#wireless temperature logger
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Reliable Data Logger Solutions at Shop Testo
If you're looking for trusted and efficient data logger solutions, Shop Testo is your go-to destination. They have a wide range of devices designed to simplify your data recording needs. Whether you're monitoring temperature, humidity, or other environmental conditions, their products ensure precision and reliability.
Why Choose Data Logger Solutions?
Data loggers are important tools for recording and monitoring environmental data over time. They are widely used in industries like pharmaceuticals, food storage, logistics, and research. At Shop Testo, you’ll find high-quality humidity data loggers and temperature data loggers to meet your specific needs.

Explore Temperature and Humidity Data Loggers
Temperature Data Loggers: These devices are perfect for keeping track of temperature changes in sensitive environments like cold storage rooms or transportation units. They ensure compliance with safety standards and protect your goods from damage.
Humidity Data Loggers: Maintaining the right humidity levels is crucial for industries like healthcare and manufacturing. Humidity data loggers accurately monitor moisture levels to ensure your products remain in optimal condition.
Benefits of Shopping at Shop Testo
Top-Quality Products: All data loggers at Shop Testo are designed to deliver precise results and are of top notch quality.
User-Friendly Features: These devices are easy to operate and provide accurate data collection and analysis.
Whether you need a standalone data logger or an advanced system for detailed monitoring, Shop Testo has a solution for you.
Start optimizing your monitoring processes today with Shop Testo's reliable humidity data loggers and temperature data loggers. Ensure accuracy, safety, and peace of mind with every use!
#testo data logger#Wireless data loggers#humidity data loggers#data loggers#temperature data loggers
0 notes
Text
Temperature Data Logger Market: Growth Driven by Cold Chain Expansion and Regulatory Compliance Demands
The temperature data logger market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by a confluence of technological advancements, increasing regulatory standards, and rising demand across diverse industry verticals. A temperature data logger is a compact, self-contained device used to record temperature readings over time, which can then be analyzed for a variety of applications. These tools are crucial in ensuring product quality, maintaining regulatory compliance, and optimizing supply chain operations.

1. Growing Demand for Cold Chain Monitoring
One of the primary drivers of the temperature data logger market is the expanding global cold chain logistics sector. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and chemicals require precise temperature control during storage and transportation to ensure product efficacy and safety. Vaccines, in particular, need to be maintained within strict temperature thresholds. The COVID-19 pandemic further amplified this demand as global vaccine distribution relied heavily on robust cold chain systems, accelerating the adoption of temperature monitoring solutions like data loggers.
2. Regulatory Compliance and Quality Assurance
Governments and industry regulatory bodies worldwide have established stringent guidelines for temperature-sensitive goods. Compliance with standards such as Good Distribution Practice (GDP), Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), and the U.S. FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11 necessitates the use of temperature data logging equipment. These regulations ensure that proper storage conditions are met and that any temperature excursions are documented and analyzed. The growing pressure to meet these regulatory requirements is a strong driver for market growth.
3. Advancements in IoT and Wireless Technology
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and wireless technologies has revolutionized the temperature data logger landscape. Modern loggers now feature real-time monitoring, wireless data transmission, cloud storage, and mobile app integration. These innovations provide greater visibility and control over environmental conditions, enabling proactive responses to potential issues. The convenience and efficiency offered by connected devices have attracted a broader range of users, further propelling market expansion.
4. Increasing Use in Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
The healthcare and pharmaceutical industries are among the largest users of temperature data loggers. These devices are used in hospitals, laboratories, and during the transportation of temperature-sensitive drugs and biological samples. The global rise in personalized medicine, biotechnology products, and biologics—many of which require strict temperature control—has contributed to increased demand. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to grow and innovate, so too does the need for reliable monitoring tools.
5. Rising Adoption in the Food and Beverage Sector
Ensuring food safety and maintaining product quality from farm to fork is critical in the food and beverage industry. Temperature data loggers are used extensively during food processing, packaging, storage, and distribution to ensure perishable goods remain within required temperature ranges. Consumer awareness and regulatory scrutiny regarding food safety have also heightened demand for temperature monitoring solutions, especially as global trade of perishable goods increases.
6. Cost Reduction and Product Innovation
Technological developments have enabled manufacturers to produce more cost-effective and compact temperature data loggers without compromising on features. Today’s models offer improved battery life, enhanced accuracy, increased memory capacity, and user-friendly interfaces. This has made them accessible to a wider range of businesses, including small and medium enterprises. The competitive landscape has also led to product differentiation, with some companies offering specialized loggers for unique applications, such as ultra-low temperature logging for cryogenic environments.
7. Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability Goals
Temperature data loggers are also gaining traction in environmental monitoring, agriculture, and climate research. As climate change continues to impact weather patterns and ecological systems, there is a growing need for accurate and long-term temperature data. Additionally, companies focused on sustainability are using these devices to monitor energy efficiency in facilities, ensuring HVAC systems are optimized and reducing overall carbon footprints.
8. Expansion of E-commerce and Global Trade
The global e-commerce boom has driven a need for enhanced logistics and delivery infrastructure. Temperature-sensitive products, including gourmet foods, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals, are increasingly sold online and shipped across long distances. Data loggers play a crucial role in preserving product integrity during last-mile delivery. As cross-border e-commerce continues to expand, especially in emerging markets, so does the need for reliable temperature monitoring.
