#what is difference between rfi
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#blog post#rfp#rfi#rfq#what is difference between rfi#rfp and rfq#partner portal#supply chain#vendor management system#procure to pay software
0 notes
Note
I'm a English native and I'm learning French I can have a short conversation in French but I'm really slow and takes time to understand some words. I used to be in French classes in highschool (I'm going to be a senior in highschool when it starts up) what would you recommend for me to use to help learn more? I'm currently using droplets and Duolingo for studying (Droplets for vocabulary and Duolingo for grammar, reading things like that) what would you recommend for me to use thats free or doesn't cost that much? It would help a lot thank you
Hi!
Duolingo and Droplets are good resources for starters.
there are several things you can do if you want to go further.
Check out RFI (Radio France International) : You'll find free listening and reading resources abt French speaking news. I highly recommend you listen and then read the podcast episodes of LES MOTS D'ACTUALITÉ (words that are the news - they will explain the origin and meanings of 1 word that is relevant these days in France). but be curious and check out the rest, they have lots of good stuff.
Read news articles for free on official news website France Info, RTBF (Belgium). you'll find some free articles on Le Monde, Libération, Le Parisien, etc.
find lessons and exercises on Francaisfacile.com to get a better understanding of grammar, conjugations, tenses, etc.
Read 19th Guy de Maupassanant's (King of French fantastique genre) short stories on Wikisource. Highly recommend "La Main" ("The Hand", kinda horror, but really famous)
-> when you're more confident abt reading novels in French, just search for any 19th writer + Wikisource and you should be able to find their works in full for free. My favs are Zola, Balzac, Victor Hugo (Les Misérables' writer !), Flaubert, Dumas (Les Trois Mousquetaires' writer !), George Sand, Stendhal (esp La Chartreuse de Parme) etc.
if you have doubts about how to say something like a native, ask someone on HiNative you'll always have some French speaking ppl to help you.
- Familiarise yourself with spoken French with youtube/podcasts/etc (anything that's material for listening skills). If you're on youtube you can check channels like
Vogue France and their street style, with subtitles and lots of fashion and slang vocab! I used it in my French lesson and it worked quite well.
Yes Vous Aime was a comedy skits channel, with French subtitles. They did parodies, you can check it out!
Paul Taylor is a British stand up comedian. He's doing skits and specials in both French and English, and he's honestly perfect at grasping and vulgarising French oddities either in the language or the french society.
Clément Viktorovitch and his weekly analysis on French politics/news on Franceinfo. As you may already know, we're very passionate about our political life in France. so you can get used to the vocab have a gist of it with these chroniques radio.
Karambolage - it's a bilingual channel (German & French - l'amitié franco-allemande is a big thing! 🙂) that explains social, cultural differences between the two countries. You can find illustrated explanations of Le Verlan, expressions like "Monter à Paris" etc etc. It worked so well with my students! they found it easier to understand.
Damon Dominique is a language American youtuber and he's good at explaining and vulgarising French grammar and slang. Sometimes you gotta look at a foreign point of view :)
Konbini (especially their Club Lecture, Vidéo Club where famous authors/film directors show their favourite works, their inspirations and talk abt it, you probably won't find any subtitles tho)
and ofc you have dozen of french youtubers like Squeezie, Seb, Lena Situation, Aurélien Prévaux, Zen (talkshow) etc.
And when you're more confident, you can pick a day when you'll try to think only in French, another day when you'll translate what's written on your food package/friends convos/emails etc etc
put your phone settings in french, follow vocab accounts on Instagram, follow French ppl on social media so that you get accustomed to read in French on a daily basis.
and find a book to read in french, or fanfics if you're into it, anything that'll make you read in French :)
I hope that answers your questions! and sorry if it looks like too much, I'm getting back at a language I used to learn in high school too, it's not easy and it takes time. so take your time with French, I just put everything I thought might help in the first months/first year!
good luck! bonne chance !
35 notes
·
View notes
Note
You know what is interesting ?! i can see you/illicite affairs. In illicite affairs there is no cheating involve per say, it's more secret language/having sex with someone but nobody knows. And i can see you feels like the beginning of that, the rush that something might happen, illicite affairs is the downfall, it was more for me than for you, and the lines "Don't call me kid, don't call me baby" could fit if the rs was with someone older...idk what do you think?
i think i can see you is like ultimate taylor because it's about the anticipation, the what-if, the fantasy... she has so many songs like this in her earlier discography, enchanted being another great example.
i don't think there's a direct connection between i can see you and illicit affairs, but there's a sort of comparative thematic connection. i can see you is about the excitement of anticipating something might happen... and illicit affairs is the ugly reality when it all falls apart. fantasy -> fallout. oh the "i don't like that falling feels like flying til the bone crush" of it all!!!
imo, treacherous is kind of i can see you's older sister. treacherous is a song about anticipation, being afraid of embarking on this risk.
and 1989 doesn't get a track like that at all, except wildest dreams, which is just fatalistic rather than a fantasy. "i can see the end as it begins..."
and we get a return to the anticipatory songs in reputation with rfi and delicate!
idk where i'm going with this exactly but it was fun lmao
(sidenote: so fascinating to see how her early discography was full of fantasy/what ifs and her latest album - midnights and sntv - is about looking back on things that actually happened, and sometimes how they could've been different!)
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
I wonder what I am wrong about.
I am an engineer. I can hack numbers. Engineering is using numbers to decide on this versus that. But I also am an ART lover. I cannot dance, but I can appreciate the perfect Ballet Jete' and the other stuff. I cannot skate or name all the jumps, but I know when a figure skater does a great performance. I am amazed by music and the people who make it. I can hear stuff on my system and in a concert hall.
All that is to say I can see both sides of arguments when one side is "technical" and the other is esthetic.
I did one of my loops through audiophile You Tube stuff and it was a trip. Started with the Audiophiliac guy reviewing a new Magnepan Speaker. He loved it. It was an upmarket version of another Maggy that cost double the existing and the difference was $4000 for basically a new cross over filter. Errr that strikes me as odd. No cross over should cost that much.
The next stop was a guy who modifies speaker cross overs including Maggies. ( G R Research ) He did a video on a less expensive Maggy showing that the factory filter was....crap. Also things about the tweeter going too low.
youtube
He seems to know what he is doing and has tests and charts and stuff.
I dug into his stuff a bit more and his business is selling modification kits for speaker cross over filters and CABLES. Fancy gourmet cables. This became a rabbit hole where he has a low intensity feud with Audio Science Review. ASR calls bullshit on fancy cables.
GR research called bullshit (in a nice way) on ASR's tests.
He sells speaker cables and power cables. Not cheap stuff. He claims changing out a cable on a preamp "opens the sound stage" and other alchemical stuff. He describes that the cable is a filter and rejects noise. OK fine. But that should not impact sound stage. His cables are braided wire which alters the inductance and capacitance of a plain wire pair, but come on. You have to appreciate orders of magnitude of Farads and Henrys. Those are TINY in cables.
He operates in the fuzzy world between numbers and opinion. And his business depends on some fuzzy stuff. Gotta feed the cats (or dogs) you know.
GRs describes his personal system uses batteries to go completely off grid. Which is ironic. If the batteries are in the audio equipment they will provide excellent regulation and huge current reserve. Good things. If he uses those to feed an inverter to generate AC to feed into normal audio equipment that will limit current as well as noise. An AC inverter IS a very low frequency amplifier (60 Hz). PS audio sells those. I think they are stupid.
My preamp has a large very regulated power supply. There is very little noise apparent. And Yes RFI can get in with our world full of wi-fi, and cell phone towers and gobs of EM radiation all measured in milliwatts or less.. But a proper audio power supply is fundamentally a big filter and energy storage device. 4 ft of fancy cable between my wall plug and it aint going to be noticeable. Am I wrong?
My power amplifiers have big power supplies. A big part of the Franken-Amp is its power supply which has lots of capacitors both electrolytic and film to block the AC noise. It also has an inductor coil on the output to block RFI getting in from that side. Amplifers with negative feedback can do bad things if you do not block RFI.
