#which is a scholarly term
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
finally finished FD Signifier's Kendrick vs Drake vid and it was very good... and useful for how I think I wanna talk about the beef academically lol
#to sum up#my idea is talking about the possibility of art under capitalism#the possibility of culture under capitalism#and the idea of culture vs industry when we're much closer to a culture industry#which is a scholarly term#anyway i'm taking a class in the fall where we're gonna talk about the culture industry#and i wanted to have a final paper idea in my back pocket
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
latest ego death experience was realizing that i was having no success finding articles of clothing i actually want because everything was coming up beige trendy hellscape, and having to type into my search engine "dark academia clothing" 😔
#the problem is that i like button downs and decorative blouses and plaid skirts and pleated trousers and waistcoats#and the only way to find out which shops sell these things was to use that search term#even though i do not identify with The Dark Academia AestheticTM#my gender is Old-Fashioned Scholarly Feminist#i identify with Evie from The Mummy and action-adventure librarians in general which is unfortunately. dark academia-adjacent#but i had to humble myself and accept that the only way to find what i was looking for was to respect dark academia as a search term.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
9th Lord in Houses
1st House
You are in a good connection with your higher spiritual side, and you seek to understand the world from a higher perspective. Due to your virtuous nature and openness, you are bound to be fortunate in life, in terms of education, wealth and health. You try always to do what is right and you may find a good support from governing powers.
2nd House
You are scholarly and knowledgeable, and you bring good fortune to your family. You may seek to understand the world through the economical accumulation and affluence. Self-expression in terms of philosophical matters may fit you very well. Your family life will be happy.
3rd House
You may seek learning and understanding of life in the way you assert yourself: in terms of initiative and action. You may be easily motivated by spiritual principles or people who are on the path of spiritual development. When asserting yourself you have to be aware of the higher purpose behind your actions. You are bound to be successful in your endeavors and your siblings will be fortunate.
4th House
Spiritual or religious principles or practices sooth your heart and give you comfort. You may have gotten introduced to such principles from your mother or someone very close to you. You will be fortunate and gain possession of good property, real-estate or land as well as vehicles.
5th House
You are a virtuous and fortunate individual, who devotes him/herself to study of higher education and knowledge. You may be a well respected teacher or a leader and you try to uplift people with your wisdom. You are respectful to your elders and you communicate well with your children, which will be very fortunate.
6th House
It might be hard for you to acquire higher education and spiritual knowledge, and even though you may gain it the process of gaining it might prove quite irritating and annoying. Your relationship with your father might be lacking and your father's profession might be linked with medical science.
7th House
You are attracted to people who are virtuous and knowledgeable, sharing their wisdom freely with you. Your build your relationship upon sound principles of devotion, respect and moral values. Due to this your marriage will be happy and your spouse will be a reservoir of moral and spiritual values.
8th House
There is a hesitation in you when it comes to accepting new doctrines of religious or spiritual principles. To you it needs to be explored and analyzed, while in actual practice it tends to confuse you. It would make you feel vulnerable and weak if you would accept a religion or a spiritual path without deep and long consideration. In a way you hold back on the flow of fortune and good luck in your life, so you merely get a meager reward that expected. Your relationship with your father may suffer.
9th House
You are very spiritual, open-minded and a fortunate person. You are endowed with higher learning, wisdom and good moral values. You feel close to the divine aspect of yourself. Consequently you'll be lucky in life, financially fortunate and gain great happiness from your siblings and your grand-children.
10th House
It is very important to you to grow into a positive role in society. You take your moral values with you to work and your reputation and social image is very important to you. Your career is therefore bound to be very fortunate and successful. You always want to do the right things, you will be popular and rise in power and influence.
11th House
You are very affluent and open minded. You always seek to expand your opportunities and you will always have plenty of resources. You can be very inspiring and uplifting to others, and good at guiding them with proper principles to realize their dreams.
12th House
It is just like all your attempts to expand your horizon, to achieve higher education or higher spiritual teaching, get diffused and aimless when you try to pull them through. You need to transcend the selfish attachment you might have to such an endeavor. Indeed when you indulge in selfless acts of kindness and charity, you may discover the reservoir of knowledge within yourself.
#astrology#astrology observations#zodiac#zodiac signs#astro community#astro observations#vedic astrology#astro notes#vedic astro notes#astrology community#9th lord in houses#9th house#9th lord in 1st house#9th lord in 2nd house
584 notes
·
View notes
Note
wondering about whether you could rec some "romance is a social construct" texts? ofc it is, but i like having books and articles to reference/learn specifics from/see how these ideas have developed.
Sure! Here's a quick reading list. Bear in mind that I am not a professional historian and my reading on this subject is a little diffuse. I'm not tackling the behavioral ecology stuff right now because a) I don't have a more direct book rec off the top of my head than Evolution's Rainbow, which is not technically focused on social monogamy, and also b) I approach that whole field with my eyes wide open for people letting their own perspectives and cultural views get in the way of their observations of animals, and I do not have the energy to go deal with it right now.
If you're going to read two books, read these two:
Stephanie Coontz, Marriage, A History: how love conquered marriage. 2006. All of Coontz' work, having to do with the social construction of the family, is relevant reading to this question (and I'd also recommend The Nostalgia Trap, because the historical context of how we conceptualize families is a major part of the construction of romantic love), but this one is most focused on the social construction of romantic love specifically and what it has replaced. Coontz is, I will disclose cheerfully, a major formative influence on my thinking.
Moira Wegel, Labor of Love: The Invention of Dating. 2016. Exactly what it says on the tin; focuses more closely on the modern invention of dating and romance.
Other useful readings to help inform your understanding of different ways that various people have conceptualized sex, sexuality, society and long-term connection include:
George Chauncey, Why Marriage? 2015. Chauncey is best known for Gay New York, which also offers a useful history of the way that relationship models and social constructs for understanding homosexuality changed among men having sex with men c. 1900 to 1950. This book, published just before Obergefell v. Hodges, is a discussion of why contemporary queer rights organizations focused on same-sex marriage as an activism plank in the wake of AIDS organizing. I find it really useful to read queer history when I'm thinking about how we understand and construct the concept of romantic relationships, because queers complicate the mainstream, heteronormative concepts of what marriage and romantic relationships actually are. More importantly, queer activist organizing around marriage has played a major role in shaping our collective understanding of romance and marriage in the past twenty years.
Elizabeth Abbott, A History of Celibacy, 2000. In order to understand how various cultures construct understandings of marriage and spousal relationships, it can be illustrative to consider what the people who are explicitly not participating in the institution are doing and why not. I found this an interesting pass over historical and social institutions that forbid (or forbade) marriage with a discussion about general trends driving these institutions, individuals, and movements towards celibacy.
Eleanor Janega, The Once and Future Sex, 2023. This is a very pointed historical look at gender roles, concepts of beauty, and concepts of sex, attraction, and marriage among medieval Europeans with an extended meditation on what ideas have and have not changed between that time and today. I include this work because I think a deep dive into medieval notions of courtly romance is useful, partly because it is an important origin of our modern notion of romantic love and partly because it is so usefully and starkly different from that modern notion! Sometimes the best way to understand the cultural construction of ideas in your own society is to go look at someone else's and see where things are the same versus different.
