#-3G Antenna Manufacturer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#GPS antenna manufacturer#Lora antenna manufacturer#868mhz antenna manufacturer#Pcb antenna manufacturer#Glonass antenna manufacturer#5g antenna manufacturer#4g antenna manufacturer#3g antenna manufacturer
0 notes
Text

This 5G 12dBi Magnetic Antenna is equipped with an SMA Male connector and includes a premium RG58 cable, ensuring dependable connectivity and improved signal reception. Its magnetic base facilitates straightforward installation on metal surfaces, rendering it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. It is an excellent choice for enhancing 5G signal strength across a range of devices.
#magnetic antenna#gps antenna#eteily technology manufactures#rf antenna#eteily india#rf antenna manufacture#manufacturing#rf antenna india#rf antenna price#entrepreneur#youtube#telecom
0 notes
Text

2G/3G/4G Combo Screw Mount Antenna with RG174 Cable (L-3MTR) + SMA (M) St. Connector
A 2G/3G/4G combo screw mount antenna is a type of antenna designed to support multiple generations of cellular technology, namely 2G (GSM), 3G (UMTS), and 4G (LTE). These antennas are typically used in applications where there's a need for reliable cellular communication across different generations of networks.
The "screw mount" aspect refers to how the antenna is installed; it typically involves screwing the antenna onto a suitable surface, such as the roof of a vehicle or a fixed structure. This type of mounting provides stability and durability, making it suitable for outdoor and rugged environments.
#rf antenna#RF Antenna#celluler antenna#5g antenna#5G Internal Antenna#5G External Antenna#5G Outdoor Antenna#4G LTE Antenna#4G Internal Antenna#4G External Antenna#4G Outdoor Antenna#3G Antenna#3G Internal Antenna#3G External Antenna#3G Outdoor Antenna#2G/GSM Antenna#2G Internal Antenna#2G External Antenna#2G Outdoor Antenna#IoT Lora LPWAN#868MHz Antenna#433MHz Antenna#915MHz Antenna#925MHz Antenna
0 notes
Text
Navigating the 5G Frontier: Unveiling the Security Challenges

Introduction to 5G Technology
Welcome to the exciting world of 5G technology, where faster speeds and seamless connectivity promise to revolutionize the way we live, work, and play. As we embark on this new frontier of ultra-fast wireless networks, it's important to take a moment to consider the security challenges that come hand in hand with these groundbreaking advancements. In this blog post, we'll delve into the benefits of 5G technology and explore how it has the potential to transform industries such as healthcare, transportation, and communication. However, we won't shy away from discussing the security risks that accompany these developments. From potential cyber threats to measures in place for securing 5G networks - we'll cover it all. So buckle up as we navigate through uncharted territory together! Let's uncover the intricacies of 5G security challenges while ensuring that we can fully embrace its benefits without compromising our safety. Are you ready? Let's dive in!
Benefits of 5G
The advent of 5G technology has brought about a myriad of benefits, revolutionizing the way we live, work, and connect with each other. With lightning-fast speeds and virtually no latency, 5G promises to unlock a world of possibilities. One major benefit of 5G is its ability to support an increasingly connected society. As more devices become interconnected through the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G provides the necessary infrastructure to handle the massive influx of data. This means that smart homes, autonomous vehicles, and even entire cities can operate seamlessly, enhancing efficiency and convenience for everyone involved. Another advantage is the enhanced mobile experience that comes with 5G. Streaming high-definition videos or playing online games will be smoother than ever before. The improved network capacity ensures that congestion becomes a thing of the past, allowing users to enjoy uninterrupted connectivity wherever they go. Moreover, industries such as healthcare and manufacturing stand to benefit tremendously from 5G technology. Remote surgeries can now be performed with minimal lag time thanks to ultra-low latency provided by 5G networks. In manufacturing plants, automated systems powered by IoT sensors can communicate in real-time using 5G connections, optimizing productivity and reducing downtime. In addition to these benefits, there are also significant economic implications associated with widespread adoption of 5G technology. It is expected that this next-generation wireless network will drive innovation across various sectors leading to job creation and economic growth on a global scale. Overall,evolving from previous generations like 3g or even LTE ,the transition towards full-scale implementationof technologies like MMwave spectrum shall enable more rapid wireless communication speedup along side improved reliability due increased number MIMO antennas which form part advanced beam forming techniques for directing signals . These developments allow delivery extremely fast download speeds which provide new opportunities services like augmented reality & virtual reality applications . The large bandwidth availability enhances multimedia experiences while supporting multiple simultaneous device connection without sacrificing performance . With all these exciting benefits, it's no wonder that 5G is highly anticipated
Security Risks and Concerns with 5G