The ARC is a tube amp with a big transformer at the output which is made from wire coils and Iron plates. That is a filter too.
There is also this thing where class D amplifiers generate very powerful radio frequencies to operate (tens or hundreds of Watts). At the end of the process there is a BIG filter using inductors and capacitors to block that and presumably any RF noise that sneaks in over the wires in front.
I have a big run of wire outside my house and the wires inside are 50 years old. I could upgrade the inside if I wanted, I have skills. But I believe I do not need to. That overwhelms what 4 ft of braided wire would do.
My impression is this person knows enough electrical engineering to come up with credible solutions to problems that might not be real. I think his Magnepan thing is cool and legit. Hey Magnepan does its own modifications for extra money. ( "Its only business" in a godfather voice)
I admit that he may actually hear something when these things are swapped out. But he may be blaming the wrong thing, or he has set a preference for a particular voice using components that are sensitive to his solutions. It can be real for the wrong reasons.
Bottom line I think he has integrity and believes these things can help. I reserve the right to be wrong about cables. Still I will not buy them.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

HDI PCB & High Interconnect PCB Manufacturing
HDI PCB Manufacturer & Assembly – One-stop service
What is a high density PCB board (HDI PCB)?
The HDI board is based on the traditional double panel as the core board, which is made by continuously accumulating. This circuit board made by a continuous layer is also called the Build-Up Multilayer (BUM). Compared with the traditional circuit board, the HDI circuit board has the advantages of "light, thin, short, small".
The electrical connection between HDI's plate layer is achieved by conductive pores, buried holes, and blind holes. Its structure is different from ordinary multi -layer circuit boards. A large number of blind holes are used in HDI boards. HDI PCB uses laser direct drilling, and standard PCB usually uses mechanical drilling, so the number of layers and high width ratio often decreases.
HDI includes the use of fine features or signal traces and spaces of 0.003” (75 µm) or less and laser-drilled blind or buried microvia technology. Microvias allow the use of micro-interconnects from one layer to another within a PCB utilizing a smaller pad diameter creating additional routing density or reducing form factor.
High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs are characterized by finer lines, closer spaces, and more dense wiring, which allow for a faster connection while reducing the size and bulk of a project. These boards also feature blind and buried vias, laser ablated microvias, sequential lamination, and via in-pads. As a result, a HDI board can house the functionality of the previous boards used. HITECH CIRCUITS is an HDI PCB manufacturer and provider in Shenzhen, China supports HDI PCB prototype and mass production with less expensive price and quick-turn lead time. Customers from a variety of industries we serve have a common that have high expectations in quality, reliability and on-time delivery in HDI PCB production. Our quality is not afterthought, but built into each process from front-end to fabrication and shipping.
HDI PCB's Advantages
1. Reduce PCB cost: When the density of PCB increases beyond the eight-layer board, it will be manufactured in HDI, and the cost will be lower than that of traditional complicated press-forming process.
2. Better reliability: Due to the thin thickness and the aspect ratio of 1:1, the micropores have higher reliability when transmitting signals than ordinary through holes.
3. Improves thermal properties: The insulating dielectric material of the HDI board has a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) and therefore has better thermal properties.
4. Improve RF interference / electromagnetic interference / electrostatic discharge (RFI / EMI )
5. Increase design efficiency: Micro-hole technology allows the circuit to be arranged in the inner layer, so that the circuit designer has more design space, so the efficiency of the line design can be higher.
HDI PCB Manufacturing Process
The overall process for manufacturing HDI PCB is essentially the same as for fabricating other PCB board, with notable differences for PCB stack-up and hole drilling. Since HDI boards generally require smaller drill holes for vias, laser drilling is usually required. Although laser drills can produce smaller and more precise holes, they are limited by depth. Therefore, a limited number of layers can be drilled through at a time. For HDI boards, which are invariably multilayer and may contain buried and blind vias, multiple drilling processes may be required. This necessitates successive layer boding to achieve the desired stack-up or sequential lamination cycles. Not surprisingly, this can significantly increase PCB manufacturing time and cost. HDI PCB fabrication is an advanced technology and therefore requires expertise along with specialized equipment like laser drills, laser direct imaging (LDI) capability, and special clean room environments. In order to efficiently manufacture high-quality and reliable HDI PCB products, you must understand the HDI board manufacturing process and coordinate with your HDI PCB supplier to implement good DFM (Design for Manufacturability) for HDI layout design. Therefore, not all board factories have the ability to do the HDI, but Hitechpcb can, we will be here to support our customer needs.
-Consumer Driven Technology
The via - in - pad process supports
More technology on fewer layers, proving that bigger is not always better. Since the late 1980's we have seen video cameras using cartridges the size of a novel, shrink to fit in the palm of your hand. Mobile computing and work at home have further promoted technology to make the computer faster and lighter, allowing consumers to do remote work from anywhere.
HDI technology is the main reason for these changes. The products do more, weigh less, and their bodies are smaller. Professional equipment, mini components and thinner materials reduce the size of electronic equipment, while expanding technology, quality and speed.
-Via in Pad Process
The inspiration from the surface installation technology pushed the restrictions of BGA, COB and CSP to a smaller square surface inch. The via in pad can be placed in the surface of flat land through the cushion process. The via is plated and filled with conductive or non-conductive epoxy resin, and then close and plat it to make it almost invisible.
It sounds simple, but there are eight steps to complete this unique process. Professional equipment and well -trained technicians followed closely to achieve perfect hiding.
-Via Fill Types
There are many different types of via fill materials: non -conductive epoxy, epoxy, copper filling, filling and electrochemical coating. All this leads to via buried in a flat land, and the land will be fully solders as normal land. Vias and mricrovias are drilled, blind or buried, plated, and then hidden under the SMT land. Processing vias of this type of Vias requires special devices and takes time. The process time of multiple drill cycles and controlling deep drills has increased.
-Cost Effective HDI
Although the size of some consumer products is reduced, quality is still the most important factor for consumers. Use HDI technology during the design process, you can reduce the 8-layer through-hole PCB to a 4 layer HDI Microvia technology packed PCB. The elaborate HDI 4-layer PCB wiring function can achieve the same or better functions as standard 8-layer PCB.
Although the Microvia process has increased the cost of HDI PCB, the appropriate design and decrease of layers of counting reduces the cost of the ingredients of the material, and the layer count is large.
-Laser Drill Technology
The smallest micro-vias can provide more technologies on the surface of the plate. Using a beam with a diameter of 20 microns (1 mil), this high impact can be cut through metal and glass to produce tiny via hole. There are new products, such as uniform glass materials, and they are low -loss layer pressure plates and low -dielectric constants. These materials have high heat resistance, can be used for lead -free components, and allows smaller holes.
-Lamination & Materials For HDI PCB Boards
Advanced multilayer technology allows designers to add other layers to form a multilayer PCB. Use laser drills to produce holes in the inner layer, and can be coated when pressed, imaging and etching. The process of this increase is called sequential construction. Hitechpcb HDI PCB manufacturing uses solid -filled VIA can better heat management, connect stronger connection and improve the reliability of the board.
The copper of the resin coating is a assistant with poor pores, with longer drilling time and thinner. Hitechpcb has ultra low contours and ultra thin copper foil, and its surface is fixed on a tiny nodule. This material has chemically treated and started chemical treatment and startup of the most fine and high quality lines and spacing technology.
The dry resistance of the layer pressure plate still uses heating scroll method to apply resistance to core materials. It is now recommended to preheat the material to the required temperature before the layer pressure process of the HDI printing circuit board. The preheating of the material can better apply dry resistance to the surface of the layer pressure plate, pull less calories from the heat roll, and keep the stable export temperature of the layer made products consistent. The consistent entrance and exit temperature cause less air clips under the movie. This is essential for the breeding of fine lines and spacing.
How difficult is the HDI Printed Circuits Board?
