#*sacroiliac region of pelvis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
my ass* hurts so bad. i hate cars**.
#*sacroiliac region of pelvis#**minor car accident on tuesday also i hate car culture#newt needs a text post tag#newt's medical posting#its hard to stay motivated to figure out my medical shit when stuff like this happens and like#how long is it even gonna be before i can get it looked at or imaged or ugh#we are at 3 minor and we'll say one medium car accident in 6 months. no medical attention yet#ok i havent eaten yet. im gonna make oatmeal and drink a protein shake
0 notes
Text
The Pathophysiology Of Spondylitis
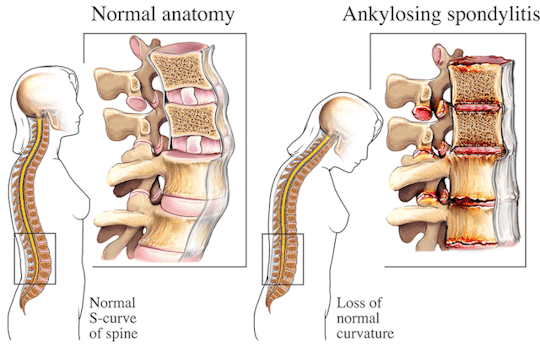
Spondylitis is a comprehensive term used to describe a group of chronic inflammatory diseases that primarily affect the joints of the spine and the sacroiliac region, which includes the pelvis and lower spine. These conditions are characterized by arthritis-like symptoms and can lead to significant discomfort, reduced mobility, and other systemic complications. This detailed exploration will indulge into the nature of spondylitis, how it differs from the related condition known as spondylosis, the various types of spondylitis, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and complementary therapies.
What is Spondylitis?
Spondylitis involves inflammation of the joints, tendons, and ligaments within the spine and sacroiliac region. Tendons are connective tissues that attach muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones. This inflammation can result in the fusion of bones (ankylosis) and the formation of new bone, leading to stiffness and reduced flexibility in the spine. In severe cases, excessive bone growth can cause significant curvature of the spine, known as kyphosis.
Spondylitis vs. Spondylosis
While both spondylitis and spondylosis cause pain in the hip and back, they are distinct conditions with different etiologies and characteristics.
Spondylitis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation, bone fusion, and excessive bone formation. This condition typically develops in teenagers and young adults and can affect multiple organs and systems within the body.
Spondylosis, on the other hand, is a degenerative condition associated with aging and the natural wear and tear of the spine. It involves the degeneration of spinal joints and discs, often accompanied by the formation of bone spurs (osteophytes). Spondylosis primarily affects older individuals, with more than 85% of people over the age of 60 experiencing this condition.
Types of Spondylitis
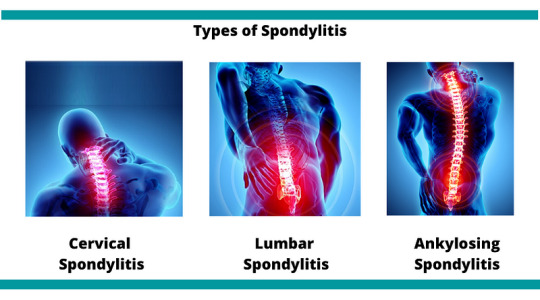
Medical professionals categorize spondylitis using two primary classification systems: the traditional system and the newer system. The traditional system recognizes six specific types of spondylitis, whereas the newer system categorizes spondylitis into two broad types based on the affected body region.
Traditional Spondylitis Classifications:
a) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Symptoms: Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine, causing symptoms such as fatigue, chronic back pain, stiffness, and inflammation in various areas of the body, including joints and tendons. Over time, the vertebrae may fuse, leading to reduced mobility and flexibility.
Causes: The exact cause of AS is unknown, but a strong genetic association exists with the HLA-B27 gene. Approximately 90% of individuals with AS carry this gene, although not all carriers develop the disease.
b) Reactive Arthritis
Symptoms: Reactive arthritis typically presents with a triad of symptoms including arthritis (swelling and pain in joints), conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eyes with a sticky discharge), and urethritis (genital and bladder inflammation with painful urination). However, not all patients exhibit all three symptoms.
Causes: often follows a gastrointestinal infection or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). The immune system overreacts to the initial infection, leading to inflammation and joint pain. The HLA-B27 gene is also strongly linked to ReA, with 30–50% of affected individuals carrying this gene.
c) Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Symptoms: Psoriatic arthritis is associated with the inflammatory skin condition psoriasis. Symptoms include dactylitis (swelling in toes and fingers), changes in nails (such as pitting), eye pain, joint pain, reduced range of motion, and fatigue. PsA typically affects people aged 30–50.
Causes: PsA often follows psoriasis, but it can also develop in individuals without skin symptoms. There is a genetic predisposition to PsA, with at least 10% of the population inheriting genes that increase susceptibility to psoriasis and PsA.
d) Enteropathic Arthritis (EnA)
Symptoms
Enteropathic arthritis is linked to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and joint swelling and pain.
Causes
The precise cause of EnA is unclear, but it is associated with chronic inflammation in the bowel. This inflammation may allow bacteria to penetrate the bowel wall, triggering an immune response that leads to joint inflammation. The HLA-B27 gene is also linked to EnA.
d) Juvenile Spondyloarthritis (JSpA)
Symptoms
Juvenile spondyloarthritis begins in individuals aged 16 or younger and typically affects the leg joints. Symptoms include joint pain, tenderness, and bowel inflammation.
Causes
Similar to adult spondylitis, JSpA is often associated with the HLA-B27 gene. The exact cause remains unknown, but genetic and environmental factors likely play a role.
e)Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis (USpA)
Symptoms
USpA is characterized by a variety of symptoms that do not fit neatly into a specific rheumatoid disorder. Symptoms may include persistent lower back pain, joint pain in small and large joints, heel pain, swelling in hands and feet, general stiffness, eye inflammation, rash, urinary tract symptoms, and intestinal inflammation.
Causes
The causes of USpA are diverse and not fully understood. It encompasses a range of symptoms that do not meet the criteria for other specific types of spondylitis.
Newer Spondylitis Categorizations
Peripheral Spondyloarthritis (pSpA)
Peripheral spondyloarthritis affects joints and tendons outside the spine and sacroiliac joints, such as the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, ankles, and feet. It includes forms of spondylitis such as reactive arthritis, enteropathic arthritis, and undifferentiated arthritis.
2. Axial Spondyloarthritis (AxSpA)
Axial spondyloarthritis involves inflammation and pain in the pelvis and spine. This category covers a broad range of spondylitis types and includes individuals with and without sacroiliac joint fusion. AxSpA is further subdivided into non-radiographic AxSpA (without visible joint damage on X-rays) and radiographic AxSpA (visible joint damage).
Diagnosis
Diagnosing spondylitis involves abroad approach, combining physical examination, medical history, and various diagnostic tests. There is no single definitive test for spondylitis, making a comprehensive evaluation essential.
a) Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and family history of autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and spondyloarthritis. The examination may include evaluating joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
b) Diagnostic Tests
Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation, such as elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP). Testing for the presence of the HLA-B27 gene can also provide valuable information, although not all individuals with spondylitis carry this gene.
Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques are crucial for diagnosing spondylitis and assessing the extent of joint and bone damage.
X-rays: X-rays can reveal changes in the spine and sacroiliac joints, such as joint fusion and bone spurs.
MRI Scans: MRI scans provide detailed images of soft tissues and can detect early signs of inflammation and joint damage that may not be visible on X-rays.
Ultrasound Scans: Ultrasound scans can be used to assess inflammation in peripheral joints and tendons.
Genetic Testing: Testing for the HLA-B27 gene can support the diagnosis, particularly in cases where clinical symptoms and imaging findings are inconclusive.
Treatment
While there is no cure for spondylitis, various treatments can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and disease severity.
Medications
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs are commonly used to reduce inflammation and pain in spondylitis patients. Examples include ibuprofen and naproxen.
Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can be prescribed for short-term use to control severe inflammation and pain.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs, including methotrexate and sulfasalazine, can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression in some types of spondylitis.