It's a mish-mash of recommendations, and I'm reaching more for books that have stuck with me over the years than a clean scholarly approach to the subject. I hope other folks will chime in for you with their own recommendations!
477 notes
·
View notes
Text
You know, I gotta say, nobody has ever done the immortal boyfriend with a mortal girlfriend trope better than the Emily Wilde books. Their relationship isn't some edgy, drama filled sex romp where everyone is unbelievably hot and cool. (Not to hate on those stories if that's your thing, to each their own.) They're literally two people who respect each other for their respective abilities and personalities. Emily is a devoted academic with little interest in anything but her area of study (which sort of happens to include Wendell). Wendell, despite being an exiled prince of Faerie, is just a lazy, slightly ridiculous dude who likes nothing better than being cozy and following his girlfriend around while she does research. He also happens to be insanely talented with a sword and with magic, but somehow that never makes him seem like a badass, just even more ridiculous.
And though the Fae in this book are often described as sort of unearthly beautiful, it's really never meant to be sexy. They're beautiful by and large in a cold and terrifying way. Like, they might drag you around partying for a while, but then they slit your throat and hang you from a tree with no warning at all, and your friends and loved ones never know what happened to you. And the story does address this as a legitimate concern in terms of Wendell's and Emily's relationship. It's totally possible that he could some day become a mad King of Faerie, and her friends try to warn her repeatedly. Wendell is aware of their warnings, and in some stories the love interest would storm about in anger and disbelief that anyone could doubt him or he would laugh it off, but Wendell being Wendell, he's pleased that her friends care enough about her to voice their concerns and he acknowledges that this is a real threat. In the end, he knows Emily is a genius, and he trusts her to stop him from tumbling headlong into disaster, as she's done time and time again. And Emily does consider these concerns as well. But if Emily is anything, she's confident in her knowledge and abilities. She doesn't refuse to believe that her beloved is incapable of being like other Fae, quite the opposite, she acknowledges his occasional strange, uncanny otherness multiple times and the fact that he could go mad. She does everything in her power to keep this from happening, and we have every reason to believe that this will continue to be the case.
Then there's the age old issue of human/immortal age gaps that so many similar books face. Emily Wilde books side step this issue nicely by making Wendell very similar in age to Emily. He's not some 500 year old dude hitting on a 30 year old, he's a teenager when he's driven out of Faerie, and he ultimately comes of age in the human world at about the same time as Emily. This takes away the kind of creepy aspect of someone hooking up with someone young enough to be their great-great-grandaughter, and it gives a nice excuse for Wendell to be less cruel and mad than other Faerie monarchs as well.
And even though I keep saying these books don't make the Fae sexy, that's not to say the books are sterile and chaste. Emily and Wendell do eventually have a sexual relationship, but it comes along very naturally, from people who start out as coworkers and academic rivals and grow to become friends and then partners and then co-rulers and spouses. When they have sex it just feels like two people who love each other and enjoy each other's company, not like some wild outburst of edgy, sexy, repressed desires. (Again, no hate if that's your thing.)
And maybe the best thing about their mortal/immortal relationship is that Emily doesn't have to change herself or abandon everything she held dear for Wendell. Emily goes through a brief phase where she tries to fit into the beauty standards of the Fae, and then she quickly realizes that's stupid and she's better off being herself. And Wendell never cared about any of that at all, he's too busy just adoring her scholarly obsessions. Many stories ask the mortal heroines to leave behind their loved ones and lives for their immortal lover, but again, Emily Wilde does it better. Wendell immediately recognizes that academia is Emily's first love. He sets her up with a library, endless journals, and most importantly, multiple points of access to the mortal realm, where she can go to research in peace, continue her connection with Cambridge, publish her work, and of course, present at the occassional academic conference now that her career has taken off.
Emily Wilde got her man, a throne, and a flourishing career. Our girl really can do it all.
#emily wilde#wendell bambleby#emily wilde's compendium of lost tales#Spoilers#Emily wilde's compendium of lost tales spoilers#Books#Wendell bambleby my beloved#heather fawcett#women in fiction
322 notes
·
View notes
Text
Short guide to varðlokkr
Briefly exploring ritual singing and spirit work in the nordic tradition, and their possible uses in neo-pagan practice.


Before performing divination, it's said that völur would sing, or more often than not, have someone sing a ritual song in order to "rouse the spirits". This ritual was a way to call upon nearby spirits—generally guardian spirits, to come and answer their questions. The practice of varðlokkur, or "ward songs/protection songs", is tightly interwoven with the art of seiðr. According to the few sources that mention the topic, it was performed by seeresses seeking to prophecize, or by women willing to sing it in their stead.
Before diving deeper into this topic however, it's important to note that the interpretation of the term varðlokkr, and in a sense, the very basis of its current scholarly understanding, depends on its possible etymology. Two hypotheses stand out in this regard: varðlokkr is either spelled with one or two k's, either varðlok or varðlokk. The former would refer to "locking", or "fastening", and is often associated with a passage in the Grógaldr (The Spell of Gróa) where the shamaness refers to Urðar lokur, or Urð's locks/bolts. In this case, the song is a matter of "locking" the spirits in. Whereas varðlokkr would stem from the same root (vǫrðr, meaning to guard or ward), but in this case, lokkr would come from lokka, meaning to lure, or entice. It's generally agreed upon that both these instances showcase how the idea of protection was a key element in the perception of this practice.
These so-called "Weird-songs" sometimes required the use of a rhythmical sound created using drum beating, rattles, or by hitting the ground with a staff. They served as an invocation to higher powers or local spirits, who would be keen to protect ("ward") the seeress as she glimpsed into the future. According to pre-Christian belief, the sound of these songs had the power to appease surrounding spirits, but also to entice and lock them into the space for the duration of the divination. Letting her spirit wander out of her body in order to scry, the völva/seiðrkona became vulnerable, hence the need for higher protection. Now "bound" to her until the completion of the ritual, the guardian spirits would be inclined to lend their help. Depending on the intepretations, this type of ritual singing could also have been a means to reach a trancelike state before fortune telling.
'Many spirits,' said she, 'have been present under its charm, and were pleased to listen to the song, who before would turn away from us, and grant us no such homage. And now are many things clear to me which before were hidden both from me and others.' Eiríks saga rauða, chapter 3
The trance aspect of this practice is often debated, however. Granted, it's possible to point out similarities between seiðr and the "out of body" travel of Sámi and Siberian shamans. After all, a few sources tell us that varðlokkr would also serve to bring the völva back into her own body once she'd prophecized. Still, scholars more often than not consider varðlokkr and other seiðr practices as putting oneself in a "receptive state" in order to comprehend messages sent from the spirit world.
