#webinar in a box
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Staatenlos Geheimwissen Videokurs Webinar

. Introducing the 'Staatenlos Geheimnis' Box of Books, a comprehensive collection of knowledge and insights. This box contains a carefully curated selection of books that delve into the secrets of the 'Staatenlos Geheimwissen' Videokurs. Dive into a world of valuable information and gain a deeper understanding of the concepts covered in the accompanying webinar. Expand your knowledge and unlock hidden wisdom with this exclusive collection
0 notes
Text
As the most consequential presidential election in a generation looms in the United States, get-out-the-vote efforts across the country are more important than ever. But multiple far-right activist groups with ties to former president Donald Trump and the Republican National Committee are mobilizing their supporters in earnest, drawing on one baseline belief: Elections in the US are rigged, and citizens need to do something about it.
All the evidence states otherwise. But in recent weeks, these groups have held training sessions about how to organize on a hyperlocal level to monitor polling places and drop boxes, challenge voter registrations en masse, and intimidate and harass voters and election officials. And some are preparing to roll out new technology to fast-track all of these efforts: One of the groups claims they’re launching a new platform for checking voter rolls that contains billions of “data elements” on every single US citizen.
These groups could have a major impact on the 2024 election. In addition to disenfranchising voters and putting additional pressure on already overstretched election offices, they could convince more and more people that US elections are fraudulent.
Catherine Engelbrecht and her organization True the Vote have effectively tried to disenfranchise voters for more than a decade by claiming that voter rolls are filled with phony voter registrations. Engelbrecht’s rhetoric was given an unprecedented boost in the wake of 2020, when Trump and other elected officials mainstreamed conspiracies that the elections had been rigged in favor of Democrats. Hundreds of national and local election denial groups were formed, and many of them amassed huge followings on social media platforms like Telegram. As the 2024 presidential election looms, they are ramping up efforts to do it again.
“It could be exponentially worse than what we saw in 2020, but we're going to be awake, we're going to be engaged, we are going to understand the process, and we're going to have options to continue to hold to those truths,” Engelbrecht said during a March webinar titled “Election Integrity Team Building 101.” “We're not going to back down. There's too much to lose.”
The hour-long presentation was delivered from a hotel room in Denver, with Engelbrecht laying out what could sound like a relatively benign plan to monitor elections and check voter rolls. “Keep a soft heart, keep a kind word in your mouth, approach people irrespective of party with love. You will find that things will be much better if that is the approach that is taken,” Engelbrecht said. The session, she said, was overbooked.
Engelbrecht then began speaking about elections being “perilously close to cracking in half,” and her presentation became a highlight reel of election conspiracies, references to crystals, Christian nationalist rhetoric, and militaristic jargon. “If this republic’s to be saved, it's because [of] people like all of you that are on this webinar right now. There are some bad actors out there and we live in particularly chaotic and caustic times,” said Engelbrecht. “If we wait on somebody to do something, we will watch freedom slip away on our watch. That's how close we are.”
“These groups are trying to lay the groundwork to potentially make later claims about the election that very well may be false. But the more chaos that can be caused along the way will give more fodder to that disinformation,” Andrew Garber, an expert at the Brennan Center for Justice’s Voting Rights and Elections Program, tells WIRED. “It's not just bad if there's a mass voter challenge because people might get kicked off the rolls. It's also bad if people then take that challenge and say, ‘See, look at all these ineligible voters,’ when in fact that's not the case.”
Engelbrecht founded True the Vote in 2010, when she was an activist for the right-wing populist Tea Party movement. After the 2020 election, Engelbrecht and her collaborator Gregg Phillips became central figures in the Stop the Steal movement, and starred in the widely-debunked election conspiracy film 2000 Mules. They were also arrested for contempt of court after refusing to identify their source behind allegations that the Chinese government had accessed US election data. True the Vote also made wild allegations of widespread ballot stuffing in Georgia during the 2020 vote and a subsequent runoff in 2021. Earlier this year, True the Vote was forced to admit in court that the group had no evidence to back up its claims.
In 2022, the group rolled out a slick new software tool known as IV3, based on technology developed by Phillips, that compared names on voter rolls to a database maintained by the US Postal Service, allowing anyone to challenge voter registrations across the country if they spotted a discrepancy. A WIRED investigation, however, revealed that the information used to challenge the registration of hundreds of thousands of people was based on unreliable data.
Undeterred, True the Vote announced last week that it was relaunching IV3. Phillips claims that the software’s database now has close to “100 billion data elements about every single voter in the United States.” WIRED has not seen proof of this claim. The new IV3 system will soon be available in all 50 states, the organization said. On Thursday, the group held a webinar to train local activists on how to use it. The new system also relies on data from the US Postal Service, but Engelbrecht claimed during the presentation that Phillips and his team had “normalized” the data from all 50 states to ensure the system would not produce inaccurate results. She also said that thousands of people across the country were already registered, and that they had a long waiting list.
Additionally, she said that another software tool developed by Phillips’ team, called Ground Fusion, would be released soon; it is aimed at organizations and PACs looking to identify voting irregularities across larger geographic regions.
Engelbrecht declined to comment, claiming without evidence that WIRED had “written unfairly about True the Vote and IV3 in the past.”
True the Vote is not the only group seeking to leverage technology to supercharge the spread of election conspiracies. A secretive Georgia-based firm called EagleAI NETwork has developed a voter information database to fast-track the deletion of ineligible voters from the system. Voter rights groups have advised against its use, as insignificant errors—such as a missing comma before the suffix “Jr.”—have led to eligible names being removed. Still, at least one county in Georgia has agreed to use EagleAI to review voter challenges and conduct list maintenance activities.
One of EagleAI’s key backers is former Trump adviser Cleta Mitchell, who in the past two years has become central to the push to spread election conspiracies on a national level through her well-funded Election Integrity Network.
The group has held in-person training seminars in recent years, with session topics including how to protect “Vulnerable Voters from Leftist Activists” and “Monitoring Voting Equipment and Systems.” More recently, the group has made its training sessions available online, and is now once again ramping up its efforts ahead of the 2024 election with an initiative called Soles to the Rolls, aimed at boosting challenges to voter registration.
Mitchell, EagleAI, and the Election Integrity Network did not respond to WIRED’s request for comment.
Another training webinar called “We the People” was also hosted last month by the America Project and its offshoot, Vote Your Vision. Broadcasted online to hundreds of attendees, the webinar featured a lineup of election conspiracists, Republican lawmakers, a guy who wrote a book about fifth-generation warfare, and former GOP presidential candidate Vivek Ramaswamy.
The webinar, the group’s website said, was designed to give people “the secrets to reclaiming our power and reshaping history” by using “state-of-the-art election tools,” including those involving artificial intelligence technology. While the details of exactly what these tools will look like and how they will be used are unclear, the America Project has already scheduled more training sessions in the coming weeks to give supporters more information. The group also did not reply to requests for comment.
The America Project was cofounded by disgraced former national security adviser Michael Flynn and former Overstock.com CEO and conspiracist Patrick Byrne, who also funds part of the organization. Both Flynn and Byrne reportedly attended a White House meeting in late 2020 to urge Trump to essentially declare martial law and seize voting machines.
While Flynn didn’t speak during last month’s webinar, he has arguably done more than anyone since 2020 to push the notion that America’s elections are fundamentally fraudulent, appearing at conferences, in podcasts, and on right-wing news shows on a near-daily basis. Trump has also indicated that Flynn will be brought back into his administration should he win.
These efforts have been given the seal of approval by the Republican National Committee, which was recently restructured by Trump to include election deniers and family members in top positions while cutting minority outreach efforts. One of those election deniers is Christina Bobb, who will be running the “election integrity unit.” A former Trump lawyer and TV presenter on far-right channel One America News, Bobb is a major promoter of the myth that the 2020 election was stolen from Trump. The RNC’s election-related priorities, according to an internal memo recently obtained by NPR, include “a broader effort over the coming months to [legally] challenge voter identification and signature verification rules which were put into place for the 2020 election.”
During the America Project webinar last month, one of the hosts apologized to listeners for being unable to get Bobb to join the call that day, but promised that she would join a future session—highlighting just how closely these conspiracy-focused groups work with the mainstream GOP apparatus.
“These groups have a playbook nationally that they tend to deploy locally,” says Garber. “Some of these playbooks that have an intended national reach are then deployed through local activists, and it's concerning because it's the voters at the local level who suffer the effects. It's the election officials at the local level trying to keep order at the polls, trying to make sure their voter rolls are up to date, who have to deal with this stuff.”
One of Flynn’s core messages over the past four years has been that “local action equals national impact” —an expression that revolves around a concept called “precinct strategy,” which aims to get people into key positions on local committees in order to push their narratives at the local level. In 2024, that strategy has been primed and polished.
“This concept of precinct strategy was actually endorsed by President Trump in the last election cycle,” Yehuda Miller, a Republican county committee member in New Jersey, said during the America Project seminar. “We want to take the strategy to the next level. We want to get more organized, we want to start organizing across multiple counties in a state, we want to start organizing across multiple states. We have the power to direct our elected officials.”
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top Online Business Ideas to Consider in 2025

Dubai's dynamic business environment offers numerous online opportunities for aspiring entrepreneurs. Here are some of the top online business ideas to consider in 2025:
E-commerce Store: Launch an online platform to sell products directly to consumers. With the UAE's e-commerce market projected to reach $9.2 billion by 2026, there's significant potential here. Focus on a specific niche, obtain the necessary e-commerce license, and develop a user-friendly website. Partnering with reliable delivery services and implementing effective marketing strategies will be crucial.
Dropshipping Business: Manage an online store without holding inventory. When a customer makes a purchase, the order is forwarded to a supplier who ships the product directly to the customer. This model reduces upfront costs and is gaining popularity globally.
Digital Marketing Agency: Offer services like social media management, SEO, and content creation to help businesses enhance their online presence. As companies increasingly recognize the importance of digital marketing, there's a growing demand for such expertise.
Online Education and Tutoring: Provide virtual classes or tutoring sessions in subjects you're knowledgeable about. The rise of online learning platforms has made education more accessible, and there's a consistent demand for quality instructors.
Content Creation and Blogging: Create engaging content through blogs, videos, or podcasts. Monetize your content via advertising, sponsorships, or affiliate marketing. Building a loyal audience can lead to significant revenue opportunities.
Affiliate Marketing: Promote products or services from other companies and earn a commission for each sale made through your referral. This model is cost-effective and can be lucrative with the right strategy.
App Development: Develop mobile or web applications to meet specific user needs. With the increasing reliance on digital solutions, innovative apps can gain rapid popularity.
Virtual Assistant Services: Offer administrative support to businesses or individuals remotely. Tasks can range from managing emails to scheduling appointments, providing flexibility for both parties.
Online Consulting: Leverage your expertise in a particular field to offer consulting services online. Whether it's business strategy, health, or finance, many are willing to pay for professional advice.
Graphic Design Services: Provide design solutions for logos, marketing materials, or websites. As businesses aim to stand out visually, skilled graphic designers are in high demand.
Social Media Influencer: Build a strong presence on platforms like Instagram or YouTube. With a substantial following, you can collaborate with brands for promotions and sponsorships.
Online Fitness Coaching: Offer virtual fitness classes or personalized training plans. The health and wellness industry continues to thrive, and many prefer the convenience of online sessions.
Stock Photography: Capture high-quality images and sell them on stock photography websites. Businesses and creators constantly seek quality visuals for their projects.
Handmade Crafts Online Store: Sell handmade items like jewelry, art, or home decor through an online platform. There's a market for unique, handcrafted products that can't be found in mass production.
Subscription Box Service: Curate and deliver boxes of niche products to subscribers regularly. This model has gained traction in various industries, from beauty products to gourmet foods.
Language Translation Services: Provide translation services for documents, websites, or media content. In a globalized world, effective communication across languages is essential.
Online Travel Agency: Assist clients in planning and booking their travel experiences. With the resurgence of travel, personalized planning services are valuable.
Virtual Event Planning: Organize and manage online events, from webinars to virtual conferences. As virtual events become more common, skilled planners are needed to ensure their success.
Print on Demand: Design custom apparel or merchandise and partner with suppliers who print and ship items as orders come in. This reduces the need for inventory and allows for creative flexibility.
Online Real Estate Brokerage: Facilitate property transactions through a digital platform. With the real estate market's evolution, online brokerages offer convenience to buyers and sellers.
Embarking on an online business in Dubai offers numerous advantages, including a strategic location, supportive government policies, and a tech-savvy population.
