#the human brain has specifically developed for language comprehension and usage in a way other animals have not
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Since I still get (well-intentioned) people telling me "Hey, did you know that you can teach apes to use sign language?", if you don't know already, Koko the gorilla almost certainly couldn't really talk with signing, the videos of her doing so have high evidence of doctoring and behind-the-scenes coaching, the majority of animals in the whole ape language project were abused (including Koko herself), and the studies were butchered and manipulated for media attention. As for now, there is no real evidence that apes can understand and use language much more than a dog can learn to connect symbols and noises with meanings, for example.
#the human brain has specifically developed for language comprehension and usage in a way other animals have not#it really makes no sense for another ape to learn to talk in that way#not jojo related#primate posting#animal abuse tw#this is probably my number three least favorite thing people bring up to me when they try to talk about apes with me#(as much as i understand they're coming from a good place)#number two being harambe and number one being those damn ''obviously abused primate doing 'cool' tricks'' videos
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Escape the Confines of Time and Space According to the CIA
She turned to me the other morning and said, “You heard of The Gateway?” It didn’t register in the moment. She continued, “It’s blowing up on TikTok.” Later on, she elaborated: it was not in fact the ill-fated 90s computer hardware company folks were freaking out about. No, they’ve gone further back in time, to find a true treasure of functional media.
The intrigue revolves around a classified 1983 CIA report on a technique called the Gateway Experience, which is a training system designed to focus brainwave output to alter consciousness and ultimately escape the restrictions of time and space. The CIA was interested in all sorts of psychic research at the time, including the theory and applications of remote viewing, which is when someone views real events with only the power of their mind. The documents have since been declassified and are available to view.
This is a comprehensive excavation of The Gateway Process report. The first section provides a timeline of the key historical developments that led to the CIA’s investigation and subsequent experimentations. The second section is a review of The Gateway Process report. It opens with a wall of theoretical context, on the other side of which lies enough understanding to begin to grasp the principles underlying the Gateway Experience training. The last section outlines the Gateway technique itself and the steps that go into achieving spacetime transcendence.
Let’s go.
Screengrab: CIA
THE TIMELINE
• 1950s – Robert Monroe, a radio broadcasting executive, begins producing evidence that specific sound patterns have identifiable effects on human capabilities. These include alertness, sleepiness, and expanded states of consciousness.
• 1956 – Monroe forms an R&D division inside his radio program production corporation RAM Enterprises. The goal is to study sound’s effect on human consciousness. He was obsessed with “Sleep-Learning," or hypnopedia, which exposes sleepers to sound recordings to boost memory of previously learned information.
• 1958 – While experimenting with Sleep-Learning, Monroe discovers an unusual phenomenon. He describes it as sensations of paralysis and vibration accompanied by bright light. It allegedly happens nine times over the proceeding six weeks, and culminates in an out-of-body experience (OBE).
• 1962 – RAM Enterprises moves to Virginia, and renames itself Monroe Industries. It becomes active in radio station ownership, cable television, and later in the production and sale of audio cassettes. These cassettes contain applied learnings from the corporate research program, which is renamed The Monroe Institute.
• 1971 – Monroe publishes Journeys Out of the Body, a book that is credited with popularizing the term “out-of-body experience.”

Books by Robert Monroe.
• 1972 – A classified report circulates in the U.S. military and intelligence communities. It claims that the Soviet Union is pouring money into research involving ESP and psychokinesis for espionage purposes.
• 1975 – Monroe registers the first of several patents concerning audio techniques designed to stimulate brain functions until the left and right hemispheres become synchronized. Monroe dubs the state "Hemi-Sync" (hemispheric synchronization), and claims it could be used to promote mental well-being or to trigger an altered state of consciousness.
• 1978 to 1984 – Army veteran Joseph McMoneagle contributes to 450 remote viewing missions under Project Stargate. He is known as “Remote View No. 1”. This is kind of a whole other story.
• June 9th, 1983 – The CIA report "Analysis and Assessment of The Gateway Process" is produced. It provides a scientific framework for understanding and expanding human consciousness, out-of-body experiments, and other altered states of mind.
• 1989 – Remote viewer Angela Dellafiora Ford helps track down a former customs agent who has gone on the run. She pinpoints his location as “Lowell, Wyoming”. U.S. Customs apprehend him 100 miles west of a Wyoming town called Lovell.
• 2003 – The CIA approves declassification of the Gateway Process report.
• 2017 – The CIA declassifies 12 million pages of records revealing previously unknown details about the program, which would eventually become known as Project Stargate.
THE REPORT

Screengrab: CIA
Personnel
The author of The Gateway Process report is Lieutenant Colonel Wayne M. McDonnell, hereon referred to simply as Wayne. There isn’t a tremendous amount of information available on the man, nor any photographs. In 1983, Wayne was tasked by the Commander of the U.S. Army Operational Group with figuring out how The Gateway Experience, astral projection and out-of-body experiences work. Wayne partnered with a bunch of different folks to produce the report, most notably Itzhak Bentov, a very Googleable American-Israeli scientist who helped pioneer the biomedical engineering industry.
A scientific approach
From the outset of the report, Wayne states his intent to employ an objective scientific method in order to understand the Gateway process. The various scientific avenues he takes include:
• A biomedical inquiry to understand the physical aspects of the process.
• Information on quantum mechanics to describe the nature and functioning of human consciousness.
• Theoretical physics to explain the time-space dimension and means by which expanded human consciousness transcends it.
• Classical physics to bring the whole phenomenon of out-of-body states into the language of physical science (and remove the stigma of an occult connotation).
Methodological frames of reference
Before diving into the Gateway Experience, Wayne develops a frame of reference by dissecting three discrete consciousness-altering methodologies. He’s basically saying, there’s no way you’re going to get through The Gateway without a solid grounding in the brain-altering techniques that came before it.
1) He begins with hypnosis. The language is extremely dense, but the basic gist is as follows: the left side of the brain screens incoming stimuli, categorizing, assessing and assigning meaning to everything through self-cognitive, verbal, and linear reasoning. The left hemisphere then dishes the carefully prepared data to the non-critical, holistic, pattern-oriented right hemisphere, which accepts everything without question. Hypnosis works by putting the left side to sleep, or at least distracting it long enough to allow incoming data direct, unchallenged entry to the right hemisphere. There, stimuli can reach the sensor and motor cortices of the right brain, which corresponds to points in the body. Suggestions then can send electrical signals from the brain to certain parts of the body. Directing these signals appropriately, according to the report, can elicit reactions ranging from left leg numbness to feelings of happiness. Same goes for increased powers of concentration.
2) Wayne continues with a snapshot of transcendental meditation. He distinguishes it from hypnotism. Through concentration the subject draws energy up the spinal cord, resulting in acoustical waves that run through the cerebral ventricles, to the right hemisphere, where they stimulate the cerebral cortex, run along the homunculus and then to the body. The waves are the altered rhythm of heart sounds, which create sympathetic vibrations in the walls of the fluid-filled cavities of the brain’s ventricles. He observed that the symptoms begin in the left side of the body, confirming the right brain’s complicity. Bentov also states that the same effect might be achieved by prolonged exposure to 4 – 7 Hertz/second acoustical vibrations. He suggests standing by an air conditioning duct might also do the trick. (David Lynch and other celebrities are committed adherents to transcendental meditation today.)
3) Biofeedback, on the other hand, uses the left hemisphere to gain access to the right brain’s lower cerebral, motor, and sensory cortices. Whereas hypnosis suppresses one side of the brain, and TM bypasses that side altogether, biofeedback teaches the left hemisphere to visualize the desired result, recognize the feelings associated with right hemisphere access, and ultimately achieve the result again. With repetition, the left brain can reliably key into the right brain, and strengthen the pathways so that it can be accessed during a conscious demand mode. A digital thermometer is subsequently placed on a target part of the body. When its temperature increases, objective affirmation is recognized and the state is reinforced. Achieving biofeedback can block pain, enhance feeling, and even suppress tumors, according to the report.

Image: e2-e4 Records.
The Gateway mechanics
With that, Wayne takes a first stab at the Gateway process. He classifies it as a “training system designed to bring enhanced strength, focus and coherence to the amplitude and frequency of brainwave output between the left and right hemispheres so as to alter consciousness.”
What distinguishes the Gateway process r from hypnosis, TM, and biofeedback, is that it requires achieving a state of consciousness in which the electrical brain patterns of both hemispheres are equal in amplitude and frequency. This is called Hemi-Sync. Lamentably, and perhaps conveniently, we cannot as humans achieve this state on our own. The audio techniques developed by Bob Monroe and his Institute (which comprise a series of tapes), claim to induce and sustain Hemi-Sync.
Here, the document shifts to the usage of quotes and other reports to describe the powers of Hemi-Sync. Wayne employs the analogy of a lamp versus a laser. Left to its own devices the human mind expends energy like a lamp, in a chaotic and incoherent way, achieving lots of diffusion but relatively little depth. Under Hemi-Sync though, the mind produces a “disciplined stream of light.” So, once the frequency and amplitude of the brain are rendered coherent it can then synchronize with the rarified energy levels of the universe. With this connection intact, the brain begins to receive symbols and display astonishing flashes of holistic intuition.
The Hemi-Sync technique takes advantage of a Frequency Following Response (FFR). It works like this: an external frequency emulating a recognized one will cause the brain to mimic it. So if a subject hears a frequency at the Theta level, it will shift from its resting Beta level. To achieve these unnatural levels, Hemi-Sync puts a single frequency in the left ear and a contrasting frequency in the right. The brain then experiences the Delta frequency, also known as the beat frequency. It’s more familiarly referred to these days as binaural music. With the FFR and beat frequency phenomena firmly in place, The Gateway Process introduces a series of frequencies at marginally audible, subliminal levels. With the left brain relaxed and the body in a virtual sleep state, the conditions are ideal to promote brainwave outputs of higher and higher amplitude and frequency. Alongside subliminal suggestions from Bob Monroe (naturally), the subject can then alter their consciousness.

Image: Thobey Campion
The Gateway system only works when the audio, which is introduced through headphones, is accompanied by a physical quietude comparable to other forms of meditation. This increases the subject’s internal resonance to the body’s sound frequencies, for example the heart. This eliminates the “bifurcation echo”, in which the heartbeat moves up and down the body seven times a second. By placing the body in a sleep-like state, The Gateway Tapes, like meditation, lessen the force and frequency of the heartbeat pushing blood into the aorta. The result is a rhythmic sine wave that in turn amplifies the sound volume of the heart three times. This then amplifies the frequency of brainwave output. The film surrounding the brain—the dura—and fluid between that film and the skull, eventually begin to move up and down, by .0005 and .010 millimeters.
