She, UK. I like tragic historical figures and morally ambiguous characters. And memes.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
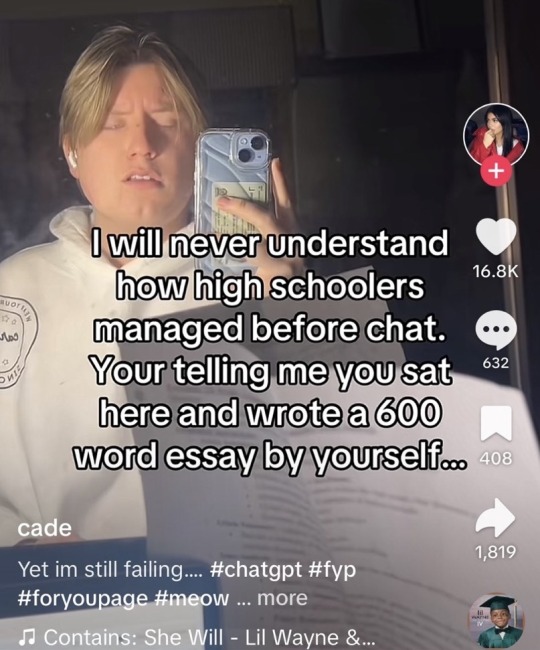
i'm entering the next phase of my life: tuesday afternoon
46K notes
·
View notes
Text
critically consume my problematic dick and balls
19K notes
·
View notes
Photo
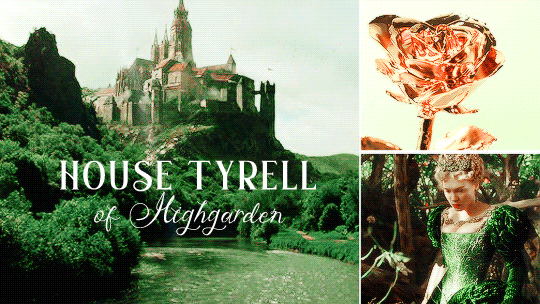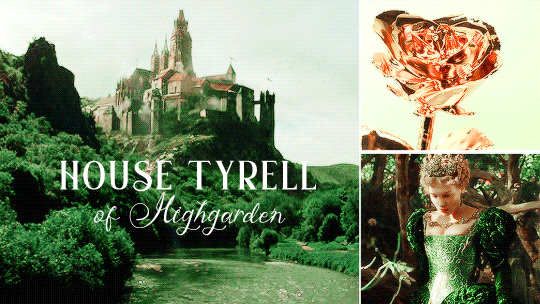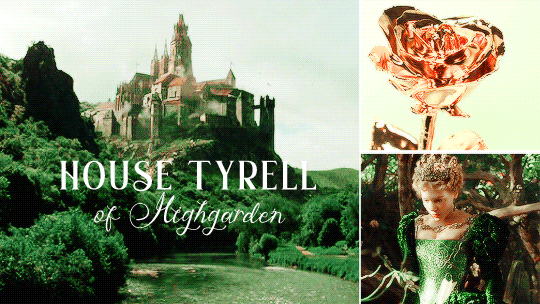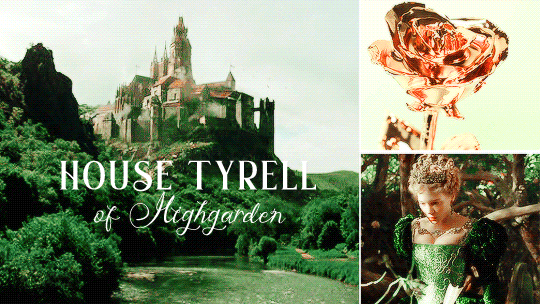
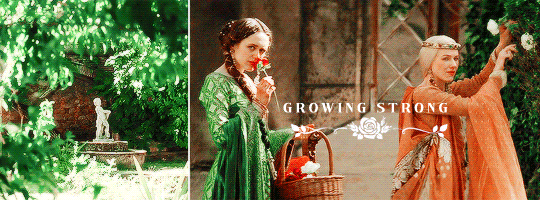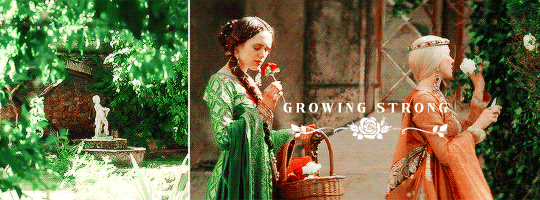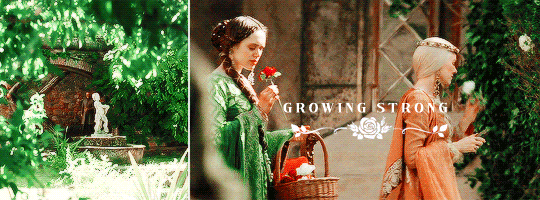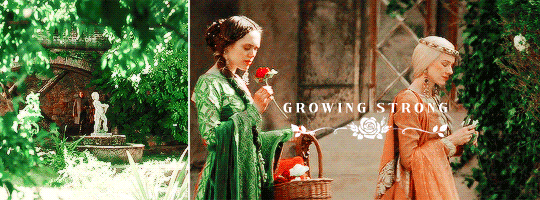
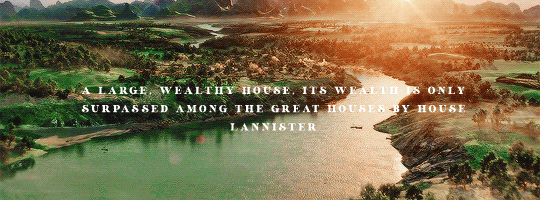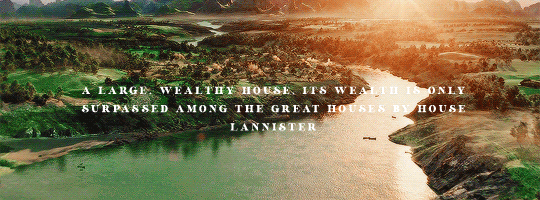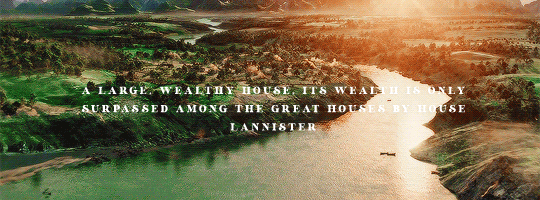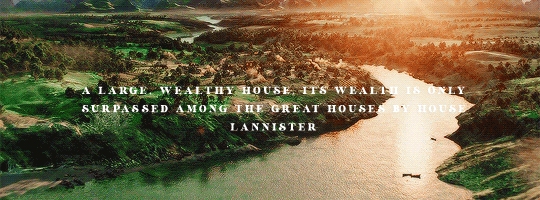

