#with his funky not-a-horse anatomy in motion
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text



various centaur au doodles :)
#trigun stampede#trigun#vash the stampede#nicholas d. wolfwood#meryl stryfe#vashwood#centaur au#centaur#andr0art#meryl is very stanced#nick is very unimpressed#vash is very worried they will start fighting#also vash being a hat thief#with his funky not-a-horse anatomy in motion#and an unnamed vashwood baby of unspecified origin#post canon vash in his single dad era :(#excuse me while i explode
577 notes
·
View notes
Text
horses? in MY westerns?
It’s exactly as likely as you think! That is, very likely! The genre wouldn’t exist without them, and I feel like people should talk about them more often, especially wrt fics and fic-writing! So, that’s exactly what I hope to do: give a little run-down of how these very strange dogs work, and how to make them seem a little more real in your transformative works.
DISCLAIMER: I’m an English rider who’s been riding English for almost ten years now! I don’t ride western, and I could count on one hand the amount of times I’ve been in a western saddle. Even so, the people in western flicks aren’t exactly competing in shows, and I think a lot of the basic principles carry through. If I get anything grievously wrong, though, feel free to correct me!
Long post below the cut:
PART ONE: ANATOMY
Both of the horses and of tack, anatomy is important for understanding how things work! Since I suppose people only really need to know the anatomy of a horse as it relates to the equipment placed on said horse, I’ll mention it as it comes up.
I. The saddle

Western saddles differ from English saddles in lots of ways, but the main difference between them is that western saddles are designed to be comfortable for the rider to be in for hours at a time. They have deep seats with a high cantle and pommel (back and front, respectively), which makes them easier to stay in than a flatter English saddle. That’s how people can stand to stay on horseback for those long trail rides, or days at a time spent in the saddle moving a herd across the desert. Saddles sit just behind the withers (above the highest point of the shoulder on a horse, that visible ‘bump’ after the neck ties into the back), usually with a saddle pad or blanket between the saddle and the horse’s back. The cinch, which is the strap that holds the saddle onto the horse, wraps around his barrel (essentially his belly and sides, the main barrel-shaped part of his body. Go figure.) just behind his front leg. Some horses also are fitted with a breast collar, which is a strap that attaches to the middle of the cinch and the front of the saddle through his front legs to keep the saddle from sliding back.
The horn on the front of a saddle might look like a tempting handhold while you’re on the horse, but it’s not meant for grabbing. The horn comes from the saddle’s purpose on cutting and reining horses, and is for tying roped cattle to. Grabbing it while riding is more liable to put you off-balance than anything, as you’re hunched forward and out of the stirrups.
Speaking of! The stirrups are the things that you put your feet in while you’re in the saddle, and they attach to the saddle with stirrup leathers. Western stirrups can’t be removed from the saddle like English stirrups can, but this is mostly because they’re a lot thicker than English stirrups, and combined with a high-heeled cowboy boot, it’s a lot harder for the rider’s foot to slip through the stirrup and get stuck, especially in the event of a fall. The stirrups are where a lot of the rider’s weight is while they’re riding, alongside their seat, and losing a stirrup can really throw you off-balance.
II. The bridle
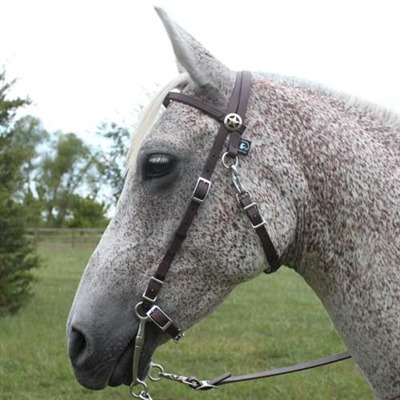

This would be the piece of tack on his head! Most western bridles don’t have nose bands (a piece of leather that wraps around a horse’s nose several inches above his nostrils) as they’re not really necessary for functionality, but most working styles do have throat latches, which is the piece of leather that goes around his cheeks, and a browband, which is the strap that goes in front of his ears, as both help keep the bridle more firmly in place. Both of these attach to the cheek straps, which run down his face lengthwise.
Honorary II.5 on this list is the bit, the piece of metal in the horse’s mouth that the reins attach to. In most of the westerns I’ve seen, most of the horses are wearing a Tom Thumb or some other kind of shank bit attached to split reins. Split reins are pretty much what they say on the tin: reins attached to either side of the bit but which do not connect with each other. This can give the rider more control, and also makes it real handy to just hop off a horse and tie one of his reins to a hitching post.
Now for the bit ipse.
