#zirconium tube
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Role of Zirconium Tubes in Advanced Engineering Solutions
Discover the unique properties of Zirconium Tubes that make them essential in high-performance industries like aerospace, chemical, and medical sectors. These tubes are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures. Zirconium Tubes are used in critical applications such as nuclear reactors and medical devices, offering unmatched durability in demanding environments.
0 notes
Text
Hm. White patina/tarnish, looks malleable based on the dings and scratches. Doesn't look dark like most lead, but that doesn't mean it isn't; or the lighting/awb hasn't fudged it. Could be zinc. Zinc is close in mass/density to iron/steel.
Difficult to get an exact sense of scale here, but maybe ~3"x1.25"x7"? If it's 15lbs and my dimensions are even in the ballpark, it's probably a lead ingot.
Neat!
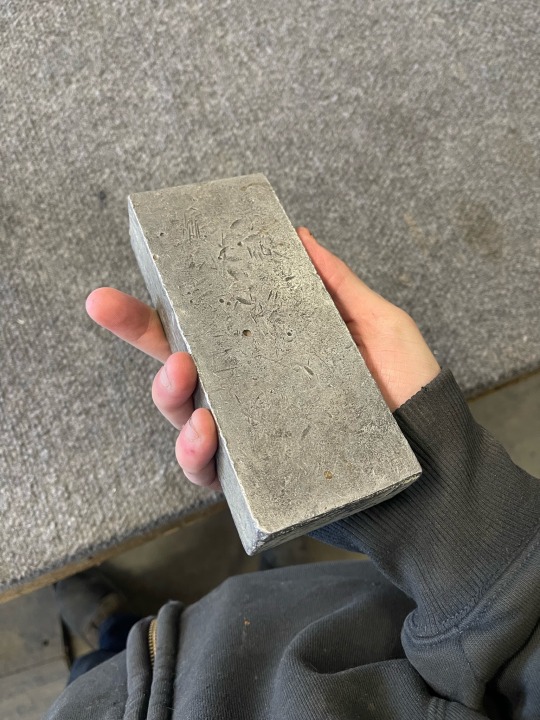


Of course it goes without saying that I am hopelessly dependent on the ingot
#i salvaged a length of zirconium tubing from my old materials science building#which was originally scrap from the diablo canyon nuclear power plant's water supply system#never installed obviously. it was about 50cm and rough cut on one end#pretty cool though.#the oxide was a really weird color. like. difficult to describe.
138K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Unique Properties of Zirconium 702 and Its Use in Additive Manufacturing
Zirconium 702, renowned for its exceptional properties, emerges as a true marvel in the realm of advanced materials, especially in the domain of additive manufacturing. Jay Steel Corporation, a prominent Zirconium 702 Manufacturer, Supplier, Stockist, and Exporter, takes immense pride in delivering an extensive array of top-notch Zirconium 702 products. As the go-to source for quality materials, we cater to diverse project needs with our range of offerings, including Zirconium 702 Round Bars, Sheets, Plates, Pipes, Tubes, and Fasteners. Whether you're in search of Zirconium 702 Round Bars suppliers, Zirconium 702 Sheets suppliers, or reputable Zirconium 702 Pipes and Tubes Manufacturers, We are committed to meeting your project needs with precision and excellence. Explore our top-notch offerings to elevate your endeavors with the unmatched properties of Zirconium 702.
This blog post delves into the unique properties of Zirconium 702 and explores its groundbreaking applications in additive manufacturing.
Understanding Zirconium 702
Zirconium 702 is a high-performance alloy known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in aggressive environments. With a composition that includes a remarkable 99.2% minimum of zirconium, this alloy demonstrates superior resistance to corrosive attack by acids, alkalis, and other aggressive chemicals.
Unveiling the Extraordinary Properties of Zirconium 702:
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance:
Zirconium 702 is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, making it an ideal choice for applications in aggressive environments. This property ensures longevity and reliability in various industrial settings.
High Thermal Conductivity:
Another noteworthy feature of Zirconium 702 is its high thermal conductivity. This characteristic makes it invaluable in applications where efficient heat transfer is critical, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Biocompatibility:
Zirconium 702's biocompatibility makes it suitable for medical applications, including implants and prosthetics. Its inert nature and resistance to corrosion in bodily fluids enhance its performance in medical devices.
Superior Strength and Durability:
The alloy's exceptional strength and durability make it an excellent choice for components subjected to high stress and demanding conditions. This is particularly advantageous in the manufacturing of parts for the chemical processing industry.
Zirconium 702 in Additive Manufacturing:
The rise of additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has opened up new avenues for materials like Zirconium 702. Its unique properties make it an ideal candidate for 3D printing applications, offering benefits such as:
Aerospace Components: Zirconium 702's resilience to corrosion and high strength make it an excellent choice for manufacturing aerospace components that must withstand extreme conditions.
Chemical Processing Equipment: In industries where exposure to corrosive substances is common, Zirconium 702 can be utilized to create durable and corrosion-resistant equipment.
Medical Implants: The biocompatibility of Zirconium 702 makes it a preferred material for producing medical implants, ensuring patient safety and long-term success.
Customized Tools and Parts: Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of intricate and customized tools and parts for various industries, and Zirconium 702's properties make it a versatile option for such applications.
Final Words!
