#the permian extinction
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Nature, 252 mya: LYSTROSAURUS SWEEEEEEEEEEEEEEP
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

#lystrosaurus#dinosaurs#paleontology#dinosaur#prehistoric animals#prehistoric#permian#triassic#sad thoughts#sadgirl#😔#worst day of my life#i wish i was dead#like a lystrosaurus#extinction is a b*
215 notes
·
View notes
Text
IT'S TIME FOR PERMIAN WEEKEND BABEY!!!
Do you like volcanoes but wish they were bigger?
Would you like to see the world choked with smoke?

Do you in all your cosmic power feel like things need a hard reset?
Then the Permian period might be for you!
Lasting from 298.9-251.9 Ma, if you compressed all of Earth's history into a year, December 7th-11th would mark the Permian period.
While it did see some innovations in life with the continued diversification of therapsids and sauropsids as they spread around Pangaea, the period is mainly known for mass extinctions, of which there were at least three.
The first was fairly minor in comparison to the others, where the end of the early Permian saw the extinction of several groups of early land vertebrates such as Dimetrodon as other tetrapods gained prominence.
And then, some time in the mid Permian, the sea began to erupt.
The Emeishan Traps are a formation in China where basalt covers an area extending approximately 250,000 square kilometers, which is roughly the size of the state of Michigan. It could have originally been twice that size, covering an area larger than the state of California with volcanic deposits an average of 700 meters thick. Originating on the sea floor, it released massive amounts of sulfur and carbon dioxides, wreaking havoc on the world's climate. A recent paper published in the journal Geology also makes the case that the eruptions also managed to heat up oil and gas deposits in the area, cooking them underground and leading to the release of even more carbon dioxide and methane gas.
Estimates on the impact of this eruption vary, but around a third of marine life went extinct, and the majority of survivors on land were burrowing animals.
This was already about as significant as the extinction that would kill the non-avian dinosaurs in the late Triassic Cretaceous in terms of severity, but it would soon be eclipsed by the single worst mass extinction in Earth's history: the end Permian, or "The Great Dying".
In what is now modern day Siberia, another massive series of eruptions took place, forming the Siberian Traps. Over the course of two million years, around a million cubic miles of basalt were laid down over an area of 7 million square kilometers. This was 14 times the size of the Emeishan Traps, and covered an area roughly the size of Australia. Most of it erupted in the first million years. The massive amounts of carbon and sulfur dioxide released led to dramatic ocean acidification and climate change.
It is speculated that the traps also lit coal fields on fire, adding to their emissions. This, combined with a possible contribution from a meteorite impact on the other side of the world led to mass die offs.
81% of Marine life, and 70% of terrestrial species went extinct.
On land, it is estimated to have taken nearly 30 million years for life to recover.
As heavy as that is though, it did recover.
When the dust settled, there was still life in the oceans, and plants still grew on the land, and animals came out from their burrows, blinking in the light of a new day. And they lived.
New species would come. Life would be made new. The sun continued to shine, and rain continued to fall, and in the end the Earth had made it through.
Life found a way to make it through a level of destruction beyond anything we have ever seen or could imagine as a species. And, with a little bit of hope, help, and luck, so can we.
Edit: ( Mistakenly wrote "Triassic" rather than Cretaceous)
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some of my favorite permian period creatures:
- GORGONOPSIDS
- Coelurosauravus
- Eryops
- Dimetrodon
- Lystrosaurus
- Scutosaurus
Also Heliocoprion gets a shoutout here because of how terrifying that creature looked.
What are your favorite ancient Permian creatures?
#permian period#permian period animals#ancient#paleontology#paleoblr#extinct animals#gorgonopsid#Coelurosauravus#Eryops#dimetrodon#lystrosaurus#Scutosaurus#Heliocoprion
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
The first "big event" I can think of that makes me think "that really sucked. It's bad that that happened" is the Permian-Triassic Extinction Event, wiping out most of Earth's life 252 million years ago. The first "big event" I can think of that makes me think "that was cool. It's a good thing that that happened" is the Reforms of Solon, establishing a more-or-less democratic Athens 2617 years ago.
Feels a little asymmetrical.
49 notes
·
View notes
Note
Would the end-permian mass extinction, also known as The Great Dying, pay child support?