Biologic Agents: Biologic agents, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (e.g., adalimumab, etanercept) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitors (e.g., secukinumab), target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage.
Analgesics: Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, may be used to manage pain when inflammation is not the primary issue.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing spondylitis by improving and maintaining spine flexibility and overall mobility. Techniques may include:
Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain.
Spinal Manipulation: Performed by a trained physical therapist or chiropractor, spinal manipulation can enhance mobility and reduce pain.
Exercises: Tailored exercise programs can help strengthen muscles, improve posture, and enhance flexibility. Stretching exercises are particularly beneficial for maintaining spine and joint flexibility.
Breathing Exercises: Breathing exercises are essential for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis, as the condition can affect chest expansion and respiratory function. These exercises help maintain normal lung function and prevent restrictive lung disease.
Surgery: Surgery is generally considered a last resort and is reserved for severe cases where conservative treatments have failed. Surgical options include:
Joint Replacement: For patients with severe joint damage, joint replacement surgery (e.g., hip or knee replacement) can restore function and relieve pain.
Spinal Surgery: In cases of severe spinal deformity or nerve compression, spinal surgery may be necessary to correct curvature and alleviate pressure on nerves.
Complementary Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, complementary therapies can provide additional symptom relief and improve overall well-being. These therapies are often used alongside standard medical treatments.
Massage Therapy: Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension, improve blood circulation, and alleviate pain and stiffness in the affected areas.
Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can help manage stress and reduce pain perception.
Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to improve flexibility, strength, and relaxation. Yoga can be particularly beneficial for maintaining spine flexibility and reducing pain.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system and promote natural pain relief and healing.
Cupping: Cupping is a traditional therapy that involves placing suction cups on the skin to improve blood flow and reduce muscle tension. It can be used to alleviate pain and stiffness in the back and other affected areas.
Summary
Spondylitis encompasses a range of chronic inflammatory diseases that affect the spine and sacroiliac region. It is characterized by autoimmune-driven inflammation, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and potential bone fusion. Spondylitis is distinct from spondylosis, a degenerative condition associated with aging. Medical professionals classify spondylitis into various types based on symptoms and affected body regions. Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, blood tests, imaging, and genetic testing. While there is no cure, treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and complementary therapies can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected by spondylitis. By understanding the nature of spondylitis and the available management strategies, individuals can better navigate their condition and maintain an active, fulfilling life.
Medical students and healthcare professionals need to stay informed about the latest advancements in diagnosing and treating spondylitis. Continuous education and expert guidance are crucial for managing these complex conditions. For additional support with challenging medical units, clinical studies, research projects, assignments, and exam preparation, Expert Academic Assignment Help offers professional resources and online classes. For personalized assistance, contact [email protected] Accessing expert guidance can significantly enhance your understanding and proficiency in medical education.
#medical students#assignment help#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#healthcare#student life#medical student#studyblr#case study#student#online writing#do my online class#essay writing#phd research#clinical research#research#phd thesis writing service#phdjourney#phd life#phdblr#studying#study blog#study motivation#studyspo#study aesthetic
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Sacroiliac Joint Brace is a specialized support device designed to stabilize the sacroiliac joints, which connect the base of the spine to the pelvis. This brace is commonly used to alleviate pain and discomfort in the lower back and pelvic region caused by conditions such as sacroiliac joint dysfunction, inflammation, or injury.
0 notes
Text
Newer Technologies For Pain Relief: Freezing Of Nerves (Cryoablation)

What is cryoablation?
Imagine being able to freeze nerves to minus 80 degrees Celsius to manage pain. This isn’t science fiction; it’s a reality with cryoablation. The term "cryoablation" breaks down to "cryo" meaning cold and "ablation" meaning destruction. This innovative, minimally invasive technique uses extreme cold to temporarily disable nerve function and reduce pain. Cryoablation interrupts pain signals transmitted to the brain, providing an alternative to traditional nerve destruction methods like alcohol neurolysis or surgery, in certain situations.
Which type of pain conditions can be treated using this technology?
Cryoablation is effective for a variety of common pain conditions, including:
Acute and Post-Surgery Pain: Used for pain associated with surgeries such as hernia repair, rib fractures, thoracotomy (chest surgery), mastectomy (breast surgery), shoulder surgery, and knee replacement surgery.
Musculoskeletal pain such as shoulder or knee pain secondary to arthritis.
Shoulder pain: arthritis, rotator cuff repair, adhesive capsulitis, bursitis.
Knee pain: osteoarthritis, persistent post-surgical pain.
Hip pain: osteoarthritis, avascular necrosis, trochanteric bursitis.
Chest pain: Post-rib fracture and persisting costochondritis pain.
Chronic longstanding painconditions such as
Chest wall pain: Including post thoracotomy, post herpetic (after herpes zoster infection) pain, and pain originating from chest nerves (intercostal Neuralgia).
Chronic groin and pelvic pain: Including genital pain.
Headache disorders: with favourable response to nerve blocks such as the Occipital, supraorbital or supratrochlear nerves.
Phantom Limb Pain:common after amputation.
Nerve (Neuropathic) pain such as headaches from occipital Neuralgia or thigh pain form meralgia paresthetica, neuroma pain after amputation. Neuromas including Morton’s and Stump neuromas.
Spinal pain: such as from the arthritis of spinal joints (facet joint pain) in neck, middle of back, lower back, and pelvis joints (Sacroiliac Joints)
Chronic post-surgical pain (CPSP)- Post-surgical pain secondary to nerve injuries and entrapments in scar tissue or mesh can be treated with cryoablation. It is frequently used for treating persisting pain after chest wall, hernia, and amputation surgery.
Cancer pain: Localized to a nerve or region, particularly in cases of tumor infiltration of nerves. Has been used for pain related to abdominal, pelvic, and thoracic neoplasms.
for more information, visit- freezing of nerves
0 notes
Photo

LOW BACK, HIP OR KNEE PAIN? CALF OR ACHILLES PROBLEMS? SACROILIAC JOINT PROBLEMS? PELVIS DYSFUNCTION? ⠀ TENSOR FASCIA LATAE (TFL) & ILIOTIBIAL BAND (ITB) ⠀ [CADAVER DISSECTION ANATOMY, FUNCTION & PATHOLOGY] ⠀ The TFL is part of the „Gluteal Region Muscle Group“ and is related to the gluteus maximus in function and structure its origin is at the ASIS then it runs distally/laterally to insert into the ITB, which attaches to the tibia (Video 1/2). ⠀ The ITB runs from the ilium proximally to the tibia, distally into the proximal anterolateral tibia (Gerdy’s tubercle) as well as into the head of the fibula (Video 3/4). It is actually a thickening laterally of the “fascia lata”, a fibrous fascial membrane that envelopes the entire thigh (Pics 8/9 ). ⠀ The TFL and the gluteus maximus attach distally into the ITB, so the ITB can be looked at as distal tendinous attachments of these muscles. ⠀ The TFL is a hip flexor, abductor, internal rotator and anteriorly rotates your pelvis. It works in conjunction with the gluteus maximus and ITB to stabilise the leg during the stance phase of walking and running. It also assists in keeping the balance of the pelvis while standing, walking, or running. ⠀ Any dysfucntion/weakness in the glutes means that the TFL needs to work proportionally harder. Gluteal inhibition is common, especially if you spend a lot of time sitting. Functionally it is part of the „Lateral Line“ and the „Spiral Line“ (@AnatomyTrainsOfficial Pic 10 ). ⠀ Overload of the TFL can lead to pain and tightness in the front of the hip. Very common is also pain and tightness in the outer part of the knee and into the ITB. This is most noticeable when walking or up and down stairs/hills. Other symptoms: knee and hip pain (especially outside), lower/upper back-, SIJ-, calf- and achilles problems. As the TFL pulls the head of the femur bone forwards, chronic increased tone is one of the prime causes of hip osteoarthritis and degeneration. ⠀ Short term treatment such as myofascial release and dry needling is very helpful, while long term building gluteal and core strength is critical to prevent a relapse. ⠀ #Physiotherapy #Osteopathy #TFL #Muscle #ITBand #Pain #Therapy (hier: Frankfurt, Germany) https://www.instagram.com/p/B5h7C1SIecq/?igshid=j1rlmzxsv5aj
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
PKD and Back Pain
New Post has been published on https://backtherapyhealth.com/pkd-and-back-pain/
PKD and Back Pain
Back pain is the most common pain symptom reported by people with polycystic kidney disease (PKD). Finding ways to manage the pain associated with this disease is a major component of treatment.
