#that’s most historic buildings in British
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
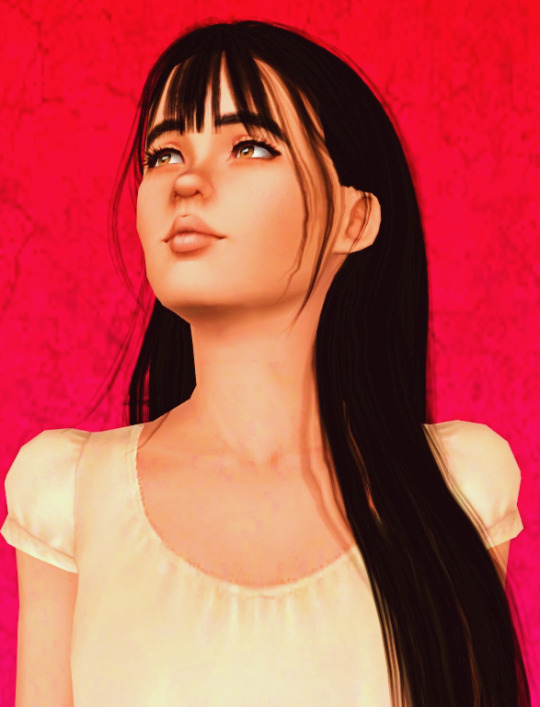
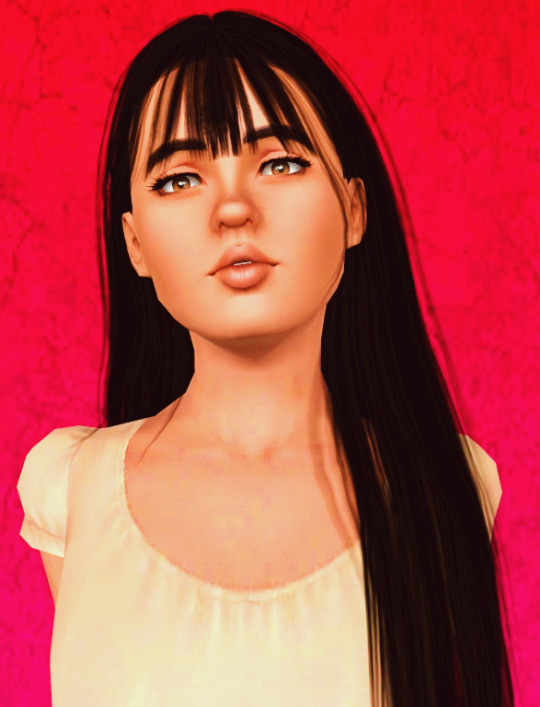


𝓐𝓵𝓲𝓬𝓮 𝓪.𝓴.𝓪 𝓐𝔂𝓮 𝓢𝓾𝓾 - အေးစု
#the sims 3#sims 3#ts3#the sims#simblr#alice mccann#first of all her full name is alice aye suu mccann#as a courtesy to her paternal grandmother who is a bamar born in Myanmar and the most and maybe only truly supportive family member#if we go to historic and therefore realistic conclusions#her grandma moved to the mainland Britain from then British Burma most likely and etc.#she is also the person who raised her mostly#and when alice came out as bisexual to her family after all and admitted being in love with the woman ( cathy )#she supported her unconditionally unlike her parents#i think she will build her future career in clothing business and both she and Cathy will move to the capital London later on
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
A guide to writing fics set in museums / with a museum worker character
Hey hi hello it’s your local museum worker here, offering you some insight and tips to writing museum-related fics! This is primarily organized as a list of different jobs you could have in a museum and what their duties entail. This post might also be useful to you if you’re considering working in museums and want to know What Goes On In There. Let’s go!
For simplicity/fic-writing purposes, I would divide museums into 2 very rough groups: large national or city museums that Have Money (think the Smithsonian or British Museums, or the Chicago Field Museum or the Royal Armouries Museum in Leeds); and smaller local museums. These could be local industry and culture/history-of-our town museums, historic houses, or really niche subject museums run by One Person With A Passion.
Big national museums have a fuckton of staff and money (museums can never have enough money. But these places are very well-off compared to somewhere small that might always be hustling and writing grant applications). If you work here you’re likely to have a specific role in a particular department, and you probably won’t do much outside this role (ex., if you work in collections management, you probably won’t also design exhibits)
The smaller the museum, the more varied your workload will be/the more likely you are to be doing a little bit of everything. You’re probably organizing collections storage, manning the front desk, and desperately running fundraising efforts, all at once.