As we embrace the exciting possibilities that 5G technology brings, it's important to also acknowledge the potential security risks and concerns that come with it. With faster speeds and increased connectivity, 5G networks have the potential to revolutionize industries and transform our daily lives. However, this newfound power also comes with its fair share of vulnerabilities. One major concern is the increased surface area for cyberattacks. With more devices connected to the network, there are more entry points for hackers to exploit. This means that securing not only our smartphones but also a plethora of other interconnected devices becomes crucial. Another concern is the reliance on virtualization and cloud-based services in 5G networks. While these technologies offer flexibility and scalability, they also introduce new attack vectors. If a hacker gains access to one virtualized network function or cloud server, they could potentially compromise an entire network. Additionally, as data traffic increases exponentially in a 5G ecosystem, ensuring privacy becomes paramount. The sheer volume of data being transmitted opens up opportunities for unauthorized access or interception of sensitive information. Moreover, there are concerns regarding supply chain security in relation to 5G infrastructure deployment. As countries compete to lead in this technological race, there may be cases where equipment from untrusted vendors is integrated into critical infrastructure systems unknowingly. Legacy systems pose another challenge when transitioning to 5G networks. These older systems were not designed with modern threats in mind and may lack necessary security measures required by today's standards. Addressing these security risks requires collaboration between governments, organizations, and individuals alike. It involves implementing robust encryption protocols throughout all layers of communication within the network architecture while continuously monitoring for any suspicious activities or anomalies. Furthermore, strict regulations need to be put in place regarding supply chain management and vendor selection processes during infrastructure development projects related to 5G networks. In conclusion, while we eagerly unlock the immense capabilities brought by 5G technology, it is crucial that we also navigate the security challenges it presents. By being proactive in
Potential Cyber Threats to 5G Networks
As we embrace the exciting possibilities that 5G technology brings, it's important to be aware of the potential cyber threats that may arise. With faster speeds and increased connectivity, 5G networks open up new avenues for hackers to exploit. One major concern is the vulnerability of IoT devices connected to these networks. As more devices become interconnected, hackers can potentially gain access to personal data or even control critical infrastructure. This could lead to privacy breaches, financial fraud, or even physical harm. Another potential threat lies in the increased use of mobile applications and cloud services on 5G networks. These platforms often store sensitive information such as passwords and credit card details, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Without proper security measures in place, users' data could be compromised. Additionally, there is a risk of Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks becoming more potent on 5G networks due to their higher bandwidth capabilities. Hackers could flood a network with traffic from multiple sources simultaneously, overwhelming it and causing disruptions or outages. Furthermore, as autonomous vehicles become more prevalent with the advent of 5G technology enabling real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure systems like traffic lights or road signs - there is an increased risk of malicious actors gaining control over these systems and causing accidents or chaos on the roads. To mitigate these risks, robust security protocols need to be implemented at both network provider and user levels. Network providers should prioritize encryption methods and regularly update their software/firmware to address vulnerabilities promptly. Users must also take responsibility by using strong passwords, keeping their devices updated with the latest patches/updates provided by manufacturers/app developers. In conclusion... While 5G offers incredible benefits in terms of speed and connectivity improvements across various industries ranging from healthcare to transportation – it's crucial that we remain vigilant about cybersecurity risks associated with this cutting-edge technology. With careful planning and proactive measures taken by all stakeholders involved – including network providers, device manufacturers, and end-users – we can navigate the 5
Current Measures in Place for Securing 5G
Current Measures in Place for Securing 5G As the world eagerly awaits the arrival of 5G technology, there is a growing concern about its security. With faster speeds and increased connectivity, it's no surprise that potential cyber threats are on everyone's mind. However, it's important to note that efforts are already underway to address these concerns. Network operators and equipment manufacturers have recognized the need for robust security measures in 5G networks. One key measure is the implementation of stronger encryption protocols to protect data transmitted over the network. This ensures that sensitive information remains secure and inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. Additionally, network segmentation is being employed as a means of isolating different parts of the network from each other. By dividing the network into smaller segments, any potential breach or attack can be contained, preventing it from spreading throughout the entire system. Another critical aspect of securing 5G is implementing strict authentication mechanisms. This involves verifying both devices and users before granting access to the network. By using advanced techniques such as biometric authentication or multi-factor authentication (MFA), unauthorized access can be significantly minimized. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and threat intelligence play an integral role in maintaining security within 5G networks. Network operators must continuously monitor for suspicious activities or anomalies that may indicate a potential cybersecurity incident. This allows them to respond swiftly and effectively if any security breaches occur. To further enhance security measures, collaborations between industry stakeholders and government agencies are essential. Sharing insights on emerging threats and best practices can help create cohesive strategies that address evolving cyber risks effectively. While current measures provide a solid foundation for securing 5G networks, continuous improvements will undoubtedly be necessary as new vulnerabilities emerge with technological advancements.