At the beginning of the séance all those present seem to have taken part in the singing, but a special choir was appointed for continuing operations: this is in several accounts said to consist of women or one woman. Singing continues throughout the séance, the purpose being to remind the shaman of his mission. Some sources indicate that the singing was concentrated or confined to the final stages of the trance, and the aim here was to wake the shaman. Louise Bäckman & Åke Hultkrantz
Think of varðlokkr as a way to blend music, divination and spirit work. A modern practitioner who already works with Dísir, vættir, ancestors, and the like can involve these familiar spirits in the ritual, for example, by calling upon a passed loved one to protect them during divination, or even to aid in finding answers. It's generally agreed upon that during the Scandinavian pre-Christian times, the wisdom of the dead occupied a vital place in many such shamanic practices. One could seek advice from passed mentors or loved ones in this manner. Even disregarding the idea of "rousing" spirits and "locking" them, I believe that one could still use to music as ritualized invocation—especially when it comes to ancestor work, in order to ask for advice or insight.
Next to nothing is known about what varðlokkr actually sounded like. However, I think it's still interesting to explore the idea of ritual singing as a shamanic practice. For someone interested in experimenting with galdr, seiðr, or any such shamanic practices in the Nordic tradition, varðlokkr seems like a great place to start.
So how does one incorporate ritual singing into neo-pagan practice? I'm sorry to say that it's exceedingly difficult to somehow reconstruct varðlokkr, as history has left us with nothing but bits and pieces to work with. However, three main particularities stand out and aid us in tracing a general outline: 1. the Weird-song is sung before divination as an opening practice; 2. its purpose is to call upon spirits; and 3. it most likely served as a sort of short-term ward for the person performing the ritual. These three concepts may be preserved, and the freedom to build around them is yours.
For this reason, we even have the option to simply pick a song which feels sacred and play it before rune casting, or tarot reading for example (needless to say such a practice also applies to any and all methods of divination, including scrying). After all, there's really no indication that the practitionner must sing the song themselves. Even in the few accounts mentioning varðlokkr, the seeress isn't always the one singing.
But if you decide to sing the varðlokkr yourself, it's also possible to learn the lyrics to a song that's already part of your practice. If working with the spirits of the dead, and especially with passed loved ones, why not play a song that a given ancestor loved in life? Artist Einar Selvik has composed a short skaldic-type song called Vardlokk, which has understandably become my own ritual song. I play it to get into a spiritual state of mind, helping me tremendously before spirit work—which coincides in many ways with the original purpose of varðlokkr. But it's safe to say any type of music may be used. And if you're interested in trance or trance adjacent practices, chanting may be used in such a manner as well.
There are many ways for us neo-pagans to adopt the practice of varðlokkr, since in one way or another, music is always tightly intertwined with religious practice. One can choose to wholly disregard the spirit work aspect and simply explore the idea of ritual song and its ties to divination. No matter the case, shamanic practices were an inherent part of Nordic religious tradition, and I think it can be useful for modern practitioners to learn about them and explore the possibilities that they offer.
If you're interested in further reading, I've linked at the beginning of this post an ask I answered a while back pertaining to seiðr, galdr, and other shamanic practices of the Norse. Within the post are also a few suggested pieces of reading that have helped my personal understanding and research.
#heathenry#norse paganism#paganism#informational post#deity work#deities#spirit work#ancestor work#spirituality#norse gods#polytheism#norse polytheism#pagan#witchcraft#divination#scrying
216 notes
·
View notes
Text


These were supposed to be part of a fic for @alectopause, but the fic simply didn't manifest in time so I'm posting them by themselves. Shitty Eighthsploitation romance from out-of-House vs. Serious and Morally Correct Romance Between Two Upstanding Young Women of the Eighth, as reviewed by one Silas Octakiseron during his brief period in office.
Bonus archival front matter for the collection containing these records below.
Select Annotated Bibliographic Works From the Archived Personal Effects of the Five Hundred Eighty-Seventh Master Templar of the Order of the White Glass (Regn. 9995-10000 YKU)
Held By: Pontifical Archives of the Order of the White Glass
Selection Compiled By: Wythren, Sr. Keren-Happuch [Senior Archival Specialist]
Date Compiled: 13 Entombment 10002
Archival Collection Code: PAWG-MT-587-OS
Abstract: Curated annotated excerpts from works of fiction purporting to depict the culture of the Eighth House released between the years 9995 and 10000, which reached the desk of then-Master Templar, Silas Octakiseron. These and accompanying notes were recovered alongside the Master Templar’s other personal effects, now archived, from his quarters within the central clerical complex of the Eighth. M∴ Octakiseron was known to leave extensive notes on pieces he was obliged to review, clearly detailing his thought processes and the reasons that leave for continued print might be granted or denied. While the task of issuance, denial, and revocation of imprimantur was and remains generally the duty of lower-ranked clergy in administrative roles, the occasional text requires closer examination from members of the curia in order to reach a final determination. M∴ Octakiseron did not leave the mother House until the age of sixteen, and therefore chose to involve himself extensively in the process of permissal in order to familiarize himself with both appropriate and unacceptable depictions of the Eighth House from offworld.
Extent of Collection: 12.5 linear feet (12 cartons, 2 flat boxes)
Biography: His Holiness Silas Octakiseron, M∴T∴ (b. 9984, d. 10000; regn. 9995-10000) was the five hundred eighty-seventh Master Templar of the Order of the White Glass. He assumed the title at age eleven and was subsequently responsible for the theocratic governance of the complete body politic of the Empire of the Necrolord Prime, coupled with similar such principality over the government and curial courts of his mother House, until [CLASSIFIED: O-10 SPECIAL CLEARANCE OR HIGHER] at age sixteen.
His scholarly corpus, though circumstantially limited, consists of several works which received significant interest in theological circles throughout both the term of his pontificate and the years that ensued. These include his “Treatise on the Comparative Necromantic Value of Spiritual and Corporeal Materials” (9998), a number of ecclesiastical orders, and the essays “Against Ecumenicalism: Arguments Opposing Proselytization on the House of the Ninth” (9999) and “Toward a Theodician Reading of the Tome” (pub. 10001, posth.; orig. title “Why Does the Emperor Allow Suffering?”, unpublished paper toward fifth-year primary certification, 9993). He left behind at the time of his death early components of an incomplete sacerdotal inquiry titled “Treatise on the Moral Inculpability of the Interfluvescent Cavalier” (forthcoming 10003, posth.). He was considered an adept of prodigious skill with the River, capable of channelling immense power from its banks. He was served in partnership by the six hundred thirteenth Cavalier Primary of the Eighth House (d. 10000).
Preferred Citation: “Archived Personal Effects of the Five Hundred Eighty-Seventh Master Templar of the Order of the White Glass” (13 Ent. 10002) Pontifical Archives of the Order of the White Glass, PAWG-MT-587-OS, Carton 7, Folder 16.
144 notes
·
View notes
Note
could you, perhaps, talk a bit about Middle English? thank you, you're so cool
Writing Notes: Middle English
Middle English alphabet

The chronological boundaries of the Middle English period:
Not easy to define, and scholarly opinions vary.
The dates that OED3 has settled on are 1150-1500.
Before 1150 being the Old English period, and after 1500 being the early modern English period.