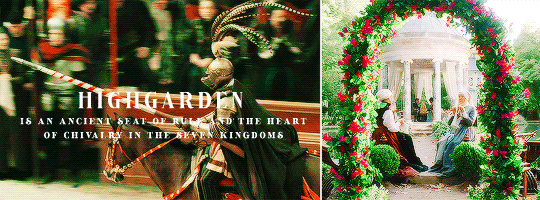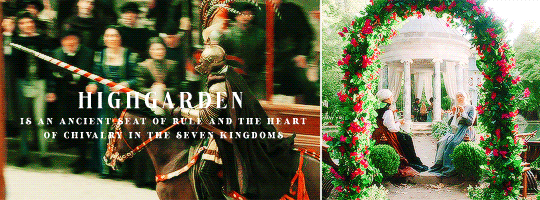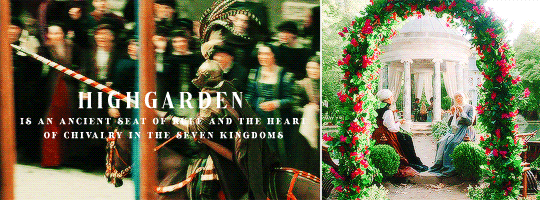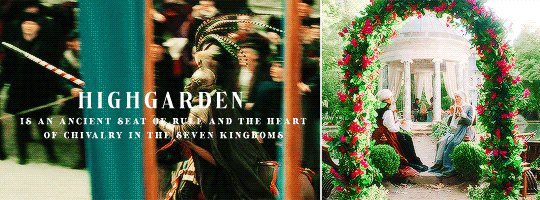
HOUSE TYRELL OF HIGHGARDEN is one of the Great Houses of the Seven Kingdoms, being Lords Paramount of the Mander and the liege lords of the Reach. A large, wealthy house, its wealth is only surpassed among the Great Houses by House Lannister, and the Tyrells can field the greatest armies. Additionally, if they call the ships of the Redwyne fleet, the lords of the Shield Islands, and the coastal lords, they can command a navy that equals if not surpasses the royal fleet of King’s Landing.
♛ 𝐻𝒪𝒰𝒮𝐸𝒮 𝒪𝐹 𝒲𝐸𝒮𝒯𝐸𝑅𝒪𝒮
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo










THE LIBRARY
“On the night of Alexander’s birth, tradition alleged, the temple of Artemis was burnt down. The local Persian Magi interpreted this as an omen of further disasters to come. They ‘ran about beating their faces and crying aloud that woe and great calamity for Asia had that day been born’, a firebrand that was destined to destroy the entire East. The night before her wedding, similarly, Olympias dreamed she was penetrated by a thunderbolt, so that fire gushed out of her womb, spreading far and wide before it was extinguished. A month or two later Philip also had a dream: he was sealing up his wife’s vagina, and the wax bore the stamped device of a lion. Some of the palace seers took this to mean that Philip should keep a closer watch on his wife. But Aristander of Telmessus - who afterwards accompanied Alexander to Asia - had a more acceptable explanation: Olympias was pregnant, and with a spirited, lion-like son. One did not, he told Philip, put a seal on an empty jar.”
Alexander of Macedon, 356-323 B.C: A Historical Biography, Peter Green, 1974 (2013 reprint).
+ complementary reading: Alexander’s Lovers (second edition), Andrew Chugg, 2006.
261 notes
·
View notes
Text




House of the Dragon — 2.02 "Rhaenyra the Cruel" Game of Thrones — 2.08 "The Prince of Winterfell"
648 notes
·
View notes
Text






Jon Snow 🐱 Balerion the Cat: Parallels
The Red Keep was full of cats [...] One by one Arya had chased them down and snatched them up and brought them proudly to Syrio Forel … all but this one, this one-eared black devil of a tomcat.
375 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Al'Naito (from “The Wheel Of Time” soundtrack)
Get your headsets and listen to the epicness! <333 A song in OLD TONGUE!
82 notes
·
View notes
Text










AARON TAYLOR-JOHNSON as FRIEDRICH HARDING NOSFERATU (2024) dir. Robert Eggers
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
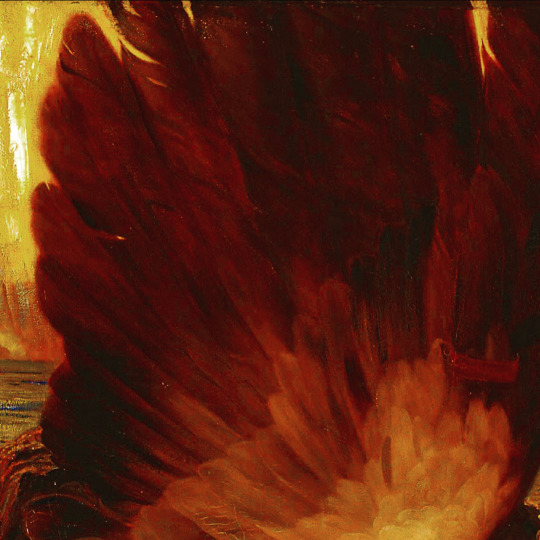
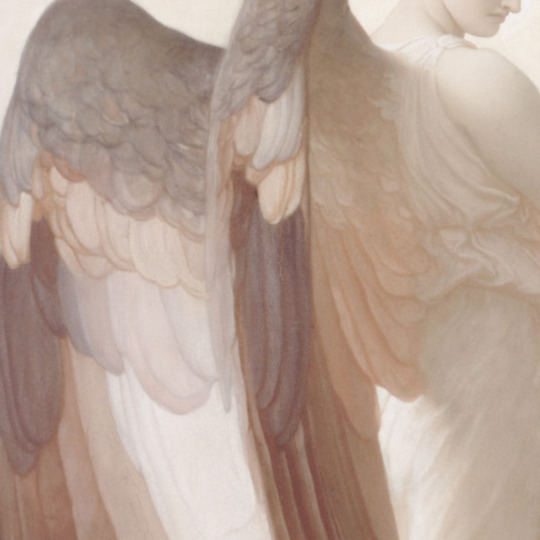
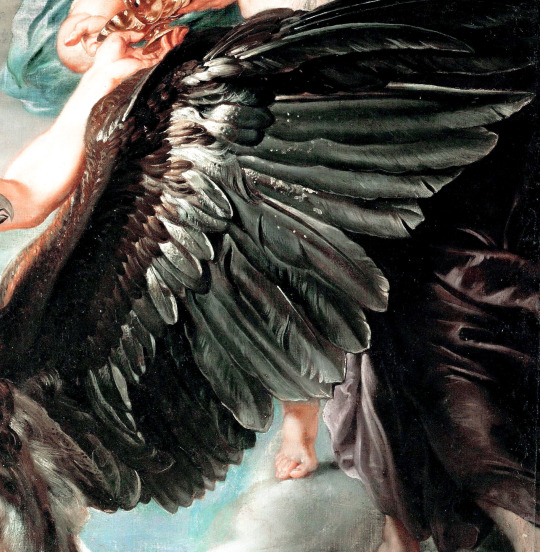
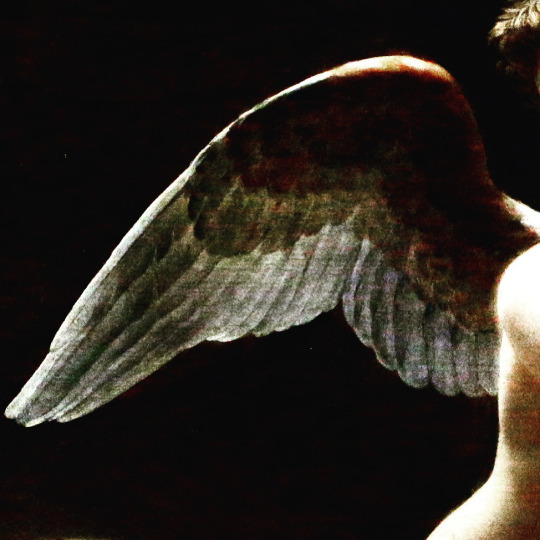
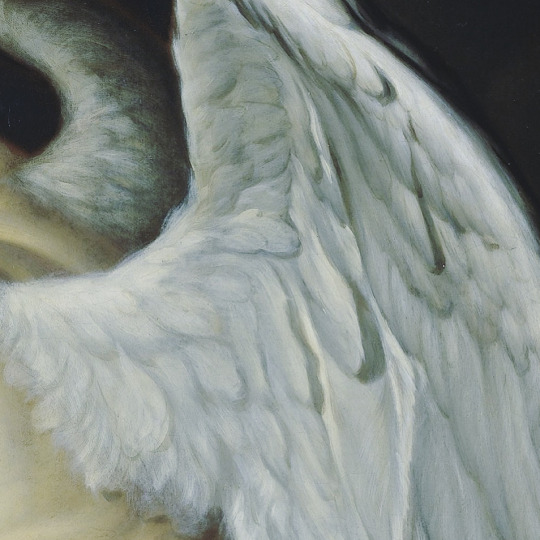