Future Steps to Address 5G Security Challenges
Future Steps to Address 5G Security Challenges As the world embraces the power of 5G technology, it is crucial that we address the security challenges that come along with it. The potential for cyber threats and attacks on 5G networks is a pressing concern that needs immediate attention. To mitigate these risks, several future steps can be taken. Investing in research and development is essential. We need to continuously evolve our understanding of the vulnerabilities associated with 5G networks and develop innovative solutions to counter them. This includes exploring new encryption techniques, enhancing authentication protocols, and improving network monitoring capabilities. Collaboration between industry stakeholders is vital. Telecom companies, device manufacturers, governments, and cybersecurity experts must work together to establish global standards for securing 5G infrastructure. Sharing best practices and exchanging threat intelligence will help build a robust defense against emerging cyber threats. Implementing stringent regulations and compliance measures can significantly enhance security in the 5G ecosystem. Governments should enforce strict guidelines for data protection, privacy rights, and network integrity. Companies operating within this space must adhere to these regulations or face consequences. Fourthly, continuous education and awareness programs are necessary to ensure all stakeholders understand their roles in securing 5G networks effectively. Training programs should be conducted regularly for employees working in telecom companies as well as end-users who rely on this cutting-edge technology. Lastly but not least importantly, investment in advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) can play a significant role in strengthening security measures for the next generation of mobile networks. By leveraging AI algorithms, we can identify anomalies, predict potential attacks, and respond swiftly before any major damage occurs. This proactive approach will be crucial in safeguarding critical infrastructure and maintaining public trust as we navigate through the vast possibilities offered by 5G technology. In conclusion, Securing our rapidly advancing digital landscape requires concerted efforts from all parties involved. By taking these future steps, we can strike a balance between embracing the benefits of 5
Conclusion: Embracing the Benefits of 5G While Mitigating its Risks
As we venture into the exciting world of 5G technology, it is important to acknowledge and address the security challenges that come along with it. While there are numerous benefits to be gained from this revolutionary network, we cannot ignore the potential risks and vulnerabilities that may arise. With faster speeds, lower latency, and increased connectivity, 5G opens up a whole new realm of possibilities for industries such as healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and more. The ability to transmit vast amounts of data in real-time will undoubtedly revolutionize these sectors and enhance our daily lives. However, alongside these incredible advancements comes an increased risk of cyber threats. As 5G networks become more complex and interconnected, they also become more susceptible to attacks. Threat actors could exploit vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure or intercept sensitive information being transmitted across the airwaves. To mitigate these risks effectively, current measures are being put in place by industry leaders and governments around the world. These include implementing stringent encryption protocols to protect data transmission and adopting advanced authentication methods for accessing network resources. Additionally, collaboration between stakeholders such as telecommunications companies, equipment manufacturers, cybersecurity experts, government agencies is crucial in establishing unified standards for securing 5G networks globally. Looking ahead into the future steps that need to be taken to address 5G security challenges comprehensively involves continuous research on emerging threats and vulnerabilities specific to this technology. This allows for timely detection of potential risks so that appropriate countermeasures can be developed promptly. Furthermore education initiatives will play a significant role in creating awareness among users about best practices when using 5G-enabled devices or applications. With knowledge comes empowerment - enabling individuals and organizations alike to make informed decisions regarding their digital security while embracing all that 5G has to offer us. In conclusion: While navigating through uncharted territories like the frontier of 5G technology presents its share of challenges when it comes down to security concerns- embracing its benefits while mitigating any associated risks is an attainable goal. By taking proactive measures, investing in advanced technologies, and fostering collaboration and education, we can create a safer and more secure 5G ecosystem for all.
0 notes
Text
Global Connected Car Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Service, Connectivity, Application, Hardware, Network, Technology, End-User, Region, and Forecast 2021-2027
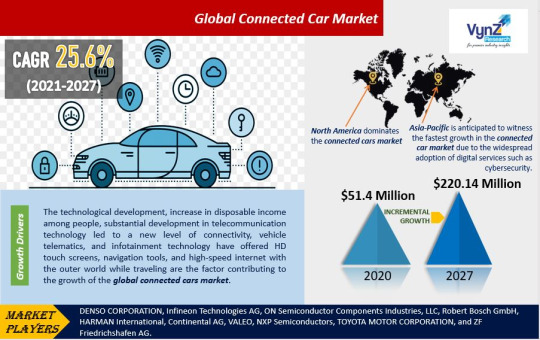
A connected car is a vehicle that is equipped with an internet connection, allowing it to communicate with other vehicles, infrastructure, and the cloud. This connectivity provides a wide range of benefits, including improved safety, convenience, and efficiency.
The global connected car market is growing rapidly, with a CAGR of 25.6% expected over the forecast period (2021–2027). This growth is being driven by a number of factors, including the increasing demand for safety features, the growing popularity of infotainment systems, and the development of 5G networks.
Get a free sample copy of the research report: https://www.vynzresearch.com/automotive-transportation/connected-car-market/request-sample
Market Segmentation
The global connected car market is segmented by service, connectivity, application, hardware, network, technology, and end-user.
By service: The market is segmented into connected services, autonomous driving, and safety & security.
By connectivity: The market is segmented into tethered, integrated, and embedded.
By application: The market is segmented into navigation, telematics, and infotainment.
By hardware: The market is segmented into displays, sensors, smart antennae, and electronic control units (ECU).
By network: The market is segmented into dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) and cellular.
By technology: The market is segmented into 3G, 4G/LTE, and 5G.
By end-user: The market is segmented into original equipment manufacturer (OEM) and aftermarket.
Regional Analysis
The global connected car market is dominated by Asia Pacific, followed by North America and Europe. Asia Pacific is expected to continue to be the leading region in the coming years, due to the increasing demand for connected cars in China, India, and South Korea.
Market Drivers and Challenges
The growth of the global connected car market is being driven by a number of factors, including:
Increasing demand for safety features
Growing popularity of infotainment systems
Development of 5G networks
Government initiatives to promote connected car technology
However, the market also faces some challenges, such as:
High cost of connected car technology
Privacy concerns
Security risks
Market Trends
Some of the key trends in the global connected car market include:
Increasing adoption of 5G networks
Growth of autonomous driving technology
Development of new connected car applications
Expansion of the aftermarket connected car market
Vendor Analysis
The global connected car market is highly competitive, with a number of major players vying for market share. Some of the leading vendors in the market include:
Delphi Technologies Plc.
DENSO Corporation
ZF Friedrichshafen
Robert Bosch GmbH
Aisin Seiki
Valeo S.A.
Autoliv Inc.
Conclusion
The global connected car market is expected to continue to grow rapidly in the coming years. The increasing demand for safety features, the growing popularity of infotainment systems, and the development of 5G networks are all driving the growth of the market. However, the market also faces some challenges, such as the high cost of connected car technology and privacy concerns.
About Us:
VynZ Research is a global market research firm offering research, analytics, and consulting services on business strategies. We have a recognized trajectory record and our research database is used by many renowned companies and institutions in the world to strategize and revolutionize business opportunities.
