#tradingsystems
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Impact of Algorithmic Trading on Modern Financial Markets: A Realistic and In-Depth Exploration

Algorithmic trading, often referred to as algo trading, has rapidly transformed modern financial markets, allowing for speed, efficiency, and precision beyond human capabilities. These automated systems execute trades based on pre-programmed instructions, including variables such as price, timing, and volume. While algorithmic trading has revolutionized markets, it has also introduced new complexities, risks, and ethical questions that continue to shape its development. This essay will explore the mechanics of algorithmic trading, its impact on market efficiency and volatility, and the broader implications for both retail and institutional investors.
1. What Is Algorithmic Trading?
At its core, algorithmic trading is the use of computer algorithms to automatically make trading decisions and execute orders. Unlike traditional trading, where humans manually enter trades, algorithms can monitor market conditions and execute trades in microseconds—far faster than any human could react.
A. Key Characteristics of Algorithmic Trading
Predefined Rules: Algorithms follow a set of predefined rules to determine when and how trades should be executed. These rules might involve price levels, volume thresholds, or technical indicators like moving averages and RSI (Relative Strength Index).
High-Speed Execution: One of the primary advantages of algorithmic trading is speed. With access to low-latency infrastructure, algorithms can react to market data faster than human traders, exploiting even the smallest price discrepancies for profit.
Minimizing Emotions: Algorithms remove human emotions—such as fear or greed—from the trading process, ensuring that decisions are made based purely on data and strategy.
Popular algorithms include trend-following strategies, statistical arbitrage, and market-making algorithms. While these systems are often proprietary and highly complex, the underlying principle is simple: use technology to exploit inefficiencies in the market faster than human traders can.
B. Types of Algorithmic Trading Strategies
High-Frequency Trading (HFT): HFT algorithms make trades at an extremely high speed, often within milliseconds. By taking advantage of tiny market inefficiencies, these algorithms can generate significant profits through large volumes of trades.
Arbitrage: Arbitrage algorithms exploit price discrepancies between different markets or financial instruments. For example, an algorithm might simultaneously buy a stock in one market where it is undervalued and sell it in another market where it is overvalued.
Execution-Based Algorithms: These algorithms aim to execute large orders without significantly impacting the market price. For example, an algorithm might break a large trade into smaller chunks and execute them over time to minimize slippage and market impact.
2. The Benefits of Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading has provided substantial benefits to both individual traders and the financial markets at large, including enhanced market efficiency, reduced trading costs, and improved liquidity.
A. Improved Market Efficiency
Algorithmic trading helps to improve market efficiency by rapidly correcting mispricings and ensuring that prices reflect all available information. This leads to tighter bid-ask spreads, which benefits all market participants by reducing transaction costs.
Example: When a stock price in the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) diverges from its equivalent in the London Stock Exchange (LSE), an arbitrage algorithm can quickly execute trades to align the prices. This increases the overall efficiency of the global market.
B. Enhanced Liquidity
By continuously placing buy and sell orders, algorithms provide liquidity to the market, allowing traders to enter and exit positions more easily. Market-making algorithms, in particular, help maintain liquidity in less actively traded assets, such as small-cap stocks or thinly traded bonds.
Example: In thin markets, market-making algorithms provide liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices. This can help reduce volatility and ensure smoother price discovery for other traders.
C. Reduced Transaction Costs
Since algorithms can execute trades with speed and precision, they often minimize slippage, which is the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual price. Additionally, because algorithms can process massive amounts of data simultaneously, they reduce the need for expensive human intervention, ultimately lowering trading costs.
Example: Large institutional investors, such as pension funds, use execution algorithms to buy or sell large volumes of shares without significantly moving the market. This reduces their overall transaction costs by avoiding price slippage.
3. Challenges and Risks Associated with Algorithmic Trading
Despite its many advantages, algorithmic trading introduces a set of challenges and risks that have garnered increasing scrutiny, particularly regarding market volatility and ethical considerations.
A. Flash Crashes
One of the most concerning risks of algorithmic trading is the possibility of flash crashes—sudden and severe drops in market prices triggered by automated trading systems. Flash crashes can occur when algorithms, responding to the same market signals, simultaneously flood the market with sell orders, overwhelming liquidity and causing prices to plummet in seconds.
Example: On May 6, 2010, U.S. stock markets experienced a flash crash, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropping nearly 1,000 points in minutes, only to recover shortly afterward. Investigations revealed that a combination of high-frequency trading and automated sell algorithms contributed to the crash.
B. Liquidity Challenges During Market Stress
While algorithms provide liquidity in normal market conditions, they may withdraw liquidity during times of extreme market stress. This can exacerbate price swings, as large sell-offs are met with fewer buyers, intensifying market volatility.