To this end, smaller museums are more likely to be closed one or two days a week- you’ll be there, probably cleaning displays or managing storage, but visitors won’t be.
A lot of (most?) universities also have museums, so a college town setting is also doable. But the same big vs small museum disparity is still possible! At Penn State University, for example, the Palmer Art Museum is its own (recently redone iirc) building in the center of campus with a lovely plaza out front, while the Matson Museum of Anthropology is uhhhhh a couple classrooms in the Anthropology Department (which they’re currently rebuilding tbf, so we’ll see what they’ve done with it in 2025).
Types of Jobs
Curator
The one museum job that everyone can name. Nominally the person in charge. Probably laments that their job is way more admin than fun hands-on stuff now.
Actually this is the role I have the least knowledge of, but I think that’s partially because this job might vary the most from place to place? Structural organization can vary a lot between institutions, but I think the higher up you get in any field, the more your job tends to consist of meetings/overseeing, designating, and ~liaising~
A list of things a curator might do:
Planning or approving events and fundraisers, schmoozing with donors and members at said events, approving or designing a schedule of exhibits, publish outreach/advertising or research materials, oversee hiring, approve new object acquisitions (or de-acquisitions), generally make sure that the museum is working within the scope of its mission and if necessary, change or refine their mission
The curator might not necessarily control a museum’s funds; in this case they’ll liaise with the people who do, likely a Board of Executives or Board of Trustees. Once they get the money from these people, though, they could potentially redistribute it as they see fit.
If you work in a fuckoff museum like the BM, you could also be the curator of a specific department, arranged by overarching subject, geographic area, time period, or even object type (eg Curator of Archaeobotany, Curator of Korean Collections, curator of coins from the medieval period). These categories can be more or less specific depending on what kind of holdings your museum has. I think these types of curators would still be able to do interesting things, as they aren’t the ones who Oversee The Whole Place.
You can also be an assistant or associate curator, like being an assistant manager.
Education/Engagement
These are the people who design fun extra activities (esp for kids) in the galleries or relevant events/workshops/lectures the public can attend. They might be called Engagement/Education Officer or Events Manager or anything similar
Again, the bigger the museum you work at, the more specific your role is likely to be. You might focus on web content/outreach and social media, manage the ‘friends/members of the museum’ program, or engage with shareholders, etc
Or you might do things like develop content and events to engage adult audiences. Workshops or lectures connected to new exhibits, after-hours visits. These people are also probably the ones with an eye on accessibility- you’ve probably seen advertisements for museums’ early or late hours for older visitors, or ‘quiet hours’ for people who might be overstimulated by normal museum hubbub, or tactile workshops designed for visually impaired folks.
I think most places would try to have someone specific for kids activities at the very least. They’ll be designing little activities or dress-up stations for the galleries, kiddie mascots or scavenger hunt trail kind of things, as well as, potentially, activities for any digital elements in the museum. They probably also coordinate school visits and act as a tour guide for classes, and will lead the kids in specific workshops or lessons in classrooms attached to the museum.
As a note on technology- some people would probably say that integrating digital elements into exhibits is the ~next big thing~, that museums have to get with the times in this regard, but opinions vary. Big science and technology museums are the most likely to have the most digital and techy elements in their exhibits, so if this is your setting, your character could also be a generic “tech person”. I would go so far as to say the smaller/more local the museum, the less technology you’re likely to have, but smaller museums are able to get grants, some of them potentially for specifically this type of thing, so it’s totally possibly that they have a few tablets with integrated activities, or some other Digital/Screen Thing.
Engagement Officers are probably the most likely people to be drafted for out-of-hours events, so that’s a potentially fun thing for your character to do. Some museums, particularly bigger ones, have event spaces attached that anybody can rent out, for weddings, galas, markets, etc, so they might also take care of these bookings as well.
Exhibit Design
This role has a lot of nebulous terms: exhibit coordinator, design constructor, exhibit programmer- but these are the people who design the exhibits. They’ll come up with a theme or narrative, a design scheme, choose the objects, write the text. They’ll probably come up with some marketing material as well, that matches the design scheme, or they’ll liaise with the marketing people who will.