Source: VynZ Research
0 notes
Text
Application For - 2G/3G/4G Signals Amplifier
Frequency Band - 900/1800/2100MHz
Coverage Area - Upto 2500 sqm
Best Work For - Home Office Shop Underground etc.
Providers - Grameenphone Robi Airtel Banglalink Teletalk etc.
GSM Services - 2G 3G for Voice Calls
Data Service - 4G LTE for Faster Internet
---------------------------
Benefits & Features---
Faster internet date speeds
Low radiation
Multiple users
Smart display
Wide coverage
Upgrade Parts
Easy Installation - Plug N Play
CE & RoHS ISO Certified
2-Years Warranty
30-Days Money Back
Available Now ! Call 01772-277088
----------------------------
Kit includes--
1x Booster/Repeater/Device
1x Power adapter
1x Indoor antenna
1x Outdoor LPDA antenna
1x 30 meters cable
1x 10 meters cable
1x Warranty card
-----------------------------
Buy any top quality mobile signal boosting products from us and we fully guarantee that will truly work for any network's in Bangladesh. It's comes with an industry leading 30 days money back guarantee and 2 years manufacturer warranty.
Our mission is to make life easier for people in terms of connectivity, providing excellent coverage for thousands of households and business areas.
0 notes
Text
5G Technology: The Future of High-Speed Connectivity

The internet has been an essential part of our daily lives, connecting us to the world around us. With the evolution of wireless technology, we’ve witnessed the growth of 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. Now, the emergence of 5G technology represents a significant leap forward in internet connectivity. In this article, we will explore the benefits of 5G technology, how it works, and its future potential.
What is 5G Technology?
5G technology is the latest wireless network technology that offers faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity compared to its predecessors. It is built upon a complex network architecture that utilizes advanced antenna technologies and higher frequency radio waves to deliver faster and more reliable connectivity.
How Does 5G Technology Work?
At the heart of 5G technology is the use of millimeter waves, which have higher frequencies than previous generations of wireless technology. These waves can transmit data at much higher speeds, resulting in faster downloads and smoother streaming experiences. To take advantage of these higher frequency waves, 5G technology also utilizes advanced antenna technologies such as massive MIMO and beamforming.
Massive MIMO technology involves the use of multiple antennas to transmit and receive data. By using more antennas, 5G networks can transmit data more efficiently, resulting in faster speeds and increased capacity. Beamforming technology, on the other hand, allows 5G networks to focus the signal towards specific devices, resulting in a stronger and more reliable connection.
What are the Benefits of 5G Technology?
The benefits of 5G technology are numerous, and they will transform the way we connect to the internet. Some of these benefits include:
Faster speeds
5G technology can deliver speeds that are up to 100 times faster than 4G technology. This means you can download movies, stream music, and play games without any lag.
Lower latency
5G technology has much lower latency than previous generations of wireless technology. This means that there is less delay in data transmission, resulting in a more responsive network. This is especially important for real-time applications such as online gaming and video conferencing.
Increased capacity
5G technology can support more devices simultaneously than previous generations of wireless technology. This means that more people can connect to the internet at the same time without experiencing a slowdown in speed. This is especially important in crowded areas such as airports, stadiums, and concert venues.
Improved reliability
5G technology is more reliable than previous generations of wireless technology, which means fewer dropped calls and better overall connectivity.
What Does the Future Hold for 5G Technology?
The future of 5G technology is exciting, and it has the potential to revolutionize various industries. In the healthcare industry, for example, 5G technology could enable remote surgeries and telemedicine, allowing doctors to treat patients who are located in remote areas. In the transportation industry, 5G technology could enable autonomous vehicles, making our roads safer and more efficient. In the manufacturing industry, 5G technology could enable the use of smart factories, which use connected devices to optimize the production process.
5G technology also has the potential to transform the way we live our daily lives. With faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity, we could see the rise of smart homes, where all our devices are connected and can communicate with each other seamlessly. We could also see the development of augmented and virtual reality applications, which would allow us to experience a new world of entertainment and education.
https://www.infradapt.com/news/5g-technology-the-future-of-high-speed-connectivity/
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Automotive Smart Antenna Market Latest Advancements And Business Opportunities up to 2032
As per the report published by FMI, the global automotive smart antenna market size is projected to have a rapid-paced CAGR of 12.2% during the forecast period. The current valuation of the market is US$ 3.94 Billion in 2022. The market value of automotive smart antennas is anticipated to reach a high of US$ 12.45 Billion by the year 2032. The base year recorded a valuation of US$ 3.44 Billion.
Key Takeaways from the Automotive Smart Antennas Market
Asia Pacific region is projected to dominate the global automotive smart antenna market with a market valuation of US$ 4,394.07 by 2032.
The current market valuation for automotive smart antennas stands at US$ 3.94 Billion in 2022.
The automotive smart antenna market is anticipated to record a CAGR of 12.2% during the period 2022-2032.
Passenger Vehicles segment is identified to be the largest adopter of automotive smart antennas.
“The rising concern about traffic congestion and the increasing demand for dashboard features are likely to create lucrative growth opportunity for the market players of the automotive smart antennas market.” – Says an FMI Analyst
For more information: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/automotive-smart-antenna-market
Competition Landscape in the Automotive Smart Antennas Market
The market can be described as a competitive market. The key companies have adopted several strategies to broaden their customer base worldwide. Furthermore, the manufacturers are indulging in several growth strategies with frequent innovation of smart automotive smart antennas to provide consumers with a seamless, safe, and comfortable experience.
