV?
Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus is a member of the calicivirus family. Other viruses in this family that do not cause rabbit health issues include norovirus, the most common cause of gastroenteritis (vomiting and diarrhea) in people, and a feline virus that causes respiratory disease.
RHDV infects wild and domestic species of rabbits and is highly contagious. It does not infect people or other animals. The virus travels through the blood stream of an infected rabbit and rapidly damages the cells of the liver. The liver makes proteins used in forming blood clots, and the classic form of RHDV causes uncontrollable bleeding in rabbits.
Clinical signs of rabbits infected with this virus will primarily include bleeding from the eyes, nose, or mouth, as well as jaundice (yellow discoloration of eyes and skin), which are related to severe liver dysfunction or failure. Affected rabbits may also develop respiratory or neurologic symptoms, or even present with more generalized signs of illness such as lethargy, reduced appetite, and lack of defecation or urination.
“Additionally, some rabbits do not exhibit symptoms prior to succumbing to the disease. This outcome, known as sudden death, illustrates how rapidly the disease can progress,” says Dr. Borsdorf.
How Does RHDV Spread?
Unfortunately, the virus survives well in any environment. Infected wild rabbits may shed the virus outside, and the virus can then be carried into the home on people’s clothing or shoes and introduced to pet rabbits. Any rabbit exposed to blood, urine, or feces of an infected rabbit could develop infection.
Because RHDV is spread between rabbits, Dr. Borsdorf advises taking steps in your home to reduce the risk of RHDV infection.
Do not allow your pet rabbit to graze in outdoor areas that are frequented by wild rabbits.
Ensure that shoes worn outside are not worn in areas of the home where your pet rabbit has access.
Weeds and flowers from outdoor areas frequented by wild rabbits should not be fed to pet rabbits.
Always wash your hands before and after handling rabbits.
Vaccinate your pet rabbit.
Vaccination Against RHDV
In other countries where RHDV circulates, vaccinations against the virus are given to pet rabbits. Now that the threat to rabbit health is present in the U.S., the U.S. Department of Agriculture has authorized emergency use of the vaccine here. Distribution of the vaccine to veterinarians began in 2021.
Although the vaccine does not yet have full FDA approval, the approval process is ongoing. Preliminary research suggests that the vaccine is safe and effective in preventing infection. This is based on a challenge study performed where 100% of vaccinated rabbits survived when exposed to the virus, while 70% of the unvaccinated rabbits died from the disease.
Side effects of the vaccine have included mild swelling at the injection site and mild fever or lethargy for a few days after the vaccine is administered. To be effective, the vaccine requires two doses administered at least 3 weeks apart, and annual boosters thereafter.
Vaccination at the University of Illinois
The zoological medicine service will continue hosting vaccine clinics to administer vaccines and their boosters to pet rabbits once monthly. (See sidebar above for the current list of dates.) Veterinary interns, residents, and students as well as certified veterinary technicians will be involved in this process under supervision of faculty members. including Dr. Borsdorf, head of the zoological medicine service.
Because the clinic is focused on delivering vaccine to healthy animals, no diagnostic testing will be performed at that time.
Because of how the vaccine is packaged, vaccination will be offered only through the scheduled vaccine clinics and not through regular appointments with the zoological medicine service at the Veterinary Teaching Hospital.
To make an appointment for your rabbit to receive the vaccine, please call the Veterinary Medicine South Clinic at (217) 244-2555.
For more information, visit:
https://www.aphis.usda.gov/publications/animal_health/fs-rhdv2.pdf
https://rabbit.org/faq-for-medgenes-rhdv2-vaccine/
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What do you need to know about Dianabol in bodybuilding?
Summary
A very popular doping product, Dianabol is an anabolic steroid widely used in the body-building world. Also known as D-bol, Danabol or Methandrostenolone, it is strictly forbidden for consumption and resale in most countries.
Despite its prohibition and health hazards, many bodybuilders use this product to gain muscle mass and strength faster. The results are certainly incredible, but not without consequences.
Dianabol pills (or methandrostenolone) is the grandfather of doping in modern bodybuilding. Many famous celebrities admit to having used this product during their bodybuilding career in the 60s and 70s, such as Arnold Schwarzenegger, who explained that his performance on the weight bench was closely linked to dianabol.
The creation of this steroid dates back to the late 50s. Moreover, it is still used in bodybuilding. John Ziegler, an American doctor, created and developed Dianabol in 1958 in Basel at the Ciba laboratory (now part of the huge Swiss pharmaceutical group Novartis).
Originally developed to treat certain diseases, the Americans did not hesitate to use methandienone at the Olympic Games to boost the performance of their team in order to compete against the Russians, who also used anabolic steroids. The Cold War even existed in bodybuilding!
Why is Dianabol used in Bodybuilding?
The scientific community has repeatedly pointed to the negative effects of Dianabol on the body. In addition to harmful effects on the liver, the "miracle" steroid is said to significantly increase blood pressure.
To clarify all this, scientists have conducted a study on a population of athletes, with the aim of finding a dosage to limit the side effects.
Conducted in the 1980s, the study consisted of administering 100 mg of Dianabol daily to athletes. Of course, this dosage allowed the athletes to maximize their gains in muscle mass, knowing that they would have gained up to 7 kg of muscle, without increasing their fat mass.
However, the study did not only show the positive effects of the steroid: there were also adverse effects on natural testosterone production and plasma GH levels.
Dianabol is a very common doping product in the world of body-building that is mostly taken orally. There is an Dianabol injection, but it is more difficult to obtain.
It is an anabolic steroid, a class of steroid hormones connected to testosterone.
Like all anabolic steroids, it will provide two effects once consumed:
An androgenic effect: that is, it will exacerbate male traits and characteristics;
An anabolic effect that promotes muscle anabolism for better muscle mass development.
Advantages of Dianabol steroid
You want to make a weight gain intensive? Are you looking for a supplement to maintain your earnings, between two cycles? Then a Dianabol cure is for you. Indeed, Dianabol will provide you with rapid and significant growth in your muscle mass.
The Dianabol cure is very popular among bodybuilders. And this is not surprising because this product allows acquiring muscles in a short time. The effects of the cure are as follows:
A significant muscle growth: this effect is primarily due to the nitrogen. Dianabol promotes the retention of this element which is necessary for the development and renewal of muscles. By retaining it in the body, the product allows a faster and more important muscle growth.
Protein synthesis and nutrients: Dianabol has above all an anabolic effect. And this is somehow related to its ability to stimulate the production of insulin by the body. For information, it is a functional protein that is involved in the muscle building process. Insulin pushes the muscle cells to feed themselves by provoking their opening. Otherwise, this element is also involved in protein synthesis.
An important weight loss: Dianabol also causes what is called "hydrosodic retention phenomenon". At the end of the treatment, the athlete loses weight.
