#what is osi model
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
I still believe the craziest form of computer program storage format from the 1980s is the cassette tape. Logical I get it but to store entire programs on little tape (that I only remember using to play music) is just crazy to me. Idk
Agreed, cassette tape for data storage was really clever. The concept had its heyday was the 1970s in a wide variety of encoding schemes for different computer platforms. It did persist into the 80s, mostly in Europe, while the US switched to floppy disks as soon as they were available for systems. The majority of my Ohio Scientific software is on cassette.

Talking with UK vs. US Commodore 64 users in particular will highlight the disparity in which storage mediums that were commonplace. I've got a few pieces of software on tape for mainly the VIC-20, but I rarely bother to use it, because it's slow and annoying. To be fair, Commodore's implementation of data storage on tape is pretty rock solid relative to the competition. It's considered more reliable than other company's but Chuck Peddle's implementation of the cassette routines are considered quite enigmatic to this day. He didn't document it super well, so CBM kept reusing his old code from the PET all the way through the end of the C128's development 7 years later because they didn't want to break any backward compatibility.

The big thing that really made alot of homebrewers and kit computer owners cozy up to the idea was the introduction of the Kansas City Standard from 1976. The idea of getting away from delicate and slow paper tape, and moving towards an inexpensive, portable, and more durable storage medium was quite enticing. Floppy disk drives and interfaces were expensive at the time, so something more accessible like off the shelf audio tapes made sense.
I've linked two places you can read about it from Byte Magazine's February 1976 issue below (check the attribution links).
You might recognize a familiar name present...


There are a few ways to encode binary data on tape designed to handle analog audio, but the KCS approach is to have 1's be 8 cycles of 2400Hz tone, and 0's be 4 cycles of 1200Hz tone. I say cycles, because while 300 baud is the initial specification, there is also a 1200 baud specification available, so the duration of marks vs spaces (another way of saying 1's and 0's), is variable based on that baud rate. Many S-100 computers implemented it, as do a few contemporary proprietary designs.
The big 3 microcomputers of 1977 that revolutionized the industry (Apple II, Commodore PET 2001, and Tandy TRS-80 Model I) each have their own cassette interface implementation. It kept costs down, and it was easy to implement, all things considered. The Apple II and TRS-80 use off-the-shelf cassette deck connections like many other machines, whereas the original variant of the PET had an integrated cassette. Commodore later used external cassette decks with a proprietary connector, whereas many other companies abandoned tape before too long. Hell, even the original IBM PC has a cassette port, not that anybody bothered to use that. Each one used a different encoding format to store their data, rather than KCS.
Here's a sample of what an OSI-formatted tape sounds like.
And here's a Commodore formatted tape, specifically one with VIC-20 programs on it.
I won't subject you to the whole program, or we'd be here all day. The initial single tone that starts the segment is called the "leader", I've truncated it for the sake of your ears, as well as recorded them kinda quietly. I don't have any other tape formats on hand to demonstrate, but I think you get the idea.
You can do alot better than storing programs on tape, but you can also do alot worse -- it beats having to type in a program every time from scratch.
274 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, I’ve been interested in mesh nets since I learned about them so I was really excited to learn you were working on this project.
How does piermesh relate to the OSI model? Which layers is this seeking to implement and which, if any, would be untouched?
Great question!
First for people who don't know the OSI model here's a rundown:
In the OSI model we're implementing layers 1-5 as well as some of 6. We're mostly following the model by nature of this being similar to the current internet though not very strictly. We're also keeping it very simple in that communication is done via msgpack serialized data so it's easy to pass the data between layers/systems/languages
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Venture Bros. #49: "Pinstripes & Poltergeists" | December 14, 2009 - 12:00AM | S04E08
The mid-season finale! The season four split of Venture Bros has been covered somewhat, but basically the boys burnt themselves out behind the scenes and needed a break, so they asked Adult Swim if they could cut season four into two halves, while also upping the episode order from 13 episodes to 16 episodes. The network went for it, and it took them nearly a whole ‘nother year to deliver the back half. So, this ends up sorta being a mini-finale.
This is another one of those episodes that’s more effective if you’re devoted to the story of Venture Bros. Meaning: it’s a little light on laughs. There are jokes in here, and they’re all fine, but there probably won’t be a big long list of all the times I laughed at this one or anything like that. It’s goal is mostly to get Brock back into the fold and to set up story elements that are going to come into play for the second half of season four. There’s nothing wrong with that, but I prefer when the show makes me laugh. But I don’t not care about the story, either.
In this one: The Monarch gets swindled by Monstroso (mentioned in a previous episode and now here in front of our eyes) into signing a bad deal thinking that he’s merely going to help the Monarch defeat Dr. Venture. Turns out he’s signed away his rights to arch Dr. Venture to Monstroso.
Monstroso’s methods are lawyerly by nature, attempting to financially ruin Dr. Venture by making him use a certain amount of square footage of his compound towards some public good. When scoping out an abandoned factory on his property he discovers that Brock and SPHINX, the super-secret organization dedicated to stopping villainy that falls outside the purview of the OSI by being non-costumed and non-Guild-of-Calamitous-Intent-affiliated, have been using the space secretly. In other words: Brock has been with the Ventures this entire time. Aww.