As a result of its distinctive properties, zirconium 702 has become a popular choice for additive manufacturing. At Jay Steel Corporation, we pride ourselves on being leading Zirconium 702 Round Bars suppliers, Zirconium 702 Sheets suppliers, and Zirconium 702 Pipes suppliers. Our commitment to delivering excellence extends globally to meet the diverse needs of our clients. As a Zirconium 702 Manufacturer, Stockist, and Exporter, we ensure top-notch products that set industry standards. Being a well-known Zirconium 702 Pipes and Tubes manufacturer, we cater to a wide-ranging like Round Bars, Strips, Sheets & plates, Tubes and pipe and fasteners globally clientele, spanning countries such as Singapore, Malaysia, Nigeria, Thailand, USA, France, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Egypt, Turkey, Oman, Jordan, Bahrain, Russia, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Italy. Jay Steel Corporation's dedication to competitive pricing guarantees that clients worldwide can access premium Zirconium 702 at the best market rates. Explore endless possibilities in your additive manufacturing projects by contacting us at [email protected] or [email protected].
#Zirconium 702 Round Bars suppliers#Zirconium 702 Pipes and Tubes Manufacturers#Zirconium 702 Sheets suppliers
0 notes
Text
Principles of the RBMK Reactor

The RBMK-1000 Boiling Water Reactor is a Soviet-designed nuclear reactor capable of generating 1,000 megawatts of electricity. The core of the reactor is a short, wide cylinder. The active zone is contained inside a large metal drum, known as the core shroud. The reactor assembly is supported by a large metal disk known as the Lower Biological Shield. This sits on top of a larger metal cross labeled “Structure S”. On top of all this rests the 2,000 ton Upper Biological Shield of the reactor, known as "Structure E". The reactor sits in a large reinforced concrete shell which provides structural support and shields plant personnel from radiation.
The core region of the reactor is a large pile of graphite 14.52m × 9.7m. This pile is composed of graphite blocks 25cm by 25cm, with a height of between 20 and 60cm depending on its location in the reactor. Drilled through these blocks is a 11.4cm diameter hole, through which a zirconium alloy tube (known as a ‘technological channel’) is inserted. These contain either a fuel assembly, a control rod, or reactor monitoring equipment. These channels can be opened in situ or removed completely to replace any fuel or equipment inside them. Zirconium is used due to its high melting point and because it allows the neurons that produce the fission reaction in the core to pass through it far easier than other alloys such as stainless steel.
These metal technological channels have water pumped into them from the bottom by the Main Circulation Pumps. The entire reactor vessel is pressurized with a helium-nitrogen mixture, to prevent the oxidization of the graphite. Graphite is flammable in oxygen, but removed from it it can become quite an efficient thermodynamic conductor.
Below: A photo of RBMK technological channels at Chernobyl Unit 2. The length of these gives a good idea as to how massive the core of the RBMK is.
This picture is a screencap from this video.

The fuel of an RBMK is small uranium oxide pellets, stacked into small metal pipes and bundled together into fuel assemblies. Uranium oxide is a ceramic material composed of Uranium 235. This element, under special conditions, can create a nuclear chain reaction which generates heat. The RBMK has three primary components that help create these special conditions to create the controlled fission reactions in the core. These are graphite, water, and boron.
Graphite is used in the core of an RBMK as a moderator. Basically, it slows down the neutrons discarded by U-236 atoms (a U 235 atom which a neutron has collided with) when they split apart. When they are released they are travelling at a tremendous speed, and have very little chance of coming into contact with another atom of uranium. Slowing them down, however, creates a higher chance of the neutrons coming into contact with an atom of U-235, creating the unstable U-236 and then pulling itself apart, thereby creating more neutrons (as well as several other elements) and sustaining a nuclear chain reaction. This sustained reaction is what creates the heat in the core of a nuclear reactor. The more neutrons there are in the core, the more reactivity (and therefore heat) is created. It should be noted that graphite is combustible at high temperatures. The core contained 1,700 tons of graphite.
Water in the core of an RBMK serves as a coolant. Because the core of a nuclear reactor gets extremely hot, it becomes necessary to cool its components if you wish to avoid destructive melting within the core region. Water is the most common coolant in nuclear reactors, as it is cheap and abundant. The water is pumped in under high pressure at about 265 C by the Main Circulation Pumps from the bottom of the reactor up into the technological channels containing the fuel and other components of the reactor. After passing through the channels and heating up to about 284 C, the water is piped out of the top of the reactor. Some of the coolant water heats up so much that it forms into steam bubbles inside the reactor. When the water is pumped out of the core it is then sent into four steam separator drums, where the steam is separated from the water. The water is then pumped back into the reactor, while the steam is sent to the turbine generators of the plant to create electricity. After this, the steam is condensed back into water using cool water from the plant cooling pond and recirculated into the cooling system.
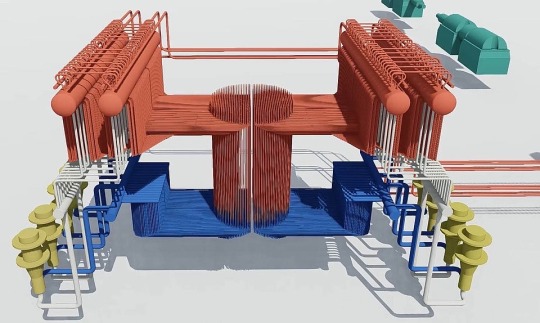
Below: A model showing the circulation system of an RBMK-1000 reactor. Coolant water is in blue and hot water/steam is in red. The yellow structures are the main cooling pumps, and the green structures are steam turbines. This model is spatially to scale, essentially what you would see if you removed every part of the reactor except for the coolant circuit.