Conclusion
The temperature data logger market is poised for robust growth, fueled by the convergence of technological innovation, regulatory demands, and the need for precision in modern logistics. As industries become more reliant on data-driven decision-making and real-time monitoring, temperature data loggers are no longer a luxury but a necessity. Whether for ensuring the safety of a life-saving drug or maintaining the freshness of perishable goods, these devices are playing a pivotal role in modern supply chain and quality assurance systems. Continued investment in R&D and evolving customer needs are expected to further drive market innovation and adoption in the years to come.
0 notes
Text
Cold Chain Monitoring Market Analysis: Key Players and Competitive Landscape
Rising Demand for Temperature-Sensitive Logistics Drives Growth in the Cold Chain Monitoring Market.
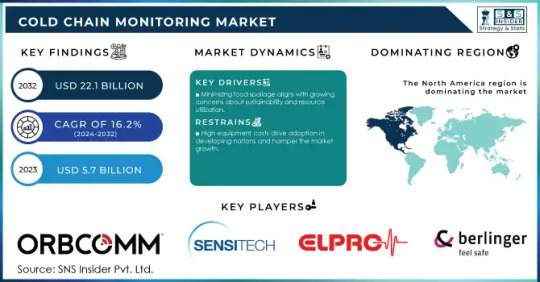
The Cold Chain Monitoring Market Size was USD 5.7 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 22.1 Billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 16.2% over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
The Cold Chain Monitoring Market is driven by the increasing need for temperature-sensitive logistics solutions across industries such as pharmaceuticals, food & beverages, and chemicals. Cold chain monitoring systems ensure that perishable goods and temperature-sensitive products maintain their required storage conditions throughout the supply chain. The rising demand for biopharmaceuticals, vaccines, and fresh food products, coupled with stringent regulations on storage and transportation, is fueling the adoption of advanced cold chain monitoring solutions.
Key Players
ORBCOMM (US) – (IoT-based cold chain monitoring solutions, Fleet Management Systems)
Sensitech (US) – (TempTale Data Loggers, Cold Chain Monitoring Software)
Elpro-buchs (Switzerland) – (ELPRO Monitoring Solutions, e-Transcript System)
Berlinger & Co. (Switzerland) – (ThermoTrack Temperature Monitoring, ActiveSense Monitoring System)
Monnit (US) – (Monnit Wireless Sensors, Monnit Cloud Platform)
Controlant (Iceland) – (Controlant Smart Cold Chain, Real-time Monitoring Solutions)
Lineage Logistics Holding – (Cold Storage Solutions, Lineage Link Digital Platform)
Tagbox – (Cold Chain IoT Sensors, Tagbox Data Analytics Platform)
DAIKIN Industries – (Refrigeration Solutions, Remote Monitoring Systems)
Savi Technology – (SaviTrack RFID Solutions, SaviSense Sensor Platform)
Future Scope
The Cold Chain Monitoring Market is set for substantial expansion as supply chain digitization, IoT-based tracking systems, and AI-driven predictive analytics enhance real-time monitoring capabilities. Government regulations and quality control mandates for pharmaceutical and food safety are pushing businesses to integrate automated and cloud-based monitoring systems. Innovations in blockchain technology for supply chain transparency and the integration of smart sensors with predictive maintenance capabilities are expected to revolutionize cold chain management, reducing spoilage and ensuring compliance.
Emerging Trends
The industry is shifting toward real-time and AI-powered cold chain monitoring solutions, ensuring greater accuracy and efficiency in tracking temperature-sensitive shipments. The demand for wireless and cloud-based monitoring systems is rising, offering 24/7 remote access to temperature data and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, blockchain technology is being explored to enhance supply chain transparency and prevent counterfeiting in pharmaceuticals. The rise of automated alert systems, GPS tracking, and energy-efficient refrigeration technologies is also contributing to market growth.
Key Points
Rising demand for temperature-sensitive logistics in pharmaceuticals and food industries.
Increased adoption of IoT, AI, and blockchain for real-time supply chain monitoring.
Stringent regulatory requirements driving investments in advanced cold chain technologies.
Growing use of cloud-based and wireless temperature monitoring systems.
Expansion of automated alert systems and GPS tracking for improved shipment security.
Conclusion
The Cold Chain Monitoring Market is poised for significant growth, fueled by technological advancements, regulatory compliance requirements, and increasing demand for perishable goods logistics. As smart monitoring solutions, blockchain integration, and predictive analytics continue to evolve, the industry is set to enhance supply chain efficiency, reduce product wastage, and ensure the safe delivery of temperature-sensitive goods worldwide.
Read Full Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/cold-chain-monitoring-market-1974
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave — Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1–315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Cold Chain Monitoring Market#Cold Chain Monitoring Market Size#Cold Chain Monitoring Market Share#Cold Chain Monitoring Market Report#Cold Chain Monitoring Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
USB Temperature Data Logger Market Future Trends: Growth, Innovation, and Emerging Industry Opportunities Worldwide
The USB temperature data logger market is undergoing significant transformation due to technological advancements, increasing demand for real-time monitoring, and regulatory requirements across various industries. These devices play a crucial role in maintaining temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals. With the rising adoption of IoT-enabled solutions and cloud connectivity, the market is set for substantial growth.