These people might not be as familiar with the collections as the collections management folk (below), depending on how strictly divided your roles are, so they’ll likely consult with the collections people on choosing objects for a particular exhibit or theme (they say that good exhibit design builds an exhibit from the objects up, but I digress).
These people will also direct and participate in the install and deinstall (the actual terms) of exhibits- putting the objects on the right plinths/stands and arranging everything just so in the cases. Genuinely there’s a lot of psychology behind exhibit design- colors, lighting, the way you might design an exhibit to be navigated vs the path people will actually take through the gallery, people’s sight lines and where their eyes go first, how the display of any given object affects people’s perception of the importance of that object. Fascinating stuff, many books on the subject.
There are also a lot of accessibility concerns to be considered here- how bright is the gallery, how large is your display text, at what height is the central eyeline of your cases?
Museums often loan objects to and from each other’s collections, so if you’re building an exhibit and you’d really like to include X type of object but your museum doesn’t have any, you can borrow some from another museum (this isn’t necessarily a guarantee- museums are allowed to say no to these requests, but I think manners would dictate that they should have a good reason)
Museums sometimes tour whole exhibitions as well- the objects, the text placards, maybe even the stands for super special or fragile items- and exhibit coordinator people are the ones who would handle those arrangements.
Potentially good opportunities for angst stories here- wow things come to life at your museum, you fall in love with a statue but oh no it’s only at your museum for three months
Collections Care
People who work in Collections Management have the most direct contact with the museum objects themselves. You probably work here if you prefer objects to people. When a museum gets new material, these are the people involved. They might not always initiate acquisitions, and the final approval is probably down to the relevant curator, but 98% of the time they’d be consulted (I hope).
A mind-boggling statistic is that most museums only have like 10% of their collections on display at any given time. Yeah. Forreal lol. But collections folk will know where the other 90% is and what’s in it (particularly the longer they’ve been there).
There’s usually a head Collections Manager. Other workers might be a Collection Assistant/Associate, Collections Officer (we like calling people Officers for some reason), Registrar, or some variant of these depending on the specific flavor of your duties.
Main job duties can be divided amongst documentation and database work, organization and storage of objects, and lite conservation. Just how much/how technical the conservation work depends on your own training, but also on the size/funding of your museum. The more money, the more likely your museum is to have its own lab with people specifically trained as conservators. More on them later.
Here’s what happens when a museum gets new stuff!:
Ideally, it goes to a ‘quarantine zone’ first. This is a separate space or room where the objects can relax for a few weeks to a few months (ultimate best practice is actually a year, but, you know. that’s a long time) to ensure that they’re not harboring anything icky (bugs, mold, etc) that will infect the rest of the collections. It’s ideally super-sealed and climate-controlled, but the primary feature should be that it’s away from the main collections store.
Collections folk do the paperwork. They’ll give each individual object a unique number (following their preexisting system that will allow it to be identified distinct from all the other objects in the collection). They’ll create a ‘collections record’ for the object- documentation containing any and all information about the object. This includes the accession paperwork (everything that says ‘we legally own this now’); provenance info (all previous owners and everywhere else the object has been in its life); measurements and description (in painful detail); and conservation history and concerns (ie ‘there’s a crack in the side so pick up with care’, ‘this was repaired in the 70s so that glue is gonna fall apart any day now’).
(I'll say as a fic writer that this would be an great time to wax poetic over a beautiful statue or painting; you can’t write “This golden crown deserved to be worn by a great king, or maybe by that broody Roman general in the painting in Gallery B” in the collections paperwork, but you can think it.)
For fiction’s sake, your collections records could be either paper or digital, but in an ideal world a museum would have both setups, for security’s sake. So you’d fill out some long forms and/or input all the information to the digital collections management system (‘the CMS’, or referred to by your specific software’s name, as there are many out there). The CMS is not a static archive, but rather a living register that’s updated every time an object is interacted with. The object records also include where an object is at any given time (‘normally in Case E in the Fancypants Gallery, currently in Conservation Lab A for repairs’).
Once the objects are done in quarantine, they’ll go to storage. If they’re being displayed immediately, they’ll probably go to some interim storage space/shelf with other objects for the same exhibit and in that case only get a temporary setting. Every object will get labeled with their object number (directly on them, with a special pen that’s safe for this. Or if it’s really tiny, like a coin or jewelry, then their own tiny box will get the label). Small or fragile items, or items grouped together, will go in their own boxes (made of acid- and lignin-free cardboard or polyethylene plastic, like Rubbermaid totes; lined with polyethylene foam and then acid-free tissue paper). Stable ceramic vessels might sit directly on lined shelving, particularly if they’re very large or heavy, like many stone objects.