Finally, it is good to know that Dianabol is often used alone. However, it also happens that some athletes stack it with other products, which can improve the effect or target certain specific points.
Dianabol Cycle Information and Dosage
Dianabol is mainly presented in the form of pills to be taken orally and the cycles vary from one practitioner to another. It all depends on the level. Dosages vary from 20mg per day to 80mg maximum depending on the level. The Dianabol cycle fluctuate between 4 and 8 weeks maximum.
Some will spread the dosage over the day in two or three doses while others will take the daily amount in one dose 30 minutes before their workout.
If you consume the maximum amount of Dianabol (i.e. 80mg per day), your cycle should not exceed 6 weeks. It is also important to take a break between cycles. This break must be equal to the duration of the cycle (at least).
Indeed, in addition to being dangerous for the health of the liver and the heart, Dianabol disrupts the hormonal system. It will then be more difficult to have a normal and natural secretion of testosterone.
For example, a beginner can take 10 mg per day: Either 10mg 30 minutes before the beginning of the workout or 5 mg in the morning to 5 mg at the end of the day.
For the intermediate profiles, generally the doses gravitate around 30 to 40 mg per day in one intake up to three intakes.
As for the confirmed bodybuilders, they will take doses up to 80 mg per day over a period of six weeks maximum.
Dianabol is often used as a "kick start" on a course of treatment before switching to other steroids. That is to say that it is used just at the beginning of a cycle to boost its power before switching to another product. In fact many bodybuilders combine DBOL with other products.
Where to buy Dianabol ?
Behind Dianabol, we find the active ingredient methandrostenolone, a powerful anabolic that has the particularity of being very weakly bound to the protein associated with serum.
The compound therefore boosts protein synthesis to promote the production of new cells, which will then be used for muscle building. You can find Dianabol for sale online.
To explain the worldwide success of Dianabol, it is important to know that most injectable steroids only release their active ingredients after the second or third week of the treatment cycle. With the famous Dianabol, the results will be visible from the first three days of treatment.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Common Liver diseases - liver transplant surgery
Although liver disease is stereotypically linked to alcohol or drugs, the truth is that there are over 100 known forms of liver disease caused by a variety of factors. liver transplant surgery.
#liver transplant surgeons in gujarat#best liver cirrhosis treatment in gujarat#best liver transplant surgery in gujarat#best kidney transplantation in gujarat#liver transplantation in india#liver transplant specialist in india#pediatric liver transplant specialist in gujarat#fatty liver diseases treatment in india
0 notes
Text
What is Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) and Why It Matters?
It’s a well-known scientific fact that our genetics is the sum of our parents, a lesser-known fact is that sometimes their actions can heavily impact our genetics as well. One of these actions is responsible for causing the single most preventable cause of intellectual disability in children – Fetal alcoholic spectrum disorder (FASD), brought about when women consume alcohol during pregnancy.
I am sure alcohol needs no introduction, it is one of the most abused psychoactive drugs in the world while also being one of the most widely used in many diverse scenarios – social drinking, cooking, as a coping mechanism by addicts, etc. Among its many toxic effects (that most of us choose to be ignorant towards) a highly overlooked one is its ability to transmit these effects from a mother to her unborn child leading to the child having to suffer with FASD for life.
As we observe ‘International FASD Day’ this 9th of September, its vital to understand the workings of this 100% preventable disorder and our role in it.
I have aforementioned that the intake of alcohol by pregnant mothers is the cause of FASD in their offspring but how exactly does alcohol reach the baby and how does it affect it?
During pregnancy the mother’s body develops a specialized structure known as the placenta which acts as a sort of bridge between the maternal body and the developing fetus. A little-known fact about the placenta is that it's not just a temporary structure but a whole organ in and of itself thus alluding to its sheer importance and complexity. The placenta makes sure that the transport of nutrients, metabolites, blood gases and other vital substances happens seamlessly between the mother and the developing baby, it also protects the fetus from any harmful substances and toxins circulating within the mother’s bloodstream. Some toxic substances (termed teratogens) like alcohol and tobacco can readily pass through the placenta due to their nature and enter the baby’s bloodstream.
Babies do cannot process alcohol the same way we do due to their immature liver and that’s why high doses of alcohol are fatal to the unborn fetus. Moreover, alcohol can enter and concentrate within the amniotic fluid thus increasing the overall exposure of the fetus to it. If this occurs during the first trimester, the fetus is at increased risk of spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, and intrauterine growth retardation. When alcohol consumption occurs during the second trimester the fetus has a higher chance of survival but will be born with a range of adverse outcomes which fall under FASD.
How does someone suffering from FASD look like?
We have so far discussed how FASD comes about but haven't really gotten into the basic symptoms and appearance of FASD. As a teratogen alcohol brings about its effects by attacking important cells within the central nervous system which are responsible for a range of important functions from brain development to proper anatomical alignment of facial features and limbs. This led to the formation of FASD classification as follows - (1) Central nervous system damage and cognitive impairments, (2) Dysmorphic facial features, and (3) Behavioral and emotional deficits.
Physical dysmorphic features of people suffering from FASD are rare but can include – a thin upper lip, smooth hypoplastic philtrum, down-slanting short palpebral fissures, hypertelorism, microcephaly, epicanthal folds, and a receding chin. Although only a few of these features may be present in a single FASD patient at a time depending on the severity of the disease. The main FASD features involve the brain and therefore can lead to other disabilities later in life. These disabilities include, but are not limited to, academic failure, substance abuse, mental health problems, frequent contact with law enforcement, and inability to live independently and obtain and/or maintain employment—all of which have lifelong implications.
How do people suffering from FASD feel about it?
A study published in May of 2024 in the MDPI Journals titled ‘FASD: The Living Experience of People with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder—Results of an Anonymous Survey’ sought out to get a comprehensive understanding of how living with FASD has affected these people in the following major life areas – Sense of self, adversity, education, employment, finances, housing instability, memory issues, familial relationships, friendships, and criminal justice. They achieved this by conducting anonymous surveys among FASD patients targeting the aforementioned areas, they received 468 complete responses which were then included in the study. The results of the study proved to be very concerning -
Sense of self – On average respondents mentioned that they felt alienated and inferior in society which impacted their sense of self greatly. This was also brought about by the fact that the majority of them did not have a clear definition of FASD provided to them leading to internal conflict.
Adversity – This are of the study was divided into childhood and adult adversities. The most common childhood adversities mentioned were being involved with alcoholics in the household in an abusive or depressed manner. Adulthood adversities involved being easily manipulated and talked into doing things against their better judgement.
Education – The main takeaway from this section of the study is that 77% of respondents who did not complete their high school believe that they would have been able to complete their education had they been provided with more individualized support pertaining to their special needs.