The body, based on its own micro-motions, then functions as a tuned vibrational system. The report claims that the entire body eventually transfers energy at between 6.8 and 7.5 Hertz, which matches Earth’s own energy (7 – 7.5 Hertz). The resulting wavelengths are long, about 40,000 kilometers, which also happens to be the perimeter of the planet. According to Bentov, the signal can move around the world’s electrostatic field in 1/7th of a second.
To recap, the Gateway Process goes like this:
• Induced state of calm
• Blood pressure lowers
• Circulatory system, skeleton and other organ systems begin to vibrate at 7 – 7.5 cycles per second
• Increased resonance is achieved
• The resulting sound waves matches the electrostatic field of the earth
• The body and earth and other similarly tuned minds become a single energy continuum.
We’ve gotten slightly ahead of ourselves here though. Back to the drawing board.

Image: kovacevicmiro via Getty Images
A psycho-quantum level deeper
Wayne then turns to the very nature of matter and energy. More materially (or less if you will), solid matter in the strict construction of the term, he explains, doesn’t exist. The atomic structure is composed of oscillating energy grids surrounded by other oscillating energy grids at tremendous speeds. These oscillation rates vary—the nucleus of an atom vibrates at 10 to the power of 22, a molecule vibrates at 10 to the power of 9, a human cell vibrates at 10 to the power of 3. The point is that the entire universe is one complex system of energy fields. States of matter in this conception then are merely variations in the state of energy.
The result of all these moving energies, bouncing off of energy at rest, projects a 3D mode, a pattern, called a hologram, A.K.A our reality as we experience it. It's best to think of it as a 3D photograph. There's a whole rabbit hole to go down here. Suffice it to say, the hologram that is our experience is incredibly good at depicting and recording all the various energies bouncing around creating matter. So good, in fact, that we buy into it hook, line, and sinker, going so far as to call it our "life."
Consciousness then can be envisaged as a 3D grid system superimposed over all energy patterns, Wayne writes. Using mathematics, each plane of the grid system can then reduce the data to a 2D form. Our binary (go/no go) minds can then process the data and compare it to other historical data saved in our memory. Our reality is then formed by comparisons. The right hemisphere of the brain acts as the primary matrix or receptor for this holographic input. The left hemisphere then compares it to other data, reducing it to its 2D form.
In keeping with our species' commitment to exceptionalism, as far as we know humans are uniquely capable of achieving this level of consciousness. Simply, humans not only know, but we know that we know. This bestows upon us the ability to duplicate aspects of our own hologram, project them out, perceive that projection, run it through a comparison with our own memory of the hologram, measure the differences using 3D geometry, then run it through our binary system to yield verbal cognition of the self.
Screengrab: CIA
The click-out phase
Wayne then shows his cards as a true punisher, issuing, "Up to this point our discussion of the Gateway process has been relatively simple and easy to follow. Now the fun begins." Shots fired, Wayne. What he's preparing the commander reading this heady report for is the reveal—how we can use the Gateway to transcend the dimension of spacetime.
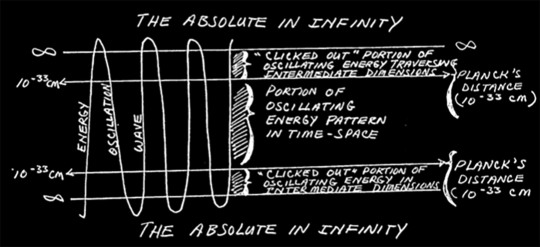
Time is a measurement of energy or force in motion; it is a measurement of change. This is really important. For energy to be classified as in motion, it must be confined within a vibratory pattern that can contain its motion, keeping it still. Energy not contained like this is boundary-less, and moves without limit or dimension, to infinity. This disqualifies boundary-less energy from the dimension of time because it has no rate of change. Energy in infinity, also called "the absolute state," is completely at rest because nothing is accelerating or decelerating it—again, no change. It therefore does not contribute to our hologram, our physical experience. We cannot perceive it.
Now back to frequencies. Wave oscillation occurs because a wave is bouncing between two rigid points of rest. It's like a game of electromagnetic hot potato (the potato being the wave and the participants' hands being the boundaries of the wave). Without these limits, there would be no oscillation. When a wave hits one of those points of rest, just for a very brief instant, it "clicks out" of spacetime and joins infinity. For this to occur, the speed of the oscillation has to drop below 10 the power of -33 centimeters per second. For a moment, the wave enters into a new world. The potato simply disappears into a dimension we cannot perceive.
Theoretically speaking, if the human consciousness wave pattern reaches a high enough frequency, the “click-outs” can reach continuity. Put another way, if the frequency of human consciousness can dip below 10 to the power of 33 centimeters per second but above a state of total rest, it can transcend spacetime. The Gateway experience and associated Hemi-Sync technique is designed for humans to achieve this state and establish a coherent pattern of perception in the newly realized dimensions.
Image: Spectral-Design via Getty Images
Passport to the hologram
In theory, we can achieve the above at any time. The entire process though is helped along if we can separate the consciousness from our body. It’s like an existential running head start where the click-out of a consciousness already separated from its body starts much closer to, and has more time to dialogue with, other dimensions.
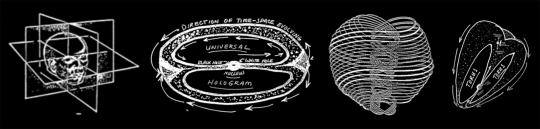
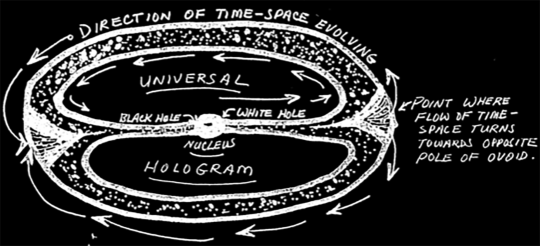
This is where things get a little slippery; hold on as best you can. The universe is in on the whole hologram thing, too, Wayne writes. This super hologram is called a "torus" because it takes the shape of a fuck-off massive self-contained spiral. Like this:
Give yourself a moment to let the above motion sink in…
This pattern of the universe conspicuously mirrors the patterns of electrons around the nucleus of an atom. Galaxies north of our own are moving away from us faster than the galaxies to the south; galaxies to the east and west of us are more distant. The energy that produced the matter that makes up the universe we presently enjoy, will turn back in on itself eventually. Its trajectory is ovoid, also known as the cosmic egg. As it curls back on itself it enters a black hole, goes through a densely packed energy nucleus then gets spat out the other side of a white hole and begins the process again. Springtime in the cosmos, baby!
Screengrab: CIA
The entire universe hologram—the torus—represents all the phases of time: the past, present, and future. The takeaway is that human consciousness brought to a sufficiently altered (focused) state could obtain information about the past, present, and future, since they all live in the universal hologram simultaneously. Wayne reasons that our all-reaching consciousness eventually participates in an all-knowing infinite continuum. Long after we depart the space-time dimension and the hologram each one of us perceives is snuffed out, our consciousness continues. Reassuring in a way.
And that is the context in which the Gateway Experience sits.
[Deep breaths.]
THE TECHNIQUE
The following is an outline of the key steps to reach focus levels necessary to defy the spacetime dimension. This is an involved and lengthy process best attempted in controlled settings. If you’re in a rush, you can apparently listen to enough Monroe Institute Gateway Tapes in 7 days to get there.
The Energy Conversion Box: The Gateway Process begins by teaching the subject to isolate any extraneous concerns using a visualization process called “the energy conversion box.”
Resonant Humming: The individual is introduced to resonant humming. Through the utterance of a protracted single tone, alongside a chorus on the tapes, the mind and body achieve a state of resonance.
The Gateway Affirmation: The participant is exposed to something close to a mantra called The Gateway Affirmation . They must repeat to themselves variations of, “I am merely a physical body and deeply desire to expand my consciousness.”
Hemi-Sync: The individual is finally exposed to the Hemi-Sync sound frequencies, and encouraged to develop a relationship with the feelings that emerge.
Additional Noise: Physical relaxation techniques are practiced while the Hemi-Sync frequencies are expanded to include “pink and white” noise. This puts the body in a state of virtual sleep, while calming the left hemisphere and raising the attentiveness of the right hemisphere.
The Energy Balloon: The individual is then encouraged to visualize the creation of an “energy balloon” beginning at the top of the head, extending down in all directions to the feet then back up again. There are a few reasons for this, the main one being that this balloon will provide protection against conscious entities possessing lower energy levels that he or she may encounter when in the out-of-body state.
Focus 12: The practitioner can consistently achieve sufficient expanded awareness to begin interacting with dimensions beyond their physical reality. To achieve this state requires conscious efforts and more “pink and white noise” from the sound stream.
Tools: Once Focus 12 is achieved, the subject can then employ a series of tools to obtain feedback from alternative dimensions.
Problem Solving: The individual identifies fundamental problems, fills their expanded awareness with them, and then projects them out into the universe. These can include personal difficulties, as well as technical or practical problems.
Patterning: Consciousness is used to achieve desired objectives in the physical, emotional, or intellectual sphere.
Color Breathing: A healing technique that revitalizes the body’s energy flows by imagining colors in a particularly vivid manner.
Energy Bar Tool: This technique involves imagining a small intensely pulsating dot of light that the participant charges up. He or she then uses the sparkling, vibrating cylinder of energy (formerly known as the dot) to channel forces from the universe to heal and revitalize the body.
Remote Viewing: A follow-on technique of the Energy Bar Tool where the dot is turned into a whirling vortex through which the individual sends their imagination in search of illuminating insights.
Living Body Map: A more organized use of the energy bar in which streams of different colors flow from the dot on to correspondingly-colored bodily systems.
Seven days of training have now occurred. Approximately 5 percent of participants get to this next level, according to the report.
Focus 15 – Travel Into the Past: Additional sound on the Hemi-Sync tapes includes more of the same, plus some subliminal suggestions to further expand the consciousness. The instructions are highly symbolic: time is a huge wheel, in which different spokes give access to the participant’s past.
Focus 21 – The Future: This is the last and most advanced state. Like Focus 15, this is a movement out of spacetime into the future.
Out-of-Body Movement: Only one tape of the many is devoted to out-of-body movement. This tape is devoted to facilitating out-of-body state when the participant’s brain wave patterns and energy levels reach harmony with the surrounding electromagnetic environment. According to Bob Monroe, the participant has to be exposed to Beta signals of around 2877.3 cycles per second.