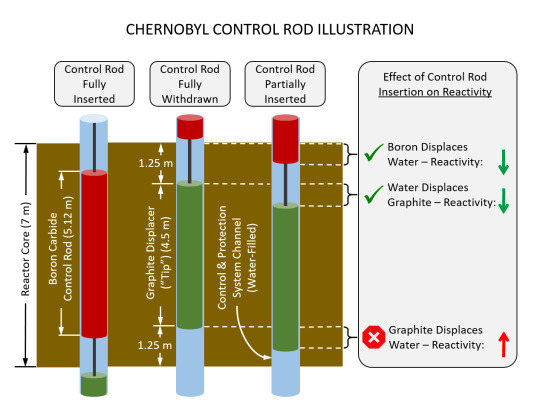
Some of the channels in the RBMK contain control rods (large boron carbide rods) that move up and down in the channel as necessary to keep the reactor within operational limits. Boron is a neutron sponge. It absorbs neutrons and can effectively eliminate a chain reaction. It functions as the brakes on a human made nuclear reaction, useful both in making sure a chain reaction does not become a runaway criticality and also in being the off switch on a nuclear reactor. The RBMK has 211 of these control rods, some of which are under operator control and some of which are under the control of a computer. A design quirk of the RBMK is that at the end of each standard control rod was a 14ft 9in graphite displacer. When a control rod was withdrawn out of the core it left behind a space that would be filled with water, a neutron absorber. Since more water in the core would kill reactivity, the designers of the reactor hung this displacer from the control rods to replace the space left by the control rod with something that would increase reactivity rather than kill it. This was a sound design choice, but it was a major factor in the events of the accident at Chernobyl.
Below: An illustration of the control rod displacers in an RBMK.
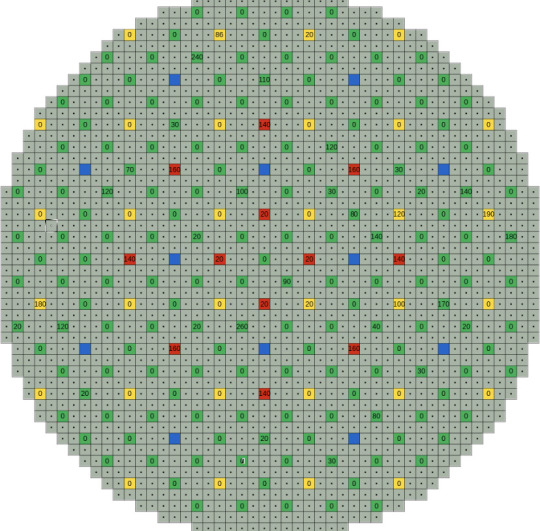
Below: A top down view of the channels of an RBMK. You can see the layout of the control rods (green), neutron detectors (blue), shortened control rods inserted from below the reactor (yellow), automatic control rods (red), and the fuel channels (grey). The number on the green, yellow, and red squares are the last recorded insertion depths of control rods in Chernobyl Unit 4 1m 30s before the explosion. Only one is fully inserted.
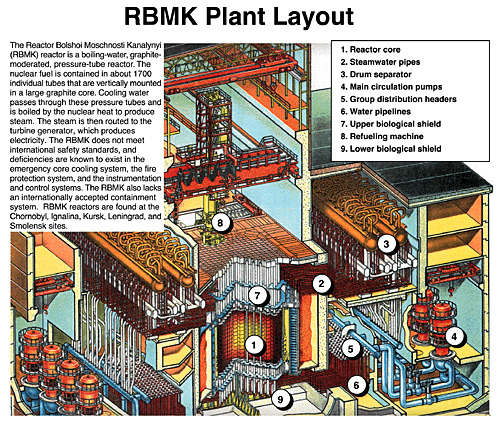
Below: A cutaway of the RBMK system layout.
Two additional factors also come into play regarding the water. Water is naturally a neutron absorber, albeit a far less effective one than boron. The more water in the core, the less neutrons are present and therefore the lower the reactivity. However, when transformed into steam, water loses nearly all of its neutron absorbing properties. The more steam in the core, the higher reactivity is. This is called a ‘positive void coefficient’, and it was a known quirk of the RBMK and indeed several other reactor designs. However, the RBMK had a much higher level of this effect in its core due to its design. This is important to the accident sequence.
It is also important to note that the RBMK is an enormous construction. It is temperamental, unstable unless operating at full power, and requires constant monitoring and guidance from its operators. It requires three operators just to run it normally, and it was notoriously difficult to operate. The core region is so large that the equipment used to monitor it could not accurately read a large portion of it, and hotspots of reactivity would often form resulting in alarming and unexplained jumps in power output and temperature. While in theory not a bad design, the RBMK was a deeply flawed machine.
An enormous thank you is owed to @nicotinebeige , who was extremely helpful in the creation of this post. If you like film photography, you should check out their blog!
This is a technical explanation of the RBMK design. For a history of the RBMK, check out this post. Apologies for any mistakes! I’m most definitely not an expert on nuclear physics, and if anything is unclear you should absolutely check out other sources for more info. As always, thank you for your interest!
#chernobyl#nuclear reactor#history#radiation#accidents and disasters#nuclear power#autism#nuclear#reactor#chnpp#rbmk#rbmk 1000
134 notes
·
View notes
Text
happy pride month 2024!
I will be continuing my yassification project this year. Apparently, I did some additional elements last year that I failed to post, so here is a brief summary of each of them.

Rubidium/Rosboy: A man who is feminine, usually in presentation. A less screwy term for femboy. Rubidium is used in vacuum tubes to bind and remove trace gases.
Strontium/Spectrasexual: The attraction to a specific spectrum of genders, as opposed to multiple select genders. Strontium is the material that times the most accurate atomic clock in the world.
Yttrium/Lavender Marriage: A marriage of convenience to disguise the homosexuality of one or both of the spouses (ultimate MLM/WLW solidarity). Yttrium was the first of the rare earth elements to be discovered, in 1787.
Zirconium/Queer: An umbrella term for the LGBTQ+ community, or a term for someone with a difficult-to-explain identity or who does not wish to classify further. Zirconium is used mainly to surround uranium in the fuel rods of nuclear reactors, due to its high resistance to corrosion and unwillingness to absorb neutrons.