Market Growth Drivers1. Rising Demand in Pharmaceutical and Healthcare IndustryThe pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors heavily rely on USB temperature data loggers for maintaining the integrity of vaccines, drugs, and other temperature-sensitive products. The global COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of advanced monitoring devices to ensure proper storage conditions.
Stringent Government RegulationsGovernments and regulatory bodies worldwide have imposed strict guidelines on temperature monitoring to ensure product safety and quality. Compliance with Good Distribution Practice (GDP) and Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) is boosting the demand for accurate and reliable data logging solutions.
Advancements in IoT and Cloud IntegrationModern USB temperature data loggers are now integrated with IoT and cloud-based platforms, allowing real-time data monitoring, automatic alerts, and remote access. These technological enhancements improve efficiency and reduce the risk of data loss. Emerging Market Trends1. Wireless and Bluetooth-Enabled Data LoggersThe integration of wireless connectivity features, including Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, is becoming a dominant trend. These loggers enable seamless data transfer and remote monitoring, reducing manual intervention and enhancing operational efficiency.
Increased Adoption in Cold Chain LogisticsCold chain logistics require precise temperature monitoring for the transportation and storage of perishable goods. The expansion of global supply chains, especially in the food and pharmaceutical industries, is driving the demand for USB temperature data loggers with real-time tracking capabilities.
AI and Machine Learning for Predictive AnalyticsArtificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being integrated into data loggers to provide predictive analytics. These smart devices can analyze historical data, predict temperature deviations, and suggest corrective actions, thereby improving decision-making. Challenges in the MarketDespite strong growth potential, the USB temperature data logger market faces several challenges: High Initial Costs: Advanced models with IoT and AI features come at a premium price. Data Security Concerns: Cloud-based systems require robust cybersecurity measures to prevent unauthorized access. Limited Awareness in Developing Markets: Many businesses in emerging economies are still unaware of the benefits of real-time data logging. Future Outlook and OpportunitiesThe future of the USB temperature data logger market looks promising with continued advancements in technology. The introduction of disposable loggers, multi-use devices, and longer battery life solutions will further enhance market penetration. Companies are focusing on providing more user-friendly and cost-effective solutions to attract a wider customer base. Moreover, as the demand for automation and precision increases, businesses will increasingly adopt data loggers with real-time alerts and cloud connectivity. This shift will further streamline operations and ensure compliance with stringent industry standards. Conclusion The USB temperature data logger market is poised for significant growth, driven by innovations in IoT, AI, and cloud computing. As industries emphasize better compliance, efficiency, and real-time monitoring, the demand for these devices will continue to rise. Companies investing in smarter, more connected, and cost-effective solutions will emerge as leaders in the evolving landscape of temperature monitoring technology.
0 notes
Text
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights Technological Advancements Driving Market Growth
The temperature data logger market is witnessing rapid growth due to increased demand for real-time temperature monitoring and enhanced product safety across various industries. These devices play a critical role in ensuring the integrity of temperature-sensitive products, especially in pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and logistics. As technological advancements continue to shape this sector, the market is evolving to meet the increasing need for precision, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. The global temperature data logger market is expected to expand significantly, driven by advancements in sensor technology, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), and the increasing need for traceability in supply chains.

Temperature data loggers are devices that continuously measure and record temperature over time. These devices are used to monitor products in transit or storage, ensuring that they remain within optimal temperature ranges. This technology is vital for maintaining the safety and quality of temperature-sensitive goods, such as pharmaceuticals, vaccines, food, and beverages.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Technological Advancements and Innovations
Technological innovation is a key driver of growth in the temperature data logger market. Recent advancements in sensor technology, connectivity, and cloud computing have enhanced the capabilities of temperature data loggers. Modern loggers feature more accurate sensors, longer battery life, and wireless communication, enabling real-time monitoring and alert systems. These innovations make it easier for industries to ensure compliance with temperature-sensitive product regulations and streamline operations.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: The Role of IoT in Temperature Monitoring
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into temperature data loggers is transforming the market. IoT-enabled devices allow for remote temperature monitoring, enabling businesses to access data from anywhere in real time. With cloud-based platforms, companies can track temperature fluctuations, receive alerts, and generate detailed reports, improving operational efficiency and reducing the risk of product spoilage. This shift toward IoT-enabled solutions is expected to drive the market's expansion, particularly in industries requiring constant temperature monitoring, such as pharmaceuticals and food.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Key Industries Driving Growth
Several industries are fueling the demand for temperature data loggers. The pharmaceutical sector is one of the biggest contributors, as it requires strict temperature control for the storage and transportation of drugs, particularly biologics and vaccines. The food and beverage industry also drives growth, as temperature monitoring is crucial to ensure food safety and prevent spoilage. Additionally, the logistics and transportation sectors require temperature data loggers to monitor shipments, especially for perishable goods. The increasing focus on cold chain logistics is expected to further propel the market.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Wireless Solutions Gaining Popularity
Wireless temperature data loggers are becoming increasingly popular due to their ease of use and ability to connect to cloud platforms. Unlike traditional wired systems, wireless loggers do not require physical connections, making them more flexible and scalable. These devices can be deployed across large storage facilities or transportation networks, enabling companies to monitor temperatures remotely and receive instant alerts when temperature thresholds are exceeded. As wireless solutions continue to evolve, they are expected to play a pivotal role in the growth of the market.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Expanding Adoption in Emerging Markets