PKD is characterized by the development of cysts, or fluid-filled sacs, in the kidneys. There are different forms of the disease, both acquired and genetic. Two kinds of genetic PKD exist, one which usually manifests in childhood (autosomal recessive) and one whose symptoms generally delay until adulthood (autosomal dominant). Autosomal dominant PKD accounts for the vast majority of cases.
Cysts grow gradually in the kidneys. Once adulthood is reached, kidney space filled by the cysts may cause urinary problems, such as blood in the urine and urinary tract infections. High blood pressure is also common among those with PKD. Though less appreciated, one of the main symptoms of the disease is back pain, which may be acute or chronic.
Back Pain and PKD
There are a number of causes of back pain, and by itself, it is not a good indicator of PKD. If you have a family history of the disease and urinary problems, however, it may be the symptom that leads to diagnosis.
People with PKD may experience back pain due to muscular changes and degenerative changes affecting spinal joints and discs. Kidney cysts can grow very large, adding weight to the abdominal region. According the National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse, a cyst-filled kidney can weigh as much as 30 pounds. Extra stomach weight pulls forward on the spine and back muscles, causing the spinal arch in the lower back to increase. This shortens the length of muscles in the lower back and creates chronic tension.
Structures of the spine may suffer from the growing cysts nearby. Often kidneys are more impacted on one side than the other, meaning weight distribution will be uneven. Slowly, posture will adjust to changes in weight distribution with and the pelvis will become uneven. As the pelvis tilts, the spine undergoes a change in alignment (the spine and pelvis are attached via the sacroiliac joints and a network of muscles). Uneven forces may cause degeneration of the sacroiliac joints, facet joints in the spine and spinal discs. Aside from localized pain, spinal misalignment and herniated discs can lead to radicular pain in the form of sciatica if the nerve is impinged by these structures.
Treatments
At present there is no cure for PKD. The disease is associated with a number of serious health complications that usually take effect after the age of 50, including polycystic liver disease and renal failure. Current treatments focus on the management of pain and correlative complications as well as slowing the growth of cysts within the kidneys.
Back pain from kidney cysts can sometimes be managed by physical therapy and postural training, such as the Alexander Technique. This helps people better cope with the uneven weight distribution characteristic of PKD. In some cases, steroid injections are used to simply numb the pain in the lower back and hips. Other medications like over-the-counter anti-inflammatories and prescription pain killers are sometimes prescribed if pain is severe. Surgery for back pain is rare, and is usually only prescribed to those who have degenerative spinal conditions and who conservative treatments have not helped.
Though a unified approach has yet to be identified, there are studies that provide evidence of ways to slow cyst development. One study found that a soy protein-based diet led to less cyst development than a diet heavy in casein protein (found in milk) in animal controls ( ). Another study showed that increasing water intake actually slowed the proliferation of PKD cells, leading to smaller kidney size in rats ( ). A number of drugs are being tested for their ability to slow cyst growth, but none are standard as of yet.
Managing high blood pressure is an important part of PKD treatment. Medication may be part of this management, as well as healthy weight maintenance and a low-sodium diet.
Though there is no cure for PKD at this time, there are steps you can take to slow the disease’s progression and manage its painful symptoms. Acting early can help to delay or prevent kidney failure later on.
Source by Amee LaTour
0 notes
Text
Bertolotti's Syndrome: All You Need To Know
Bertolotti's Syndrome is not very common but happens to very few people. It should be properly diagnosed and carefully treated. Let’s learn more about it.
Bertolotti syndrome is an unusual reason for low back pain, concentrated along the waistline, barely off to the side. Usually twisted with sacroiliitis, this diagnosis involves less than 10% of people, and it continually goes undiagnosed. The syndrome is an infrequent reason for back pain and can get treated by a competent spinal expert with modern spinal healthcare.
Patients with Bertolotti's Syndrome, or the momentary vertebra, often experience no side effects. Notwithstanding, the patients usually experience low back pain that transfers from the sides of their waistline. The irritation might be considered sacroiliac joint pain or lumbar circle, or lumbar feature joint agony. For this reason, the condition is usually go misdiagnosed.
What is Bertolotti Syndrome?
Italian doctor Mario Bertolotti lent his name to this intrinsic condition. It's found — regardless of lower back pain— in 10 to 20 percent of the people.
Bertolotti disorder happens when the last lumbar vertebra — the lumbosacral momentary vertebra, or LSTV —and the sacrum either combine or make a misleading joint thanks to an extended cross-over process (hard knocks on the vertebrae where muscles and tendons connect) on the LSTV.
When a combination of the LSTV and sacrum (called sacralization) or pseudo-joint doesn't do any damage — and many don't — it's simply a part of your life system, present since birth. When it generates LBP, it is Bertolotti disorder.
What causes Bertolotti disorder?
Bertolotti disorder can bring LBP in various cases, leading to aggravation and reactive muscle cramps. Here are a few distinct ways.
An imbalance in the designs of the lumbar vertebrae assuming the LSTV gets melded to the sacrum and iliac bone (the "wings" of the pelvic bone), can pressure the sacroiliac joint, which could cause anguish you'd feel over your bum.
A pseudo-joint will not have the pad or oil between the bones that different joints in the body need to assist with shock. It causes bone-on-bone crushing, which can stimulate osteoarthritis. It might likewise cause increased weight on the rings of the pseudo-joint.
Sacralization could diminish your spine's versatility, accelerating the mileage of the vertebrae and shock-engrossing intravertebral circles over this area.
What are the signs of Bertolotti Syndrome?
The vast majority could never realize they had a sacralization or pseudo-joint, except if it's found coincidentally during an X-ray for something unrelated. Yet, for those cases that do cause side effects, they can fluctuate significantly from one individual to another and will show up in adulthood — in your 20s or 30s.
Side effects can include:
Limited LBP that doesn't transmit down the legs
Conceivable suffering or uneasiness in the area of the sacroiliac joint
Unexplained firmness or trouble moving in some ways with pain
Further developed side effects with sitting and laying
How is Bertolotti Syndrome diagnosed?
Bertolotti's condition can get analyzed in light of clinical history, a comprehensive physical test and X-rays. The physical test will incorporate copying the actions that trigger aggravation or pain. Then, at that point, X-rays of the lower back and pelvis can locate any problematic structure irregularities.
How is Bertolotti Syndrome treated?
Much of the time, Bertolotti's condition gets dealt with non-or negligibly obtrusive medicines. Bertolotti syndrome treatment includes:
Lifestyle improvement reduces the pressure on the affected regions of the backbone, such as repetitive rotation and elongation.
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, like Aleve, Advil, or Tylenol
Exercise-based recuperation assists with a change in specific regions and possibly increases mobility.
Local anesthetic and occasionally corticosteroid injections under fluoroscopic guidance along the affected nerves or directly into the pseudoarthrosis reduce inflammation. Fluoroscopy can also get utilized for diagnosis.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment uses the body's platelets to reduce pain and aggravation and mend damaged joints through an infusion with fluoroscopic guidance. It keeps away from the adverse consequences of corticosteroids, for example, raising glucose levels and decreasing recovery.
Prolotherapy is an elective Bertolotti syndrome treatment that utilizes a mix of concentrated sedatives and dextrose infused into the impacted region to improve the body's enduring ability to recuperate naturally.
Radiofrequency ablation is a procedure that uses heat to stifle the impacted nerves around a pseudo-joint.
Conclusion
Bertolotti's Syndrome (BS) indicates the presence of pain related to the physical interpretation of the presence of a lumbosacral momentary vertebra (LSTV). It is perceived when a prolonged cross-over course of the last lumbar vertebra intertwines with the first sacral section, and this oddity is known as an uncommon reason for lower back pain.
