#“The impact of AI-generated content on the writing industry”
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Can Artificial Intelligence Replace Human Writers? Unveiling the True Potential of ChatGPT and Google Bard
#AI-generated content#ML-generated text#GPT-3 vs. Google Bard#impact of AI on writing#NLP-based writing#language processing in AI writing#“How can AI-driven writing enhance content creation?”#“Exploring the true potential of ChatGPT and Google Bard”#“Can artificial intelligence completely replace human writers?”#“How does ChatGPT and Google Bard differ in their writing capabilities?”#“The impact of AI-generated content on the writing industry”#“The role of AI in transforming the writing landscape”
1 note
·
View note
Text
The WEF’s report is behind the information curve by at least 6-9 months, during which time AI has doubled intelligence and ability twice over. The best estimates now predict that AGI – Artificial General intelligence – will be achieved by midyear 2025. By 2030, virtually 100% of companies worldwide will be impacted. ⁃ Patrick Wood, Editor.
Artificial intelligence is coming for your job: 41% of employers intend to downsize their workforce as AI automates certain tasks, a World Economic Forum survey showed Wednesday.
Out of hundreds of large companies surveyed around the world, 77% also said they were planning to reskill and upskill their existing workers between 2025-2030 to better work alongside AI, according to findings published in the WEF’s Future of Jobs Report. But, unlike the previous, 2023 edition, this year’s report did not say that most technologies, including AI, were expected to be “a net positive” for job numbers.
“Advances in AI and renewable energy are reshaping the (labor) market — driving an increase in demand for many technology or specialist roles while driving a decline for others, such as graphic designers,” the WEF said in a press release ahead of its annual meeting in Davos later this month.
Writing in the wide-ranging report, Saadia Zahidi, the forum’s managing director, highlighted the role of generative AI in reshaping industries and tasks across all sectors. The technology can create original text, images and other content in response to prompts from users.
Postal service clerks, executive secretaries and payroll clerks are among jobs that employers expect to experience the fastest decline in numbers in coming years, whether due to the spread of AI or other trends.
“The presence of both graphic designers and legal secretaries just outside the top 10 fastest-declining job roles, a first-time prediction not seen in previous editions of the Future of Jobs Report, may illustrate GenAI’s increasing capacity to perform knowledge work,” the report said.
Conversely, AI skills are increasingly in demand. Close to 70% of companies are planning to hire new workers with skills to design AI tools and enhancements, and 62% intend to recruit more people with skills to better work alongside AI, according to the latest survey, conducted last year.
Striking an optimistic note, the report said the primary impact of technologies such as generative AI on jobs might lie in their potential for “augmenting” human skills through “human-machine collaboration,” rather than in outright replacement, “particularly given the continued importance of human-centered skills.”
However, many workers have already been replaced by AI. In recent years, some tech firms, including file storage service Dropbox and language-learning app Duolingo, have cited AI as a reason for making layoffs.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Adobe is Shielding Artists from AI Misuse
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/how-adobe-is-shielding-artists-from-ai-misuse/
How Adobe is Shielding Artists from AI Misuse
In recent years, the growing ability of generative AI to create realistic visuals, mimic artistic styles, and produce entirely new forms of expression has redefined how art is made and experienced. While this transformation offers remarkable opportunities for innovation and productivity in the creative sector, it also raises concerns about intellectual property rights and the potential misuse of artistic works. A recent study found that 56% of creators believe generative AI poses a threat to them, primarily due to the unauthorized use of their work in training datasets. Recognizing this challenges, Adobe—an American software company known for its multimedia and creativity software products—is taking proactive measures to protect artists from AI misuse. In this article, we’ll explore how Adobe is empowering artists to safeguard their intellectual property in the face of evolving AI threats.
The Rise of AI in Creative Industries
Artificial intelligence is transforming the creative industries, reshaping how we create, edit, and engage with content. From generating music and designing graphics to writing scripts and building entire virtual worlds, AI-driven tools are evolving at a rapid pace. However, as AI’s capabilities expand, so do the challenges it presents—particularly for artists. Models like DALL-E and Midjourney can replicate famous styles or mimic artwork with impressive accuracy, often using publicly available images without consent. This raises serious legal and ethical concerns about copyright and artistic integrity. For many creators, the fear is that AI will learn from their copyrighted work and produce something similar, potentially diminishing the value of their art. The lack of clear legal frameworks for AI-generated content further complicates the issue, leaving the creative community vulnerable. To address these concerns, Adobe is taking proactive measures to develop technologies that can protect artists from the potential misuse of AI.
Adobe’s Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI)
One of Adobe’s most impactful efforts in protecting artists is its Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI). Launched in 2019, the CAI is a collaborative, open-source initiative that aims to provide creators with tools to verify the authenticity of their digital content. By embedding metadata into images and other digital files, Adobe enables artists to assert ownership and trace the origin of their work. This “digital fingerprint” not only ensures that creators are credited but also helps identify when and where their work has been altered or misused.
In addition to protecting copyrights, the CAI addresses the broader issue of content manipulation, which has become increasingly concerned with the rise of deepfakes and AI-generated images that distort reality. By enabling users to verify the provenance and authenticity of digital content, the CAI protects both artists and the public from deceptive or harmful uses of AI technology.
Adobe Firefly
In early 2023, Adobe launched Firefly, an AI-powered collection of creative tools designed to generate images, videos, and text effects using generative AI. One of the key features of Firefly is its underlying data model. Adobe has ensured that Firefly is trained entirely on legally sourced content, including Adobe Stock and publicly licensed or copyright-free images. By building a dataset that respects intellectual property, Adobe aims to mitigate the ethical concerns artists have expressed about their work being scraped from the web and used without their consent.
Additionally, Adobe has implemented licensing mechanisms within Firefly that empower artists to be part of the AI training process on their own terms. Artists can choose to license their work for use in Firefly’s dataset and are compensated if their work is used to train AI models or generate content. This not only ensures fair treatment but also creates a revenue stream for artists who wish to contribute to the AI revolution without compromising their rights.
Adobe’s Licensing Solutions
In addition to protecting the integrity of artistic work, Adobe has also focused on ensuring fair compensation for creators who contribute to the datasets used by AI models. Through Adobe Stock, artists can license their work to be used in various applications, including AI-generated art. Adobe’s compensation model allows artists to benefit from the growing use of AI in the creative sector, rather than being left behind or exploited.
By enabling proper licensing for stock content used in generative AI models, Adobe offers a sustainable way for artists to participate in the future of AI-powered creativity. This is especially important in an era where digital content is increasingly driven by machine learning algorithms. Adobe’s licensing solutions help bridge the gap between AI innovation and artist protection, ensuring that creators are rewarded for their contributions to these advanced technologies.
Protecting Artists in the Era of NFTs
Another area where Adobe is protecting artists from AI misuse is in the escalating field of non-fungible tokens (NFTs). As digital art becomes increasingly valuable in the NFT marketplace, artists face new risks from AI-driven art theft. Unauthorized copies of their work could be minted as NFTs without their knowledge or consent, undermining the ownership and value of their creations.
To combat this, Adobe has integrated CAI technology with leading NFT platforms like Rarible and KnownOrigin. By embedding CAI metadata into NFT art, Adobe allows artists to prove the originality and ownership of their digital work on the blockchain. This helps artists maintain control over their creations in the fast-moving NFT field, where authenticity is the key.
Furthermore, Adobe’s authentication tools are being expanded to include NFTs generated by AI. By binding AI-generated art to the same CAI standards, Adobe ensures that artists can trace and control how their work is used, even when it becomes part of an AI-generated output.
Adobe’s New Tool for Content Authenticity
Adobe recently unveiled a new web app set to launch in early 2025, designed to help creators protect their work from misuse by AI. This app is part of Adobe’s enhanced Content Credentials system, enabling artists to easily add their information—such as name, website, and social media links—directly to their digital creations, including images, videos, and audio.
A key feature of the app is the option for users to opt out of having their work used to train AI models. This directly addresses the growing concerns among artists about their creations being utilized without permission in generative AI datasets. The app also simplifies the tedious process of submitting requests to various AI providers.
Additionally, the app integrates with Adobe’s well-known platforms like Photoshop and Firefly, while also supporting content created with non-Adobe tools. Users can embed tamper-evident metadata, ensuring their work remains protected, even if it’s altered or screenshot.
The Bottom Line
Adobe’s efforts to shield artists from AI misuse demonstrate a forward-thinking approach to an urgent issue in the creative world. With initiatives like the Content Authenticity Initiative, the ethical training models of Firefly, and licensing solutions such as Adobe Stock along with the new content authenticity web tool, Adobe is laying the groundwork for a future where AI serves as a tool for creators rather than a threat to their creativity. As the distinction between AI-generated and human-made art becomes increasingly unclear, Adobe’s dedication to transparency, fairness, and empowering artists plays a crucial role in keeping creativity firmly in the hands of creators.