#official periodic table#lgbtq#pride 2024#rubidium#rosboy#strontium#spectrasexual#yttrium#lavender marriage#zirconium#queer
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
.Lazy mornings. .Sharing a bed.
Aether/roadie!oc | 760 words | sleepy morning cuddles | established relationship(early days)
Pure true fluff. AO3
It wasn't planned. No, really. That Andea would move into Aether's room was a spur of the moment. Technically not forbidden by the clergy, but after her lease was up & she was applying to get on-site housing, the ghoul found out. He didn't see a reason not to share his space with her, & she couldn't find one either. As much as she tried. So she moved in, 'temporarily' she'd say as Aether unpacks her bags, slotting her clothes alongside his. He nodded along but to anyone else it was obvious she was staying.
Andea has found since 'crashing' at Aether's that mornings are something to be savoured. She never enjoyed them before, always quick to leave, had commutes to make, or slept right through them. But waking up to the weight of a 6ft ghoul on her, his face buried in her chest, & rumbling in a way that had her bones vibrate? It was strangely soothing.
Knowing she couldn't get out from under him, Eleanor took the time to look around the room again. It was decent sized, not too big to be annoying to clean, & Aether had made good use of the high ceiling for storage. The walls were lined with guitars, records & an almost daunting amount of banana themed merchandise. Andea had always wondered what the band did with all the tour gifts. Now she knows.
A tinted light filtered in through a series of solar tubes along one side of the underground room, bathing it in a mix of colours, not unlike the stained glass windows of the chapel above. The depth made it impossible to denote weather but at least it was clear the sun was rising.
Andea tilts her chin down to see a still dozing Aether washed with the multiple refractions of light. His short white hair picked up the cool tones & appears almost purple. She drags her hands over his head, grazing the scalp & causing a shiver in his spine. His breathing hitches but the rumble continues. Reaching his horns Andea busied herself with running the pads of her fingertips over the grooves in his horns; the loose spiralling pattern reminding her of sand gardens. Her mind wanders as her thumb follows a line down.
"Murnin'" Aether's hoarse voice is muffled against her skin but she feels the kiss he places on her sternum; lazy & tender. She loosens her hold on his horns to allow him to look up at her. He does so, resting his chin on her softness & opens one eye just enough to make her out in the morning light. His smile could only be described as dopey. The same as every lazy morning. Andea refocuses on him, trading his horns for the fur-like hair on the sides of his head that are sticking out in sleep-ruffled glory.
He tastes the sleep on the roof of his dry mouth & yawns. His thin lips retreat to show sturdy fangs of dark zirconium & his pointed purple tongue with its own mark where a piercing will go.
'Big yawn.' Andea muses at the wide open maw inches from her face.
Aether squints at her once more before pouting & deciding arbitrarily it was too early, he buries his head back into her chest. She slaps his shoulder only to hear a grumble & have his arms tighten under her.
She wasn't complaining, of course, never had someone so intent on staying with her, but she knew he would keep them like this until someone is sent in to pry them apart. Andea had only just been able to look Custos Eulogy in the eyes again.
"C'mon big cat, I want breakfast." She tries.
A long pause follows before an eventual huff of agreement. Gradually Aether unfurls from around her, pulling himself up onto his forearms he leans up to kiss his mate good morning. She reciprocates & he has to shake off the desire to monopolise her time for just an hour more. His sleep-addled mind comes up with an idea.
Andea tries to sit up with him only for Aether to push her back down. He kisses her forehead one last time before dressing himself. Smiling at her confused expression he gathers just enough clothes to not be given another penalty on the whiteboard. Satisfied with his booty shorts & t-shirt he nods.
"Breakfast!" He points to Andea, who'd given up on guessing his train of thought, & walks out the room.
He did indeed get a penalty, not for his clothes, but for the crimes he committed in the kitchen to bring Andea breakfast in bed.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are the applications for niobium products?

Niobium product is dominated by its use as additive to high strength low alloy steel and stainless steel for oil and gas pipelines, car and truck bodies, architectural requirements, tool steels, ships hulls, railroad tracks. However, there are many other applications for niobium metal and compounds.
Niobium product application & technical benefits Niobium oxide - Manufacture lithium niobate for surface acoustic wave filters - Camera lenses - Coating on glass for computer screens - Ceramic capacitors - High index of refraction - High dielectric constant - Increase light transmittance
Niobium carbide -Cutting tool compositions -High temperature deformation, controls grain growth
Niobium powder -Niobium capacitors for electronic circuits -High dielectric constant, stability of oxide dielectric
Niobium metal plates, sheets, wire, rod, tubing
- Sputtering targets - Cathode protection systems for large steel structures - Chemical processing equipment -Corrosion resistance, formation of oxide and nitride films. Increase in high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, improved creep resistance, reduced erosion at high temperatures.
Niobium-titanium alloy Niobium-tin alloy Superconducting magnetic coils in magnetic resonance imagery (MRI), magnetoencephalography, magnetic levitation transport systems, particle physics experiments. Electrical resistance of alloy wire drops to virtually zero at or below temperature of liquid helium (-268.8°C).
Niobium-1% zirconium alloy - Sodium vapor lamps - Chemical processing equipment -Corrosion resistance, fixation of oxygen, resistance to embrittlement. -Vacuum-grade ferro-niobium and nickel-niobium -Superalloy additions for turbine blade applications in jet engines and land-based turbines.