Employment – Among those who were employed, majority of the respondents felt fulfilled and enjoyed their work but also felt heavy stress and disorientation leading to mental stress due to the nature of job stress itself. They felt like they did not do their job properly and would take extra care in this regard leading to more stress. Majority of the respondents also hid their diagnosis from their coworkers and employers due to the stigma surrounding it. Something more concerning this area of the study revealed was that majority of the respondents were laid off or quit at least thrice in their career journey.
Finances – Just over half of the respondents revealed that they received some sort of financial support (albeit small) from the government or their family members, this adds to their level of dependency.
Housing instability – Of those who had been evicted at least once in the past, they reported issues like not having enough finances to cover their rent or failing to remember that their rent was due.
Memory issues – The respondents indicated a number of problems arising due to memory issues which included failing to remember to pay rent, to eat, to maintain hygiene, and to take their medications.
Familial relationships – Only a very small percent of the respondents were raised by their birth family, the majority of them were raised in a variety of living situations. This had led to more childhood trauma in addition to already existing trauma.
Friendships – Majority of the respondents indicated that it was difficult for them to make friends and even more so to keep them. They also added that making and keeping friends was very exhausting and caused a lot of anxiety for them.
Is FASD treatable? To date, there is no known treatment to reverse alcohol-induced damage to the fetus. The only treatment options available deal with trying to reduce symptoms and increase support as much as possible.
It's scary to think of all these lifelong implications and problems caused by a disease which is 100% preventable. So, in the spirit of International FASD Day, Lets tackle the most important question now – How can we help in the battle against FASD?
We can further divide this problem into two smaller issues – How to help prevent FASD? And how to help those existing with FASD?
The aforementioned study actually answers the second problem very effectively in the following ten points -
Access to a mental health clinician who specializes in FASD.
Availability of a doctor or nurse practitioner who knows about FASD.
A person who can help when something goes wrong.
A person who can be trusted to give advice when needed.
Enough money to meet monthly needs.
Help with tasks of daily living such as cleaning and laundry.
Having a trusted person who, with permission, can speak and act for the person with FASD.
A trusted person to manage or help with money so that the person with FASD is less likely to be taken advantage of. This may also include being able to attend appointments so that there is someone present to support the person’s understanding of what has been said and recommended.
Help to obtain and sustain employment (this would be a person who understands what is and is not possible).
The ability to engage in activities that are important to the person.
When it comes to preventing FASD, remember that a pregnant woman almost never drinks alone so doing our best to engage with pregnant women who have a history of alcohol abuse and raising awareness among them during social gatherings or your inner circles goes a long way in preventing FASD.
You can also use this opportunity to reach out to anyone you know who suffers from FASD and give them the support they need.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Seroflo Rotacaps 100mcg

Seroflo Rotacaps 100mcg is a combination inhaler used to manage asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It contains two active ingredients: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate. Here's a breakdown of its components and usage:
Active Ingredients:
Salmeterol (50 mcg): A long-acting beta-2 agonist (LABA) that helps relax the muscles in the airways, allowing them to remain open for a longer duration. This helps in preventing asthma attacks or bronchospasms.
Fluticasone Propionate (100 mcg): A corticosteroid that reduces inflammation in the lungs, helping to prevent breathing difficulties and providing long-term control of asthma and COPD symptoms.
How it Works:
Salmeterol: By acting on beta-2 receptors in the lungs, it relaxes bronchial muscles, which allows for easier breathing. It works for up to 12 hours after inhalation.
Fluticasone Propionate: Reduces the inflammation in the airways, which is the root cause of many asthma and COPD symptoms. It also helps prevent the frequency and severity of attacks.
Indications:
Asthma: For the maintenance treatment of asthma, especially for those requiring a combination of a LABA and an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS).
COPD: It is used in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to reduce exacerbations and manage symptoms over time.
Dosage and Administration:
Seroflo Rotacaps 100 mcg are usually used twice a day, once in the morning and once at night.
A device known as a Rotahaler is used to administer the inhalation powder, allowing the drug to be inhaled straight into the lungs.
Important Points on Usage:
In order to avoid oral thrush, which is a potential side effect of inhaled steroids, always rinse your mouth after taking Seroflo.
When suffering from an acute asthma attack, never use Seroflo as a rescue inhaler. A short-acting bronchodilator, such as salbutamol, should be given in these situations.
Even if you feel better, take your medication as directed in order to maintain long-term management.
Common Side Effects:
Oral thrush or fungal infection in the mouth
Hoarseness of voice
Headache
Respiratory infections like cold or flu
Muscle pain
Precautions:
Steer clear of abrupt stops as they could exacerbate symptoms.
If you have any pre-existing medical illnesses such as diabetes, liver issues, or heart disease, see a doctor.
When using on expectant or nursing mothers, exercise caution.
0 notes
Text
Cancer: Types, Risk Factors, Prevention, and Causes
Cancer is a word that strikes fear into the hearts of many, but understanding it can empower us to take proactive steps in managing our health. This guide will walk you through the different types of cancer, the risk factors involved, preventive measures you can take, and the underlying causes that lead to this complex disease.
Understanding Cancer
Cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the body begin to grow uncontrollably. These cells can form tumors, which may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Malignant tumors can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body, making them more dangerous.
Types of Cancer
There are more than 100 types of cancer, but they can be broadly categorized into a few major groups:
Carcinomas: These are the most common types of cancer, originating in the skin or the lining of internal organs. Examples include lung cancer, breast cancer, and colon cancer.
Sarcomas: This type of cancer begins in the bones, muscles, fat, or connective tissues. Osteosarcoma (bone cancer) and liposarcoma (fat cancer) are examples.
Leukemias: Unlike other cancers, leukemias don't form solid tumors. Instead, they affect the blood and bone marrow, leading to an overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
Lymphomas: These cancers start in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system. Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma are two main types.
Melanomas: Melanomas originate in the melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment in the skin. Although they are less common, they are more dangerous due to their tendency to spread rapidly.
Central Nervous System (CNS) Cancers: These cancers begin in the brain or spinal cord. Glioblastoma and astrocytoma are examples of CNS cancers.
Risk Factors for Cancer
Cancer is caused by a combination of factors, some of which are within our control, while others are not. Understanding these risk factors can help in early detection and prevention.
1. Genetic Factors
Family History: If cancer runs in your family, you may be at a higher risk. Certain inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can significantly increase the likelihood of breast and ovarian cancers.
Genetic Mutations: Sometimes, mutations in your DNA can occur spontaneously or due to environmental exposures, leading to cancer.
2. Lifestyle Choices
Smoking: Tobacco use is the leading cause of cancer, especially lung cancer. It’s also linked to cancers of the mouth, throat, pancreas, bladder, and more.
Diet: A diet high in processed foods, red meat, and low in fruits and vegetables can increase your cancer risk. On the other hand, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants can help reduce this risk.
Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is associated with cancers of the liver, mouth, throat, and esophagus.
Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to obesity, a known risk factor for various cancers, including breast, colon, and kidney cancer.