Also of note: 21 is shown speaking to 24’s ghost. We’d seen him chatting with 24’s skull throughout this season. He also confronts Brock, a callback to the scene in Tag-Sale, You’re It (apparently repeating the same dialogue) where 21 tries to take Brock on with a non-working light-saber. Brock’s dismissive “boo.” to get 21 to run away is now met with a punch to Brock’s face. Brock doesn’t kill 21, but his newfound respect for giving him a decent fight leads him to team up with him to go beat up Monstroso. The episode ends with Brock casually eating a bowl of cereal in the Venture’s kitchen and Hank, in a delayed reaction, being stunned to find him there.
SPHINX were previously portrayed as bad guys, but it’s explained that when they were conquered, it was decided to just take all their Egypt-themed crap and use it to start what’s essentially a new group. This explanation seems squarely aimed at the fans of the show who just wish it were an unironic action cartoon. But it's alright! I like it fine, okay! I'm not pissed off at all! At this, I mean.
EPHEMERA CORNER

The Family Guy Chicken Star Wars Double Feature (December 20, 2009)
Sometimes I’ll make note of something to cover for Ephemera Corner; like some kind of specially scheduling thing Adult Swim does that in theory is worth mentioning. But then it comes time to talk about it and it’s like damn, I do not care about this at all. Consider how now in 2024, it seems like they run marathons of certain shows all the time, just because that’s a proven-to-work model for cable television nowadays. So, I might get choosier with these EPHEMERA CORNER programming things.
But for those of you who care: Take note, Star Wars heads! Your favorite Seths went head to head and did a Star War double feature rivaling the Ewok TV Movies. The sci-fi epic about one man turning to the darkside and deciding to deprive his children of committing incest with each other by moving them to different planets will knock your socks off, because that’s what this is: It’s just the movie Star Wars but with cartoon guys in it. I don’t even think they changed the words or anything. Have fun imagining how it must’ve played with 2009-era commercial breaks.
5 notes
·
View notes
Note
liz do you have any security podcast recs?👀 and also, in general, some recs for someone who is now very interested in cybersecurity but knows basically nothing heh?
Hi there!
The main security podcast that I listen to is the SANS Internet Stormcenter podcast. The episodes are about 5 minutes long and are published every weekday morning. They're a good way to stay up to date on general things happening in the security world: big vulnerabilities, observed attack trends, patch Tuesday, that kind of stuff. That's the only security podcast that I listen to consistently, but people have told me that the Google Cloud Security Podcast is good, too. I mostly stay up to date with the industry via blogs, so if anyone is interested in that let me know & I can share a list!
As for the second part of your question, my main recommendation is to start exploring and see what kinds of things you're interested in! I'm on the tech side of security, so my recommendations will be centered around that. If you don't enjoy the tech side but are still interested in security, you can look into the governance/privacy/risk management/threat intelligence side of things. Some basic tech skills will always be helpful, though.
Off the top of my head, these are some main areas to start looking into:
Linux (how to use the GUI/CLI, understanding of how operating systems generally work)
Networking (OSI model, how the internet works)
programming/scripting - not required, but incredibly helpful. even just having a general understanding of the basics (variables, arrays, basic syntax) will be beneficial.
Generally, you'll need a solid understanding of IT stuff before you can get into the specifics of security. There are a lot of different areas of security, though, so start exploring and finding out which topics interest you!
YouTube is a good place to start learning these sorts of things. I highly recommend Professor Messer's channel. Start with the A+ playlists if you know nothing about tech, or start with the Network+ course if you feel like you could already be decent at tech support (you know the OSI model, you could probably build a computer, you know how to troubleshoot Windows). Check your school/local library to see if you get free access to LinkedIn Learning courses, there are some good ones there, too.
A good way to get started is to try a beginner-oriented CTF. I listed some resources in this post. Cyber FastTrack starts in October, usually, so if you're a college student in the U.S. you should keep an eye on that.
I hope that was helpful! let me know if you have any more questions :D
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the CCNA Certification Journey: What You Need to Know
Introduction: Embarking on the journey to obtain the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification is an exciting and rewarding endeavor. Whether you're a networking enthusiast looking to enhance your skills or a professional aiming to boost your career prospects, the CCNA certification can open doors to a world of opportunities. In this blog post, we'll explore the essential aspects you need to know to successfully pass the CCNA certifications. CCNA Classes in Nagpur
Understanding the CCNA Exam Structure: The CCNA certification is designed to validate your knowledge and skills in networking fundamentals, routing and switching technologies, and more. Familiarize yourself with the exam structure, which typically includes multiple-choice questions, simulations, and hands-on labs. Cisco regularly updates its exam blueprints, so staying informed about the latest changes is crucial.
Mastering Networking Fundamentals: A solid understanding of networking fundamentals lays the foundation for CCNA success. Concepts such as OSI model, TCP/IP, subnetting, and VLANs are fundamental to the CCNA exam. Take the time to grasp these concepts thoroughly, as they form the basis for more advanced topics.
Deep Dive into Routing and Switching Technologies: Routing and switching are core components of the CCNA certification. Ensure you are well-versed in configuring and troubleshooting routers and switches. Understand routing protocols like OSPF and EIGRP, and be comfortable with configuring VLANs and spanning-tree protocol.
Hands-On Practice with Cisco Equipment: Practical experience is key to success in the CCNA exams. Set up a lab environment with Cisco routers and switches to gain hands-on experience. Use tools like Packet Tracer or GNS3 to simulate network scenarios and practice troubleshooting. The more you immerse yourself in real-world scenarios, the more confident you'll be during the exam. CCNA Training in Nagpur
Leverage Official Cisco Resources: Cisco provides a wealth of official resources to aid your preparation. Utilize the Cisco Learning Network, official study guides, and documentation to supplement your studies. Cisco's official materials are aligned with the exam objectives, ensuring you cover all the necessary topics.