Example: During the COVID-19 market crash in March 2020, liquidity across many asset classes dried up as market-making algorithms either withdrew from the market or aggressively reduced risk exposure. This led to increased volatility and sharp declines in asset prices.
C. Unintended Consequences of Complex Algorithms
As algorithms become increasingly complex, there is a growing risk of unintended consequences due to coding errors or unforeseen market conditions. These so-called "black swan" events are difficult to predict and can have devastating consequences for markets and investors.
Example: In August 2012, Knight Capital, a U.S.-based market maker, lost over $440 million in 30 minutes due to a software glitch in its algorithmic trading system. The firm had to liquidate shortly afterward, illustrating the devastating impact of unintended algorithmic behavior.
4. Algorithmic Trading and Retail Investors
While algorithmic trading was initially the domain of institutional investors, retail traders are increasingly gaining access to algorithmic trading tools through platforms like MetaTrader, NinjaTrader, and TradeStation. This democratization of algo trading has both positive and negative implications for individual traders.
A. Advantages for Retail Traders
Retail traders can now build and deploy their own algorithmic strategies without requiring access to institutional-grade infrastructure. Many brokers offer Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that allow retail traders to automate their strategies, giving them the speed and efficiency of algorithmic trading without needing to manually enter orders.
Example: Platforms like QuantConnect allow retail traders to backtest and deploy algorithmic strategies in real time. This enables small-scale traders to participate in the same fast-paced environment as hedge funds, increasing their potential for profits.
B. Challenges for Retail Traders
Despite these advancements, retail traders face several challenges when adopting algorithmic trading, including the need for technical expertise and the risk of over-optimization. Many retail traders fall into the trap of curve fitting—optimizing their algorithms based on historical data to such a degree that the system only performs well under specific market conditions, but fails when conditions change.
Example: A retail trader might create a trend-following algorithm that works perfectly in a bull market but fails to account for bear markets or periods of high volatility. Without proper risk management, such an algorithm could result in significant losses when market conditions shift.
5. The Future of Algorithmic Trading: A New Frontier
Looking ahead, algorithmic trading will continue to evolve as new technologies emerge, particularly in the areas of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These innovations will allow for more sophisticated algorithms that can learn from market data in real time, adapt to changing conditions, and even anticipate future trends.
A. AI-Driven Algorithmic Trading
AI-driven algorithms will take algo trading to new levels by incorporating deep learning and reinforcement learning techniques. Unlike traditional algorithms, which follow fixed rules, AI algorithms can adapt and learn from the data they process, improving their performance over time. These algorithms could even detect and exploit patterns that are invisible to human traders.
Example: AI hedge funds like Numerai use machine learning models to make market predictions based on complex datasets. These funds have demonstrated superior performance compared to traditional hedge funds, highlighting the potential for AI-driven algorithms to outperform human-driven strategies.
B. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
As algorithmic trading continues to grow, regulators are paying closer attention to its impact on market integrity. Flash crashes, market manipulation, and the potential for AI algorithms to amplify biases in market data are all concerns that regulators will need to address in the coming years.
In response to these concerns, organizations such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) have introduced regulations aimed at curbing the risks of high-frequency trading and ensuring that algorithmic trading systems operate transparently and fairly.
Conclusion
Algorithmic trading represents a profound shift in how financial markets operate, offering unparalleled speed, efficiency, and precision. While it has undoubtedly improved market efficiency and lowered transaction costs, it has also introduced new risks, including flash crashes, liquidity challenges, and unintended consequences. Retail investors now have access to the same tools as institutional traders, but they must remain cautious, as the complexities of algo trading require technical knowledge and careful risk management.
As we look to the future, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into algorithmic trading will further revolutionize financial markets. AI-driven systems have the potential to discover patterns and make decisions that go beyond human capabilities, but they also present ethical and regulatory challenges that must be carefully addressed. Ensuring that these systems remain transparent, fair, and compliant with market regulations will be critical to maintaining market stability.
In summary, algorithmic trading has reshaped the landscape of global financial markets, offering significant advantages in terms of efficiency and liquidity. However, with these benefits come considerable risks, including market volatility and the potential for technical failures. As the technology evolves, both institutional and retail investors will need to stay informed about the opportunities and challenges presented by algorithmic systems, ensuring that they strike a balance between innovation and responsible trading practices.
