Text
Dealing With Executive Dysfunction - A Masterpost
The “getting it done in an unconventional way” method.
The “it’s not cheating to do it the easy way” method.
The “fuck what you’re supposed to do” method.
The “get stuff done while you wait” method.
The “you don’t have to do everything at once” method.
The “it doesn’t have to be permanent to be helpful” method.
The “break the task into smaller steps” method.
The “treat yourself like a pet” method.
The “it doesn’t have to be all or nothing” method.
The “put on a persona” method.
The “act like you’re filming a tutorial” method.
The “you don’t have to do it perfectly” method.
The “wait for a trigger” method.
The “do it for your future self” method.
The “might as well” method.
The “when self discipline doesn’t cut it” method.
The “taking care of yourself to take care of your pet” method.
The “make it easy” method.
The “junebugging” method.
The “just show up” method.
The “accept when you need help” method.
The “make it into a game” method.
The “everything worth doing is worth doing poorly” method.
The “trick yourself” method.
The “break it into even smaller steps” method.
The “let go of should” method.
The “your body is an animal you have to take care of” method.
The “fork theory” method.
The “effectivity over aesthetics” method.
191K notes
·
View notes
Text


I will succeed. Not instantly. But definitely.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


Uranus (left) and Neptune (right) on January 18, 2025 // wittinobi
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
hello!! i am an a level student living in the uk :D
i take maths, fm, cs, and chemistry and im hoping to study cs at uni!!
as well as doing all the fun tumblr study stuff on here i will also post longer articles that i wrote myself on different topics that interest me so keep an eye out for those <333
0 notes
Text
im great with deadlines and rubbish with the stress that comes with it
1 note
·
View note
Text
GIVE ME REAL MESSY AND CHAOTIC ACADEMIA!!!! NONE OF THIS GORGEOUS NEAT AND BEAUTIFUL NONESENSE GIVE ME BOOKS AND FOLDERS ON THE FLOOR AND STATIONARY SCATTERED ACROSS DESKS. please
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
i wanna study.... i wanna study.. (im not studying)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Moon waves goodbye to Hera
As ESA's Hera mission for planetary defense departed its homeworld, it looked back to Earth to show the moon orbiting around it. In this sequence of images the terrestrial disk gradually shrinks as the spacecraft recedes away from it, and the moon moving around Earth changes from a half to full moon.
The images were acquired during the initial checkout of Hera's Thermal Infrared Imager (TIRI) instrument, provided to the mission by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, JAXA.
These Earth and moon thermal images were acquired by TIRI as it looked down obliquely from the north relative to lunar orbit. The distance between Earth to Hera spacecraft was about 1.4 million km for the first image acquired on 10 October to about 3.8 million km for the last image acquired on 15 October.
Launched on 7 October, Hera is ESA's first planetary defense mission, on its way to visit the first asteroid to have had its orbit altered by human action. By gathering close-up data about the Dimorphos asteroid, which was impacted by NASA's DART spacecraft in 2022, Hera will help turn asteroid deflection into a well understood and potentially repeatable technique.
One of a suite of instruments hosted on Hera's Asteroid Deck, TIRI will image Dimorphos in the mid-infrared spectral region to chart the temperature on the asteroid's surface. By charting the "thermal inertia" of surface regions—or how rapidly their temperature changes—physical properties such as roughness, particle size distribution and porosity can be deduced.