In terms of ‘external’ history, Middle English is framed at its beginning by the after-effects of the Norman Conquest of 1066, and at its end by the arrival in Britain of printing (in 1476) and by the important social and cultural impacts of the English Reformation (from the 1530s onwards) and of the ideas of the continental Renaissance.

Two very important linguistic developments characterize Middle English:
in grammar, English came to rely less on inflectional endings and more on word order to convey grammatical information. (If we put this in more technical terms, it became less ‘synthetic’ and more ‘analytic’.) Change was gradual, and has different outcomes in different regional varieties of Middle English, but the ultimate effects were huge: the grammar of English c.1500 was radically different from that of Old English. Grammatical gender was lost early in Middle English. The range of inflections, particularly in the noun, was reduced drastically (partly as a result of reduction of vowels in unstressed final syllables), as was the number of distinct paradigms: in most early Middle English texts most nouns have distinctive forms only for singular vs. plural, genitive, and occasional traces of the old dative in forms with final –e occurring after a preposition. In some other parts of the system some distinctions were more persistent, but by late Middle English the range of endings and their use among London writers shows relatively few differences from the sixteenth-century language of, for example, Shakespeare: probably the most prominent morphological difference from Shakespeare’s language is that verb plurals and infinitives still generally ended in –en (at least in writing).
in vocabulary, English became much more heterogeneous, showing many borrowings from French, Latin, and Scandinavian. Large-scale borrowing of new words often had serious consequences for the meanings and the stylistic register of those words which survived from Old English. Eventually, various new stylistic layers emerged in the lexicon, which could be employed for a variety of different purposes.
One other factor marks out the bulk of our Middle English evidence from the bulk of our Old English or early modern English evidence, although it is less directly a matter of change in the language than in how it is represented in writing:
the surviving Middle English material is dominated by regional variation, and by (sometimes extreme) variation in how the same underlying linguistic units are represented in writing.
This is not because people suddenly started using language in different ways in different places in the Middle English period, but because the fairly standardized late Old English literary variety broke down completely, and writing in English became fragmented, localized, and to a large extent, improvised.
Some Terminology
Great Vowel Shift - A systematic change in the long vowels in late Middle English that resulted in a new array of vowels, which includes diphthongs and tense vowels but which no longer generates a systematic distinction for length. Also called the Tudor Vowel Shift.
Lengthening - The change of a short vowel to a long vowel; it took place systematically during Middle English.
Levelling - The loss of distinctions in inflected endings, especially in early Middle English.
Thorn - A letter from the Germanic runic alphabet added to the Latin alphabet in Anglo-Saxon England to transcribe dental fricatives. It was used through the Middle English period and was gradually replaced by the sequence [th].
Wynn - A letter form adapted from the Germanic futhorc to indicate the sound [w] in the writing of Old English. It was used up to the Middle English period.
Yogh - A letter form used in Middle English and derived from the earlier insular letter form for [g]. In Middle English it was used for one of several consonant sounds.
Sources: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ⚜ More: Notes ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
Some French Loans in Middle English Part 1 2
Some Renaissance & Latin Loan Words in Middle English
"Beautiful" Middle English Words
You are too sweet (I'm farthest away from the definition of "cool" haha). Do go through the links above for more details as well as an online Middle English dictionary. Hope this helps with your writing!
#anonymous#middle english#literature#writers on tumblr#writeblr#writing reference#dark academia#langblr#spilled ink#writing prompt#creative writing#writing inspiration#language#linguistics#history#writing resources
116 notes
·
View notes
Text
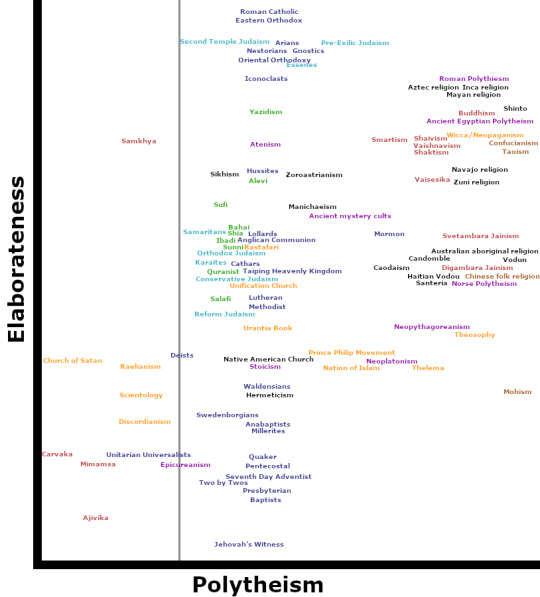
Revised version of "polytheism vs elaborateness" religion chart. I started with a list of around 150 religions, sects, denominations, philosophies, and spiritual tendencies, whittled down to 100 based on what I could find information on and what meaningful differences would actually show up in a chart like this. Dark blue is Christianity and Christian-derived tendencies; light blue is Judaism and Jewish-derived tendencies; green is Islam and Islam-influenced tendencies; purple is ancient Mediterranean polytheism and related schools of thought; red is Dharmic/Hindu-influenced schools of thought; tan is Chinese religion and philosophy; orange is new religious movements; black is other, unaffiliated religions and movements.
Obviously, "what is a religion" is a complicated topic. Some of the things on this chart might strike you more as philosophical schools (Carvaka, Stoicism), epistemological approaches (Unitarian Universalism), or different ways of slicing the same tradition. The scholarly definition of "religion" is sort of fundamentally circular, and that's not something I'm interested in trying to untangle for this entirely non-scientific exercise.
Religions etc. are scored on two axis: polytheism vs elaborateness of practice. Polytheism is a rank from zero to 11, thus:
0. Strict atheist and materialist, denying the possibility of both gods and the supernatural, e.g., Carvaka.
1. Atheist. Denies the existence of significant supernatural agents worthy of worship, but may not deny all supernatural (or psychic, paranormal, etc.) beings and phenomena (e.g., Mimamsa).
2. Agnostic. This religion makes no dogmatic claims about the existence of supernatural beings worthy of worship, and it may not matter for this religion if such beings exist (e.g., Unitarian Universalists). It does not preclude--and may actually incorporate--other supernatural, psychic, or paranormal phenomena (e.g., Scientology).
3. Deist. This religion acknowledges at least one god or Supreme Being, but rejects this being's active intervention in the world after its creation (e.g., Christian Deism). Deism is marked with a gray line on the chart, in case you want to distinguish religions that specifically care about all this God business from ones that don't.
4. Tawhid monotheist. This religion acknowledges only a single transcendent god above all other natural or supernatural beings, who is usually the creator of the universe and the ground of being, and is without parts, division, or internal distinction (e.g., Islam).
5. Formal monotheism. This religion acknowledges a single god, usually transcendent above all other natural or supernatural beings, but who may have aspects, hypostases, or distinct parts (e.g., Trinitarian Christianity). Pantheism may be considered a special case of formal monotheism that identifies the universe and its many discrete phenomena with a single god or divine force.
6. Dualism. This religion acknowledges a single god worthy of worship, alongside a second inferior, often malevolent being that nevertheless wields great power in or over the world (e.g., Zoroastrianism or Gnosticism).