Explore Training Courses and Study Groups: Consider enrolling in CCNA training courses or joining study groups. Engaging with peers and instructors can provide valuable insights, tips, and support. Online platforms offer a variety of courses, both self-paced and instructor-led, to cater to different learning preferences.
Practice Time Management: Time management is crucial during the CCNA exam. Develop a strategy to allocate time to different sections of the exam. Practice with timed mock exams to improve your pacing and ensure you can complete the entire exam within the allotted time.
Conclusion: Passing the CCNA certification requires dedication, hands-on experience, and a thorough understanding of networking principles. By focusing on the exam objectives, mastering key concepts, and leveraging available resources, you'll be well-prepared to ace the CCNA certification and take the next step in your networking career. Good luck on your CCNA journey! CCNA Course in Nagpur
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
[https://open.spotify.com/episode/7p883Qd9pJismqTjaVa8qH ]
Jonah and Wednesday are joined by their guest Kerry as they delve into The part of the deep web that we aren't supposed to see.
Hear from our hosts again after winter break!
If you have a small horror or web fiction project you want in the spotlight, email us! Send your name, pronouns and project to [email protected].
Music Credits: https://patriciataxxon.bandcamp.com/
The Story: https://www.reddit.com/r/nosleep/comments/78td1x/the_part_of_the_deep_web_that_we_arent_supposed/
Our Tumblr: https://creepypastabookclub.tumblr.com/
Our Twitter: https://twitter.com/CreepypastaBC
Featuring Hosts:
Jonah (he/they) (https://withswords.tumblr.com/)
Wednesday (they/them) (https://wormsday.tumblr.com/)
Guest host:
Kerry (they/them)
Works Cited: 7 layers of OSI; https://www.networkworld.com/article/3239677/the-osi-model-explained-and-how-to-easily-remember-its-7-layers.html
Closed Shell System; https://www.reddit.com/r/AskReddit/comments/21q99r/whats_a_closed_shell_system/
Deep-Sea Audio from the Marnina Trenches; https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pabfhDQ0fgY Deep Web Iceberg; https://www.reddit.com/r/explainlikeimfive/comments/1pzmv3/eli5_how_much_of_the_iceberg_deep_web_diagram_is/ Fury of the Demon; https://www.imdb.com/title/tt4161438/
I work on the fifteenth floor, and something just knocked on my window.; https://www.reddit.com/r/nosleep/comments/77h76n/i_work_on_the_fifteenth_floor_and_something_just/ Kitten that leaked the no-flight list; https://maia.crimew.gay/
Project PARAGON; https://scp-wiki.wikidot.com/project-paragon-hub
Tsar Bomba; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tsar_Bomba
Unknown Armies; http://www.modernfables.net/alan/unknown_armies/Unknown_Armies_2nd_Edition%20-%20Copy.pdf What is a cult and why do people join them?; https://www.teenvogue.com/story/what-is-cult
Questions? Comments? Email us at: [email protected]
#creepypasta book club#deep web#creepypasta#podcast#the part of the deep web you aren't suppose to see
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
tell me anything you know about Networking
Whether it's big or small, limited or unlimited, in a packet or a circuit network, has some interesting challenges. (For small networks, this is usually the case for the same reason that a small family with 3 kids is easier to deal with than one with 10 or 20 kids: you only have a few edges to keep track of per node, so it's harder to forget something and accidentally block one of the kids from getting to another kid.)
I think any of the people who actually know anything about networking in practice could probably make this ask obsolete by dumping 10,000 words of research results on it, but I'm a dilettante so I'm gonna skip that.
If you really want to understand this, you probably need to go to university and major in CS/ECE/similar -- I don't think either of the graduate courses I took in networking really went below the level of details you need for a B.S.
At the high-level, the reason the "big interconnected network" situation is so hard is that you have to remember all the networks that the nodes in your network have connections to, and any node may have multiple networks associated with it. (So for instance, if A sends something to B, and B only has Ethernet but wants to send it to C, and C only has Wi-Fi and can't communicate with A, you have a network that looks like this:
B > Ethernet
A > Ethernet
C > Wi-Fi
But you need to be able to store the connections you have with all your neighbors in a way that is also transportable, because you might need to send that information to your other neighbors, so the information needs to be somewhat compact. If you were to just write down "this is my neighbor network B, here's B's information," then of course the other nodes would need to write down all their neighbors' information, which is exponentially growing, and that's not a good idea. (In the example above, B would have to write down A's information.)
The popular way of doing this is to create a series of "layers," with the outermost layer being the least verbose (it only stores information about one other network), and the innermost layer being the most verbose (all of the network's neighbors are stored there). That way, each node only has one copy of everything, since the information they need is always in the same place and they don't need to store neighbor information for neighbors that can communicate with them by some other route.
There are 4 Layers in the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model:
Network Interface (the hardware that actually communicates with the wires),
Network (Routing) Layer (sets up connections between nodes),
Transport Layer (packets get passed back and forth),
Application Layer (word processors, Minecraft, etc.)