#2023#ADD#adobe#Adobe Stock#ai#AI in Creative Industries#AI models#ai training#ai-generated content#AI-powered#Algorithms#American#app#applications#approach#Art#Article#Artificial Intelligence#artists#audio#authentication#Blockchain#bridge#Building#CAI#collaborative#Community#content#Content Authenticity Initiative#copyright
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi I was wondering what your thoughts are about the WGA going on strike? Would like to know what you think the effect that would have on media and what that actually means when writers going strike.
I unequivocally support the strike, anon.
To say that the negotiations between the Writers Guild of America (WGA) and the Alliance of Motion Picture and Television Producers (AMPTP) have broken down would be to imply that they ever got anywhere at all. Pretty much all of WGA’s proposals have been met with rejections and no counter offers, effectively resulting in AMPTP forcing the WGA’s hand. You can read the summary of the negotiations here if you’re interested, but in essence, it boils down to five factors:
Increasing wages and base residuals
Establishing viewership-based residuals and transparency around audience
Preserving the writers room through minimum staffing + more secure contracts as opposed to freelancing
Every staffed writer to get pension and healthcare
Regulating use of AI, ensuring AI can’t write or rewrite literary material, can’t be used as source material, and MBA-covered material can’t be used to train AI.
Pretty much all of these were either outright refused by the AMPTP or seriously lowballed, which not only hugely devalues the writing industry as a whole, but is outright insulting when you see the producers and CEOs of these major corporations taking pay packets of between $40-$230million while writing residuals have dropped so much as to not even cover a writer’s monthly rent for an apartment anymore.
For some context on that, and those five factors I summarized above, I’d highly recommend watching this:
youtube
So, how did we get here?
This is partially answered in the above video, but ultimately the erosion of the writers room and writing residuals comes from streaming. The ways in which corporations make money off TV shows and movies has drastically changed, particularly around international sales (which I talked about a bit here) and re-runs, as international streamers have effectively killed both. What this means is that sales which used to lead to backend payments bolstering network profits, advertising sales and residuals for the creatives are all diluted.
This dilution is then obscured by corporations such as Netflix and Amazon Prime being deliberately vague about viewership, subscribers and more, creating a new industry culture that utilizes lack of transparency to ensure corporations make bank, while the creatives involved in various shows see increasingly less of the backend profits of their work.
This devalues creative talent, particularly writers. It’s company over content, it’s brand over story, and it’s profits over people.
A quick note on auteur TV
This is neither here nor there for the strike in particular (and really feels like a whole other post), but I do think that the focus on auteur-driven TV from streamers has also had a huge impact on dividing and conquering writers, and making certain writers complicit in the system that devalues their artform as a whole.
The streaming wars saw a huge uptick in auteur driven shows, as snapping up creative talent effectively took Hollywood back to the old studio system (which is fascinating in and of itself), but while these writers got big deals (The Duffer Brothers reportedly got a nine-figure deal) it saw budget reduce for writers rooms generally. There’s notorious industry gossip about the Duffers’ making their writers assistant redundant and replacing her with an unpaid intern, for instance, a story that’s becoming increasingly less and less surprising with auteur showrunners. The diminishment of junior roles in the writers room has a huge tap-on effect to the industry at large, limiting career pathways, creative experience, and flattening the writing ecosystem.
While it's about snapping up creative talent, I also do think it's about these corporations having something they can point to to show they're not the only ones making serious money, but showrunners like the Duffers' are red herrings, and often not paying it forwards to the industry they're treated as giants in. Again - whole other post though, haha.
So what happens now?
Kind of a lot of things, actually. Late night’s shutting down, as is SNL, and all shows that were still actively writing will cease production. Yelllowjackets, Abbott Elementary, Big Mouth, Good Omens and more have been stopped, and we’ll likely see pretty much everything else stop too in the coming weeks, especially if crews go on strike in solidarity, which is looking like a real possibility. I also imagine AMPTP will probably want the strike to go for 45 days themselves, because that’s when the force majeure parts of existing deals activate, meaning they can cancel development on shows and movies they’d previously greenlit and effectively scrap their development slates and start over.
The Directors Guild of America and the Screen Actors Guild are about to go into negotiations with AMPTP as well (the WGA deadline was 1 May, DGA and SAG-AFTRAs is 30 June), and given the hardline the AMPTP took with writers, it seems like the directors and actors are poised to strike too, which would have a lot of implications.
Matthew Belloni, a longstanding, very legit entertainment journalist, posited three potential outcomes in his newsletter this week after talking to industry insiders. He said:
If there is a strike, here are three different scenarios for how it could play out, based on conversations I’ve had this week with labor veterans:
1. The July Scenario: If both the DGA and SAG-AFTRA make deals at the end of June, the writers will find themselves on a lonely island and will likely settle. 2. The September Scenario: The fall broadcast schedule is impacted, the movie pipeline begins to suffer, the Emmys are threatened, and the companies feel they have made their cost cuts over the summer and can justify giving a little to make a deal. 3. The December Scenario: Everyone, including the streamers, begins to run out of scripted programs, the substitutes and unscripted fare aren’t generating equivalent viewership, and people start canceling subscriptions. Both sides panic, get together, and make a deal.
Here’s hoping for either the September or December scenario at this point, as they’re what’s going to give the writers leverage in negotiating, but yeah – it does mean we’re in for the long haul.
In the meantime, I think the media landscape is going to be a lot of unscripted shows and probably a lot of foreign imports. We're just going to have to wait and see.
#wga strike#tv asks#kinda#welcome to my ama#i do think it's going to be a long one#especially since the rumours are the streamers have been banking shows for a while in preparation#so they've got a lead#i hope it blows up in their faces
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Generative AI: Unleashing Creativity through Algorithms
Generative AI, a fascinating branch of artificial intelligence, has been making waves across various fields from art and music to literature and design. At its core, generative AI enables computers to autonomously produce content that mimics human creativity, leveraging complex algorithms and vast datasets.
One of the most compelling applications of generative AI is in the realm of art. Using techniques such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), AI systems can generate original artworks that blur the line between human and machine creativity. Artists and researchers alike are exploring how these algorithms can inspire new forms of expression or augment traditional creative processes.
In the realm of music, generative AI algorithms can compose melodies, harmonies, and even entire pieces that resonate with listeners. By analyzing existing compositions and patterns, AI can generate music that adapts to different styles or moods, providing musicians with novel ideas and inspirations.
Literature and storytelling have also been transformed by generative AI. Natural Language Processing (NLP) models can generate coherent and engaging narratives, write poetry, or even draft news articles. While these outputs may still lack the depth of human emotional understanding, they showcase AI's potential to assist writers, editors, and journalists in content creation and ideation.
Beyond the arts, generative AI has practical applications in fields like healthcare, where it can simulate biological processes or generate synthetic data for research purposes. In manufacturing and design, AI-driven generative design can optimize product designs based on specified parameters, leading to more efficient and innovative solutions.
However, the rise of generative AI also raises ethical considerations, such as intellectual property rights, bias in generated content, and the societal impact on creative industries. As these technologies continue to evolve, it's crucial to navigate these challenges responsibly and ensure that AI augments human creativity rather than replacing it.
In conclusion, generative AI represents a groundbreaking frontier in technology, unleashing new possibilities across creative disciplines and beyond. As researchers push the boundaries of what AI can achieve, the future promises exciting developments that could redefine how we create, innovate, and interact with technology in the years to come.
If you want to become a Generative AI Expert in India join the Digital Marketing class from Abhay Ranjan
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
You know it’s bad when the cocreator of The Matrix thinks your artificial intelligence plan stinks. In June, as the Directors Guild of America was about to sign its union contract with Hollywood studios, Lilly Wachowski sent out a series of tweets explaining why she was voting no. The contact’s AI clause, which stipulates that generative AI can’t be considered a “person” or perform duties normally done by DGA members, didn’t go far enough. “We need to change the language to imply that we won’t use AI in any department, on any show we work on,” Wachowski wrote. “I strongly believe the fight we [are] in right now in our industry is a microcosm of a much larger and critical crisis.”
On Thursday, that crisis hit another major milestone when the Screen Actors Guild—American Federation of Television and Radio Artists (SAG-AFTRA)—went on strike. Like the Writers Guild of America, which is also on strike, one of the biggest disputes was over AI. Leading up to the strike, one SAG member told Deadline that actors were beginning to see Black Mirror’s “Joan Is Awful” episode as a “documentary of the future” and another told the outlet that the streamers and studios—which include Warner Bros., Netflix, Disney, Apple, Paramount, and others—“can’t pretend we won’t be used digitally or become the source of new, cheap, AI-created content.”
A few weeks ago, I wrote about the WGA strike and its parallels with the Luddite labor movement. Like the Luddites, writers worry about new forms of automation taking their jobs, but also aren’t anti-tech hard-liners. If AI tools could be used to help writers—to, say, drum up new names for some sci-fi planet—they could serve a purpose without threatening anyone’s livelihood. If writers could be trained to use large language models as tools, that’s one thing. But if they’re used in lieu of writers, or used to write scripts that humans need to fix for lower fees, that’s a problem, the WGA argues. Ultimately, they want a say in how AI gets used in filmmaking.