7. Monolatrist. This religion or practice acknowledges the existence of many gods or divine beings worthy of worship, but focuses on, or happens to be devoted to only one of them (e.g., ancient mystery cults; pre-exilic Judaism).
8. Oligotheist. This religion worships a small group of divine beings, who may function for devotional or rhetorical purposes as a single entity (e.g., Mormonism, Smartism).
9. Monogenic polytheism/Henotheism. This religion worships many gods, which it sees as proceeding from or owing their existence to, a single underlying or overarching force or supreme god (e.g., many forms of Hinduism).
10. Heterogenic polytheism. This religion worships many gods, who have diverse origins and/or natures. Though the number of gods is in practical terms probably unlimited, gods are discrete entities or personalities, i.e., they are "countably infinite" (e.g., many polytheistic traditions).
11. Animism. This religion worships many gods which may or may not be discrete entities, and which may or may not be innumerable even in principle, i.e., they are "uncountably infinite" (e.g., many animist traditions).
What counts as a god is naturally a bit of a judgement call, as is exactly where a religion falls on this scale.
Elaborateness of practice is based on assigning one point per feature from the following list of features:
Uses vs forbids accompanied music in worship
Saints or intermediary beings accept prayers/devotion
Liturgical calendar with specific rituals or festivals
Practices monasticism
Venerates relics or holy objects
Clerics have special, elaborate clothing
Clerics have special qualificiations, e.g., must be celibate or must go through elaborate initiation/training
Elaborate sacred art or architecture used in places of worship
Sites of pilgrimage, or other form of cult centralization
Sophisticated religious hierarchy beyond the congregational level
Mandatory periods of fasting and/or complex dietary rules
Specific clothing requirements for laypeople
Specific body modifications either required or forbidden for laypeople
Liturgical language
Complex ritual purity rules
Performs sacrifice
Performs human sacrifice (or cannibalism)
Uses entheogens
Uses meditation or engages in mystical practice
Additionally, a point is taken away for austerity for each of the following features:
Forbids secular music outside worship
Claims sola scriptura tradition
Practices pacifism or ahimsa
Requires vegetarianism of all adherents
These scores are probably pretty inexact, since I am not a scholar of world religion.
This chart is not scientific, it's just a goof based on that @apricops post.
Other fun dimensions along which to chart religions might be:
Orthodoxy vs orthopraxy
Authoritarianism/control of members. This would add some much needed distinctions to Christian sects in particular, and to the new religious movements.
Elaborateness of cosmological claims. Some religions (looking at you, Buddhism) really go hog-wild here.
Social egalitarianism. Even within the same framework/tradition/philosophy, some practices differ radically on how egalitarian they are.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Are people aware that the Bachelor's quoting of Latin is a very common part of the academic field? With all those posts calling him pretentious for Latin, I can't be too sure. The difference is that, today, Latin is not necessarily the academic standard when it comes to terminology and so readers can find Latin phrases mixed with German, French, Russian (etc.), too - depending on the subject.
I pulled a random article on Italian futurism and it uses the terms/phrases unheimlichkeit, homo faber, il linguaggio nascosto della tecnologia (so on, so forth). It becomes natural to the essay's conversation (in this case, futurism).
The Western academic world, for centuries, was fed off Roman stories and for most of the Western world's past, Latin was the predominant "intellectual" language until French became the status quo, and now it's English. So when it comes to studying in a certain era, not knowing Latin might bar a person from scholarly work.
Someone who spoke and wrote in Latin very prolifically was Thomas De Quincey (Englishman early, mid-1800s), and he wrote a few short stories. One of which, he's sitting with a coachman and speaks a Latin phrase in passing and then immediately strikes himself as silly because the working class coachman probably doesn't understand him.
Just one example of many where Daniil is clearly expressed as someone completely out of their usual, personally comfortable social circle. Sometimes one language just doesn't cut it for the description of things, but now an avenue of regular expression has been completely shut off from him.
Though I wonder if he uses Latin with general abandon in the town, is mostly speaking to himself when he uses Latin, or if, like De Quincey, is going you fucking fool, he doesn't understand you!
#pathologic#daniil dankovsky#almost completely shut off#andrey has named his pub factus est and probably the kains and peter are familiar with latin#man-of-letters
175 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello! I am trying to read “the right to maim” by jasbir k puar and I am getting almost nothing out of it, bc of the depth + breadth of academic concepts :( I’m particularly frustrated by it bc it seems to talk about subjects I think about, talk about and do daily, like disability, transness, and (anti)colonialism. I’m most of the way through the intro and it’s gone almost entirely over my head except for a couple isolated paragraphs that are meaningful.
Do you have any advice for how I can get the most out of this book? My main limiter is time, bc I got it out from the library and it is highly requested so I can’t have it for very long
Hi anon! First of all, in terms of time, I recommend piracy. I recommend it in general. I'm not going to post links here in order to protect the places I use, but dm me if you want them.
If you're having difficulty with the concepts (which makes sense - right to maim is a challenging book!) I recommend going back to basics with some background reading. You can get some of Puar's rec'd background reading from the bibliography, and from the keywords she uses in the preface of the text. a few that I see (i'm looking at the PDF now) include debility, rhizome/rhizomatic, soverignty, biopolitics, homonationalism, impairment [in the disability studies sense], precarity, and neoliberalism. if i was teaching this preface, i'd have students break down each of these terms (and probably others, this is just from a skim) using outside readings. it's totally normal to feel overwhelmed when jumping into a scholarly text w/o any context, and most people who use and cite this book have past experience reading Puar's interlocutors and existing familiarity with this language.
you can get up-to-date while reading using resources in tandem with this text. For example, you can read Puar's discussion of debility at that link to get a sense of the context. You can read a decent summary of Foucault (the coiner of the term "biopower") and his thought at Brittanica. I recommend using Google Scholar for terms you're not familiar with, and taking quick notes so that you don't have to google them all over again each time. if you think you have enough context with a new word but aren't 100%, keep reading and use other clues. think about academic reading like learning a new language. the strategies are very similar! because it basically is.
I recommend using the annotation strategies i just mentioned in this post (and/or developing your own). i also recommend looking up Puar's talks on youtube - she's a well-known scholar who does a lot of events, and has spoken extensively about this book and its genealogy (especially in relation to praxis / Palestinian liberation). You can also read her talk with the hosts of Death Panel, my absolute favorite podcast.