CONCLUSIONS
Wayne expresses concern about the fidelity of information brought back from out-of-body states using the Gateway technique. Practical applications are of particular concern because of the potential for “information distortion.”
The Monroe Institute also ran into a bunch of issues in which they had individuals travel from the West to the East Coast of the U.S. to read a series of numbers off of a computer screen. They never got them exactly right. Wayne chalks this up to the trouble of differentiating between physical entities and extra-time-space dimensions when in the out-of-body state.
Wayne swings back to support mode though, lending credence to the physics foundation of the report. He cites multiple belief systems that have established identical findings. These include the Tibetan Shoug, the Hindu heaven of Indra, the Hebrew mystical philosophy, and the Christian concept of the Trinity. Here he seems more interested in hammering home the theoretical underpinnings that make The Gateway Experience possible, rather than the practical possibilities promised by The Gateway Tapes.
Possibly with his CIA top brass audience in mind, Wayne then gives an A-type nod to The Gateway Experience for providing a faster, more efficient, less subservient, energy-saving route to expanded consciousness. This finishes with a series of recommendations to the CIA for how to exploit Gateway’s potential for national defense purposes.

Screengrab: CIA

Screengrab: CIA
The missing page
One curious feature of The Gateway Report is that it seems to be missing page 25. It’s a real cliffhanger too. The bottom of page 24 reads “And, the eternal thought or concept of self which results from this self-consciousness serves the,” The report picks back up on page 26 and 3 sections later as if Wayne hadn’t just revealed the very secret of existence.
The gap has not gone unnoticed. There's a Change.org petition requesting its release. Multiple Freedom of Information Act requests have demanded the same. In all cases, the CIA has said they never had the page to begin with. Here’s a 2019 response from Mark Lilly, the CIA’s Information and Privacy Coordinator, to one Bailey Stoner regarding these records:

Screengrab: CIA via Muckrock
One theory goes that that rascal Wayne M.-fricking-McDonnell left the page out on purpose. The theory contends that it was a litmus test—if anyone truly defies time-space dimensions, they’ll certainly be able to locate page 25.
[Cosmic shrug.]
Thobey Campion is the former Publisher of Motherboard. You can subscribe to his Substack here.
How to Escape the Confines of Time and Space According to the CIA syndicated from https://triviaqaweb.wordpress.com/feed/
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Voice Search Will Impact SEO in 2020?
Every year some new creation of technology takes place that alters the business productivity. Resultantly it can be hard for any industry, be it digital, manufacturing or IT to survive in the modern digital era. One such innovation in the field of digital marketing is the increased usage of voice search that is influencing the traditional SEO techniques in several ways.
To ensure that your website ranks well on the search engine, it is vital to check your website’s performance with the voice search. In 2020, internet voice search will increase tenfolds that will significantly alter the traditional search engine optimization methods. Every marketer and business must be aware of the role voice search will play in SEO from 2020 onwards as this will determine their revenue and productivity.

SOURCE: How Voice Search Will Impact SEO in 2020?
The Hike in Voice Search Innovation
The launch of Watson by IBM in 2010 metamorphosed the technology of voice recognition enabled devices. Watson is an improved voice Q&A recognition program that astonished the world by transforming computers into smart droids. The program was intelligent and fast enough to overcome Trivia grandmasters on Jeopardy (TV quiz show.) In the same year, Google launched its Voice Search feature, and Apple introduced Siri on iPhone 4S, the introductory digital personal voice assistant. Later in 2014, Microsoft introduced its Voice Search known as Cortana, and Amazon Echo also released in the same year.
Amazon Echo is a unique smart voice-enabled speaker that can react to the human voice and reply with its artificial brain called Alexa. Google Assistant was introduced back in 2016, as well as the Voice Search enabled speaker Google Home. Till 2019 Amazon Alexa steered the smart speakers market, but according to the current rise in Google Home users, it overtaking Alexa seems inevitable.
Voice recognition innovation has been continuously in development, and it is improving day by day since its genesis. Google claims that its voice recognition system is 95% accurate, but it is nothing comparable to the Chinese iFlytek voice recognition program that is 98% accurate.
The comprehensive voice search in 2019 was not only limited to smartphones and smart speakers, but it is also integrated into several other devices such as on Televisions, Internet of Things, smart thermostats, and in home kits. While 2019 was a big year for development in voice search, 2020 will revolutionize the digital world with the expansion of voice search.
According to statistics, 31% of smart mobile users access voice search feature at least one in a week while 20 percent of searches on Google app and Android phones are done via voice recognition system. While the above statics of usage of voice search may be shocking, 2020 will dominate the manual screen web searches by 50 %.
According to a prediction by a media analytics organization Comscore, half of the internet searches will be done via voice in 2020. Gartner, another analytics firm, speculates that in 2020 30 % of the user queries on the internet will be made without using keypads. These predictions suggest that you need to be ready for the voice search’s effect on your business as well as modify the marketing plan that might be friendly with voice recognition systems. Another research organization speculates that 3.25 billion voice searches were in-use at the beginning of 2020. They forecast that until 2023 it may rise to eight billion voice search systems in use.
The Effect of Voice Search on SEO
The voice recognition innovation is meant to comfort your life and offer ease of access to web information. However, it may be a sudden sharp turn for marketers and SEO specialists. Let’s discuss in what way it influences your search engine optimization:
Natural Language
With the new and upgraded voice search detection programs, voice detection feature is now adept in analyzing day-to-day common language we use while talking to a regular human. The developers of voice detection systems analyze user’s voice queries, and then they optimize their voice detection systems accordingly. This makes voice identification programs much smarter in learning and understanding a natural language spoken by a human. So the point here is about the language you use in your online content should be natural and moderate. If it gets too formal, then the voice searches may not include or rank your site in the search engines. So your business website should have a standard conversational language that is used in day to day life.
Keyword Length
The method we were using until now was ranking our sites for 2-3 phrases keyword or short keywords, but it is now changing. When a person uses voice search is likely to speak out a lengthy keyword such as “Nike red men’s running shoes” instead of typing “Nike shoes.” This happens because while talking to someone, we mostly use descriptive sentences instead of saying two-three words. However, while using keypads, most of us are quite lazy and only types two-three terms to get the result. According to Backlinko, voice searches are mostly 29 words long and include natural conversational language. That means from now on, your online business content must contain keywords that are likely to be spoken via voice search. To get a better ROI in 2020, one should always long-tail keywords and may avoid excess usage of short-tail keywords.
Question Keywords
Voice search based web queries will be made up with question terms like how, what, when, which, who, and where. These words are avoided while searching from a keypad. The SEO executives, leaders, and professionals need to bear in mind that the content provides accurate and to the point answer to these question keywords. Business website contents must include the relevant answers to their questions keywords to generate considerable traffic via voice searches.

It would help if you also used the verbs in your content that are likely to be used by users with the question keywords be it can, do, make, and other. You can also consider using the adjectives and nouns related to the query to get the most out of voice search.
Semantic Search
Instead of lexical searches, Google and other users are likely to use Semantic search algorithms. It does not only ranks websites based on used words but also considers the user’s geolocation, search history, glocal search history, and spelling variations of the user’s search terms. Google has a dedicated artificial intelligent system called RankBrain for this purpose, which identifies the arranged order of the words in a keyword. This helps Google understand the user’s purpose behind using the specific terms, and it also considers the other aspects mentioned above in this paragraph. Another program, Hummingbird, is used by Google to recognize and learn the natural language of a user. In short, voice search is related to a semantic search system as the voice searches sometimes have different intentions even if other users use the same terms for another purpose.
Local Search
Voice innovation in smartphones is significantly focused more on the local search. It is at least three times more drawn towards local search than the non-location-based searches. For example, if someone is looking for a bakery shop nearby, then the user is likely to say, “Hey Google, best bakeries near me.” This is why voice search has a significant impact on the local search ration, and it is rapidly increasing as more and more people are getting aware of this feature.
SERPs
The sites optimized with the voice search are mostly ranked in the top three positions on the search engine result page. You don’t need to be on the first rank on SERP to appear on the Answer Boxes located at the upper of the SERP. If your site is providing the most relevant answer to the user query, then your site will appear in the featured snippet. To appear in Google’s featured snippet, your website must have the most appropriate and logical answer to the user keyword. The voice search keywords are a great way to appear in these featured boxes.
Ecommerce
Users are using a voice assistant to find their products online, and most of the e-commerce keywords are made through voice search. Approximately 40% of the users use voice search before making the final deal, and this means they prefer voice search while shopping online. If you are managing the SEO of an e-commerce website, then you need to use voice friendly keywords in your products.
How to Adapt to Voice Search SEO?
As you now aware of how voice is influencing the world of SEO, here are the tips that may help marketers adapt to the voice search change:
Site Loading Speed: Google Voice search apps are preferring a lightweight website that can load quickly without any delay. So marketers are advised to optimize the loading time of their websites. One can do this by compressing the images of the website as well as avoiding the auto-play videos, which slows down the loading time.
Use of long-tail keywords: Voice searches are long-tail keywords, and optimizing your site accordingly, will help you in generating traffic through voice searches.
Featured Snippets: Voice searches are likely to contain question words, and by answering these question keywords with a relevant and short answer, you can list your site into the featured snippet. These snippets only consider summary answers from particular webpages.
Use Structured Data and Schema Markup: Your content must be well organized and should follow an excellent order and structure to appear in voice searches. Always use Schema markups on your website while posting traffic-generating content.
Provide Local Information: If your site is for your local business where you provide products and services, then you should include the details like physical address and map of your store or company. You can embed Google My Business on your site to boost the performance in local voice searches.
Enhance the Domain Authority: Site that has higher DA is likely to appear in the voice searches because this increases the trust of search engines on your site. You can boost the Domain authority of your website by creating high-quality backlinks on your domain.
The voice search innovation is influencing search engine optimization for sure and recently it has significantly developed. In 2020 it will increase more than ever, so marketers should not be surprised if the traditional SEO techniques stop incurring the general revenue. It is time to buckle up and take advantage of voice search and get even more customers through the web.
Harry Williams is an inventive person who has been doing intensive research in particular topics and writing blogs and articles for AOI Tech Solutions, TekWire, Wire IT Solutions, Fegon Group, Zone Firewall. He is a very knowledgeable person with lots of experience. To get in touch with the internet security service provider, just visit on these given sites.