#AlgorithmicTrading#AlgoTrading#QuantitativeTrading#AutomatedTrading#HighFrequencyTrading#MathematicalFinance#FinancialMarkets#TradingStrategies#MachineLearning#ArtificialIntelligence#DataAnalysis#MarketEfficiency#Liquidity#RiskManagement#TradingSystems#FinancialTechnology
0 notes
Text

The Evolution of Forex Trading: From Manual Trading to Automated Systems
#Forex#ForexTrading#ForexEvolution#AutomatedTrading#AlgorithmicTrading#AIinForex#ForexAutomation#MachineLearningForex#TradingSystems#ForexHistory#CurrencyMarkets#ForexStrategies#TradingAlgorithms#ForexBacktesting#TechInTrading#TradingAutomation#FinancialTechnology#FinTech#TradingRevolution#ManualToAutomatedTrading#AITrading#AlgoTrading#TradingInnovation#DataDrivenTrading#AutomatedForexSystems#AlgorithmicFinance#TradingTechnology#QuantitativeTrading#DigitalTrading#TradingTools
1 note
·
View note
Text
#TradingSystems#Forexexpertadvisors#indicators#MT4indicators#Forexscripts#Bestforexrobot#BestEA#Bestexpertadvisor#MT4#MetaTrader
1 note
·
View note
Text
High-Frequency Trading Server Market Overview: Understanding Market Dynamics and Growth Factors
The global high-frequency trading server market size is expected to reach USD 918.0 million by 2030, registering a CAGR of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030, according to a study conducted by Grand View Research, Inc. In the trading industry, servers play a pivotal role in reducing tick-to-trade delays; this is driving the product demand. Furthermore, with improvements in server technology over the years, high-frequency trading (HFT) servers, in particular, have witnessed several advancements in terms of processor technology, which is creating opportunities for industry growth. These advancements are fueled by the need to track stock markets where every nanosecond counts and are expected to become an indispensable element of the finance sector over the coming years.

High-frequency Trading Server Market Report Highlights
The x-86 based processor segment accounted for the highest revenue share in 2022 and is estimated to retain the dominant position throughout the forecast period registering a steady CAGR from 2023 to 2030
The large-scale adoption of operating systems based on x86-based architecture for high computing applications is expected to drive the segment growth over the forecast period
4U form factor is anticipated to register a Significant CAGR over the forecast period due to rising usage on account of its capability to handle high-performance computing application
Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing region capturing a CAGR of 8.6% over the forecast period. Initiatives undertaken by the Chinese government to promote automated trading in financial markets contributed to market growth, and this trend is expected to continue over the next few years.
For More Details or Sample Copy please visit link @: High-Frequency Trading Server Market Report
Increased adoption of algorithmic trading in global financial markets has encouraged companies in the financial sector to opt for high-speed transactions. Technological advancements, such as integrating AI and social media feeds with electronic trading, are expected to drive the demand for high-speed trading transactions. Thus, the demand for low-latency trading servers has increased tremendously among the derivatives, quantitative, and proprietary trading firms. Asia Pacific has become one of the new revenue pockets for market growth.
Favorable government regulations for the implementation of automated trading and new investment law in China have emerged as potential revenue streams for the vendors. Furthermore, the surge in adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning technology by small-sized hedge fund firms, is anticipated to drive the overall product demand over the forecast period. A competitive edge is now determined by nanoseconds and microseconds. Speed is important to market participants, such as large investment banks, hedge funds, and other financial companies, because it impacts profitability, and hence the deployment of HFT servers is of paramount importance.
#HighFrequencyTrading#TradingServers#FinancialTechnology#TechnologyTrends#AlgorithmicTrading#FinancialMarkets#ServerInfrastructure#TradingSystems#TradingTechnology#FinancialServices#InvestmentStrategies#ElectronicTrading#TradingPlatforms#TradingInfrastructure
0 notes
Text
Flux Nebula Review
Become A Success Forex Trader and Boost Your Income

If you're looking for a comprehensive review of the Flux Nebula trading system, then look no further! This system can help you become a successful Forex trader and boost your income. With step-by-step guidance and proven strategies, Flux Nebula is perfect for traders of all levels. Say goodbye to inconsistent profits and hello to financial success with Flux Nebula!
Introduction: The Genesis of Flux Nebula™
At the core of Flux Nebula™ lies a revolutionary AI algorithm meticulously crafted by Farhad Campbell, a visionary in the field of trading technology. Campbell's deep understanding of market dynamics and his relentless pursuit of excellence culminated in the creation of Flux Nebula™, a tool that promises to decipher complex market signals and provide traders with actionable insights derived from advanced data analysis.
Overview
Product : Flux Nebula™ Trading System
Creator : Marketro LLC
Check it out : Click Here
Discount Price : $186.96
Recommendation : Highly Recommend!