Network interfaces are the fun part of this, but the basic gist of the model is that you should have to create different "internal" networks that can communicate with each other at different levels. So, like in the example above, we could create
network A > Ethernet
(Ethernet needs a service called "IP" and can only talk to other IP networks via "IP", so if you're using IP you need to connect to something like a "DNS" to get an IP address),
network B > Ethernet
<<==> I'm supposed to put more text here but I'm incoherent, so just ignore this line
(B's service is called "GNUnet" because they really hate Google),
network C > Wi-Fi
and all these can communicate by saying "I want to talk to this network! I have an IP address here, does that network know how to talk to this network with that IP address?" and so on.
What makes it "interesting," IMO, is that you now have multiple couplings in your system. If I go to sleep for a while, my router stops keeping the connection alive, so the other half of the connection is down, but my computer just lost one thing to think about, but the computer I was talking to has lost both of its connections and thinks I just disappeared, and then if I open up a new browser tab, my computer has to start the connection process all over, and now it has two things to do -- it has to get the new connection started, and it has to relay messages between the other computer and the rest of the network.
Normally you're doing that by "multithreading," which in the computer industry means "putting some of the work to be done on a different thread of execution than the thing that started it." So if your browser has a separate thread for downloading images, it can go ahead and look for the next image on the webpage while waiting for the first image to download, because each thread has its own memory (the "working set" per thread) where it can keep track of the things it needs to remember between its own calculations. (Threads share memory as far as the rest of the system is concerned, so they can read and write from it, but they don't know what other threads are doing at any given time, so they don't step on each other's toes.)
Except multithreading makes it easier to lose track of important information, and the computer might easily forget that it is still communicating with the other computer when it is done with the connection, but it is still connected to the network by other networks, and it also needs to remember what other networks it is talking to. It also has to remember which networks it needs to keep up with, and what it is waiting for from the networks it is waiting for, and all sorts of other information about what it is doing.
It's really easy to make a mistake at
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Can I Do With A Cisco CCNA Certification?
Cisco Certified Network Associates (CCNA) are one of the world's most sought-after network professionals. Having a CCNA certification opens up a wide variety of job opportunities and can lead to higher salaries.

A Cisco CCNA certification is valuable in terms of the potential salary and employment opportunities that result from this certification. MyComputerCareer also offers his CCNA training as part of the Cybersecurity Specialist Curriculum. For more information, please contact us immediately.
This article explains what a CCNA certification is, what it includes, and the skills it teaches. We will also discuss the different positions you can get with a CCNA certificate and the salaries you can earn with this certificate.
What Is The CCNA Certification?
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification is a well-known computer networking credential. CCNA certification helps entry-level network engineers, professional network engineers, support network engineers, and network administrators learn basic networking concepts.
Over one million CCNA certificates have been distributed to fully certified professionals since Cisco first introduced certificates in 1998. CCNA certifications cover a wide range of networking topics and help prepare learners for future advances in networking technology.
CCNA certification topics include:
OSI model: Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Network Layer, Transport Layer, and Application Layer
IP routing: static and dynamic routing protocols
IP addressing: Fourth Generation IPv4 (IPv), Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), and Cisco IOS
Network security: Firewalls, password security, virtual private networks (VPNs), and intrusion detection systems
VLANs and WLANs: Access Control Lists (ACLs), VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP), and Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) IP Services
Routing protocols (OSPF, EIGRP, and RIP): Cisco IOS, Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF), and Cisco Dynamic Multiprotocol Label Switching (DMVPN) WAN
CCNA certification validates many of the skills a network engineer needs. You will also need various soft skills such as communication, problem solving, organization and customer service. CCNA certification also provides network professionals with the information and skills they need to effectively operate Cisco and Microsoft Office suite applications. This certification empowers aspiring and current network engineers to use industry-specific tools in their daily work.
However, please note that Cisco certifications are valid for three years. If the certification expires, the holder may retake her CCNA certification exam, obtain another Associate certification, pass the Core Technology exam, or for renewal she must complete 40 Continuing Education (CE) credit must be obtained.
What IT Jobs Can You Get With a CCNA Certification?
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification validates a user's knowledge and skills in network administration. Salaries for this degree average about $80,000 per year. Many employees are looking for Cisco certified professionals because of their extensive experience with Cisco routers and switches. Cisco network equipment is used by most of the Fortune 500 companies.
Network administrator: Network administrators are responsible for the day-to-day operation of computer networks. Keep your network running smoothly and resolve any issues that may arise.
System Administrator: System administrators are responsible for the maintenance and operation of computer systems. It installs new software, patches existing software, and performs other tasks to keep your system running smoothly.
Network analyst: Network analysts are responsible for analyzing computer networks and making recommendations to improve their efficiency. They may also be responsible for designing new networks or implementing changes to existing networks.
Network design engineer: Network design engineers are responsible for designing and implementing computer networks. We work with our customers to understand their needs and design networks that meet those needs.
Infrastructure Engineer: Infrastructure engineers are responsible for the physical components of computer networks such as routers, switches, and cables. Install and maintain these components to keep your network running smoothly.
Unified Communications Engineer: Unified Communications Engineers are responsible for designing and implementing unified communications systems. Unified communication systems allow users to communicate across multiple devices such as phones, computers, and tablets.
Solution designer: Solution design engineers are responsible for designing and implementing solutions to problems encountered in computer networks. They work with customers to understand their needs and design solutions that meet those needs.
Cloud Engineer: Cloud engineers are responsible for designing and implementing cloud-based solutions. Cloud-based solutions allow users to access data and applications from anywhere in the world.
Data Center Engineer: Data center engineers are responsible for the operation of data centers. Install and maintain the hardware and software that make up your data center.