Below, I'm going to give you an example of how I close-read, annotate, and analyze a paragraph from Right to Maim (and, by extension, other academic texts. This strategy may not work for you 100%, but hopefully it gives you some solid suggestions. Overall, remember that learning to read scholarly work takes time. A long ass time. Even when it's about things you've experienced yourself! Academia has its own conventions, verbiage, knowledge base, etc, and it's a learning curve for everyone. Don't expect yourself to read as fast or get as much as someone more familiar with the conventions of academic writing - anticipate reading all of these works many, many times, and getting more with each reading. Progress is more important than perfection, and improvement, even if slow, *will* happen, as long as you don't give up. <3
Below is a quote from the preface to Right to Maim, where Puar lays out her argument. I recommend everyone highlight/remember paragraphs like these (pretty much every ac text will have something like this in the beginning as a roadmap) to anchor their reading practice and help them get the most from a book (emphasis mine):
In The Right to Maim, I focus less on an important project of disability rights and disability studies, which is to refute disability as lack, as inherently undesirable, and as the sign, evidence, or fetish of injustice and victimhood. I am not sidestepping this issue. Rather, I centralize the quest for justice to situate what material conditions of possibility are necessary for such positive reenvisionings of disability to flourish, and what happens when those conditions are not available. My goal here is to examine how disability is produced, how certain bodies and populations come into biopolitical being through having greater risk to become disabled than others. The difference between disability and debility that I schematize is not derived from expounding upon and contrasting phenomenological experiences of corporeality, but from evaluating the violences of biopolitical risk and metrics of health, fertility, longevity, education, and geography.
In the bolded part, Puar outlines what she's not doing: she's not taking a mainstream (white, colonial) disability studies approach, which is, in her words, to refute disability as "lack." She's stating that her goal isn't simply to prove disabled people as equal to able-bodied people, or to claim that disability can be good and liberating (though it is/can be!). Her point is to look at the conditions in which people become disabled, and stay disabled. Often, these conditions are violent and unjust. Acknowledging this injustice kinda throws a wrench into western models of disability pride.
So, if she's not interested in just arguing that disability ≠ badness, what is she arguing? she's looking, in the latter half of the paragraph, to how people become disabled in multiple ways. One, using the verbiage in the book, she's interested in how people become debilitated - physically incapacitated in a way that may not line up with the social category of "disability"). She's also interested in how "disability" as a social identity is constructed - that is, why do disability rights groups look at Palestinians maimed by the IOF and see an injured civilian, but not a disabled comrade? words and context matter immensely. she's looking at why, and what are the implications.
that last sentence sums up the distinction she's making: "The difference between disability and debility that I schematize is not derived from expounding upon and contrasting phenomenological experiences of corporeality, but from evaluating the violences of biopolitical risk and metrics of health, fertility, longevity, education, and geography."
the difference, she argues, between disability as western disability studies sees it and debility as experienced by people under colonial occupation isn't because we experience our bodyminds differently, or because Palestinians (for example) magically aren't as hurt by occupation as their white/western counterparts would be. rather, the reason she's using debility over disability is because the category of disability isn't objective: it's informed by biopolitical forces such as the ones she listed. her meta-argument is that what we call "disability" can't be divorced from its settler colonial context, not because colonized peoples are immune to disabling violence, but because the category of disability (and health, and violence) is itself affected by settler colonialism.
in "right to maim," Puar is offering a major shift in the way we collectively discuss disability, because the category is not applied equally across sociopolitical, geographical context. it means Palestinians and others living under occupation are either left out entirely, or unsuccessfully co-opted into western-/colonizer-centric disability discourse that doesn't acknowledge the different conditions under which they live. ultimately, "right to maim" means to make that difference, and its implications, visible.
Let me know if this makes sense! it's wordy and tedious, but lots of academic texts are. i hope that breakdown helps you make some more sense of Puar's main argument/the architecture of the text, and maybe serves as a model for future engagement. :)
#palestine#reading#academia#ask#anonymous#do not be ashamed of having a hard time. we have ALL been there. everyone has been new to this language/these conventions before.#keep trying and you will get better. i promise!
234 notes
·
View notes
Note
what are sunnis and salafists? sorry that this out of nowhere im a white anon so i dont know alot and you can ignore this if you want
Sunnis are adherents of Ahlul Sunnah wal Jumu'ah (the people of the Sunnah) or the Sunni branch of Islam. It constitutes the majority of followers of Islam, with Shi'as being the second largest group of Muslims. The name is derived from the term Sunnah, which means Prophetic traditions and practices.
Historically, Sunni Islam did not originate at the onset of Islam and following the historical disagreement regarding the successorship of Muhammed (pbuh&hf), but is rather the culmination and consensus of centuries of legal and scholarly opinions, debate and theological studies, thus is it is a misconception to assume that Sunnism was brought about during the political schism in the early years of Islam, whereas Shi'ism were a partisan group before forming its own theology and jurisprudence a century later. Sunni Islam derives its laws and jurisprudence through the Qur'an, Sunnah, consensus and analogical reasoning. Sunni Islam is represented by four school of thoughts: the Hanbali school, the Hanafi school, the Maliki school and the Shafi'i school. Each school of though represents a particular geographic location, and lay people following Sunnism may follow the scholarly opinion corresponding to their geographic origin and location. Most Sunnis follow the Maturidi and Ashari rationalist schools of theology and rely on scriptural sources to derive their understanding regarding God's nature and the material and metaphysical reality.
Salafism is a reformist/revivalist movement within Sunni Islam that holds that the purest form of Islam can only be derived through the opinions and practices of the honorable ancestors (Salaf al-Saleh). They hold that the best generation of Muslims were the Sahabas (companions), the Tab'iun (the second generation) and the Taba al-tab'iun (The third generation), according to a prophetic tradition, viewing later interpretations of Islam as innovations or deviation from the Qur'an and the Sunnah. They believe that only through the Salafs can absolute monotheism be understood and that anyone who rejects them or derive different opinions are deviants or heretics, such as the Shi'as (and some Sunnis), who venerate saints. They reject the concept of Taqlid (emulating), that is, following the four schools of thought, holding that ijtihad (independent reasoning) takes precedence over Taqlid through the study of the Qur'an, the Sunnah and consensus of the Salaf al Saleheen. Salafists tend to reject the rationalist schools of mainstream Sunni theology and adheres to a literalist and traditionalist (Athari) interpretation of Islamic theology as understood from classical scholars such as Ibn Taymiyyah, Ibn Kathir and Ibn Qayyim. They may also derive their understanding of religion through the legal opinions of other modern Salafist scholars. There are several Salafist movements, such as Madkhalism (the quietist school), Wahhabism, Salafi-Jihadism, Ahlul al-Hadith and etc. Salafists are known for their puritanical view on Islamic monotheism and literalist interpretation of scripture, hence their intolerance toward other co-religionists that do not conform to their religious interpretations. They most notably hate Shi'a Muslims.
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
Many other people have already posted their thoughts on the various peaks of Cang Qiong Mountain sect, so I figure I might as well throw my own thoughts and preferred headcanons out there.
First, my thoughts on the peaks we know exist but don't know much about in terms of their specialties:
Xian Shu Peak: Textiles Peak
This is my favorite headcanon for the all women's peak! The textiles industry is a big part of Chinese history, and was traditionally considered to be women's work, so it would only make sense for it to be Xian Shu Peak's peak specialty. It's not just one specific skill either, as spinning, weaving, dying, garment making, embroidery, rope/cord-making, etc. are all a part of the industry.
As they are a cultivation peak, I expect some of the products of their work to be defensive robes with talismans or incantations stitched into the fabric, Qiankun bags or sleeves, spirit trapping pouches, etc. If rope making is included in their preview, they could also be involved in making immortal binding cables, nets, and so forth.