TIRI was manufactured for JAXA by Meisei Electric Co. Ltd. Its design is derived from a previous instrument onboard the agency's Hayabusa2 asteroid mission.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
it is absolutely mental to me how difficult the first searches for pi were
this might be my lack of mathematical knowledge showing but honestly pi is just some funky thing that exists and is useful to me most of the time
but the very first mathematicians had to sit there and work all this out!!! insane
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Skeleton Panda Sea Tunicate Appreciation Post!!! 💀 🐼 🌊
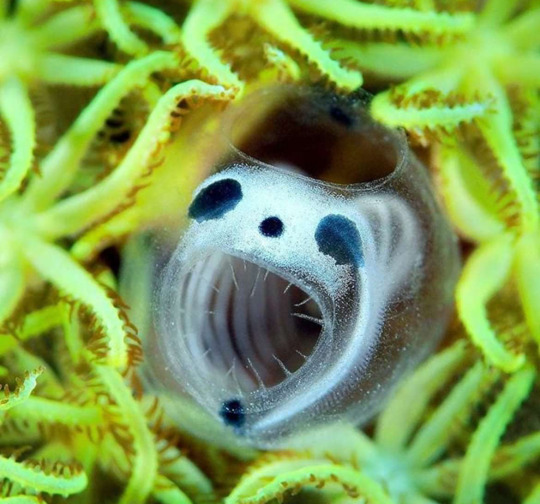
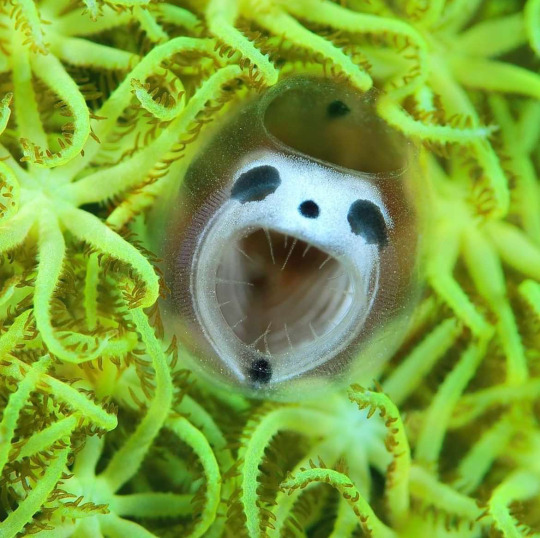







Clavelina ossipandae, the skeleton panda sea tunicate is a species of colonial ascidian, also known as sea tunicates, a group of sessile, marine filter-feeding invertebrates. Just some funky little guys!
First discovered near Kume Island in Japan by local divers, pictures of the animal attracted media attention in 2017. But they weren't given their formal taxonomic description until 2024
Love to sea it 🌊
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
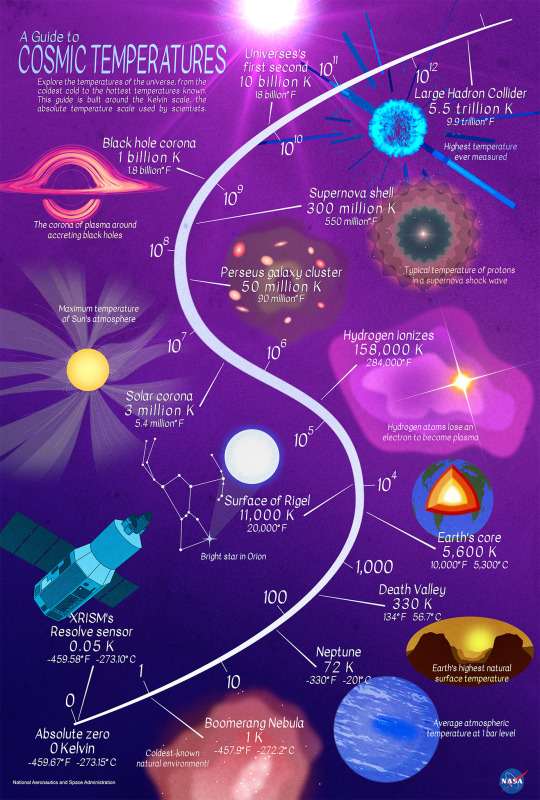
A Tour of Cosmic Temperatures
We often think of space as “cold,” but its temperature can vary enormously depending on where you visit. If the difference between summer and winter on Earth feels extreme, imagine the range of temperatures between the coldest and hottest places in the universe — it’s trillions of degrees! So let’s take a tour of cosmic temperatures … from the coldest spots to the hottest temperatures yet achieved.
First, a little vocabulary: Astronomers use the Kelvin temperature scale, which is represented by the symbol K. Going up by 1 K is the same as going up 1°C, but the scale begins at 0 K, or -273°C, which is also called absolute zero. This is the temperature where the atoms in stuff stop moving. We’ll measure our temperatures in this tour in kelvins, but also convert them to make them more familiar!
We’ll start on the chilly end of the scale with our CAL (Cold Atom Lab) on the International Space Station, which can chill atoms to within one ten billionth of a degree above 0 K, just a fraction above absolute zero.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Just slightly warmer is the Resolve sensor inside XRISM, pronounced “crism,” short for the X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission. This is an international collaboration led by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) with NASA and ESA (European Space Agency). Resolve operates at one twentieth of a degree above 0 K. Why? To measure the heat from individual X-rays striking its 36 pixels!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Resolve and CAL are both colder than the Boomerang Nebula, the coldest known region in the cosmos at just 1 K! This cloud of dust and gas left over from a Sun-like star is about 5,000 light-years from Earth. Scientists are studying why it’s colder than the natural background temperature of deep space.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Let’s talk about some temperatures closer to home. Icy gas giant Neptune is the coldest major planet. It has an average temperature of 72 K at the height in its atmosphere where the pressure is equivalent to sea level on Earth. Explore how that compares to other objects in our solar system!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
How about Earth? According to NOAA, Death Valley set the world’s surface air temperature record on July 10, 1913. This record of 330 K has yet to be broken — but recent heat waves have come close. (If you’re curious about the coldest temperature measured on Earth, that’d be 183.95 K (-128.6°F or -89.2°C) at Vostok Station, Antarctica, on July 21, 1983.)