Network administrator: Network administrators are responsible for the day-to-day operation of computer networks. Ensure the smooth operation of your network and fix any problems that may arise.
Cloud Architect: Cloud architects are responsible for designing and implementing cloud-based solutions. Cloud-based solutions allow users to access data and applications from anywhere in the world.
VoIP Engineer: VoIP engineers are responsible for designing and implementing Voice over IP (VoIP) solutions. VoIP solutions allow users to communicate using voice and video over the Internet.
Cooperating engineer: Collaboration engineers are responsible for designing and implementing solutions that enable users to collaborate. Collaboration solutions allow users to share data, applications, and files.
Telecom Engineer: Telecommunications engineers are responsible for the design and implementation of telecommunications systems. Telecommunications systems allow users to communicate using voice, video, and data.
Depending on your skills, years of experience, valid qualifications, and other criteria, you may be better suited for one job than another. The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) is a great place to start for anyone looking to get into networking.
Conclusion
Earning the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification is a great way to start your networking career. A CCNA certification contains a wealth of knowledge that will help you in your career. A CCNA certification can lead to higher salaries and help you find jobs in a variety of occupations. There are a variety of Cisco certifications you can earn, each useful in your career. A CCNA certification is just the beginning of your journey to a successful networking career.
591cert offers a certification program that includes CCNA Certification. If you're interested in becoming a CCNA and growing your IT career, take a free career assessment. We are happy to answer your questions.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Telecommunication protocols application interaction
Let's look at the basics of transferring information between two application processes in the OSI model.
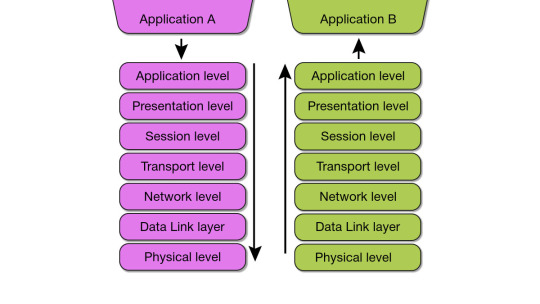
Say an application (in the picture above) needs to access a file service on another computer. It sends a request to the application layer. Based on it, the software generates a standard format message consisting of a data field and a service header. The latter contains a description of actions for the application layer of the other machine to perform, as well as instructions for the adjacent lower layer. The presentation layer, in turn, formats the data according to the instructions received and adds its own header (some protocol implementations also include service data at the end of the message), after which the information is sent to the session layer. This procedure, called encapsulation, is repeated further as data and service information move to the physical layer.
When arriving at the physical layer, i.e., the network, data passes through many other devices (network adapters, hubs, routers, bridges, etc.) and, upon reaching the destination (for example, a SIP phone), undergoes a reverse encapsulation process (right side of the picture).
Data networks can be of two types: local (local area network, LAN) and global (wide area network, WAN). The latter connects any two networks within the globe with dedicated or switched communication channels. Local networks differ in transmission medium, topology, and access control. Depending on the transmission medium, they are divided into wired (using coaxial, twisted pair, or fiber-optic cable) and wireless (WLAN), and according to the type of topology, into networks with 'bus', 'ring', or 'star' topologies.
Each computer on the local network is connected to the transmission medium through a special adapter that "sees" what any other adapter on the same network is transmitting; such systems are called broadcasts.
The MAC protocol regulates the sequence of nodes' access to the transmission medium. It is implemented using two types of schemes: polling or contention-based MAC schemes.
MAC polling networks can be centralized or distributed. Centralized ones have a star topology with a hub as the control node. In contrast, distributed ones have a ring or bus topology with token passing. Contention-based MACs are often implemented as carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) or carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA). The first is used in all types of Ethernet LANs, and the second is used in most wireless WLANs.
The unrivaled leader among local networks is the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet network, where coaxial, twisted pair (designated by the letter T for 'twisted') and fiber-optic cables are used as transmission media. The transition to twisted-pair cable made it possible to implement full-duplex transmission over two twisted pairs, leaving the concept of collision meaningless since transmission and reception became independent operations. Ethernet has transmission speeds of 10, 100 ('Fast Ethernet'), 1000 Mbit/s (1 Gbit/s, 'Gigabit Ethernet'), and up to 400 Gigabit Ethernet.
Wireless local networks (wireless LAN, WLAN) have also become widespread. Their parameters are stated in the IEEE 802.11 specifications, known as Wi-Fi.
Today, the most common Wi-Fi 5 or 802.11ac defines the operation of wireless local area networks in the 2.4/5 GHz ranges with a data transfer rate of 1.3 Gbit/s. Shortly, speeds will reach 9.6 Gbit/s over 6 GHz frequency bands.
The range of most WLAN systems is 120 m, depending on the number and type of obstacles encountered. Additional access points will help expand the coverage area. Using two or three carrier frequencies instead of one can increase the number of users and network capacity.
Obviously, with Wi-Fi, network security becomes an important issue. A priori, wireless networks must be equipped with additional means of ensuring reliability compared to wired ones. WLAN uses direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technology, which is highly resistant to data corruption and interference, including intentional ones. The problem of user authentication can be solved by introducing system identifiers. The wired equivalent privacy (WEP) mode is provided to transmit necessary information. In this case, the signal is encrypted with an additional algorithm, and the data is controlled using an electronic key.
Like all IEEE 802.3 standards, 802.11 refers to the lower two layers of the OSI model: physical and link. Any network application, operating system, or protocol (such as TCP/IP) will function equally well on an 802.11 network or Ethernet one.