Actors want that, too. But the way AI could impact their work looks very different. Unlike writers, actors can’t necessarily be trained to use those tools to produce their work—the AI was trained on them. Yes, if generative AI creates, say, a scene in a film, actors will have to be hired to give those performances, but it’s easy to see why they want protections on the use of their likenesses—and are willing to strike to get them.
Hollywood’s glitzy stars taking a stand to keep AI in check feels like a turning point, especially this week when the US Federal Trade Commission also launched an investigation into ChatGPT maker OpenAI. The FTC is looking into OpenAI’s data collection practices and its potential to give consumers bad information, but these things happening at once create a sense that AI is about more than just asking ChatGPT to write poetry or getting Stable Diffusion to draw a fish on a bicycle.
Though AI’s potential to impact human labor has been a topic of conversation for months, in recent days those conversations have begun to bubble over across industries. This week, the WGA East slammed G/O Media over its use of AI, following a Star Wars article that appeared on Gizmodo full of errors. The union called AI-generated articles an “existential threat to journalism” and noted the similarities between journalists and the striking screenwriters. Meanwhile, on Monday, comedian Sarah Silverman became the face of a pair of class-action lawsuits against OpenAI and Meta, accusing the companies of copyright infringement for allegedly training their AIs on her book The Bedwetter. Hulk actor Mark Ruffalo backed her, saying it “will most likely become a landmark case.”
Will any of this stop the rise of the bots? No. It doesn’t even negate that AI could be useful in a lot of fields. But what it does do is demonstrate that people are paying attention—especially now that bold-faced names like Meryl Streep and Jennifer Lawrence are talking about artificial intelligence. On Tuesday, Deadline reported that the Alliance of Motion Picture and Television Producers, which represents the studios, was prepared for the WGA to strike for a long time, with one exec telling the publication “the end game is to allow things to drag on until union members start losing their apartments and losing their houses.” Soon, Hollywood will find out if actors are willing to go that far, too.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 Publishing Trends Authors Can't Afford to Ignore in 2025
Staying ahead of trends is essential to making sure your work reaches the correct audience as the publishing industry changes. Here's a brief straightforward look at the market trends for 2025 and how authors might prosper in this ever-changing environment.

1. The Development of Content Creation with AI
Content creation has been transformed by artificial intelligence techniques. AI is becoming into a useful tool for authors, helping with everything from book idea generation to editing and marketing text. Although some people worry that it might supplant creativity, it's preferable to see it as a tool to increase productivity. Early adoption of this technology allows authors to save time and concentrate on telling stories.
2. The Use of Hybrid Publishing Models
Self-publishing and traditional publishing are becoming increasingly muddled. With hybrid models, authors can benefit from professional services like editing, distribution, and marketing while still maintaining creative control. In 2025, this could be your path if you're searching for adaptable solutions without sacrificing quality.
3. Subscription Websites Broaden Their Audience
The reading market is being dominated by subscription services like Scribd and Kindle Unlimited. This requires authors to adjust to a business paradigm in which page reads, rather than direct sales, determine revenue. You can thrive in this area by writing books that emphasize reader retention. Remember to make your book descriptions and keywords as discoverable as possible.
4. Audio Content Is No Longer Optional
While audiobooks are still on the rise, audio storytelling will become the main focus in 2025. Serialized audio literature, dramatized audiobooks, and podcasts are all growing in popularity. Now is the perfect moment to think about turning your work into an audiobook if you haven't already.

5. The Shift Toward Niche Markets!
Broad appeal is giving way to niche specificity. Whether it's historical romances with a twist, space operas, or cozy mysteries, readers today want stories that speak to their own interests. Instead of attempting to please everyone, find your specialty and concentrate your marketing efforts on developing a devoted fanbase.
For example Fantasy-Romance novels like A Court of Thorns and Roses bring together magic and romance, captivating readers from both genres and contributing to a 15% increase in cross-genre fantasy popularity.
6. Readers Call for Sustainability
Publishing methods are being impacted by environmental consciousness. Digital formats, books with minimum packaging, and books produced on recycled paper are becoming more and more popular among readers. It might be simpler for authors to engage with today's conscientious readership if their publishing methods are in line with sustainable principles.
7. Short-Form Content Takes Over in Marketing
The marketing industry is being dominated by TikTok and Instagram Reels. By connecting with readers through brief films, authors are use these platforms to creatively promote their novels. If social media seems too much to handle, concentrate on just one site and try creating short pieces that highlight your writing style or main ideas. the episodic content is another form of short form content that is in rise. Have a look on attached image to see the details.

8. Improved Interaction With Readers Through Technology
Emerging trends include tailored reader experiences, augmented reality (AR) components, and interactive ebooks. Consider a fantasy book where readers can use an app to access character backstories or maps. These characteristics can enhance reader engagement and give stories a fresh perspective.
9. Stories Are Globalized!
With translations and cross-cultural themes growing more popular, publishing is expanding globally. This trend gives writers the opportunity to connect with readers around the world. Think of collaborating with a publisher who can disseminate your work outside of your native market or translating your book into other languages.
10. A New Attention to Author Branding!
In 2025, developing a brand is more important for authors than simply penning outstanding works. Branding plays a crucial role in an author's success, from interacting with readers online to selling goods or related content. Make the effort to build a polished author website, manage your social media accounts, and establish genuine connections with your readers.
Maintaining Our Lead in 2025
These trends highlight the value of flexibility even as they offer intriguing new opportunities. Always keep your audience at the center of your work, embrace new technologies, and never stop learning. See the complete blog article here for a deeper look at these patterns and practical advice.
Plan your 2025 strategy now; you have all you need to be successful in this dynamic environment.
Blog link: https://proghostwritinghub.com/the-future-of-publishing-trends-and-insights-in-2025/

#writing tips#writer resources#self publishing#aspiring author#aspiring writer#indie author#authors#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#writeblr#creative writing#ao3 writer
1 note
·
View note
Text
Visual Effects Trends to Watch Out for in 2024

2024 is anticipated to be a highly exciting year for visual effects. In 2023 we saw a rapid shift in the VFX industry with the expected boom of Artificial Intelligence. Today, AI and other new tools and technologies make a huge impact, including in the filmmaking processes like the screenplay, visual concept, VFX creation, editing, and sound. Artificial Intelligence will be employed almost everywhere. This will be an exciting change that will make storytelling tools to start becoming more accessible to all, while also fostering a more competitive and healthy environment for content creators across the board. Naturally, this will make it easier for artists to produce visually stunning content and shall provide wider access to technology, whether it is for writing filmmaking
Umpteen candidates. Infinite opportunities
The last year’s trend shift completely changed the horoscope of the visual effects sector. Studies show that the number of candidates enrolling for Animation and VFX courses has recently doubled effectively proving the popularity it gained among the general public. And, the reason being the scope of studying VFX has broadened worldwide never as before. Every VFX artist dream of working in premium studios like Disney, DNEG, Warner Bros etc or individually start their own business. Just like the boom in visual effects industry there is a similar boom happening in the film industry as well. The average amount of movies being released every year easily surpasses the former years. As most of the movies make use of VFX shots for the better theatrical experience, VFX industry effortlessly benefitted from this trend paving way for more opportunities for VFX artists.
Industry Statistics
India's visual effects and animation sector was estimated to be worth 107 billion Indian rupees in 2022, even after the pandemic's negative impact caused a decline in market value the year before. With revenue of over 50 billion Indian rupees, the VFX segment contributed the most to the overall market size. India's growing prosperity fuels the country's appetite for entertainment. Like other nations in the Asia-Pacific area, India's population is getting wealthier and its economy is expanding. The nation's media and entertainment sector has expanded as a result of rising income and improved connectivity.
Visual effects (VFX) and animation are widely growing media categories. A change towards more convenient and customized digital encounters occurred with the spread of the internet and its revolutionary technologies. These changes made more room for India's animation and visual effects industries to expand, and in 2022, the sector grew by almost 29%. In India, the media sector is dominated by animation and visual effects (VFX), which is expected to increase at a robust rate of 35 percent CAGR between 2022 and 2023.
The most recent developments in technology are establishing new avenues for creativity. As tools and techniques advance with time, VFX artists are experimenting and exploring new artistic possibilities. Traditional pipelines are being challenged by these innovative strategies, and 2024 will be a fascinating year for revaluating how the technology will interact with audience. In order to maximize ambition and minimize risk, VFX studios will be more involved and integrated, leveraging their knowledge of emerging technology and methods of operation.
The speed at which technological innovations are occurring is truly astounding. It is anticipated that in 2024, real-time technologies like Unreal Engine will continue to be adopted for virtual production applications and other uses. Although there are certain difficulties in this field, the opportunities and possible gains for studios are quite alluring. The widespread acceptance of these tactics has been greatly aided by the instruments' accessibility, and this envision is sure to be continued into 2024.
How to get into VFX industry?