By selecting the right niche and implementing effective strategies, you can build a successful venture in this thriving market.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
closed starter for @kenxmatsui
The sun was low in the sky, and Haru could not fucking believe what a day they had. It felt like within the previous twelve hours, they had lived a whole century. Who knew settling in a new job would be so arduous? All the small webinars Haru completed bored them, and they were thankful tomorrow they'd start actually doing something in their job. Fidgeting with the uncomfortable bottom up shirt they wore, they rolled up their sleeves, showcasing the previously hidden tattoos, not that their shirt covered the tattoos on their hands. Still an attempt was made. Letting out possibly the biggest sigh of the day, they pulled out a small red and white box to pull out a cigarette only realizing that they didn't have a lighter. Of course, those heathens (their cats) must have taken it. Still, they checked each one of their pockets before looking around and spotting another smoker. They hated this, but they needed to smoke before driving back to the hotel or they would lose their mind. "Excuse me." They started talking not really looking at the other person in the face, just focusing on their shirt. "Do you have a light? I'll only bother you for that." (meaning don't make conversation with me) Haru prayed this wasn't a talkative person because they didn't have the energy to deal with it.
Raising their hand to ruffle their own short hair, they finally looked up at the other person. It didn't take much for Haru to immediately notice just how fucking tall this guy was, but the real shocker was when their brown eyes landed on his face. Were they hallucinating? Surely not. Was someone playing a trick on them? But who? They knew close to nobody in this small town. "Kenji?" The name fell of their lips before they could register. Surely not. They've lost their mind. Yes, that made more sense that for their brother to be here in Lunar Cove smoking outside just as Haru got off work. Brown eyes studied him like a hawk. They wanted to reach out and pinch him, to see if this was real, but instead they took a step back as if gaining some distance could clear their mind. "I must have lost my damn fucking mind." Ruffling their hair with more intensity, Haru's eyes ventured away from his face and onto his body. He was well-dressed. He was tall. He looked like Kenji except older. Part of them wanted to say their last name, to fully confirm if it was him except they didn't want to. The distaste for the name lived on fiercely inside of them and they'd rather keep staring in silence as they awaited confirmation. If this wasn't their brother, it was an awful look-a-like, and Haru should possibly move out of town to avoid any further confusion. Then it dawned on them, as they fidgeted with the unlit cigarette, what if it was him and he didn't recognize them?

#s: harumi#a/n: no need to match length but i know ure an absolute heathen#harumi feat. kenji#harumi feat. kenji 001#smoking tw
7 notes
·
View notes
Note
is the raffle for TRC graphic novel? I can't find it online omg
AH i'm sorry, I should have been more clear about this. The raffle was for attendees of the Penguin Summer 2025 title showcase only! (aka the Zoom webinar I was just in.) I was there because I'm a librarian and at some point I ended up on Penguin's "teachers & librarians" marketing list.
idk how many people were in that zoom but given my known family history for never winning anything, I don't think I'm likely to get one of the boxes. If by some miracle I do win though and there is indeed a release date schedule in it, I'll let yall know.
#asks#here I go accidentally spreading misinformation again 😔 not very librarian of me alas#but like listen even if i don't win it at least one of the 3 ppl who do are GONNA leak that info#not like they can include an NDA in the box or something
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anyway, happy America Recycles Week. Tomorrow's the actual day (the 15th.) I don't have a curbside bin where I live so I just collect it myself and manually drop it off at the center. So that's what I just did after getting off work!
If you have the ability to recycle, please check what your local municipality can process. It's important to making sure everything can be properly sorted. Plastic shopping bags normally cannot be accepted, nor styrofoam. Also, be sure to avoid food contamination like with takeout containers or pizza boxes (grease.) I normally rinse my bottles and cans. I attended a webinar this week at work given by some people who run a materials recovery facility (MRF) and they said they're able to clean things pretty well as long as it doesn't still contain food, so you don't have to wash items.
And if you have materials like medication, look up ways to turn them in instead of trashing or flushing them. And please recycle your electronics, the minerals in them are valuable and li-on batteries can be dangerous if improperly disposed of (you ever seen a puffy one? yeah....)
This has been your 30 second recycling run down
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: James Esses
Published: Nov 8, 2023
Two weeks ago, I was privileged to speak at the Battle of Ideas in Westminster, debating some of the biggest issues facing society. Below is a transcript of the opening speech I gave on the ‘The Tyranny of Lived Experience’:
“According to some, I am nothing more than a straight, white, ‘cis’, male. Minus the ‘cis’, these descriptors are all factually accurate. Yet, tellingly, they are almost always used as a putdown and, crucially, they tell you next to nothing about me or my unique life experiences.
Identity politics, where one’s ‘lived experience’ is prized above all else and where groups of individuals are placed into categories of ‘privilege’ or ‘victimhood’, is the fashion of the day.
At best, I argue that the concept of ‘lived experience’ is an utter irrelevance – what other experience does one have than that which they have lived? The moment at which you stop experiencing ‘lived experience’ is surely, the moment at which you die? I recently came across an NHS Trust hiring a ‘Director for Lived Experience’ – what are the job requirements – to have the ability breathe to oxygen?!
However, at its worst, it is a regressive tool, used to shut down conversation and place people into rigid boxes from which they cannot escape, solely based on personal characteristics often completely outside of their control.
I recently attended a webinar hosted by Pink News, an organisation known for its pushing of identity politics in its supposed journalism.
At the very beginning of the day, the host told us he and his panellists were “open to challenge and debate but that should not be around ‘lived experience”. This was the ultimate oxymoron – in other words, there was to be no challenge.
I hear time and time again of important debate and dialogue, including in educational institutions, coming to a grinding halt the moment someone utters: “you don’t have my lived experience”. There is no comeback to that and the individuals who use it, know it. It places people into the ultimate double bind – “you must understand me but you can never understand me”. So it can pay dividends to invoke ‘lived experience’, especially if you are lacking any coherent or substantive arguments to support the case you are making.
I have spent the last number of years advocating on behalf of child safeguarding and women’s rights. And yet, not infrequently, I am effectively told to sit down and shut up because I have no children and am a man.
However, this type of approach flies completely in the face of one of the core tenets of psychotherapy, and indeed humanity in general, empathy.
As human beings, we have the unique ability to put ourselves into the shoes of others and conjure up a sense of what is going on for them in that moment. One does not need to be Ukrainian to empathise with and understand the plight of the Ukrainian people. One does not need to have been a migrant to be eligible to debate a country’s migration policy.
I thought we as a ‘liberal’ society were moving away from regressive stereotypes and judging appearances. However, it appears as if we are right back in the bad ol’ days.
I recently came across an “educational tool” being used in schools called the Wheel of Power/Privilege. Its purpose is to teach about ‘intersectionality’ and ‘lived experience’ and people are placed into buckets entitled ‘power’ or ‘marginalised’ based on their personal characteristics.
Here are some of the characteristics, which, if you possess them, should signal to you that you are ‘privileged’ or ‘powerful’:
Being married – Would a wife living in an abusive relationship consider herself powerful?
Being slim – Would someone struggling with anorexia consider themselves privileged?
Being European – Would someone on the front line in Ukraine consider themselves privileged?
I could go on.
This type of rhetoric ignores the complexity of human existence and the fact that you cannot make such sweeping judgments about individuals with such limited knowledge. It also shames people – sending a message that if you possess certain characteristics, that you are not deserving of praise when you succeed or empathy when you struggle, on the basis that you are inherently ‘privileged’.
Furthermore, far from instilling resiliency in our children, crucial in a world often unpredictable and unfair, it tells swathes that they are victims because of certain characteristics they possess and that they will, to some extent, always remain victims.
Finally, a word on this. The obsession over ‘lived experience’ relating to objective, factual characteristics is bad enough. However, in a world of postmodernism, we are now witnessing people claim ‘lived experience’ over a ‘self-identity’ that they have essentially invented. We see this in the ongoing ‘trans’ debate – how can a male who has never been biologically female have any comprehension of what it feels like to be the other sex? Should we now start to allow adults to self-identify as children, if that aligns with their internal ‘lived experience’? I fear it is only a matter of time.
The assumption that we can break down the complexities of a fellow human being into bitesize labels based on a perception of ‘lived experience’ from certain immutable characteristics they possess is disingenuous and dangerous. ‘Straight, white, men’ can also suffer from poverty, ill-health, abuse, lack of education, relationship conflict, etc.
We all have ‘lived experience’ – in fact, it is the only experience we have. The sooner we start to treat each other as the complex, unique humans that we are, rather than homogenous blobs, the better.”
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Skip to main content
Skip to Table of Contents
U.S. flag
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Notice
The Public Right-of-Way Accessibility Guidelines (PROWAG) rulemaking has concluded. The PROWAG final rule has been published in the Federal Register. Please visit the Access Board’s PROWAG page for the guidelines.
USAB star logo
U.S. Access Board
Advancing Full Access and Inclusion for All
Information and Communication Technology
Revised 508 Standards and 255 Guidelines
PDF
About the ICT Accessibility 508 Standards and 255 Guidelines
These standards address access to information and communication technology (ICT) under Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act and Section 255 of the Communications Act.
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act charges the Access Board with developing and promulgating this rule. The statute also charges the Access Board with providing Technical Assistance on Section 508, which is provided through webinars, trainings, and in close collaboration with GSA and materials available from Section508.gov.
Section 508 requires access to ICT developed, procured, maintained, or used by federal agencies. Examples include computers, telecommunications equipment, multifunction office machines such as copiers that also operate as printers, software, websites, information kiosks and transaction machines, and electronic documents. The Section 508 Standards, which are part of the Federal Acquisition Regulation, ensure access for people with physical, sensory, or cognitive disabilities.
The Section 255 Guidelines cover telecommunications equipment and customer-premises equipment — such as telephones, cell phones, routers, set-top boxes, and computers with modems, interconnected Voice over Internet Protocol products, and software integral to the operation of telecommunications function of such equipment.
Background
February 3, 1998 – The Board publishes the original Telecommunications Act Accessibility Guidelines.
December 21, 2000 – The Board issues the original Section 508 Standards.
July 6, 2006 – The Board organizes TEITAC, the Telecommunications and Electronic and Information Technology Advisory Committee, to assist in updating the Section 508 Standards and Telecommunications Act Guidelines.
April 3, 2008 – The Advisory Committee presents its final report to the Board.
March 22, 2010 – The Board releases a draft proposed rule for public comment, docket ATBCB-2010-0001.
December 8, 2011 – The Board issues a revised draft proposed rule for public comment, docket ATBCB-2011-0007.
February 27, 2015 – The Board ICT proposed rule for public comment, docket ATBCB-2015-0002.
January 18, 2017 – The Board issues the final rule, docket ATBCB-2015-0002-014.
January 22, 2018 – The Board issues correction to the final rule to restore provisions for TTY access, docket document ATBCB-2015-0002-0146.
Additional Resources
Section508.gov — GSA’s Government-wide IT Accessibility Program
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act (29 U.S.C. §794d)
Final Regulatory Impact Analysis (FRIA)
Comparison Table of WCAG 2.0 to Original 508 Standards
Mapping of WCAG 2.0 to Functional Performance Criteria
ICT Testing Baseline for Web Accessibility
Appendix A to Part 1194 – Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act: Application and Scoping Requirements
508 Chapter 1: Application and Administration
E101 General
E101.1 Purpose
These Revised 508 Standards, which consist of 508 Chapters 1 and 2 (Appendix A), along with Chapters 3 through 7 (Appendix C), contain scoping and technical requirements for information and communication technology (ICT) to ensure accessibility and usability by individuals with disabilities. Compliance with these standards is mandatory for Federal agencies subject to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended (29 U.S.C. 794d).
E101.2 Equivalent Facilitation
The use of an alternative design or technology that results in substantially equivalent or greater accessibility and usability by individuals with disabilities than would be provided by conformance to one or more of the requirements in Chapters 4 and 5 of the Revised 508 Standards is permitted. The functional performance criteria in Chapter 3 shall be used to determine whether substantially equivalent or greater accessibility and usability is provided to individuals with disabilities.
E101.3 Conventional Industry Tolerances
Dimensions are subject to conventional industry tolerances except where dimensions are stated as a range with specific minimum or maximum end points.
E101.4 Units of Measurement
Measurements are stated in metric and U.S. customary units. The values stated in each system (metric and U.S. customary units) may not be exact equivalents, and each system shall be used independently of the other.
E102 Referenced Standards
E102.1 Application
The specific editions of the standards listed in Chapter 7 are incorporated by reference into 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements) and Chapters 3 through 6 to the prescribed extent of each such reference. Where conflicts occur between the Revised 508 Standards and the referenced standards, these Revised 508 Standards apply.
E103 Definitions
E103.1 Terms Defined in Referenced Standards
Terms defined in referenced standards and not defined in E103.4 shall have the meaning as defined in the referenced standards.
E103.2 Undefined Terms
Any term not defined in E103.4 or in referenced standards shall be given its ordinarily accepted meaning in the sense that the context implies.
E103.3 Interchangeability
Words, terms, and phrases used in the singular include the plural and those used in the plural include the singular.
E103.4 Defined Terms
For the purpose of the Revised 508 Standards, the terms defined in E103.4 have the indicated meaning.
Agency
Any agency or department of the United States as defined in 44 U.S.C. 3502, and the United States Postal Service.