3. Environmental and Occupational Exposures
Radiation: Exposure to high levels of radiation, whether from medical treatments or environmental sources, can increase the risk of cancer. This includes ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, which are a significant risk factor for skin cancer.
Carcinogens: Certain chemicals, like asbestos, benzene, and formaldehyde, are known to cause cancer. These may be encountered in certain workplaces or through pollution.
Infections: Some infections are linked to cancer. For example, human papillomavirus (HPV) is a leading cause of cervical cancer, and Hepatitis B and C can increase the risk of liver cancer.
4. Hormonal Factors
Hormone Replacement Therapy: Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) during menopause has been linked to an increased risk of breast cancer.
Reproductive History: Factors like age at first menstruation, age at menopause, and number of pregnancies can influence cancer risk.
Causes of Cancer
While risk factors increase the likelihood of developing cancer, the exact cause often remains elusive. However, most cancers are caused by a combination of genetic mutations and environmental influences. Here's how these elements interplay:
DNA Damage: Cancer begins when the DNA inside cells gets damaged. This damage can be due to exposure to carcinogens, like tobacco smoke or UV rays, or it can occur due to random genetic mutations during cell division.
Cell Mutation and Proliferation: Normally, cells with damaged DNA either repair themselves or die. But sometimes, these cells survive and continue to divide uncontrollably, leading to cancer.
Tumor Formation: As these abnormal cells continue to grow and divide, they can form a tumor. If the tumor is malignant, it can invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, a process known as metastasis.
Prevention of Cancer
While not all cancers can be prevented, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk:
Avoid Tobacco: The single most effective way to prevent cancer is to avoid smoking and using other forms of tobacco. If you currently smoke, seek help to quit.
Eat a Healthy Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limiting processed foods, red meat, and sugary beverages can also reduce your risk.
Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and lowers the risk of several types of cancer.
Protect Yourself from the Sun: Use sunscreen with at least SPF 30, wear protective clothing, and avoid tanning beds to reduce the risk of skin cancer.
Get Vaccinated: Vaccines like the HPV vaccine and Hepatitis B vaccine can protect against infections that are known to cause cancer.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For women, this means up to one drink per day, and for men, up to two drinks per day.
Screenings and Regular Check-ups: Regular screenings for cancers like breast, cervical, colorectal, and prostate cancer can detect the disease early when it is most treatable. Discuss with your healthcare provider which screenings are appropriate for you based on your age, gender, and risk factors.
Conclusion
Cancer is a multifaceted disease with numerous types, each having its own set of risk factors, causes, and preventive measures. While it is impossible to eliminate all risks, making informed lifestyle choices and staying vigilant with regular screenings can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing cancer. By understanding the types of cancer and the factors that contribute to it, you can take charge of your health and make decisions that may save your life.
Stay informed, stay proactive, and consult with healthcare professionals regularly to ensure you are on the right path to cancer prevention.
1 note
·
View note
Link
0 notes
Text
How to Diagnose and Prevent Stomach Cancer?
Most of us are unaware that stomach is the root cause of maximum number of diseases. Our stomach is related to nearly 100 problems and issues. Diet, exercise and maintaining the balance of vat, pitta, kapha can help to prevent or even eradicate multiple problems and concerns.

Our sedentary lifestyle and poor eating habits are the predominant reason behind the health issues. One of the serious medical problems that most people are confronting is stomach cancer also referred to as gastric cancer. Few years ago stomach cancer was a term that never existed. The first case of the gastric cancer was diagnosed in the late 19th century, by Swiss surgeon Karl Schlatter. The cases of cancer witnessed a surge after that. A report by SEER points out the cases witnessed in year. 2024 is around 26000 plus till now. The survival rate is just 36 percent from 2014 to 2020. Consequently there arises a need of taking careful understanding of concept of the stomach cancer.
This blog post will throw flood light on the concept of Stomach cancer and how it can be prevented as well as treated. We will see how stomach cancer treatment is possible if diagnosed at early stage.
Understanding Stomach cancer and its reasons:
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a dangerous and typically aggressive tumor that begins in the stomach lining. It is fifth most common type of cancer and can prove to be fatal too. Generally, it begins in the cells of the stomach's innermost layer (the mucosa) and spreads to the outer layers as it grows. It can be difficult to identify in its early stages since it often grows slowly, and symptoms may be difficult to recognize until it has advanced sufficiently.
Symptoms of Stomach cancer
Early Symptoms:
Indigestion, sometimes known as heartburn, is persistent stomach discomfort or burning.
Mild Stomach ache: Constant ache or discomfort in the stomach area.
Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick or vomiting, which can occur with or without blood.
Appetite Loss: A decreased desire to eat can lead to accidental weight loss.
Feeling Full Quickly: Early satiety, which occurs after eating a modest amount of food.
Advanced symptoms:
Unexplained Weight reduction: Significant, unplanned weight reduction that occurs without effort.
Severe Stomach ache: Consistent and severe stomachache.
Difficulty Swallowing: The sensation that food is caught in the throat or chest.
Hematemesis refers to the vomiting of blood.
Melena (black, tarry stools) indicates gastrointestinal bleeding.
Jaundice: Yellow skin and eyes indicate liver impairment.
Fatigue and weakness: persistent weariness and low energy.
Fluid build-up can cause abdominal enlargement.
Lymph Node Enlargement: Swelling in the neck and armpits.
Recognizing these symptoms early on and obtaining medical attention is critical for an accurate diagnosis and treatment of stomach cancer. If you observe any of these symptoms, especially if they continue or worsen, visit a doctor.
Possible causes of stomach cancer include Helicobacter Pylori infection.
Chronic infection with H. pylori bacteria increases the risk of developing stomach cancer. The bacteria create long-term inflammation of the stomach lining, which can culminate in cancer.
Dietary Considerations:
We tend to like spicy and salty foods these days. We choose salty and smoked foods over plain foods, which increases our risk of developing stomach cancer. These foods contain chemicals that may irritate the stomach lining. A diet low in fruits and vegetables, which are high in antioxidants and other important elements, may raise the risk of stomach cancer.
Genetic predisposition:
Genetic predisposition defines us; if your family has a history of gastric cancer, you are more likely to inherit stomach-related illnesses or cancer. To put it simply, persons with a family history of stomach cancer are at a greater risk. Certain inherited genetic mutations, such as those in the CDH1 gene, are known to increase the likelihood of developing this illness.
Lifestyle Aspects:
Lifestyle defines what kind of health we will have at present and in the future. poor lifestyle habits are the breeding ground for uncountable health issues. Smoking is a recognized risk factor for stomach cancer. Tobacco smoke contains toxins that can reach the stomach and cause harm. Excessive alcohol use might also irritate the stomach lining.
Medical Conditions:
Chronic gastritis and pernicious anemia are associated with an increased risk of stomach cancer. Chronic inflammation induced by these conditions can damage the stomach lining, making people more likely to develop cancer. Previous stomach surgery for benign conditions may alter the stomach's ecology, increasing the risk of cancer.