The manufacturing of the HDI PCB (High Denity PCB) is relatively difficult because it needs to use complex manufacturing technique and technology. The following is some difficulties made by HDI PCB:
Multi-layer plate lamination: HDI Printed Circuits Boards are usually composed of multi-layer boards, and multi-layer boards need to be laminated. Multi-layer plates need to control parameters such as temperature, time, pressure to ensure the control quality and thickness control between multi-layer boards.
Blind holes and buried holes: HDI Printed Circuits Boards need to create blind holes and buried holes, which requires technologies such as laser drilling and chemical corrosion to ensure the accuracy and quality of the hole.
Impedance control: HDI Printed Circuit Boards need to control impedance, which requires fine design of the layout and circuit of the circuit board, and uses special materials and processes to achieve impedance control.
Small track space manufacturing: HDI Printed Circuits Boards need to make very small spacing tracks (conductions), which requires high-precision manufacturing equipment and technologies to ensure the accuracy and quality of the circuits.
The difference between HDI board and normal PCB
The HDI board is generally made of accumulation method. The more times the accumulation layer, the higher the technical grade of the board. Ordinary HDI boards are basically one accumulation. The high-end HDI uses two or more accumulated technologies, and at the same time, advanced PCB technology such as stacked holes, plating filling, and laser direct punching. When the density of PCB increases more than eight layers board, it is made by HDI, and its cost will be lower than the traditional complex compact process.
The electrical performance and signal of the HDI board are higher than that of traditional PCB. In addition, HDI boards have improved better for radio frequency interference, electromagnetic wave interference, electrostatic release, and thermal conduction. High density integration (HDI) technology can make terminal product design more miniaturized, while meeting higher standards for electronic performance and efficiency.
The HDI board uses a blind hole plating to perform secondary pressure, divided into one order, second order, third order, fourth, fifth order, etc. The first order is relatively simple, and the processes and processes are easy to control. The main problem of the second order is the issue of the place, and the other is the problem of punching and copper plating. There are many second order design. One is the wrong position of each order. When connecting the secondary neighborhood, it is connected to the middle layer through the wire. The method is equivalent to two first order HDI. The second is that the two order holes are overlapped. The second -order is realized by the superposition method. The processing is similar to the two first order, but there are many key points of the process. The third type is to punch perforation directly from the outer layer to the third layer (or N-2 layer). There are many different techniques from the front, and the difficulty of punching is even more difficult.
In PCB proofing, HDI costs high, so general PCB proofing manufacturers are unwilling to do it. HITECHPCB can be a HDI Blind PCB board that others are unwilling to do. At this stage, the HDI technology adopted by HITECH has exceeded the highest number of layers of 20 layers; the number of blind holes is 1st to 4th; the minimum pore diameter is 0.076mm, and the process is laser drilling.
HDI PCB Manufacturer & Assembly – One-stop services from China
-HDI (high-density interconnection board) is a compact circuit board designed for small capacity users. Compared with ordinary PCB, the most significant feature of HDI is that the wiring density is high.
HDI PCB Manufacturer & Assembly – One-stop service The HDI PCB is defined as a micro via with a hole diameter of 6 mils or less and a hole diameter of 0.25 mm or less. The contact density is above 130 points/square, and the wiring density is with a line width/pitch of 3 mil/3 mil or less. HDI PCB, the full name is High Density Interconnect PCB, it requires much higher wiring density with finer trace and spacing, smaller vias and higher connection pad density. Blind and buried vias’ design is one of their marked feature. HDI PCB board is widely used in Cell phone, tablet computer, digital camera mother board PCB, GPS, Automobile board, LCD module and other different area.
HDI pcb is the abbreviation for High Density Interconnect pcb or High Density pcb. An HDI PCB is defined as a printed circuit board with a higher wiring density per unit area than a conventional PCB. Hitech Circuits Co., Limited is a professional high density interconnect pcbs, HDI pcb board manufacturer, supplier and design company from China, if you are looking for reliable high density interconnect PCB board partner from China, please don’t hesitate to contact [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Different Types of Wires & Cables
Essential Guide for Safe Electrical Installations

Wires and cables are everywhere, even if we don’t always see them. They power our homes, connect us to the internet, and keep our world running smoothly. Without them, many of the things we rely on every day wouldn’t be possible. So today we are discussing about different types of Wires and Cables.
What Are Wires?
Wires are the basic building blocks of electrical systems. Made from conductive materials like copper or aluminum, they are designed to carry electrical current. Wires can be solid or stranded; solid wires consist of a single piece of metal, while stranded wires are made up of many small strands twisted together. This design allows stranded wires to be more flexible, making them ideal for applications where movement is necessary.
youtube
Types of Wires
Solid Wires: Solid wires make up of a single metal conductor, typically aluminum or copper. When a strong, reliable connection is required, they are used in electrical wiring and other applications.
Stranded Wires: Stranded wires consist of several tiny metal strands, typically made of copper or aluminum, twisted together to create a single conductor. They are flexible and suitable for a wider range of uses.
Flexible Wires: Flexible wires are perfect for applications where movement is required because of their ability to bend, twist, and move without breaking. Compared to solid or even stranded wires, they are usually made up of several thin wire strands, which gives them more flexibility.
Single-Core Wires: Single-conductor wires are key to home electrical systems. They are in homes nationwide. They carry power through walls and ceilings, ensuring our comforts and needs.
Multi-Core Wires: Multi-core cables contain several conductors in one jacket. They efficiently serve both appliances and industrial needs. Their compact design simplifies wiring in complex setups. Thus, they are ideal for power-hungry equipment.
Shielded Wires: Electrical conductors that are covered in a shield to prevent radio frequency interference (RFI) and electromagnetic interference (EMI) are known as shielded wires. Signal integrity is maintained with the help of this shielding, particularly in cases when electrical noise is common.
Twisted Pair Wires: Twisted pair wires consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to produce a single cable. This design helps reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between nearby pairs, making them appropriate for many communication applications.
What Are Cables?
Cables are essentially groups of wires bundled together, often with additional layers of insulation for protection. This design not only helps with organization but also enhances safety and efficiency. Cables can come in various types, depending on their intended use.
youtube
Types of Cables
Power Cables: Power cables are electrical cables made especially for moving electrical power between locations. They are appropriate for both high-voltage and low-voltage applications since they are composed of one or more conductors, insulation, and protective layers.
Data Cables: Data cables are electrical cables designed to transfer data between devices. They are essential for the operation of many electronic devices, telecommunications, and computer networks.
Fiber Optic Cables: High-speed data transmission cables known as fiber optic cables are made up of tiny glass or plastic fiber strands. These cables enable effective and quick communication over great distances by transmitting data as light signals.
Twisted Pair Cables: Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between adjacent pairs. They are widely used for data and voice transmission in various networking and telecommunications applications.
Specialty Cables:
FRLS (Fire Resistant Low Smoke) Wires: These wires are for fire-prone areas. They produce less smoke and toxic gas when they burn.
HT Cables (High Tension Cables): Used in high-voltage transmission for long-distance power supply.
Coaxial Cables: These are used for data transmission. They have a central conductor, an insulating layer, and a grounded shield.
Conclusion
Whether you need high-performance cables for industrial machinery or specialized wires for control systems, ensuring you work with a supplier who understands the nuances of your needs is crucial. Various platforms offer a one-stop solution, providing not only the products but also expert advice on making the right selection.
1 note
·
View note
Text

HDI PCB & High Interconnect PCB Manufacturing--Hitech Circuits
What is a high density PCB board (HDI PCB)?
The HDI board is based on the traditional double panel as the core board, which is made by continuously accumulating. This circuit board made by a continuous layer is also called the Build-Up Multilayer (BUM). Compared with the traditional circuit board, the HDI circuit board has the advantages of "light, thin, short, small".