Ace Technologies Corp., Antenova Ltd., Beijing BDStar Navigation Co. Ltd., Calearo Antenne SPA, Continental AG, Harada Industry Co. Ltd., INFAC Corp., INPAQ Technology Co. Ltd., Koch Industries Inc., Lorom Industrial Co. Ltd., LS MTRON Ltd., Panasonic Corp., Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. are some of the key players in the market.
The automotive smart antenna is anticipated to play an integral role in establishing communication to enhance the safety and performance of the vehicles. This product is allowing original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to fulfill customer requirements for infotainment services.
While analyzing the automotive smart antenna market, an expert analyst reveals that gradual increase in the incorporation of wireless technology and positioning technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 3G/4 LTE, vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), and vehicle-to-anything (V2X) connecting technologies in vehicles is expected to drive the global automotive smart antenna market in the current and future years.
0 notes
Text
#cellular antenna#LTE cellular antenna#Cellular Antennas For Buildings#Cellular Antenna for Cars & Trucks#cellular antenna for home#high-gain 3G cellular antenna#4G/LTE Cellular Antennas#high-performance LTE networks#cellular antenna indoor#cellular antenna outdoor#outdoor antennas for homes#Cellular Antenna Solutions#Antennas for Cellular Gateways#Cellular External Antenna supplier#5G / LTE Cellular External Antenna manufacturer#Cellular 5G Antenna Solutions#Cellular Antenna Guide for 5G#LTE/5G Cellular External Antennas#Cellular Antennas 5G#Cellular Antennas LTE#Cellular Antennas CBRS#Cellular Antennas 2G#Cellular Antennas 3G#Cellular Antennas 4G#Internal & External 5G Antenna#5G Antennas - Weatherproof#Best LTE Antennas in the World#5G MIMO antenna#SMA Antenna 4G LTE 12Dbi#700-2700MHz Cellular Antenna
0 notes
Text
youtube
Eteily Technologies India Pvt Ltd | Manufacturer | Telecom Products | India
Eteily is well known brand in India for RF Antennas Radio frequency Antenna. Radio frequencies from DC to 18GHz and RF Families like IoT Antenna, 868MHz Antenna, LoRa Antenna, 433MHz Antenna,5G Antenna, LTE Antenna, 4G Antenna, WCDMA 3G Antenna, 5.8GHz Antenna, 2.4GHz Antenna, Bluetooth Antenna, RF Antenna Solutions, Cellular Antenna, General ISM Antenna, Navigation Antenna, Wi-Fi Antenna, and 802.15 Antenna.
0 notes
Text
IIOT Smart 12 – The New IIOT Solution
Arya Electronics And Controls is designed and manufacture IIOT Smart 12 device, this device is a versatile device which reads the MODBUS memory map of any RS-485 MODBUS protocol device and sends the data to the cloud server. The stored data can be observed as per client necessity on dashboard.
IIOT Smart 12 is a data acquisition solution brings greater versatility for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
The IIOT Smart 12 has Wi-Fi connectivity, which will serve the growing number of devices and M2M Gateway with M2M Gateway solution providers with applications that require wireless communication.
Arya Electronics now offers a range of flexible data acquisition solutions for wired Ethernet, Wi-Fi, 2G GPRS and 3G networks. We want to create it as easy as possible for manufacturing operators to assemble and share sensor data in diverse situations and conditions.
IIOT Smart 12 mainly consist of GSM module and micro controller-based control circuit. IIOT Smart 12 supports generic MODBUS RTU protocol for data acquisition and uses MQTT protocol to communicate with IT application database on cloud. The Device can be easily configured within one minute to send your data on Any MQTT Server / Arya Electronics hosted dashboard.
Features
1. Supply Voltage 90-270V AC
2. Uarts 3 Nos : RS232 +1
– Non isolated RS485 + 1
– GPRS or Wifi
3. Storage memory – SD Card available
4. Cloud-based support system
5. ADC – 16 channel add on module for 4-20mA or 0-5V input
6. DI – 4Nos.
7. DO – 2 Nos.
8. Microcontroller based
9. GSM/GPRS with External Antenna or wifi module
10. Enclosure – Din rail mount IP20
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Strengthen Your Mobile Phone Signals?
Know how signal boosters can strengthen your network connectivity:
In this modern world, you are expected to stay updated with your phone irrespective of the place you are going. The problem of poor network and lower connectivity are no longer limited to rural places. They are faced by urban and metropolitan people too. Even if you are in your home, signal obstacles will arise. These network disturbances can be sorted with the help of signal boosters in an effective manner. It can be used as a wifi-booster that will help you to optimize your network.
Solve the causes behind poor signals and connectivity:
Let’s first figure out why are you facing poor signals. There is a huge possibility that you are inside a room or any building. Bricks, cement and glasses act as a disturbance in your network. The continuous disturbance leads to lesser productivity of calls and interrupts video streaming. Also, the fact that the population is constantly rising in the country that we live in leads to poor signal. Signals are not transmitted at a good speed because of the increase in the number of users.
Know why mobile signal booster is used in home and offices:
Mobile signal booster is broadly used in homes and offices to amplify the signals. Signal boosters come in a compact size. They can be installed anywhere you want them to. You can carry them along with you to evade connection problems. You can choose from a large variety of signal booster for both your home and office according to their specifications and you need.
Enhance the quality and coverage of your signals:
Antenna plays a very important role in transmitting signals. Earlier phones had antenna outside them. Currently, mobiles come with in build antennas. This feature was first launched by Apple and then followed by every mobile phone manufacturing companies.