Alteration
A change to existing ICT that affects interoperability, the user interface, or access to information or data.
Application.
Software designed to perform, or to help the user to perform, a specific task or tasks.
Assistive Technology (AT)
Any item, piece of equipment, or product system, whether acquired commercially, modified, or customized, that is used to increase, maintain, or improve functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities.
Audio Description.
Narration added to the soundtrack to describe important visual details that cannot be understood from the main soundtrack alone. Audio description is a means to inform individuals who are blind or who have low vision about visual content essential for comprehension. Audio description of video provides information about actions, characters, scene changes, on-screen text, and other visual content. Audio description supplements the regular audio track of a program. Audio description is usually added during existing pauses in dialogue. Audio description is also called “video description” and “descriptive narration”.
Authoring Tool
Any software, or collection of software components, that can be used by authors, alone or collaboratively, to create or modify content for use by others, including other authors.
Closed Functionality
Characteristics that limit functionality or prevent a user from attaching or installing assistive technology. Examples of ICT with closed functionality are self-service machines, information kiosks, set-top boxes, fax machines, calculators, and computers that are locked down so that users may not adjust settings due to a policy such as Desktop Core Configuration.
Content
Electronic information and data, as well as the encoding that defines its structure, presentation, and interactions.
Document
Logically distinct assembly of content (such as a file, set of files, or streamed media) that: functions as a single entity rather than a collection; is not part of software; and does not include its own software to retrieve and present content for users. Examples of documents include, but are not limited to, letters, email messages, spreadsheets, presentations, podcasts, images, and movies.
Existing ICT
ICT that has been procured, maintained or used on or before January 18, 2018.
Hardware
A tangible device, equipment, or physical component of ICT, such as telephones, computers, multifunction copy machines, and keyboards.
Information Technology
Shall have the same meaning as the term “information technology” set forth in 40 U.S.C. 11101(6).
Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Information technology and other equipment, systems, technologies, or processes, for which the principal function is the creation, manipulation, storage, display, receipt, or transmission of electronic data and information, as well as any associated content. Examples of ICT include, but are not limited to: computers and peripheral equipment; information kiosks and transaction machines; telecommunications equipment; customer premises equipment; multifunction office machines; software; applications; Web sites; videos; and, electronic documents.
Keyboard
A set of systematically arranged alphanumeric keys or a control that generates alphanumeric input by which a machine or device is operated. A keyboard includes tactilely discernible keys used in conjunction with the alphanumeric keys if their function maps to keys on the keyboard interfaces.
Label
Text, or a component with a text alternative, that is presented to a user to identify content. A label is presented to all users, whereas a name may be hidden and only exposed by assistive technology. In many cases, the name and the label are the same.
Menu
A set of selectable options.
Name
Text by which software can identify a component to the user. A name may be hidden and only exposed by assistive technology, whereas a label is presented to all users. In many cases, the label and the name are the same. Name is unrelated to the name attribute in HTML.
Non-Web Document
A document that is not: a Web page, embedded in a Web page, or used in the rendering or functioning of Web pages.
Non-Web Software
Software that is not: a Web page, not embedded in a Web page, and not used in the rendering or functioning of Web pages.
Operable Part
Hardware-based user controls for activating, deactivating, or adjusting ICT.
Platform Accessibility Services
Services provided by a platform enabling interoperability with assistive technology. Examples are Application Programming Interfaces (API) and the Document Object Model (DOM).
Platform Software
Software that interacts with hardware or provides services for other software. Platform software may run or host other software, and may isolate them from underlying software or hardware layers. A single software component may have both platform and non-platform aspects. Examples of platforms are: desktop operating systems; embedded operating systems, including mobile systems; Web browsers; plug-ins to Web browsers that render a particular media or format; and sets of components that allow other applications to execute, such as applications which support macros or scripting.
Programmatically Determinable
Ability to be determined by software from author-supplied data that is provided in a way that different user agents, including assistive technologies, can extract and present the information to users in different modalities.
Public Facing
Content made available by an agency to members of the general public. Examples include, but are not limited to, an agency Web site, blog post, or social media pages.
Real-Time Text (RTT)
Communications using the transmission of text by which characters are transmitted by a terminal as they are typed. Real-time text is used for conversational purposes. Real-time text also may be used in voicemail, interactive voice response systems, and other similar application.
Revised 508 Standards
The standards for ICT developed, procured, maintained, or used by agencies subject to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act as set forth in 508 Chapters 1 and 2 (36 CFR part 1194, Appendix A), and Chapters 3 through 7 (36 CFR part 1194, Appendix C).
Software
Programs, procedures, rules, and related data and documentation that direct the use and operation of ICT and instruct it to perform a given task or function. Software includes, but is not limited to, applications, non-Web software, and platform software.
Software Tools
Software for which the primary function is the development of other software. Software tools usually come in the form of an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) and are a suite of related products and utilities. Examples of IDEs include Microsoft® Visual Studio®, Apple® Xcode®, and Eclipse Foundation Eclipse®.
Telecommunications
The signal transmission, between or among points specified by the user, of information of the user’s choosing, without change in the form or content of the information as sent and received.
Terminal
Device or software with which the end user directly interacts and that provides the user interface. For some systems, the software that provides the user interface may reside on more than one device such as a telephone and a server.
Text
A sequence of characters that can be programmatically determined and that expresses something in human language.
TTY
Equipment that enables interactive text based communications through the transmission of frequency-shift-keying audio tones across the public switched telephone network. TTYs include devices for real-time text communications and voice and text intermixed communications. Examples of intermixed communications are voice carry over and hearing carry over. One example of a TTY is a computer with TTY emulating software and modem.
Variable Message Signs (VMS)
Non-interactive electronic signs with scrolling, streaming, or paging-down capability. An example of a VMS is an electronic message board at a transit station that displays the gate and time information associated with the next train arrival.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
A technology that provides real-time voice communications. VoIP requires a broadband connection from the user’s location and customer premises equipment compatible with Internet protocol.
Web page
A non-embedded resource obtained from a single Universal Resource Identifier (URI) using HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) plus any other resources that are provided for the rendering, retrieval, and presentation of content.
508 Chapter 2: Scoping Requirements
E201 Application
E201.1 Scope
ICT that is procured, developed, maintained, or used by agencies shall conform to the Revised 508 Standards.
E202 General Exceptions
E202.1 General
ICT shall be exempt from compliance with the Revised 508 Standards to the extent specified by E202.
E202.2 Legacy ICT
Any component or portion of existing ICT that complies with an earlier standard issued pursuant to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended (as republished in Appendix D), and that has not been altered on or after January 18, 2018, shall not be required to be modified to conform to the Revised 508 Standards.
E202.3 National Security Systems
The Revised 508 Standards do not apply to ICT operated by agencies as part of a national security system, as defined by 40 U.S.C. 11103(a).
E202.4 Federal Contracts
ICT acquired by a contractor incidental to a contract shall not be required to conform to the Revised 508 Standards.
E202.5 ICT Functions Located in Maintenance or Monitoring Spaces
Where status indicators and operable parts for ICT functions are located in spaces that are frequented only by service personnel for maintenance, repair, or occasional monitoring of equipment, such status indicators and operable parts shall not be required to conform to the Revised 508 Standards.
E202.6 Undue Burden or Fundamental Alteration
Where an agency determines in accordance with E202.6 that conformance to requirements in the Revised 508 Standards would impose an undue burden or would result in a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT, conformance shall be required only to the extent that it does not impose an undue burden, or result in a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT.
E202.6.1 Basis for a Determination of Undue Burden
In determining whether conformance to requirements in the Revised 508 Standards would impose an undue burden on the agency, the agency shall consider the extent to which conformance would impose significant difficulty or expense considering the agency resources available to the program or component for which the ICT is to be procured, developed, maintained, or used.
E202.6.2 Required Documentation
The responsible agency official shall document in writing the basis for determining that conformance to requirements in the Revised 508 Standards constitute an undue burden on the agency, or would result in a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT. The documentation shall include an explanation of why and to what extent compliance with applicable requirements would create an undue burden or result in a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT.
E202.6.3 Alternative Means
Where conformance to one or more requirements in the Revised 508 Standards imposes an undue burden or a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT, the agency shall provide individuals with disabilities access to and use of information and data by an alternative means that meets identified needs.
E202.7 Best Meets
Where ICT conforming to one or more requirements in the Revised 508 Standards is not commercially available, the agency shall procure the ICT that best meets the Revised 508 Standards consistent with the agency’s business needs.
E202.7.1 Required Documentation
The responsible agency official shall document in writing: (a) the non-availability of conforming ICT, including a description of market research performed and which provisions cannot be met, and (b) the basis for determining that the ICT to be procured best meets the requirements in the Revised 508 Standards consistent with the agency’s business needs.
E202.7.2 Alternative Means
Where ICT that fully conforms to the Revised 508 Standards is not commercially available, the agency shall provide individuals with disabilities access to and use of information and data by an alternative means that meets identified needs.
E203 Access to Functionality
E203.1 General
Agencies shall ensure that all functionality of ICT is accessible to and usable by individuals with disabilities, either directly or by supporting the use of assistive technology, and shall comply with E203. In providing access to all functionality of ICT, agencies shall ensure the following:
That Federal employees with disabilities have access to and use of information and data that is comparable to the access and use by Federal employees who are not individuals with disabilities; and
That members of the public with disabilities who are seeking information or data from a Federal agency have access to and use of information and data that is comparable to that provided to members of the public who are not individuals with disabilities.
E203.2 User Needs
When agencies procure, develop, maintain or use ICT they shall identify the needs of users with disabilities to determine:
How users with disabilities will perform the functions supported by the ICT; and
How the ICT will be developed, installed, configured, and maintained to support users with disabilities.
E204 Functional Performance Criteria
E204.1 General
Where the requirements in Chapters 4 and 5 do not address one or more functions of ICT, the functions not addressed shall conform to the Functional Performance Criteria specified in Chapter 3.
E205 Electronic Content
E205.1 General
Electronic content shall comply with E205.
E205.2 Public Facing
Electronic content that is public facing shall conform to the accessibility requirements specified in E205.4.
E205.3 Agency Official Communication
Electronic content that is not public facing shall conform to the accessibility requirements specified in E205.4 when such content constitutes official business and is communicated by an agency through one or more of the following:
An emergency notification;
An initial or final decision adjudicating an administrative claim or proceeding;
An internal or external program or policy announcement;
A notice of benefits, program eligibility, employment opportunity, or personnel action;
A formal acknowledgement of receipt;
A survey questionnaire;
A template or form;
Educational or training materials; or
Intranet content designed as a Web page.
EXCEPTION: Records maintained by the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) pursuant to Federal recordkeeping statutes shall not be required to conform to the Revised 508 Standards unless public facing.
E205.4 Accessibility Standard
Electronic content shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
EXCEPTION: Non-Web documents shall not be required to conform to the following four WCAG 2.0 Success Criteria: 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks, 2.4.5 Multiple Ways, 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation, and 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
E205.4.1 Word Substitution when Applying WCAG to Non-Web Documents
For non-Web documents, wherever the term “Web page” or “page” appears in WCAG 2.0 Level A and AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements, the term “document” shall be substituted for the terms “Web page” and “page”. In addition, in Success Criterion in 1.4.2, the phrase “in a document” shall be substituted for the phrase “on a Web page”.
E206 Hardware
E206.1 General
Where components of ICT are hardware and transmit information or have a user interface, such components shall conform to the requirements in Chapter 4.
E207 Software
E207.1 General
Where components of ICT are software and transmit information or have a user interface, such components shall conform to E207 and the requirements in Chapter 5.
EXCEPTION: Software that is assistive technology and that supports the accessibility services of the platform shall not be required to conform to the requirements in Chapter 5.
E207.2 WCAG Conformance
User interface components, as well as the content of platforms and applications, shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
EXCEPTIONS:
Software that is assistive technology and that supports the accessibility services of the platform shall not be required to conform to E207.2.
Non-Web software shall not be required to conform to the following four Success Criteria in WCAG 2.0: 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks; 2.4.5 Multiple Ways; 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation; and 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
Non-Web software shall not be required to conform to Conformance Requirement 3 Complete Processes in WCAG 2.0.
E207.2.1 Word Substitution when Applying WCAG to Non-Web Software
For non-Web software, wherever the term “Web page” or “page” appears in WCAG 2.0 Level A and AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements, the term “software” shall be substituted for the terms “Web page” and “page”. In addition, in Success Criterion in 1.4.2, the phrase “in software” shall be substituted for the phrase “on a Web page.”
E207.3 Complete Processes for Non-Web Software
Where non-Web software requires multiple steps to accomplish an activity, all software related to the activity to be accomplished shall conform to WCAG 2.0 as specified in E207.2.
E208 Support Documentation and Services
E208.1 General
Where an agency provides support documentation or services for ICT, such documentation and services shall conform to the requirements in Chapter 6.