The fact that you’re reading this blog and you’ve read it this far is itself a sign that you’re already into the step one of this process. Yes, step one is reading and studying intensively about VFX industry; Knowing the latest trends, range of opportunities, field that matches your taste and everything related which you can do research in. No matter whatever field you choose, having a thorough knowledge about what you’re getting yourself into is mandatory. The second step is opting a suitable program suited to your taste and interests. To pursue a career in VFX, select a that is well-reputated and has nice studio set-up. If you’re interested in only one of the genres of visual effects sector, taking a full-time 3 year degree programme won’t be a good idea. Whether you did 3 year degree program or certificate/diploma course, the opportunities will knock at your door if you’ve a top-noch bunch of works/showreels that showcase your talent and hardwork. Basically, it’s not the education certificate that matters but its the quality of your showreels that decides your future.
However, enrolling in a suitable VFX course at a respectable institution is the simplest approach to get into the VFX and animation industries. This will have a profound impact on how you pursue employment in the sector as well as how your future is shaped.
Salary of a VFX Artist in India
You can offer yourself a solid foundation by enrolling in a reputable VFX and animation course in India. As to the April 2020 update, a VFX artist’s average monthly remuneration is INR 37.5k. As you advance to the position of assistant technical director or assistant animator/creative director, you can expect to generate more income accordingly. In India, the average monthly salary for a VFX artist is presently around INR 15-25k. It is possible to take on freelance work in addition to your full-time employment if you have at least four to five years of expertise in the business. You can make up to INR 45k to 60k a month working as a freelancer, depending on your expertise, reputation, and caliber of work. Expert animators and visual effects artists also bill by the hour. Anyhow, let’s patiently sit back and watch what 2024 has in store for the VFX industry.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of SEO Content Writing and Its Impact on Digital Marketing

As you so very well know, the worlds of SEO content writing and digital marketing are undergoing significant transformations. The global SEO industry, valued at $68 billion in 2022, is projected to reach a staggering $129.6 billion by 2030. However, it's not just the financial numbers that are changing. The advent of AI-powered solutions like ChatGPT is blurring the lines between human-created content and machine-generated text in digital marketing. This article delves into the profound implications of these changes, exploring how SEO content writing is reshaping digital marketing strategies.
A Game-Changer in SEO
The future of SEO content writing is taking an unprecedented leap with the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Gone are the days when human writers held a monopoly over content creation. AI tools such as Heliograf, Wordsmith, ChatGPT, and Content at Scale have already made substantial strides in generating content at scale. News organizations like the Washington Post and the Associated Press have harnessed AI to produce thousands of articles, significantly boosting their content volume.
Impact on SEO Strategies
The proliferation of AI-generated content ushers in a more competitive landscape in search engine results pages (SERPs). To stand out, creating valuable, user-focused content becomes paramount. Prioritizing keyword research, meta tags, and content performance optimization remains essential to outperform competitors in this increasingly crowded arena.
E-commerce Evolution
E-commerce giants are embracing AI-powered content to streamline the creation of high-quality product descriptions. AI algorithms analyze data to generate compelling product information, enhancing customers' shopping experiences. Personalized messaging based on individual preferences further boosts engagement and conversions.
News Outlets' Efficiency
News outlets are turning to automated journalism powered by AI to cover breaking news stories efficiently. Tools like Heliograf allow for rapid and accurate reporting, freeing up reporters to focus on in-depth analysis.
Financial Insights
In the financial industry, AI-powered tools like COIN are revolutionizing data-driven analysis. AI-generated reports provide timely and accurate market trend insights, saving time and improving accuracy.
Human Writers vs. AI: Balancing Quality and Connection
While AI-generated content offers efficiency, it falls short in establishing genuine connections with readers. Human writers infuse content with emotion, creativity, and cultural sensitivity that machines lack. AI-generated content sometimes veers into duplication, while human writers provide original perspectives and unique experiences that resonate with audiences.
The Role of Generative AI in Content Writing
The introduction of GPT-4 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4) has sparked discussions about its potential impact on content creation. GPT-4 boasts increased productivity, improved quality, reduced costs, and broader reach. It allows SEO professionals to focus on complex tasks while relying on AI for content generation and distribution.
Responsible Use of AI in Content Creation
Relying solely on AI for content creation has its pitfalls. Inaccuracy, lack of relevance, absence of creativity, and cultural insensitivity are potential drawbacks. Responsible use involves combining AI with human expertise to create high-quality, user-centric content.
Preparing for the Future of Content Creation
To thrive in the evolving content landscape, businesses must:
Build Skilled Teams
Invest in skilled writers who can enhance AI-generated content with a personal touch that resonates with readers emotionally.
Embrace Innovation
Diversify strategies by combining traditional methods with cutting-edge AI technologies, ensuring content remains relevant and engaging.
Prioritize Quality
Maintain a focus on content quality over quantity, implementing quality assurance processes for both human and AI-generated content.
Harness Data-Driven Insights
Utilize AI-generated content to gain valuable insights, identify trends, and optimize existing content for better search engine performance.
Conclusion: The Exciting Future of SEO Content Writing
The future of SEO content writing holds immense promise. As technology advances and search engines prioritize user-focused content, content creators have the tools and opportunities to thrive. Content creation is no longer about keyword stuffing but crafting engaging, informative, and optimized content that resonates with audiences. Multimedia elements, voice search optimization, and AI-driven insights will shape the landscape. By staying informed and embracing innovation, content creators can excel in this ever-evolving digital world.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Are There Chances of Chatgpt Replacing Programmers?

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is creating waves across various industries including the tech industry. The emergence of the various language models that include Chatgpt has left may wondering whether AI will be replacing the programmers. Chatgpt is a natural language chatbot that helps people write emails, college essays, song lyrics etc. Some of the earliest users of chatgpt have even used it to write the python code. The popularity of chatgpt has grown because of its practical applications. The question that however arises here is whether it will be able to replace the developers and the writers just as computers and robots have replaced cashiers and assembly line workers or perhaps the taxi drivers in the future. If you are interested in understanding how you can improve your work with chatgpt, you can pursue a good Search Engine Marketing Course In Gurugram.
Reasons for The Growing Popularity of Chatgpt
Chatgpt has been able to impress several people as it is able to simulate human conversations and also sounds quite knowledgeable. Chatgpt has been developed by OpenAI which is the creator of the most popular text to image AI engine called Dall- E. Chatgpt uses algorithms that helps in analysing and humans fine tune the system’s training to respond to the questions of the user with full sentences that sound similar to that of human beings.
Statistics Related to Chatgpt
A recent paper that was published by OpenAI revealed that as many as 80% of the US workforce have a minimum of 10% of their tasks affected by Chatgpt and other language models. Another research revealed that as many as 20% of the workers will find that 50% of their tasks will get affected by AI. If you want to become a web designer, you can get in touch with the best Search engine marketing institute in Gurgaon. Here you will get to learn about the use of chatgpt in the best way so that you are able to stay ahead in the competition.
The programmers can be relieved for now as it is not among the hundred professions that are going to be impacted by Chatgpt. Some of the professions that will be impacted include:
Why Will It Not Affect The Programmers?
Though Chatgpt is able to generate code and is also able to write programs, however, the process lacks proper understanding, problem solving ability and creativity that human beings have. It operates based on the patterns of the data that he was trained on. Like human programmers, it is not able to understand the code that it writes. It is also not able to understand the requirements of the projects and is not able to make It can’t understand project requirements, make architectural decisions to solve the human problems in a creative manner.
It is true that AI is able to automate repetitive tasks but programming is not just about writing codes. It is much more than that. Programming requires high level decision, personal interaction and strategic planning that AI is not able to do as these are elements that cannot be automated.
Software development is a creative field that requires users' understanding, based on feedback and sometimes abandoning the initial plans and starting all over again. All of these fall outside the realm of the AI capabilities. Pursuing a good online SEM course in Gurgaon will certainly benefit you.
Flaws of Chatgpt
1. Chatgpt has some flaws and limitations and that is why it cannot be a perfect content writing tool. It is also not a very reliable tool for creating codes as it is based on data and not on human intelligence. The sentences might sound coherent but they are not critically informed responses.
2. It is true that in the website of Chatgpt, you will find out ways that will help you debug code using this tool. But the responses are generated from prior code and it is incapable of replicating human based QA. This means that the code that it will generate will have bugs and errors. OpenAI have themselves accepted the fact that the tool at times writes plausible sounding but nonsensical and incorrect answers. So it is important for you to not use it directly in the production of any program.
3. The lack of reliability is creating a lot of problems for the developer community. In a question and answer website called Stack Overflow, where the coders used chatgpt to write and troubleshoot codes have banned its use. The reason for this is that there is such a huge volume of response generated by Chatgpt that it could not keep up with the quality which is done by humans. The average rate of getting correct answers in chatgpt is quite less. So, chatgpt is harmful for the site and for those people who are looking for correct answers from that site.