#seo 2020#seo specialists#seo techniques#seo tips#tireless it services#best network security solutions#Network Security#internet security#Tekwire#AOI Tech Solutions#Wire-IT Solutions#Fegon Group#zone firewall
0 notes
Text
Camera Color Spaces Explained – sRGB vs Adobe RGB vs RAW
The post Camera Color Spaces Explained – sRGB vs Adobe RGB vs RAW appeared first on Digital Photography School. It was authored by Herb Paynter.
Your camera is probably able to capture color images in a variety of different color containers called “spaces.” These camera color spaces collect colors in one of several size light buckets labeled sRGB, AdobeRGB, and RAW.
Each bucket gathers slightly increased varieties of light, similar to the way Crayola crayons are packaged and sold in increasingly inclusive collections of colors; small, large, and jumbo.
Camera color spaces offer photographers a variety of different size boxes.
Camera color spaces
Scenes that include both brilliant colors and bright lighting are excellent candidates for capture with AdobeRGB color space.F/3.5, 1/1000, ISO 400, Lumix G Vario 2.8, 35mm
A debate in the photo community usually arises over which camera color spaces to choose in the camera’s preferences. Some color spaces capture more of the hues and saturated colors than others. Pictures captured in one space may include more colors than another.
Each space is ideally suited for certain purposes, and the question of which camera color space to choose needs a bit of explanation. In addition to the capture question, choosing a color space for post-production editing will depend on the image’s ultimate usage.
Your camera’s color spaces involve not just color data, but additional parking space on the drive. Larger color spaces provide more bit-depth (explained below), which occupies more digital real estate on the memory card. So, the choice of which to use does have practical importance.
What camera color space to use
There is no singularly perfect color space choice, so let’s examine which is best for specific situations.
Images that do not include highly-saturated color but contain significant detail in the shadow areas will benefit from RAW format capture and high-bit processing. F/10, 1/1600, ISO 800, Lumix G Vario 2.8, 200mm
Unless the sole purpose of a photo is to display as a high-resolution digital image, you might want to convert the file’s original color space for a less demanding result. However, keep in mind that every time a file mutates from a larger color space to a smaller color space (RAW to AdobeRGB, or AdobeRGB to sRGB), the image’s color intensity and integrity may diminish in the process. Some imaging applications are less demanding than others.
While copies of digital files remain identical in size and intensity to the original regardless of how many times they have been copied, when a digital file mutates to a lesser color space, it will always lose some critical color information. Your camera color spaces in general, and device color spaces, in particular, are all unique. Each serves a particular purpose.
The extreme dynamic range and saturated skies benefitted from the RAW capture and editing in AdobeRGB. Detail buried in the shadows was possible because of the 14-bit capture. F/14, 1/300, ISO 3200, Lumix G Vario 2.8, 12mm
It’s a matter of depth
The difference between camera color spaces boils down to an issue called bit depth. Bit depth is a mathematical description of how many visible distinctions between shades of color can be recognized and reproduced by different devices (a techie term for scanners, cameras, computer monitors, and printing machines). Unfortunately, not all devices can reproduce all colors the same (which is the primary stumbling block amidst all color issues).
Every device reads and reproduces color using a different process. While this sounds like a fixable problem, there is a sad and unsolvable reality behind the problem. There are at least three different interpretations of color at play in every capture-display-print cycle.
These colorful seat cushions and deep shadows were captured in RAW format, edited in AdobeRGB, and saved in sRGB for upload to our camera club’s server for display as part of a club field trip slideshow. F/7.1, 1/320, ISO 400, Lumix G Vario 2.8, 19mm
First, cameras capture color by recording intensities of light as electrical signals and interpreting those signals as colors. Each color is assigned a specific number.
Second, these numbers are then sent to the computer. Here, they get translated into another process that interprets those electrical signals into a process that turns on tiny lights (called pixels) on a backlit screen.
And third, those pixels are then sent to a printing machine that instructs those pixel values to spit tiny splatters of colored ink onto paper.
It’s a very complicated process that color scientists have tried for years to make simple. Unfortunately, it just ain’t that simple!
Anyway, during this hair-on-fire digital transition, different methods are employed that utilize the various color spaces in a way that transforms the colors from one device to another as accurately as possible. Sometimes the color translations don’t convey the colors as accurately as we would like, which is why sometimes the monitor colors don’t match the printer colors.
Science uses charts like this to plot the characteristics of camera color spaces. While these charts are referred to as “theoretical” because they are not visible to the human eye but represent what each color “bucket” can capture versus what the eye can see.
The ultimate referee
The only comprehensive color space that plots the full scope of what the human eye can see is what the science community calls L*a*b* (inverted horseshoe diagram) space.
The human eye is the ultimate arbitrator in the color wars, and all device capabilities (camera, display, and printer) are defined by how they match up to the eye’s master gamut. This is why this strange horseshoe shape is referred to as the Reference Space. All other devices, whether camera, display, or printer, can only recognize and utilize portions of this “reference space,” and they usually disagree with each other.
Color is a very diverse and dysfunctional family. Each device speaks a different dialect of a similar language. Each produces colors that cannot be faithfully reproduced on other devices. Color is a very messy topic.
Crayola crayon boxes contain varying numbers of colors just as color spaces collect varying amounts of color. The lightest and darkest color crayons are the same value, but larger boxes contain more colors than smaller ones.
Some devices can express color more completely than others. Unfortunately, no device created by humans can reproduce all the colors that can be seen by humans. Also, the colors captured by one device that fall outside the gamut (Crayola box size) of other devices, get clipped, lost, or compressed during the handoff. Those colors never come back home.
This is the tragic truth about digital color reproduction. The trick to color reproduction is in retaining as much of the common color as possible during the process. Fortunately, this same human eye (and brain) are very forgiving about accepting the limitations of non-human devices.
Color reproduction is a true application of the law of diminishing returns and the visual science of physics. Photographers understand this law quite well.
Very rarely can a camera actually capture all the color and dynamics of an original scene. Moreover, nature’s color gamut extends even further than the colors that the human eye can identify. Any time a digital image gets transposed from one form into any another form, that transformation is a diminished-value exchange.
As an image is transferred from one device to another, those pixel values located outside the color gamut of the destination device always get lost in the translation. The object of color management is to mitigate color loss and maintain as much of the appearance of the original as possible, all the way through the reproduction process.
RGB spaces (sRGB, AdobeRGB, ProPhoto RGB)
It all begins with the camera’s color settings that are in place when you capture the scene. All cameras capture light through red, green, and blue filters (RGB color space). While there are a number of RGB color spaces to choose from, each sports a slightly different color gamut.
Each device in the photography chain interprets colors slightly differently, and each responds to the individual color spaces uniquely.
Each color space (sRGB, AdobeRGB, ProPhoto RGB, etc.) provides a unique collection of color attributes, and each space satisfies specific display and reproduction requirements.
Gamuts are descriptions of the range of colors that a device can recognize, record, display, or print.
Shooting a vibrant, saturated scene with the camera requires a larger color space. Using a camera color space with a smaller gamut could significantly diminish the raw, harsh emotion of the scene. This is why most photography experts encourage photographers to set their cameras to capture images in AdobeRGB.
sRGB
Almost all digital cameras are factory-set to capture colors using sRGB as the default color space for a plausible reason; most of the pictures we take never get printed! At best, we view them on computer monitors or social media. Quite honestly, most of the pictures we capture never make it past the initial glance at the camera’s LCD screen. Capturing those images in higher-bit color space is a total waste of disk space.
sRGB color space remains largely unchanged since it was defined in the 1950s to compress video images into a manageable size for broadcast. While the format has been updated slightly, the basic intent is the same.
sRGB was developed by HP, Microsoft (and others) back in the early days of television to address the color gamut needs of most televisions (early versions of computer monitors), and the standard was set long ago. The airwaves and Internet browsers live on an sRGB diet. As such, the sRGB color space standardizes the way images are still viewed on monitors and televisions.
Adobe RGB
If the ultimate destination for your picture is monitor or display-based presence (presentations, Internet, or television displays), this is probably the best choice to capture images. However, if you shoot for print on paper, both AdobeRGB 1998 and ProPhoto RGB RGB contain a wider gamut of colors and are thus more suited for preparing images for print.
The brilliant dynamics and saturated colors are always captured best in the deepest color bucket of all – RAW. The degree of adjustments provided by RAW capture and ProPhoto RGB editing is perfect for images like this. F/6.3, 1/800, ISO 400, Lumix G Vario 2.8, 26mm
RAW
Actually, the most ideal bucket for capturing images actually exceeds the gamuts of all three of these camera color spaces. I’m speaking of course of your camera’s ability to capture images in RAW format. This is a format that supersedes any defined color spaces.
RAW files capture color in the highest bit depth possible; up to 14-bits per color. RAW is not an acronym; it is more of a description. It is the recording of all the limited color depth and uncompressed dynamic range of the original scene. Start RAW and strip down from there.
Camera color spaces explained – Conclusion
Congratulations on sticking with this article through all the minutia.
By now, it probably seems like camera color space is more like outer space, but it doesn’t have to remain this technical. Simply remember to capture images in RAW format (perhaps in addition to capturing them as JPG) and then transform the colors down the chain of reproduction as the need dictates.
Edit images in the camera color spaces of ProPhoto RGB or AdobeRGB to retain as much color elbow room as necessary. Those images destined for print should be transposed to AdobeRGB, and reduce those images destined for the Internet or slideshows to sRGB. Simple, enough!
The post Camera Color Spaces Explained – sRGB vs Adobe RGB vs RAW appeared first on Digital Photography School. It was authored by Herb Paynter.
Read more about this at digital-photography-school.com
https://bestcamaccessories.com/camera-color-spaces-explained-srgb-vs-adobe-rgb-vs-raw/
0 notes
Link
With so many of us now constantly tethered to digital technology via our smartphones, computers, tablets, and even watches, there is a huge experiment underway that we didn’t exactly sign up for.
Companies like Google, Facebook, Twitter, Apple, even Vox (if we’re being completely honest) are competing for our attention, and they’re doing so savvily, knowing the psychological buttons to push to keep us coming back for more. It’s now common for an American kid to get a smartphone by age 10. That’s a distraction device they carry in their pockets all the time.
The more adapted to the attention economy we become, the more we fear it could be hurting us. In Silicon Valley, we’re told more parents are limiting their kids’ screen time and even writing no-screen clauses into their contracts with nannies. Which makes us wonder: Do they know something we don’t?