Environmental Factors:
Certain environmental contaminants, such as those utilized in specific industries (for example, rubber and coal), have been linked to an increased risk of developing stomach cancer.
How it can be prevented?
Stomach cancer can be prevented by
Healthy diet: Consuming a healthy diet, including fresh fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants.
Avoid smoking:
Limit your exposure to smoking, try distancing yourself from chain smokers.
To reduce alcohol consumption, consume in moderation or avoid altogether.
To manage Helicobacter Pylori infection, consult your doctor and seek treatment if recommended.
To keep a healthy weight, it's essential to engage in regular physical activity.
routine medical check-ups :Schedule regular check-ups, especially if you have a family history of stomach cancer or other chronic health problems.
genetic counselling:
If you have a strong family history of stomach cancer, you should seek genetic counseling and testing.
Treatment Options for Stomach Cancer: Surgical
Subtotal Gastrectomy is the removal of a portion of the stomach containing the tumor.
Total Gastrectomy: Complete stomach excision followed by digestive system repair.
Lymph node dissection is the removal of neighboring lymph nodes to detect cancer spread.
Radiation Therapy: High-energy beams are used to destroy cancer cells and decrease tumors, and they are commonly employed before or after surgery.
Chemotherapy: Drugs used to destroy or inhibit the growth of cancer cells before surgery (neoadjuvant), after surgery (adjuvant), or for advanced cancer.
5-fluorouracil (5-FU), cisplatin, and capecitabine are three common chemotherapy medicines.
Targeted therapy
HER2 inhibitors target molecules involved in cancer cell proliferation and survival.
Palliative care involves
The emphasis is on reducing symptoms and enhancing quality of life for people with advanced cancer.
Pain management, nutritional support, and psychological support are all options.
Clinical studies: Participation in clinical trials allows patients to have access to new and experimental medicines that are not yet publicly available.
A multidisciplinary approach:
Collaboration among healthcare specialists, including oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and dietitians, to provide complete care tailored to the patient's needs.
To sum up, it can be said that stomach cancer can be prevented, and the situation can be controlled with timely diagnoses and awareness about the signs and symptoms. Knowledge about symptoms and better lifestyle options can help in controlling the factors that can lead to stomach cancer. If you need to gain any information about stomach cancer or any other blood related you can consult Kingman Oncology, an institute developed to help cancer patients.
#kingman oncology institute#blood cancer treatment#cancer care institute#cancer treatment process#cancer chemotherapy types
0 notes
Text
Malaria presents with periodic flu-like symptoms and should be suspected in any ill patient with a history of travel from an endemic region. Diagnosis is primarily made by examining thick and thin blood smears for speciation and percent parasitemia. All malarial species produce intra-erythrocytic rings (trophozoites). Rapid antigen testing may also be available and can distinguish between P. falciparum and P. vivax. Treatment with chloroquine is standard for mild-to-moderate disease. Due to chloroquine resistance, however, artemisinin combination therapy (ACT) is commonly used. ACT options include dihydroartemisinin, artesunate, mefloquine, or artemether in combination with other antimalarials (eg, piperaquine or mefloquine).
Severe disease should be treated with intravenous artesunate. The anti-hypnozoite drug primaquine is also necessary for P. vivax and P. ovale because of their ability to cause relapse due to dormant hypnozoite forms within the liver. To prevent acute hemolysis, it is important to test for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency prior to initiating primaquine. Of note, P. falciparum is known to produce fulminant disease, including hemolytic anemia, renal failure, pulmonary edema, central nervous system disease, hypoglycemia, liver failure, and lactic acidosis. Rapid treatment is therefore essential to prevent poor outcomes.
Gonorrhea is diagnosed with NAAT of a swab or culture on Thayer-Martin media. Once the samples have been obtained, the patient can be initiated on antimicrobial therapy. The standard therapy would be ceftriaxone 250 mg intramuscularly (IM) as a single dose, plus azithromycin 1 g orally (due to increasing resistance) or doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for 7 days.
Wilson disease results in inappropriate deposition of copper in the liver, brain, and other tissues due to impaired clearance of copper into the bile. It is an autosomal-recessive disease affecting chromosome 13. Signs and symptoms are the consequence of cirrhosis, basal ganglia deterioration, and deposition of copper in other tissues, causing hepatic failure, neurologic abnormalities, hemolytic anemia, and Kayser-Fleischer rings around the iris.
Basic labs will reveal hemolytic anemia (decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit with elevated bilirubin as well as decreased haptoglobin and increased reticulocyte count) and elevated liver enzymes due to liver inflammation and cirrhosis. Decreased ceruloplasmin (less than 20 mg/dL) and low serum copper concentration are consistent with Wilson disease and should prompt confirmatory workup, including 24-hour urine copper excretion. Low serum copper levels may seem paradoxical; however, it should be remembered that ceruloplasmin is the primary copper binding protein and is responsible for the majority of copper contained in the serum. Low ceruloplasmin results in a low total serum copper, despite the fact that total-body copper is in excess. This excess, while not measurable in the serum at a specific point in time, is measurable as increased urinary excretion over the course of the day, which is why a 24-hour urine copper is needed.
Kayser-Fleischer rings are present in 50% of patients with active liver disease but without any neurologic involvement. When neurologic symptoms present (dysarthria, dystonia, tremor, parkinsonism, choreoathetosis, ataxia, cognitive impairment), Kayser-Fleischer rings are present in 98% of patients.
Gastric cancer presents with left supraclavicular lymphadenopathy. Left supraclavicular adenopathy (known as the Virchow node) suggests an abdominal source, such as the stomach, gallbladder, or pancreas.
In any patient with an upper GI bleed, it is important to ask for recent anticoagulation use and a history of prior bleeding or endoscopy as up to 60% of recurrent GI bleeding is from the same lesion. Other important considerations in the history include: if the patient has a history of H. pylori, cirrhosis, odynophagia, or the use of antiplatelet agents.
Esophageal varices and peptic ulcers are common and easily treatable causes of bleeding in pts with cirrhosis.
Bottom Line: The most common causes of upper GI bleeding include peptic ulcer disease, severe or erosive gastritis/duodenitis/esophagitis, esophagogastric varices, portal hypertensive gastropathy, angiodysplasia, Mallory-Weiss syndrome, mass lesions (polyps/cancers).
Besides varices, other major complications of cirrhosis include ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatopulmonary syndrome, however, in patients with acute decompensation due to upper GI bleeding, the most urgent conditions to evaluate for include the development of hepatic encephalopathy, SBP, and hepatorenal syndrome.