Image from this article
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

I still think of him
(cwilbur)
#(from the speech im writing on the permian extinction)#cwilbur would like the permian extinction#regrettably the word symphony is his still in my mind#cwilbur#dsmp posting#wss dni#^dont just not interact. question your position in life and then dni
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

These youtube challenges are getting out of hand
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ya know, I get that mass extinctions happen in an evolutionary blink of an eye, but they didn’t happen in a literal blink of an eye. I want more documentaries that take place during these extinctions. Show me what life was like during the Great Dying, don’t just tell me. Show me the survivors of Chicxulub and how they did or didn’t survive through Impact Winter.
#paleontology#evolution#extinction#great dying#end Permian extinction#chicxulub#end Cretaceous extinction#dinosaur#documentary#rewatching#life on our planet#peregrine op
42 notes
·
View notes
Text

The great dying: Permo-Triassic extinction | A grande morte: Extinção Permo-Triássica
🇬🇧
The Permian-Triassic Extinction is the most devastating mass extinction event in Earth's history, occurring approximately 252 million years ago, at the end of the Permian period and the beginning of the Triassic period. This mass extinction resulted in the loss of up to 96% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial species.
The exact causes of the Permian-Triassic Extinction are still debated among scientists, but several theories have been proposed. One of them is intense volcanic activity, such as the massive eruption of the Siberian Traps, a large volcanic province in Russia. This activity released huge amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, causing drastic climate change and ocean acidification.
These catastrophic events caused widespread mass extinctions, affecting both marine and terrestrial organisms. The recovery of biodiversity after the Permian-Triassic Extinction took millions of years and profoundly influenced the subsequent evolution of life on Earth.
The relationship between the Permian-Triassic Extinction and current climate events can be observed through similarities in causative factors and consequences for life on Earth. Similarly, contemporary climate events are largely influenced by human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, which releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This anthropogenic activity has led to global warming, changes in precipitation patterns, rising sea levels, and ocean acidification, among other impacts. These changes are putting immense pressure on ecosystems and biodiversity, leading to species extinctions and ecosystem degradation. Both the Permian-Triassic Extinction and current climate events highlight the profound impact that changes in climate can have on life on Earth. Understanding the parallels between these events can help inform efforts to mitigate the current climate crisis and protect the planet's biodiversity and ecosystems.
🇧🇷
A Extinção Permiano-Triássica é o evento de extinção em massa mais devastador da história da Terra, ocorrido há cerca de 252 milhões de anos, no final do período Permiano e início do período Triássico. Esta extinção em massa resultou na perda de até 96% das espécies marinhas e 70% das espécies terrestres.
As causas exatas da Extinção Permiano-Triássica ainda são objeto de debate entre os cientistas, mas várias teorias foram propostas. Uma delas é a atividade vulcânica intensa, como a erupção em massa dos Trapps Siberianos, uma grande província magmática na Rússia. Essa atividade liberou enormes quantidades de gases de efeito estufa na atmosfera, causando mudanças climáticas drásticas e acidificação dos oceanos.
Esses eventos catastróficos causaram extinções em massa generalizadas, afetando tanto organismos marinhos quanto terrestres. A recuperação da biodiversidade após a Extinção Permiano-Triássica levou milhões de anos e influenciou profundamente a evolução subsequente da vida na Terra.
A relação entre a Extinção Permiano-Triássica e os eventos climáticos atuais pode ser observada através de semelhanças nos fatores causadores e nas consequências para a vida na Terra. Da mesma forma, os eventos climáticos contemporâneos são amplamente influenciados por atividades humanas, particularmente a queima de combustíveis fósseis, que libera gases de efeito estufa na atmosfera. Essa atividade antropogênica tem causado o aquecimento global, mudanças nos padrões de precipitação, aumento do nível do mar e acidificação dos oceanos, entre outros impactos. Essas mudanças estão exercendo uma pressão imensa sobre os ecossistemas e a biodiversidade, levando a extinções de espécies e degradação dos ecossistemas. Tanto a Extinção Permiano-Triássica quanto os eventos climáticos atuais destacam o profundo impacto que as mudanças climáticas podem ter na vida na Terra. Compreender os paralelos entre esses eventos pode ajudar a informar esforços para mitigar a atual crise climática e proteger a biodiversidade e os ecossistemas do planeta.
#science#paleontology#geology#universe#earth#paleobotany#biology#digital painting#space#artwork#climate#climate crisis#climate change#paleontologia brasileira#paleozóico#paleobotânica#paleomedia#paleoblr#paleoarte#paleozoic#paleontologia#paleoart#paleostream#permian#mass extinction#extinction
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