If it’s true that constant digital distractions are changing our cognitive functions for the worse — leaving many of us more scatter-brained, more prone to lapses in memory, and more anxious — it means we’re living through a profound transformation of human cognition. Or could it be that we’re overreacting, like people in the past who panicked about new technologies like the printing press or the radio?
To find out, we decided to ask experts: How is our constant use of digital technologies affecting our brain health?
The answers, you’ll see, are far from certain or even consistent. There’s a lot yet not known about the connection between media use and brain health in adults and kids. The evidence that does exist on multitasking and memory, for instance, suggests a negative correlation, but a causal link is still elusive. Still, many of the researchers and human behavior experts we spoke with still feel an unease about where the constant use of digital technology is taking us.
“We’re all pawns in a grand experiment to be manipulated by digital stimuli to which no one has given explicit consent,” Richard Davidson, neuroscientist at the University of Wisconsin, told us. But what are the results of the experiment?
Our conversations were edited for length and clarity.
Richard Davidson, neuroscientist at the University of Wisconsin Madison and founder and director of the Center for Healthy Minds
I am most worried about the increase in distractability, the national attention deficit we all suffer from, and the consequences that arise from this.
Our attention is being captured by devices rather than being voluntarily regulated. We are like a sailor without a rudder on the ocean — pushed and pulled by the digital stimuli to which we are exposed rather than by the intentional direction of our own mind.
The ability to voluntarily regulate attention is more developed in humans than other species. As William James, the great psychologist, wrote in 1890, “The faculty of voluntarily bringing back a wandering attention, over and over again, is the very root of judgment, character, and will.”
But we are becoming impaired in that capacity, globally. We’re all pawns in a grand experiment to be manipulated by digital stimuli to which no one has given explicit consent. This is happening insidiously under the radar.
This, to me, underscores the urgency of training our minds with meditation so we don’t have to check our phone 80 times a day.
Christopher Burr, philosopher of cognitive science and postdoctoral researcher at the Oxford Internet Institute
Our constant use of digital technologies is allowing intelligent systems to learn more and more about our psychological traits, with varying degrees of validity or accuracy. For instance, our smartphone’s accelerometer might be used to infer our stress levels at work, or an automated analysis of our vocal patterns could determine that we’re depressed.
But what’s concerning to me is that users are rarely fully informed that their data could be used in this way. Furthermore, there is often insufficient consideration by the companies who develop the growing variety of “health and well-being” technologies of the risks of intervening. For instance, companies may be nudging a user to change sleep patterns, mood, or dietary preferences and causing unintended harm.
In a health care setting, a doctor will try to avoid interventions that do not involve the patient in the decision-making process. Instead, doctors try to respect and promote the patient’s self-understanding and self-determination. We need to find ways of upholding this relationship in the domain of health and well-being technologies as well.
Any inference or subsequent intervention that aims at changing the behavior of a user should be fully transparent, and ideally scrutinized by an ethical review committee. This would help to minimize the chance of unintended consequences (e.g., increased stress, anxiety, or even the risk of behavioral addiction).
Anthony Wagner, chair of the department of psychology at Stanford
The science tells us that there is a negative relationship between using more media simultaneously and working memory capacity. And we know working memory capacity correlates with language comprehension, academic performance, and a whole host of outcome variables that we care about.
The science tells us that the negative relationship exists, but the science doesn’t tell us whether the media behavior is causing the change. It’s too early to really conclude. The answer is we have no idea.
But if there’s a causal relationship, and we are transforming the underlying cognitive functional capabilities, that could have a consequence for academic performance or achievement. One would want to know that.
The field needs to go to big science, we need to go to really large [number of study participants]. I’d take the early studies as suggestions of relationships, but now, let’s actually do the science with using design and power that would lead us to believe things might be more trustworthy in terms of the result that everyone finds.
Paul Murphy, Alzheimer’s researcher in the Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry at the University of Kentucky
Neurodegenerative diseases take decades to develop, and widespread use of electronic devices like smartphones etc., is a still a relatively recent thing. So the scary way to look at this is that we are conducting a risky experiment with some potentially serious public health consequences, and we won’t know for another decade or so if we’ve made some terrible mistakes.
In a way, this is analogous to the problems that we have on studying the long-term effects of screen time on children. We can suspect that this may be bad, but we are still many years away from knowing, and we are nowhere near knowing what sort of exposure is safe, or how much might be dangerous.
Gary Small, author of the book iBrain and director of UCLA’s Memory and Aging Research Center at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior
My biggest concern is with young people, whose brains are still developing from birth through adolescence. There’s a process called pruning [the process of removing neurons that are damaged or degraded to improve the brain’s networking capacity]. This could be affected through all the time using tech. We don’t have data on that — but it certainly can raise a concern.
[The constant use of technology] does affect our brain health. It has an upside and a downside. The downside is that when people are using it all the time it interferes with their memory because they are not paying attention to what’s going on. They are distracted.
As far as I know, there are not systematic studies looking at that. You can only look indirectly at this. So we have studied the frequency of memory complaints according to age. You find about 15 percent of young adults complain about their memory, which suggests there might be things going on such as distraction.
On the positive side, there are certain mental tasks, when using these technologies, that exercise our brains. Some studies have shown some games video games and apps can improve working memory, fluid intelligence [problem solving], and multitasking skills.
Susanne Baumgartner, Center for Research on Children, Adolescents, and the Media, University of Amsterdam
I am researching the potential impacts of social media and smartphone use on adolescents’ attention and sleep. I am particularly interested in the effects of media multitasking, that is using media while engaging in other media activities or doing homework, or being in a conversation. Most teenagers nowadays have their own smartphones and therefore access to all kinds of media content whenever they want.
We find in our studies that adolescents [in the Netherlands] who engage in media multitasking more frequently report more sleep problems and more attention problems. They also show lower academic performance. However, this does not necessarily indicate that media use was the cause of this.
When looking at sleep problems, we found that stress related to social media use was a better indicator of sleep problems than the amount of social media use. This seems to indicate that it is not social media use per se that is related to sleep problems, but rather whether adolescents feel stressed by their usage.
So overall, I am still a bit hesitant about the conclusion that digital media use is detrimental to adolescents’ cognitive development. At this point we need more studies that truly investigate these impacts in long-term studies and with better measurements (e.g., tracking smartphone behavior instead of just asking teenagers about their media use).
And we should also not forget to look at potential beneficial effects. For example, studies conducted by other researchers found that specific types of media use, such as playing action video games, can be beneficial for cognitive abilities.
Elizabeth Englander, director and founder of the Massachusetts Aggression Reduction Center
One of the most striking things we’ve been looking at in the lab is that teens often tell us almost all characteristics of social media can make them feel more anxious.
If they see what their friends are doing, that can make them feel anxious about not being a part of it. If they don’t see what friends are doing, that also makes them anxious — they worry about being left out. The times they don’t feel anxious is when they are using social media and actively engaging with their friends in a positive way. But at other times it does seem to increase anxiety.
That’s striking. It’s a model of an interaction where there’s this strong reward system — and that it kind of seems to keep kids on an emotional tether. One girl described it as a leash.
In terms of direct evidence [showing mobile phones and social media impede human connections in person], it’s limited. But think about it: How do people connect with each other? They do it through social skills. And how do you build social skills? There’s only one way we are aware of — through face to face interactions with other peers your age.
When you have a society where other things are displacing face to face social interactions, it’s reasonable to assume those are going to impact the development of social skills. It does seem to be what we are seeing now.
Heather Kirkorian, associate professor in the school of human ecology at the University of Wisconsin Madison
One thing is clear: The impact of digital media depends partly on how we use them.
In the case of infants and young children, researchers often refer to content and context. That is, the impact of digital media on young children depends on what children are doing and how those activities are structured by the adults who are — or are not — in the room.
For instance, we might compare video-chatting with a grandparent versus watching an educational TV show versus playing a violent video game versus using a finger-painting app. Young children are the most likely to benefit from digital media when the content is engaging, educational, and relevant to their own lives; when they use it together with others — when parents help children understand what they see on-screen and connect it to what they experience off-screen. And when digital-media activities are balanced with off-screen activities like playing outside, playing with toys, reading books with caregivers, and getting the recommended amount of sleep.
So the research with teens and adults isn’t much different. For instance, the effects of social media depend on whether we use them to connect with loved ones throughout the day and get social support versus compare our lives to the often highly filtered lives of others and expose ourselves to bullying or other negative content.
Similarly, the impact of video games on attention depends on the type of game that is played and the type of attention that is being measured.
Adam Gazzaley, professor of neurology at University of California San Francisco and author of The Distracted Mind
I’ve written a lot about the direct impact of digital technology on emotional regulation, attention, and stress, as driven by over-exposure to information, rapid reward cycles, and simultaneous engagement in multiple tasks. These are certainly reasons to be concerned.
But personally, I find one of the most challenging aspects of our digital preoccupation to be the displacement it induces from nature, face-to-face communication, physical activity, and quiet, internally-focused moments.
I’m currently deep into a trip to New Zealand with limited technology exposure so that I can focus on connecting with friends, nature and my own mind. I realize now more than ever before how important these experiences are for my brain health.
That being said, I do believe that technology can offer us an incredible opportunity to enhance our cognition and enrich our lives. Figuring this out is our next great technological and human challenge.
Ethan Zuckerman, director of the Center for Civic Media at MIT
With any new technology, there is always a pattern of people saying, “This is addictive, and it’s destroying society as we know it.” There’s often something real to those concerns. There’s also often something which is moral panic.
One of the ways you sense moral panic is that it tends to be focused on our kids or sexuality. So when you see someone saying we are going to have a lost generation, or that Bluetooth is leading youth to have sex at an unprecedented rates — these are always indications of moral panic rather than concern about real things.
From what I can tell, parenting culture in Silicon Valley is this performative craziness. I’m going to virtue signal harder than anyone else. I am a better parent than you are because i put crazier restrictions on my family than you do. [Banning screens] feels very consistent with that.
The reason those stories are satisfying is you come out of it thinking, “What assholes. If they think this stuff isn’t good — why do they continue to do it?” Then you have folks like Jaron Lanier who say, “Quit your social media now, it’s bad for you.” That feels irresponsible in another way — there are clearly billions of people who aren’t going to quit social media in part because it’s become a critical communications tech. It’s core to how they interact with the world. For a lot of work and play — it’s essential these days.
So what I want to say to Lanier is make it better. We’re not putting this genie back in the bottle. There’s a lot of stuff from it that’s turned out to be good. There’s no one seriously proposing we’re going to turn all of this off.