Appendix B to Part 1194 – Section 255 of the Communications Act: Application and Scoping Requirements
255 Chapter 1: Application and Administration
C101 General
C101.1 Purpose
These Revised 255 Guidelines, which consist of 255 Chapters 1 and 2 (Appendix B), along with Chapters 3 through 7 (Appendix C), contain scoping and technical requirements for the design, development, and fabrication of telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment, content, and support documentation and services, to ensure accessibility and usability by individuals with disabilities. These Revised 255 Guidelines are to be applied to the extent required by regulations issued by the Federal Communications Commission under Section 255 of the Communications Act of 1934, as amended (47 U.S.C. 255).
C101.2 Equivalent Facilitation
The use of an alternative design or technology that results in substantially equivalent or greater accessibility and usability by individuals with disabilities than would be provided by conformance to one or more of the requirements in Chapters 4 and 5 of the Revised 255 Guidelines is permitted. The functional performance criteria in Chapter 3 shall be used to determine whether substantially equivalent or greater accessibility and usability is provided to individuals with disabilities.
C101.3 Conventional Industry Tolerances
Dimensions are subject to conventional industry tolerances except where dimensions are stated as a range with specific minimum or maximum end points.
C101.4 Units of Measurement
Measurements are stated in metric and U.S. customary units. The values stated in each system (metric and U.S. customary units) may not be exact equivalents, and each system shall be used independently of the other.
C102 Referenced Standards
C102.1 Application
The specific editions of the standards listed in Chapter 7 are incorporated by reference into 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements) and Chapters 3 through 6 to the prescribed extent of each such reference. Where conflicts occur between the Revised 255 Guidelines and the referenced standards, these Revised 255 Guidelines apply.
C103 Definitions
C103.1 Terms Defined in Referenced Standards
Terms defined in referenced standards and not defined in C103.4 shall have the meaning as defined in the referenced standards.
C103.2 Undefined Terms
Any term not defined in C103.4 or in referenced standards shall be given its ordinarily accepted meaning in the sense that the context implies.
C103.3 Interchangeability
Words, terms, and phrases used in the singular include the plural and those used in the plural include the singular.
C103.4 Defined Terms
For the purpose of the Revised 255 Guidelines, the terms defined in C103.4 have the indicated meaning.
Application
Software designed to perform, or to help the user perform, a specific task or tasks.
Assistive Technology (AT)
Any item, piece of equipment, or product system, whether acquired commercially, modified, or customized, that is used to increase, maintain, or improve functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities.
Audio Description
Narration added to the soundtrack to describe important visual details that cannot be understood from the main soundtrack alone. Audio description is a means to inform individuals who are blind or who have low vision about visual content essential for comprehension. Audio description of video provides information about actions, characters, scene changes, on-screen text, and other visual content. Audio description supplements the regular audio track of a program. Audio description is usually added during existing pauses in dialogue. Audio description is also called “video description” and “descriptive narration.”
Authoring Tool
Any software, or collection of software components, that can be used by authors, alone or collaboratively, to create or modify content for use by others, including other authors.
Closed Functionality
Characteristics that limit functionality or prevent a user from attaching or installing assistive technology.
Content
Electronic information and data, as well as the encoding that defines its structure, presentation, and interactions.
Customer Premises Equipment (CPE)
Equipment used on the premises of a person (other than a carrier) to originate, route, or terminate telecommunications service or interconnected VoIP service, including software integral to the operation of telecommunications function of such equipment. Examples of CPE are telephones, routers, switches, residential gateways, set-top boxes, fixed mobile convergence products, home networking adaptors and Internet access gateways which enable consumers to access communications service providers’ services and distribute them around their house via a Local Access Network (LAN).
Document
Logically distinct assembly of content (such as a file, set of files, or streamed media) that: functions as a single entity rather than a collection; is not part of software; and does not include its own software to retrieve and present content for users. Examples of documents include, but are not limited to, letters, email messages, spreadsheets, presentations, podcasts, images, and movies.
Hardware
A tangible device, equipment, or physical component of ICT, such as telephones, computers, multifunction copy machines, and keyboards.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Information technology and other equipment, systems, technologies, or processes, for which the principal function is the creation, manipulation, storage, display, receipt, or transmission of electronic data and information, as well as any associated content.
Keyboard
A set of systematically arranged alphanumeric keys or a control that generates alphanumeric input by which a machine or device is operated. A keyboard includes tactilely discernible keys used in conjunction with the alphanumeric keys if their function maps to keys on the keyboard interfaces.
Label
Text, or a component with a text alternative, that is presented to a user to identify content. A label is presented to all users, whereas a name may be hidden and only exposed by assistive technology. In many cases, the name and the label are the same.
Manufacturer
A final assembler of telecommunications equipment or customer premises equipment that sells such equipment to the public or to vendors that sell to the public.
Menu
A set of selectable options.
Name
Text by which software can identify a component to the user. A name may be hidden and only exposed by assistive technology, whereas a label is presented to all users. In many cases, the label and the name are the same. Name is unrelated to the name attribute in HTML.
Non-Web Document
A document that is not: a Web page, embedded in a Web page, or used in the rendering or functioning of Web pages.
Non-Web Software
Software that is not: a Web page, not embedded in a Web page, and not used in the rendering or functioning of Web pages.
Operable Part
Hardware-based user controls for activating, deactivating, or adjusting ICT.
Platform Accessibility Services
Services provided by a platform enabling interoperability with assistive technology. Examples are Application Programming Interfaces (API) and the Document Object Model (DOM).
Platform Software
Software that interacts with hardware or provides services for other software. Platform software may run or host other software, and may isolate them from underlying software or hardware layers. A single software component may have both platform and non-platform aspects. Examples of platforms are: desktop operating systems; embedded operating systems, including mobile systems; Web browsers; plug-ins to Web browsers that render a particular media or format; and sets of components that allow other applications to execute, such as applications which support macros or scripting.
Programmatically Determinable
Ability to be determined by software from author-supplied data that is provided in a way that different user agents, including assistive technologies, can extract and present the information to users in different modalities.
Real-Time Text (RTT)
Communications using the transmission of text by which characters are transmitted by a terminal as they are typed. Real-time text is used for conversational purposes. Real-time text also may be used in voicemail, interactive voice response systems, and other similar application.
Revised 255 Guidelines
The guidelines for telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment covered by Section 255 of the Communications Act as set forth in 255 Chapters 1 and 2 (36 CFR part 1194, Appendix B), and Chapters 3 through 7 (36 CFR part 1193, Appendix C).
Software
Programs, procedures, rules, and related data and documentation that direct the use and operation of ICT and instruct it to perform a given task or function. Software includes, but is not limited to, applications, non-Web software, and platform software.
Software Tools
Software for which the primary function is the development of other software. Software tools usually come in the form of an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) and are a suite of related products and utilities. Examples of IDEs include Microsoft® Visual Studio®, Apple® Xcode®, and Eclipse Foundation Eclipse®
Specialized Customer Premises Equipment
Assistive technology used by individuals with disabilities to originate, route, or terminate telecommunications or interconnected VoIP service. Examples are TTYs and amplified telephones.
Telecommunications
The signal transmission between or among points specified by the user of information and of the user’s choosing without change in the form or content of the information as sent and received.
Telecommunications Equipment
Equipment, other than customer premises equipment, used by a carrier to provide telecommunications service or interconnected VoIP service and includes software integral to the operation of telecommunications function of such equipment.
Terminal
Device or software with which the end user directly interacts and that provides the user interface. For some systems, the software that provides the user interface may reside on more than one device such as a telephone and a server.
Text
A sequence of characters that can be programmatically determined and that expresses something in human language.
TTY
Equipment that enables interactive text based communications through the transmission of frequency-shift-keying audio tones across the public switched telephone network. TTYs include devices for real-time text communications and voice and text intermixed communications. Examples of intermixed communications are voice carry over and hearing carry over. One example of a TTY is a computer with TTY emulating software and modem.
Variable Message Signs (VMS)
Non-interactive electronic signs with scrolling, streaming, or paging-down capability. An example of a VMS is an electronic message board at a transit station that displays the gate and time information associated with the next train arrival.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
A technology that provides real-time voice communications. VoIP requires a broadband connection from the user’s location and customer premises equipment compatible with Internet protocol.
Web page
A non-embedded resource obtained from a single Universal Resource Identifier (URI) using HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) plus any other resources that are provided for the rendering, retrieval, and presentation of content.
255 Chapter 2: Scoping Requirements
C201 Application
C201.1 Scope
Manufacturers shall comply with the requirements in the Revised 255 Guidelines applicable to telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment (and related software integral to the operation of telecommunications functions) when newly released, upgraded, or substantially changed from an earlier version or model. Manufacturers shall also conform to the requirements in the Revised 255 Guidelines for support documentation and services, including electronic documents and Web-based product support.
C201.2. Readily Achievable
When a manufacturer determines that conformance to one or more requirements in Chapter 4 (Hardware) or Chapter 5 (Software) would not be readily achievable, it shall ensure that the equipment or software is compatible with existing peripheral devices or specialized customer premises equipment commonly used by individuals with disabilities to the extent readily achievable.
C201.3 Access to Functionality
Manufacturers shall ensure that telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment is accessible to and usable by individuals with disabilities by providing direct access to all telecommunications functionality. Where manufacturers can demonstrate that it is not readily achievable for such equipment to provide direct access to all functionality, the equipment shall support the use of assistive technology and specialized customer premises equipment where readily achievable.
C201.4 Prohibited Reduction of Accessibility, Usability, and Compatibility
No change shall be undertaken that decreases, or has the effect of decreasing, the net accessibility, usability, or compatibility of telecommunications equipment or customer premises equipment.
EXCEPTION: Discontinuation of a product shall not be prohibited.
C201.5 Design, Development, and Fabrication
Manufacturers shall evaluate the accessibility, usability, and interoperability of telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment during its product design, development, and fabrication.
C202 Functional Performance Criteria
C202.1 General
Where the requirements in Chapters 4 and 5 do not address one or more functions of telecommunications or customer premises equipment, the functions not addressed shall conform to the Functional Performance Criteria specified in Chapter 3.
C203 Electronic Content
C203.1 General
Electronic content that is integral to the use of telecommunications or customer premises equipment shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
EXCEPTION: Non-Web documents shall not be required to conform to the following four WCAG 2.0 Success Criteria: 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks, 2.4.5 Multiple Ways, 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation, and 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
C203.1.1 Word Substitution when Applying WCAG to Non-Web Documents
For non-Web documents, wherever the term “Web page” or “page” appears in WCAG 2.0 Level A and AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements, the term “document’ shall be substituted for the terms “Web page” and “page.” In addition, in Success Criterion in 1.4.2, the phrase “in a document” shall be substituted for the phrase “on a Web page.”
C204 Hardware
C204.1 General
Where components of telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment are hardware, and transmit information or have a user interface, those components shall conform to applicable requirements in Chapter 4.
EXCEPTION: Components of telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment shall not be required to conform to 402, 407.7, 407.8, 408, 412.8.4, and 415.
C205 Software
C205.1 General
Where software is integral to the use of telecommunications functions of telecommunications equipment or customer premises equipment and has a user interface, such software shall conform to C205 and applicable requirements in Chapter 5.
EXCEPTION: Software that is assistive technology and that supports the accessibility services of the platform shall not be required to conform to the requirements in Chapter 5.
C205.2 WCAG Conformance
User interface components, as well as the content of platforms and applications shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
EXCEPTIONS:
Software that is assistive technology and that supports the accessibility services of the platform shall not be required to conform to C205.2.
Non-Web software shall not be required to conform to the following four Success Criteria in WCAG 2.0: 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks; 2.4.5 Multiple Ways; 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation; and 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
Non-Web software shall not be required to conform to Conformance Requirement 3 Complete Processes in WCAG 2.0.
C205.2.1 Word Substitution when Applying WCAG to Non-Web Software
For non-Web software, wherever the term “Web page” or “page” appears in WCAG 2.0 Level A and AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements, the term “software” shall be substituted for the terms “Web page” and “page.” In addition, in Success Criterion 1.4.2, the phrase “in software” shall be substituted for the phrase “on a Web page.”
C205.3 Complete Processes for Non-Web Software
Where non-Web software requires multiple steps to accomplish an activity, all software related to the activity to be accomplished shall conform to WCAG 2.0 as specified in C205.2.
C206 Support Documentation and Services
C206.1 General
Where support documentation and services are provided for telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment, manufacturers shall ensure that such documentation and services conform to Chapter 6 and are made available upon request at no additional charge.
Appendix C to Part 1194 – Functional Performance Criteria and Technical Requirements
Chapter 3: Functional Performance Criteria
301 General
301.1 Scope
The requirements of Chapter 3 shall apply to ICT where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where otherwise referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
302 Functional Performance Criteria
302.1 Without Vision
Where a visual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require user vision.
302.2 With Limited Vision
Where a visual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that enables users to make use of limited vision.