Thoughts?
#permian extinction#paleontology#i made this because i got an excuse to talk about it in class and i got so excited#i am not excited for the actual concept of the great dying. to be clear#mad rambling
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
this planet needs approximately 3000% more volcanism i need to blow this place the shit up
#ONE MILLION PER CENT VOLCANISM!!!!!!!!!!!! BLOW IT UP NOW#PERMIAN EXTINCTION NOW IN SPACE!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! FUCK#Con stop yapping#KIRBY RAMBLES
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
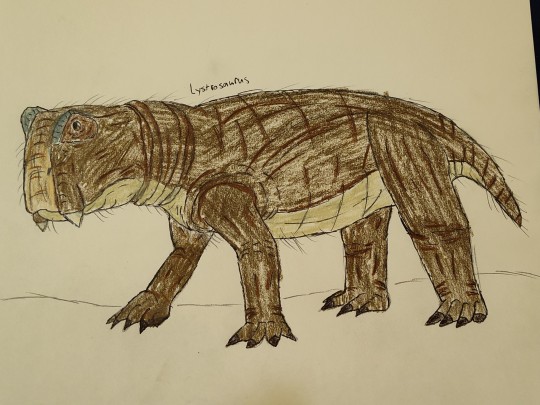
Lystrosaurus was a genus of synapsid that originated in the late Permian period some 250 mya, and was one of the few survivors of the most devastating mass extinction the world has ever seen. After around 95% of life on earth had gone extinct, Lystrosaurus thrived on what little vegetation had survived and made up a large portion of the global population at the time.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
San people found Permian era Dicynodont fossils then, created myth about the fossils and created artwork based on those myths.
Dicynodont have been found all over South Africa by scientists.
The first scientific description of dicynodonts take place in 1845 by British paleontologist Sir Richard Owen.
#san people#south africa#fossils#rock painting#archeology#science article#extinct animals#extinct species#permian
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

A recent series of volcanic eruptions causes the Sun to rise in astonishing colours over the vast Pangaean deserts. An Inostrancevia family gets ready for the day, the cubs playing with everything in sight, from their mother to a very dismayed Dvinia. A little way away, a Vivaxosaurus browses a shrub for breakfast.
#inostrancevia#dvinia#vicaxosaurus#gorgonopsid#therapsid#synapsid#cynodont#dicynodont#permian#paleoart#my art#desert#red#the great dying#honestly the volcanism is just an excuse i felt like going ham with my reds on a desert#the extinction took a very long time btw all of these animals will be fine during their own lifetimes#palaeoblr
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Have you ever watched a history of the earth documentary that you're filled with love, respect and grief for all those that came before you. You're filled with respect that they lived, thrived and entire generations of creatures had to develop to us to ve studying them as mere fossils, their body being replaced by mineral. Have you ever felt sad because a creature that survived for millions of years suddenly became extinct. Have you ever looked at a fossil and thought "you were alive once, and I have the privilege of seeing your once-body recorded in rock, and now you help me to understand my place in the word"?
Anyways I watched this and I am still mourning the Trilobites okay

83 notes
·
View notes