4. It is important to understand here that Chatgpt, like the other machine learning tools, is trained on data that suits its outcome. It is therefore unable to understand the human context of computing to do the programming properly. It is essential for the software engineers to understand the purpose of the software that they are developing and also the purpose of the people using it. It is not possible to create good software just by cobbling programs together.
Conclusion
So the simple answer to the question as to whether chatgpt will be able to replace the programmers is “No”. Chatgpt and the other AI tools can certainly automate the tasks, however they cannot replace human creativity, understanding and the problem solving capabilities. As of now we should consider AI as an augmenting force. It is a tool that helps programmers and software developers to be much more effective in their respective roles. Though chatgpt does have some flaws, if you want to learn to use it in the most effective way, you can get in touch with the Best SEM Training Institute in Gurgaon.
#digitaldrive360#seo#digital marketing training institute in gurgaon#sem course in gurgaon#digital marketing#online sem course in gurgaon#best sem training institute#digital marketing courses in gurgaon#digital marketing training in gurgaon#sem#digital marketing training institute#digital marketing institute#Digital Marketing Courses#Digital Marketing Course#Digital Marketing Course Gurgaon#Digital Marketing Course in Gurgaon#digital marketing institute Gurgaon#Digital Marketing Institute in Gurgaon#Online Digital Marketing Course gurgaon#Digital Marketing Courses Gurgaon#Online digital marketing course in gurgaon#best digital marketing institute in gurgaon#SEO Training Course Gurgaon#SEO Training in Gurgaon#SEO Training Course in Gurgaon#Search engine optimizaton institute in Gurgaon#SEO institute in Gurgaon#Best SEO Training in Gurgaon#SEO Course in Gurgaon#SEO Training Classes in Gurgaon
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Extrapolation of the potential effects of generative AI based on the effects of the invention of the printing press
Here are some of the major historical events closely related to the invention of the printing press:
Gutenberg Bible (1455): Considered the earliest surviving book printed with movable metal type in Europe. This was Johannes Gutenberg's magnum opus and demonstrated the viability of printing. It helped spread the printing press technology across Europe rapidly.
Spread of Humanism (15th century): The rise of humanism emphasized classical learning and education of the population. This created demand for books which fueled the growth of printing. Works of scholars like Erasmus were widely printed and disseminated.
Protestant Reformation (16th century): Martin Luther effectively used the printing press to mass produce and distribute his 95 Theses and other writings criticizing the Catholic church. This helped spark the Protestant Reformation movement by disseminating ideas to a wider audience.
Decline of scriptoria (15th century): As the printing press became dominant, it replaced handwritten manuscript production in scriptoria attached to monasteries. This was a major cultural shift from manuscript to print culture.
Vernacular literature (15th-16th century): The printing press enabled literature to be published in local languages rather than just Latin, making it accessible to the general populace and helping establish national identities and cultures.
Scientific revolution (16th-17th century): New scientific ideas could be widely shared through printing, accelerating processes of data collection, experimentation and debate. This was instrumental to the scientific revolution.
In summary, the printing press was a key driver of the dissemination of ideas during major social, religious and intellectual changes in the early modern period in Europe. It helped enable the spread of humanism, Reformation, rise of vernacular languages and acceleration of scientific progress.
Here is an extrapolation of the potential effects of generative AI based on the effects of the invention of the printing press:
Democratization of content creation: Generative AI tools may allow more people to easily generate all kinds of creative works like images, videos, writing, music etc. This could mirror how printing expanded authorship.
Accelerated spread of ideas: AI-generated content could propagate new concepts rapidly online, just as printing disseminated humanist texts and revolutionary writings more broadly.
Shift from scarcity to abundance: Generating AI may replace scarce, costly manual production with abundant, cheap automated creation like printing replaced hand-copied manuscripts. This could impact creative industries.
Empowerment of grassroots movements: Citizen-led causes may leverage AI tools to amplify messages through generated visuals/narratives online, paralleling how printing aided reformers like Luther.
Rise of AI-generated literature: Entire books, stories, poems could be algorithmically written, analogous to printed vernacular texts establishing new cultural forms.
Democratization of knowledge: Open-source generative models may make specialized expertise like science/medicine/law more accessible to all through synthesized content.
Accelerated scientific progress: AI models generate hypothesis, analyze data at vast scales, freeing up researchers to confirm/falsify ideas faster through collaborative online science like printing sped up process.
Changes to intellectual property: Widespread AI generation may challenge existing models of ownership over creative works as printing did for copying manuscripts.
Of course, there are also risks such as misuse, bias, and economic disruption to consider with generative AI that echo concerns raised historically over printing technologies.
Overall impacts will depend on how generative tools are developed and governed.
r56CCGBPsF1s1g1lQ5PX
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
TOP SEO TRENDS TO RANK YOUR WEBSITE

In today’s digital age, having a website is essential for any business to establish an online presence. However, creating a website alone is not enough to attract potential customers to your site. Search engine optimization (SEO) is crucial to improve your website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). As search algorithms and user behavior continue to evolve, staying updated with the latest SEO trends is vital to ensure that your website ranks well in search engines. In this article, we will discuss the top SEO trends that you need to know to improve your website’s ranking. By implementing these trends in your SEO strategy, you can enhance your website’s online visibility and drive more organic traffic to your site.
WHAT ARE SEO TRENDS AND WHY DO YOU NEED TO KNOW THEM?
SEO trends refer to the latest techniques and strategies that website owners, digital marketers, and SEO professionals follow to improve their website’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). These trends are constantly evolving as search algorithms and user behavior changes, so it’s crucial to stay updated with the latest trends to ensure that your website remains relevant and visible to potential customers.
By following SEO trends, you can improve your website’s online visibility, attract more organic traffic to your site, and ultimately increase your business’s revenue. For example, if you implement multimedia content promotion, such as adding videos with transcripts to your website, it can significantly increase traffic to your site. This can result in more people discovering your brand and potentially becoming customers.
An example of how following SEO trends can affect website traffic is the Almco project we are currently working on. By adding a video with a transcript as a blog post, the page began to show up in Google Discovery, which significantly increased the website’s traffic.
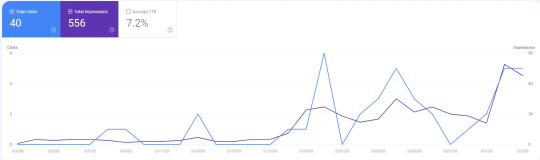
This is an example of how following SEO trends, such as multimedia content promotion, can positively impact a website’s traffic and ultimately the success of the business.
HOW TO KEEP UP WITH SEO TRENDS?
Staying up-to-date with SEO trends is essential to ensure that your website remains visible and competitive in search engine results pages (SERPs). Here are some ways to keep up with SEO trends:
Hire an SEO specialist: an experienced SEO specialist can help you stay up-to-date with the latest trends and techniques in search engine optimization.
Communication among other specialists: network with other SEO professionals and attend industry events to stay informed about the latest trends.
Read industry sources: read blogs and websites such as Search Engine Journal, Moz, and Search Engine Land to keep up with the latest news and trends in SEO.
Subscribe to industry newsletters: subscribe to newsletters from industry experts and publications to receive the latest updates on SEO trends and techniques.
Monitor search algorithm updates: keep an eye on major search algorithm updates, such as Google’s MUM and Penguin updates, to understand how they may impact your website’s ranking.
By staying informed and implementing the latest SEO trends and techniques, you can improve your website’s visibility, attract more organic traffic to your site, and ultimately grow your business.
To learn more about our SEO services, visit the SEO Promotion Services page.
NEW SEO TRENDS IN 2023
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, new SEO trends are emerging in 2023 that businesses should be aware of. In the following paragraphs, we will explore some of these emerging trends and discuss how they are shaping the future of SEO.
AI becomes an important SEO tool
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an increasingly important tool for SEO specialists in recent years, as it offers many benefits for content creation and optimization. ChatGPT is just one example of an AI-powered tool that can write text, generate unique product descriptions, and develop effective link-building strategies, among other things. Other AI tools available for SEO include Bing from Microsoft, Jasper, Anyword, and Rytr.
Companies such as CNN and Ukrainian retailer Epicentr have already started using AI-generated content to improve their productivity and create unique content faster. However, it’s important to note that AI has its limitations and cannot yet fully replace human SEO specialists. While AI can improve productivity and make SEO optimization faster and easier, it still requires human oversight and editing to ensure quality and accuracy. Overall, AI is a valuable tool for SEO specialists, but it should be used in conjunction with human expertise for optimal results.
One example of how AI-generated content can be effective is a case in which we used ChatGPT to create an article for a website. The article was indexed immediately, within one day, and began to bring traffic to the site. What’s particularly interesting about this case is that when we used an OpenAI tool for detecting AI-written articles, it showed that the article was generated by a human, despite the fact that it was actually written by ChatGPT. This demonstrates the high quality and authenticity of the content generated by AI tools like ChatGPT, and how it can seamlessly integrate into a website’s SEO strategy.