Refund: 30 Days Money-Back Guarantee
Features for the Flux Nebula™ Trading System Review:
AI-Powered Analysis:
Harnessing advanced artificial intelligence algorithms, Flux Nebula™ conducts in-depth analysis of market trends and price movements to generate accurate trading signals.
Comprehensive Asset Coverage:
Flux Nebula™ supports a wide range of trading assets including stocks, Forex pairs, cryptocurrencies, commodities, and indices, allowing traders to diversify their portfolios.
Real-Time Alerts:
Traders receive real-time alerts directly on their preferred devices, including mobile phones and desktops, ensuring they never miss out on potential trading opportunities.
Intuitive Dashboard:
Flux Nebula™ features an intuitive dashboard interface that provides traders with clear insights into market trends, signal strengths, and recommended actions, simplifying the decision-making process.
Customizable Settings:
Traders have the flexibility to customize settings according to their trading preferences and risk tolerance levels, allowing for a personalized trading experience.
Compatibility with Leading Platforms:
Flux Nebula™ seamlessly integrates with popular trading platforms such as Metatrader 4, Metatrader 5, TradingView, and NinjaTrader, providing traders with flexibility and convenience.
No-Repaint Signals:
Flux Nebula™ signals are reliable and non-repainting, ensuring traders can trust the signals they receive for making informed trading decisions.
Multiple Trading Styles Supported: Whether traders prefer scalping, day trading, swing trading, or long-term investing, Flux Nebula™ accommodates various trading styles, catering to diverse trading preferences.
Educational Resources:
Flux Nebula™ provides educational resources and tutorials to help traders understand how to effectively use the system and improve their trading skills.
More Info: Click Here
#Flux Nebula Review#FluxNebula#forex#forextrading#tradingsystems#make money online#make money tips#make money fast
0 notes
Text
CRAFTING AN EFFECTIVE STRATEGY PORTFOLIO

Discover the significance of crafting an effective strategy portfolio in both long-term investing and short-term trading. Diversification goes beyond asset classes, emphasizing the importance of avoiding overlap and reduced performance when running multiple similar strategies in one market. The holy grail in trading lies in the accumulation and trading of diverse, well-structured strategies across various markets and instruments.
0 notes
Text

Investment without an algomaster strategy is like a car without petrol. Algomaster strategies use algorithms and data analysis to make informed investment decisions, helping navigate the dynamic stock market. Just as petrol powers a car, a well-designed algorithmic strategy can fuel investment success, enhancing decision-making and optimizing returns over time.
0 notes
Text
In-Depth Exploration of Algorithmic Trading: Strategies, Technologies, and Impact on Markets

Algorithmic trading, often referred to as algo trading, has revolutionized the financial markets by allowing traders to execute orders at lightning speed and with mathematical precision. It involves using complex mathematical models, automated systems, and advanced technologies to make decisions based on pre-set conditions or algorithms. This essay delves into the strategies employed in algorithmic trading, the technology driving it, and its overall impact on financial markets, providing an in-depth look at how algo trading has shaped modern finance.
1. Core Strategies in Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading is built on various strategies that rely on historical data analysis, statistical methods, and predictive models. Some of the most prominent strategies used in this field include High-Frequency Trading (HFT), Statistical Arbitrage, Market Making, and Trend-Following Algorithms. These strategies cater to different market conditions and investor needs, from short-term profit opportunities to long-term market-making services.
A. High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
High-frequency trading (HFT) is one of the most well-known and controversial forms of algorithmic trading. It focuses on executing a large number of orders in fractions of a second. HFT firms use sophisticated algorithms to analyze vast amounts of market data and make split-second decisions. These strategies rely on speed—traders look to exploit very small price inefficiencies that exist for only milliseconds.
How It Works:
HFT algorithms rely on technologies such as low-latency networks and co-location services (where traders place their servers close to the exchange’s infrastructure) to reduce the time it takes to execute trades. These firms also leverage tick data, which refers to real-time price data that changes every time a trade is made.
Real-World Example:
A well-known HFT firm is Virtu Financial, which became famous for having only one day of trading losses over a five-year period between 2009 and 2014. Virtu’s algorithms analyzed market data to exploit tiny price inefficiencies, allowing it to profit on both rising and falling markets. Its success underscores the power of speed in HFT.
Impact and Controversy:
While HFT has contributed to increased liquidity and tighter bid-ask spreads, it has also attracted criticism. Critics argue that HFT can lead to increased volatility, and market “flash crashes” have been attributed to high-frequency algorithms. One such event occurred in May 2010, when the U.S. stock market experienced a sudden and dramatic crash, wiping out nearly $1 trillion in market value within minutes. Investigations revealed that HFT firms exacerbated the decline by pulling out of the market during the sell-off, creating a liquidity vacuum.