302.3 Without Perception of Color
Where a visual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one visual mode of operation that does not require user perception of color.
302.4 Without Hearing
Where an audible mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require user hearing.
302.5 With Limited Hearing
Where an audible mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that enables users to make use of limited hearing.
302.6 Without Speech
Where speech is used for input, control, or operation, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require user speech.
302.7 With Limited Manipulation
Where a manual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require fine motor control or simultaneous manual operations.
302.8 With Limited Reach and Strength
Where a manual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that is operable with limited reach and limited strength.
302.9 With Limited Language, Cognitive, and Learning Abilities
ICT shall provide features making its use by individuals with limited cognitive, language, and learning abilities simpler and easier.
Chapter 4: Hardware
401 General
401.1 Scope
The requirements of Chapter 4 shall apply to ICT that is hardware where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where otherwise referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
EXCEPTION: Hardware that is assistive technology shall not be required to conform to the requirements of this chapter.
402 Closed Functionality
402.1 General
ICT with closed functionality shall be operable without requiring the user to attach or install assistive technology other than personal headsets or other audio couplers, and shall conform to 402.
402.2 Speech-Output Enabled
ICT with a display screen shall be speech-output enabled for full and independent use by individuals with vision impairments.
EXCEPTIONS:
Variable message signs conforming to 402.5 shall not be required to be speech-output enabled.
Speech output shall not be required where ICT display screens only provide status indicators and those indicators conform to 409.
Where speech output cannot be supported due to constraints in available memory or processor capability, ICT shall be permitted to conform to 409 in lieu of 402.2.
Audible tones shall be permitted instead of speech output where the content of user input is not displayed as entered for security purposes, including, but not limited to, asterisks representing personal identification numbers.
Speech output shall not be required for: the machine location; date and time of transaction; customer account number; and the machine identifier or label.
Speech output shall not be required for advertisements and other similar information unless they convey information that can be used for the transaction being conducted.
402.2.1 Information Displayed On-Screen
Speech output shall be provided for all information displayed on-screen.
402.2.2 Transactional Outputs
Where transactional outputs are provided, the speech output shall audibly provide all information necessary to verify a transaction.
402.2.3 Speech Delivery Type and Coordination
Speech output shall be delivered through a mechanism that is readily available to all users, including, but not limited to, an industry standard connector or a telephone handset. Speech shall be recorded or digitized human, or synthesized. Speech output shall be coordinated with information displayed on the screen.
402.2.4 User Control
Speech output for any single function shall be automatically interrupted when a transaction is selected. Speech output shall be capable of being repeated and paused.
402.2.5 Braille Instructions
Where speech output is required by 402.2, braille instructions for initiating the speech mode of operation shall be provided. Braille shall be contracted and shall conform to 36 CFR part 1191, Appendix D, Section 703.3.1.
EXCEPTION: Devices for personal use shall not be required to conform to 402.2.5.
402.3 Volume
ICT that delivers sound, including speech output required by 402.2, shall provide volume control and output amplification conforming to 402.3.
EXCEPTION: ICT conforming to 412.2 shall not be required to conform to 402.3.
402.3.1 Private Listening
Where ICT provides private listening, it shall provide a mode of operation for controlling the volume. Where ICT delivers output by an audio transducer typically held up to the ear, a means for effective magnetic wireless coupling to hearing technologies shall be provided.
402.3.2 Non-private Listening
Where ICT provides non-private listening, incremental volume control shall be provided with output amplification up to a level of at least 65 dB. A function shall be provided to automatically reset the volume to the default level after every use.
402.4 Characters on Display Screens
At least one mode of characters displayed on the screen shall be in a sans serif font. Where ICT does not provide a screen enlargement feature, characters shall be 3/16 inch (4.8 mm) high minimum based on the uppercase letter “I”. Characters shall contrast with their background with either light characters on a dark background or dark characters on a light background.
402.5 Characters on Variable Message Signs
Characters on variable message signs shall conform to section 703.7 Variable Message Signs of ICC A117.1-2009 (incorporated by reference, see 702.6.1).
403 Biometrics
403.1 General
Where provided, biometrics shall not be the only means for user identification or control.
EXCEPTION: Where at least two biometric options that use different biological characteristics are provided, ICT shall be permitted to use biometrics as the only means for user identification or control.
404 Preservation of Information Provided for Accessibility
404.1 General
ICT that transmits or converts information or communication shall not remove non-proprietary information provided for accessibility or shall restore it upon delivery.
405 Privacy
405.1 General
The same degree of privacy of input and output shall be provided to all individuals. When speech output required by 402.2 is enabled, the screen shall not blank automatically.
406 Standard Connections
406.1 General
Where data connections used for input and output are provided, at least one of each type of connection shall conform to industry standard non-proprietary formats.
407 Operable Parts
407.1 General
Where provided, operable parts used in the normal operation of ICT shall conform to 407.
407.2 Contrast
Where provided, keys and controls shall contrast visually from background surfaces. Characters and symbols shall contrast visually from background surfaces with either light characters or symbols on a dark background or dark characters or symbols on a light background.
407.3 Input Controls
At least one input control conforming to 407.3 shall be provided for each function.
EXCEPTION: Devices for personal use with input controls that are audibly discernable without activation and operable by touch shall not be required to conform to 407.3.
407.3.1 Tactilely Discernible
Input controls shall be operable by touch and tactilely discernible without activation.
407.3.2 Alphabetic Keys
Where provided, individual alphabetic keys shall be arranged in a QWERTY-based keyboard layout and the “F” and “J” keys shall be tactilely distinct from the other keys.
407.3.3 Numeric Keys
Where provided, numeric keys shall be arranged in a 12-key ascending or descending keypad layout. The number five key shall be tactilely distinct from the other keys. Where the ICT provides an alphabetic overlay on numeric keys, the relationships between letters and digits shall conform to ITU-T Recommendation E.161 (incorporated by reference, see 702.7.1).
407.4 Key Repeat
Where a keyboard with key repeat is provided, the delay before the key repeat feature is activated shall be fixed at, or adjustable to, 2 seconds minimum.
407.5 Timed Response
Where a timed response is required, the user shall be alerted visually, as well as by touch or sound, and shall be given the opportunity to indicate that more time is needed.
407.6 Operation
At least one mode of operation shall be operable with one hand and shall not require tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist. The force required to activate operable parts shall be 5 pounds (22.2 N) maximum.
407.7 Tickets, Fare Cards, and Keycards
Where tickets, fare cards, or keycards are provided, they shall have an orientation that is tactilely discernible if orientation is important to further use of the ticket, fare card, or keycard.
407.8 Reach Height and Depth
At least one of each type of operable part of stationary ICT shall be at a height conforming to 407.8.2 or 407.8.3 according to its position established by the vertical reference plane specified in 407.8.1 for a side reach or a forward reach. Operable parts used with speech output required by 402.2 shall not be the only type of operable part complying with 407.8 unless that part is the only operable part of its type.
407.8.1 Vertical Reference Plane
Operable parts shall be positioned for a side reach or a forward reach determined with respect to a vertical reference plane. The vertical reference plane shall be located in conformance to 407.8.2 or 407.8.3.
407.8.1.1 Vertical Plane for Side Reach
Where a side reach is provided, the vertical reference plane shall be 48 inches (1220 mm) long minimum.
graphical representation of dimensions for vertical plane side reach
407.8.1.2 Vertical Plane for Forward Reach
Where a forward reach is provided, the vertical reference plane shall be 30 inches (760 mm) long minimum.
graphical representation of dimensions for vertical plane forward reach
407.8.2 Side Reach
Operable parts of ICT providing a side reach shall conform to 407.8.2.1 or 407.8.2.2. The vertical reference plane shall be centered on the operable part and placed at the leading edge of the maximum protrusion of the ICT within the length of the vertical reference plane. Where a side reach requires a reach over a portion of the ICT, the height of that portion of the ICT shall be 34 inches (865 mm) maximum.
407.8.2.1 Unobstructed Side Reach
Where the operable part is located 10 inches (255 mm) or less beyond the vertical reference plane, the operable part shall be 48 inches (1220 mm) high maximum and 15 inches (380 mm) high minimum above the floor.
graphical representation of dimensions for unobstructed side reach
407.8.2.2 Obstructed Side Reach
Where the operable part is located more than 10 inches (255 mm), but not more than 24 inches (610 mm), beyond the vertical reference plane, the height of the operable part shall be 46 inches (1170 mm) high maximum and 15 inches (380 mm) high minimum above the floor. The operable part shall not be located more than 24 inches (610 mm) beyond the vertical reference plane.
graphical representation of dimensions for obstructed side reach
407.8.3 Forward Reach
Operable parts of ICT providing a forward reach shall conform to 407.8.3.1 or 407.8.3.2. The vertical reference plane shall be centered, and intersect with, the operable part. Where a forward reach allows a reach over a portion of the ICT, the height of that portion of the ICT shall be 34 inches (865 mm) maximum.
407.8.3.1 Unobstructed Forward Reach
Where the operable part is located at the leading edge of the maximum protrusion within the length of the vertical reference plane of the ICT, the operable part shall be 48 inches (1220 mm) high maximum and 15 inches (380 mm) high minimum above the floor.
graphical representation of dimensions for unobstructed forward reach
407.8.3.2 Obstructed Forward Reach
Where the operable part is located beyond the leading edge of the maximum protrusion within the length of the vertical reference plane, the operable part shall conform to 407.8.3.2. The maximum allowable forward reach to an operable part shall be 25 inches (635 mm).
graphical representation of dimensions for obstructed forward reach
407.8.3.2.1 Operable Part Height for ICT with Obstructed Forward Reach
The height of the operable part shall conform to Table 407.8.3.2.1.
Table 407.8.3.2.1 Operable Part Height for ICT with Obstructed Forward Reach Reach Depth Operable Part Height
Less than 20 inches (510 mm) 48 inches (1220 mm) maximum
20 inches (510 mm) to 25 inches (635 mm) 44 inches (1120 mm) maximum
graphical representation of dimensions for operable part height for obstructed forward reach
407.8.3.2.2 Knee and Toe Space under ICT with Obstructed Forward Reach
Knee and toe space under ICT shall be 27 inches (685 mm) high minimum, 25 inches (635 mm) deep maximum, and 30 inches (760 mm) wide minimum and shall be clear of obstructions.
graphical representation of dimensions for knee and toe space for obstructed forward reach
EXCEPTIONS:
Toe space shall be permitted to provide a clear height of 9 inches (230 mm) minimum above the floor and a clear depth of 6 inches (150 mm) maximum from the vertical reference plane toward the leading edge of the ICT.
graphical representation of dimensions for knee and toe space for obstructed forward reach exception one
At a depth of 6 inches (150 mm) maximum from the vertical reference plane toward the leading edge of the ICT, space between 9 inches (230 mm) and 27 inches (685 mm) minimum above the floor shall be permitted to reduce at a rate of 1 inch (25 mm) in depth for every 6 inches (150 mm) in height.
graphical representation of dimensions for knee and toe space for obstructed forward reach exception two
Supplemental graphic combining both Exceptions 1 and 2:
graphical representation of dimensions for knee and toe space for obstructed forward reach exceptions one and two
408 Display Screens
408.1 General
Where provided, display screens shall conform to 408.
408.2 Visibility
Where stationary ICT provides one or more display screens, at least one of each type of display screen shall be visible from a point located 40 inches (1015 mm) above the floor space where the display screen is viewed.
408.3 Flashing
Where ICT emits lights in flashes, there shall be no more than three flashes in any one-second period.
EXCEPTION: Flashes that do not exceed the general flash and red flash thresholds defined in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1) are not required to conform to 408.3.
409 Status Indicators
409.1 General
Where provided, status indicators shall be discernible visually and by touch or sound.
410 Color Coding
410.1 General
Where provided, color coding shall not be used as the only means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element.
411 Audible Signals
411.1 General
Where provided, audible signals or cues shall not be used as the only means of conveying information, indicating an action, or prompting a response
412 ICT with Two-Way Voice Communication
412.1 General
ICT that provides two-way voice communication shall conform to 412.
412.2 Volume Gain
ICT that provides two-way voice communication shall conform to 412.2.1 or 412.2.2.
412.2.1 Volume Gain for Wireline Telephones
Volume gain conforming to 47 CFR 68.317 shall be provided on analog and digital wireline telephones.
412.2.2 Volume Gain for Non-Wireline ICT
A method for increasing volume shall be provided for non-wireline ICT.
412.3 Interference Reduction and Magnetic Coupling
Where ICT delivers output by a handset or other type of audio transducer that is typically held up to the ear, ICT shall reduce interference with hearing technologies and provide a means for effective magnetic wireless coupling in conformance with 412.3.1 or 412.3.2.
412.3.1 Wireless Handsets
ICT in the form of wireless handsets shall conform to ANSI/IEEE C63.19-2011 (incorporated by reference, see 702.5.1).