Bottom Line: A patient with cirrhosis and acute upper GI bleeding should have 2 large-bore IVs or a large-bore, single-lumen central catheter placed, be resuscitated with IV fluids, transfused blood as needed, started on an IV proton pump inhibitor drip, an IV octreotide drip, and IV antibiotics for SBP prophylaxis, and will generally require ICU admission. An EGD should be performed within 24 hours of admission, but ideally as soon as possible, once the patient is hemodynamically stable.
Management of critical patients with upper GI bleeding generally follows the same trajectory. Get as much history as possible to localize risk factors for bleeding and options to inform immediate pharmacologic treatment (PPI vs octreotide vs both). Give blood and fluids. Consult gastroenterology for EGD. If the patient cannot undergo EGD or this is not available or had a recent EGD with bleeding that is not amenable to further endoscopic therapy, consult IR for embolization.
Those patients found to have SBP should receive hepatorenal syndrome prophylaxis with albumin on days 1 (1.5g/kg) and 3 (1g/kg) of admission if they meet the criteria.
Multiple trials evaluating the effectiveness of prophylactic antibiotics in cirrhotic patients hospitalized for GI bleeding suggest an overall reduction in infectious complications and possibly decreased mortality. Antibiotics may also reduce the risk of recurrent bleeding in hospitalized patients who bled from esophageal varices.
Diagnose pheochromocytoma with urine metanephrine and normetanephrine levels. The most appropriate drug therapy prior to adrenalectomy for suspected pheochromocytoma consists of phenoxybenzamine followed by the addition of propranolol (if needed for heart rate control). Preoperative treatment for surgical resection of pheochromocytoma involves alpha-receptor blockade. This can be followed by beta-receptor blockade if needed for further heart rate control, usually 2 to 3 days before surgery.
7 to 14 days of phenoxybenzamine and 2 to 3 days of propranolol prior to surgery (if needed for heart rate control), with the continuation of propranolol perioperatively. The most important aspect of treatment in patients with pheochromocytoma with respect to preoperative antihypertensive therapy is alpha-receptor blockade. Alpha-receptor blockade prevents the hypertensive effect of overstimulation by the catecholamines released from the adrenal medulla. Beta-receptor blockade should follow, which prevents rebound tachycardia (goal heart rate should be 60-80/min) in the setting of unopposed alpha blockade. The clinical guidelines from the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism released in 2014 currently support the use of alpha-blockers for blood pressure control prior to surgery. Beta-blockers can be added afterward if needed. Of note, selective alpha-1-receptor blockers, such as prazosin or doxazosin, may be used instead of phenoxybenzamine in certain situations, such as in patients who have significant benign prostatic hyperplasia and may already be on low doses of these medications or if the patient cannot tolerate the first-line agents listed above. Metoprolol can also be administered instead of propranolol or atenolol.
There is a rule of 10's associated with pheochromocytoma: 10% are extra-adrenal, 10% are bilateral, 10% are malignant, and 10% occur in children. Some people add that 10% will recur after excision within 10 years and 10% will be found after a significant stroke. It was previously thought that about 10% were familial; however, that number has been adjusted upward as more and more genetic and familial diseases have been linked with the development of pheochromocytoma. It is now thought that about 40% of pheochromocytomas are associated with some kind of underlying genetic predisposition. Malignant pheochromocytomas are biologically and histologically indistinguishable from benign pheochromocytomas. The only way to determine malignancy is to observe local infiltrative disease or find evidence of metastatic spread. Thus, even benign pheochromocytomas found on excision will need clinical follow-up.
Most authors advocate obtaining 24-hour fractionated urine metanephrines if the clinical suspicion is low, and serum metanephrines if the clinical suspicion is high. Serum metanephrines have a decreased specificity, and positive testing may result in unnecessary imaging and follow-up, which is why it is not recommended as the first-line test for all patients.
HAs, diaphoresis, HTN = pheo
Gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison) - initial test that should be ordered is a fasting serum gastrin level. If elevated, it should be followed by a secretin infusion test. Somatostatin-receptor scintigraphy is the imaging test of choice as it detects for primary or metastatic lesions. Treatment includes intravenous (IV) proton pump inhibitors and surgical resection. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is also associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type 1. MEN 1 is also known as Werner's syndrome and presents with the 3 Ps: parathyroid tumors; pituitary tumors, including prolactinoma; and pancreatic endocrine tumors, including insulinomas, vipomas, glucagonomas, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
The initial test of choice for Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is a fasting serum gastrin (off proton pump inhibitors). The diagnosis is confirmed with a secretin infusion test. It is associated with MEN1.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vitamin D Deficit
Vitamin D Deficit may be subclinical and may go disregarded, even in evolved international locations. This deficiency is related to osteoporosis and extended chance of fractures.
“ Vitamin D stocks decrease with age and especially in winter.”
Therefore, the identification and treatment of vitamin D deficiency is important in women at risk. As is the menopause where the frequency of bone decalcification and osteoporosis also increases.
At the Instituteaskdoctors carried out gynaecological reviews in which we request analytical controls quantifying vitamin D. In case of deficiency we advise and give supplements.
For more information, you can of our free online gynecologist consultation
What levels of vitamin D are recommended?
Vitamin D is a vitamin that must be at optimal concentrations in our body. Its specific name is 25-hydroxyvitamin D serum.
The concept of serum means that it is found in the blood and can be quantified with an analysis.
Optimal vitamin D levels are not always clear. According to the recommendations of the National Academy of Medicine, these are in favour of maintaining a concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in blood between 20 and 40 ng/ml, or in other measures, between 50 and 100 nmol/L.
” The concept that is clear is that contractions below 20 ng/ml are not optimal for the health of the skeleton.”
On the other hand, levels above 100 ng/ml or 250 nmol/L are not recommended, as these levels could be toxic in adults who ingest significant amounts of calcium.
How can I increase vitamin D naturally?
To growth vitamin D certainly, it ought to be recognised that the assets of this substance include the weight-reduction plan, supplements and sun publicity.
With regard to food regimen, we must spotlight that there aren't many meals assets wealthy in vitamin D, but we can find it in a few foods.
We can eat it thru salmon, cooked onion, canned tuna, fortified milk with nutrition D, yogurt enriched with vitamin D, orange juice with diet D, margarine enriched with this nutrition, canned sardines, cereals enriched with nutrition, and eggs.
On the opposite hand, adults who do now not showcase themselves in the sun often all through the 12 months must eat as a minimum six hundred-800 international units / IU, or 15 to 20 micrograms, of nutrition D3 additionally known as colecalciferol. This supplement would be introduced to the full weight loss plan.
Some clinical societies advise a slightly better dose of nutrition D complement in adults over sixty five to reduce the chance of fractures and falls. This supplement must be among 800 and 1000 IU.
Current nutrition D deficiency
The present day nutrition D deficit depends at the definition used. Levels of this nutrition underneath 20ng/ml are very common in most of the nations studied, that could affect 18% of the population.
What are the reasons of nutrition D deficiency?