Inconel family of alloys, superalloys. Increase in high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, improved creep resistance, reduced erosion at high temperatures.
https://www.etimaterials.org/niobium/
https://www.edge-techind.com/Products/Refractory-Metals/Niobium/Niobium-Alloys/Niobium-Zirconium-Alloy-179-1.html
0 notes
Text
Magnesium oxide ceramics
Magnesium oxide is widely used as an industrial refractory material because its melting point is almost the highest among common oxides, about 2800℃, which is higher than common refractory materials such as zirconium oxide (about 2700℃) and aluminum oxide (about 2050℃). In addition to its high melting point, magnesium oxide also has other advantages, such as good chemical stability, and is not easy to react with metals when used for alloy casting; magnesium oxide is prone to hydration reaction, especially in the presence of acid, it will dissolve quickly; magnesium oxide has a stable structure and good high-temperature thermal insulation performance... With various advantages, magnesium oxide has been developed into refractory materials such as crucibles for melting metals, ceramic cores for metal casting, thermocouple sleeves, and electric heating tubes, while other properties and uses have been ignored.
In recent years, due to the increasing requirements of modern industrial technology for materials, some other excellent properties of magnesium oxide ceramics have gradually attracted people's attention, especially microwave dielectric properties and optical properties.

1. Microwave dielectric properties. Magnesium oxide ceramics are very excellent low-dielectric microwave dielectric materials with extremely low dielectric loss. Their dielectric constant is about 9, and tanδ<1.6×10-6, which is comparable to or even better than the microwave dielectric properties of the most commonly used alumina ceramics. More importantly, the sintering temperature of alumina ceramics is relatively high, usually above 1500°C. Although liquid phase sintering greatly reduces the sintering temperature, the microwave dielectric properties will also deteriorate. In contrast, magnesium oxide microwave dielectric ceramics can be obtained at very low temperatures. For example, someone added 4% LiF to MgO and sintered it at 950°C to obtain magnesium oxide microwave dielectric ceramics with good microwave dielectric properties. Its dielectric constant is 9.6, and the Q×f value can reach 282230GHz. By extending the insulation time, its Q×f value can even be greatly increased to 751500GHz. Considering that the density of magnesium oxide is also lower than that of alumina, and its thermal conductivity is good (the thermal conductivity of pure magnesium oxide is about 55W/m·K), it can be expected that it should have good application prospects as a substrate material.
2. Optical properties. As an inorganic non-metal with a face-centered cubic structure, magnesium oxide crystals are transparent, and their linear transmittance under visible light exceeds 80%. Therefore, through appropriate sintering processes, magnesium oxide ceramics can obtain higher transparency. For example, someone used SPS technology to obtain transparent 0.02at%Yb-doped magnesium oxide ceramics at 1100℃/60min, and its linear transparency under visible light exceeded 70%. Another special feature of magnesium oxide transparent ceramics is that the wavelength range of transmission is very wide, and the transmittance is higher at infrared wavelengths. For example, someone prepared 1%LiF-doped magnesium oxide ceramics, and its light transmittance exceeded 80% in the wavelength range of 2000-6000nm, and the highest was about 86%, which is not much lower than the current magnesium aluminum spinel with too high infrared transmittance. Another feature of transparent magnesium oxide is that it is relatively easy to prepare. We know that under pressureless conditions, transparent aluminum oxide often needs to be sintered at a high temperature of about 1800℃ in a hydrogen furnace to obtain it. In comparison, it is much easier to prepare transparent magnesium oxide. For example, someone used nano-magnesium oxide powder as raw material, sintered it at 1400℃ in an ordinary muffle furnace for 2 hours, and obtained translucent magnesium oxide with a density of 98.1%. Therefore, we can reasonably infer that transparent magnesium oxide ceramics have the potential to become high-performance infrared window materials.
0 notes
Text
India's Green Hydrogen Market: Paving the Way for a Sustainable and Carbon-Neutral Energy Future - UnivDatos
According to a new report by UnivDatos Market Insights, the India green hydrogen Market is expected to reach USD 2686.78 million in 2032 by growing at a CAGR of 69.8%. India is emerging as a key player in the Asian energy market. In late 2022, India announced a $2 billion incentive program for the green hydrogen industry. This program aims to reduce emissions and support India's efforts to become Asia's first major hydrogen exporter. Recently, the Indian and Australian governments finalized a deal to establish a task force for expanding green hydrogen cooperation between the two countries. India has ambitious goals of becoming energy-independent by 2047 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 through a decarbonization strategy.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=59021&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
The Union Cabinet approved this mission on 4th January 2023, with a budget allocation of ₹ 19,744 crore. The ultimate objective of the mission is to make India the global hub for the production, usage, and export of green hydrogen and its derivatives. By 2030, the mission aims to establish capacities to produce at least 5 million metric tons (MMT) of green hydrogen annually, potentially reaching 10 MMT per annum through expansion of export markets and international partnerships.
Research and Development Program:
India is currently undergoing a major development of green hydrogen infrastructure. To support this initiative, the focus should be on the development of electrolyzers, fuel cells, and associated components. This development should aim to improve efficiency, reduce costs, extend stack life, and create a technology that is less dependent on metal and material imports. The program can be a collaborative effort between key industry players and renowned academic institutions.
NITI Aayog recommends a mission-mode R&D drive in collaboration with the industries in the following areas:
· Early-stage R&D to enable technologies that reduces the cost of hydrogen delivery and dispensing.
· Manufacturing techniques to reduce the cost of automotive fuel cell stacks at high volume.
· R&D that reduces the costs of manufacturing electrolyser components, using advanced techniques such as additive manufacturing.
· Compression of hydrogen to 875 bar using electrochemical cells and metal hydride materials. Improve efficiency and reduce the capital cost of hydrogen liquefaction, using a vortex tube concept. Establish the potential for magnetocaloric technologies to liquefy hydrogen at twice the energy efficiency of conventional liquefaction plants.
· Secure critical mineral supply either through indigenous development or global collaborations for the supply chain of Nickel, Zirconium, Lanthanum, Yttrium, Platinum, Iridium, and other key raw materials used in electrolysers.