The original 802.11 standard defines the basic architecture - the features of 802.11 services. The 802.11x specification only addresses the physical layer, introducing higher access speeds.
In conclusion, we should note that thanks to the close ties between Ethernet and the IP protocol, the scope of Ethernet applications is expanding, particularly in broadband subscriber access (BSA) networks.
0 notes
Text
The Future of Load Balancing: Trends and Innovations in Application Load Balancer
The future of load balancing is rapidly evolving with advancements in technology, particularly in the realm of application load balancers (ALBs). As businesses increasingly shift to cloud-native architectures and microservices, ALBs are becoming more crucial in ensuring efficient traffic distribution across applications. Innovations such as AI-powered load balancing, real-time traffic analytics, and integration with containerized environments like Kubernetes are enhancing the scalability and performance of ALBs. Additionally, the rise of edge computing is pushing ALBs closer to end-users, reducing latency and improving overall user experience. As security concerns grow, ALBs are also incorporating advanced threat detection and DDoS protection features. These trends promise a more reliable, efficient, and secure approach to managing application traffic in the future.
What is an Application Load Balancer (ALB) and How Does It Work?
Application Load Balancer (ALB) is a cloud-based service designed to distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers, ensuring optimal performance and high availability of applications. ALBs operate at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model, which means they can make intelligent routing decisions based on the content of the request, such as URL, host headers, or HTTP methods. This differs from traditional load balancers that operate at the network layer. ALBs offer more sophisticated features for modern web applications, making them essential for scalable, highly available cloud environments.
Key Features of Application Load Balancer (ALB)
ALBs provide several features that make them highly suitable for distributed applications:
Content-Based Routing: ALBs can route traffic based on the URL path, host headers, or HTTP methods, enabling fine-grained control over the distribution of requests.
SSL Termination: ALBs can offload SSL termination, decrypting HTTPS requests before forwarding them to backend servers, thus improving performance.
Auto Scaling Integration: ALBs integrate seamlessly with auto-scaling groups, ensuring that traffic is evenly distributed across new and existing resources.
WebSocket Support: ALBs support WebSocket connections, making them ideal for applications requiring real-time, two-way communication.
Advantages of Using an Application Load Balancer in Cloud Environments
Application Load Balancers offer several benefits, particularly in cloud environments:
Improved Availability and Fault Tolerance: ALBs distribute traffic to healthy instances, ensuring high availability even if some backend servers fail.
Better Performance and Latency Optimization: By routing traffic based on specific parameters, ALBs can reduce response times and ensure efficient resource utilization.
Scalability: With ALBs, applications can scale horizontally by adding or removing instances without affecting performance, making them ideal for elastic cloud environments like AWS and Azure.
Security Enhancements: ALBs provide SSL termination, reducing the load on backend servers and offering better security for user data during transmission.
Application Load Balancer vs. Classic Load Balancer: Which One Should You Choose?
When choosing a load balancer for your application, understanding the difference between an Application Load Balancer (ALB) and a Classic Load Balancer (CLB) is crucial:
Layer 7 vs. Layer 4: ALBs operate at Layer 7 (application layer), while CLBs work at Layer 4 (transport layer). ALBs offer more sophisticated routing capabilities, whereas CLBs are simpler and more suitable for TCP/UDP-based applications.
Routing Based on Content: ALBs can route traffic based on URLs, headers, or query parameters, whereas CLBs route traffic at the IP level.
Support for Modern Web Apps: ALBs are designed to support modern web application architectures, including microservices and containerized apps, while CLBs are more suited for monolithic architectures.
SSL Offloading: ALBs offer SSL offloading, whereas CLBs only support SSL pass-through.
How to Set Up an Application Load Balancer on AWS?
Setting up an ALB on AWS involves several steps:
Step 1: Create a Load Balancer: Begin by creating an Application Load Balancer in the AWS Management Console. Choose a name, select the VPC, and configure listeners (typically HTTP/HTTPS).
Step 2: Configure Target Groups: Define target groups that represent the backend services or instances that will handle the requests. Configure health checks to ensure traffic is only sent to healthy targets.
Step 3: Define Routing Rules: Configure routing rules based on URL paths, hostnames, or HTTP methods. You can create multiple rules to direct traffic to different target groups based on incoming request details.
Step 4: Configure Security: Enable SSL certificates for secure communication and set up access control policies for your load balancer to protect against unwanted traffic.
Step 5: Test and Monitor: Once the ALB is set up, monitor its performance via AWS CloudWatch to ensure it is handling traffic as expected.
Common Use Cases for Application Load Balancer
Application Load Balancers are suitable for various use cases, including:
Microservices Architectures: ALBs are well-suited for routing traffic to different microservices based on specific API routes or URLs.
Web Applications: ALBs can efficiently handle HTTP/HTTPS traffic for websites, ensuring high availability and minimal latency.
Containerized Applications: In environments like AWS ECS or Kubernetes, ALBs can distribute traffic to containerized instances, allowing seamless scaling.
Real-Time Applications: ALBs are ideal for applications that rely on WebSockets or require low-latency responses, such as online gaming or live chat systems.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Application Load Balancer
While ALBs offer powerful functionality, users may encounter issues that need troubleshooting:
Health Check Failures: Ensure that the health check settings (like path and response code) are correct. Misconfigured health checks can result in unhealthy targets.
SSL/TLS Configuration Issues: If SSL termination isn’t set up properly, users might experience errors or failed connections. Ensure SSL certificates are valid and correctly configured.