The electrical connection between HDI's plate layer is achieved by conductive pores, buried holes, and blind holes. Its structure is different from ordinary multi -layer circuit boards. A large number of blind holes are used in HDI boards. HDI PCB uses laser direct drilling, and standard PCB usually uses mechanical drilling, so the number of layers and high width ratio often decreases.
HDI includes the use of fine features or signal traces and spaces of 0.003” (75 µm) or less and laser-drilled blind or buried microvia technology. Microvias allow the use of micro-interconnects from one layer to another within a PCB utilizing a smaller pad diameter creating additional routing density or reducing form factor.
High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs are characterized by finer lines, closer spaces, and more dense wiring, which allow for a faster connection while reducing the size and bulk of a project. These boards also feature blind and buried vias, laser ablated microvias, sequential lamination, and via in-pads. As a result, a HDI board can house the functionality of the previous boards used. HITECH CIRCUITS is an HDI PCB manufacturer and provider in Shenzhen, China supports HDI PCB prototype and mass production with less expensive price and quick-turn lead time. Customers from a variety of industries we serve have a common that have high expectations in quality, reliability and on-time delivery in HDI PCB production. Our quality is not afterthought, but built into each process from front-end to fabrication and shipping.
HDI PCB's Advantages
1. Reduce PCB cost: When the density of PCB increases beyond the eight-layer board, it will be manufactured in HDI, and the cost will be lower than that of traditional complicated press-forming process.
2. Better reliability: Due to the thin thickness and the aspect ratio of 1:1, the micropores have higher reliability when transmitting signals than ordinary through holes.
3. Improves thermal properties: The insulating dielectric material of the HDI board has a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) and therefore has better thermal properties.
4. Improve RF interference / electromagnetic interference / electrostatic discharge (RFI / EMI )
5. Increase design efficiency: Micro-hole technology allows the circuit to be arranged in the inner layer, so that the circuit designer has more design space, so the efficiency of the line design can be higher.
HDI PCB Manufacturing Process
The overall process for manufacturing HDI PCB is essentially the same as for fabricating other PCB board, with notable differences for PCB stack-up and hole drilling. Since HDI boards generally require smaller drill holes for vias, laser drilling is usually required. Although laser drills can produce smaller and more precise holes, they are limited by depth. Therefore, a limited number of layers can be drilled through at a time. For HDI boards, which are invariably multilayer and may contain buried and blind vias, multiple drilling processes may be required. This necessitates successive layer boding to achieve the desired stack-up or sequential lamination cycles. Not surprisingly, this can significantly increase PCB manufacturing time and cost. HDI PCB fabrication is an advanced technology and therefore requires expertise along with specialized equipment like laser drills, laser direct imaging (LDI) capability, and special clean room environments. In order to efficiently manufacture high-quality and reliable HDI PCB products, you must understand the HDI board manufacturing process and coordinate with your HDI PCB supplier to implement good DFM (Design for Manufacturability) for HDI layout design. Therefore, not all board factories have the ability to do the HDI, but Hitechpcb can, we will be here to support our customer needs. If you are looking for reliable high density interconnect PCB board partner from China, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
0 notes
Text
Exploring What Is A Bulk Current Injection?: A Deep Understanding of the Working Principles and Applications of Bulk Current Injection Test System(BCI)
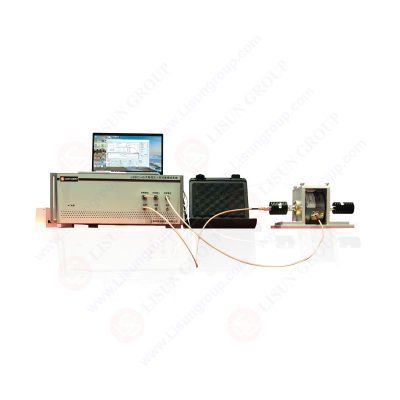

What Is A Bulk Current Injection: High current injection is a testing technique in automotive electronics used to verify whether a product will experience functional degradation or exceed tolerance limits when subjected to electromagnetic interference of different frequency ranges. This test is commonly encountered in EMC testing for automotive electronics, as in actual vehicle scenarios, the connecting cables for different onboard components are often bundled together. This leads to the coupling of electromagnetic interference signals of different frequencies, which in extreme cases, can result in failure of the affected components, posing a risk to the safety of the vehicle. Hence, the purpose of high current injection testing is to simulate the injection of RF signals onto the power or signal lines of the product being tested in order to verify whether its function will degrade or its performance indicators will remain within tolerance limits. High current injection testing is a commonly used method and has widespread applications in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) laboratories. It is mainly used to measure the EMI/RFI disturbance characteristics of devices in the high frequency to ultra-high frequency range. In practical applications, high current injection testing can be used to evaluate the relative compatibility between equipment and other electronic devices or systems. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
What Causes I/O Noise and Interference in PLC Systems? 8 Common Culprits Revealed!
Exploring Common Causes and Solutions for I/O Noise and Interference in PLC Systems
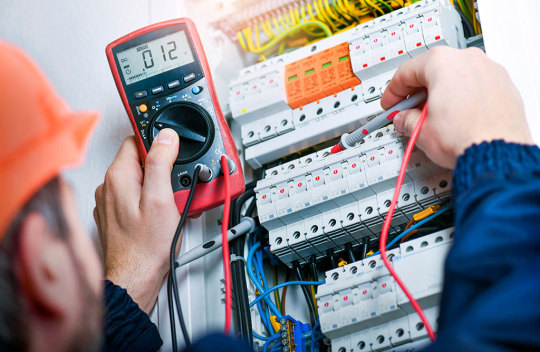
In the realm of industrial automation, PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems are indispensable, overseeing the operation of machinery and processes efficiently. However, they face a challenge: I/O (Input/Output) noise and interference. These disruptions can disrupt system stability, leading to malfunctions and downtime. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the causes and solutions for I/O noise and interference in PLC systems, addressing 8 common culprits that engineers and technicians should understand well.
Understanding I/O Noise and Interference
Before delving into specific causes and solutions, it's crucial to understand the nature of I/O noise and interference. I/O noise refers to unwanted electrical signals or disturbances that corrupt intended signals in PLC systems. Interference includes external factors like electromagnetic radiation, radio frequency interference (RFI), and electromagnetic interference (EMI) disrupting communication between PLC components.
Power Supply Issues: The Silent Saboteur
A stable power supply is crucial for any PLC system. However, fluctuations or disturbances can introduce noise, jeopardizing performance. Issues like voltage spikes, dips, and harmonics can arise, impacting power quality and increasing I/O noise.
Grounding Problems: Unearthing the Root Cause
Proper grounding is vital in mitigating I/O noise and interference. However, inadequate practices can amplify noise within the system. Ground loops and poor connections can create pathways for unwanted currents, resulting in signal distortion and ground noise.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Taming the Invisible Beast
EMI originates from various sources like nearby motors and power lines, inducing unwanted voltages in nearby cables and components. Shielding cables, using twisted pair wiring, and relocating sensitive components can mitigate EMI.
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI): Navigating the Airwaves
RFI, found in industrial environments bustling with wireless devices, poses a threat to PLC systems. Employing frequency filtering techniques and shielding can mitigate RFI.
Crosstalk: When Signals Collide
Crosstalk occurs when adjacent conductors induce voltages in neighboring cables, leading to signal interference. Shielding, spacing, and wiring techniques can mitigate crosstalk.
Environmental Factors: Nature's Influence
External factors like temperature fluctuations and humidity can impact PLC systems. Extreme temperatures and humidity levels accelerate corrosion and compromise signal integrity, while contaminants can lead to short circuits.
Component Aging: The Silent Deterioration
Over time, components within PLC systems deteriorate, impacting performance and reliability. Regular maintenance and component inspection are essential to mitigate aging's impact.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How do I identify I/O noise in PLC systems? Signal integrity tests using oscilloscopes help pinpoint irregularities in waveforms indicative of noise interference.
2. Can inadequate shielding contribute to I/O noise? Yes, it allows external electromagnetic fields to penetrate cables. Proper shielding minimizes noise ingress.