Click here to view the Report Description & TOC : https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=59021&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Conclusion:
In conclusion, India's initiatives in green hydrogen research and development, spearheaded by government and research institutions, herald a promising future for renewable energy in the region. The government's commitment, exemplified by policies like the National Hydrogen Mission, aims to make India a global hub for green hydrogen production and export. The anticipated growth in this field is expected to drive not only energy sustainability but also significant economic and employment benefits. With continuous support and progressive policies, India's green hydrogen sector is poised for exponential growth, contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape globally.
0 notes
Text

TZM Alloy Disc, by Edgetech Industries. Also named as TZM Molybdenum Alloy, Titanium-Zirconium-Molybdenum (TZM) Alloy. Tube, disc, plate, sheet, and wire forms are available, tailor-made parts can be provided per drawings.
0 notes
Text
Zirconium Tube & Titanium Wire: Unmatched Durability and Versatility for Modern Industries
Zirconium Tube is renowned for its incredible corrosion resistance, particularly in highly acidic and aggressive environments. This makes it the perfect material for industries like chemical processing, nuclear energy, and even medical implants. Zirconium’s ability to withstand extreme conditions without degrading ensures long-term reliability and safety.
0 notes
Text
The Development of Refractory Ramming Mass
The ramming mass refers to ramming (manual or mechanical) method of construction, and hardened in the heating effect is higher than normal temperature under the unshaped refractory materials.
By refractory aggregate, with certain gradation of powder, binder, additive water or other liquid after mixing.According to the material classification with high alumina, clay, magnesite, dolomite, zirconium and silicon carbide carbon refractory ramming material.
Refractory Ramming Mass Function:
ramming material is made of silicon carbide, graphite, electric calcined anthracite as raw material, mixed with a variety of ultra-fine powder additives, fused cement or composite resin as the binder made of bulk cement.To fill the gap or stack cooling equipment and masonry masonry filler.
Refractory Ramming Mass Types:
The leveling layer with acidic, neutral and alkaline ramming material widely used in intermediate frequency coreless furnace core induction furnace, as if furnace ramming material used for melting aluminum and its alloys, melting of copper, brass, copper and bronze and copper alloy etc.
The carbon ramming mass as an example: according to the different type of blast furnace and the material design requirements of different carbon ramming material is mainly used for blast furnace carbon brick and bottom sealing gaps between plates and carbon bricks and the cooling wall, and filling the furnace bottom water cooling tube over the central line of the leveling and cooling wall, all parts are required by ramming carbon ramming after ramming mass has a certain strength and density, and filled every corner of a small gap, to achieve no leakage of hot metal and gas demand,Classification and construction: all ceramic ramming material consisting of material is divided into: clay, high alumina, carbon, magnesium and dolomite.
Refractory Ramming Mass Advantages:
High erosion resistance.
High bonding strength.
Short lead time.
Free engineering services to guarantee service life.
Ramming mass is used in various industrial places for manufacturing of many refractory materials. It is prepared with great precision using modern techniques and quality materials. Corrosion resistant with a high level of thermal stability, it offers maximum output and last longer. It can be used in lining of iron, lining the trough of blast furnaces, lining of induction furnaces, used as insulation for rapid drying. Also, available in a premixed form allows lesser wastage, consistent and longer lining and patching life. Ramming mass is prepared using quality components and other raw material as per the industrial set standards and norms with great precision. The even and regular granule of the powder are appreciated by the clientele.
Neutral Ramming Mass VS Silica Linings
Silica ramming mass can safely be used up to an operating temperature of 1600 deg C. Since it expands very little, it is superior to both alumina and magnesia refractories to resist thermal shocks. Though silica lining has good endurance against thermal shock, it has poor resistance against steelmaking slags. Temperature control is very necessary for a satisfactory lining life.
The addition of right quantity of boric acid is very important for optimum life of lining.
The quantity depends upon (i) temperature of liquid metal bath, (ii) chemical composition of quartzite mass, and (iii) thickness of crucible wall.
Silica linings are the conventional lining solution widely used in both ferrous and non-ferrous foundries. Mainly made of crystalline silica and commonly known as acidic ramming mass, the typical binding agents that aid in the sintering of silica linings are boron-based. This refractory lining exhibits mainly low thermal expansion and have excellent thermal shock resistance.
Neutral ramming mass are a unique, chemically neutral foundry solution that form joint-less linings. The in-situ spinels synthesise at high temperatures inside the refractory lining, creating a unique 3-layer structure. The outermost layer in contact with the molten metal is a hard, sintered surface, followed by an intermediate fritted layer. The innermost layer stays in a powdery form.
Neutral ramming mass
Lining wear and the causes of wear
The lining life of induction furnace lined with silica ramming mass depends upon the lining practice and operating practice of the furnace besides quality of the silica ramming mass. It is quite common to get inconsistent lining life of the furnace. There are cases when sudden failure of lining takes place.
The main factors which affects the lining life of the induction furnace are
(i) incorrect granulometry of the ramming mass,
(ii) non-uniform distribution of the binding agent,
(iii) superheating of the metal bath in the furnace,
(iv) penetration of metal,
(v) minimum slag free metal resulting in minimum erosion at slag line,
(vi) loss of refractory powder, and (vii) topping/lining interface cracking
For the proper failure analysis in case of pre-mature failure of the refractory lining, it is important that proper records about output, working temperature, and other parameters are maintained. These records not only help in finding the cause of failure but also help in the continuous performance of the lining life.