Routing Misconfigurations: Ensure that routing rules are properly defined, as incorrect routing can lead to traffic being sent to the wrong target.
Scaling Issues: If targets are not scaling properly, review auto-scaling group configurations to ensure they align with the ALB's scaling behavior.
Conclusion
Application Load Balancers are critical in optimizing the performance, availability, and scalability of modern web applications. By providing intelligent routing based on content, ALBs enable efficient handling of complex application architectures, such as microservices and containerized environments. Their ability to handle high volumes of traffic with low latency, integrate seamlessly with auto-scaling solutions, and enhance security makes them an invaluable tool for businesses looking to scale their operations efficiently. When setting up an ALB, it is essential to understand its key features, use cases, and best practices to maximize its potential. Whether deployed on AWS, Azure, or other cloud platforms, an Application Load Balancer ensures your applications remain responsive and available to users worldwide.
0 notes
Text
CompTIA Network+: The Essential Certification for Networking Professionals
In today’s interconnected world, networking is the backbone of almost all IT systems. From businesses to data centers, networks enable communication and data transfer across different devices and locations. As the demand for skilled network professionals increases, certifications like CompTIA Network+ have become essential for IT professionals seeking to demonstrate their expertise in network administration. Whether you’re an aspiring network engineer or an IT specialist looking to enhance your skill set, the CompTIA Network+ certification offers a solid foundation for building and managing modern network infrastructures. In this blog, we’ll explore what CompTIA Network+ is, why it’s important, and how to prepare for the certification exam.
What is CompTIA Network+?
CompTIA Network+ is a globally recognized entry-level certification designed to validate the essential skills needed for a career in networking. It covers a broad range of networking topics, from basic network troubleshooting to complex network design, security, and management. The certification is ideal for individuals who are looking to start their careers in IT, as well as those who want to validate their knowledge and enhance their credentials.
The CompTIA Network+ exam (N10-008) tests your understanding of networking concepts, operations, and protocols, and it helps ensure you have the skills necessary to manage and troubleshoot networks. The certification is vendor-neutral, meaning it doesn’t focus on any specific technology or manufacturer, such as Cisco, Microsoft, or Juniper, making it applicable to any network environment.

Key Topics Covered in CompTIA Network+
The CompTIA Network+ exam tests a wide range of networking topics, ensuring that certified professionals have a comprehensive understanding of network operations. These topics are broken down into several key domains:
1. Networking Concepts
This domain covers the foundational networking principles and concepts, such as the OSI model, TCP/IP stack, and network protocols. Understanding how data is transmitted over a network and how different protocols interact is critical for anyone working with networks. It also includes understanding the differences between network types (LAN, WAN, MAN, etc.) and IP addressing (IPv4 and IPv6).
2. Infrastructure
In this domain, candidates learn about network devices like routers, switches, access points, and firewalls. You will also learn how to set up and configure various types of network infrastructure, including cabling and wireless networks. This section teaches you the physical and logical components required to build and maintain networks, along with the tools and techniques used to monitor and troubleshoot them.
3. Network Operations
Network operations involve the ongoing management and optimization of networks. This domain covers topics like network monitoring, performance tuning, and fault tolerance. You’ll learn how to maintain a network’s health and ensure that all systems are running efficiently. You’ll also learn about backup solutions, disaster recovery, and business continuity, which are key to maintaining a robust network environment.
4. Network Security
Security is a crucial aspect of network management, especially with the increasing threat of cyberattacks. The Network+ certification covers essential security practices like encryption, firewall management, and access control methods. It also includes an understanding of network vulnerabilities, common attacks (like DDoS and phishing), and how to protect a network from security threats.
5. Troubleshooting and Tools
Effective troubleshooting is a critical skill for network professionals. This domain teaches you how to identify, diagnose, and resolve network issues using various diagnostic tools, such as ping, tracert, and netstat. You’ll also learn how to handle common network problems, such as slow performance, connectivity issues, and misconfigured devices.
Why CompTIA Network+ is Important
1. Industry Recognition
As a globally recognized certification, CompTIA Network+ is highly regarded by employers across a wide range of industries. It demonstrates that you possess the core networking skills required to support and troubleshoot modern network environments. Whether you’re working for a small business, a large enterprise, or a service provider, this certification serves as a standard of competency and reliability in the networking field.
2. Foundational Networking Skills
CompTIA Network+ provides a comprehensive foundation for anyone interested in pursuing a career in IT or network administration. It covers essential concepts, from basic networking protocols to advanced security techniques, giving you the knowledge you need to design, implement, and maintain network systems. This foundational understanding is critical for further specialization in networking or related areas, such as security or cloud computing.
3. Job Opportunities
Holding a CompTIA Network+ certification opens up a wide range of job opportunities in IT, including roles such as:
Network Administrator
IT Support Specialist
Systems Administrator
Help Desk Technician
Network Technician
As businesses rely more on complex IT infrastructures, skilled networking professionals are in high demand. The Network+ certification gives you the credibility and recognition to pursue these positions and stand out in a competitive job market.
4. Career Advancement
For current IT professionals, CompTIA Network+ can serve as a springboard for advancing in your career. Having this certification can make you eligible for higher-paying roles, promotions, and leadership positions in the networking domain. It also lays the groundwork for pursuing more advanced certifications, such as Cisco’s CCNA or CompTIA Security+, which can help you specialize further in specific areas of networking and security.