B. Statistical Arbitrage (StatArb)
Statistical arbitrage, often abbreviated as StatArb, is a type of algorithmic trading strategy that attempts to exploit the pricing inefficiencies between correlated securities. StatArb strategies involve identifying relationships between different securities and executing trades when these relationships deviate from historical norms.
How It Works:
StatArb algorithms use historical data to calculate the statistical likelihood of one asset’s price moving in relation to another. For example, the algorithm might identify a strong historical correlation between two stocks, and if one deviates from its expected relationship with the other, the algorithm will place trades anticipating a return to equilibrium.
Real-World Example:
During the 2007–2008 financial crisis, many hedge funds employing StatArb strategies saw significant losses due to the breakdown of historical correlations in highly stressed market conditions. However, firms that quickly adapted their algorithms to account for the new volatility, like D.E. Shaw and Renaissance Technologies, were able to capitalize on the increased market inefficiencies by identifying new relationships between assets.
Evidence:
StatArb remains one of the most popular algorithmic strategies among hedge funds, with quants (quantitative analysts) developing increasingly complex models to exploit ever smaller inefficiencies. The effectiveness of StatArb has been documented in academic research, such as Avellaneda and Lee (2010), who demonstrated that StatArb models outperform traditional arbitrage strategies during periods of high volatility.
C. Market Making
Market making is another algorithmic strategy where traders provide liquidity to the market by continuously quoting buy (bid) and sell (ask) prices for a security. Market makers profit from the bid-ask spread—the difference between the price at which they buy and sell an asset.
How It Works:
Market-making algorithms are designed to ensure that a market maker has an offer to both buy and sell an asset simultaneously, making money from the difference between these prices. They must carefully balance their inventory (the amount of stock they hold) to avoid significant exposure to market risk. These algorithms analyze the market’s depth, size of orders, and historical patterns to maintain liquidity efficiently.
Real-World Example:
The NYSE Designated Market Makers (DMM) use market-making algorithms to maintain orderly trading on the exchange. Firms like Citadel Securities and KCG Holdings have been instrumental in providing liquidity and ensuring that even during times of high volatility, buyers and sellers can still find counterparties.
Impact:
Market making is essential for maintaining liquidity in financial markets, especially in less liquid securities like small-cap stocks or thinly traded ETFs. Without market makers, these markets could become illiquid, leading to wider spreads and greater volatility. Algorithmic market makers ensure that liquidity is always present, reducing the costs for individual traders and investors.
D. Trend-Following Algorithms
Trend-following algorithms are designed to identify market trends and execute trades that follow the direction of these trends. Unlike HFT strategies that rely on ultra-short timeframes, trend-following algorithms operate on longer time horizons, typically days, weeks, or even months.
How It Works:
Trend-following algorithms use various technical indicators, such as moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and Relative Strength Index (RSI), to identify the onset of a new trend. Once a trend is detected, the algorithm will enter a trade in the direction of the trend, aiming to ride the wave until signs of a reversal appear.
Real-World Example:
A prime example of trend-following success comes from Winton Capital, a hedge fund known for using algorithmic trend-following strategies. Founded by David Harding in 1997, Winton has consistently outperformed many competitors by focusing on long-term trends across various asset classes, including equities, bonds, and commodities.
Evidence:
Trend-following strategies have proven effective in markets where clear trends develop over time, such as the commodities market. A study by Hurst et al. (2012) showed that trend-following strategies outperform during periods of economic uncertainty when large trends tend to develop as markets digest new information slowly. However, they can underperform in sideways or choppy markets where no clear trend exists.
2. Technological Advancements Driving Algorithmic Trading
The success of algorithmic trading is driven by the rapid advancement of technology. From machine learning (ML) to artificial intelligence (AI), these technologies are transforming the way algorithms are developed, tested, and deployed. Moreover, advancements in hardware infrastructure and cloud computing allow firms to process massive amounts of data at unprecedented speeds.
A. Machine Learning and AI in Algorithmic Trading
Machine learning and AI have become game-changers in algorithmic trading. These technologies allow algorithms to improve over time by learning from historical data and making predictions based on evolving market conditions. Traders no longer need to manually adjust their strategies; instead, AI-driven models adapt autonomously to new data.
How It Works:
In machine learning-based trading, algorithms are trained using historical price data, volume, and other market inputs. These models then identify patterns that have historically been profitable and apply them in real-time trading. Reinforcement learning, a branch of ML, is particularly suited to trading as it allows the algorithm to learn from both successful and unsuccessful trades, refining its strategy over time.