Ku Xing Peak: Rites, Rituals and Purification Peak
We don't know much about Ku Xing Peak except that they live an aesthetic lifestyle. As it's common for individuals to take on certain aspects of aestheticism (simple clothes, restricted diets, abstinence, etc.) before engaging in many types of rituals, I'm inclined to believe a peak that practices aestheticism at all times would be particularly well suited for such tasks.
I tend to imagine their peak being similar to the Gusu Lan Clan, minus the music aspect (music being Qing Jing's purview). They could specialize in things like summoning spirits, communing with the dead, dispelling resentment, exorcisms, purifying objects or locations, properly laying the dead to rest, etc.
Since SVSSS predominantly focuses on demons, not ghosts, it's only natural a peak that deals more in spiritual cleansing and laying the dead to rest wouldn't be involved in the plot much.
Zui Xian Peak: Potions and Elixers Peak
While lot of fanfics make jokes about Zui Xian being a peak for alcoholics (which is completely fair, as this is the dick joke filled world of SVSSS we're talking about), my first thought upon learning of Zui Xian Peak's specialty was the immorality granting heavenly wine in the Journey to the West. Looking into the matter more, I've since learned that wine has actually been a huge part of Chinese medicine since the Han Dynasty. The traditional character for medicine even includes the radical for wine!
With this kind of precedent, it seems only logical that Zui Xian Peak doesn't merely make alcohol for social and/or enjoyment purposes, it's quite likely to be the ‘external alchemy’ peak of Cang Qiong Mountain. I expect they grow and process at least some of their own herbs and ingredients, along with performing other alcohol and potion making tasks like brewing, distilling, extracting, fermenting, filtering, infusing, and so on.
Next, my thoughts on what the three mystery peaks might be:
I am not going to try and name these peaks, as I struggle with naming things even in my own native tongue.
Hunting, Trapping and Scouting Peak
Having read MDZS before SVSSS, I found the distinct lack of archery in SVSSS to be quite peculiar. As the peak of scholars and strategists, I suppose it's only logical Qing Jing Peak focuses on the four scholarly arts (the guqin, strategy games, calligraphy, and painting), rather then the six arts of Confucian gentlemen (rites, music, archery, equestrianism, calligraphy, and mathematics), but that does leave several ‘arts’ free to be claimed by other peaks! This inspired me to think up a hunting and scouting peak, where disciples excel at archery and equestrianism.
Since mounted archers became a significant aspect of Chinese warfare in the 4th century BC, thanks to King Wuling of Zhao, I'd say having cultivators of this sort in a Xianxia setting is perfectly reasonable. Giving Cang Qiong Mountain sect scouts also nicely fills the gap in their martial capabilities. Without this peak they have strategists, weapon craftsman, ground troops, and suppliers, but no reconnaissance forces!
I also consider this peak to be the rough equivalent of the ‘Beast Taming Peak’ so many works are fond of. Who else could breed and control hundreds of spirit eagles for the Immortal Alliance Conference but a group of cultivators focused on scouting missions? As supernaturally superior mounts and spirit (hunting) dogs would be incredibly helpful to them, they'd likely engage in horse and dog breeding programs as well! Their skill as hunters and trappers would also permit them both to provide game for Cang Qiong Mountain sect, and to aid in the rounding up of various living monsters for both alchemical ingredient harvesting and for releasing at events like the Immortal Alliance Conference.
In summary, this peak would produce disciples skilled at equestrianism, archery, falconry, animal husbandry, scouting, herb gathering, hunting, trapping, etc. For anyone familiar with D&D, I did basically make a Ranger peak here, but I stand by that decision!
Artifacts, Arrays and Invention Peak
Every time I read a work with some variation on the "Mad Scientist Peak" I adore it, so naturally I have to include this type of peak as well. This peak would be for the Wei Wuxians of the cultivation world, hoping to revolutionize cultivation society!
Their focus would be mathematics, spell geometry, arrays, talismans, non-medicinal alchemy (aka ancient materials science), engineering, glassforming, and of course artifact recovery, study and creation. The crystal mirror ‘surveillance equipment’ from the Immortal Alliance Conference? These guys would be the ones that developed it!
Agriculture, Earthworks and Architecture Peak
While I admittedly don't know the nuances of feng shui, I am at least aware there is far more to it then what you usually see in western depictions. In MDZS, it's noted that an area having bad feng shui (like Yi City) can cause premature death, disaster, and an increase in all sorts of nasty supernatural phenomena! With this in mind, a peak that focuses on connecting to and harmonizing with one's environment seems perfect for the final Cang Qiong Mountain peak.
I don't imagine this peak doing much of the actual building in the sect (that's An Ding's job) but when it comes to designing the sect's buildings, or altering its geography through earthworks, they're the ones to talk to. They probably would study weather patterns, rivers, and other aspects of nature and energy flow as well. I also see them as producing at least some of the sect’s food supply, using their skills to encourage a positively supernatural abundance of plants.
In short, disciples of this peak would be skilled with things like architectural design, earthworks, geography, topography, hydrology, irrigation, agriculture, meteorology, element manipulation, etc.
If SVSSS’s heavenly realms have anything akin to TGCF’s elemental masters, there is probably an unusually high chance they come from this peak.
#SVSSS#Scum Villain's Self Saving System#Cang Qiong Mountain Sect#Cang Qiong Mountain#Xian Shu Peak#Ku Xing Peak#Zui Xian Peak#* I just realized I made not only a Ranger peak but both Druid and Artificer ones too.#* My D&D background betrays me!#* Now I feel like I should match up the rest of the peaks with their D&D classes too.#* Qing Jing is the bard and rogue peak for sure!
384 notes
·
View notes
Note
I saw something about generative AI on JSTOR. Can you confirm whether you really are implementing it and explain why? I’m pretty sure most of your userbase hates AI.
A generative AI/machine learning research tool on JSTOR is currently in beta, meaning that it's not fully integrated into the platform. This is an opportunity to determine how this technology may be helpful in parsing through dense academic texts to make them more accessible and gauge their relevancy.
To JSTOR, this is primarily a learning experience. We're looking at how beta users are engaging with the tool and the results that the tool is producing to get a sense of its place in academia.
In order to understand what we're doing a bit more, it may help to take a look at what the tool actually does. From a recent blog post:
Content evaluation
Problem: Traditionally, researchers rely on metadata, abstracts, and the first few pages of an article to evaluate its relevance to their work. In humanities and social sciences scholarship, which makes up the majority of JSTOR’s content, many items lack abstracts, meaning scholars in these areas (who in turn are our core cohort of users) have one less option for efficient evaluation.
When using a traditional keyword search in a scholarly database, a query might return thousands of articles that a user needs significant time and considerable skill to wade through, simply to ascertain which might in fact be relevant to what they’re looking for, before beginning their search in earnest.
Solution: We’ve introduced two capabilities to help make evaluation more efficient, with the aim of opening the researcher’s time for deeper reading and analysis:
Summarize, which appears in the tool interface as “What is this text about,” provides users with concise descriptions of key document points. On the back-end, we’ve optimized the Large Language Model (LLM) prompt for a concise but thorough response, taking on the task of prompt engineering for the user by providing advanced direction to:
Extract the background, purpose, and motivations of the text provided.