As industries in emerging economies continue to grow, the adoption of temperature data loggers is expanding. Countries in regions like Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East are witnessing increased demand for temperature monitoring solutions, driven by growing pharmaceutical, food, and logistics sectors. Emerging markets are experiencing significant investments in cold chain logistics, healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory compliance, further fueling the adoption of temperature data loggers. This trend is expected to create new opportunities for market players in these regions.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in driving the temperature data logger market. In industries like pharmaceuticals and food, stringent regulations require companies to ensure that products are stored and transported under the correct temperature conditions. Non-compliance can lead to product spoilage, safety risks, and legal consequences. As regulations continue to tighten globally, temperature data loggers are becoming essential tools for ensuring compliance and meeting industry standards. This focus on regulatory compliance will continue to influence market growth.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite the promising growth of the temperature data logger market, several challenges remain. High initial costs, particularly for advanced temperature monitoring systems, may deter small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) from adopting these solutions. Additionally, limited access to reliable internet connectivity in remote areas may hinder the use of IoT-enabled devices in some regions. Companies will need to address these barriers to adoption in order to unlock the full potential of the market.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Advancements in Sensor Accuracy
Improved sensor accuracy is a key trend in the temperature data logger market. Modern temperature data loggers are equipped with high-precision sensors that provide real-time and accurate temperature measurements. This accuracy is particularly important in industries such as pharmaceuticals, where even small temperature fluctuations can compromise product quality. Advancements in sensor technology are expected to drive further innovation in the market, improving the reliability and performance of temperature monitoring systems.
Temperature Data Logger Market Insights: Future Outlook and Market Projections
The future of the temperature data logger market looks promising, with strong growth projected across various industries. As technology continues to improve, the demand for more sophisticated temperature monitoring solutions will rise. The adoption of IoT-enabled devices, wireless solutions, and cloud-based platforms will continue to shape the market, providing businesses with more efficient, cost-effective ways to ensure the safety and quality of their products. With increasing regulatory pressure and the need for enhanced supply chain visibility, the temperature data logger market is poised for continued expansion.
Conclusion
The temperature data logger market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovations, increasing demand for real-time temperature monitoring, and the need for regulatory compliance across various industries. As advancements in sensor technology, IoT integration, and wireless solutions continue to reshape the market, businesses in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food, and logistics are increasingly adopting temperature data loggers to ensure product safety and quality. While challenges such as high costs and limited connectivity persist, the market's growth prospects remain strong, with significant opportunities for innovation and expansion in emerging markets.
#Temperature Data Logger Market#Temperature Data Logger Market trends#Temperature Data Logger#Temperature Data Logger measures#Temperature Data#Temperature
0 notes
Text
Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market Outlook, Competitive Strategies And Forecast
The global real-time monitoring solutions for cold chain market size was valued at USD 12,427.8 million in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 23.1% from 2024 to 2030. The rising demand for global real-time monitoring solutions in the cold chain market is driven by the need for greater control and efficiency in temperature-sensitive supply chains, particularly in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and chemicals. With stricter regulations on product safety, companies are increasingly adopting these solutions to ensure compliance with international standards.
Additionally, the growing trend of online retail, particularly for groceries and pharmaceuticals, is amplifying the need for precise cold chain management. Companies delivering fresh food, dairy, frozen products, and medicines must guarantee that their goods remain within ideal temperature conditions from dispatch to doorstep. Real-time monitoring solutions allow companies to provide end-to-end visibility into cold chain logistics, helping mitigate the risks of spoilage, reducing waste, and enhancing customer satisfaction through reliable delivery of fresh goods.
The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) devices in cold chain logistics is further driving demand for real-time monitoring solutions. IoT sensors placed within storage units and transport vehicles can continuously track environmental conditions and transmit data in real-time to centralized monitoring platforms. This ensures uninterrupted monitoring and reporting, providing companies with the ability to act immediately if parameters deviate from safe levels. The advent of AI and machine learning is also helping companies predict potential risks in the cold chain, optimize routes, and manage fleet operations more efficiently.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market
Key Real-time Monitoring Solutions for Cold Chain Company Insights
Some of the key companies operating in the market include Carrier (Sensitech), among others.
• Carrier (Sensitech) is a prominent player in real-time monitoring solutions for cold chain logistics, specializing in temperature monitoring and data logging technologies. Sensitech is a subsidiary of Carrier Global Corporation, a leading global provider of heating, ventilation, air conditioning, refrigeration, and fire and security solutions. It offers a range of temperature monitoring solutions designed to ensure the integrity of temperature-sensitive products throughout the cold chain. Their products include data loggers, wireless monitoring systems, and integrated software platforms that provide real-time tracking and data management.
• Accent Advanced Systems, SLU is a technology company specializing in advanced solutions for real-time monitoring in various industries, including cold chain logistics. Their offerings include advanced monitoring systems that track temperature and humidity, utilizing Internet of Things (IoT) technology for seamless data collection and transmission. These solutions provide stakeholders with real-time access to critical environmental data and alerts, supported by analytics software that helps optimize logistics operations and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Recent Developments
• In August 2024, Carrier (Sensitech) announced that it had completed the acquisition of Berlinger & Co. AG, a provider of temperature monitoring solutions for the cold chain logistics industry. This strategic acquisition aims to enhance Sensitech's product offerings and strengthen its position in the pharmaceutical and food sectors. This move aligns with Sensitech's commitment to delivering comprehensive solutions that meet the evolving demands of customers in global supply chains.