Medical surgery is generally the last option to treat this condition and is ordinarily performed to remove a pseudo-joint. Surgery can carry the condition of decreasing or eliminating the extended transverse procedure, typically executed as a same-day process. Be cautioned that there’s not much substantial proof that surgery treats Bertolotti Syndrome. Visit advantage medical clinic for the right diagnosis and treatment for BS.
#bertolotti'ssyndrome#bertolottisyndrometreatment#whatisbertolottisyndrome#bertolotti'ssyndromesymptoms
0 notes
Text
What You Need To Know About Sciatica

Sciatica is a term used to describe nerve pain in the leg that is caused by irritation and/or compression of the sciatic nerve. Sciatica originates in the lower back, radiates deep into the buttock, and travels down the leg.
What Does Sciatica Feel Like ?
The symptoms of sciatica are commonly felt along the path of the large sciatic nerve. Sciatica is often characterized by one or more of the following features:
Pain. Sciatica pain is typically felt like a constant burning sensation or a shooting pain starting in the lower back or buttock and radiating down the front or back of the thigh and leg and/or feet.
Numbness. Sciatica pain may be accompanied by numbness in the back of the leg. Sometimes, tingling and/or weakness may also be present.
One-sided symptoms. Sciatica typically affects one leg. The condition often results in a feeling of heaviness in the affected leg. Rarely, both legs may be affected together.
Posture-induced symptoms. Sciatica symptoms may feel worse while sitting, trying to stand up, bending the spine forward, twisting the spine, lying down, and/or while coughing. The symptoms may be relieved by walking or applying a heat pack over the rear pelvic region.
It is important to note that any type of lower back pain or radiating leg pain is not sciatica. Sciatica is specific to pain that originates from the sciatic nerve.
Sciatica Is The Symptom Of An Underlying Medical Condition
Sciatica is a term used to describe a set of symptoms caused by an underlying medical condition; it is not a medical diagnosis.
Common medical conditions that may cause sciatica include :
A herniated lumbar disc
Lumbar spinal stenosis
Lumbar degenerative disc disease, general degenerative changes in vertebrae or discs
Spondylolisthesis
Muscle spasm and/or inflammation of the lumbar and/or pelvic muscles
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Rarely, tumors, blood clots, or other conditions in the lower spine may cause sciatica.
The sciatic nerve is the largest single nerve in the body and is formed by the union of 5 nerve roots in the lumbar and sacral spine. There are 2 sciatic nerves in the body—the right and left nerves, supplying the corresponding lower limb.
A few anatomical characteristics of the sciatic nerve include:
Origin. Starting at the level of the spinal segment L4, the sciatic nerve is formed by the merging of spinal nerves roots from L4 to S3. The emerging nerve roots converge into a single sciatic nerve making it large and bulky, typically up to 2cms in diameter.
Path. After its individual contributions end, the sciatic nerve exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, below the piriformis muscle. The nerve then runs along the back of the thigh, into the leg, and finally ends in the foot.
Branches. The sciatic nerve branches into 2 main divisions behind the knee—the tibial nerve and the common peroneal nerve. The tibial nerve courses down and supplies the back of the leg and the sole of the foot. The common peroneal nerve supplies the front of the leg and foot.
Rarely, the sciatic nerve may split into 2 nerves near the sciatic foramen, which merge again into a single nerve.
The specific sciatica symptoms largely depend on the nerve root that is pinched. For example, an L5 nerve impingement can cause pain in the back of the thigh and weakness in lifting the big toe and the ankle.
The Course Of Sciatica
Often, a particular event or injury does not cause sciatica—rather it tends to develop over time. Sciatica affects 10% to 40% of the population, typically around the age of 40 years. Sciatica is found to be common in certain types of occupations where physically strenuous positions are used, such as machine operators or truck drivers. Specifically, people who often bend their spine forward or sideways or raise their arms frequently above the shoulder level may be at risk of sciatica.
The vast majority of people who experience sciatica typically get better within 4 to 6 weeks with nonsurgical sciatica treatments. If severe neurological deficits are present, recovery may take longer. An estimated 33% of people, however, may have persistent symptoms up to 1 year. When severe nerve compression is present with progressive symptoms, surgery may be indicated.
When Sciatica Is Serious ?
Certain symptoms of sciatica may indicate a serious medical condition, such as cauda equina syndrome, infection, or spinal tumors. These symptoms may include, but are not limited to:
Progressive neurological symptoms, such as leg weakness
Symptoms in both legs
Bowel and/or bladder dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction
It is advised to seek medical attention immediately if such symptoms develop. Sciatica that occurs after an accident or trauma, or if it develops in tandem with other symptoms like fever or loss of appetite, also causes for prompt medical evaluation.
#spinespecialistinpimprichinchwad#spinesurgeoninpimprichinchwad#bestspinespecialistinpimprichinchwad
0 notes
Text
What causes iliac peak torment and activities to lessen torment
The iliac peak is joint pain the bended part at the highest point of the hip. It frames the wing-like piece of the pelvis on which an individual will in some cases rest their hands.
Muscles, tendons, and sash (a flimsy packaging of connective tissue) join to the iliac peak, and agony is caused when these are pulled or stressed. The aggravation can likewise emanate to other body regions, including the back, mid-region, and crotch.
This article investigates the reasons for iliac peak torment, what it seems like, medicines, and activities that might assist with forestalling and assuage torment.
The hip bone or hard pelvis gives strength, steadiness, and backing for the spine and organs. It contains three bones, including the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
The iliac peak is the most conspicuous piece of the ilium, the biggest of the three major bones.
As well as isolating the pelvis and the mid-region, the iliac peak associates with numerous significant muscles. These muscles include:
the gluteus maximus of the actual hip
the primary abs

the latissimus dorsi or biggest muscle toward the back
Causes
There are a few reasons for iliac peak torment. These can include:
Feeble muscles
Solid center muscles are expected to help the joints and to appropriately move. Hip agony can happen on the off chance that the abs or lower back muscles are feeble.
Get more familiar with activities to reinforce the center muscles here.
Injury
Injury can harm the iliac peak, like a fall or auto crash. This can bring about muscle pulling away from the bone, causing delicacy and torment in the hip region and at times in the lower back.
This kind of injury might be known as a hip pointerTrusted Source, as an individual will point with one finger to the area of the aggravation (for this situation the hip).
Sacroiliac joint brokenness
Harm or irritation of the sacroiliac joint can cause torment in the lower back, mid-region, or crotch.
This joint sits in the pelvis and associates the iliac to the lower part of the spine. Joint inflammation, maturing, or work out, like running, can all harm the sacroiliac joint.
The aggravation generally begins in a single side of the lower back and rear end and can reachTrusted Source up to the lower hip, crotch, and upper thigh.
Individuals may likewise feel deadness, shivering, or shortcoming in their legs. The side effects might deteriorate while sitting, dozing, or strolling up and ground floor.
Ilium apophysitis
An apophysis is a development plate and the point on a bone where muscles are appended. It is the area of bone that the remainder of the bone develops from, as is the last area of unresolved issue solidify. In that capacity, it is somewhat delicate in youngsters and teens.
In the event that the muscles are over and over pulled from the development plate, during sports, for instance, this can make it become disturbed and aroused, or it might even be pulled off the bone. The condition will sort itself out whenever development has gotten done and the bone has completely solidified.
Ilium apophysitis happens in kids and youths. Abuse causes the condition and results in a dull agony toward the front of the hip. The region can at times grow and is normally delicate, and the aggravation will in general deteriorate with movement.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Know About The Pelvic Pain
Patients with pelvic pain usually get pain in the front of the body, from the hips to the groin region. The pelvis is composed of three bones, it very often patients present with low back pain or hip pain they are in the sacroiliac joints and the pubic symphysis or the muscles and ligaments surrounding the area.