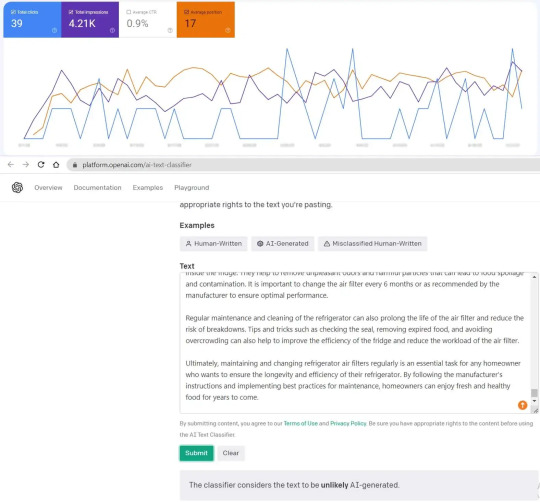
You may be interested: The impact of ChatGPT on marketing, advertising, SMM, and SEO
Showing Experience to comply with new EEAT requirements
In 2022, Google updated its Quality Rater Guidelines to emphasize the importance of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (EAT) in website content. They added an additional “E” to EAT, making it EEAT. This means that now, in addition to expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness, Google also considers first-hand experience to be a crucial aspect of a website’s content. To comply with this new requirement, it’s important for websites to have reviews, author bios, an “about us” page, and a privacy policy page. These elements can help demonstrate a website’s expertise, authoritativeness, trustworthiness, and first-hand experience. This is particularly important for sites in the YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) niche, but it’s important for all websites to take EEAT into consideration, as it can affect their traffic after a core update. To learn more about EEAT and how to demonstrate first-hand experience, check out the Google Search Central Blog and a very informative article from Search Engine Journal.
Importance of multimedia content
Adding multimedia content such as images to a website is crucial for a positive user experience and can also have a positive impact on SEO. It is important to use unique images and optimize them properly, including adding a title when saving the image, adding title and alt text in the admin panel, using images in the proper context, and saving metadata. This is especially important for local businesses to ensure that their images are properly indexed and appear in relevant local searches.
One option for creating unique images is to take your own photos, but there are also AI-powered tools available such as Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL-E. Out of these options, Midjourney we recommend as the best.
By incorporating video content on the website, you can also enhance the user experience and potentially improve SEO. Google has even included a separate tab for pages with video content, indicating its importance. It is recommended to create your own videos, even if they are simple, to make them unique. Tools such as Invideo, Synthesia, Elai, and Steve AI can help create and edit videos. Don’t forget to optimize videos by adding descriptions.
Voice search and the growing importance of low-frequency queries
Voice search is becoming increasingly popular and has changed the way people search for information. This means that SEO strategies should consider how people speak and formulate questions when using voice search, which may differ from how they would type the same query. As an instance, someone may use voice search to ask, “What are the latest SEO trends for 2022?” whereas typing in the words “2022 SEO trends.”
As for low-frequency queries, these are longer and more specific search terms that are not as commonly used but are highly relevant to the user’s search intent. SEO specialists should focus on these types of queries as they can have a higher conversion rate than generic, high-frequency keywords.
To optimize for voice search and long-tailed queries, SEO specialists should focus on creating high-quality content that directly answers the user’s question, using natural language that reflects how people speak in everyday conversations, and including structured data to help search engines better understand the content.
To learn more about our SEO services, visit the Free SEO Audit page.
Increasing the importance of your own research and publishing your own unique content
In today’s digital landscape, it is essential for companies to invest in conducting their own research, surveys, and experiments. Simply writing unique content is no longer enough to stand out from the competition. Rather, companies must provide their own unique information that cannot be found elsewhere on the internet. This means that articles should not only provide comprehensive information, but also offer insights and perspectives that are exclusive to the company. As a result, longer articles that go into greater depth are becoming increasingly valued in the industry.
In the case of Decks Toronto , we added an article with detailed information comparing two popular brands. The article contained a lot of unique criteria, technical information, and tables that were not readily available on the internet. This approach of conducting research and providing unique information in their content helped Decks Toronto stand out from their competitors and establish themselves as a credible source of information in their industry.
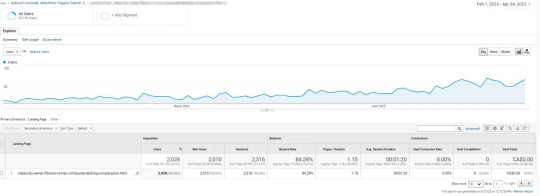
Learn more about SEO strategy for local e-commerce businesses in our article “SEO case study: strategy to overcome seasonality, PPC competition and niche crisis for local ecommerce business”
Optimizing for user’s intent
Optimizing for user intent involves analyzing the target audience and understanding their needs, questions, and problems, rather than simply optimizing for one keyword. This approach ensures that the article provides valuable and relevant information that meets the user’s search intent. By understanding the user’s intent, content creators can optimize their articles by using relevant keywords, structuring the content to answer specific questions, and providing valuable insights that address the user’s needs. This approach not only improves the user experience but also increases the chances of the article ranking higher in search engine results pages.
Semantic SEO optimization: knowledge graphs & entities
Semantic SEO optimization focuses on using contextual information and understanding the relationships between different entities to improve the relevance of search results. This involves optimizing for knowledge graphs and entities, which are the building blocks of information that search engines use to understand the meaning behind queries and content. By structuring your content in a way that aligns with the way search engines interpret and present information, you can improve the visibility and relevance of your website in search results. For example, you can use schema markup to define the relationships between entities and provide additional context for search engines. This can help search engines understand the meaning behind queries and present more relevant results to users. Additionally, you can optimize your content for featured snippets and other rich snippets, which are designed to provide users with quick answers to their queries.
SEO TRENDS THAT ARE KEEPING THEIR IMPORTANCE IN 2023
While there are always new SEO trends emerging, it’s important to remember that the foundational elements of SEO are still critical to success. Further we will explore some of the common SEO trends that have been relevant in the past, are currently relevant, and are expected to continue to be relevant in the future.
Site loading speed and Core Web Vitals
In 2023, site loading speed and Core Web Vitals will continue to be important SEO trends. Core Web Vitals, which consist of three metrics – Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – are used to measure the user experience of a website. Improving these metrics can lead to a better user experience, which can result in better search engine rankings. Additionally, site loading speed plays a crucial role in both user experience and search engine rankings. Slow loading times can lead to increased bounce rates and lower rankings. Tools like PageSpeed Insights can help website owners identify areas for improvement and optimize their site for faster loading times. By prioritizing site speed and Core Web Vitals, website owners can improve their SEO and provide a better user experience for their visitors.
Recently, on the 24th of April, Google announced that they will no longer support some ranking signals, including Page Speed Insights. However, this does not mean that site speed is no longer important for SEO. Google’s intention is to encourage a holistic approach to website optimization and not to focus solely on numbers. Instead of Page Speed Insights, developers can use Google Lighthouse to measure the speed and performance of their sites. Additionally, SEO professionals can continue to use GTmetrix, which provides website speed test results and detailed performance reports.
High-quality content
High-quality content is an essential element of SEO, as it ensures that users find what they are looking for when they land on a website. Google’s “helpful content update” emphasizes the importance of creating content that is genuinely useful to users, answering their queries and providing helpful information. To create high-quality content, it’s important to research your topic thoroughly and use reputable sources. A clear and engaging writing style is also essential, as well as incorporating multimedia elements such as images and videos. Google provides guidelines for creating helpful content, which include prioritizing the user’s needs, ensuring accuracy and expertise, and creating content that is easy to understand and access. By creating high-quality content, websites can improve their rankings in search results and attract more traffic.
Linkbuilding
Link building is an important part of any SEO strategy and involves acquiring links from other websites to your own site. One effective way to start link building is by analyzing your competitors’ pages and identifying the websites that are linking to them. You can use tools like Ahrefs to check your domain rating and the number of referring domains pointing to your site.
In a case where we invested in low-budget link building, the results might not be immediately noticeable. However, after a few months, we started seeing an increase in traffic. This is because links from high-quality, relevant websites can help improve your website’s authority and search engine rankings.
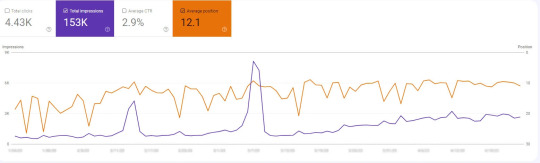
It’s important to note that link building should be done carefully and with a focus on quality over quantity. Low-quality or spammy links can actually harm your website’s rankings and reputation. Instead, aim to build relationships with other website owners in your industry and create valuable content that others will want to link to naturally.
Mobile friendliness
Mobile friendliness is a critical aspect of website optimization, as more and more users access the internet from their mobile devices. To ensure that your website is mobile-friendly, you can use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool, which analyzes your website’s pages and reports if they are designed to be viewed on mobile devices. The tool evaluates factors such as the text size, page loading speed, and responsiveness of your website on different mobile devices. By making your website mobile-friendly, you can improve the user experience for your mobile audience, boost your search engine rankings, and drive more traffic to your site.