Listen, every type of object has a particular way(s) of storing that’s best for them, you’re gonna have to look that up yourself or consult someone if you need that level of detail
Ideally, before being stored away, objects are also photographed. This could be part of the Collection Officer’s duty, and/or your museum could have a photographer on staff. (say it with me:) This is more likely if your museum is really huge and/or has a backlog of unphotographed collections and has hired someone specifically, even if temporarily, to improve its collections documentation.
I would say a collections person, or anyone with a museum studies degree, should have some minimum amount of conservation knowledge that includes basic storage standards for different object materials, how to spot potential preservation problems (like if your bronze axe head is actively oxidizing or if that green spot looks the same as it always has since starting and pausing decaying), and maybe how to give objects a basic clean or deal with certain types of problems. But the nitty-gritty science is more the realm of Conservators, someone with a degree that ends in -Sci or who’s done some other certification course.
The general collections store should always be dark, slightly too cool for prolonged human comfort, and labeled to high heaven. Objects will most likely be grouped by material- ceramics/pottery, metals, precious metals and stones (jewelry or beads), stone, glass, wood, bone/ivory/other organic material like feathers or teeth or anything that can be decorative, textiles, paintings. A museum often has some paper material/documents, usually part of or related to a group of objects they acquired, but generally paper and photographic material is the realm of archives and archivists. Yet again, the bigger/more well-funded the museum, the more likely it to have a separate archive department, so your character could also work as an archivist in a museum.
Another thing the collections care folk probably do is ship objects. Remember how I said that museums loan objects and exhibitions to each other? The stuff’s gotta travel somehow! If things are being shipped internationally, they’ll go in big wooden crates, with specifically dimensioned partitions inside. Then it will be lined with our favorite foam and tissue paper, cut so the objects sit snugly inside. I haven’t personally worked anywhere with a possibility of local shipments, so I can’t say where the threshold might be as to when a museum would just pay an employee to drive the objects over vs ship them with a shipping company. But the preparations would be similar, minus the big wooden crate but with extra-careful packing (and paperwork and insurance etc)
Conservation
Conservators are the people who work in labs with fancy equipment. Not every museum will have a formal conservator or a lab of any kind; sometimes the collections care person fills this role, or if something urgently needs care beyond the abilities of the museum’s equipment, they might send it away to a lab elsewhere, the same way you can send your old VHS home videos to a professional archive to be digitized.
If an object is actively deteriorating in a way that could harm itself or other objects (as opposed to like, at risk of fading bc the lighting is wrong, which is a straightforward fix related to the environment), that’s when a conservator would intervene.
Some methods/machinery by which you can analyze objects:
Ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) light - Different materials absorb and react to light differently, which you can use to identify them. Useful for seeing things like the different layers of paintings
Stereo-microscopy (microscopes, of varying strengths)
At magnifications of x5-x100 you can see things like tool marks from an object’s manufacture, traces from wear, deposits, and coatings
At x50-x500, with a thin sliver of a sample, you can see (and hopefully identify) fibers, layers, particles, metallographic structures
You can get information from objects without taking samples, but samples are usually worth the information.
energy dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectrometry (EDXRF) - EDXRF allows you to identify the elemental composition of the surface layer of an object. So it might tell you what a tool is made of, and also the composition of the objects it was used on, if they left traces
scanning electron microscopy (SEM) - an SEM uses a focused beam of electrons to produce a magnified, high-resolution image of the surface of an object
X-radiography, both film and digital - X-rayy are beneficial for objects that might be covered by dirt or corrosion and can show you details of an object’s construction or hidden structural weaknesses
I’m not a conservator, so if you want more hard science-based info, ask one of them lol
Listen to me. If you take nothing else away from this post, let it be this:
Once an object is in a museum, it is never seeing natural daylight again. Sunlight is the ultimate enemy of every object’s lifespan. If you need to see an object in the sun or moon light for ~magical spell reasons~, you will straight up be stealing that object to smuggle it outside.
Okay. That being said, you do hear (and could probably google) stories about museum employees stealing things from their museums on purpose to prove a point about security or insurance to their higher-ups, so like. Depending on your type of museum, it might not be impossible to steal from lmao. (Don’t tell anyone I said that.)