#Pelvic Pain#Health Care#Chiropractic Care#Physical Health#Chiropractic#Acupuncture#Pinched Nerve#Bodypain Relax#Hip Pain#Knee Pain
0 notes
Text
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment: What is Sacroiliac Joint

Do you have a nagging ache in your lower back that won't go away? Or do you have pain in the buttocks and down the leg? If so, the root of your discomfort might stem from your sacroiliac joints (SI joints).
Inflammation of the SI joint is often a common cause of low back and hip pain. Injury, strenuous activity, poor body mechanics, and pregnancy can all contribute to SI joint issues. In this article, we will explore the causes and symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome, as well as effective treatments options.
What are the Sacroiliac Joints?
The sacroiliac joint is located on both sides of the pelvis. These joints are the points where the sacrum meets with both sides of the hip bone (or ilium). SI joints have a small range of motion and minimal stability, and they do not have much room for movement due to how closely it is wedged between the pelvic bones.
The primary function of the two SI joints is to connect your lower body to your spine. This joint allows you to walk, run, bend over and pick things up off the floor. It also helps transfer weight from side to side when you change directions while walking.
Another function of the SI joints is shock absorption. The SI joints are also responsible for absorbing power which is generated by our gluteal muscles. This power is then transferred through the SI joints into the legs, moving us forward or upward.
Signs and Symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome?
Individuals who have sacroiliac joint syndrome have varying symptoms. However, some of the most common symptoms are:
Stinging Pain on Buttocks After Sitting
Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome can result in stinging pain on one side of the body, particularly in the buttocks. This is because the sacroiliac joints are responsible for transferring all of your weight from the pelvis to the legs and feet every time you take a step, sit down, or stand up. This transfer happens every time you take a step or sit down after standing for some amount of time. When this joint is injured or not functioning as it should, the symptoms may be noticed right away.
Sacrum Pain
The sacrum is located in the lower back and is connected to the pelvic bone. It sits right between the hips and creates an area that can be easily irritated or aggravated by muscle spasms, injuries, or conditions such as sciatica.
Difficulty Walking
Some individuals may feel a sensation of pain and stiffness when walking if their SI joints are inflamed. As well, they might experience muscle spasms or other mobility problems.
Sudden Jerky Movements While Sleeping or Awake
The sacroiliac joints play a prominent role in supporting other joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. As such, when you have Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome, you might experience sudden jerky movements while you are asleep or awake.
Tingling Sensation or Numbness in the Legs or Toes
Sudden tingling or numbness in the legs or toes may also be a sign of SI Joint syndrome. These types of discomfort is often caused by sciatic nerve irritation or pressure from the sacroiliac joint.
Common Causes of Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome
There are several conditions that can cause Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome. Some of these conditions include:
Osteoarthritis
The breakdown of cartilage in the joints is known as osteoarthritis. Over time, this condition can become very painful for individuals and can make walking or moving around extremely difficult. There are different types of arthritis, but most often, people experience symptoms associated with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a condition in which pain is felt in multiple parts of one’s body, including the sacroiliac region. The pain being experienced can radiate throughout the legs, hips, feet, lower back, or upper buttocks area as well.
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but it has been reported that specific genes are most likely involved. Hence, this is one reason why women are more likely than men to develop this condition.
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
People with lumbar spinal stenosis may experience leg pain while walking. This is due to the fact that their nerves are being compressed at the spine level. Lumbar spinal stenosis is usually caused by abnormal growth or a herniated disc in the low back area. Other causes include obesity and aging.
Hip Dislocation
A dislocated hip can also be a potential cause of sacroiliac joint syndrome. A hip dislocation can be extremely serious and should be attended to by a professional immediately. If the condition is severe, surgery might be required to realign the hips.
Sprain or Strain
Any sprain or strain of the ankles can lead to pain in the sacroiliac joints and its surrounding areas. Spraining or straining of the ankles is often caused by falls or instances where one lands awkwardly on one's foot.
Pregnancy
If you are pregnant, you may experience pain in the sacroiliac area. This is due to the extra weight which the body has to support, as well as the increased pressure which is placed on the muscles, joints, and bones of the pelvic region.
Gouty Arthritis
Gouty arthritis occurs when uric acid crystals form within the joints of one’s body. Among other places, these crystals can be found in the sacroiliac area of the hips and lower back. Gouty Arthritis is often caused by an unhealthy diet that contains too much animal protein, by being overweight for extended periods of time, or by constant dehydration.
Those that are afflicted with gouty arthritis often experience severe pain throughout their affected joints or muscles - including those within the the hips, low back, and sacroiliac region.
Treatment for Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome
Sacroiliac joint syndrome is a condition that can be treated with both surgical and non-surgical methods. Depending on its severity, treatment for Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome can range from simply taking painkillers to undergoing surgery.
Medication
Oftentimes, doctors will prescribe painkillers for Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome. Patients diagnosed with this condition will usually take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxers, and even more potent opioid-based drugs to help cope with the pain they feel. As well, muscle relaxants may be prescribed in order to alleviate lower back tension.
Surgery
Surgery involving the sacroiliac joint may sometimes include fusing it using metal plates and screws. This procedure consists of making an incision near the hip area of a patient in order to access the joint and tissues surrounding it. If you are considering surgery as a way to treat Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome, you should consult a doctor about trying non-surgical methods first before undergoing more invasive treatment options.
Physical Therapy
Individuals who are diagnosed with Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome usually benefit from physical therapy regimens consisting of exercises which help to increase strength, stability, and flexibility throughout the body's core region. The stronger your core muscles are, the more stable your hips will be, thus decreasing the amount of pressure which is applied to the sacroiliac area.
Exercise Options for Managing Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome
There are several exercises you can do at home to alleviate the symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome. They are as follows:
Knee Roll-Outs
Begin by laying down flat on your stomach. Bend one knee up towards your chest while keeping the other leg straight out on the ground. Slowly roll out your bent knee side to side. You can also lift on your extended leg's toes so that you are using your calf to help keep your balance as you move your leg back and forth.
Stretches for Hip Flexors/Psoas
The hip flexor, also known as the psoas, can be a major factor in how much pain you feel through your hips and lower back. This is because your hip flexors are attached to your sacroiliac joint area, and can cause increased sensitivity or discomfort when its surrounding muscles are tight.
To stretch your hip flexors, start by laying on your back with one knee bent up towards your chest. Then, lean over towards that leg until you feel a stretch in the front of your hip (where groin meets leg). Hold this stretch for 10 seconds, and then switch sides. Repeat this stretch as often as needed throughout the day to help alleviate the pain which is associated with Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome.
Walking
Going for a walk at least three times per week can do wonders in alleviating the symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome. By going for walks regularly, you will be able to reduce the amount of stiffness and pain being felt throughout your hips, and also maintain a healthy weight, which can mitigate the long-term effects of Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome.
Resting
Rest is essential when trying to heal from Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome and to ensure that the muscles surrounding your pelvic area can function at an optimal level. By restricting activity and staying off your feet as much as possible when having an episode of pain, you will speed up the healing process. While it may be difficult to completely restrict activity in your daily life, taking short breaks when needed can make a big difference in how long it takes to recover from this Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome.
Hip Abductor Stretches
Hip abductor stretches are great for alleviating tension which is felt in the hip area. Begin these exercises by standing up straight with your feet together. Slowly take a comprehensive step out to one side, making sure that you have enough room to come down towards the floor without having to worry about hitting anything or placing your knee into a potentially painful position. Keep your upper body tall and straight while allowing your hips to bend over towards the ground, such that you can feel the tension in the outer hip area of whichever leg you stepped out with. If you are struggling to keep your balance, hold onto something sturdy in front of you for support. You want to maintain a 90-degree angle at the knee during this stretch, and be sure not to let it drop below that level as it will put more pressure on your joints and back.
Conclusion
Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome is a condition that requires one to be proactive in its treatment and not just settle for painkillers or other remedies that don't address the root problem. By partaking in regular exercises which target the sacroiliac joints and its surrounding areas (such as the ones listed above), individuals could find relief from their symptoms, while also helping to prevent future episodes of this condition once it has been adequately treated.