The interesting question is: What are the real problems and how do we address them and make them better? How would you mitigate those harmful effects? What are the positive effects we want out of it?
Nir Eyal, author of Hooked: How to Build Habit-Forming Products
Technology is like smoking cannabis.
Ninety percent of people who smoke cannabis do not get addicted. But the point is that you’re going to get some people who misuse a product if it’s sufficiently good and engaging, that’s bound to happen. The solution to that, is we should fix the harm, not the technology itself but the harm it does. I want companies to look for the addicts and help them.
Lots of companies make addictive products — I guarantee somebody is addicted to Vox. The good news is that these companies know how much you’re using their product. So if they wanted to they could simply look at their log and say, “Look if you use the product 30 hours a week, 40 hours a week, we’re gonna reach out and say, ��Hey can we help you moderate your behavior? You’re showing a behavioral pattern consistent with someone who may be struggling with an addiction. How can we help?’”
And you know what, the fact is, it would actually make the platform better. It is in their interest to do this. I know that some of them are working on it.
Original Source -> Is our constant use of digital technologies affecting our brain health? We asked 11 experts.
via The Conservative Brief
0 notes
Text
The Nuiances of All Basic Lifestyle Theory
Standard Lifestyle Theory Options
Human mind is a Intricate make which wishes to Keep a Equilibrium of the precious and negative emotions in order to sustain a fair thought process. This way, the human body and brain aren't mutually exclusive. So ideally, it is a superb idea to try and consume near precisely the exact same amount of Carbs for each single meal daily. It is not a very straightforward notion to clinic or understand. The concept of differential reinforcement identifies the association between the criminal action and the result for a consequence of it.
Not Just a Diet, You May use the Basics to build a wholesome diet to your metabolism that can help you remove weight and keep it off. The basic concept isn't hard to comprehend. Social learning theory has been implemented broadly ot the understanding of aggression. Well, it's important to not forget the endosymbiotic theory is that, a idea. Basically, sufferer precipitation concept focuses on the thought that passive precipitation of violence is due to a power battle.
Lifestyle Theory Learning how to convince and Influence is likely to make the Gap between hoping to have a larger income and with a bigger income. The need to meet individual potential comes following bodily and societal ones are happy. The requirements of the many and also the necessity to control the numerous has developed a society that's government reliant. The need for self actualization comes after the rest prerequisites are fulfilled. It is suggested that sattvic food options are chosen at every meal to market a healthy diet plan and nutrition for every one the senses.
Bad societal Encounters can cause Psychological difficulties. Imagine you have completed all you have ever wanted to perform in this lifetime (materially this isn't possible) and have nothing more to do. Therefore, obtaining a lifestyle isn't the distinct same as choosing it's essential to emphasize that well-being is decided by the manner lifestyle has been. It is a sustainable lifestyle program, and if you stay with it, effects WILL come. Segmenting people in agreement with their way of life and value, and the way they translate purchases or consumption of merchandise or services is precisely what psychographic segmentation is all about.
Generally All Of the nutrition is Removed and We are left with calories. Though a lot of men and women advise this specific diet, you will find a couple who criticize it poorly. It merely wants a suitable diet and regular exercise.
Some Individuals have considerably superior Genetics than other People do if it is to do with building your body up enormous. Thus, more research is needed to prove the benefits of a vegetarian diet program. It profoundly studies and comprehends that the disposition of language, the way that it aids in communication, and how it pertains to the minds of the people which are communicating. Various studies have proven that kids need interaction to grow and grow. In order to have this completed, the analysis of ethnography is done covertly rather than simply as a means to be certain that the ethnographer doesn't interfere with the behavior of these people he is analyzing which is referred to as the audience effect. This form of evaluation could lead to several reasons like a protracted psychological harm, social aloofness and very low self-esteem.
Cognitive Behavior is a comprehensive Issue which cannot be Coated daily. People's behaviour is the automobile that is used to fulfill their needs. Thus, diet is essential for a healthy life. Communication to attain your best self matches in this category. Furthermore, it involves analyzing how language is about the fact in Earth, and also the way it impacts our thoughts. An individualas civilization will specify the form of breakfast such as the traditional full English breakfast including as baked beans.
Presenting
There is a status of an Elevated Implication to Tracking Afterward to theory since the usage of research is to analyze concepts and expand material for the growth of laws. Esteem Needs The following level of individual motivation is the requirement for self-esteem. The level of closeness between the child and her environment is quite significant. It's based on economic variables and is all about the notion of standing. Motives Emotional matters incorporate the notion of motives. The basic component of the speech is advice, and this highlights the value of an exhaustive research about the subject that's been chosen to be exhibited from the address.
0 notes
Link
Love to skip ahead? Check out the table of contents below
1.1 What is Dyslexia? 1.2 How did the word ‘DYSLEXIA’ come into existence? 1.3 Understanding the cause behind dyslexia 1.4 How do you know if you have dyslexia 1.5 How is the condition diagnosed? 1.6 Dealing with dyslexia 1.7 Important Notes
What is dyslexia?
Dyslexia can be defined as a condition that is specific to learning disability. A person with dyslexia might experience troubles in his/her learning activities.
Thus, dyslexia can be put as a term that is used to specifically define people who have reading complexities even though they are inclined to learn something of their interest.
How did the word dyslexia come into existence?
The word has its roots in the ancient Greek language.
Dys: Being impaired or abnormal
Lexis: Words or Language
The disorder is often seen to be a highly debatable subject with much arguing dyslexia should never be considered as a disease and rather treat it as a unique condition that one inherits it at the time of birth.
Nevertheless, many individuals with learning problems are known to overcome their dyslexia symptoms by a certain extent with necessary precautions being in place.
The causes behind Dyslexia
Extensive researches that have been carried out have shown the disorder can be attributed to the different ways a human brain might process information.
For instance, brain pictographs taken with high-resolution modernized imaging tools; indicate dyslexic people perceive an information that is being read in a different way in comparison to the ones without the condition.
That is one of the major reason, reading activities seem to be a daunting task to the ones who have the condition.
Many people are seen to have misinformed or misinterpreted communications such as, those who are dyslexic makes them read numbers and letters in a reverse order.
However, the actual reality is these are a part of normal development and can be seen in kids until they have attained their grade two.
The major complexities in dyslexia are the blocks that one hits while recognizing common phonemes (basic sounds of speech).
This is further seen to make it harder for people with dyslexia to recognize familiar sounding words. Often, a dyslexic person might spend more time in sounding out the correct pronunciation.
This often ends up in the word losing its meaning completely which directly affects their comprehensiveness. Thus it doesn’t come as a surprise for many dyslexics to have a varying amount of complexities to spell words of different lengths.
The disorder can be seen as a language processing disability as it is seen to affect languages, irrespective of their forms, whether written or spoken.
At times some people diagnosed with dyslexia are seen to have milder symptoms. This makes them less prone to written or spoken language omissions.
Interestingly, there are some people who accept their condition and work around diligently to outgrow themselves. Nevertheless, it takes a lot of time and effort.
With necessary steps being in place, one can learn different strategies to help them steer clear of their learning complexities. These strategies are further seen to be useful and a person can re-implement them to lead a successful life.
How do you know if you have dyslexia?
Many people wonder how can one identify dyslexia symptoms. A simple way to identify the condition is through careful observation.
Observe if you face any difficulties while reading words that are simple in nature. Identify if you are having trouble to read something that your other peers have no trouble doing so.
How is the condition diagnosed?
Although many people with the condition are good at hiding or working around their condition, getting help could go a long way in making things easier.
The condition is not just specific to kids, at times adults or teens too can be diagnosed at later stages.
A look at some of the obvious symptoms
Below average writing or reading skills
Frequent spell-errors
Being unable to complete things such as assignment on time
Being unable to or experiencing difficulties in recalling common names
Being unable to memorize telephone numbers
Nevertheless, it is always important not to jump to any immediate conclusion. If you are in doubt, consult a medical practitioner. A trained learning specialist would be the right person to measure an individual’s writing, spelling and reading abilities.
How to deal with dyslexia
Dealing with learning disabilities such as dyslexia can be tough, at times. Federal law mandates timely support from its wide network of public school system to a person with a known case of learning disabilities such as dyslexia.
A trained teacher can help a dyslexic person through well-crafted practice activities and customized learning courses.
A student who is diagnosed with dyslexia is eligible to seek additional time while completing tests or assignment. A computer equipped with a spell-check tool can assist one in completing written assignments.
Sophisticated computer software’s that are capable to read printed material aloud are widely available in the market.
The best persons to discuss your needs could be your neighborhood doctor, parents or teachers who will have a greater understanding about dyslexic service providers in your vicinity.
Important Notes
At times of seeking help, many of you might come across suggestions such as eye exercises or prolonged usage of tinted glasses is helpful in treating the condition.
However, it is important to note that these things will not help treat the condition.
Dyslexia is a language disorder and eye-exercises have nothing to do with the condition.
Emotional support is important to each and every person and dyslexic people are no different.
However, it should be noted at times dyslexic people get highly frustrated due to the fact of being unable to keep up with their other peers. At times, these things make them feel unworthy.
However, with proper support and care, everyone involved can guide dyslexic people with their condition and help them achieve the necessary success.
The post An Insightful Guide to Help YOU Understand Everything about Dyslexia appeared first on The Autism Times.
0 notes
Text
Toddlers and Tablets: The effects of touchscreen device usage on cognitive development in children
youtube
Written by: Neha Ogale
The Times Are A-Changing
In the last decade or so, smartphones and tablets have gone from rare luxury devices to essential components of everyday life. Used both interactively and autonomously, these handy smart devices have evolved to serve many purposes, varying from GPS navigation to games and interactive educational games, and even as an apparatus to occupy children’s attention. However, for all its entertainment value and capacity to enrich, many argue that the excessive amount of screen time consumed by children is causing more harm than most would care to acknowledge.
As of 2017, 66 percent of U.S. households own some type of tablet. This means that entire families have access to these devices. However, the proliferation of tablet ownership has been met with an onslaught of criticism: Many fear that tablets have become brainwashing devices that are no longer used as tools, but as digital pacifiers used to quiet petulant children. We can all picture a common scenario: An overwhelmed parent in a crowded restaurant – sensing a massive oncoming temper tantrum from their toddler – reaches into a bag and pulls out an iPad, instantly hypnotizing the kid. Chaos is evaded, and the restaurant keeps its peace.
Though critics of childhood tablet usage may come off as luddites, some of their concerns may be valid. Technology shapes the brain through a phenomenon called neuroplasticity, which is the nervous system’s ability to change in response to experience. Considering that 75 percent of brain development occurs in the first six years of life, questioning the role of tablets in children’s lives is not so bizarre.