On the 24th of April, Google announced that it will retire its Mobile-Friendly test tool. This tool has been used by many SEO professionals to check if their website is mobile-friendly. However, this announcement does not mean that responsible design is not important. Developers from Google want SEO to focus on a more holistic approach rather than just numbers. They recommend using other tools, such as the Mobile Usability report in Search Console, to ensure your website is mobile-friendly. This change is in line with Google’s focus on improving user experience on the web.
Targeting the audience and its needs, not bots
In the world of SEO, it’s important to remember that we write for people, not just for search engine bots. In the past, there was a tendency to focus too much on keyword density and stuffing pages with exact-match keywords in order to rank higher. However, with Google’s implementation of the BERT algorithm, the focus has shifted to understanding the context of the content and providing value to the reader. This means that you can focus on creating high-quality content that addresses the needs of your target audience, rather than worrying about exact keyword matches. By crafting content that is relevant, engaging, and informative to your audience, you’ll be able to build trust and credibility, ultimately leading to higher rankings and better engagement.

IM4U DIGITAL MARKETING AGENCY WILL HELP YOU TO STAY UP-DO-DATE ON SEO TRENDS
Don’t let your website fall behind in search engine rankings. Trust IM4U Digital Marketing Agency to keep you up-to-date with the latest SEO trends and strategies. Book our SEO website audit now and watch your website climb to the top of the search results. Contact us to learn more!
#seo#search engine optimization#website ranking#search algorithms#video content#voice search#long-tail keywords#high-quality content#website loading speed#core web vitals
5 notes
·
View notes
Note
Don’t you feel that if you go on the “loves ao3 more than their own mom” website aka the “can't throw a rock without hitting a writer” website and put in the main tag the opinion that AI writing models are no big deal and don’t do any harm and nobody has any reason to feel hurt over their unethical training in a tone that distinctly resembles the “toughen up snowflake” rhetoric, you might, in fact, just be the one out of line and also an asshole?
*rolls eyes* not what i did nor what i said.
there are many concerns to have with generative AI, such as the ability to extract privatized information from their training datasets, the exploitation of human workers for AI services (tho this one frankly goes for all internet services, not just AI), AI's reinforced biases and lack of learning, and the current lack of regulation against AI developers and AI usage to name a few. in terms of a direct impact on the creative industry, there are several concerns about the uncompensated and unregulated use of copyrighted materials in training data (paper discussing BookCorpus, courtlistener link for writers suing over Books2), the even worse image scraping for diffusion models, screen production companies trying to pressure people into selling their personal image rights for AI use, and publishers getting slammed with various AI generated content while the copyright laws for it are still massively in flux.
i said fanfic does not intersect with AI. actually, i vaguely whined about it in the tags of an untagged post, because i'm allowed to do that on my personal whine-into-the-void space. (which, tumblr is bad about filtering properly in tags and i'm sorry if it popped up anyways, but i also can't control tumblr search not functioning properly.)
there are concerns to be had about AI training datasets (developers refusing to remove or protect private information because it weakens the training data even tho this is a bigger issue for bigger models is my primary concern personally, but the book shadow libraries and mass image scraping are shady ass shit too). but AO3 was never used to train AI. there is a lot of sketchiness involved with AI training data, but AO3 is not one of them.
i get irked when people compare AI generated writing to AI generated art, because the technology behind it is different. to make art, AI has to directly use the source image to create the final output. this is why people can reverse the process on AI art models to extract the source images. written models (LLMs) learn how to string words into sentences and in terms of remembering the specific training data, LLMs actually have a known issue of wandering attention for general written training material like books/articles/etc. (re the writers' lawsuit -- we know AI developers are pulling shady shit with their use of books, AI developers know they're pulling shady shit with their use of books, but unfortunately the specific proof the writers' are using for their case very closely resembles the summaries and written reviews on their books' wikipedia pages. the burden of proof for copyright violation is really hard to prove for books, esp because copyright protects the expression of an idea, not the idea or individual sentences of a work, and LLMs do not retain their written training material in that way.) these are different issues that can't truly be conflated because the methods in which the materials are used and the potential regulation/the impact of potential regulation on them are different.
anyways, back to my annoyances with fanfic x AI -- fanfic is not involved in its development, and if you don't want to read fic made by AI, don't click on fic that involves AI. ultimately, if you read a fic and it turns out AI was involved...nothing happens. if you don't like it, you click a back button, delete a bookmark, and/or mute a user. AI just strings words together. that's it. acting like AI will have a great impact on fandom, or that fandom will be some final bastion against it, is really fucking annoying to me because fandom does not have any stakes in this. there are legitimate issues in regards to developing and regulating AI (link to the US senate hearing again, because there are so many), but "oh no, what if i read a fic written by AI" is a rather tone fucking deaf complaint, don't you think?
#which is also why i whined in the tags of /an untagged post/#honestly my bigger issue is people trying to give fandom stakes in this#fandom can be culturally important and not at all impacted by this specific issue
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
7 Applications of AI Video in the Entertainment Industry - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/7-applications-of-ai-video-in-the-entertainment-industry-technology-org/
7 Applications of AI Video in the Entertainment Industry - Technology Org
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various industries, and the entertainment sector is no exception. In recent years, AI has found numerous applications in video production, enhancing creativity, efficiency, and audience engagement. From video editing to content recommendation, AI-driven technologies are transforming the way we create, distribute, and consume entertainment content. In this article, we will explore seven exciting applications of generative AI video in the entertainment industry.
Video editing. Image credit: DaleshTV via Wikimedia, CC-BY-SA-4.0
Video Editing and Post-Production
One of the most prominent applications of AI in the entertainment industry is in video editing and post-production. AI-powered editing tools can analyze video footage to automatically select the best shots, correct color and lighting, and even add special effects. For instance, Adobe’s Premiere Pro offers AI-powered features like Auto Reframe, which automatically adjusts the aspect ratio of videos for different platforms, saving creators valuable time.
Deepfake Technology
Deepfake technology, which uses AI algorithms to superimpose one person’s face onto another’s body, has garnered significant attention in the entertainment industry. While controversial, deepfakes have been used in movies and TV shows to recreate the likeness of actors who are no longer available or to de-age actors. This technology allows filmmakers to create realistic digital people and characters, opening up new creative possibilities.
Personalized Content Recommendation
AI-driven recommendation algorithms have become a staple in the entertainment industry, helping platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube suggest content tailored to individual preferences. These algorithms analyze users’ viewing habits, likes, and dislikes to recommend movies, TV shows, and music that align with their tastes. This personalized content recommendation not only enhances user experience but also keeps viewers engaged for longer periods, increasing platform revenue.
Virtual Production
AI video is also revolutionizing virtual production techniques. Filmmakers can now use AI-driven tools to create realistic virtual sets and environments. This technology allows for more cost-effective and efficient filmmaking, as it eliminates the need for physical sets and on-location shoots. Additionally, it enables real-time visualization of scenes, empowering directors and actors to make instant creative decisions.
Video Restoration and Enhancement
AI algorithms are invaluable in restoring and enhancing old or damaged video footage. Whether it’s restoring classic films or enhancing historical footage, AI-driven tools can significantly improve the quality of visuals and audio. This not only preserves valuable cultural artifacts but also offers a new way to experience old content with modern clarity and vibrancy.
Content Creation and Generation
AI-generated content is gaining traction in the entertainment industry. AI systems can analyze trends, generate scripts, and even compose music. OpenAI’s GPT-3, for example, has been used to write articles, stories, and dialogues for video games. While AI-generated content is not replacing human creativity, it can be a valuable tool for generating ideas and streamlining content creation processes.
Audience Engagement and Interaction
AI is enhancing audience engagement in various entertainment forms, including interactive videos, virtual reality experiences, and augmented reality games. Interactive storytelling powered by AI allows viewers to make choices that impact the narrative, creating personalized experiences. Virtual reality and augmented reality experiences are also made more immersive and interactive with AI, providing audiences with captivating and engaging entertainment options.
AI video technology is reshaping the entertainment industry in remarkable ways. From video editing and deepfake technology to personalized content recommendation and virtual production, AI is enhancing creativity and efficiency throughout the production process. Additionally, AI is contributing to the preservation and enhancement of historical content and generating new forms of creative expression. As AI continues to evolve, we can expect even more exciting applications in the entertainment industry, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the world of video and media. It’s an exciting time for both creators and audiences as AI-driven innovations continue to transform the entertainment landscape.
#A.I. & Neural Networks news#adobe#ai#AI-powered#Algorithms#applications#Article#Articles#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#audio#augmented reality#Color#content creation#creativity#creators#deepfake#deepfakes#Editing#effects#efficiency#entertainment#Features#Forms#games#generative#generative ai#GPT#GPT-3#human
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How To Forecast and Calculate the ROI of SEO (With Template)
March 22, 2023
By: Dan Ansaldo, SEO Specialist
With the continued rise of AI and ChatGPT, constant algorithm updates, and the never-ending goal of beating the competition, understanding the ROI (return on investment) of SEO has arguably never been more important.