The leading causes for Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome is typically poor posture, injury, strenuous activity, and pregnancy. If you are experiencing symptoms associated with Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome, make sure to seek help from a medical professional promptly, such that he or she could pinpoint the cause of the issue and to prescribe an effective treatment plan.
Treatment for Sacroiliac Joint Syndrome does not have to be complicated, invasive, nor overwhelming. When treatment is initiated timely and followed through, patients often experience better overall health and begin feeling like their normal self again within no time.
0 notes
Photo

LOWER BACK, BUTTOCK OR LEG PAIN? SACROILIAC JOINT PROBLEMS? PELVIS DYSFUNCTION? SCIATICA? ⠀ PIRIFORMIS MUSCLE VS. SCIATIC NERVE & PIRIFORMIS MUSCLE SYNDROME (PMS) ⠀ [ANATOMY AND PATHOLOGY] ⠀ The piriformis is a small, relatively short, and little-known muscle buried deep within the muscle tissue in your hips. In each hip, it runs from the back of your pelvis to the top of your femur. Because of its unique positioning, the piriformis helps rotate your leg outward when your hip is extended, but rotates your leg inward and into abduction when your hip is flexed. ⠀ The piriformis is positioned immediately adjacent to the sciatic nerve (Pic 1/2/3/4), a very thick nerve which runs from the base of your spine along your glute muscles and down the back of your legs, providing the nerve signals that allow all of the muscles on the back side of your lower body to fire when needed. ⠀ Usual anatomy is for the sciatic nerve to exit into the gluteal region between the piriformis and the superior gemellus. But in approximately 15% of people, the sciatic nerve relationship with the piriformis is different: Sometimes the entire sciatic nerve or part of it (usually the common fibular nerve part) goes through the piriformis. Or perhaps it travels between the piriformis and the gluteus medius (Pic 6). ⠀ When the piriformis muscle is irritated/tight it can compress or entrap the sciatic nerve and therefore lead to PMS (Pic 7/8). ⠀ PMS is related to sciatica, a painful irritation which also involves following symptoms: ▪️Aching, soreness, or tightness in your butt, between the back of your pelvis and the top of your femur. ▪️Pain, tightness, tingling, weakness, or numbness can also radiate into your lower back and down the back side of your leg, through your hamstrings and calves or even feet. ▪️Buttock pain and tightness with prolonged sitting is also a common occurrence. ⠀ DD: Gluteal and leg pain can be vascular in origin and a result of compression of the superior gluteal artery and the inferior gluteal artery + branches. The human anatomy includes many fascial layers that can compress these arteries as well. Don't forget the vascular connections when assessing the body (Pic 10). (hier: Frankfurt, Germany) https://www.instagram.com/p/B5XiQsWCda2/?igshid=b5a2hq9t9idq
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ayurvedic treatment for Ankylosing spondylitis
What are Spondylitis and Spondylosis? What is difference between Spondylosis and spondylitis ? Spondylosis and spondylitis are conditions of the joints of the spine. The spine is formed from bones called vertebrae, and also the material between every vertebra within the joints is termed disc. The joints and discs, over time, will become worn out or inflamed. First, we will try to understand Spondylitis and Spondylosis and further will address Ayurvedic treatment for Ankylosing Spondylitis Types of Spondylitis Spondylitis is the result of an inflammatory condition of the joint that causes arthritis. Some types of Spondylitis are as below1) Ankylosing spondylitis2) Enteropathic Arthritis3) Psoriatic Arthritis4) Reactive Arthritis5) Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis6) Juvenile Spondyloarthritis Types of Spondylosis Spondylosis describes the vertebral joints' general wear and tear that results in degeneration of the discs and joints. Some common types of Spondylosis is as follows1) Lumbar Spondylosis2) Cervical Spondylosis3) Thoracic spondylolysisIn this article, we are going to discuss ankylosing spondylitis and Ayurveda treatment for ankylosing spondylitis. What is ankylosing spondylitis? Inflammation of the joints of the spine occurs with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). It is a form of autoimmune disease that usually occurs earlier in life, from adolescence to around 40, with stiffness and pain that worsens in the morning and improved with exercise. The sacroiliac joints, which are large joints between the lower spine (sacrum) and the pelvis are often affected. As it is a condition that is a progressive process for over several years until structural damage manifests, it’s called sacroiliitis. loss of spinal mobility, extra-articular symptoms, peripheral arthritis, and reduction of quality of life. What are the Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Pain and stiffness are the primary signs one may experience. Pain can be seen in the areas of the low back, hip joint.
Bony fusion is another sign in this condition where the vertebrae fuse together leading to a hunched back posture.
It also can have an effect on the neck, which is leading to the lack of ability to move the neck.
It is likewise related to different systemic signs like Iritis (Inflammation, redness in the eyes), Fever, Fatigue, and Loss of appetite.
In a few uncommon cases, it may additionally be related to coronary heart and lung diseases.
In chronic cases, it leads to restriction in the ability to breathe freely.
Ayurveda Management and View
Can Ayurveda Cure ankylosing spondylitis Various Panchakarma procedures and internal Ayurvedic drug treatments are proven beneficial in the control of AS. Asthi-majja gata vata is a term that is correlated with AS. According to Ayurveda, Ankylosing spondylitis is caused because of aggravated vata dosha. This imbalance is the reason for degeneration &inflammation of the spine and might even result in disability in a lengthy time period. In this autoimmune disorder, the disc between the vertebrae gets swollen up inflicting drawback of movement. Ayurvedic remedy aims at digesting the ama by giving herbs and balancing aggravated vata. External Therapy along with Lepanam, Pichu, Kati Basti, Sarvangadhara, and Patrapinda swedana is useful for this disorder. Panchakarma Therapy such as Virechanam, Nasyam, Snehavasthy, Vaitharana vasthy, Kashayavasthy are useful to reduce pain and stop the progress of AS. Along with Panchakarma treatments diet, lifestyle modifications are equally important to get relief from AS
Diet and Lifestyle advice for ankylosing spondylitis
Avoid Vatha and pitta pacifying food.
Include ghee in your diet.
Take light meals and avoid extra oily meals and curds.
Ensuring proper evacuation of bowels, constipation ought to be avoided.
Applying heat to affected regions will assist to alleviate pain and stiffness.
Avoid sleeping during the daytime
Yoga asanas which includes Pawana muktasana, Bhujangasana, Dhanurasana, Paschimottasana, are useful for this disease.
Practice Pranayama which includes Nadi shodhana, Chandrabhedi Sheethali & Bhramari.
SUMMERY
Ayurveda advocates a holistic approach towards Ankolysisng Spondylitis. The medications along with different therapies are aimed at addressing the existing condition effectively. It also aids in retarding the progress of the condition.
0 notes
Text
Sacroiliac Fusion Implants Market Report Analysis With Industry Share
Sacroiliac joints (SI) are joints between the sacrum and ilium bones of the pelvis. The sacrum supports the spine and ilium bone supports sacrum. The sacroiliac joint is highly dependent on its strong ligamentous structure for providing support and stability to complete human body. Commonly observed conditions for which SI joint fusion is indicated include sacroiliac joint dysfunction, sacroiliac joint disruption, and degenerative sacroilitis. Sacroilitis is inflammation or dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint which could result in the unilateral low back pain. Sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be diagnosed using provocative and non-provocative maneuvers. SI joint dysfunction can be treated with minimally invasive surgery performed in either of the two ways: immediate fixation or SI joint fusion. Sacroiliac fusion systems are intended to stabilize the sacroiliac joint and provide an environment for fusion. During immediate fixation, an implant is placed across the joints. Bone grafts can be delivered within the device to promote fusion. Sacroiliac fusion surgery is gaining popularity among physicians to treat the pain related to the sacroiliac joint. According to SI-Bone, Inc., 82% of patients were satisfied with SI joint fusion surgery. Hence, patient satisfaction and least requirement of repetition of the procedure are likely to increase demand for sacroiliac fusion systems in the next few years.