• In June 2024, ELPRO-BUCHS AG and Cold Chain Technologies announced a partnership to enhance cold chain monitoring solutions. This collaboration aims to integrate ELPRO's advanced temperature monitoring technology with Cold Chain Technologies' logistics expertise. Together, they will provide comprehensive solutions for temperature-sensitive products, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and maintaining product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Global Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2017 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global real-time monitoring solutions for cold chain market report based on component, application, and region:
Component Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2030)
• Hardware
o Sensors
o RFID Devices
o Telematics
o Networking Devices
o Others
• Software
o On-premise
o Cloud
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2030)
o Food & Beverages
o Pharmaceuticals
o Others
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2030)
• North America
o U.S.
o Canada
o Mexico
• Europe
o UK
o Germany
o France
• Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Australia
• Latin America
o Brazil
• Middle East and Africa (MEA)
o KSA
o UAE
o South Africa
Order a free sample PDF of the Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
#Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market#Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market Size#Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market Share#Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market Analysis#Real-time Monitoring Solutions For Cold Chain Market Growth
0 notes
Text
Remote temperature monitoring devices are crucial for maintaining cold chain integrity. Key types include data loggers, wireless temperature sensors, and probe thermometers, each offering unique benefits like real-time monitoring and precise temperature readings. Huse Live provides advanced solutions to optimize cold chain management and ensure product safety.
0 notes
Text
Accurate Monitoring with Temperature Data Loggers
Ensure precise temperature tracking with advanced Temperature Data Loggers, designed for reliability and efficiency. Ideal for industries requiring accurate environmental monitoring, these devices provide seamless data recording, ensuring compliance and quality control in every application.
0 notes
Text

Best VLSI Projects for Final Year Students
Here are some great VLSI project ideas for final-year students:
1. Image Processing System on FPGA: Algorithm, such as edge detection or image filtering should be performed through the usage of FPGAs for optimal performance.
2. Low-Power SRAM Design: Design and simulate a low-power Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) cell, targetting leakage and dynamic power dissipation.
3. Digital Signal Processor (DSP) Design: Design an example of a DSP that will allow a specific signal to be filtered or, for instance, undergo FFT.
4. Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Protocol Implementation: Devise a VLSI based sensor node for wireless communication that will support protocols used in data transmission.
5. Reconfigurable Hardware Architecture: It is necessary to elaborate a box which is able to evolve in order to support several applications: in this context, it is possible to try to reconfigure parts of the hardware during the runtime according to the specific needs of the client application.
6. Cryptographic Hardware Accelerator: Propose and design a device for which you could use cryptographic algorithms or primitives including AES or RSA where optimization of both speed optimization and security is important.
7. System-on-Chip (SoC) Design: Selected h/w architects use Verilog or VHDL to design a including microcontroller, memory and other peripherals.
8. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) on FPGA: Devise a mini ANN for image recognition and other related work and optimally use the features of parallel processing provisioned by FPGAs.9. Automated VLSI Testing Tool: Design a testing and validation software system that has reduced time and eliminated errors in conducting tests of VLSI designs (Very Large Scale Integration).
10. Temperature Sensor with Data Logger: It will be a VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) chip for measuring temperature and recording data, with the capability to display the data on a PC or a mobile connection.
All these project proposals present prospects to learn diverse aspects of VLSI design and implementation in addition to enhancing creativity. Choose one that you are interested in and which you can afford to do!
#vlsi#finalyear#verylargescaleintegration#VLSIDesign#engineeringstudents#studentsprojects#takeoffedugroup#takeoffprojects
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Data Acquisition Equipment: Key Features and Benefits
Data acquisition equipment is a critical component in various industries, enabling the collection, measurement, and analysis of data from physical systems. Whether you’re in engineering, manufacturing, or scientific research, understanding how to select and use the right data acquisition system can significantly impact the quality and accuracy of your work. This blog will explore the essential features, benefits, and considerations when choosing Data Acquisition Equipment.
What is Data Acquisition Equipment?
Data acquisition (DAQ) equipment is used to gather information from physical phenomena and convert it into a digital format that can be analyzed by computers. This equipment typically includes sensors, data loggers, and software to capture and process data from various sources like temperature, pressure, voltage, or sound.
Essential Features to Look For
Sampling Rate
Importance: The sampling rate determines how frequently data is collected. A higher sampling rate allows for more detailed data but requires more processing power and storage.
Tip: Match the sampling rate to your application’s requirements. For high-speed processes, you’ll need a higher sampling rate.
Resolution
Importance: Resolution refers to the precision of the measurements. Higher resolution provides more detailed data, which is crucial for applications requiring fine measurements.
Tip: Choose equipment with the highest resolution that fits your budget to ensure the accuracy of your data.
Input Channels
Importance: The number of input channels determines how many signals can be measured simultaneously. This is important for complex systems with multiple data points.
Tip: Select equipment with enough input channels to handle your current and future needs.