Possibly the most useful advice for you to keep in mind when writing your conservator or collections care characters would be that touching objects hurts them. It might not hurt them now, it might not even hurt them in ten years, but every time you handle an object, there’s a risk that you’ll damage it. Not on purpose, obviously, but to err is human. The simplest, most effective advice my conservation professor ever gave us was “don’t handle an object if you don’t have to.” That means don’t move an object without a plan and a place to put it, first examination should always be visual, not tactile, etc. Unfortunately, that means that your character cannot walk around lovingly handling and caressing their favorite objects (unless this is a Night at the Museum situation where the objects are caressing them back, ykwim)
Museum Technician
These people probably have a lot of different names, but basically, technicians are the background muscle of the museum. They do the technical construction of bigger pieces of exhibition material, up to and including the exhibition cases themselves.
So they wouldn’t deal with the small mount that the object rests on, but they might build the big plinth that the mount sits on. They’ll help move things around the building, particularly big heavy things, hang big framed works, assist with exhibit installs, and generally do most things which might involve power tools/equipment or heavy lifting
I worked in a big museum that hired a third party company to supply their technicians; I interviewed at another place that hired their own. If you’re a small museum, you might just have a freelance person that comes in once or twice a week to help move things.
Other
Other miscellaneous roles one could have in a museum: researcher (for exhibits and/or collections), gift shop or cafe worker, security guard, room attendant, translator, archaeologist, consultant
Honestly, TL;DR? Just have your character be a consultant of some kind. “Oh no, I don’t work here, I’m Y’s friend. They called me in to provide some expertise on X subject that they’re doing an exhibit on.” This could work for literally any subject- history/archaeology/anthropology, art, transportation, science and technology, anything you might find pictures of in an archive, idk. This could get you into an office or meeting room of some kind in the ‘employee only’ space of the museum, or potentially all the way into the collections store if you’re giving them information they were missing about some objects. Otherwise you’d probably (hopefully) need a key or some other kind of security clearance to get into the collections store.
Whew, that was a ride, huh? I hope this guide was useful to someone! I’m always open to answering questions if you think I forgot something or if anyone wants more details <3
#hopefully this is useful to people as Gladiator II comes out <3#i dont really know how to tag this lol#museums#fic advice#writing advice#reference#writing resources
520 notes
·
View notes
Text
Employers desire foreign workers who are accustomed to the hazardous work sites of industrial construction; in particular, they specifically solicit migrants who do not have a history of labor organizing within SWANA. In response, labor brokerage firms brand themselves as offering migrant workers who are deferential. Often, labor brokers conflate the category of South Asian with docility; [...] as inherently passive, disciplined, and, most important, unfettered by volatile working conditions. "We say quality, they [U.S. employers] say seasoned. We both know what it means. Workers who are not going to quit, not going to run away in the foreign country and do as they are told.” [...]
For migrants, the U.S. oil industry presents a rare chance to apply their existing skill set in a country with options for permanent residency and sponsorship of family members. Migrants wish to find an end to their temporary worker status; they imagine the United States as a liberal economy in which labor standards are enforced and there are opportunities for citizenship and building a life for their family. [...] What brokers fail to explain is that South Asian migrants are being recruited as guest workers. Migrants will not have access to U.S. citizenship or visas for family members; in fact, their employment status will be quite similar to their SWANA migration.
While nations such as the Philippines have both state-mandated and independent migrant rights agencies, the Indian government has minimal avenues for worker protection. These are limited to hotlines for reporting abusive foreign employers and Indian consulates located in a few select countries of the SWANA region. [... Brokers] emphasize the docility of Indian migrants in comparison to the disruptive tendencies of other Asian migrant workers. [...] “Some of these Filipino men you see make a lot of trouble in the Arab countries. Even their women, who work as maids and such, lash out. The employer says one wrong thing and the workers get the whole country [the Philippines] on the street. [...] But you don’t see our people creating a tamasha [spectacle] overseas.” [...] Just as Filipinx migrants are racialized to be undisciplined labor, Indian brokers construct divisions within the South Asian workforce to promote the primacy of their own firms. In particular, Pakistani workers are racialized as an abrasive population.