Read Report Overview: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sacroiliac-fusion-implants-market.html
Release of the treatment guidelines by the North American Spine Society and the International Society for the Advancement of Spinal Surgery and favorable reimbursement policies for the procedure by the U.S. Medicare are expected to increase the adoption of sacroiliac fusion surgeries during the forecast period. According to recent statistics released by BIBA Medical Ltd., about 18% of lower back pain is associated with the dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint. Sedentary lifestyles resulting in hypo-motility of the joint is the major reason for the rise in prevalence of the disease across the globe. Hence, rise in prevalence of the disease, increase in adoption of minimally invasive fusion procedure, economic growth, surge in per capita health care spending, and increase in the number of skilled orthopedic surgeons are anticipated to drive the sacroiliac fusion implants market during the forecast period. Sacroiliac joint fusion technique is not new; however, its penetration has been limited due to extensive nature of the open fusion surgery and lack of consistent data to prove the effectiveness of the minimally invasive procedure. Moreover, lack of awareness in the developing regions and high cost of the procedure is projected to restrain the sacroiliac fusion implants market during the forecast period.
Request a PDF Brochure - https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=B&rep_id=63636
The global sacroiliac fusion implants market can be segmented based on product, surgery type, end-user, and region. In terms of product, the sacroiliac fusion implants market can be classified into triangular implants, porous implants, hollow modular screws, titanium coated implants, titanium cages, and allograft dowels. Based on surgery type, the global sacroiliac joint fusion implants market can be bifurcated into lateral transarticular surgery and posterior surgery. In terms of end-user, the sacroiliac fusion implants market can be divided into hospitals, orthopedic clinics, ambulatory surgery centers, and others. The hospitals segment is anticipated to dominate the global sacroiliac fusion implants market, owing to high preference for hospitals due to availability of various facilities under one roof and favorable reimbursement scenario.
Request for Analysis of COVID19 Impact on Sacroiliac Fusion Implants Market - https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=covid19&rep_id=63636
Based on region, the global sacroiliac fusion implants market can be segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. North America is a leading market for sacroiliac fusion implants owing to the presence of large geriatric population and rise in prevalence of SI joint dysfunction. High health care spending, rise in the number of minimally invasive procedures performed in the region, and high adoption of advanced technologies by the population are expected to boost sacroiliac fusion implants market growth in North America. Europe and Asia Pacific are likely to experience increased market traction due to rise in the number cases of SI joint disability and pain. Additionally, surge in adoption of SI joint fusion surgery among surgeons, economic empowerment of emerging regions such as Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa leading to an increase in affordability for minimally invasive surgery procedure, and rise in the number of sports-related injuries are anticipated to contribute to the growth of the market in emerging regions.
Pre-Book Sacroiliac Fusion Implants Market Report - https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/checkout.php?rep_id=63636<ype=S
Key players operating in the global total sacroiliac fusion implants market include RTI Surgical, Inc., Medtronic, SI-BONE, Inc., Camber Spine, Zimmer Biomet, and Xtant Medical. These players focus on expanding product portfolios through mergers and acquisitions. For instance, in January 2018, RTI Surgical, Inc. signed an agreement to acquire Zyga Technology, Inc., a leading medical device company which has developed SImmetry Sacroiliac Joint Fusion System.
More Trending Reports by Transparency Market Research:
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/rising-number-of-cancer-related-deaths-and-the-need-for-efficient-treatment-options-to-tackle-the-swelling-fatality-rate-will-aid-in-boosting-the-growth-of-the-radiation-therapy-market-says-tmr-301304147.html
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/increased-number-of-patients-with-hereditary-antithrombin-deficiency-boosts-sales-in-antithrombin-market-tmr-301309026.html
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/developers-of-robotic-technologies-lean-on-safety-and-accuracy-to-boost-patient-outcomes-in-surgical-robots-market-global-valuation-to-touch-us-13-1-bn-by-2022-tmr-301312625.html
About Us
Transparency Market Research (TMR) is a global market intelligence company providing business information reports and services. The company’s exclusive blend of quantitative forecasting and trend analysis provides forward-looking insight for thousands of decision makers. TMR’s experienced team of analysts, researchers, and consultants use proprietary data sources and various tools and techniques to gather and analyze information.
TMR’s data repository is continuously updated and revised by a team of research experts so that it always reflects the latest trends and information. With extensive research and analysis capabilities, Transparency Market Research employs rigorous primary and secondary research techniques to develop distinctive data sets and research material for business reports.
Contact
90 State Street, Suite 700 Albany, NY 12207 Tel: +1-518-618-1030 USA - Canada Toll Free: 866-552-3453 Website: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/
0 notes
Text
Here’s Everything You Need To Know About Bertolotti Syndrome
A rare form of low back pain that primarily affects the waist area somewhat off to the side is the Bertolotti syndrome. This illness, sometimes mistaken with sacroiliitis, affects less than 10% of the population and goes undiagnosed.
The syndrome is a rare source of back pain that a competent spine expert can address with current spinal healthcare.
Here in this article you will learn What is Bertolotti’s syndrome is and the different treatment options available for it.

What is Bertolotti syndrome?
This congenital, frequent disease got named after Italian physician Mario Bertolotti. It affects 10 to 20% of the population, whether or not they have lower back pain.
This syndrome is caused by an enlarged transverse process (bony bumps on the vertebrae where muscles and ligaments attach) on the LSTV, which causes the last lumbar vertebra—the lumbosacral transitional vertebra, or LSTV—and the sacrum to merge or form a false joint.
What causes this syndrome?
Bertolotti syndrome, which causes inflammation and reactive muscular spasm, can cause LBP in various conditions. Here are a few ideas.
If the LSTV gets fused to the sacrum and iliac bone (the "wings" of the pelvic bone), an asymmetry in the structures of the lumbar vertebrae might stress the sacroiliac joint causing pain above the buttocks.
A pseudo-joint will lack the cushioning and lubricant between the bones that other joints have to absorb shock. It produces severe grinding of the bones against each other, which can progress to osteoarthritis. It could also put more strain on the pseudo-discs.
Sacralization may reduce your spine's movement, causing the vertebrae and shock-absorbing intervertebral discs above this location to wear out faster.
Muscle imbalances and tiredness can be caused by unequal stresses on surrounding muscle tissue caused by a misaligned spine. Even though both sides of the back might be affected, tightness and spasms in the lower back and/or pelvis usually only occur on one side.
Symptoms
For Bertolotti syndrome treatment, it’s essential to figure out the symptoms. Most people aren't aware they have a sacralization or pseudo-joint unless it's discovered by chance during an X-ray for something else. However, in those cases where symptoms do occur, they can vary considerably from person to person and usually appear in maturity, in your 20s or 30s.
Among the signs and symptoms are:
Improved symptoms with sitting and laying
Pain or discomfort in the sacroiliac joint area
Unexplained stiffness or trouble moving in specific ways with pain.
How is the syndrome diagnosed?
A good medical history, a thorough physical exam, and X-rays can all be used to identify the syndrome. Recreating the movements that cause pain or discomfort will be part of the physical evaluation. An X-ray of the lower back and pelvis can identify any aberrant bone architecture.
Bertolotti syndrome treatment
The syndrome often gets treated with non-invasive or minimally invasive procedures. These can include the following:
Lifestyle modifications
Repetitive rotation and extension, as well as other lifestyle changes, can help to relieve the strain on the afflicted regions of the spine.
Over the counter medications
Pain relievers sold over the counter (OTC), such as Aleve, Advil, or Tylenol.
Physical therapy
It can help strengthen key muscles and promote mobility.
Local anesthetic and occasionally corticosteroid injections
To alleviate inflammation, local anesthetic and corticosteroid injections are given under fluoroscopic supervision along the afflicted nerves or directly into the pseudoarthrosis. Diagnoses can also be made via fluoroscopy.
Prolotherapy
Prolotherapy is an alternative treatment that involves injecting a mixture of concentrated local anesthetic and dextrose into the damaged area to boost the body's natural healing abilities.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is an injection with fluoroscopic guidance that uses the body's platelets to alleviate pain and inflammation while also promoting healing in injured joints. It eliminates the side effects of corticosteroids, such as blood sugar elevation and slowed recovery. These treatments for syndrome have not been properly explored and are not covered by insurance.