Evidence:
Hedge funds like Man AHL and Two Sigma are pioneers in using AI-driven strategies. These firms apply machine learning to vast datasets, ranging from price feeds to social media sentiment, to identify new trading opportunities. Two Sigma, for example, uses AI to scan millions of data points, including weather patterns, satellite imagery, and corporate earnings, to uncover hidden market signals.
B. Low-Latency Trading and Infrastructure
Low-latency trading refers to the practice of executing trades as quickly as possible to gain an advantage over competitors. Technological improvements in server infrastructure, fiber-optic cables, and co-location services have drastically reduced the time it takes for orders to reach exchanges.
Real-World Example:
One notable low-latency trade is the construction of the Spread Networks fiber-optic cable between Chicago and New York. This cable, completed in 2010, shortened the time it took for trading signals to travel between the two financial hubs from 17 milliseconds to 13 milliseconds. This 4-millisecond advantage was worth millions to HFT firms competing to execute trades faster than their rivals.
3. Impact of Algorithmic Trading on Markets
Algorithmic trading has transformed global financial markets, influencing everything from liquidity and market depth to volatility and price discovery. While algo trading has introduced efficiencies, it has also brought new challenges and risks.
A. Increased Liquidity
Algorithmic trading has significantly increased liquidity in many markets, particularly in equities and foreign exchange. By providing a continuous flow of buy and sell orders, algo traders reduce the bid-ask spread, making it cheaper for all market participants to trade.
B. Increased Liquidity
Algorithmic trading, especially through market-making strategies, ensures that there is a ready buyer and seller for various assets, even during volatile times. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, algorithmic traders played a crucial role in maintaining liquidity across multiple asset classes, allowing markets to function more smoothly despite the global uncertainty. Studies from financial institutions, such as Citadel Securities, showed that algorithmic liquidity providers absorbed market shocks better than traditional human market makers during this period.
Impact on Retail Traders:
For retail traders, the increase in liquidity means lower transaction costs and faster execution of trades. However, it also raises concerns about the fairness of market access, as large institutional players equipped with advanced algorithms often gain a competitive edge through technologies like low-latency trading and co-location.
C. Market Volatility and "Flash Crashes"
While algorithmic trading contributes to liquidity, it can also increase market volatility, especially when multiple algorithms interact in unexpected ways. One of the most prominent examples of this is the Flash Crash of May 6, 2010, when the U.S. stock market experienced a sharp decline within minutes, followed by a rapid recovery. This event wiped out approximately $1 trillion in market value within half an hour before bouncing back.
What Happened:
Investigations revealed that a large sell order, executed by a mutual fund using an algorithmic strategy, triggered a chain reaction. High-frequency trading algorithms began aggressively selling, creating a feedback loop that sent prices plummeting. The event demonstrated how interconnected and reactive algorithms can lead to systemic risks, especially when they amplify market movements rather than stabilize them.
Efforts to Mitigate Volatility:
In response to the Flash Crash and similar events, regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have introduced measures like circuit breakers—temporary halts in trading when extreme volatility is detected. Moreover, algorithmic traders have become more cautious, implementing safeguards like throttle mechanisms that prevent excessive trading during volatile periods.
D. Impact on Price Discovery
Price discovery—the process of determining the market value of an asset based on supply and demand—has been significantly influenced by algorithmic trading. In many cases, algo trading improves price discovery by rapidly incorporating new information into asset prices. For example, news events, economic data releases, or corporate earnings reports are processed by algorithms in milliseconds, allowing markets to adjust almost instantaneously.
Challenges in Price Discovery:
However, some critics argue that the speed at which algorithms process information can distort price discovery, especially during periods of low liquidity. In certain cases, algorithms may react to false signals or minor market inefficiencies, creating temporary price distortions. These price anomalies, although short-lived, can impact retail and institutional traders alike, especially those who are slower to react.
Real-World Impact:
During the Brexit referendum in 2016, algorithmic traders played a critical role in driving market reactions. As the results of the vote became clear, algorithms began selling British assets, leading to a sharp drop in the value of the British pound. The rapid adjustment of prices reflected the efficiency of algorithmic trading in reacting to geopolitical events, but it also highlighted the potential for exacerbating sharp market movements.
4. Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
As algorithmic trading continues to evolve, regulators and market participants are faced with new ethical and legal challenges. The speed, complexity, and opacity of algorithmic trading make it difficult for traditional regulatory frameworks to keep pace with these developments.