[...] While the public image of the South Asian American community remains as model minorities, presumed to be primarily upwardly mobile professionals, the global reality of the population is quite to the contrary. [...] From the historic colonial routes initiated by British occupation of South Asia to the emergence of energy markets within the countries of SWANA, migrants have been recruited to build industries by contributing their labor to construction projects. Within the last decade, these South Asian migrants, with experience in the SWANA oil industry, have been actively solicited as guest workers into the energy sector of the United States. The growth of hydraulic fracturing has opened new territory for oil extraction; capitalizing on the potential market are numerous stakeholders who have invested in industrial construction projects across the southwestern United States. The solicitation of South Asian construction workers is not coincidental. [...] Kartik, a globally competitive firm’s broker, explains the connection of Indian labor to practices of the past. “You know we come from a long history of working in foreign lands. Even the British used to send us to Africa and the Arab regions to work in the mines and oil fields. It’s part of our history.”
Seasoning Labor: Contemporary South Asian Migrations and the Racialization of Immigrant Workers, Saunjuhi Verma in the Journal of Asian American Studies
669 notes
·
View notes
Text





So, with the new legends there's a neat way we can take a guess at some of the time frame. Although it's largely aesthetic and hard to gauge the intended historical parallels of, the not-Eiffel Tower at the center of the city could presumably have been completed in the late 1880s like the real thing. Interestingly that places it pretty concurrent to the construction of the Hokkaido Government building in the 1870s that served as the basis of the Galaxy Team HQ in the first Legends game.

But with the keywords being "urban redevelopment" the setting could only possibly be Haussman's renovation of Paris that took place from the 1850s-1920s. So given that the tower is already standing, that places Legends Z-A between 1889 and 1927.
And I doubt it would play into the setting of a Pokemon game but I think it's neat that it would mean taking place firmly in the 3rd French Republic, as that's not typically the most romanticized period of French history. (Kind of shocking given just how much Japanese pop culture loves to fixate on the Ancien Regime and Rococco architecture.) It's right at the height of the French Colonial empire and their rivalry with the British... Even if they don't address the history directly, certainly not the darker bits, I wonder if we'll see an ancestor of Rose* and some mention of Kalos and Galar's relation as a hint at the Pokemon world's equivalent of India. (Elephant, what elephant...)
*put a pin in that... Well come back to Rose later...

Also I know a lot of the stupid "leaks" that were just running with any/every rumor they could find had been talking about Celebi, despite there being no signs of it in the direct, but it's possible that the Z-A title and the fadethru of the sort of sci-fi looking city diagram into a pencil and parchment one is indicating going back in time --backwards, from Z to A, end to start.
and just so long as I'm just picking at edges of things...
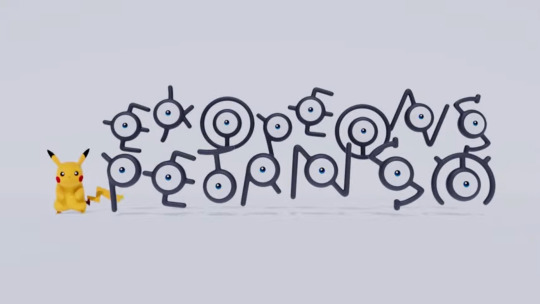

The unknown are an anagram of, "POKEMON PRESENTS"(oh and the SOEYUE one at the end is just "SEE YOU") and the ""confidential"" stamp on the documents likely reads "Gokuhi" as in gokuhi[極秘]: "Top Secret," but the rest of the text doesn't seem to match either Japanese, French, or English,




Hito to POKEMON no kyouzon o yumemite[人と ポケモンの共存を夢見て]: "Dreaming of people and Pokemon's coexistence" Toshisaikaibatsu hassou MIARE CITY[都市再開発発想ミアレシティ]: "Urban Redevelopment Concept Miare City"
The obvious exception being that redacted text is clearly the romanized MIARE from the Japanese MIARE[ミアレ] and the English CITY, which is the Japanese name for what was localized as "Lumiose."
Curiously the word "Pokemon" is very clearly missing from the passage, and also in both cases there are too few "Galarian" characters for how long the phrases are in any actual language.

and finally, given some of the existing examples of handwritten Galarian in SwSh, I'm guessing the text on the big logo is as i've transcribed into the more standard Galar font, although I'm really uncertain about that second one, and a bit iffy about the big "X"s, but the little cyclone O, the V with the underbar, and the E seem certain enough.
Also there's a logo I know I remember seeing that looks like this one but I can't remember where it is or what it's associated with.... It's the logo on the Macro Cosmos power plant. Not Rose's personal logo with the stylized rose, and not the Cosmos business logo with the big star system orbital ring Cs, but the power plant in Hammerlock where you go to fight Eternatus specifically.