3. What role does firmware/software play in mitigating I/O noise? Updates may include optimizations or algorithms to filter noise, reducing its impact.
4. Are there industry standards for mitigating I/O noise? Yes, standards like IEC 61000 provide guidelines for EMC.
5. How can ground loops be prevented? Ensuring all ground connections are made at a single point eliminates potential differences and minimizes ground loop currents.
6. What measures mitigate environmental factors' impact? Installing PLCs in controlled environments and using protective enclosures safeguard components from environmental hazards. For more information visit here👉PujaControls
#PLCInterference#EMIandRFI#IndustrialAutomation#ElectricalNoise#PLCTroubleshooting#SignalInterference#ElectricalEngineering#AutomationTechnology#IndustrialControl#NoiseFiltering#ControlSystem#EMIProtection#RFISuppression#FactoryAutomation
0 notes
Text
Explore the Different Types of RFI Shield
We often notice abnormal behavior or disturbances from our electronic gadgets but ignore them. For example, flickering of lights on phones, muffled audio, poor network connectivity, etc. Have you ever wondered what the reason behind such malfunctions could be? RFI is one of the leading reasons behind such disruptions.
However, there's a way to prevent it and protect your electronic gadgets using Radio Frequency Interference RFI Shield. These crucial components are utilized in various electronic devices and systems to combat electromagnetic interference, ensuring optimal functionality and signal integrity. They come in different varieties, and we shall discuss them in this article, so continue reading.
Here are some of the common types of RFI Shields:
Conductive Coatings
One common type of RFI shielding is the application of conductive coatings onto electronic components or enclosures. These coatings typically contain materials like copper, nickel, or silver. They create a conductive barrier that absorbs or reflects electromagnetic waves. By doing so, conductive coatings effectively reduce interference, maintaining the integrity of electronic signals.
Metal Enclosures
Metal enclosures are robust shields against RFI and are widely used in various electronic devices and systems. Technicians make them using materials like aluminum or steel. These enclosures cover electronic components, forming what is commonly referred to as a Faraday cage. This cage effectively blocks external electromagnetic radiation, safeguarding sensitive electronics from interference.
Gaskets and Seals
Technicians make gaskets and seals from conductive materials. These materials, often made of silicone rubber and embedded with metal particles, play a crucial role in RFI shielding by sealing gaps and joints in electronic enclosures. Gaskets and seals create a barrier between components, preventing RFI leakage and maintaining the integrity of enclosed systems.
Ferrite Beads and Chokes
Passive components like ferrite beads and chokes suppress high-frequency interference in signal cables. Technicians fabricate ferrite beads and chokes using ceramic materials composed of iron oxide and a mixture of other metal oxides. These components mitigate noise in signal lines by absorbing and dissipating electromagnetic energy, ensuring reliable electronic data transmission.
Shielded Cables
Shielded cables showcase an additional layer of conductive material surrounding signal-carrying conductors. They serve as an effective barrier against RFI to protect electronics. This RFI shield, typically composed of metal foil or braided wire, provides a path for induced currents to flow, preventing them from interfering with the signal transmitted through the cable.
RFI Filters
RFI filters are composed of capacitors, inductors, and resistors. They are strategically inserted into power lines or signal lines to cancel specific frequency ranges of electromagnetic interference. By shunting or blocking unwanted RFI, these filters ensure the integrity of electronic signals and the reliable operation of electronic systems.
PCB Layout Techniques
Proper Printed Circuit Board (PCB) layout techniques minimize RFI susceptibility and emissions at the circuit board level. Techniques like star grounding, signal routing optimization, and component placement contribute to effective RFI shielding, ensuring robust electronic systems performance.
How Does RFI Shielding Work Exactly?
Radio-frequency interference (RFI) shielding operates by forming a barrier to block electromagnetic radiation within the radio frequency range. This prevents radio frequency from entering or exiting a specific area. This shielding is achieved by utilizing diverse materials such as metals, conductive fabrics, or specialized coatings, which absorb or reflect interfering signals.
When RFI encounters the shielding material, it induces electric currents on its surface, generating electromagnetic fields that counter and neutralize the incoming RFI. Furthermore, factors such as the shielding material's thickness, conductivity, and structure significantly impact its effectiveness.
By effectively impeding or weakening undesired radio frequencies, RFI shields ensure the smooth operation of electronic devices, minimize interference, and preserve signal integrity.
0 notes
Text
Ariba ABB

Ariba and ABB: Streamlining Procurement for Global Efficiency
ABB is a leading global technology company with operations in over 100 countries. ABB has adopted the powerful Ariba platform to manage its vast supply chain and procurement needs effectively. In this blog, we’ll explore what Ariba is, how ABB leverages it, and the advantages of this partnership.
What is Ariba?
Ariba, now part of SAP, is a cloud-based B2B marketplace and procurement platform. It connects buyers and suppliers across the globe, enabling them to collaborate digitally on:
Sourcing: Finding and evaluating potential suppliers
Procurement: Managing the purchase-to-pay process (requisitions, purchase orders, invoicing)
Supplier Management: Maintaining supplier information, performance data, and collaboration
Contract Management: Creating, negotiating, and storing contracts
How ABB Uses Ariba
ABB implemented the SAP Ariba Strategic Sourcing Suite to streamline its global procurement operations. Here’s how they leverage different aspects of the platform:
Supplier Discovery and Qualification: ABB uses Ariba to search for and qualify new suppliers based on specific criteria. This broadens their pool of potential partners and promotes competitive bidding.
E-Sourcing: ABB runs sourcing events like RFIs, RFQs, RFPs, and auctions directly within the Ariba platform to find the best suppliers at optimal pricing.
Contract Collaboration: ABB can negotiate and manage contracts digitally with suppliers within Ariba, reducing paperwork and speeding up the contract lifecycle.
Spend Visibility: Ariba provides ABB with in-depth insights into their spending patterns, helping them identify areas for cost savings and make informed procurement decisions.
Benefits of Ariba for Suppliers
Expanded Reach: Suppliers on Ariba gain visibility to a vast network of buyers, including large multinational companies like ABB.
Efficient Processes: Ariba streamlines communication and transactions between suppliers and ABB.
Reduced Costs: Digital processes reduce the administrative overhead for suppliers involved with ABB.
Data Insights: Suppliers can access their performance and spend data within Ariba to improve their offerings and relationship with ABB.
Benefits of Ariba for ABB
Cost Savings: Ariba helps ABB achieve significant cost savings through competitive bidding, spend analysis, and process automation.
Process Efficiency: Ariba digitizes and automates procurement processes, reducing manual labor and errors leading to faster cycle times.
Risk Mitigation: Ariba’s supplier management and qualification features help ABB mitigate supply chain risks.
Improved Compliance: Ariba provides tools to track and manage regulatory compliance within procurement processes.
In Conclusion
Ariba has transformed the way ABB manages its global procurement operations. This powerful platform boosts efficiency, strengthens supplier collaboration, delivers cost savings, and supports ABB’s commitment to innovation and sustainability. For suppliers, being part of the Ariba network represents a significant advantage in securing business relationships with global leaders like ABB.
youtube
You can find more information about SAP ARIBA in this SAP ARIBA Link
Conclusion:
Unogeeks is the No.1 IT Training Institute for SAP Training. Anyone Disagree? Please drop in a comment
You can check out our other latest blogs on SAP ARIBA here – SAP ARIBA Blogs
You can check out our Best In Class SAP ARIBA Details here – SAP ARIBA Training
Follow & Connect with us:
———————————-
For Training inquiries:
Call/Whatsapp: +91 73960 33555
Mail us at: [email protected]
Our Website ➜ https://unogeeks.com
Follow us:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/unogeeks
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/UnogeeksSoftwareTrainingInstitute
Twitter: https://twitter.com/unogeek
1 note
·
View note
Text
SAP Ariba Sourcing

SAP Ariba Sourcing: Your Path to Procurement Excellence
Optimizing your procurement processes in today’s rapidly shifting business environment is more critical than ever. That’s where SAP Ariba Sourcing comes in, offering a powerful suite of tools to streamline your sourcing operations, cut costs, and drive business value. In this blog, we’ll dive into what SAP Ariba Sourcing is, its key benefits, and why it’s an essential toolkit for businesses.