The goal of this article is to examine how tablet usage impacts the cognitive aspect of childhood development. Specifically, we will explore the effects of tablets on spatial and verbal reasoning skills.
Education vs. Entertainment: Tapping your way into trouble?
Concern about media’s impact on child development is not new. For decades, researchers have warned that watching TV for more than two hours a day can adversely affect children’s behavior, achievement, and health. Toddlers, in particular, are susceptible. According to the Urban Childhood Institute, the first infant-directed videos and television programs began to appear in the late 90s. Most shows were marketed as educational but many parents used the TV as a babysitter to distract and pacify their children. As a result, infant and toddler exposure to television increased dramatically, with around two-thirds of mothers with three-year-olds reporting that their child watched two hours or more per day. With this increased exposure to TV, researchers studied its impact on toddlers and found a link to behavior problems and to long-term effects on social development, classroom engagement, and academic achievement.
But this is not the whole story. Not all screen time has been found to hinder children’s brain development, particularly when the question turns to what and how children watch rather than just saturation. Research has also shown that co-viewing educational TV shows with a parent can have a positive impact on children’s executive function – this comprises decision making skills, attention, impulse control, and higher-order thinking.
The same benefits can be applied to using educational apps on tablets. The brain responds to stimuli, and children’s brains are especially receptive to them. Tablets, as well as other touchscreen devices, inundate users with a host of visual and auditory signals. Therefore, we should distinguish between passive viewing where a child simply stares at a screen, and active engagement where, for example, a child might use an interactive educational app with other children. Engaging with apps and peers is a useful mechanism of socialization. It gives children the opportunity to learn practical skills like reading and math, as well as social skills like cooperation and conflict resolution.
Another important point to note is that interacting with tablets is largely intuitive. Children as young as one or two years old are learning to swipe and tap at screens before developing fine motor control. These are the skills necessary to grasp a pencil or play an instrument, and typically do not begin developing until early childhood. While educational apps may positively impact expressive language and numeracy, tablets cannot replace children’s need for imagination and unstructured play. Further, research suggests that overuse impedes the sensorimotor and visual skills needed to learn and apply math and science.
In education, tablets have recently gained popularity as e-readers for their convenience of transport. Instead of having to lug stacks of books around everywhere, users have entire on-demand libraries stored on a device weighing under five pounds. Despite the ease of use, reading on tablets may bring about its share of difficulties. A study conducted by the University of Leicester found that students who gleaned information from books understood what they read better than those who read material from tablets.
The difference between reading traditional text versus tablets was limited to comprehension; it does not affect retention. While students who read from traditional text understood the information better than their tablet-reading counterparts, those who read from tablets retained just as much information as those who read from books. However, the study also suggested that reading solely and frequently from tablets may impede children’s ability to understand complex language in later years.
So far, we have discussed the effects of only educational tablet use on development. Moderate and active usage poses cognitive benefits, while overuse threatens impairment. But in a world of easily accessible hollow entertainment like Angry Birds and Candy Crush, we must also address noneducational tablet use and how it affects brain development.
Unlike educational apps, using tablets to play noneducational games doesn’t foster cognitive development – in fact, it seems to do the opposite. A study conducted by Cohen Children’s Medical Center of New York revealed that children ages 0-3 who played noneducational games on tablets had lower verbal scores on developmental tests. Another study found that children who played noneducational games also scored lower in measures of receptive and expressive language compared to children who played educational games. Despite the results, many parents believe that their children would gain some sort of educational benefits solely by using smart phones and tablets.
A common theme in the current research on early and excessive tablet usage – regardless of the type of content – is its correlation with impaired language development. Correlation does not imply causation. But in a time where even professional adults misuse “your/you’re”, children need all the help they can get as early as possible. Struggling to understand language beyond simple sentences and Internet slang is potentially problematic in the name of education. Many high school English curricula teach classic works that often use complex language; students are tested on their understanding of these works and on their ability to discuss what they read intelligently. After all, it’s not easy to talk about or write an essay on something you know nothing about.
Standardized testing is another pressing problem to consider. With the recent redesign of the SAT, 800 of the 1600 possible points are allotted for the verbal reasoning section. This section tests students on sentence completion and reading comprehension, the latter of which can feature a range of topics encompassing natural history, memoir, and 19th century drama – often in succession. Failure to adapt to each type of passage is worrisome, because each section is timed and there are multiple choice questions to be answered after each reading. The SAT predicts college performance and influences admissions decisions, so the importance of earning a good score is paramount.
In higher education, students are often required to read material that is largely theoretical. Government, Political Science, and Economics are just some examples of classes that would require students to read analytical and abstract texts. Furthermore, classes are often flipped classroom style and therefore self-taught, so it is up to the students to be diligent with their reading. College is already an academic challenge; if students lack the cognitive ability to understand what they read, they no doubt face four exceptionally difficult years.
Despite the criticisms, tablets have the potential to be a useful supplement to education. However, icons on screens cannot replace human interaction and imagination. Human interaction is vital during early childhood development and helps to create strong emotional and social bonds between parents and children. While our smart devices may promote learning, we should bear in mind that human interaction is positively correlated with child growth and development. As the technology is still relatively new, the full extent of the effects of tablet usage on childhood development is still unknown. There is simply not enough empirical and statistically significant evidence yet from which to draw definitive conclusions; behavioral scientists face an ocean of uncertainties that they must navigate. After all, the brain is a complex machine, and every answer we find yields many more questions.
via MicroHealth http://ift.tt/2t9D7gk phillip mazzotta
youtube
Written by: Neha Ogale
The Times Are A-Changing
In the last decade or so, smartphones and tablets have gone from rare luxury devices to essential components of everyday life. Used both interactively and autonomously, these handy smart devices have evolved to serve many purposes, varying from GPS navigation to games and interactive educational games, and even as an apparatus to occupy children’s attention. However, for all its entertainment value and capacity to enrich, many argue that the excessive amount of screen time consumed by children is causing more harm than most would care to acknowledge.
As of 2017, 66 percent of U.S. households own some type of tablet. This means that entire families have access to these devices. However, the proliferation of tablet ownership has been met with an onslaught of criticism: Many fear that tablets have become brainwashing devices that are no longer used as tools, but as digital pacifiers used to quiet petulant children. We can all picture a common scenario: An overwhelmed parent in a crowded restaurant – sensing a massive oncoming temper tantrum from their toddler – reaches into a bag and pulls out an iPad, instantly hypnotizing the kid. Chaos is evaded, and the restaurant keeps its peace.
Though critics of childhood tablet usage may come off as luddites, some of their concerns may be valid. Technology shapes the brain through a phenomenon called neuroplasticity, which is the nervous system’s ability to change in response to experience. Considering that 75 percent of brain development occurs in the first six years of life, questioning the role of tablets in children’s lives is not so bizarre.
The goal of this article is to examine how tablet usage impacts the cognitive aspect of childhood development. Specifically, we will explore the effects of tablets on spatial and verbal reasoning skills.
Education vs. Entertainment: Tapping your way into trouble?
Concern about media’s impact on child development is not new. For decades, researchers have warned that watching TV for more than two hours a day can adversely affect children’s behavior, achievement, and health. Toddlers, in particular, are susceptible. According to the Urban Childhood Institute, the first infant-directed videos and television programs began to appear in the late 90s. Most shows were marketed as educational but many parents used the TV as a babysitter to distract and pacify their children. As a result, infant and toddler exposure to television increased dramatically, with around two-thirds of mothers with three-year-olds reporting that their child watched two hours or more per day. With this increased exposure to TV, researchers studied its impact on toddlers and found a link to behavior problems and to long-term effects on social development, classroom engagement, and academic achievement.
But this is not the whole story. Not all screen time has been found to hinder children’s brain development, particularly when the question turns to what and how children watch rather than just saturation. Research has also shown that co-viewing educational TV shows with a parent can have a positive impact on children’s executive function – this comprises decision making skills, attention, impulse control, and higher-order thinking.
The same benefits can be applied to using educational apps on tablets. The brain responds to stimuli, and children’s brains are especially receptive to them. Tablets, as well as other touchscreen devices, inundate users with a host of visual and auditory signals. Therefore, we should distinguish between passive viewing where a child simply stares at a screen, and active engagement where, for example, a child might use an interactive educational app with other children. Engaging with apps and peers is a useful mechanism of socialization. It gives children the opportunity to learn practical skills like reading and math, as well as social skills like cooperation and conflict resolution.
Another important point to note is that interacting with tablets is largely intuitive. Children as young as one or two years old are learning to swipe and tap at screens before developing fine motor control. These are the skills necessary to grasp a pencil or play an instrument, and typically do not begin developing until early childhood. While educational apps may positively impact expressive language and numeracy, tablets cannot replace children’s need for imagination and unstructured play. Further, research suggests that overuse impedes the sensorimotor and visual skills needed to learn and apply math and science.
In education, tablets have recently gained popularity as e-readers for their convenience of transport. Instead of having to lug stacks of books around everywhere, users have entire on-demand libraries stored on a device weighing under five pounds. Despite the ease of use, reading on tablets may bring about its share of difficulties. A study conducted by the University of Leicester found that students who gleaned information from books understood what they read better than those who read material from tablets.
The difference between reading traditional text versus tablets was limited to comprehension; it does not affect retention. While students who read from traditional text understood the information better than their tablet-reading counterparts, those who read from tablets retained just as much information as those who read from books. However, the study also suggested that reading solely and frequently from tablets may impede children’s ability to understand complex language in later years.
So far, we have discussed the effects of only educational tablet use on development. Moderate and active usage poses cognitive benefits, while overuse threatens impairment. But in a world of easily accessible hollow entertainment like Angry Birds and Candy Crush, we must also address noneducational tablet use and how it affects brain development.
Unlike educational apps, using tablets to play noneducational games doesn’t foster cognitive development – in fact, it seems to do the opposite. A study conducted by Cohen Children’s Medical Center of New York revealed that children ages 0-3 who played noneducational games on tablets had lower verbal scores on developmental tests. Another study found that children who played noneducational games also scored lower in measures of receptive and expressive language compared to children who played educational games. Despite the results, many parents believe that their children would gain some sort of educational benefits solely by using smart phones and tablets.