How do you know if your SEO is effective? How can you determine if it’s going to create positive ROI? Is it even possible to forecast like other marketing channels?
These are critical questions to ask and answer. Let’s dive in!
What is the ROI of SEO?
Return on Investment (ROI) is the monetary gain you receive from investing in Search Engine Optimization (SEO). The goal of SEO — and all marketing efforts for that matter — is to earn you (or your client) more money than what you spend.
When you receive more website traffic, conversions, and ultimately leads and sales from your SEO efforts, that’s the positive return coming into effect.
While SEO is very effective, and arguably the most effective digital marketing channel long term, it’s complicated to understand — especially when calculating SEO ROI or forecasting potential ROI.
So can it be done? Yes, but it can be a bit cumbersome at times.
Why It’s Important To Determine the ROI of SEO
Like any other business investment, it's crucial to determine the impact of your SEO campaigns. Understanding the effect is key to making the most of your SEO efforts. If left in the wrong hands, SEO can become nothing more than an expensive housekeeping service for your website.
But when in the right hands, a thorough SEO strategy can be a powerful tool that sets you (or your client) up as an authority in the industry and attracts invaluable, converting website traffic. Being cognizant of the cost and conversions stemming from SEO helps you better understand the impact SEO is having.
How To Calculate The ROI Of SEO
Calculating the ROI of SEO for Ecommerce sites is different from lead generation sites. No matter what kind of business you operate, this process starts with conversion tracking and a solid look at your Google Analytics account, so have that handy before moving on.
Identify Your SEO Expenditures
First, you need to identify your SEO expenditures. If you hired a freelancer or an agency to do your SEO for you, this is simple. Your SEO cost is the price you pay the freelancer/agency each month.
If you’re doing SEO in-house, you need to take all of the following into consideration:
Software/tools: Whether it be cloud-based or downloaded on your computer, every successful SEO needs their tools. Moz, Semrush, Surfer, Screaming Frog, ContentKing…the list goes on and on.
Content Production: If you have a copywriter in-house, calculate the time (and cost) it takes them to write each article. If you outsource, how much do you pay for your content?
Editing and Plagiarism: Do you use Grammarly or Hemmingway to edit your articles? How about running through CopyScape to check for plagiarism? These may be small costs, but they all add up.
Graphics: If you use graphic or image software like Canva, Adobe, or iStock, you’ll want to account for these.
Misc: There are other SEO-related costs that can come up (speed optimizations, citation building, etc.), so make sure you track them all to make your ROI calculations as accurate as possible.
Set Up Conversions for Ecommerce Sites
The first thing you need to do for your Ecommerce site is set up conversions in Google Analytics. This allows you to capture the conversions occurring on your site. Once Ecommerce tracking is set up, you can see the overview of your sales data by going to the Conversions tab on the left navigation panel, then Ecommerce, then Overview if you still have Universal Analytics.
This is what that looks like:

Remember, Google is putting Universal Analytics to rest for good, so switch to GA4 as soon as possible if you have not done so.
If you are using GA4, then you would go to Reports, then Monetization, and finally Ecommerce purchases. Below is an example of Google’s online store. The chart and data will automatically sort by items viewed, largest to smallest, but you can select items purchased to see the items that have been purchased the most for the time frame.

Now, in GA4, click on the plus sign at the top next to “Item name” to add a filter, and filter to include Session source/medium. Then click google/organic (click apply) to see conversions coming from organic search or at least partially attributed to organic search.

Set Up Conversions for Lead Generation Sites
If you don’t sell items directly on your site, it can be a bit more challenging to know how much money comes from your site. The first step you need to do is create events in your Google Analytics account and then mark them as conversions. You also need to assign a value to each conversion. Here’s how you do that:
Identify your top conversion events (form submission, “call us today” button, “get a free quote” button, etc.)
Count how many of those conversion events/leads become paying customers
Calculate the average amount of money your customers spend
Divide the total revenue by the total number of conversions to get a value per conversion.
For example, let's say 100 people clicked on your “call us today” button in a given month. If you have that selected as a converting event, you get 100 conversions.
Of those 100 people that clicked, 10 became customers and spent $6000 collectively. That means on average, each “call us today” conversion was worth $60 ($6000 total revenue/ 100 conversions).
Now you can mark the “call us today” button with a $60 value. Repeat this process for the other conversions. When you’re done, you’ll have a nice list of conversions set.

If you don’t know how many conversions you get from each event (and thus can’t calculate the value of each conversion type), you’ll have to gather data for a couple months.
From this point on, you’ll be able to see how many conversions were attributed to organic search by going to the Advertising tab.
Calculate Your ROI!
Once you have all of the above information at your fingertips, it’s time to calculate! This is by far the easiest step. Here’s how you calculate your ROI:
SEO ROI = (Revenue From Organic Conversions - Cost of SEO Investment) / Cost of SEO Investment
Time for another hypothetical. Let’s say your revenue from organic conversions in one quarter was $80K and you spent $15K on SEO services. This would be your calculation:
($80K - $15K) / $15K = 4.33
Multiple 4.33 by 100 to get your percent, and your ROI from your SEO for that quarter was 433%. Not bad at all!
How To Forecast Potential ROI from SEO
Perhaps you are not investing in SEO at the moment (you probably should though) and you’re curious about what the potential ROI could be. Or, you need to calculate it for a potential client, here’s how you would go about forecasting potential ROI.
Disclaimer: This is a forecast, not a guarantee. Since there are many moving parts to the equation, the final ROI can be different from what you calculate.
Identify the Keyword Search Volume
The first step is to go to your favorite SEO tool (like Semrush) and look at the search volume for your target keyword. If you wanted to rank for “San Francisco SEO Company,” you’d plug that into Semrush and see that it is searched about 210 times per month.
Now, multiply that number by 0.276 because that’s the average click-through rate (CTR) of the number one organic ranking position in Google. That gives us 58 (rounding up).
That means if you rank #1 for that keyword on Google, you can assume you’ll get about 58 people coming to your website from that term each month.
Multiply 58 by your average conversion rate for all of your conversion events. Remember those from earlier? To get your average conversion rate, divide the number of paying customers by the number of leads/converting events.
Using the lead generation example from earlier, if 100 people total clicked on a converting event (form submission, “call us today” button, “get a free quote" button, etc.) in one month and 7 of those became paying customers, your conversation rate is 7% (7/100 = 0.07 x 100 = 7%).
If we multiply 58 (the number of monthly assumed visitors from the keyword “San Francisco SEO Company,”) by .07 or 7% (your average website conversion rate) you get 4.06. This is the average number of MONTHLY purchasers you can expect to gain from ranking #1 on Google.
Finally, multiply 4 (round down to the whole number) by your average order value (AOV) to get the potential income from that keyword on a monthly basis. For instance, if your average customer spends $5K monthly (not too bad for an SEO company) then your potential monthly revenue if you rank #1 for “San Francisco SEO Company” is about $20K (4 x $5K).
Annually that would be over $243,000 from a single keyword. Now do you see why SEO is so valuable?
Here is the ROI forecasting spreadsheet you can use to calculate the potential SEO ROI
Need Help With SEO?
If you need help with your SEO — as a business owner or an agency — shoot us a message. Whether you’re an Ecommerce business or a lead generation business, we can help you (or your client) gain visibility in the SERPs and take advantage of the compounding power of SEO.
READ OUR LAST ARTICLE: 5 Tips For Your Next Influencer Campaign
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

The AI Revolution: 15 Jobs at Risk as ChatGPT Makes Waves in the Business World
Just a few months after its launch, ChatGPT is already leaving an indelible mark on the business landscape. This powerful AI has demonstrated its capabilities in diverse applications, from writing cover letters to creating children's books and assisting students in their academic pursuits. Although ChatGPT has some limitations, its potential impact on the job market cannot be understated.
As AI technology advances, a plethora of jobs could face the risk of being replaced. Here, we've compiled a list of 15 jobs that experts believe could be threatened by ChatGPT and similar AI technologies:
Tech jobs (Coders, computer programmers, software engineers, data analysts)
Media jobs (Advertising, content creation, technical writing, journalism)
Legal industry jobs (Paralegals, legal assistants)
Market research analysts
Teachers
Finance jobs (Financial analysts, personal financial advisors)
Traders
Graphic designers
Accountants
Customer service agents
Data Analysts
Transportation Workers
Manufacturing Workers
Healthcare Professionals
While AI advancements like ChatGPT could lead to significant disruptions in the job market, it is crucial to consider these technologies as productivity-enhancing tools rather than complete replacements for human workers. Ultimately, human judgment is still necessary to prevent errors and biases in AI-generated work. The future will likely see a blend of human expertise and AI technology working in tandem to achieve greater productivity and efficiency.
About Mark Matos
Mark Matos Blog
#AIRevolution#ChatGPT#FutureOfWork#ArtificialIntelligence#JobDisruption#TechTrends#CareerAdvice#Automation#DigitalTransformation
1 note
·
View note