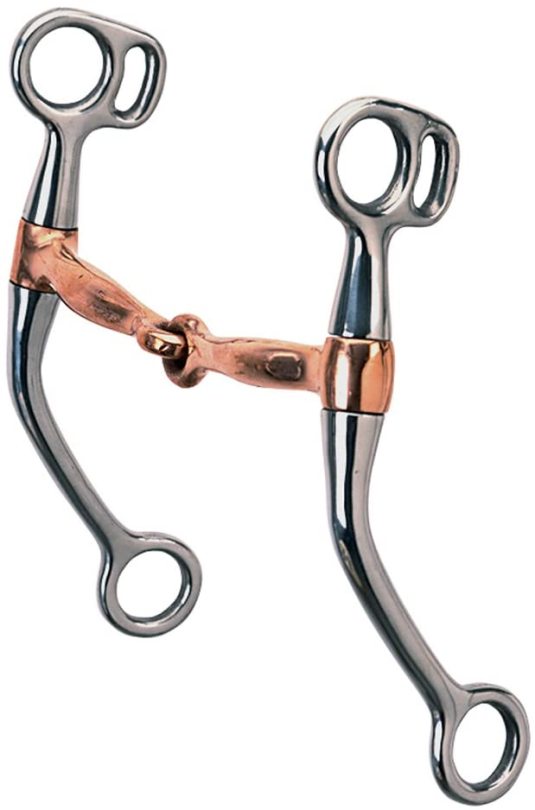
The above is what a modern Tom Thumb bit looks like. It’s a jointed piece of metal that goes inside a horse’s mouth, attached to a shank that’s anywhere from 5 to 7 inches long. I’m grouping all shank bits together here, since they all have basically the same effect: pressure at the poll (the top of a horse’s head behind his ears) and pressure on the mouth. Since the reins are attached to the bottom of the shank, the rider is given a significant amount of leverage when they pull on the reins; a general rule of thumb is that with a 5″ shank, every pound of pressure the rider puts on the reins is multiplied by three in the horse’s mouth. This lever motion puts pressure on his poll and his mouth, and when the rider pulls sharply, a lot of pressure on the corners of his mouth, and a twisting of the jointed part of the bit that makes it come into contact with the roof of a horse’s mouth. This can cause a horse to toss his head and gape his mouth, something that’s unfortunately seen in lots of westerns.
Shank bits like this can be incredibly harsh in the wrong hands, and can damage a horse’s mouth if they’re used too aggressively. Honestly, I feel bad for most of the horses in these films, where they’re under an inexperienced rider who often saws away at their mouth with a harsh bit like this. If you’re writing a story, remember that for most horses, it isn’t necessary to haul back on the reins to get a horse, even a hot horse, to slow or stop.
III: miscellaneous
Shoes: shoeing a horse makes him better suited to hard surfaces and long-term work. Any horse expected to be used for work would be shod. Horses can throw (somehow get rid of, don’t ask me how, little buggers. . .) shoes to varying degrees of trauma to the hoof, and while it should be fixed as soon as possible, it’s rarely too serious.
Spurs: technically a piece of apparel for the rider, but since everything else a rider wears is kind of a given for any self-respecting cowboy, I’ll chat about spurs. The stereotypical janglin’ cowboy spur is a rowel spur, named after that funky star-shaped thing that spins. Spurs are used to help encourage forward motion, and trained riders can ride a horse in rowels without any harm done to the horse. Even so, overuse or misuse can lead to damage and bleeding on a horse’s side, and deaden him to your legs.
PART TWO: ACTUALLY RIDING A HORSE
Unsurprisingly, riding a horse for a long time can be very tiring. Even in a saddle designed for comfort, someone unaccustomed to riding for long distances will find their back and core hurting something fierce. Worst of all, though, would be the strain it would put on a rider’s legs. Riding for extended periods of time makes your thighs ache, and can rub you pretty raw in the inner thighs and knees even with proper trousers. It can also have you walking bowlegged, which is pretty funny to watch.
Stability when riding starts from the bottom up. A good rider has a steady seat and good legs that grip the horse without pinching at the knees or the ankles (remember those big spurs you’re wearing, cowboy? ouch!). They stay with the motion of the horse, which can be difficult when you're just starting out. Beginner riders might find themselves too tense and easily thrown off-balance, since they're not working with the horse. Though western saddles make the act of staying on easier, developing a good seat and the muscles necessary to stay balanced on horseback can take a while.
In western riding especially, the reins don’t need to be taut while you’re riding. The horse isn’t responding to aids from your hand, he’s responding to your seat and your legs. The reins are helpful to direct and to slow him, but they’re not the star attraction. A horse moves forward in response to pressure from the lower leg, and if he doesn’t listen to that, a rider can angle their foot to press the spur into his side, removing the spur and the pressure as soon as the horse responds to the aid. To slow, a rider settles into the saddle and applies gentle pressure on the reins, escalating as needed, but again, removing the pressure as soon as a horse responds. Anything else is more energy expended than necessary on the rider’s part, and it’s also just kind of mean.