There are several causes of the vitamin deficiency. Possible reasons include:
Decrease in intake or absorption.
Reduction of sun exposure.
Increase in liver removal.
Decrease in own production in the kidney.
Resistance to use by the organs of the body.
What is the population at risk?
The at-risk population is the elderly confined inside their homes or residences that are not exposed to the sun.
“ This skin production of vitamin D decreases with age and northern countries.”
In addition, the intake of this vitamin is usually low for older people. Women in menopause are also a population at risk.
This type of deficit can also be common in:
People who take medications that accelerate the metabolism of the vitamin.
Hospitalized patients.
People living in residences.
Individuals with increased skin pigmentation.
Obesity cases.
Presence of osteoporosis.
Diseases such as intestinal absorption and celiac disease.
Who should be asked for vitamin D levels?
Although it is currently requested in a majority way, according to the studies carried out, there is no consensus to justify a comprehensive study in the general population, or during pregnancy.
Only in people with risk factors should a blood test be requested.
What does the vitamin D deficit produce?
Vitamin D deficiency, in most cases, is asymptomatic and does no longer produce scientific manifestations. If the deficit is moderate or moderate, it is not typically manifested with any unique effect.
In these cases, calcium, phosphorus ranges, and alkaline phosphatase inside the blood check are typically everyday.
If the deficit is greater important, the parathyroid hormone may be excessive, an alarm being capable of revel in accelerated bone loss and increase the chance of fractures.
A take a look at called bone densitometry may check the decrease in bone density due to this growth in parathyroid hormone.
In cases of excessive and extended deficits, there is also a decrease in intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus. This causes hyperparathyroidism with bone demineralization and more skeletal affectation.
This is followed by way of bone pain and tenderness, muscle weakness, fractures and issue on foot.
When is it endorsed to provide vitamin D complement?
Vitamin D supplements should be encouraged in adults at high danger of diet deficiency and with blood ranges under 20 ng/ml or 50 nmol/L.
According to vitamin D ranges, distinct doses of supplement are encouraged in a blood check:
If levels are significantly less than 12 ng/ml or 30 nmol/L, treatment usually consists of 25000 to 50000 global devices / IU or 625 to 1250 micrograms of nutritional D2 or D3, orally, for 6 to 8 weeks and then 800 doses IU or 20 micrograms of food daily Dose is reduced to D2 or D3.
Supplements ranging from 800 to 1000 IU or 20 to 25 micrograms corresponding to 12 to 20 ng/ml or 30 and 50 nmol/liter per day.
A dose of 20 to 30 ng/mL or 50 to 75 nmol/L is 600 to 800 IU or 15 to 20 micrograms per day.
In persons for whom vitamin D supplementation is recommended, monitoring should then be done with blood tests, approximately 3 to 4 months after starting treatment. The dosage should be adjusted based on the results.
What vitamin D preparations are recommended?
The preparation of vitamin D that is recommended to supplement the deficit of this vitamin arecolecalciferol, i.e. vitamin D3.
If it is not available, ergocalciferol, i.e. vitamin D2, can be used.
Existing studies suggest that normalization of vitamin D levels is faster using vitamin D3.
Is calcium levels important when there is a vitamin D deficiency?
Calcium ranges in instances of diet D deficiency are very important.
Whenever nutrition D dietary supplements are taken it's far important to preserve accurate degrees of calcium consumption. The endorsed calcium tiers are one thousand milligrams for a while 19 to 70.
The dose of 1200 milligrams is usually recommended for girls aged fifty one to 70 and all adults seventy one years and older.
If these stages can't be secured thru the eating regimen, calcium supplementation will even have to be furnished.
All those hints are covered in the facts we provide of a way to save you osteoporosis.
If you're someone with risk factors or want to recognise more about the diet D deficiency, do not hesitate to seek advice from the experts at the Dra. Gomez Roig. The second you take a gynaecological take a look at-up or consult for any other cause you may continually ask for recommendation on this type of affectation.
The gynecologists on our crew have enjoy and assist you to if you need diet D supplementation.
Visit More Information:- www.askdoctors.co.in
#online gynecologist consult#free online gynecologist consultation#gynecologist#gynecologist consultation
0 notes
Text
Anadrol (Oxymetholone): A Comprehensive Overview
Anadrol (Oxymetholone): A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Anadrol, scientifically known as Oxymetholone, is one of the most potent oral anabolic steroids available today. Originally developed in the 1960s by Syntex Pharmaceuticals, it was initially used to treat medical conditions such as anemia and muscle wasting diseases. Over the years, its powerful anabolic effects have made it a popular choice among athletes and bodybuilders aiming to enhance muscle mass and strength.
Uses of Anadrol
Medical Uses:
Anemia Treatment: Anadrol stimulates erythropoiesis, the production of red blood cells, making it effective in treating anemia.
Muscle Wasting Diseases: It is used to combat muscle wasting in patients suffering from severe illnesses like HIV/AIDS.
Bone Marrow Disorders: Anadrol has shown effectiveness in treating various bone marrow disorders.
Performance Enhancement:
Bodybuilding: Anadrol is favored for its ability to promote rapid gains in muscle mass and strength, making it a staple in bulking cycles.
Athletics: Some athletes use Anadrol to enhance performance due to its significant strength-boosting properties.
Benefits of Anadrol
Rapid Muscle Gains: Anadrol is known for producing substantial increases in muscle mass within a short period, often yielding noticeable results within the first few weeks of use.
Increased Strength: Users experience significant strength gains, allowing for improved performance in both athletic and bodybuilding contexts.
Enhanced Protein Synthesis: Anadrol enhances the body's ability to synthesize protein, which is crucial for muscle growth and recovery.
Boosted Red Blood Cell Production: This leads to improved oxygen delivery to muscles, enhancing endurance and reducing fatigue during intense workouts.
Dosage and Cycle Use
Dosage:
The typical dosage of Anadrol for performance enhancement ranges from 25 mg to 100 mg per day. However, most users find that 50 mg per day strikes an effective balance between benefits and side effects.
For medical purposes, dosages may vary based on the condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication.
Cycle Use:
Bulking Cycles: Anadrol is commonly used at the start of a bulking cycle for its ability to rapidly increase muscle mass. A typical cycle lasts 4-6 weeks, as prolonged use can lead to significant side effects.
Stacking: Many users stack Anadrol with other anabolic steroids such as Testosterone or Deca-Durabolin to maximize muscle gains. However, this should be done cautiously due to the increased risk of adverse effects.
Forms of Anadrol
Anadrol is primarily available in oral tablet form, commonly in 50 mg dosages. It is also available in lower dosages, but the 50 mg tablet is the most prevalent and widely used in both medical and bodybuilding communities.
Side Effects and Considerations
While Anadrol offers numerous benefits, it is associated with a range of potential side effects, particularly when used in high doses or for extended periods. These include:
Liver Toxicity: Anadrol is hepatotoxic, meaning it can cause liver damage. Users are advised to limit cycle lengths and avoid alcohol and other hepatotoxic substances.