How to Prepare for the CompTIA Network+ Exam
1. Review Exam Objectives
CompTIA provides a detailed list of exam objectives, outlining the knowledge areas you’ll be tested on. Reviewing these objectives is the first step in ensuring that your studies are focused on the right areas. By understanding the exam objectives, you can create a study plan that targets the key topics and helps you stay organized.
2. Hands-On Practice
The best way to solidify your understanding of networking concepts is through hands-on practice. Setting up a home lab with virtual machines or using simulation tools like Packet Tracer or GNS3 allows you to practice configuring networks and troubleshooting issues in a controlled environment. Practical experience helps reinforce theoretical knowledge and prepares you for real-world scenarios.
3. Join Online Communities
Joining study groups or forums can provide additional insights and support. Online communities like Reddit’s r/CompTIA, TechExams.net, and other networking forums allow you to connect with others who are studying for the same certification. Sharing experiences, asking questions, and getting feedback from peers can boost your confidence and help you clarify complex concepts.
Conclusion
The CompTIA Network+ certification is an excellent starting point for anyone looking to pursue a career in networking or IT infrastructure. It offers a comprehensive understanding of essential networking concepts, security protocols, and troubleshooting techniques, making it a valuable credential for entry-level network professionals. In addition, the vendor-neutral nature of the certification means that it is relevant for a wide range of network environments and job roles.
With a growing demand for network professionals and the continuous evolution of technology, obtaining CompTIA Network+ certification can be the key to unlocking new career opportunities and advancing in the IT industry. By preparing effectively and gaining hands-on experience, you can ensure that you’re ready to succeed in this fast-paced and rewarding field.
0 notes
Text

Channeling my inner 1970s homebrew computer hacker using Byte Magazine Volume 00, Issue No. 1 for help with a surplus Sanders 720 keyboard. It's not the exact same model featured in the article, but it's close! What's more, that OSI-440 video board I'm working on has provisions in the manual for interfacing with a Sanders 720.
#sanders 720#byte magazine#ohio scientific#osi 440#osi 400#kit computer#you have no idea how exciting this is
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
online software testing training - forget the rest
In the constantly changing digital environment, security continues to be a major concern for companies and organizations globally. The demand for knowledgeable network security experts is at an all-time high, and acquiring a CCNA Security+ certification is an impactful move toward a thriving career in this sector. For individuals aiming to enhance their skills or break into the cybersecurity field, an online CCNA Security+ Training offers the adaptability and strong knowledge foundation required to succeed in today’s technology-focused landscape.
Reasons to Select CCNA Security+?
The CCNA Security+ certification offered by Cisco is regarded as one of the most highly valued credentials in the realm of IT security. Designed for individuals passionate about protecting digital assets, this certification validates crucial networking expertise and highlights security fundamentals, tools, and methods for minimizing threats. Covering topics from access control to cryptography, CCNA Security+ prepares students to safeguard systems against cyber threats while becoming proficient in handling and configuring Cisco devices.
Advantages of Online CCNA Security+ Training
Choosing an online format allows this training to be accessible to students with different locations and lifestyles.
Here’s what makes online CCNA Security+ training a smart choice:
Adaptable Learning Timetables: Virtual training allows students to learn at their speed, facilitating the balance between personal and work commitments.
Practical Application: Engaging labs and simulation exercises are integrated to offer real-world experience, enabling students to confidently apply their knowledge in actual situations.
Expert Guidance: Interactive online sessions with experienced instructors provide insight into real-world security challenges, keeping learners up-to-date with industry practices.
Comprehensive Curriculum: The CCNA Security+ curriculum covers essential areas, including network access, security protocols, firewall implementation, VPNs, and much more.
Career Paths with CCNA Security+ Certification
Earning a CCNA Security+ certification opens a wide range of career opportunities in networking and cybersecurity, including:
Network Security Administrator: Secure network architectures and protect data assets with configurations that ensure safe data exchange.
Cybersecurity Analyst: Analyze and prevent security breaches while staying ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Security Consultant: Offer expert guidance to organizations on best practices in network protection, compliance, and digital defense.
Penetration Tester (Ethical Hacker): Test the resilience of a company’s network through controlled simulations, identifying vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
In a competitive job market, this certification distinguishes you as a knowledgeable and proactive professional. It enhances your credibility and gives employers confidence that you’re equipped to protect valuable digital assets.
Course Highlights
Online CCNA Security+ training programs focus on both theoretical understanding and hands-on application:
Network Fundamentals: Learn the foundations of networking, including the OSI model, IP addressing, and routing protocols, essential for secure network operations.
Threat Prevention: Understand common network threats, including phishing, malware, and DoS attacks, and learn how to defend against them.
Device Configuration and Management: Gain insights into configuring and managing Cisco devices, including routers, switches, and firewalls, to establish a secure network perimeter.
Access Control & Identity Management: Master methods for controlling user access and managing identities, which is crucial in maintaining network integrity.
Who Should Enroll?
This program is perfect for IT specialists, network engineers, and anyone looking to enter the field of cybersecurity. Regardless of whether you are a seasoned technician or a new graduate, CCNA Security+ is an important certification that improves your abilities and provides access to positions in cybersecurity, network management, and more.
CCNA Security+ online training provides students with the skills needed to combat cyber threats, making them essential contributors in the modern tech environment. Seize control of your cybersecurity career by obtaining an online CCNA Security+certification and connect with a network of experts committed to safeguarding digital boundaries.
For more information visit:- https://www.softcrayons.com/ccna-security-training
0 notes