With the easy and affordable installation of mobile signal booster for home, you can do your work tension free. You can talk with any person in the corner of your world with a good quality network. The voice and image will be of good quality with good signals. Cell phone boosters work to enhance the quality and coverage of your cell signals. It allows you to go for better inbound and outbound calls and communications.
Get 4g signal booster for your home and office:
It’s very easy to boost and strengthen the network. You can easily get 2G, 3G or 4g signal booster for home on our stores. These signal boosters have recently become a necessity for all the people in urban and metropolitan cities because of the rapid increases in the population ratio. We have come up with new products that have the capacity to increase the bandwidth of your network. For any cell phone signal booster in India or mobile signal booster in India, you can contact us at 9015846846. We will help you to get good connectivity that will certainly decrease the dropped calls and network issues. The frequency of the signals will be increased by the help of signal boosters.
#mobile signal booster#signal booster#cell phone signal booster#network booster#4G signal booster for home#cell phone signal booster India
1 note
·
View note
Text
ISP Supplies | Wireless Networking Equipment | Wired Equipment | Routers | Buy Routers |Switches | Cambium Networks
ISP Supplies | Wireless Networking Equipment | Wired Equipment | Routers | Buy Routers |Switches | Cambium Networks ISP Supplies is the leader in wireless networking equipment and wired equipment here in the US since 2008. The Customer’s priority is our priority and that’s why we have always served the best equipment and services to our customers that’s why our customers love us. Our customers are being facilitated by almost 20,000 products and services since 2008 and we have 50+ manufacturers/brands with whom we are working.
Now let’s talk about our services. Our services are : Baicells
Antennas Cellular Modems Cellular, 3G, 4G, LTE Coax Cable, Adapters & Pigtails Education, Training, Consulting Enclosures-Indoor & Outdoor Featured Items Fiber Products Infrastructure Installation Equipment LTE & CBRS MikroTik Software & Licenses Network Cabling & Accessories Network Expansion Power Systems & POE Remote Power, Solar & Wind RouterBoards & SBC's Routers, Switches & Modems Surveillance & Automation VoIP You can contact us for more details about products, services, training, courses, certification Phone: 855-WISP-PRODirect: 855-947-7776 Canada: 647-559-2559 International: 979-431-0304 Fax: 866-585-2175
#ISP#Supplies#rohn tower#cambium#cambium networks#wireless routers#ptp backhaul#lte system#routers and switches#wireless equipment#wired equipment#routers#buy routers
1 note
·
View note
Text
Leaked documents reveal Huawei’s secret operations to build North Korea’s wireless network
https://wapo.st/2JLjoPz
Leaked documents reveal Huawei’s secret operations to build North Korea’s wireless network
By Ellen Nakashima, Gerry Shih and John Hudson | Published July 22 at 6:54 AM ET | Washington Post | Posted July 22, 2019 |
Huawei Technologies Co., the Chinese tech giant embroiled in President Trump’s trade war with China and blacklisted as a national security threat, secretly helped the North Korean government build and maintain the country’s commercial wireless network, according to internal documents obtained by The Washington Post and people familiar with the arrangement.
Huawei partnered with a Chinese state-owned firm, Panda International Information Technology Co. Ltd., on a variety of projects there spanning at least eight years, according to past work orders, contracts and detailed spreadsheets taken from a database that charts the company’s telecom operations worldwide. The arrangement made it difficult to discern Huawei’s involvement.
The spreadsheets were provided to The Post by a former Huawei employee who considered the information to be of public interest. The former employee spoke on the condition of anonymity, citing a fear of retribution. Two additional sets of documents were shared by others with a desire to see the material made public. They also spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Taken together, the revelations raise questions about whether Huawei, which has used American technology in its components, violated U.S. export controls to furnish equipment to North Korea, where the isolated regime has faced extensive international sanctions over its nuclear weapons program and human rights abuses.
The Commerce Department, which declined to comment, has investigated alleged links between Huawei and North Korea since 2016 but has never publicly connected the two. Its probe remains active, however. Separately, the Justice Department has charged Huawei with bank fraud and violations of U.S. sanctions on Iran. The company has pleaded not guilty.
In a statement, Huawei said it “has no business presence” in North Korea. Spokesman Joe Kelly declined, however, to address detailed questions, including whether Huawei had conducted business there in the past, either directly or indirectly. He did not dispute the authenticity of documents shared with the company, though he also declined to verify them.
“Huawei is fully committed to comply with all applicable laws and regulations in the countries and regions where we operate, including all export control and sanction laws and regulations” of the United Nations, United States and European Union, the statement says.
A spokeswoman for Panda Group, the state-owned parent company for Panda International, declined to comment.
Discovery of a link between North Korea and Huawei, whose activities, ambitions and suspected ties to the Chinese government have alarmed U.S. and European security officials, is likely to fuel even deeper suspicion among Western nations contemplating whether to ban the company, in full or in part, from their next-generation 5G wireless networks. It comes, too, at a particularly vulnerable moment for the Trump administration, which remains at odds with Beijing over trade, and as the president seeks to restart nuclear negotiations with North Korean leader Kim Jong Un.
“Just the fact that you’ve got a Huawei-North Korea connection is bound to raise political and diplomatic hackles in Washington, if nothing else,” said Evans J.R. Revere, a former State Department official focused on East Asia. “Just when you thought the U.S.-China relationship couldn’t get more complicated, and the U.S.-North Korea relationship couldn’t get more complicated, you have this instance of China and North Korea working together to enable Korea to make strides in an area of potentially sensitive technology.”