A common theme in the current research on early and excessive tablet usage – regardless of the type of content – is its correlation with impaired language development. Correlation does not imply causation. But in a time where even professional adults misuse “your/you’re”, children need all the help they can get as early as possible. Struggling to understand language beyond simple sentences and Internet slang is potentially problematic in the name of education. Many high school English curricula teach classic works that often use complex language; students are tested on their understanding of these works and on their ability to discuss what they read intelligently. After all, it’s not easy to talk about or write an essay on something you know nothing about.
Standardized testing is another pressing problem to consider. With the recent redesign of the SAT, 800 of the 1600 possible points are allotted for the verbal reasoning section. This section tests students on sentence completion and reading comprehension, the latter of which can feature a range of topics encompassing natural history, memoir, and 19th century drama – often in succession. Failure to adapt to each type of passage is worrisome, because each section is timed and there are multiple choice questions to be answered after each reading. The SAT predicts college performance and influences admissions decisions, so the importance of earning a good score is paramount.
In higher education, students are often required to read material that is largely theoretical. Government, Political Science, and Economics are just some examples of classes that would require students to read analytical and abstract texts. Furthermore, classes are often flipped classroom style and therefore self-taught, so it is up to the students to be diligent with their reading. College is already an academic challenge; if students lack the cognitive ability to understand what they read, they no doubt face four exceptionally difficult years.
Despite the criticisms, tablets have the potential to be a useful supplement to education. However, icons on screens cannot replace human interaction and imagination. Human interaction is vital during early childhood development and helps to create strong emotional and social bonds between parents and children. While our smart devices may promote learning, we should bear in mind that human interaction is positively correlated with child growth and development. As the technology is still relatively new, the full extent of the effects of tablet usage on childhood development is still unknown. There is simply not enough empirical and statistically significant evidence yet from which to draw definitive conclusions; behavioral scientists face an ocean of uncertainties that they must navigate. After all, the brain is a complex machine, and every answer we find yields many more questions.
0 notes
Text
The microbiome goes viral
In this post, I want to return to a topic that started to fascinate me in 2007, namely the microbiome. I published an article (with Iina Hellsten) about the metaphors used to make the microbiome public, but then didn’t do any further research on the topic, apart from writing a blog post stimulated by Jon Turney’s 2015 book I, Superorganism. I recently noticed that over the last few years the microbiome has attracted renewed attention and, indeed, inspired another important book by Ed Yong, I Contain Multitudes. So, I thought it would be worth looking again at the origins and spread of this increasing interest in microbes and us. See also the previous post by Nicholas Staropoli.
The Microbiome Project
In the year 2000, scientists published a first draft of the human genome. In 2003 the Human Genome Project, which had begun in 1990, was completed and the human genome was fully sequenced. In 2001 two microbiologists, David Relman and Stanley Falkow, set out their vision for a second human genome project, the ‘human biome project’.
Relman and Falkow pointed out that: “The human body is host to a myriad of microorganisms. We are still woefully ignorant of the composition and variability of our endogenous microflora. Many of these microorganisms depend on humans for their survival, and yet we still do not fully appreciate to what extent human life is dependent on its microflora. In the spirit of the recent ‘human genome project’ and in the hopes of capturing the imagination of the broad scientific community, it is time to embark on a comprehensive genomic inventory of the large portion of cellular life within the human body that has been ignored so far, the endogenous microflora. […] The human biome is as much an unexplored frontier as the collection of life found at deep-sea thermal vents, if not more so.” (2001: 208)
“The concept of the human microbiome was first suggested by Joshua Lederberg, who coined the term ‘microbiome, to signify the ecological community of commensal, symbiotic, and pathogenic microorganisms that literally share our body space’ (Lederberg and McCray 2001)” (See NIH microbiome project article, 2009).
So, 2001 was the year that the microbiome became a topic for research.
In 2007, the US National Institutes for Health (NIH) launched the Human Microbiome Project (HMP) (a meta-genomics project), stating that “The Microbiome is the full collection of microbes (bacteria, fungi, viruses, etc.) that naturally exist within the human body. Initiatives in this area would focus on developing a deeper understanding of these communities of microbes in order to determine how they affect human health”. In 2008, the International Human Microbiome Consortium was launched “with the mission of generating resources that would enable the comprehensive characterization of the human microbiome and analysis of its role in human health and disease.” (HMP)
At that time a blogger in a (no longer available) post asked “what field might strike the popular consciousness in the coming years. Could it be that it will be the realization that we are all ‘superorganisms’ […] and that our health does not only depend on our personal genome […] and our environment, but also on the extended genome provided by our very private microbiome?”
At first, this realisation didn’t seem happen and the microbiome didn’t really enter ‘popular consciousness’. However, in the last few years it has and the ‘microbiome’ has become a hot topic in science and in the popular media.
The multiple meanings of ‘microbiome’
Before I demonstrate just how popular the microbiome has become, I want to point out that the word ‘microbiome’ has multiple meanings (you can learn more about this here). There are at least two dominant meanings which have emerged over the last two hundred years or so. Formerly, the main meaning was, according to the Oxford English Dictionary: “A population of microorganisms inhabiting a specific environment; a microbial community or ecosystem, now esp. that of the body”. This use is attested in the OED from 1952 onwards (but probably goes back much further). Latterly, the main meaning has become “The collective genomes of all the microorganisms inhabiting a specific environment, esp. that of the body”. This usage is attested in the OED from 2001 onwards and attributed to Lederberg.
The microbiome goes viral
I had looked at early discussions of the microbiome in the news, shortly after the HMP had started. But I hadn’t really checked up on the microbiome’s fate in science and the media since 2008. So, I was surprised when I created various graphs which demonstrated how much the microbiome has risen to prominence, both in science and the media.
Some observers other than me had the same impression. One said: “Over the past decade, research into the microbial organisms that live in and on human beings has exploded dramatically.” Another even talked about a “Cambrian explosion“.
Science
Let’s have a closer look at that explosion. To do that I have used Scopus, the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature (thanks Barbara Ribeiro for pointing me to Scopus analytics).
The following graph shows how scientific interest in the microbiome gradually grew after 2002 and then picked up speed around 2012 (there is a dip in 2017, because Scopus produced the graph for me on 5 May 2017).
In 2002 two seminal papers were published to which I shall come below in the media section, and in 2012 The Human Microbiome Project Consortium published two ‘milestone’ papers in Nature and PLOS. Overall, 12.419 scientific papers on the microbiome have been published up to now (according to Scopus, checked on 5 May, 2017). They appeared in the following journals, with Frontiers in Microbiology playing an important role in the recent wave of publications.
The top three institutions involved in microbiome research are Harvard Medical School, University of California, San Diego and VA Medical Center.
They are mostly situated in the United States, the UK, Canada, Germany and China.
Some of the most prolific authors are Rob Knight (paediatrics and computer science), John F. Cryan (anatomy and neuroscience) and Curtis Huttenhower (computational biology and bioinformatics) – with others on a more or less equal footing:
The subject areas that focus most on microbiome research are medicine, biochemistry, immunology and microbiology, and agriculture and biological sciences. There are 67 articles from the Social Sciences and 56 from the Arts and Humanities (as compared to 7971 from medicine).
Media
What about the media, at least the English language ones? The following graph, counting all articles produced by English speaking news (newspapers, some online sources, magazines etc) and captured by Lexis Nexis, mirrors the rise in scientific interest.
The first article that uses the word ‘microbiome’ was published on 1 April 2003 and was entitled “Aliens Inside US: A (Mostly Friendly) Bacterial Nation” (by James Gorman for The New York Times).
One paragraph is quite significant, as it started a myth that has been dispelled only recently, namely that a human being has 10 times as many bacteria as human cells: “There is a world within each of us, a living, evolving ecological system of 500 to 1,000 species of microbes, a ‘bacterial nation’ in the words of Dr. Jeffrey I. Gordon, a microbiologist at Washington University in St. Louis. In fact, by numbers of cells, a human being has 10 times as many bacteria as human cells. The bacterial cells are much smaller, which is why we do not look like an overgrown petri dish.”
The article was triggered by a paper in Science and a commentary entitled ‘Honor thy symbionts” (by Dr. Gordon, Dr. Jian Xu and others) which suggests that “the powerful techniques of genomic research are providing new ways to investigate the lives of these bacterial cells. In separate reports, scientists describe the genomes of two different, common bacteria. One is Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, a friendly symbiont; the other is a traitorous drug-resistant variant of Enterococcus faecalis, an otherwise mild-mannered garden-variety citizen of the gastrointestinal consortium.”
He introduces the word ‘microbiome’ in the following way: “The possibilities of genomic research into the bacteria of the gut are almost unlimited. Dr. Gordon suggested that one could think of the collected genomes of the bacterial species as a single unit, a microbiome. It would be similar in size to the human genome on the basis of the amount of raw DNA. But it would be much larger, 100 times as large, in terms of actual genes — DNA sequences that code for proteins.”
Jeffrey I. Gordon became, for a while, one of the most prolific metaphor users in the press coverage overall. However, two more articles explored this topic in 2003, one of them written by Lederberg and entitled “We must find a new inner peace” (Milwaukee Journal Sentinel, Wisconsin, 27 April, 2003).
Gordon framed bacteria metaphorically as communities — either a ‘nation’ or an alien race, while Lederberg waged war against the war metaphor according to which bacteria are our enemies. Instead, Lederberg wanted to make peace with bacteria, that is between human and bacterial communities.
Media, marketing and confusion
Then, in 2012, the two landmarks papers mentioned above were published and media interest picked up steadily after that with a current peak in 2016. Now the microbiome (like synthetic biology) meets industry, marketing and (like epigenetics) media confusion.
So, as Matthew Niederhuber points out on blog hosted by Harvard University: “There is promising evidence that the microbiome is intimately involved in human health, including brain function and behavior. But there is equally clear evidence that media coverage walks far ahead of the scientific work it intends to report, too often condensing preliminary, correlative and complex data into pat headlines. As a result, the public impression of microbiotic research differs from the present-day reality, creating the serious risk that pre/probiotics will be marketed as miracle cures for a laundry list of physical and psychological ailments under a pseudo-academic purview. The likely end result is the degradation of public trust in the integrity and validity of scientific research.”
I would be great, if somebody had the time to study changes in metaphors and framing of the microbiome over time from 2007 to 2017, as well as shift in topics from the gut to the brain, from probiotics to faecal microbial transplants and beyond, while also keeping an eye on the fluctuating relationship between hype and reality.
Image: Flickr: Tony Webster – uBiome – Microbiome Sequencing Gut Bacteria Sample Kit
The post The microbiome goes viral appeared first on Making Science Public.
via Making Science Public http://ift.tt/2pF7PN9
0 notes