Hormonal Imbalances: It can cause significant hormonal changes, leading to side effects such as gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue in men) and water retention.
Cardiovascular Issues: Anadrol can negatively impact cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Androgenic Effects: These include acne, hair loss, and increased body hair growth, particularly in individuals predisposed to these conditions.
Conclusion
Anadrol (Oxymetholone) is a powerful anabolic steroid with significant benefits for muscle growth and strength enhancement. Its medical applications highlight its effectiveness in treating serious health conditions, while its popularity in the bodybuilding community underscores its potency. However, potential users must approach Anadrol with caution, respecting recommended dosages and cycle lengths to mitigate its substantial side effects. As with any steroid use, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective use.
#Anadrol (Oxymetholone) 50 mg#Oxymetholone#Anabolic steroids#Muscle mass#Strength enhancement#Dosage and cycle#Bulking cycles#Performance enhancement
0 notes
Text
Cancer Treatment in India: A Comprehensive Guide

Cancer Treatment in India: A Comprehensive Guide
Cancer remains one of the most frightening health challenges worldwide, with millions of lives affected by its impact every year. Cancer is characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. Understanding cancer, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is essential for everyone.
In this article, we’ll cover all aspects of cancer to provide you with the necessary information.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by the abnormal growth of cells that invade and destroy surrounding tissues. These abnormal cells can form tumors, impair the functioning of vital organs, and spread to other parts of the body through a process called metastasis.
How Many Types of Cancer Are There?
There are over 100 different types of cancer, each with its own set of characteristics and treatment approaches.
Common types of cancer include:
Liver cancer
Lung cancer
Breast cancer
Gallbladder cancer
Food pipe cancer
Prostate cancer
Colorectal cancer
Skin cancer
Leukemia
Leukemia
Lymphoma
Ovarian cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Bladder cancer
Cancer Surgeon in Delhi
What Can Cause Cancer?
The precise cause of cancer is often complex and multifactorial. While genetic factors play a role in some cases, environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and exposure to carcinogens also contribute to the development of cancer.
Common risk factors include:
Tobacco use
Excessive alcohol consumption
Unhealthy diet
Physical inactivity
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation
Certain infections
Cancer Surgeon in Delhi
What Are the Common Symptoms of Cancer?
The symptoms of cancer vary depending on the type and location of the disease. However, some common signs and symptoms of cancer include:
Persistent fatigue
Unexplained weight loss
Persistent cough or hoarseness
Changes in bowel or bladder habits
Persistent indigestion or discomfort after eating
Changes in moles or skin growths
Persistent pain that doesn’t improve with treatment
Difficulty swallowing
Cancer Surgeon in Delhi
Changes in the appearance of a wart or mole
Persistent headaches or vision changes
Persistent fevers or night sweats
Unexplained bruising or bleeding
Presence of lumps or swelling
How Do I Get Cancer Diagnosed?
Getting a cancer diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
Medical history and physical examination
Diagnostic tests:
Blood tests
Imaging tests, like X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, PET scans, and ultrasound
Biopsy
Cancer Surgeon in Delhi
Specialized tests:
Genetic testing
Endoscopy
Colonoscopy
What Are the Different Treatment Options for Cancer?
Treatment options for cancer vary depending on the type and stage of cancer, as well as individual factors such as overall health and personal preferences.
Common treatment modalities include:
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
Immunotherapy
Cancer Surgeon in Delhi
Targeted therapy
Hormone therapy
Stem cell transplantation
Precision medicine
Treatment plans are often personalized based on the individual’s cancer type, stage, overall health, and treatment goals. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including oncologists, surgeons, radiation oncologists, and others, collaborates to develop the most effective treatment plan for each patient. The goal of treatment is to eradicate cancer cells, shrink tumors, lessen symptoms, and improve quality of life.
How do I Prevent Cancer?
While not all cancers are preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle and avoiding known risk factors can help reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Strategies for cancer prevention include:
Maintaining a healthy weight
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
Staying physically active
Avoiding tobacco
Cancer Surgeon in Delhi
Limiting alcohol consumption
Protecting against sun exposure
Getting regular cancer screenings done
Getting vaccinated
What Are the Key Aspects of Cancer Treatment in India?
Advanced technology: Indian hospitals boast advanced technology and state-of-the-art equipment for accurate diagnosis and precise treatment delivery.
Experienced oncologists: The country is home to some of the world’s most renowned oncologists, who specialize in various cancer types and treatment modalities.
Multidisciplinary care: Cancer treatment in India follows a multidisciplinary approach, involving collaboration among oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, pathologists, and other specialists.
Affordable treatment: Despite offering world-class facilities, cancer treatment in India is significantly more affordable compared to many western countries, making it accessible to a wider population.
Cancer Surgeon in Delhi
Holistic support: Indian hospitals prioritize holistic support for cancer patients, providing psychological counseling, nutritional guidance, pain management, and palliative care services.
Final Words from Dr. Neeraj Goel
Cancer is a complex and challenging disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis, treatment, and support. By understanding the nature of cancer, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Cancer treatment in India has evolved significantly with its blend of advanced technology, experienced oncologists, multidisciplinary care, and affordable treatment options. Whether it’s access to innovative therapies, personalized care, or holistic support services, patients can find comprehensive solutions for their cancer treatment in India.
Dr. Neeraj Goel, renowned as the best Cancer Surgeon in Delhi, offers unparalleled expertise in cancer treatment. With vast experience and advanced techniques, he provides personalized care, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients. Trust Dr. Neeraj Goel for the best cancer treatment in Delhi, tailored to your individual needs.
FAQs on Cancer Treatment in India
What types of cancer treatments are available in India?
India offers a wide range of cancer treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, hormone therapy, and stem cell transplants.
How experienced are oncologists in India?
India has highly experienced oncologists who have received training from prestigious institutions worldwide and are renowned for their expertise in cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Are cancer treatments in India affordable?
Yes, compared to many western countries, cancer treatments in India are often more affordable.
What is the success rate of cancer treatment in India?
The success rate of cancer treatment in India varies depending on the type and stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the chosen treatment approach. However, many patients achieve positive outcomes and improved quality of life with appropriate treatment.
What should I expect during cancer treatment?
Treatment plans are personalized based on cancer type, stage, and individual health factors, often involving a combination of therapies to target cancer cells while minimizing side effects.
To schedule an appointment With Dr. Neeraj Goel for Cancer Surgeon in Delhi, please contact:
Name: Dr. Neeraj Goel (Cancer Surgeon in Delhi)
Address: D-1, Hakikat Rai Rd, Block D, Adarsh Nagar, Delhi, 110033
Phone: +91–9667365169, +91–9599294453
Website: www.gastrodelhi.com
0 notes