Connectivity
Importance: Modern DAQ systems often need to interface with various devices and networks. USB, Ethernet, and wireless options offer flexibility in data transfer.
Tip: Ensure your equipment supports the connectivity options you need for seamless integration into your workflow.
Software Compatibility
Importance: The software that comes with your DAQ system plays a crucial role in data analysis. It should be user-friendly and compatible with your existing systems.
Tip: Look for software that offers robust analysis tools and is compatible with popular operating systems and programming environments.
Portability
Importance: For fieldwork or on-site testing, portable DAQ systems are invaluable. They allow for data collection in remote or challenging environments.
Tip: Consider battery life, weight, and durability when choosing a portable system.
Benefits of Using Data Acquisition Equipment
Enhanced Data Accuracy
Data acquisition systems offer high levels of precision, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving the reliability of your analysis.
Real-Time Monitoring
Many DAQ systems provide real-time data monitoring, enabling instant decision-making and troubleshooting.
Versatility Across Applications
From automotive testing to environmental monitoring, DAQ systems are versatile tools that can be adapted to various industries and applications.
Data Integration and Analysis
DAQ systems often come with advanced software that allows for seamless data integration and analysis, making it easier to interpret complex data sets.
Cost-Efficiency
Investing in the right DAQ equipment can lead to long-term cost savings by reducing the need for repeated testing and improving process efficiency.
Choosing the Right Data Acquisition Equipment
When selecting data acquisition equipment, consider the following:
Application Requirements
Define what you need the system to measure and the conditions under which it will operate. This will guide you in choosing the right specifications.
Budget Constraints
While higher-end systems offer more features, ensure that the equipment you choose fits within your budget while meeting your essential requirements.
Vendor Support
Work with reputable vendors who offer reliable support, as setting up and maintaining DAQ systems can be complex.
Scalability
Consider future needs. Investing in a scalable system allows you to expand your data acquisition capabilities without needing a complete overhaul.
Conclusion
Data acquisition equipment is a cornerstone of modern research and industrial processes. By understanding the key features and benefits, you can make informed decisions that enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of your data collection efforts. Whether you’re working in a lab, a factory, or out in the field, the right DAQ system can be a powerful tool in achieving your goals.
0 notes
Text

Testo Data Loggers are advanced monitoring devices designed to record critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels across diverse applications. Whether dealing with extreme temperature conditions or ambient environments, these devices ensure accurate and reliable data collection. Ideal for industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and logistics, Testo Data Loggers help maintain compliance with regulatory standards, ensuring optimal storage and transport conditions for sensitive goods.
#testo data logger#testo dataloggers#Data logger solutions#Wireless data loggers#humidity data loggers#Industrial data logging systems#data loggers#data loggers UAE#temperature data loggers
0 notes
Text
The Amazing World of Sensor Detectors are devices that detect and respond

What are Detectors? Detectors are devices that detect and respond to some type of input from the physical environment. The specific input could be light, heat, motion, moisture, pressure, or any other physical phenomenon that can be measured. By converting the input to an electronic signal, detectors enable monitoring and automating real-world processes.
Types of Common Detectors There are many different types of detectors based on the specific input they are designed to detect. Here are some of the most common detectors used today:
Light Detectors Light detectors detect illumination levels and are used commonly in automatic lighting controls, camera auto-focus systems, and digital clocks that glow in the dark. Common light detectors include photo resistors, photo diodes, and photo transistors that change their electrical properties depending on the amount of light striking their active surface.
Temperature Sensor Temperature detectors measure ambient or surface temperature and often output an analog voltage that varies with temperature. Sensor Thermistors and thermocouples are widely used temperature detectors. Thermocouples generate a small voltage proportional to the temperature difference between two junctions of dissimilar metals. Thermistors change their electrical resistance with temperature in a known manner. Temperature detectors find applications in thermostats, medical equipment, heating/cooling systems and more.
Motion Detectors Motion detectors detect movement of objects and people. Passive infrared (PIR) motion detectors are commonly seen in outdoor lighting and security systems. Ultrasonic motion detectors detect motion by sensing changes in ultrasonic patterns. Optical mouse detectors also fall into this category as they sense motion and movement. Industrial robots often use motion detectors to detect position and speed.
Pressure Detectors Pressure detectors measure the force per unit area applied on their surface. Strain gauge pressure detectors change their electrical resistance with the amount of applied pressure. They are used to measure everything from tire pressure to blood pressure. Capacitive pressure detectors use capacitance changes to sense pressure. Piezoresistive pressure detectors alter their electrical resistance when strained under pressure.
Proximity Detectors Proximity detectors indicate if an object is near or within a given distance range without physically touching it. Common proximity detector technologies include ultrasonic, infrared, inductive loops, and laser optical. They find widespread use in industrial machine automation, assembly lines, and object detection applications.
Advancing Micro-Detector Technology As microchip fabrication technology advances, detectors are becoming smaller, cheaper, and more powerful. Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) allow detector features to be integrated directly onto silicon chips alongside digital circuits. This opens up many new possibilities for pervasive sensing across diverse industries.