412.3.2 Wireline Handsets
ICT in the form of wireline handsets, including cordless handsets, shall conform to TIA-1083-B (incorporated by reference, see702.9.1).
412.4 Digital Encoding of Speech
ICT in IP-based networks shall transmit and receive speech that is digitally encoded in the manner specified by ITU-T Recommendation G.722.2 (incorporated by reference, see 702.7.2) or IETF RFC 6716 (incorporated by reference, see 702.8.1).
412.5 Real-Time Text Functionality
[Reserved].
412.6 Caller ID
Where provided, caller identification and similar telecommunications functions shall be visible and audible.
412.7 Video Communication
Where ICT provides real-time video functionality, the quality of the video shall be sufficient to support communication using sign language.
412.8 Legacy TTY Support
ICT equipment or systems with two-way voice communication that do not themselves provide TTY functionality shall conform to 412.8.
412.8.1 TTY Connectability
ICT shall include a standard non-acoustic connection point for TTYs.
412.8.2 Voice and Hearing Carry Over
ICT shall provide a microphone capable of being turned on and off to allow the user to intermix speech with TTY use.
412.8.3 Signal Compatibility
ICT shall support all commonly used cross-manufacturer non-proprietary standard TTY signal protocols where the system interoperates with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
412.8.4 Voice Mail and Other Messaging Systems
Where provided, voice mail, auto-attendant, interactive voice response, and caller identification systems shall be usable with a TTY.
413 Closed Caption Processing Technologies
413.1 General
Where ICT displays or processes video with synchronized audio, ICT shall provide closed caption processing technology that conforms to 413.1.1 or 413.1.2.
413.1.1 Decoding and Display of Closed Captions
Players and displays shall decode closed caption data and support display of captions.
413.1.2 Pass-Through of Closed Caption Data
Cabling and ancillary equipment shall pass through caption data.
414 Audio Description Processing Technologies
414.1 General
Where ICT displays or processes video with synchronized audio, ICT shall provide audio description processing technology conforming to 414.1.1 or 414.1.2.
414.1.1 Digital Television Tuners
Digital television tuners shall provide audio description processing that conforms to ATSC A/53 Digital Television Standard, Part 5 (2014) (incorporated by reference, see 702.2.1). Digital television tuners shall provide processing of audio description when encoded as a Visually Impaired (VI) associated audio service that is provided as a complete program mix containing audio description according to the ATSC A/53 standard.
414.1.2 Other ICT
ICT other than digital television tuners shall provide audio description processing.
415 User Controls for Captions and Audio Descriptions
415.1 General
Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio, ICT shall provide user controls for closed captions and audio descriptions conforming to 415.1.
EXCEPTION: Devices for personal use shall not be required to conform to 415.1 provided that captions and audio descriptions can be enabled through system-wide platform settings.
415.1.1 Caption Controls
Where ICT provides operable parts for volume control, ICT shall also provide operable parts for caption selection.
415.1.2 Audio Description Controls
Where ICT provides operable parts for program selection, ICT shall also provide operable parts for the selection of audio description.
Chapter 5: Software
501 General
501.1 Scope
The requirements of Chapter 5 shall apply to software where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where otherwise referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
EXCEPTION: Where Web applications do not have access to platform accessibility services and do not include components that have access to platform accessibility services, they shall not be required to conform to 502 or 503 provided that they conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
502 Interoperability with Assistive Technology
502.1 General
Software shall interoperate with assistive technology and shall conform to 502.
EXCEPTION: ICT conforming to 402 shall not be required to conform to 502.
502.2 Documented Accessibility Features
Software with platform features defined in platform documentation as accessibility features shall conform to 502.2.
502.2.1 User Control of Accessibility Features
Platform software shall provide user control over platform features that are defined in the platform documentation as accessibility features.
502.2.2 No Disruption of Accessibility Features
Software shall not disrupt platform features that are defined in the platform documentation as accessibility features.
502.3 Accessibility Services
Platform software and software tools that are provided by the platform developer shall provide a documented set of accessibility services that support applications running on the platform to interoperate with assistive technology and shall conform to 502.3. Applications that are also platforms shall expose the underlying platform accessibility services or implement other documented accessibility services.
502.3.1 Object Information
The object role, state(s), properties, boundary, name, and description shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.2 Modification of Object Information
States and properties that can be set by the user shall be capable of being set programmatically, including through assistive technology.
502.3.3 Row, Column, and Headers
If an object is in a data table, the occupied rows and columns, and any headers associated with those rows or columns, shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.4 Values
Any current value(s), and any set or range of allowable values associated with an object, shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.5 Modification of Values
Values that can be set by the user shall be capable of being set programmatically, including through assistive technology.
502.3.6 Label Relationships
Any relationship that a component has as a label for another component, or of being labeled by another component, shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.7 Hierarchical Relationships
Any hierarchical (parent-child) relationship that a component has as a container for, or being contained by, another component shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.8 Text
The content of text objects, text attributes, and the boundary of text rendered to the screen, shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.9 Modification of Text
Text that can be set by the user shall be capable of being set programmatically, including through assistive technology.
502.3.10 List of Actions
A list of all actions that can be executed on an object shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.11 Actions on Objects
Applications shall allow assistive technology to programmatically execute available actions on objects.
502.3.12 Focus Cursor
Applications shall expose information and mechanisms necessary to track focus, text insertion point, and selection attributes of user interface components.
502.3.13 Modification of Focus Cursor
Focus, text insertion point, and selection attributes that can be set by the user shall be capable of being set programmatically, including through the use of assistive technology.
502.3.14 Event Notification
Notification of events relevant to user interactions, including but not limited to, changes in the component’s state(s), value, name, description, or boundary, shall be available to assistive technology.
502.4 Platform Accessibility Features
Platforms and platform software shall conform to the requirements in ANSI/HFES 200.2, Human Factors Engineering of Software User Interfaces — Part 2: Accessibility (2008) (incorporated by reference, see 702.4.1) listed below:
Section 9.3.3 Enable sequential entry of multiple (chorded) keystrokes;
Section 9.3.4 Provide adjustment of delay before key acceptance;
Section 9.3.5 Provide adjustment of same-key double-strike acceptance;
Section 10.6.7 Allow users to choose visual alternative for audio output;
Section 10.6.8 Synchronize audio equivalents for visual events;
Section 10.6.9 Provide speech output services; and
Section 10.7.1 Display any captions provided.
503 Applications
503.1 General
Applications shall conform to 503.
503.2 User Preferences
Applications shall permit user preferences from platform settings for color, contrast, font type, font size, and focus cursor.
EXCEPTION: Applications that are designed to be isolated from their underlying platform software, including Web applications, shall not be required to conform to 503.2.
503.3 Alternative User Interfaces
Where an application provides an alternative user interface that functions as assistive technology, the application shall use platform and other industry standard accessibility services.
503.4 User Controls for Captions and Audio Description
Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio, ICT shall provide user controls for closed captions and audio descriptions conforming to 503.4.
503.4.1 Caption Controls
Where user controls are provided for volume adjustment, ICT shall provide user controls for the selection of captions at the same menu level as the user controls for volume or program selection.
503.4.2 Audio Description Controls
Where user controls are provided for program selection, ICT shall provide user controls for the selection of audio descriptions at the same menu level as the user controls for volume or program selection.
504 Authoring Tools
504.1 General
Where an application is an authoring tool, the application shall conform to 504 to the extent that information required for accessibility is supported by the destination format.
504.2 Content Creation or Editing
Authoring tools shall provide a mode of operation to create or edit content that conforms to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1) for all supported features and, as applicable, to file formats supported by the authoring tool. Authoring tools shall permit authors the option of overriding information required for accessibility.
EXCEPTION: Authoring tools shall not be required to conform to 504.2 when used to directly edit plain text source code.
504.2.1 Preservation of Information Provided for Accessibility in Format Conversion
Authoring tools shall, when converting content from one format to another or saving content in multiple formats, preserve the information required for accessibility to the extent that the information is supported by the destination format.
504.2.2 PDF Export
Authoring tools capable of exporting PDF files that conform to ISO 32000-1:2008 (PDF 1.7) shall also be capable of exporting PDF files that conform to ANSI/AIIM/ISO 14289-1:2016 (PDF/UA-1) (incorporated by reference, see 702.3.1).
504.3 Prompts
Authoring tools shall provide a mode of operation that prompts authors to create content that conforms to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1) for supported features and, as applicable, to file formats supported by the authoring tool.
504.4 Templates
Where templates are provided, templates allowing content creation that conforms to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1) shall be provided for a range of template uses for supported features and, as applicable, to file formats supported by the authoring tool.
Chapter 6: Support Documentation and Services
601 General
601.1 Scope
The technical requirements in Chapter 6 shall apply to ICT support documentation and services where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where otherwise referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
602 Support Documentation
602.1 General
Documentation that supports the use of ICT shall conform to 602.
602.2 Accessibility and Compatibility Features
Documentation shall list and explain how to use the accessibility and compatibility features required by Chapters 4 and 5. Documentation shall include accessibility features that are built-in and accessibility features that provide compatibility with assistive technology.
602.3 Electronic Support Documentation
Documentation in electronic format, including Web-based self-service support, shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
602.4 Alternate Formats for Non-Electronic Support Documentation
Where support documentation is only provided in non-electronic formats, alternate formats usable by individuals with disabilities shall be provided upon request.
603 Support Services
603.1 General
ICT support services including, but not limited to, help desks, call centers, training services, and automated self-service technical support, shall conform to 603.
603.2 Information on Accessibility and Compatibility Features
ICT support services shall include information on the accessibility and compatibility features required by 602.2.
603.3 Accommodation of Communication Needs
Support services shall be provided directly to the user or through a referral to a point of contact. Such ICT support services shall accommodate the communication needs of individuals with disabilities.
Chapter 7: Referenced Standards
701 General
701.1 Scope
The standards referenced in Chapter 7 shall apply to ICT where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
702 Incorporation by Reference
702.1 Approved IBR Standards
The Director of the Office of the Federal Register has approved these standards for incorporation by reference into this part in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR part 51. Copies of the referenced standards may be inspected at the U.S. Access Board, 1331 F Street, NW, Suite 1000, Washington, DC 20004, (202) 272-0080, and may also be obtained from the sources listed below. They are also available for inspection at the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA). For information on the availability of this material at NARA, call 202–741–6030 or go to National Archives Code of Federal Regulations Incorporation by Reference.
702.2 Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the Advanced Television Systems Committee, 1776 K Street NW, Suite 200, Washington, DC 20006–2304.
702.2.1 ATSC A/53 Part 5:2014
Digital Television Standard, Part 5—AC-3 Audio System Characteristics, August 28, 2014.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 414.1.1.
702.3 Association for Information and Image Management (AIIM)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from AIIM, 1100 Wayne Ave., Ste. 1100, Silver Spring, Maryland 20910.
702.3.1 ANSI/AIIM/ISO 14289-1-2016
Document Management Applications — Electronic Document File Format Enhancement for Accessibility — Part 1: Use of ISO 32000-1 (PDF/UA-1), ANSI-approved February 8, 2016.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 504.2.2.
702.4 Human Factors and Ergonomics Society (HFES)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society, P.O. Box 1369, Santa Monica, CA 90406–1369.
702.4.1 ANSI/HFES 200.2
Human Factors Engineering of Software User Interfaces — Part 2: Accessibility, copyright 2008.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 502.4.
702.5 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 10662 Los Vaqueros Circle, P.O. Box 3014, Los Alamitos, CA 90720–1264.
702.5.1 ANSI/IEEE C63.19-2011
American National Standard for Methods of Measurement of Compatibility between Wireless Communications Devices and Hearing Aids, May 27, 2011.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 412.3.1.
702.6 International Code Council (ICC)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from ICC Publications, 4051 W. Flossmoor Road, Country Club Hills, IL 60478–5795.
702.6.1 ICC A117.1-2009
Accessible and Usable Buildings and Facilities, approved October 20, 2010.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 402.5.
702.7 International Telecommunications Union Telecommunications Standardization Sector (ITU-T)
Copies of the referenced standards may be obtained from the International Telecommunication Union, Telecommunications Standardization Sector, Place des Nations CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland.
702.7.1 ITU-T Recommendation E.161
Series E. Overall Network Operation, Telephone Service, Service Operation and Human Factors—International operation - Numbering plan of the international telephone service, Arrangement of digits, letters and symbols on telephones and other devices that can be used for gaining access to a telephone network, February 2001.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 407.3.3.
702.7.2 ITU-T Recommendation G.722.2
Series G. Transmission Systems and Media, Digital Systems and Networks – Digital terminal equipment – Coding of analogue signals by methods other than PCM, Wideband coding of speech at around 16 kbit/s using Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (AMR-WB), July 2003.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 412.4.
702.8 Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the Internet Engineering Task Force.
702.8.1 IETF RFC 6716
Definition of the Opus Codec, September 2012, J.M. Valin, Mozilla Corporation, K. Vos, Skype Technologies S.A., T. Terriberry, Mozilla Corporation.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 412.4.