A. Market Manipulation and Ethical Concerns
One of the primary concerns surrounding algorithmic trading is the potential for market manipulation. Algorithms can be designed to engage in practices such as spoofing—where traders place orders they do not intend to execute to create false demand or supply in the market. In 2015, the U.S. Department of Justice charged a British trader, Navinder Sarao, with using spoofing algorithms to contribute to the Flash Crash of 2010.
Spoofing Explained:
Spoofing involves placing large buy or sell orders with no intention of executing them. Once other market participants react by adjusting their orders in response to the perceived demand or supply, the spoofer cancels the initial orders and profits from the market’s reaction. While regulatory bodies such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the SEC have cracked down on spoofing, the complexity of algorithms makes it challenging to detect and prevent such practices.
B. Regulatory Efforts
To address the risks associated with algorithmic trading, regulators around the world have implemented new rules aimed at increasing transparency, reducing systemic risks, and preventing market manipulation. For example, in Europe, the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) introduced stricter reporting requirements for algorithmic traders, including the need to register their algorithms and adhere to pre-trade risk controls.
In the U.S., the SEC and CFTC have taken steps to monitor high-frequency trading firms more closely. Additionally, exchanges have introduced mechanisms such as kill switches, which automatically shut down trading algorithms if they exhibit erratic behavior.
C. Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Trading
As machine learning and artificial intelligence become more integrated into algorithmic trading, new ethical concerns have emerged. Unlike traditional algorithms that follow explicit instructions, AI-driven models often operate in "black box" systems, meaning that even their creators may not fully understand how the algorithms arrive at certain decisions. This lack of transparency raises questions about accountability, particularly if an AI-driven algorithm were to cause significant market disruptions.
Moreover, AI algorithms can potentially reinforce biases present in historical data, leading to unintended consequences in trading strategies. Ensuring fairness and preventing unintended discrimination in financial markets is a growing challenge for regulators and AI developers alike.
5. The Future of Algorithmic Trading
The future of algorithmic trading is poised to be shaped by several key developments, including advances in quantum computing, blockchain technology, and the democratization of algorithmic tools for retail investors.
A. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize algorithmic trading by vastly increasing computational power. Unlike classical computers, which process information in binary (0s and 1s), quantum computers can process multiple states simultaneously, allowing them to solve complex problems at speeds unimaginable with today’s technology.
Potential Impact on Trading:
In algorithmic trading, quantum computing could enable the development of more sophisticated models that consider an exponentially larger number of variables and scenarios. This could lead to more accurate predictive algorithms, faster arbitrage opportunities, and even the ability to model entire financial ecosystems. While quantum computing is still in its early stages, firms like IBM and Google are investing heavily in the technology, and its eventual impact on financial markets could be transformative.
B. Blockchain and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain technology, particularly its application in Decentralized Finance (DeFi), presents new opportunities and challenges for algorithmic trading. DeFi platforms, which allow for peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, are growing in popularity. Algorithms designed to trade on these platforms will need to adapt to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and navigate the unique challenges of smart contracts and automated market makers (AMMs).
Example:
In the world of cryptocurrency, algorithmic traders are already active participants in automated liquidity pools on platforms like Uniswap and SushiSwap. These decentralized exchanges rely on algorithms to match buyers and sellers, and traders use bots to exploit price inefficiencies and arbitrage opportunities across different DeFi platforms.
C. Democratization of Algorithmic Trading
As technology continues to advance, algorithmic trading tools are becoming more accessible to retail investors. Platforms like QuantConnect, AlgoTrader, and MetaTrader offer retail traders the ability to develop and backtest their own algorithms using professional-grade tools. This democratization of algo trading has the potential to level the playing field, allowing individual investors to compete with institutional players in ways that were previously impossible.
Challenges:
However, with increased access comes increased risk. Retail traders may lack the technical expertise to develop robust algorithms, and without proper risk management, they could expose themselves to significant losses. Moreover, the proliferation of algorithmic trading among retail investors could introduce new forms of market volatility, as large numbers of amateur traders execute similar strategies simultaneously.
Conclusion
Algorithmic trading has undeniably transformed global financial markets, bringing increased liquidity, faster execution, and more efficient price discovery. However, it has also introduced new risks, including market volatility, ethical concerns, and the potential for market manipulation. As technology continues to evolve, particularly with the advent of quantum computing and AI, algorithmic trading will likely become even more sophisticated and widespread. Regulatory bodies must continue to adapt to these changes to ensure that markets remain fair, transparent, and stable.
The future of algorithmic trading is filled with both promise and challenges. With the right balance of innovation and regulation, algo trading can continue to drive the financial industry forward while mitigating the risks inherent in such a fast-paced and highly automated environment.