We monitor Earth's global average temperature to understand how our planet is changing due to human activities. Last year, 2023, was the warmest year on our record, which stretches back to 1880.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
The inside of our planet is even hotter. Earth’s inner core is a solid sphere made of iron and nickel that’s about 759 miles (1,221 kilometers) in radius. It reaches temperatures up to 5,600 K.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We might assume stars would be much hotter than our planet, but the surface of Rigel is only about twice the temperature of Earth’s core at 11,000 K. Rigel is a young, blue star in the constellation Orion, and one of the brightest stars in our night sky.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We study temperatures on large and small scales. The electrons in hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, can be stripped away from their atoms in a process called ionization at a temperature around 158,000 K. When these electrons join back up with ionized atoms, light is produced. Ionization is what makes some clouds of gas and dust, like the Orion Nebula, glow.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We already talked about the temperature on a star’s surface, but the material surrounding a star gets much, much hotter! Our Sun’s surface is about 5,800 K (10,000°F or 5,500°C), but the outermost layer of the solar atmosphere, called the corona, can reach millions of kelvins.
Our Parker Solar Probe became the first spacecraft to fly through the corona in 2021, helping us answer questions like why it is so much hotter than the Sun's surface. This is one of the mysteries of the Sun that solar scientists have been trying to figure out for years.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Looking for a hotter spot? Located about 240 million light-years away, the Perseus galaxy cluster contains thousands of galaxies. It’s surrounded by a vast cloud of gas heated up to tens of millions of kelvins that glows in X-ray light. Our telescopes found a giant wave rolling through this cluster’s hot gas, likely due to a smaller cluster grazing it billions of years ago.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Now things are really starting to heat up! When massive stars — ones with eight times the mass of our Sun or more — run out of fuel, they put on a show. On their way to becoming black holes or neutron stars, these stars will shed their outer layers in a supernova explosion. These layers can reach temperatures of 300 million K!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Jeremy Schnittman
We couldn’t explore cosmic temperatures without talking about black holes. When stuff gets too close to a black hole, it can become part of a hot, orbiting debris disk with a conical corona swirling above it. As the material churns, it heats up and emits light, making it glow. This hot environment, which can reach temperatures of a billion kelvins, helps us find and study black holes even though they don’t emit light themselves.
JAXA’s XRISM telescope, which we mentioned at the start of our tour, uses its supercool Resolve detector to explore the scorching conditions around these intriguing, extreme objects.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/CI Lab
Our universe’s origins are even hotter. Just one second after the big bang, our tiny, baby universe consisted of an extremely hot — around 10 billion K — “soup” of light and particles. It had to cool for a few minutes before the first elements could form. The oldest light we can see, the cosmic microwave background, is from about 380,000 years after the big bang, and shows us the heat left over from these earlier moments.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We’ve ventured far in distance and time … but the final spot on our temperature adventure is back on Earth! Scientists use the Large Hadron Collider at CERN to smash teensy particles together at superspeeds to simulate the conditions of the early universe. In 2012, they generated a plasma that was over 5 trillion K, setting a world record for the highest human-made temperature.
Want this tour as a poster? You can download it here in a vertical or horizontal version!
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Explore the wonderful and weird cosmos with NASA Universe on X, Facebook, and Instagram. And make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
ive had horrendous hiccups all day today and i had a quick search online about them
and so today i learnt (according to the nhs) that gps can prescribe you chlorpromazine to treat ur hiccups??? the medication commonly used for schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders???
that's quite cool i think
#there's a disclaimer that states that this doesn't work for everyone obviously#hiccups are an enigma to us all#sciblr#science side of tumblr#stem#medicine
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
PLUTO NEWS!!!! FROM TODAY!!!!
well technically it's about Charon which is Pluto's biggest moon which is half its size.... so it counts
carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide have been detected on detected for the first time traces of carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on Charon's surface!!! hell yeah james webb telescope
for reference, water ice, ammonia, and organic materials were detected on the moon beforehand and scientists couldn't get much further than that

look at this fella
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
being smart and knowledgeable would be cool i think (let me know if i accidentally post absolute gibberish)
1 note
·
View note