Article Source: The Development of Refractory Ramming Mass Company name: Henan Changxing Refractory Materials Co.,Ltd More refractory products:https://www.cxrefractories.com/en-all-refractory-products Email:[email protected] Website:https://www.cxrefractories.com
0 notes
Text
T1, T2 copper is mainly used as conductive, heat-conducting and corrosion-resistant components, such as wires, cables, conductive screws, shells and various conduits, etc. T3 copper is mainly used as structural materials, such as the production of electrical switches, washers, rivets, nozzles and various conduits, etc.; it is also commonly used in some less important conductive components. components.
What Materials are Available in Copper CNC?
Copper classification and characteristics
1. Pure copper in China commonly known as 'purple copper' in Japan and Taiwan commonly known as 'red copper' a common grades: T1, T2, T3, TU1, TU2 b characteristics: conductive with c common uses: electrical switches, motor coils, electronic parts.
2. Brass with zinc a Common grades: H59, H62, H65, H68, HPb59-1 Free-cutting brass b Characteristics Higher strength, wear resistance, water vapor corrosion resistance c Common uses Architectural hardware, heat exchanger tubes, pumps, power cylinders and bushings, munitions.
3. White brass: Nickel-containing Common grades: B19, B25, BFe10-1-1, BZn15-20, BA13-3 b characteristics: stable physical properties at room temperature c common use medical apparatus, precision instruments, thermocouples, watch parts, glasses frame
4. Bronze: a definition: the old name that tin bronze such as the ancient bell, tripod, wine ware New definition: purple, yellow, white copper other than the three categories of the collective name b according to the practical physical and chemical indicators such as hardness, strength, elasticity, high-temperature conductivity, thermal conductivity and so on the engineering composite index and have different formulations. c uses: tin-phosphor bronze, good elasticity, for lamps Spring piece, switch spring piece. Resistance welding electrode material roll welder, butt welder, touch welder, rivet welder. Chrome zirconium copper, beryllium cobalt copper.
About Copper CNC Machining
Using a computer-controlled machining tool, copper is shaped into a variety of components during the copper CNC machining process. Due to its precision and reproducibility, it is one of the most flexible and popular machining methods for copper objects. Both basic pieces with simple shapes and complicated parts with detailed shapes can be produced using this method. For applications requiring high levels of dimensional accuracy, close tolerances, and outstanding surface polish, copper CNC machining is appropriate.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Titanium's Superhero Qualities of Toughness, Resistance, and Sturdiness
Titanium is most definitely a superhero of a metal. It is highly resistant to deterioration. It is lighter than steel, much heavier than aluminum, and stronger than both of those steels. While it is more costly to purchase at first, titanium is cheaper over the long run. This is since there is no solution, maintenance, or repair services needed. What causes titanium to be so ... heroic?
Discovered in 1793 by German chemist M.H. Klaproth, titanium was named after the Titans in Greek mythology given that they are the manifestation of all-natural strength. The aspect was not isolated until 1910. Titanium is the nine most bountiful aspect on earth as it makes up 25% of the planet's crust. It takes place in nature just in chemical mixes of oxygen and also iron.
Titanium is has high laziness. This permits it to have corrosion resistance to many minerals as well as chlorides. Titanium is really valuable in the medical area due to its non-toxicity. It is likewise biologically suitable human bone as well as tissue. Titanium is commonly found in clinical implantation products as well as prosthetics.
Titanium Tube
Titanium is created first with Australian coastline sand. The sand is formed into titanium-containing rutile-ore and also chlorinated into a sponge. Chlorine and coke are incorporated with rutile to produce titanium tetrachloride.
Tetrachloride is reacted to magnesium in a shut system, making the results sponge as well as magnesium chloride. The magnesium and mag chloride can be eliminated utilizing the Vacuum cleaner Distillation Refine to be recycled once more.
The sponge is melted with scrap and alloying aspects. This can include vanadium, zirconium, tin, light weight aluminum, as well as molybdenum. This is carried out in a Vacuum cleaner Arc Reduction heating system to create VAR ingots. It can likewise be performed in an Electron Beam Cold Fireplace heater to produce remote electrodes. They can be VAR melted to fulfill aerospace needs, or to direct pieces.
VAR ingots are cylindrical forms considering as much as 17,500 pounds. The ingots are built right into pieces, or rectangle-shaped forms. They can also be built right into billets, or bar forms. Ingots can be used for investment casting supply too.
More processing or rolling of created or cast slab or billet lead to mill items. These consist of titanium plates, bars, rods, and also titanium cord forms. Manufacturing can additionally develop sheets of titanium that can be cut into strips. These strips are after that created right into tubes or pipelines.
There are many different grades of titanium to be made use of for various objectives. Grade 1 is among the four readily pure titanium grades, in addition to qualities 3 with 4. Quality 1 is soft and also the most pliable. It has excellent formability, toughness, and high corrosion resistance. Grade 1 is readily available in titanium plate and also tubes.
Grade 2 is the workhorse as a result of its different usability and also availability. It is similar to quality 1 but stronger. Quality 2 has excellent weldability, toughness, ductility, and also formability. Quality 2 is readily available in bar as well as sheet kind.
Titanium Sheet
Grade 3 is the least used, yet is stronger than qualities 1 and also 2. It is much less flexible yet has higher mechanicals. Application of quality 3 is made use of when strength and also major deterioration resistance is needed. Quality 4 is the toughest and also has all the attributes of previous grades. When high toughness is required, quality 4 is used.
One of the most fantastic things regarding titanium is its use in the clinical world. Titanium is used for joint repair. The all-natural residential or commercial properties in titanium, such as being safe and naturally suitable, make it best for body component restoration.
Titanium is genuinely a superhero amongst the different type of metals. Its stamina, resilience, reduced upkeep demands, as well as corrosion resistance make it a preferred and beneficial metal. The development and also qualities of titanium show how numerous applications and also makes use of the steel holds.