Capture the intent of the author without drawing conclusions.
Limit the response to a short paragraph to provide the most important ideas presented in the text.

Search term context is automatically generated as soon as a user opens a text from search results, and provides information on how that text relates to the search terms the user has used. Whereas the summary allows the user to quickly assess what the item is about, this feature takes evaluation to the next level by automatically telling the user how the item is related to their search query, streamlining the evaluation process.

Discovering new paths for exploration
Problem: Once a researcher has discovered content of value to their work, it’s not always easy to know where to go from there. While JSTOR provides some resources, including a “Cited by” list as well as related texts and images, these pathways are limited in scope and not available for all texts. Especially for novice researchers, or those just getting started on a new project or exploring a novel area of literature, it can be needlessly difficult and frustrating to gain traction.
Solution: Two capabilities make further exploration less cumbersome, paving a smoother path for researchers to follow a line of inquiry:
Recommended topics are designed to assist users, particularly those who may be less familiar with certain concepts, by helping them identify additional search terms or refine and narrow their existing searches. This feature generates a list of up to 10 potential related search queries based on the document’s content. Researchers can simply click to run these searches.

Related content empowers users in two significant ways. First, it aids in quickly assessing the relevance of the current item by presenting a list of up to 10 conceptually similar items on JSTOR. This allows users to gauge the document’s helpfulness based on its relation to other relevant content. Second, this feature provides a pathway to more content, especially materials that may not have surfaced in the initial search. By generating a list of related items, complete with metadata and direct links, users can extend their research journey, uncovering additional sources that align with their interests and questions.

Supporting comprehension
Problem: You think you have found something that could be helpful for your work. It’s time to settle in and read the full document… working through the details, making sure they make sense, figuring out how they fit into your thesis, etc. This all takes time and can be tedious, especially when working through many items.
Solution: To help ensure that users find high quality items, the tool incorporates a conversational element that allows users to query specific points of interest. This functionality, reminiscent of CTRL+F but for concepts, offers a quicker alternative to reading through lengthy documents.
By asking questions that can be answered by the text, users receive responses only if the information is present. The conversational interface adds an accessibility layer as well, making the tool more user-friendly and tailored to the diverse needs of the JSTOR user community.
Credibility and source transparency
We knew that, for an AI-powered tool to truly address user problems, it would need to be held to extremely high standards of credibility and transparency. On the credibility side, JSTOR’s AI tool uses only the content of the item being viewed to generate answers to questions, effectively reducing hallucinations and misinformation.
On the transparency front, responses include inline references that highlight the specific snippet of text used, along with a link to the source page. This makes it clear to the user where the response came from (and that it is a credible source) and also helps them find the most relevant parts of the text.
293 notes
·
View notes
Note
have you read about sacred prostitution? i know you have opinions on sexual devotion to the gods. i also totes recognize that like, the culture was WILDLY different then, and i guess maybe they were more "vetted," for lack of a better term? i'll admit i haven't done the absolute most reading on aphrodite's connection with prostitutes in ancient greece. i'd just like to hear what you have to say about it considering your stance on masturbation as a devotional act.
I have, and the scholarly consensus is that "scared prostitution" was a myth.
If "sacred prostitutes" existed in ancient Greece, they were enslaved girls. And they didn't dedicate the act of sex to Aphrodite. They dedicated their commission (which they weren't allowed to keep) and the tools of their trade to her.
There's an entire book about this called "The Myth of Sacred Prostitution in Antiquity" by Stephanie Lynn Budin. The premise is that there was no sacred prostitution in any sense of the word.
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
okay but the fact that we hear all about kaveh's life post-fall out with alhaitham, the fact he graduated, worked at construction firms and continued taking on others' burdens, had a hard time finding solo work because of how arts are perceived in sumeru, that he went to his mother's wedding in fontaine, that he took a vacation from work because he was stifled by the environment and felt he had lost motivation and worth as an artist, was determined to complete the palace of alcazarzaray at the cost of everything he owned just to have a tangible object of his efforts and view of art only for its outcome to further emaciate him, until he meets alhaitham for the first time in years, is understood at once, has no need to don a front as he does for everyone else in his life, is listened to, is challenged once more and reinvigorated in his perception of his ideals, is offered a second chance, a home, and accepts it, although he cannot comprehend why alhaitham would offer such a thing and yet not ask anything of relevant substance in return, other than rent
all of this, and we hear virtually nothing of alhaitham's life post-fall out with kaveh, besides his graduation and his taking on the job of the scribe. his character stories omit this part of his life whereas kaveh's is full of detail and emotion, mostly suffering. the first instance we see of alhaitham in this time is from kaveh's perspective when the two meet again in the tavern, and in this alhaitham endeavours to understand kaveh once more, before offering his house - the research centre previously allocated to the both of them for the success of their joint thesis before they fell apart - to kaveh.
we don't know why alhaitham moved out of his grandmother's house and into the research centre, why he renovated it from a research centre into a livable home, only that he did so after kaveh informed alhaitham through a third party that he was not in need of a house, nor do we know his thought processes and emotions in the years spent apart - the years that are carefully documented in kaveh's character stories. the image we are presented with is that of stasis; alhaitham pursues no other close friendships, he works as the scribe, owns a nice house within sumeru, is financially secure, and functions within, and carries out, his own ideals - is content with this way of life. in this, from alhaitham's perspective, there are no details necessary to give from this time
but in inviting kaveh to live with him, his character stories tell us that what he gains by doing so is the mirror of himself, both in personality and scholarly thinking, and in this, he is able to gain an enhanced view of the world, which otherwise would be limited. with kaveh being present in alhaitham's life, alhaitham believes that his vision is perfected, whereas it could not be before, with kaveh's absence. it is in this that we hear what alhaitham has been missing in his life, and ultimately, it is kaveh, not just as a scholar, but as a person
what is omitted from alhaitham's character stories is provided in kaveh's character stories; where we hear about kaveh's struggles, we don't hear about alhaitham's. perhaps this is because alhaitham did not struggle as kaveh did in terms of realising and achieving his ideals, but instead his struggles were in silence, recognising that his vision, and himself, had been compromised because he had rejected the ideals that served to enhance his own vision, that he had inadvertently rejected, and thus had been rejected by, kaveh.
#basically alhaitham's silence of this time period is very telling#its giving that inazuman proverb#is it basically that kaveh wasnt in his life and everything stayed the same and therefore there was nothing to challenge him?#yeah basically? obviously im not whittling his character down to him solely revolving around kaveh#but that doesn't mean he can't do it to himself#youre not helping your case my guy#but seriously alhaithams character stories explain the differences between him and kaveh in terms of their views#on the talented and the collective which contextualises the cause of their argument#their character stories are intrinsically linked because mirrors#which is why it is so interesting to me that alhaitham basically gives no information about his life after kaveh#and any information he does give is to do with kaveh in terms of the house which kaveh also mentions#haikaveh#kaveh#kavetham#alhaitham#haikaveh meta#anyway IM GOING INSANE
389 notes
·
View notes