A current senior State Department official, who, like others interviewed for this report, spoke on the condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive information, summarized the administration’s frustration.
“All of this fits into a general concern we have about corporate responsibility and a company like Huawei that is not trustworthy because of its company culture and numerous incidents indicating a willingness to evade or outright violate laws,” the official said. “Working with regimes like North Korea, who deprive individuals on a regular basis of their basic human rights, raises concern.”
SECRET VISIT TO CHINA
Since its founding in 1987 by a former engineer with the People’s Liberation Army, Huawei has grown from a humble phone switch maker into an icon of China’s technological prowess — the world’s largest telecom equipment manufacturer. Today, it is a “national champion” promoted by Beijing and does business in more than 170 countries.
Before 2008, North Korea struggled to find multinational companies willing to build a 3G network in such a risky business environment. That ended with the creation of the wireless provider Koryolink, which emerged from a secret visit in 2006 by Kim’s father, Kim Jong Il, to Huawei’s headquarters in Shenzhen, China.
“This was the time that confirmed not only the top leadership’s interest in dealing with Huawei but pretty much revealed a choice of Huawei as the primary supplier of technology,” said Alexandre Mansourov, an adjunct professor at Georgetown University’s School of Foreign Service, who in 2011 wrote about North Korea’s digital transformation. “They decided to work with Huawei from that time on.”
Koryolink was built through a 2008 joint venture of Orascom Telecom Holding, an Egyptian firm, and the state-owned Korea Post and Telecommunications Corp. Together, they were called CHEO Technology. Attempts to reach CHEO were unsuccessful.
A key player was Panda International, part of the storied electronics conglomerate Panda Group that has sometimes served China’s foreign policy. In 2001, for instance, during a visit to Havana, China’s president at the time, Jiang Zemin, gave Cuba 1 million Panda-made TV sets and introduced a company representative to Cuban leader Fidel Castro, who “excitedly shook hands and embraced” him, the firm recounts on its website.
Huawei worked closely with Panda, using it as the conduit to provide North Korea with base stations, antennas and other equipment needed to launch Koryolink, internal documents show. For years, Huawei and Panda employees worked out of an inexpensive hotel near Kim Il Sung Square in Pyongyang, according to a person familiar with the arrangement.
Huawei was involved in “network integration” and “software” services as well as at least one “expansion” project for Koryolink, the documents show. It also provided “managed service” and “network assurance” services. One current Huawei employee reached by The Post, Yin Chao, said he worked in 2012 and 2013 on Koryolink’s automated callback system, one of several improvements the company offered the North Koreans.
According to a 2008 contract, Panda would transport Huawei equipment to Dandong, a town in northeastern China known for cross-border trade. From there, it would be taken by rail into Pyongyang.
Internal documents show that Huawei has done business with a separate Chinese company, Dandong Kehua, which in November 2017 was sanctioned by the U.S. Treasury Department for exporting and importing goods to and from North Korea — trade seen by U.S. officials as financing Pyongyang’s nuclear and ballistic missile programs. Dandong Kehua has not publicly addressed the sanctions.
It is unclear what role, if any, Dandong Kehua played in Huawei’s dealings with North Korea and whether Huawei has done business with the company since it was sanctioned. Attempts to contact the firm were unsuccessful.
COUNTRY ‘A9 ’
In internal company documents and among employees, Huawei referred to certain countries, such as North Korea, Iran and Syria, by code. North Korea, for instance, was listed as A9 in the project database.
“You’d run a query on the projects and you’d see Germany, United States, Mexico. Then instead of a country name, you’d see A5, A7, A9, and you’d say, ‘What’s that?’ ” said the former employee. “I assume it’s because they didn’t want to say ‘Iran’ or ‘Syria.’ ”
In a semiprivate online forum used by Huawei employees, one man reminisced last year about how he helped launch Koryolink in “A9” during the summer of 2008, before rushing back to China to offer tech support for the Beijing Olympics. In parentheses, the man wrote “chaoxian,” which means North Korea, in Roman letters — an apparent effort to avoid mentioning the country by name using Chinese characters.
Documents obtained by The Post also illustrate the North Koreans’ concern with foreign spying on regime officials and their family members who would be using Koryolink. In spring 2008, Orascom and Korea Post tasked Huawei with developing an encryption protocol for the network, noting that the government would create its own encryption algorithm, according to the documents.
“Both sides had common agreement that the ordinary people will use the international standard mobile phones and special users will use different mobile phones which will contain locally developed encrypted algorithm,” state the minutes of a 2008 meeting, a document signed by Korea Post’s chief engineer and an Orascom board member.
An encryption “test bed” was built by Huawei in Shenzhen, the documents show. According to two individuals familiar with the system, North Korea also intercepted and monitored all domestic and international calls.
The website 38 North, which closely tracks activity in and involving North Korea, detailed the arrangement in a post published Monday.
NORTH KOREA: ‘RADIOACTIVE ’
Orascom was bought in 2011 by a Russian company, Vimpelcom, which spun off Koryolink to a newly created subsidiary. That firm is now called Orascom Investment Holding, which did not respond to requests for comment.
The original joint venture agreement gave Orascom exclusive license to operate the mobile network through 2015, according to media reports, but the North Korean government launched a rival network, Kang Song, in 2013 using another Chinese telecom equipment supplier, ZTE. Kang Song quickly supplanted Koryolink as the dominant wireless provider in North Korea.