0 notes
Text
About Zirconia Partially Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics (Mg-PSZ)
Introduction:Magnesium oxide partially stabilized zirconia with magnesium oxide (MgO) as the stabilizer of zirconia, after forming the crystal structure for a cube, more stable. Magnesium zirconium has better resistance to high temperature and moisture because it is not affected by phase migration. - What is magnesium oxide partially stabilized zirconia ceramics The oxidase-partially stable zirconia ceramics (MG-PSZ), which is commonly referred to as magnesium-zirconia ceramics, are all yellow with a density of about 5.7g/cm³. Magnesium oxide partially stabilized zirconia with magnesium oxide (MgO) as the stabilizer of zirconia, after forming the crystal structure for a cube, more stable. Magnesium zirconium has better resistance to high temperature and moisture because it is not affected by phase migration. Magnesium zirconium retains its strength even in humid, high temperature environments where the mechanical properties of yttrium partially stabilized zirconia begin to deteriorate.2. Advantages and disadvantages of magnesium stabilized zirconia ceramics - Advantages and disadvantages of magnesium stabilized zirconia ceramics Compared with yttrium oxide, magnesium oxide partially stabilized zirconia has the outstanding advantages of excellent mechanical properties and creep resistance at relatively high temperatures. However, the research and development of magnesium stabilized zirconia is restricted by two adverse factors: one is that the solution temperature of magnesium oxide in the cubic zone of zirconia is very high, resulting in magnesium stabilized zirconia is not easy to completely sintering; First, when zirconia is higher than 1000℃, magnesium oxide is easy to produce crystal phase separation and a large number of tetragonal phase instability, which makes the material properties decline and seriously restricts its application in high temperature region. 3.Application - Wire forming/drawing mold; • Precision in high-wear environments; • Axis; - furnace treatment tube; - Wear pad; • thermocouple protection tube; • sand blast nozzle; • Refractory materials; • Furnishing crucible; - Knives and blades; • fuel cell parts; • Bearings and rollers; • Weld nozzles and pins; - Gas igniter; • Electric insulator; • Ceramic guide plate; • Oxygen sensor; - Mechanical seal; - Performance Magnesium partially stabilized zirconia Mechanical property thermal property electrical property Color Yellow maximum service temperature(°C) 1000 dielectric constant 28 Density (g/cm³) 6.05 thermal conductivity@25°C 2.2 dielectric strength(6.35mm) 9.4 Vickers hardness Gpa) 12.5 linear coefficient of thermal expansion (40 - 400℃, × 10^ -6/℃) 10.2 dielectric loss 10 x 10^-4 compressive strengthc (Mpa) 2100 Specific heat(J/(kg ・ K) 400 volume resistance @25°C >10^12 flexure strength (Mpa) 850 thermal shock resistance(°C) 350 volume resistance @500°C >10^3 Fracture Toughness (Mpa·m1/m2) 4~5 Young modulus (Gpa) 200 Poisson's ratio 200 - Note: Performance may vary depending on the batch

Zirconia Partially Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics (Mg-PSZ) Any more information about advance materail, Click website ..... Read the full article
0 notes
Text
What’s the Difference Between Steel Pipe and Steel Tube

A hollow section of steel with a round cross-section has been manufactured in the United States since the early 1800s. It is made for the transportation of a wide variety of products, including fluids, gas, pellets, powders, and more. There are many uses for steel pipes, including underground transportation of water and gas, construction to protect electrical wires, and even the transport of liquids and gases. Steel pipes are not only strong, but they also can be lightweight. In addition to this, they are also used for making parts for automobiles, refrigeration units, heating and plumbing systems, flagpoles, and street lamps, just to name a few. This makes them ideal for bicycle frames and other products.
The most important dimension for a pipe is the outer diameter (OD) along with the wall thickness (WT). By subtracting the outer diameter from the wall thickness (WT), the inside diameter (ID) of a pipe is determined, and the amount of liquid it can hold. When we talk about pipe in our industry, we often refer to the pipe as a schedule (ID), such as 2 inches schedule 40 or 14 inches extra heavy. This is what the industry refers to as a pipe. For instance, we can use the walls or schedules below, including the standard (STD), and the XS/XH. The majority of pipe is sold in lengths of 21 or 42 feet, depending on the manufacturer.
What is Tube?
In engineering, a tube refers to hollow sections that are shaped like rounds, squares, rectangles, or ovals. The tubes are used for pressure equipment, mechanical applications, and instrumentation applications.
There are several raw materials used to make steel tubing, including iron, carbon, manganese, vanadium, and zirconium. Seamless tubing can also be welded, while welded tubing is a solid block of steel that is rolled into a round shape and pierced and stretched to its final length. The same thing is done to play dough when you roll it into a cylinder. If you have extra dough, push your finger through the middle and stretch it out to make it longer. It is produced in the same way, but the raw materials are hot and spinning, and everything is completely machine operated. A welded steel tubing, on the other hand, is made from coils of steel that are welded together. Initially, the coil is slit and rolled up into a round shape, then welded together at the ends. As a result, the tubing can either be simply cut to a certain length and used as round tubes, or it can be altered into other shapes such as square, rectangular, oval, etc. based on the location of the tubing.
It is common for buyers in our industry to refer to the item they are considering as an (OD) and a (WT) in inches or millimeters. The outer diameter (OD) and the wall thickness (WT) of the tube are indicated in inches or millimeters. Tubes can be purchased in a variety of wall thicknesses, such as 11 gauge, 1/4″, 3/8″, or 5/8″. They are available in lengths of 20, 24, 40, and 48 feet, but they can also be manufactured in custom lengths.
For more information visit
https://tronixalloys.com/whats-the-difference-between-steel-pipe-and-steel-tube/
#differencebetween #steel #pipe #steeltube #steelexporter #thesteelexporter #supplier
0 notes