What is SAP Ariba Sourcing?
SAP Ariba Sourcing is a cloud-based solution that helps organizations manage their strategic sourcing process, from identifying potential suppliers to negotiating contracts. It empowers you to:
Source Strategically: Automate and centralize sourcing activities like RFIs, RFPs, RFQs, and auctions on a single platform.
Collaborate Effectively: Facilitate seamless communication and collaboration with suppliers, enabling better sourcing decisions.
Leverage Data-Driven Insights: Utilize analytics and market intelligence to make informed sourcing choices that reduce costs and mitigate risk.
Drive Contract Compliance: Manage and track contract performance, ensuring negotiated terms and conditions adherence.
Key Benefits of SAP Ariba Sourcing
Enhanced Cost Savings: SAP Ariba Sourcing helps you identify the best suppliers at optimal prices, negotiate better terms, and uncover new savings opportunities.
Improved Efficiency: The platform streamlines and automates sourcing processes, reducing time and effort spent on manual tasks leading to faster sourcing cycles.
Reduced Risk: SAP Ariba Sourcing provides deep supplier insights and analytics, helping you evaluate risks, ensure compliance, and mitigate supply chain disruptions.
Increased Collaboration: Its intuitive interface fosters real-time collaboration between procurement teams and suppliers, improving transparency and solidifying business relationships.
Scalability: SAP Ariba Sourcing can quickly adapt to your changing business needs, offering flexibility to support growth and expansion.
Why Choose SAP Ariba Sourcing?
Industry Leader: Backed by SAP’s expertise, SAP Ariba is a recognized leader in procurement solutions.
Integration with SAP Business Network: Seamless integration with the massive SAP Business Network connects you with a vast network of suppliers on a single platform.
Intuitive User Experience: SAP Ariba Sourcing features a user-friendly interface, ensuring rapid adoption and increased efficiency.
Mobile Accessibility: The platform offers mobile access, enabling you to manage sourcing events and collaborate with suppliers even when you’re on the go.
Getting Started with SAP Ariba Sourcing
If you’re ready to transform your procurement processes, consider SAP Ariba Sourcing. Its robust capabilities provide the tools to make smarter sourcing decisions, achieve significant cost savings, and enhance collaboration with your suppliers.
Here are some additional points to consider:
SAP Ariba Sourcing supports different sourcing methodologies to fit your business needs.
Advanced features like supplier performance management help you measure and track supplier performance.
youtube
You can find more information about SAP ARIBA in this SAP ARIBA Link
Conclusion:
Unogeeks is the No.1 IT Training Institute for SAP Training. Anyone Disagree? Please drop in a comment
You can check out our other latest blogs on SAP ARIBA here – SAP ARIBA Blogs
You can check out our Best In Class SAP ARIBA Details here – SAP ARIBA Training
Follow & Connect with us:
———————————-
For Training inquiries:
Call/Whatsapp: +91 73960 33555
Mail us at: [email protected]
Our Website ➜ https://unogeeks.com
Follow us:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/unogeeks
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/UnogeeksSoftwareTrainingInstitute
Twitter: https://twitter.com/unogeek
1 note
·
View note
Text
HDI PCB & High Interconnect PCB Manufacturing(from Hitech Circuits Co., Limited)
What is a high density PCB board (HDI PCB)?
The HDI board is based on the traditional double panel as the core board, which is made by continuously accumulating. This circuit board made by a continuous layer is also called the Build-Up Multilayer (BUM). Compared with the traditional circuit board, the HDI circuit board has the advantages of "light, thin, short, small".
The electrical connection between HDI's plate layer is achieved by conductive pores, buried holes, and blind holes. Its structure is different from ordinary multi -layer circuit boards. A large number of blind holes are used in HDI boards. HDI PCB uses laser direct drilling, and standard PCB usually uses mechanical drilling, so the number of layers and high width ratio often decreases.
HDI includes the use of fine features or signal traces and spaces of 0.003” (75 µm) or less and laser-drilled blind or buried microvia technology. Microvias allow the use of micro-interconnects from one layer to another within a PCB utilizing a smaller pad diameter creating additional routing density or reducing form factor.
High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs are characterized by finer lines, closer spaces, and more dense wiring, which allow for a faster connection while reducing the size and bulk of a project. These boards also feature blind and buried vias, laser ablated microvias, sequential lamination, and via in-pads. As a result, a HDI board can house the functionality of the previous boards used. HITECH CIRCUITS is an HDI PCB manufacturer and provider in Shenzhen, China supports HDI PCB prototype and mass production with less expensive price and quick-turn lead time. Customers from a variety of industries we serve have a common that have high expectations in quality, reliability and on-time delivery in HDI PCB production. Our quality is not afterthought, but built into each process from front-end to fabrication and shipping.
HDI PCB's advantages
1. Reduce PCB cost: When the density of PCB increases beyond the eight-layer board, it will be manufactured in HDI, and the cost will be lower than that of traditional complicated press-forming process.
2. Better reliability: Due to the thin thickness and the aspect ratio of 1:1, the micropores have higher reliability when transmitting signals than ordinary through holes.
3. Improves thermal properties: The insulating dielectric material of the HDI board has a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) and therefore has better thermal properties.
4. Improve RF interference / electromagnetic interference / electrostatic discharge (RFI / EMI )
5. Increase design efficiency: Micro-hole technology allows the circuit to be arranged in the inner layer, so that the circuit designer has more design space, so the efficiency of the line design can be higher.
HDI PCB Manufacturing Process
The overall process for manufacturing HDI PCB is essentially the same as for fabricating other PCB board, with notable differences for PCB stack-up and hole drilling. Since HDI boards generally require smaller drill holes for vias, laser drilling is usually required. Although laser drills can produce smaller and more precise holes, they are limited by depth. Therefore, a limited number of layers can be drilled through at a time. For HDI boards, which are invariably multilayer and may contain buried and blind vias, multiple drilling processes may be required. This necessitates successive layer boding to achieve the desired stack-up or sequential lamination cycles. Not surprisingly, this can significantly increase PCB manufacturing time and cost. HDI PCB fabrication is an advanced technology and therefore requires expertise along with specialized equipment like laser drills, laser direct imaging (LDI) capability, and special clean room environments. In order to efficiently manufacture high-quality and reliable HDI PCB products, you must understand the HDI board manufacturing process and coordinate with your HDI PCB supplier to implement good DFM (Design for Manufacturability) for HDI layout design. Therefore, not all board factories have the ability to do the HDI, but Hitechpcb can, we will be here to support our customer needs.
-Consumer Driven Technology
The via - in - pad process supports
More technology on fewer layers, proving that bigger is not always better. Since the late 1980's we have seen video cameras using cartridges the size of a novel, shrink to fit in the palm of your hand. Mobile computing and work at home have further promoted technology to make the computer faster and lighter, allowing consumers to do remote work from anywhere.
HDI technology is the main reason for these changes. The products do more, weigh less, and their bodies are smaller. Professional equipment, mini components and thinner materials reduce the size of electronic equipment, while expanding technology, quality and speed.
-Via in Pad Process
The inspiration from the surface installation technology pushed the restrictions of BGA, COB and CSP to a smaller square surface inch. The via in pad can be placed in the surface of flat land through the cushion process. The via is plated and filled with conductive or non-conductive epoxy resin, and then close and plat it to make it almost invisible.
It sounds simple, but there are eight steps to complete this unique process. Professional equipment and well -trained technicians followed closely to achieve perfect hiding.