To Conclude:
Surgery is normally used as a last resort to address this condition and is used to remove a pseudo-joint. The extended transverse process can be reduced or removed through surgery. This surgery is usually done on the same day. Be aware that there isn't much high-quality evidence that surgery can successfully treat Bertolotti's syndrome. Find more information about Bertolotti's syndrome here on Advantage health system.
0 notes
Text
Can use a lower back belt prevent back injuries?
Use a lower back belt to prevent back injury
Back pain has almost become an occupational disease of modern people. Is it a good idea to use a back support belt to prevent waist injuries? Next, we will explore this issue together.
Back injuries account for 20% of all workplace injuries and cause approximately US$2-50 billion in damage to the United States every year. This is the largest single injury category.
Given this data, security leaders and companies around the world are desperately searching for answers. And you don’t have to search too far to find a simple way to prevent waist discomfort, pain, and injury-back support straps.
It was originally used for medical rehabilitation. Athletes also use back support straps when lifting weights. Recently, back support belts have become popular among office workers. Although there are many types of back belts on the market, the most common is the lower back belt.
The benefits of using a back support belt are:
Reduce pressure on the spine when straining on the back
Increase intra-abdominal pressure to provide support for the spine
Strengthen the spine and maintain the correct posture
Limit bending (range of motion)
Benefits of wearing a back support belt

People suffering from back pain-related issues are at most times in the fear of encountering a sudden jerk while functioning or moving their body, which might increase their level of back pain. While in some cases this sudden jerk could be temporary and would disappear after a brief rest or reduction in physical activity, in the worst case this might trigger a more severe attack and could possibly cause the current situation of back pain to deteriorate.
Therefore, from the moment that you start experiencing slight back pain issues on a regular basis that appear and disappear occasionally, it is better to consult a doctor and ask for his advice on which back support belt should you buy and start using. Buying a back pain relief support belt from the right place could help you in the following ways –
Providing relief from back pain: The main and overall objective of wearing a back pain relief support belt is to eliminate or significantly reduce the amount of back pain in a person. Back support belts create compression and pressure that actually works against the stress levels in the lumbar region. By working in a counteractive manner, supports muscles, enhances the forward motion of the spine, and decreases the amount of back pain.
Help in maintaining your body posture: A person suffering from back pain could easily become unable to either lift heavy objects or even operate heavy machinery and equipment where applying physical strength is important. Back support belts are designed in a way to help discourage any improper posture formation by a person while moving, the consequences of which could result in more back pain.
Having a back pain relief support belt on the body keeps reminding the person to not engage in an act of turning, bending, raising, lowering, or lifting in a way that brings the above consequence. Therefore, by wearing a back support belt, a person can perform his duties just like any other person while also maintaining his body posture in a correct manner.
Best for people having sacroiliac joint problems: The body of a person having sacroiliac joint issues will be unable to absorb shocks while walking or moving. Usually, sacroiliac joints in a person’s body deal with shock factors due to any sort of movement. By using a back support belt which is particularly designed for people with sacroiliac joint problems, a person does not only feel relief from such pain but will also notice better stability in the sacroiliac joint area since the stress levels on the pelvis are reduced.
Experience normal lifestyle: Back pain can be a great cause of obstructing a person from carrying on his normal lifestyle routines such as walking, sitting, running, or even lifting average weight objects, etc. By using the right kind of back pain support belt, such obstructed lifestyle can be revived, helping the person to interact with its surroundings once again in a normal manner.
Support during pregnancy: Many women suffer from back pain during their pregnancy, due to the extra weight that they have to carry. This pain could make them feel uncomfortable and prevent their normal everyday mobility. But by using a back pain support belt, pregnant ladies could easily carry out their routine tasks since the back support belts help in putting off the extra-weight and pressure feeling on their spine and lower back.
The best back support belts in 2021
The best lower back support belt 2021 entails all the basic and supplementary key features that a lower back support belt should have. You can buy yourself a good quality back support belt from the best back support belt selling website in 2021.
You do not need any consultation before buying a back support belt from lowerbackbelt.com because you can have a complete product description that is 100% effective for the selection of a back support belt according to the level of your pain and disorder. The variety of products found on this website helps you make a better choice. Moreover, the quality of the manufacturing material also makes it enduring and durable.
The best back support belt for pain relief
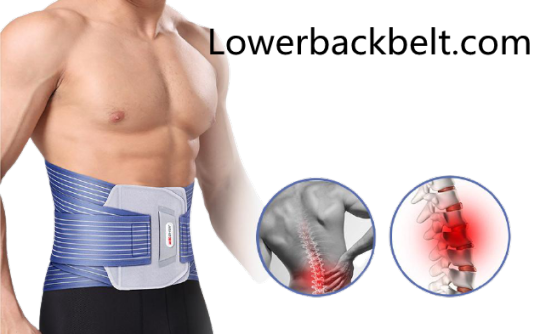
Lower back pain is one of the most common causes of job-related debility which is affecting more than 80% of American adults in their lifetimes. It has been observed that the most emblematic originators of lower back pain are sprains, strains, and overexertion.
Back support belts help their wearers alleviate this pain, providing particularly designed support and compression system in the belt to boost healing from surgery or injury and protection against damage. They help to enhance the correct posture by reminding the user to balance their proper body mechanism for any movement or lifting task.
For pain relief dual pulse graphene massage belt is highly effective as it is a universal adjustable back support belt 2021. It is designed to provide a personalized and finely-tuned fitting that guarantees the appropriate support you need.
The back pad of the belt is lightweight, sits contentedly against your lower back, and is enclosed in a back panel for more rigid support. To ensure the users’ satisfaction and providing them with the right level of stiffness, firm sheets are added. An adjustable pressure system is installed to allow the wearer to manage the pressure according to the need.
The best back support belt for medical use
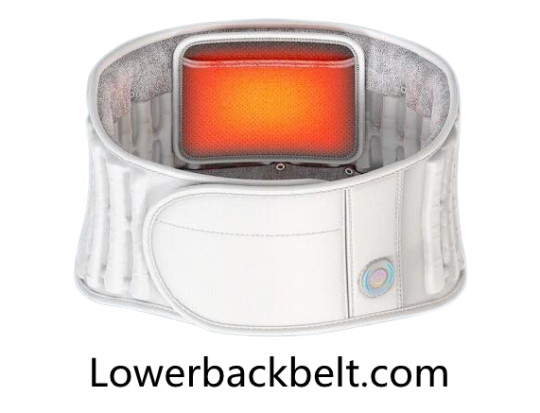

For medical use, you should have to choose an infrared inflatable heating lower back belt that not only supports your lumbar region but also maintains its temperature within the desired limit.
It is equipped with an electric air pump and a removable graphene pad. This belt has three temperature settings and all these things are insulated in a comfortable fabric. It not only helps you to maintain the lumbar temperature at 26 degrees Celsius but also promotes your waist strength with the lightweight hot compression through graphene far-infrared. It maintains the temperature intelligibility and controls it between three set points. This belt is made up of five layers of high-quality fabric which is very comfortable and durable.
These belts provide some restriction in loose body movement and are typically designed to confine the posture and movement mechanics. The best back support belt can help you improve lumber region temperature and enhanced blood circulation in muscles to some extent it is effective in releasing lower back pain.
Where to buy the best lower back support belts?
Choosing the best back support belt according to your treatment level is a very important step when buying a back support belt. If you can make a good choice, you can get benefits from the product you are going to buy. But if you have no proper information or for the required data, your choice may harm you.
Choose the best suitable back support belt for your back pain or disorder from lowerbackbelt.com. Here you can find a diversity of different back support belts from which you can easily choose your belt for treatment.
It is very important to consider every single detail of your spine problem or back pain before buying a back support belt. Match the specifications of the product with your treatment level to buy the best suitable product.
We mention all the specifications functions and suitability of their product in the description. It is truly helpful for or anyone to pick the back support belt by reading the description and salient features. Not all back support belts are suitable for the same type of disorder.
For example, if you want to use a back support belt for pain relief you should buy the product with a massage option. Similarly, other types of back support belts are adaptive and operative with their related problems.
0 notes