In 2014, the Commerce Department banned the export of U.S.-origin components to Panda, alleging it had furnished such parts to the Chinese military “and/or” to countries under U.S. sanctions. Since then, any company to provide Panda with telecom items intended for North Korea and containing at least 10 percent U.S.-origin content without a license would be in violation of the export ban.
Several experts, including the supply-chain analysis firm Interos, consider it to be likely that Huawei’s 3G equipment contained American components, though it is difficult to know whether it surpassed the 10-percent threshold outlined in export regulations.
Huawei was placed on the same Commerce Department blacklist in May, with officials citing the company’s alleged violations of U.S. sanctions on Iran. Huawei has denied violating export controls with regards to Iran or that it poses a security threat, saying that the Trump administration is targeting it for political reasons.
Huawei and Panda vacated their offices in Pyongyang during the first half of 2016, according to people familiar with the matter. In that period, efforts to impose more stringent U.S. and U.N. sanctions against North Korea were gaining momentum. Orascom obtained a U.N. waiver to operate the Koryolink joint venture in September 2018. Koryolink, according to a person familiar with the matter, operates today on aging equipment as Huawei no longer provides upgrades and maintenance.
U.S. officials served Huawei with a subpoena in 2016, demanding information on the export of American technology to sanctioned countries, including North Korea. If Huawei was found to have violated U.S. sanctions against North Korea, it could face additional export-control sanctions, civil penalties, forfeitures or criminal prosecution.
“North Korea is radioactive in the proliferation world because of international sanctions,” said James Mulvenon, an expert on Chinese economic espionage and general manager at the defense contractor SOS International. “Huawei wouldn’t want to be caught dealing directly with North Korea, so they work through other companies like Panda.”
The website for Panda International boasts of the company’s long-standing partnership with Huawei, collaboration that dates to 2007, it says — around the time of the Koryolink launch — spanning “various countries and product sectors.” Panda also notes that it is licensed by the Chinese government to “distribute foreign aid.”
A mobile telephone number listed on Panda’s website as its sales hotline was connected to a WeChat social media account selling Huawei products. The executive running the account, Andy Wang, declined to answer questions about its work in North Korea.
Panda’s headquarters in Beijing appears to be a bare-bones operation based out of a dingy commercial tower with a basement karaoke bar and a low-end nightclub. When a Post reporter visited one afternoon in July, the office was largely empty.
A Panda executive, who another employee said was responsible for media inquiries, refused to meet with the reporter and instead locked the office doors.
Shih reported from Beijing. Yuan Wang in Beijing, Heba Mahfouz in Cairo, Reed Albergotti in San Francisco and Julie Tate in Washington contributed to this report.
#u.s. news#politics#donald trump#trump administration#politics and government#president donald trump#white house#republican politics#us: news#trump#republican party#international news#must reads#national security#maga#world news#corruption#u. s. foreign policy#china news#china#north korea#huwawei#tech news#technology#tech
1 note
·
View note
Text
Outdoor Camera Surveillance - How to Protect Your Outdoor Environment
Outdoor camera surveillance for your boat, garage, shop or outside your house are just some of the areas you may need to protect. Many people do not know that construction sites are high theft areas; in fact, most contractors estimate they lose 3% to 4% of their profit to construction site theft. Although all digital video cameras are not made the same, there are some unique features that make outdoor camera surveillance very versatile to use.
Outdoor camera surveillance equipment is made especially for use outdoors in stand-alone situations where they may be exposed to the weather and other elements. In fact, many outdoor camera surveillance cameras are rated by their manufacturer with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Ingress Protection (IP) code. An IP code gives the user a definitive rating of what type of conditions the camera is rated for. Check out our blog post for a complete description on how to read IP codes Glass Break Sensor.
Outdoor camera surveillance equipment has a wide variety of extra features so that a camera can be purchased to satisfy a specific need. A multiple camera system doesn't have to have all the same cameras and one should use different cameras that are specific for the application. Each camera can have different features to suit the condition, yet all can easily work in unison on one system.

The following is just a partial list of some of the optional features available on outdoor camera surveillance cameras:
- Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) function. These cameras can move horizontally or vertically to greatly increase the total field of view area of the camera. They have a telephoto lens that can enlarge the view as well. These cameras can be used with Digital Video Recorder software that can automatically track or follow a moving object.
- Day/Night vision or Day/Infrared or IR cameras are incredibly sensitive to light and can require very little light to produce a high quality color video. Some cameras can produce video in lighting conditions equivalent to that of a clear, moonless night. Other cameras make use of infrared radiation in the near infrared spectrum to illuminate their field of view. These cameras usually use infrared Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) to illuminate their target areas. Human eyes cannot detect this infrared light so it is invisible to us in the dark. When operating in this mode these cameras produce high quality black and white or monochromatic video as there are no "colors" associated with infrared illumination.
- Wireless technology cameras. These cameras have their own built-in transmitter and antenna that send the video signal to a corresponding receiver (or Digital Video Recorder with a built-in receiver). This eliminates the need for running a video transmission cable for each camera to the Digital Video Recorder. These cameras can also be battery operated allowing them to be mounted almost anywhere.
- Internet Protocol (IP) ready cameras. These cameras can be connected to a broadband internet connection and be both controlled and monitored in a remote location anywhere in the world that there is internet accessibility (this includes 3G and 4G smartphones as well).
It's pretty easy to see the versatility of outdoor security camera surveillance, and the above list doesn't even contain all the features that are available. The point is to spend some time doing your research so you can build the best system for your particular application.
1 note
·
View note