-Via Fill Types
There are many different types of via fill materials: non -conductive epoxy, epoxy, copper filling, filling and electrochemical coating. All this leads to via buried in a flat land, and the land will be fully solders as normal land. Vias and mricrovias are drilled, blind or buried, plated, and then hidden under the SMT land. Processing vias of this type of Vias requires special devices and takes time. The process time of multiple drill cycles and controlling deep drills has increased.
-Cost Effective HDI
Although the size of some consumer products is reduced, quality is still the most important factor for consumers. Use HDI technology during the design process, you can reduce the 8-layer through-hole PCB to a 4 layer HDI Microvia technology packed PCB. The elaborate HDI 4-layer PCB wiring function can achieve the same or better functions as standard 8-layer PCB.
Although the Microvia process has increased the cost of HDI PCB, the appropriate design and decrease of layers of counting reduces the cost of the ingredients of the material, and the layer count is large.
-Laser Drill Technology
The smallest micro-vias can provide more technologies on the surface of the plate. Using a beam with a diameter of 20 microns (1 mil), this high impact can be cut through metal and glass to produce tiny via hole. There are new products, such as uniform glass materials, and they are low -loss layer pressure plates and low -dielectric constants. These materials have high heat resistance, can be used for lead -free components, and allows smaller holes.
-Lamination & Materials For HDI PCB Boards
Advanced multilayer technology allows designers to add other layers to form a multilayer PCB. Use laser drills to produce holes in the inner layer, and can be coated when pressed, imaging and etching. The process of this increase is called sequential construction. Hitechpcb HDI PCB manufacturing uses solid -filled VIA can better heat management, connect stronger connection and improve the reliability of the board.
The copper of the resin coating is a assistant with poor pores, with longer drilling time and thinner. Hitechpcb has ultra low contours and ultra thin copper foil, and its surface is fixed on a tiny nodule. This material has chemically treated and started chemical treatment and startup of the most fine and high quality lines and spacing technology.
The dry resistance of the layer pressure plate still uses heating scroll method to apply resistance to core materials. It is now recommended to preheat the material to the required temperature before the layer pressure process of the HDI printing circuit board. The preheating of the material can better apply dry resistance to the surface of the layer pressure plate, pull less calories from the heat roll, and keep the stable export temperature of the layer made products consistent. The consistent entrance and exit temperature cause less air clips under the movie. This is essential for the breeding of fine lines and spacing.
-How difficult is the HDI Printed Circuits Board?
The manufacturing of the HDI PCB (High Denity PCB) is relatively difficult because it needs to use complex manufacturing technique and technology. The following is some difficulties made by HDI PCB:
Multi-layer plate lamination: HDI Printed Circuits Boards are usually composed of multi-layer boards, and multi-layer boards need to be laminated. Multi-layer plates need to control parameters such as temperature, time, pressure to ensure the control quality and thickness control between multi-layer boards.
Blind holes and buried holes: HDI Printed Circuits Boards need to create blind holes and buried holes, which requires technologies such as laser drilling and chemical corrosion to ensure the accuracy and quality of the hole.
Impedance control: HDI Printed Circuit Boards need to control impedance, which requires fine design of the layout and circuit of the circuit board, and uses special materials and processes to achieve impedance control.
Small track space manufacturing: HDI Printed Circuits Boards need to make very small spacing tracks (conductions), which requires high-precision manufacturing equipment and technologies to ensure the accuracy and quality of the circuits.
-The difference between HDI board and normal PCB
The HDI board is generally made of accumulation method. The more times the accumulation layer, the higher the technical grade of the board. Ordinary HDI boards are basically one accumulation. The high-end HDI uses two or more accumulated technologies, and at the same time, advanced PCB technology such as stacked holes, plating filling, and laser direct punching. When the density of PCB increases more than eight layers board, it is made by HDI, and its cost will be lower than the traditional complex compact process.
The electrical performance and signal of the HDI board are higher than that of traditional PCB. In addition, HDI boards have improved better for radio frequency interference, electromagnetic wave interference, electrostatic release, and thermal conduction. High density integration (HDI) technology can make terminal product design more miniaturized, while meeting higher standards for electronic performance and efficiency.
The HDI board uses a blind hole plating to perform secondary pressure, divided into one order, second order, third order, fourth, fifth order, etc. The first order is relatively simple, and the processes and processes are easy to control. The main problem of the second order is the issue of the place, and the other is the problem of punching and copper plating. There are many second order design. One is the wrong position of each order. When connecting the secondary neighborhood, it is connected to the middle layer through the wire. The method is equivalent to two first order HDI. The second is that the two order holes are overlapped. The second -order is realized by the superposition method. The processing is similar to the two first order, but there are many key points of the process. The third type is to punch perforation directly from the outer layer to the third layer (or N-2 layer). There are many different techniques from the front, and the difficulty of punching is even more difficult.
In PCB proofing, HDI costs high, so general PCB proofing manufacturers are unwilling to do it. HITECHPCB can be a HDI Blind PCB board that others are unwilling to do. At this stage, the HDI technology adopted by HITECH has exceeded the highest number of layers of 20 layers; the number of blind holes is 1st to 4th; the minimum pore diameter is 0.076mm, and the process is laser drilling.
HDI PCB Manufacturer & Assembly – One-stop services from China
-HDI (high-density interconnection board) is a compact circuit board designed for small capacity users. Compared with ordinary PCB, the most significant feature of HDI is that the wiring density is high.
HDI PCB Manufacturer & Assembly – One-stop service The HDI PCB is defined as a micro via with a hole diameter of 6 mils or less and a hole diameter of 0.25 mm or less. The contact density is above 130 points/square, and the wiring density is with a line width/pitch of 3 mil/3 mil or less. HDI PCB, the full name is High Density Interconnect PCB, it requires much higher wiring density with finer trace and spacing, smaller vias and higher connection pad density. Blind and buried vias’ design is one of their marked feature. HDI PCB board is widely used in Cell phone, tablet computer, digital camera mother board PCB, GPS, Automobile board, LCD module and other different area.
HDI PCB is the abbreviation for High Density Interconnect PCB or High Density PCB. An HDI PCB is defined as a printed circuit board with a higher wiring density per unit area than a conventional PCB. Hitech Circuits Co., Limited is a professional high density interconnect PCBs, HDI PCB board manufacturer, supplier and design company from China, if you are looking for reliable high density interconnect PCB board partner from China, please don’t hesitate to contact [email protected], from Cynthia.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What Fittings to use with Flexible Conduit?

Introduction
In the intricate web of electrical installations, the role of flexible conduit cannot be overstated. As a conduit capable of adapting to dynamic environments, its flexibility is a key asset. However, the true potential of flexible conduits can only be harnessed with the right selection of Flexible Conduit Accessories. In this detailed exploration, we delve into the nuances of these accessories, uncovering the secrets to seamless installations and robust electrical systems.
Understanding the Backbone: Flexible Conduit
Before we embark on the journey through the realm of accessories, let's establish a solid foundation by revisiting the essence of flexible conduit. This conduit, often constructed from materials like PVC, nylon, or metal, is revered for its adaptability. Its flexibility enables it to navigate through tight spaces, around corners, and accommodate the twists and turns inherent in complex electrical layouts.
Benefits of Flexible Conduit
Before unravelling the mystery of accessories, let's briefly acknowledge why flexible conduit is a preferred choice in various applications:
1. Durability: Resistant to physical damage and environmental factors.
2. Flexibility: Adaptable to complex routing requirements.
3. Protection: Safeguards wires from moisture, chemicals, and physical impact.
Now, with our groundwork laid, let's shift our focus to the star of the show – the accessories that elevate flexible conduit from merely functional to exceptionally versatile.
Types of Flexible Conduit Accessories
1. Connectors
At the heart of any flexible conduit system lies the connectors. the unsung heroes that seamlessly link sections of conduit, creating a unified path for electrical wiring. Common connectors include:
Straight Connectors: For linear connections.
90-Degree Connectors: Facilitate turns without compromising the conduit's integrity.