Tiny environmental detectors based on MEMS accelerometers and gyroscopes enable motion-activated user interfaces and electronic stability control in vehicles. MEMS pressure detectors monitor engine performance and structural stress. MEMS microphone arrays support speech-enabled user interfaces and noise cancellation. Miniature biodetectors based on chemical detectors, bio-implants, and DNA/RNA identification promise to revolutionize personal healthcare.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is accelerating detector innovations further by connecting everyday objects and environments to the internet. Embedded with detectors, things like home appliances, industrial equipment, vehicles, medical devices, infrastructure, and consumer goods continuously monitor their own status and environmental conditions. Wireless MEMS pressure and temperature loggers track shipments. Smart lighting uses embedded motion and light detectors for enhanced efficiency and user experiences. Detectors will further shrink and proliferate in the coming years towards realizing a fully sensed world.
Future Directions in Sensor Technologay By combining multiple detector capabilities on single chips, we can sense increasingly complex phenomena. Multidetectory systems merge data from MEMS accelerometers, magnetometers, gyroscopes, and microphones to accurately track motion, orientation, and location in three-dimensional spaces. Advanced data processing allows taking inputs from diverse detector arrays to identify odors, flavors, textures, and properties beyond the scope of individual detectors.
Biodetectors and chemical detectors hold much promise in areas like biomedical testing, environmental monitoring, and healthcare. Rapid DNA sequencing using nanodetectors may enable non-invasive, real-time medical diagnostic tests. Taste detectors that mimic human physiology could revolutionize food quality assessment. Small, low power gas detectors networked throughout smart buildings may help detect hazardous leaks instantly. Continued research is sure to yield new types of detectors we have not even imagined yet.
Sensor play a huge role in our world by enabling the interaction between electronics and the real world. Constant advancements in microfabrication and computing power are expanding sensing capabilities to unprecedented levels with each new generation of technology. In the future, sensing will become even more pervasive, intelligent and seamlessly integrated into our daily lives for enhanced convenience, safety, sustainability and scientific discovery. Get More Insights On, Sensor About Author: Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)
0 notes
Text
Strategies for Preventing Temperature Fluctuations in Reefer Vans

Preventing temperature fluctuations in reefer vans is crucial to maintaining the quality and safety of perishable goods during transportation. Here are some strategies to help minimize temperature variations and ensure consistent temperature control inside reefer vans:
1. Proper Loading and Stowage:
Ensure that perishable goods are loaded and stowed properly inside the reefer van to facilitate optimal airflow and temperature distribution. Avoid overloading the van or blocking airflow vents, which can restrict air circulation and lead to temperature variations. Use pallets or shelves to elevate goods off the floor and allow cold air to circulate evenly around the cargo.
2. Pre-cooling:
Pre-cool the reefer van to the desired temperature before loading perishable goods. Pre-cooling helps stabilize the internal temperature of the van and ensures that the refrigeration system doesn't have to work harder to reach the target temperature once the cargo is loaded. Start pre-cooling well in advance of loading to allow sufficient time for the van to reach the desired temperature.
3. Temperature Monitoring Systems:
Install advanced temperature monitoring systems in reefer vans to continuously monitor and record temperature data during transportation. Use digital thermometers, data loggers, or wireless monitoring devices to track temperature readings in real-time and receive alerts if the temperature deviates from the set range. Regularly review temperature data logs to identify trends or anomalies and take corrective action as needed.
4. Regular Maintenance and Inspections:
Conduct regular maintenance and inspections of the refrigeration system and the reefer van to ensure proper operation and performance. Schedule routine servicing, cleaning, and calibration of temperature control devices, sensors, and components to prevent malfunctions or breakdowns that could lead to temperature fluctuations. Inspect seals, gaskets, and insulation for signs of wear or damage and repair or replace as necessary to maintain thermal integrity.
5. Driver Training and Procedures:
Provide comprehensive training to drivers on proper handling, operation, and monitoring of reefer vans and refrigeration systems. Establish standard operating procedures (SOPs) for temperature control, loading, and unloading processes to minimize the risk of human error and ensure compliance with best practices. Train drivers to respond promptly to temperature alerts or deviations and take corrective action to mitigate potential risks.
6. Emergency Preparedness:
Develop contingency plans and protocols for responding to temperature-related emergencies or equipment failures during transportation. Equip reefer vans with backup power sources, such as auxiliary generators or battery backup systems, to maintain temperature control in the event of a power outage or mechanical failure. Train drivers on emergency procedures and protocols for safely handling perishable goods during unexpected situations.
7. Optimize Airflow and Ventilation:
Ensure proper airflow and ventilation inside the reefer van to facilitate efficient heat exchange and temperature regulation. Keep air vents, ducts, and evaporator coils clean and free from obstructions to maximize airflow and prevent temperature stratification. Use airflow baffles or curtains to direct cold air evenly around the cargo area and minimize temperature differentials between the front and rear of the van.
8. Weatherproofing and Insulation:
Inspect and maintain the weatherproofing seals and insulation of the reefer van to prevent heat infiltration or air leaks that could compromise temperature control. Repair or replace damaged seals, gaskets, or insulation materials to maintain thermal integrity and prevent external factors, such as ambient temperature fluctuations or humidity, from affecting the internal temperature of the van.