#AlgorithmicTrading#AlgoTrading#QuantitativeTrading#AutomatedTrading#HighFrequencyTrading#MathematicalFinance#FinancialMarkets#TradingStrategies#MachineLearning#ArtificialIntelligence#DataAnalysis#MarketEfficiency#Liquidity#RiskManagement#TradingSystems#FinancialTechnology#Fintech#MarketMicrostructure#TradingAlgorithms#Backtesting#Optimization#StatisticalArbitrage#EventDrivenTrading
0 notes
Text
Unlock Winning Secrets with Lottery Defeater Software: Boost Your Odds
How does Lottery Defeater Software increase your odds of winning the lottery, and what sets it apart from other similar products?
Can you share real-life success stories or testimonials from people who have used this software to win the lottery?
What strategies and techniques does the software employ to analyze and predict winning numbers?
Are there any specific lottery games or regions where the software is particularly effective?
How user-friendly is the software, and do you offer any training or support for new users?
What is the pricing structure for Lottery Defeater Software, and are there any special promotions or discounts available?
Can you explain the technology behind the software and how it continuously updates its algorithms for improved results?
Are there any guarantees or refunds if users don't achieve the desired results?
How can potential customers access and start using Lottery Defeater Software?
Is there a community or forum where users can share their experiences and strategies for winning the lottery with this software?
you can get more detailed information and product link by clicking on 👈🏿
#bettingstrategy#sportsbetting#bettingsystems#sportsbettingstrategies#bettingsystem#sportsbettingtips#dalembertbettingsystem#footballbetting#bettingtips#arbitragebetting#sportsbettingexplained#roulettebettingsystem#progressivebettingsystem#footballbettingstrategy#tradingsystem#howtowinatsportsbetting#makemoneyonsportsbetting#dobettingsystemswork#betting#footballbettingsystems
0 notes
Text
#ForexXcode#MT4Indicators#ExpertAdvisors#ForexIndicators#ForexRobots#ForexTrading#TradingSystem#ForexTradingSignals#ForexRobotsPRO
0 notes
Text

Putting all your eggs in one basket? Not a wise choice. Experts do the opposite. They hedge and split their idea into multiple trades. Don't know how to hedge? Multi-trader can do it for you.
Book your free demo to know more. https://tradersir.com/true-fibonacci-arbitrage-multi-trading-system/
#truefibonacci#tradingsystem#multitrader#forextool#technicaltool#mt4#mt5#AIbasedtool#tradingtool#tradersir
0 notes
Text
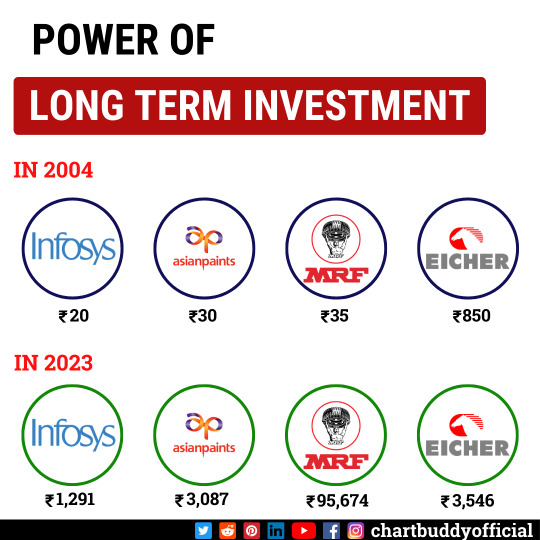
🌐 Join a Thriving Community: Connect with fellow traders, share insights, and learn from each other's experiences. ChartBuddy's vibrant trading community provides a platform to elevate your skills and expand your trading network. 🤝
Follow + Like + Share + Comment
Follow us for daily tips and setups Turn on post notifications
Follow more update @chartbuddyofficial
#tradingforex#tradingstrategy#tradingcards#tradingsignals#tradingtips#tradingstocks#tradinglifestyle#tradingsetup#tradingview#forextrading#cryptotrading#daytrading#optionstrading#tradingsystem#tradingcardgame tradinglife#tradingonline#tradingplan#tradingeducation
1 note
·
View note
Text
#MegaFXProfit#MT4Indicators#ExpertAdvisors#ForexIndicators#ForexRobots#ForexTrading#TradingSystem#ForexTradingSignals#ForexRobotsPRO
0 notes
Text
youtube
Identify trend direction quickly and get precise entry and exit points. Non-repainting and identifies best trade opportunities. Make the most out of it now. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DqIsCEmx-yM
#trendpower#nonrepainting#accurateindicator#mt4indicatormt5#mt5indicator#takeprofit#stoploss#trendreversal#tradingsystem#tradersir#Youtube
0 notes