2. Couplings
While connectors join sections, couplings extend conduit lengths, offering continuity and cohesion. Noteworthy variants include:
Reducing Couplings: For transitioning between conduits of different diameters.
Rigid-to-Flexible Couplings: Bridging the gap between rigid and flexible conduits.
3. Fittings for Directional Changes
In the intricate dance of electrical pathways, bends and turns are inevitable. Specialized fittings ensure the conduit gracefully negotiates these changes without compromising efficiency. Notable fittings include:
Sweeps: Gentle curves for gradual directional changes.
Elbows: Sharp bends at specific angles to redirect conduit paths.
4. Support and Fastening Accessories
To ensure longevity and stability, support and fastening accessories play a pivotal role:
Conduit Straps: Secure conduits to surfaces.
Hangers: Provide vertical support for hanging conduits.
5. Sealing and Termination Accessories
The integrity of any conduit system relies on effective sealing and termination. Key accessories in this category include:
End Caps: Seal conduit ends, preventing debris and moisture ingress.
Conduit Nuts and Washers: Essential for a secure termination.
Flexing Technical Muscles:
As we traverse the intricate landscape of flexible conduit accessories, let's spice things up with some less common yet vital terms:
1. Gland Nut: A threaded nut that secures the conduit to an enclosure, maintaining a watertight seal.
2. Convoluted Tubing: An advanced form of flexible conduit with a spiral design, enhancing flexibility.
3.Liquidtight Connector: A fitting that ensures a liquid-tight seal, ideal for environments where moisture is a concern.
4. EMI/RFI Shielding: Accessories designed to shield against electromagnetic and radiofrequency interference, ensuring signal integrity.
Making the Right Choices: Considerations for Selection
Selecting the right flexible conduit accessories involves a meticulous evaluation of the specific needs of your electrical system. Consider the following factors:
1. Environmental Conditions: Choose accessories that can withstand the temperature, moisture, and chemical conditions of the installation environment.
2. Type of Conduit: Different conduits demand specific accessories. Ensure compatibility for optimal performance.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Adhere to industry standards and regulations to guarantee a safe and compliant electrical system.
4. Future Expansion: Select accessories that allow for future modifications and expansions without significant overhauls.
Conclusion
In the grand tapestry of electrical installations, each component plays a unique role. Flexible conduit, with its adaptability, lays the groundwork, while the carefully chosen accessories elevate it to new heights of functionality and resilience. The dance of connectors, the stability of couplings, the grace of directional fittings all converge to create a symphony of electrical efficiency.
0 notes
Text
https://terotam.com/blog/differences-between-rfi-rfq-rfp-and-rft
What is the Differences Between RFI, RFQ, RFP, and RFT
Distinctions between RFI, RFQ, RFP, and RFT in our comprehensive guide. Understand the nuances of procurement processes for informed decisions.
0 notes
Text
What Are the Different Types of UPS Systems?
In today’s technologically driven world, uninterrupted power supply is crucial for the smooth functioning of various industries, businesses, and even households. Power outages, voltage fluctuations, and electrical disturbances can result in data loss, equipment damage, and productivity disruptions. This is where UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems come into play. A UPS is a device that acts as a reliable power backup, providing continuous and stable power to connected devices, even during electrical disruptions.
UPS systems are designed to bridge the gap between the main power source and the devices or systems they support. They work by storing electrical energy in internal batteries, which can be rapidly deployed in the event of a power outage. UPS systems also incorporate various protective features such as voltage regulation, surge suppression, and power conditioning, ensuring that the connected devices receive clean and stable power.
Importance of UPS in Maintaining Power Stability:
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) systems play a crucial role in maintaining power stability in various settings, ranging from critical business operations to residential environments. Here are some key reasons why UPS systems are important in ensuring power stability:
Protection against Power Outages:
Power outages can occur due to severe weather conditions, infrastructure failures, or other unforeseen circumstances. These disruptions can lead to data loss, system crashes, and operational downtime, resulting in significant financial losses and productivity setbacks. UPS systems act as a reliable backup power source, instantly supplying electricity to connected devices during outages. By bridging the gap between the loss of utility power and the activation of backup generators, UPS systems provide uninterrupted power, preventing data corruption and allowing for a smooth transition to alternate power sources.
Mitigation of Voltage Fluctuations:
Voltage fluctuations, such as sags, surges, and spikes, can occur due to electrical grid issues or sudden changes in power demand. These fluctuations can damage sensitive electronic equipment and disrupt the performance of critical systems. UPS systems employ voltage regulation mechanisms that stabilize and regulate the incoming power supply. They ensure that the connected devices receive consistent voltage levels, eliminating the risk of damage and ensuring optimal performance.
Protection against Electrical Disturbances:
Electrical disturbances, such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), can disrupt the proper functioning of electronic devices. UPS systems incorporate power conditioning features that filter out these disturbances, providing clean and reliable power to connected equipment. This enhances the longevity and performance of sensitive devices, minimizing the risk of malfunctions or data corruption caused by electrical noise.
Seamless Power Transitions:
UPS systems offer automatic switchover capabilities, seamlessly transitioning between different power sources. In case of a power outage or other disruptions, UPS systems switch from utility power to battery power instantaneously, ensuring a continuous and uninterrupted power supply to critical devices. This uninterrupted power transfer helps prevent service interruptions, data loss, and system failures, allowing businesses and individuals to operate seamlessly even during power fluctuations.
The Different Types of UPS Systems:
Standby UPS Systems:
Standby UPS systems, also known as offline UPS systems, are commonly used for residential and small business applications. These systems operate by allowing the connected devices to run on utility power directly, while also charging the internal battery. In the event of a power outage or voltage anomaly, the standby UPS swiftly switches to battery power, providing uninterrupted power to the connected devices. Standby UPS systems offer basic protection against power disruptions, making them cost-effective solutions for non-critical applications.
Line-Interactive UPS Systems:
Line-interactive UPS systems are suitable for small to medium-sized businesses and networks. These systems are designed to regulate voltage fluctuations while providing battery backup during outages. Line-interactive UPS units incorporate an automatic voltage regulator (AVR) that adjusts and stabilizes the incoming voltage to protect connected devices from power sags and surges. This type of UPS is known for its energy efficiency and ability to provide reliable power protection in areas with moderate power quality issues.
Online UPS Systems:
Online UPS systems, also referred to as double-conversion UPS systems, are widely used in mission-critical applications such as data centers, medical facilities, and industrial settings. These systems continuously supply power from the battery source, providing the highest level of power protection. Online UPS units convert the incoming AC power to DC power, which then charges the batteries. The connected devices receive power from the batteries via an inverter, ensuring a clean and stable power supply, regardless of the quality of the utility power. This type of UPS offers excellent voltage regulation, surge protection, and isolation from power anomalies, making it ideal for sensitive and critical equipment.
Delta Conversion UPS Systems:
Delta conversion UPS systems, also known as double-conversion online UPS systems with a delta topology, are advanced UPS units that provide exceptional power protection. These systems use a three-phase power conversion process, which results in higher efficiency, reduced harmonics, and enhanced fault tolerance. Delta conversion UPS units offer seamless power transfer, fast response time to power disturbances, and excellent power conditioning capabilities. They are commonly used in large data centers, telecommunications, and industries where high reliability and performance are paramount.
Hybrid UPS Systems:
Hybrid UPS systems combine the features of standby and line-interactive UPS units, offering a balanced solution for power protection needs. These systems are capable of providing both voltage regulation and battery backup during outages. Hybrid UPS units optimize energy efficiency by intelligently switching between standby and line-interactive modes, depending on the power conditions. They are suitable for applications where moderate power fluctuations occur, and a balance between cost-effectiveness and power protection is desired.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of UPS systems empowers businesses, organizations, and individuals to make well-informed choices to protect their valuable equipment, data, and operations. By investing in a reliable UPS system, one can ensure uninterrupted power supply, mitigate the risks of power-related issues, and maintain business continuity even in the face of unforeseen power disruptions.
0 notes