702.9 Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
Copies of the referenced standard, published by the Telecommunications Industry Association, may be obtained from IHS Markit, 15 Inverness Way East, Englewood, CO 80112.
702.9.1 TIA-1083-B
Telecommunications—Communications Products—Handset Magnetic Measurement Procedures and Performance Requirements, October 2015.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 412.3.2.
702.10 Worldwide Web Consortium (W3C)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the W3C Web Accessibility Initiative, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 32 Vassar Street, Room 32-G515, Cambridge, MA 02139.
702.10.1 WCAG 2.0
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0, W3C Recommendation, December 11, 2008.
IBR approved for: Appendix A (Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act: Application and Scoping Requirements), Sections E205.4, E205.4 Exception, E205.4.1, E207.2, E207.2 Exception 2, E207.2 Exception 3, E207.2.1, E207.3; Appendix B (Section 255 of the Communications Act: Application and Scoping Requirements), C203.1, C203.1 Exception, C203.1.1, C205.2, C205.2 Exception 2, C205.2 Exception 3, C205.2.1, C205.3; and Appendix C (Functional Performance Criteria and Technical Requirements), 408.3 Exception, 501.1 Exception, 504.2, 504.3, 504.4, and 602.3.
Appendix D to Part 1194: Electronic and Information Technology Accessibility Standards as Originally Published on December 21, 2000
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR 5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
Subpart A — General
§ D1194.1 Purpose.
The purpose of this part is to implement section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended (29 U.S.C. 794d). Section 508 requires that when Federal agencies develop, procure, maintain, or use electronic and information technology, Federal employees with disabilities have access to and use of information and data that is comparable to the access and use by Federal employees who are not individuals with disabilities, unless an undue burden would be imposed on the agency. Section 508 also requires that individuals with disabilities, who are members of the public seeking information or services from a Federal agency, have access to and use of information and data that is comparable to that provided to the public who are not individuals with disabilities, unless an undue burden would be imposed on the agency.
§ D1194.2 Application.
(a) Products covered by this part shall comply with all applicable provisions of this part. When developing, procuring, maintaining, or using electronic and information technology, each agency shall ensure that the products comply with the applicable provisions of this part, unless an undue burden would be imposed on the agency.
(1) When compliance with the provisions of this part imposes an undue burden, agencies shall provide individuals with disabilities with the information and data involved by an alternative means of access that allows the individual to use the information and data.
(2) When procuring a product, if an agency determines that compliance with any provision of this part imposes an undue burden, the documentation by the agency supporting the procurement shall explain why, and to what extent, compliance with each such provision creates an undue burden.
(b) When procuring a product, each agency shall procure products which comply with the provisions in this part when such products are available in the commercial marketplace or when such products are developed in response to a Government solicitation. Agencies cannot claim a product as a whole is not commercially available because no product in the marketplace meets all the standards. If products are commercially available that meet some but not all of the standards, the agency must procure the product that best meets the standards.
(c) Except as provided by §1194.3(b), this part applies to electronic and information technology developed, procured, maintained, or used by agencies directly or used by a contractor under a contract with an agency which requires the use of such product, or requires the use, to a significant extent, of such product in the performance of a service or the furnishing of a product.
§ 1194.3 General exceptions.
(a) This part does not apply to any electronic and information technology operated by agencies, the function, operation, or use of which involves intelligence activities, cryptologic activities related to national security, command and control of military forces, equipment that is an integral part of a weapon or weapons system, or systems which are critical to the direct fulfillment of military or intelligence missions. Systems which are critical to the direct fulfillment of military or intelligence missions do not include a system that is to be used for routine administrative and business applications (including payroll, finance, logistics, and personnel management applications).
(b) This part does not apply to electronic and information technology that is acquired by a contractor incidental to a contract.
(c) Except as required to comply with the provisions in this part, this part does not require the installation of specific accessibility-related software or the attachment of an assistive technology device at a workstation of a Federal employee who is not an individual with a disability.
(d) When agencies provide access to the public to information or data through electronic and information technology, agencies are not required to make products owned by the agency available for access and use by individuals with disabilities at a location other than that where the electronic and information technology is provided to the public, or to purchase products for access and use by individuals with disabilities at a location other than that where the electronic and information technology is provided to the public.
(e) This part shall not be construed to require a fundamental alteration in the nature of a product or its components.
(f) Products located in spaces frequented only by service personnel for maintenance, repair, or occasional monitoring of equipment are not required to comply with this part.
§ D1194.4 Definitions.
The following definitions apply to this part:
Agency
Any Federal department or agency, including the United States Postal Service.
Alternate formats
Alternate formats usable by people with disabilities may include, but are not limited to, Braille, ASCII text, large print, recorded audio, and electronic formats that comply with this part.
Alternate methods
Different means of providing information, including product documentation, to people with disabilities. Alternate methods may include, but are not limited to, voice, fax, relay service, TTY, Internet posting, captioning, text-to-speech synthesis, and audio description.
Assistive technology
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excelling in Digital Marketing: Ten Strategies for Success
In today's fast-paced digital world, mastering the art of digital marketing is essential for career growth and professional success. Whether you're starting your journey or aiming to enhance your skills, here are ten proven strategies to help you become an exceptional digital marketer:

1. Formal Education: Establishing a Strong Foundation
Begin by enrolling in reputable digital marketing courses or degree programs offered by universities or online platforms. These programs cover a wide range of topics, including SEO, social media marketing, content marketing, analytics, and more. By investing in formal education, you'll gain a comprehensive understanding of digital marketing fundamentals to build upon.
2. Online Resources: Leveraging Knowledge from Experts
Tap into online resources such as blogs, webinars, tutorials, and e-books provided by industry leaders like Moz, HubSpot, Neil Patel, and Social Media Examiner. These platforms offer valuable insights and tips to keep you informed about the latest trends, strategies, and tools in digital marketing.
3. Hands-On Experience: Learning Through Practice
Gain practical experience by working on real-world projects through internships, freelance opportunities, or personal ventures. Applying theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios allows you to hone your skills, gain insights, and build a portfolio that showcases your capabilities.
4. Networking: Connecting with Peers and Mentors
Attend industry events, conferences, and meetups to expand your professional network and connect with peers and mentors. Networking provides valuable opportunities for learning, collaboration, and career advancement in the digital marketing field.
5. Lifelong Learning: Embracing Continuous Growth
Digital marketing is an ever-evolving field, so commit to continuous learning through online courses, workshops, certifications, and industry publications. Staying updated on emerging trends and best practices ensures that you remain competitive and adaptable in the dynamic digital landscape.
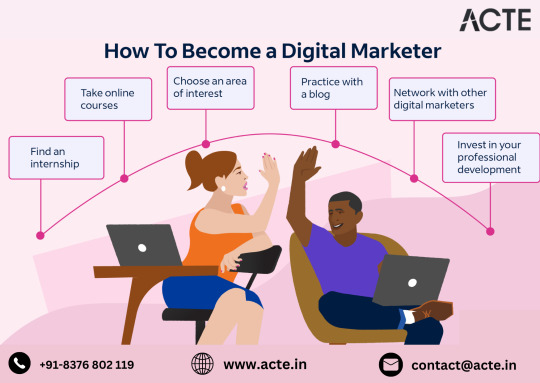
6. Analytical Skills: Making Informed Decisions with Data
Develop strong analytical skills to interpret data effectively and make data-driven decisions. Familiarize yourself with analytics tools like Google Analytics, SEMrush, and Hootsuite to measure and optimize the performance of digital marketing campaigns.
7. Creativity and Innovation: Thinking Outside the Box
Harness your creativity to craft compelling content, design engaging campaigns, and explore innovative strategies. Embrace experimentation and push the boundaries to captivate your audience and differentiate your brand in a crowded digital space.
8. Specialization: Focusing Your Expertise
Identify your strengths and interests within digital marketing and specialize in a specific niche such as SEO, PPC advertising, email marketing, or social media management. Deepening your expertise in a particular area allows you to stand out and command higher value in the marketplace.
9. Seek Mentorship: Learning from Experienced Professionals
Find mentors or industry experts who can provide guidance, advice, and support as you progress in your digital marketing career. Learning from seasoned professionals accelerates your growth and equips you with valuable insights and perspectives.
10. Stay Passionate: Fueling Your Drive for Success
Maintain your passion and enthusiasm for digital marketing, and embrace challenges as opportunities for growth. Stay curious, resilient, and committed to your professional development to achieve long-term success in the dynamic digital landscape.
In conclusion, becoming the best digital marketer requires a combination of education, experience, networking, continuous learning, analytical skills, creativity, specialization, mentorship, and passion. By incorporating these strategies into your career journey, you can elevate your skills, expand your opportunities, and achieve excellence in the exciting and ever-evolving field of digital marketing.
#tech#training#digital marketing#digital marketing company#digital marketing course#email marketing#online marketing#search engine optimization#seo
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
This panel event was originally recorded on September 18, 2020, as part of GreenThumb's international virtual event in partnership with Capital Growth in London and Toronto Urban Growers.
Hear from community gardeners and urban farmers from London, Toronto, and New York City around how gardens and farms are contributing toward these cities’ resilience, food security, and COVID-19 response. Organised by Capital Growth in London, NYC Parks GreenThumb in New York, and Toronto Urban Growers, this webinar shares lessons from across the pond on how community gardens and urban farms are responding to the COVID-19 crisis, building solidarity among neighbours, and preparing the road ahead.
Intros by organizations:
o Sarah Williams, Capital Growth, London → introduce Bill
o Bill LoSasso, NYC Parks GreenThumb → introduce Rhonda
o Rhonda Teitel-Payne, Toronto Urban Growers → introduce Melana
Welcome and intro from moderator - Melana Roberts, chairperson of the board of Food Secure Canada
Panelists:
• NYC: Karen Washington, from the Garden of Happiness, speaking about Bronx Community Farm Hubs
• NYC: Mark Leger, gardener at Phoenix Community Garden speaking about Phoenix’s food access and COVID response activities
• London: Kiloran O’Leary from Global Generation speaking about The Story Garden’s involvement in Community Harvest and other COVID responses
• London: Alice Holden, Head Grower at Growing Communities Dagenham Farm - an organic farm based in outer London growing produce for sale locally and through a box scheme, while supporting various community initiatives
• Toronto: Jessey Njau, www.zawadi.farm - backyard farmer building community in Thistletown neighbourhood
• Toronto: Isaac Crosby, Lead Hand in Urban Agriculture and Indigenous Gardens at Evergreen Brick Works
#NYC Parks GreenThumb#solarpunk#webinar#garden#gardening#urban farming#urban farm#farm#farming#Capital Growth#London#england#Toronto Urban Growers#Toronto#canada#new york#new york city#USA#covid 19#food security#community#Youtube
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pre-Launch Strategies for Your Festive WooCommerce Store
The festive season is approaching, and if you're planning to launch a brand new WooCommerce store, now is the perfect time to prepare for a successful start. Building anticipation and creating a buzz around your store before the official launch can help you hit the ground running. Let's dive into some pre-launch strategies that will set the stage for a smooth festive eCommerce workflow.
1. Craft a Memorable Brand Identity: Your brand and business should align seamlessly. Choose a color scheme that complements your brand, and focus on creating a unique and memorable experience for your customers. Tools like Elementor can simplify the process of customizing your product pages, allowing you to design them exactly as you envision.
2. Verify Your Store's Functionality: Before launching, thoroughly check your store's functionality. Ensure that everything, from product listings to payment processing, is working smoothly. A flawless shopping experience is crucial.
3. Build Anticipation with Announcements: Make some noise about your brand! Utilize all available platforms to spread the word about your products and brand values. Create 'COMING SOON' pages on social media, complete with countdown timers. Use your blog to provide sneak peeks of your product line and generate excitement.
4. Create Lead-Generating Landing Pages: Landing pages are an excellent way to establish your brand's presence. Craft unique landing pages with customer-friendly and SEO-friendly content. Don't forget to analyze your competitors' strategies for inspiration.
5. Craft Compelling Product Descriptions: Enhance your product pages with product add-ons. Add fields like text boxes, checkboxes, and dropdowns, and include variations with sample images. This level of detail can make a significant impact on your product listings.
6. Optimize Speed and Responsiveness: Consult WooCommerce experts to evaluate your store's speed, responsiveness, and overall performance. Ensure that your website is optimized for quick loading and displays beautifully on various devices.
7. Quality Assurance Testing: Thoroughly test all website features, functionalities, and design layouts. Identify and address any bugs or technical issues to ensure a seamless shopping experience.
8. Beta Version Testing: Before the official launch, release a beta version of your e-commerce website. This phase helps evaluate the success of earlier testing and gather user feedback in real-world scenarios.
9. Content Marketing: Provide relevant content related to your products or services before your launch. Address the problems your products solve and the solutions you offer through your brand. Use blog posts, tutorials, webinars, eBooks, and other content forms to engage your audience.