By implementing these strategies and best practices, reefer van operators can minimize temperature fluctuations and ensure consistent temperature control to safeguard the quality and safety of perishable goods during transportation. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and training are essential components of an effective temperature management program that helps mitigate risks and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
0 notes
Text
Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Data Logger for Your Application
Data loggers are indispensable tools in various industries, from environmental monitoring to scientific research and beyond. With a plethora of options available in the market, selecting the Best data logger for your specific application can feel daunting.
Fear not! In this ultimate guide, we'll walk you through everything you need to know to make an informed decision.
Understanding Your Application Needs
Before diving into the world of data loggers, it's crucial to understand the specific requirements of your application. Ask yourself questions such as:
What type of data am I looking to collect?
What environmental conditions will the data logger be exposed to?
How frequently will I need to retrieve or access the data?
By identifying your needs upfront, you'll be better equipped to narrow down your options and find the ideal data logger.
Key Features to Consider
When evaluating data loggers, several key features should be on your radar:
Measurement Parameters: Different data loggers specialise in recording various parameters, including temperature, humidity, pressure, voltage, and more. Ensure the data logger you choose can accurately measure the parameters relevant to your application.
Accuracy and Precision: The accuracy and precision of a data logger can significantly impact the reliability of your data. Look for devices with high-quality sensors and calibration options to ensure precise measurements.
Memory Capacity: Consider the amount of data storage required for your application. Some data loggers offer ample onboard memory, while others may require external storage options like SD cards or cloud-based solutions.
Battery Life and Power Options: For applications in remote or inaccessible locations, battery life is paramount. Evaluate the data logger's power consumption and consider options for battery replacement or alternative power sources.
Durability and Environmental Ratings: Depending on your application environment, you may need a data logger that can withstand harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, or dust. Look for devices with robust construction and appropriate environmental ratings.
Choosing the Right Type of Data Logger
Data loggers come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored to specific applications:
Standalone Data Loggers: Standalone data loggers are self-contained devices that operate independently, making them ideal for applications where portability and simplicity are key.
Wireless Data Loggers: Wireless data loggers offer the convenience of remote monitoring and data retrieval via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks. These are perfect for applications that require real-time data access or monitoring from a distance.
USB Data Loggers: USB data loggers are compact devices that connect directly to a computer or mobile device for data retrieval and analysis. They are suitable for applications where frequent data downloads are necessary.
Budget Considerations
While it's tempting to splurge on the latest and greatest data logger, it's essential to balance your needs with your budget. Consider the long-term costs of ownership, including maintenance, calibration, and support services.
Conclusion
If you're still unsure which data logger is right for your application, don't hesitate to seek advice from experts in the field. Reach out to data logger manufacturers, distributors, or industry professionals who can provide guidance based on their experience and expertise.
With these tips in mind, you're now equipped to navigate the vast landscape of data loggers and choose the perfect solution for your application.
Remember, the right data logger can make all the difference in the accuracy and reliability of your data, so choose wisely!
Source by - Choosing the Right Data Logger for Your Application
0 notes
Text
Smart Features in Temperature Data Loggers Enhancing Market Potential
The temperature data logger market is experiencing substantial growth as industries seek precise and efficient solutions for monitoring temperature-sensitive products. These devices are essential for ensuring product quality, safety, and compliance with industry regulations. With advancements in technology, temperature data loggers now offer real-time data collection, wireless communication, and integration with IoT platforms.

Advancements in Temperature Data Logger Technology
One of the key drivers of the temperature data logger market is the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things). This enables real-time monitoring and seamless data transfer across multiple devices and platforms. Smart temperature data loggers offer features like remote access, automated alerts, and predictive analytics, making them indispensable for industries such as pharmaceuticals, food & beverages, and logistics.
Key Drivers Influencing the Temperature Data Logger Market
Increased Regulatory Compliance As industries face stricter regulations regarding the storage and transportation of temperature-sensitive products, the demand for accurate data loggers has risen. These devices ensure compliance with industry standards, particularly in pharmaceuticals and food safety.
Growth of Wireless and IoT-enabled Solutions Wireless temperature data loggers are becoming increasingly popular due to their ease of use and ability to provide real-time data without physical connections. The adoption of IoT technologies allows seamless data integration with other smart systems, improving operational efficiency.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Companies are focusing on sustainable solutions, driving the development of energy-efficient temperature data loggers. These devices reduce power consumption while maintaining high precision, catering to eco-conscious industries.
Cost-Efficiency and Accessibility With advancements in technology, temperature data loggers have become more cost-effective and accessible to businesses of all sizes. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly adopting these devices to ensure quality control without heavy investments.
Smart Features Enhancing Data Security Security remains a top priority for temperature data loggers, especially with sensitive data being stored and transmitted. Advanced security features such as encryption and secure wireless communication protocols are being integrated to protect against cyber threats.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
While the market for temperature data loggers is expanding rapidly, challenges such as data privacy concerns and varying regional regulations persist. However, opportunities lie in the development of more specialized solutions for industries like biotechnology, where high precision and reliability are critical.
Conclusion
The temperature data logger market is evolving at a rapid pace, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for accurate monitoring of temperature-sensitive products. From wireless IoT solutions to energy-efficient devices, these innovations are reshaping how industries manage their temperature data, ensuring product integrity and safety across various sectors.
#Temperature Data Logger Market#Temperature Data Logger Market trends#Temperature Data Logger#Temperature Data Logger measurements#Temperature Data giver#Data Logger Market
0 notes