In addition, though I hope I don’t actually have to say this, flicking the reins will not make a single horse on god’s green earth go forward. Why is this a thing.
SO, LIKE, HOW LONG CAN I KEEP DOING THIS?
Mileage varies a lot as to how long a horse can run before he gets tired. A good average is about twenty miles a day if you’re planning on going long distances, which obviously can also vary depending on an individual horse or rider’s endurance. A horse can only gallop (their fastest, four-beat gait--think racehorses) for a mile or two before he’s exhausted, but he can canter (a three-beat gait that’s generally around 10 or 12 mph) for a while longer. Quarter horses, which I assume most of the horses in these movies are meant to be since they're the standard horse for working cattle and ranching in the U.S., aren't built for running long distances; they're significantly better at running short sprints. If a rider wants to cover a long distance in a short amount of time, it behooves them to switch horses along the way so he’s never riding a tired horse, and can run the horse they do have harder while they’ve got him.
An important thing to remember is that a horse should always have a chance to walk for a bit after he’s been working hard. Walking is more effective to cool a horse than just standing still is, as it allows the blood flowing through their legs to cool down. As well, it’s generally a bad idea to let a horse just drink his fill after he’s been working. Ideally, he gets smaller amounts of water over time.
A lot of these examples of less than stellar horsemanship might seem a bit like splitting hairs in fiction, but I think they can serve lots of different purposes. Does your villain have a horse whose skin is rubbed raw behind the cinch since he never lets up on his spurs? Does your hero have to make a daring escape, only to find his horse sick from exhaustion? Horses are a pivotal part of many stories, and there's lots of aspects to them as creatures and as methods of transportation that can be used in many different ways!
BONUS PART THREE: COLORS
Horses of every color show up in westerns, mostly because quarter horses can come in just about every color! Here’s a brief rundown of what different colors are called in horses, so you’ve got some words better than ‘brown’ to work with.
Chestnut: also called ‘sorrel’ when talking about western horses, a chestnut is a horse whose mane and tail are the same color brown as their body. They can range from light, cool browns to deep red browns, but the main thing is that their mane is the same color as their body.
Bay: a bay horse can have any of the same colors as a chestnut, but his points (that is, his ears, nose, mane, tail, and all four feet) are black. A bay horse can still have white markings on his feet, as long as all of his other points are black.
Palomino: a classic western horse, a palomino is a golden or yellow horse with a white mane and tail. A chocolate palomino has a body darker than a normal palomino's, but maintains a white mane and tail.
White/gray: while many horses may have white hair, very few are truly white. A white horse has white hair and pink skin, while a gray horse has white hair and black or brown skin. Most ‘white’ horses are, technically, gray. Generally, it’s safer to refer to a horse as a gray. Horses will also become a darker gray as they age, even if they’re born white.
Buckskin: A buckskin horse has tan or gold hair similar to a palomino, but black points like a bay. Similarly, a dun horse also has a tan coat and black points, but also has a black stripe called a “dorsal” stripe down his spine, a remnant of ancient breeds of horse.
Roan: a roan horse has a coat that’s equal parts white hairs and colored hairs, and solid-colored points. They can have a blueish or blush-colored look, depending on what colors are mixed in their coats.
HEAD AND LEG MARKINGS
Stars and snips: a star is a white mark on a horse’s forehead, and a snip is a white mark on his nose.
Stripe: a stripe is, rather self-evidently, a white stripe that runs from a horse’s forehead to his nose. They’re generally fairly thin, because when they’re thick they’re called a
Blaze: a blaze is a thick stripe of white down a horse’s face that does not cover his eyes.
Bald face: a horse with a bald face has white on his face that does cover his eyes, and usually most of his nose.
Socks/stockings: socks are white marks on a horse’s leg that only goes about to his fetlock, the first joint above his hoof. Stockings are white markings that come up between his fetlocks and his knees on his front legs and his hocks on his back legs.
IN FINE
Wow, that was longer than I thought it would be! Hopefully it helped someone.
I thought about talking about feed on here, but honestly, I have no idea what feed looked like in those days, and this post is long enough without advice that amounts to “probably they got lots of grazing on what you can find in the desert”, so. . .
Most of the information here is pretty basic, but there’s lots of resources online for further research!
Happy riding and happy writing!
#writing#writing ref#horses#western#oh god im sorry in advance#spaghetti western#reference#the good the bad and the ugly
18 notes
·
View notes