10. Analytics Tools: Equip your WooCommerce store with essential analytics tools like Lighthouse, Search Console, SEMRush, and Google Analytics. These tools will help you track and improve your website's performance and conversion rate.
By implementing these pre-launch strategies, you'll set the foundation for a successful festive season for your WooCommerce store. Building excitement and anticipation among your audience can lead to a memorable launch and a strong start in the competitive world of e-commerce.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlocking LinkedIn: Creative Tactics for Lead Generation

LinkedIn is more than just a digital resume; it’s a bustling marketplace brimming with opportunities for those daring enough to think outside the box. While the basics are essential, a sprinkle of creativity can sometimes differentiate you from the crowd. Dive into these ingenious tactics to boost your lead generation on the platform:
Cold Messaging with a Twist: The cold approach isn’t new, but the secret lies in the delivery. Instead of launching into a sales pitch, why not start with value? Share a relevant article, a compliment about their recent work, or even a free tool. Your prospects will appreciate the non-pushy approach.
Profile Funneling: Your LinkedIn profile shouldn’t just be about past jobs; it should guide visitors toward a desired action. This could be visiting your website, subscribing to a newsletter, or dropping you a message. Craft your profile strategically to funnel visitors seamlessly.
Engage with Comments on Popular Posts: Visibility is the game. You can get your profile in front of a vast audience by commenting on popular industry posts. But remember, your comments should be insightful and add value to the conversation.
Run Thought-Provoking Polls: LinkedIn’s polling feature isn’t just for fun questions. Use it to generate insights, understand market needs, or spark a debate. Engaging in polls can set the stage for deeper conversations with participants.
Harness Advanced Search: This feature is a gold mine. Find prospects based on specific criteria such as job titles, locations, etc. Creating a targeted list can make your outreach more personalized and effective.
Dive into Video with Cover Story: With LinkedIn’s “Cover Story”, make a lasting first impression. Create a personalized video pitch that gives visitors a snapshot of who you are and how you can help.
Host LinkedIn Live Sessions: If you can access LinkedIn Live, you’re sitting on a treasure. Hosting live sessions, be it Q&As, webinars, or discussions, can attract a large, engaged audience.
Engage with Your New Followers: A simple “thank you” can go a long way. Reach out to new followers with a warm message. This can open the door for more profound interactions down the line.
Showcase Recommendations and Endorsements: Social proof is powerful. Encourage satisfied clients or colleagues to endorse your skills and pen down recommendations. This not only builds credibility but also showcases your expertise.
Launch a LinkedIn Newsletter: Regular updates, insights, and valuable content sent straight to your network can solidify your position as an industry thought leader.
Reconnect with Alumni: Old classmates or colleagues could be potential leads or offer referrals. Use LinkedIn’s Alumni feature to rekindle those connections.
Humanize with Employee Testimonials: Let your team share their stories. Employee testimonials humanize your brand and portray a positive company culture.
Collaborative Ventures: Partner with non-competing businesses on LinkedIn. Whether it’s sharing each other’s content, co-hosting webinars, or running promotions, collaboration can amplify your reach.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Begin Your Web Design Journey: A Step-by-Step Guide in Simple Terms

Understanding the Basics:
Learn about HTML, which is like a web page’s skeleton.
Understand CSS, which is like makeup for web pages.
Know how to make websites look good on different screens.
2. Choose your tools:
Start with simple text editors like Notepad (for Windows) or TextEdit (for Mac).
Later, try fancier editors like Visual Studio Code.
For making pictures, try Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator.
3. Learn HTML and CSS:
Use websites like W3Schools or Codecademy.
If you want to learn more about web design with certification and placement, ACTE Institute offers comprehensive machine learning training courses that can give you the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in this field. Consider the infinite possibilities for data analysis, automation, and decision-making that machine learning may create.
YouTube: There are many video tutorials covering HTML and CSS for beginners.
They teach you how to make web pages and make them look nice.
You can also learn from courses on Coursera or edX.
4. Practice your skills.
Besides learning, make simple web pages to get better.
Try harder projects as you get more confident.
Make your own website to practice lots.
5. Responsive Web Design:
Make sure your websites work well on phones and computers.
Learn about media queries (they help your design fit different screens).
6. Master CSS Layouts:
Get really good at arranging web stuff using CSS (like making boxes and arranging them nicely).
7. Web Design Frameworks:
Think about using ready-made kits like Bootstrap.
They have pre-made pieces to help you design faster.
8. UI/UX Design:
Learn to make websites easy to use and nice to look at.
Think about how people will use your site.
9. Web Hosting and Domain:
To show your website to people, you need a place to put it (hosting) and a name for it (domain).
Lots of companies can help with this, like Bluehost or HostGator.
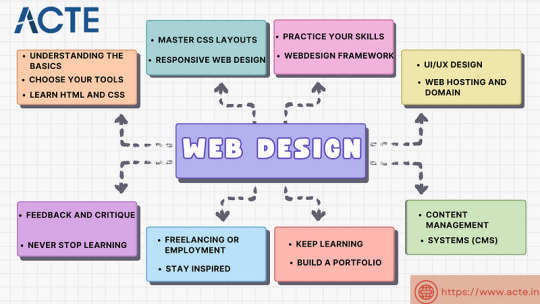
10. Content Management Systems (CMS):
Consider using tools like WordPress to manage your website easily.
11. Keep Learning:
Web design keeps changing, so keep learning new stuff.
Read blogs, watch webinars, and take more advanced classes.
12. Build a portfolio.
Make a collection of your best work to show others.
People who might hire you want to see what you can do.
13. Freelancing or employment:
Decide if you want to work alone or with a company.
Both ways have good things and not-so-good things, so pick what you like.
14. Networking:
Join groups of web designers to meet others like you.
Learning from others can help you become better.
15. Feedback and criticism:
Don’t be shy to ask for advice on your work.
When people give you tips, it helps you improve.
16. Launch your projects:
When you’re good enough, work on real websites.
Offer to make websites for friends or local businesses.
17. Stay Inspired:
Be creative and get ideas from different places.
Nature, art, and other designers can help you think of cool stuff.
18. Never Stop Learning:
Web design always changes, so keep learning new things.
Stay curious and open to learning more tricks and tools.
The secret to success in web design is to start with the fundamentals and gradually advance your abilities. Keep in mind that on this trip, patience and practice are the keys to success. As your skills advance, you’ll have the imagination needed to realise your ideas for websites. So put your hands in your pockets, launch your preferred coding editor, and start your web design experience!
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Now available on demand: Writing Bisexual and Pansexual Characters Master Class!
Bisexual author Cecilia Tan walks writers through the process of researching and representing characters who are not attracted exclusively to people of a single gender. Termed pansexual by some, bisexual by others (the “B” in LGBTQ), these sexual identities are among the most stigmatized and misunderstood, and are often represented by cliches and inaccurate stereotypes.
This $60 Master Class includes:
1 hour 15 minute lecture covering topics such as the pitfalls and negative stigmas commonly applied to bisexual and pansexual people, their relationship to gender, bisexual invisibility, and more
A list of resources
A writing exercise
A transcript
And in honor of Bi Visibility Day we’re offering a 20% discount on this new Master Class! Use code bipanmc in the Discount Code box on Gumroad to get this special offer.
Code expires September 30, 2023!
Learn More or Buy This Webinar
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
UK Home Secretary sounds alarm over deepfakes ahead of elections
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/uk-home-secretary-sounds-alarm-over-deepfakes-ahead-of-elections/
UK Home Secretary sounds alarm over deepfakes ahead of elections
.pp-multiple-authors-boxes-wrapper display:none; img width:100%;
Criminals and hostile state actors could hijack Britain’s democratic process by deploying AI-generated “deepfakes” to mislead voters, UK Home Secretary James Cleverly cautioned in remarks ahead of meetings with major tech companies.
Speaking to The Times, Cleverly emphasised the rapid advancement of AI technology and its potential to undermine elections not just in the UK but globally. He warned that malign actors working on behalf of nations like Russia and Iran could generate thousands of highly realistic deepfake images and videos to disrupt the democratic process.
“Increasingly today the battle of ideas and policies takes place in the ever-changing and expanding digital sphere,” Cleverly told the newspaper. “The era of deepfake and AI-generated content to mislead and disrupt is already in play.”
The Home Secretary plans to urge collective action from Silicon Valley giants like Google, Meta, Apple, and YouTube when he meets with them this week. His aim is to implement “rules, transparency, and safeguards” to protect democracy from deepfake disinformation.
Cleverly’s warnings come after a series of deepfake audios imitating Labour leader Keir Starmer and London Mayor Sadiq Khan circulated online last year. Fake BBC News videos purporting to examine PM Rishi Sunak’s finances have also surfaced.
The tech meetings follow a recent pact signed by major AI companies like Adobe, Amazon, Google, and Microsoft during the Munich Security Conference to take “reasonable precautions” against disruptions caused by deepfake content during elections worldwide.
As concerns over the proliferation of deepfakes continue to grow, the world must confront the challenges they pose in shaping public discourse and potentially influencing electoral outcomes.
(Image Credit: Lauren Hurley / No 10 Downing Street under OGL 3 license)
See also: Stability AI previews Stable Diffusion 3 text-to-image model
Want to learn more about AI and big data from industry leaders? Check out AI & Big Data Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. The comprehensive event is co-located with other leading events including BlockX, Digital Transformation Week, and Cyber Security & Cloud Expo.
Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
Tags: ai, artificial intelligence, deepfakes, democracy, disinformation, elections, ethics, government, home secretary, james cleverly, misinformation, Society, uk, uk election, usa election, vote, voting
#2024#adobe#ai#ai & big data expo#ai news#ai-generated content#Amazon#amp#apple#applications#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#Big Data#Britain#Cloud#coffee#Collective#Companies#comprehensive#conference#content#cyber#cyber security#data#deepfake#deepfakes#Democracy#democratic#diffusion#Digital Transformation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Free Affiliate Link Promotion(step by step guide)- Only Few Knows.
Introduction:

Today's blog post will discuss a totally free and efficient way to advertise your affiliate links and perhaps increase sales. By advertising other people's items and earning rewards, affiliate marketing provides a fantastic opportunity to generate passive money. You may quickly learn how to market your affiliate links to a large audience by following the step-by-step instructions provided below. So let's get going!
Step 1: Select an Affiliate Product
You must first choose an affiliate product to market. Digistore24, which offers a large selection of products in numerous categories, is one well-known portal for finding digital products to market. To find a product, go to the Digistore24 marketplace and browse the categories, an increased commission rate. In order to attract clients, look for products that answer big problems.
Learn More: Step by Step guide to Affiliate Marketing
Step 2: Get Your Affiliate Link
After deciding on a product to advertise, you must get your special affiliate link. This link keeps track of the sales generated by your promotions and makes sure you get the proper commission. Find your affiliate link for the selected product after becoming an affiliate on Digistore24. For later usage, copy and store the link.
Step 3: Create a PDF from the sales page.
It's advantageous to turn the product's sales page into a PDF document so that your promotions are easier to access and more interesting. You can add your affiliate link and customise the content in this step. Use a service like webtopdfconvert.com to create a PDF version of the sales page. Download the PDF file after that.
Step 4: Edit the PDF in with your affiliate link.
Once you get the PDF file, utilise a free online PDF editor like sejda.com to alter it and add your affiliate link. A call-to-action phrase, such as "Click on the video to watch and learn more," should be included at the top of the PDF. In order for readers to access the product's sales page directly, include a clickable link box with your affiliate link.
Step 5: Upload the PDF to Google Drive
Then, use Google Drive, a free cloud storage service, to submit the updated PDF file. Create a new account if you don't already have one. Create a shareable link for the PDF file once it has been uploaded. Make sure that everyone who has the link can view the file.
Step 6: Promote your affiliate link
Use the website Worldprofit.com to direct traffic to your affiliate link. Go to the "Free Classified Ads" area after creating a free account on the platform. Create an eye-catching advertisement for the product you are promoting by using the "Post Ad" tool. Create a catchy title and description that highlight the free PDF content. As the destination URL, enter the PDF's Google Drive link. Choose pertinent categories to increase exposure, such as those that pertain to health, weight loss, or certain product-related niches.
Learn more: Affiliate Marketing Course- Freedom Asselator
Conclusion:
By taking the procedures outlined above, you can successfully and freely promote your affiliate links to a large audience. Recall to select high-quality products, customise the sales page as a PDF with your affiliate link, and make use of online traffic-generating tools like Worldprofit.com. Affiliate marketing can assist you in creating a full-time passive income business and achieving financial independence if you are persistent and committed. Start putting these tactics into practise right away to see the potential for success in the affiliate marketing industry.
If you really Want To Transform your life and want to make money from Affiliate Marketing
Their is a Big opportunity for You. We are Offering a Free Webinar On Affiliate Marketing.
Click here to Register ( Limited Seats )
#affiliate#affiliate marketing tips#affiliate marketing#passive income#make money online#digital marketing
6 notes
·
View notes