There are all sorts of angels. Details of painted wings. (The first one is digital art.)
51K notes
·
View notes
Text
One of my favorite things about both Theon and Jeyne's stories both coming to the forefront again in ADWD is how Winterfell/Stark heavy their stories are with neither of them being true Starks. Their entire lives prior to the series kicking off had been to be the yes man/woman, number 2 choice, best friend to the actual heir - firstborn lord and lady of Winterfell - in their friendships with Robb and Sansa. I don't doubt that their friendships were true and that they really cared about them, but they definitely must have known their own statuses in comparison to Robb and Sansa. And so having Jeyne return as 'Lady Arya' and Theon as both the Prince and Ghost of Winterfell AND both of them reclaiming themselves in a way all while in the bedrocks of their childhood home....is really good lol.
l as well like how their ending (so far) is one of the truest to 'undissected' high fantasy romance we have seen so far. By romance I don't mean like they're actually in love with each other. I enjoy Theyne as a ship but only as a several years later type AU lol. But by romantic I mean how the actions Theon takes to save Jeyne are absolutely the kind of deeds that get people songs written about them in this series, romantic in the idealized way people imagine stories like this, and I think that's kind of beautiful as well as horrible. It is dissecting classic high fantasy in a way as it's showcasing the absolutely monstrous things that precede someone doing something like saving a maiden from an impenetrable fortress, all of the awful and unsavory parts that go along with it. But Jeyne and Theon still get that almost fairytale ending in Dance and I greatly enjoy that Jeyne - our lady of a minor noble house sold into sexual slavery and then forced to pass herself off as Arya, and Theon - our hostage turned turncloak turned regretful turned Reek turned Theon once more - are the ones who get to experience it. 🥲
"Abel had doomed them. All singers were half-mad. In songs, the hero always saved the maiden from the monster's castle, but life was not a song, no more than Jeyne was Arya Stark."
This quote is fantastic because I think it cuts deep into the heart of Jeyne and Theon's story. In any other story this is true and honestly in this one it is as well. No one would find it worth remembering Reek and Ramsay's frightened wife or Jeyne the whore. But in a song they can be more than that. They ARE the hero and the maiden escaping from the monsters castle, regardless of what anyone else may tell them. It doesn't matter that Jeyme is not truly Arya bc they still live out that trope and live to see another day for it. They are the antithesis and the blueprint of what makes up the songs of this series.
Anyway, I'm a little wine drunk and Jeyne and Theon subverting and also living out the tropes of fantasy as part of their regaining themselves plot is very special to me. 🥲
200 notes
·
View notes
Text


LIAH O'PREY as JULIA THE ELDER Domina 1.04: Secrets
284 notes
·
View notes