It would be really neat if whatever this organization is was tied back to an ancestor of Rose and Peony and the origins of Macro Cosmos somehow.


682 notes
·
View notes
Note
Gender and Harry Potter is such a hydra that just keeps revealing more heads the more you try and chop through it. Case in point: Today I just realized Harry Potter might've been originally intended as a book for boys, which if it was *wow*, way to miss the mark Joanne. Do you think it was actually intended for a male audience? To me it kinda makes sense if it was because of the way most women and girls are portrayed in it.
Bloomsbury Publishing definitely requested that JK Rowling publish with her (gender neutral) initials instead of 'Joanne Rowling' because they were concerned boys would not buy a book with a woman's name on the cover.
My guess is that her British publishers slotted it more firmly under 'boy' than her American publishers did. Harry Potter is 100% a school story, a super established British children's book genre. Historically, there are boy school stories (set in all-male posh public schools) and girl school stories (set in all-female posh public schools.) Hogwarts is of course co-ed, but that fact that it comes out of a literary tradition in which all the characters are the same gender... might help explain why in-universe gender politics seem remarkably absent from the wizarding world.
It actually kind of bugs me, when a canon-compliant fic makes a big deal about male-only inheritance or something, because that's just not something we see. There's one line about "Black family tradition" saying that the house goes to the next oldest guy, but since Dumbledore is worried that *Bellatrix* is about to inherit, it clearly isn't that important.
JKR has made a fantasy society where gender doesn't really matter - Augusta Longbottom and Walburga Black are clearly the powerful matriarchs of their respective families, Maxime and McGonagall are headmistresses, no problem. There isn't the boys quidditch team vs girl's quidditch team, the locker rooms and the prefects bathroom seem to be co-ed, "robes" are gender neutral, there isn't a sense that a specific discipline or type of magic is gendered (we see both male and female Transfiguration, Care of Magical creatures, and Defense Against the Dark arts professors...) There is kind of a sense that the boys are supposed to ask the girls to the yule ball... but multiple girls still ask out Harry. Gender comes up a lot in these books yes, but not so much in the actual worldbuilding. We have gendered bathrooms and dorms, and the rule that the girls can go into the boy's dormitory, but not vice-versa. Ron considers lace a girly fabric. Of the top of my head, that's all of the "gendered" rules I can think of.
But, since the main character is a boy, it makes sense that her British publishers would slot it more into the category of "school story (boy)" and market accordingly. I think it's extremely likely that she was asked to lean more heavily into quidditch, an aspect of the world building that JKR is clearly not interested in. She's said multiple times that she dislikes writing quidditch games - which is why she throws in comedy with the commentary, or makes some magical thing go down, or finds ways to cancel quidditch entirely. The mechanics and tension of the game *itself* are not interesting to her. I think it's also possible this is a reason for Hermione's relatively late intro into the friend group during Book 1? Harry can be friends with a girl, but first we need to establish that Ron is his *best* friend.
But then the books hit America, and the whole "school story" thing didn't read as "boy" as much as it just read "British." There was a sense in American advertising, especially in the 90s, that girl's products were for girls, but boy's products were for everyone. Scholastic Publishing seemed less interested in gendering the book, and more interested in making sure it didn't come off as too high-brow to American children - so we get the name change from "Philosopher's Stone" to "Sorcerer's Stone," things like that.
But then right before the publication of Book 4 the series exploded, and JKR could have just self-published the thing if her publishers didn't behave. So I think that you can see the fingerprints of that marketing push on Book 1, which grandfathered in a number of worldbuilding choices that JKR maybe wouldn't have made later. But pretty quickly it just became JKR doing her thing.
75 notes
·
View notes
Note
I honestly don’t think Pentious coming forward about Jack the Ripper would have even led to him getting caught. At least viewing the Ripper case historically. Depending on when Pentious would nut up, anyway.
Part of what made Jack the Ripper so hard to catch was how huge the case exploded out of control. Authorities had a consistent stream of phoney accounts, fakes claiming someone they knew was/encountered Jack, and the dozens and dozens of letters being sent by people pretending to be him. Some factory owner claiming he saw the Super Secret Unknown TRUE First Victim of Jack the Ripper would get discarded, buried, and lost as some asshole looking to get a piece of the fame.
The other part that left the case unsolved is the same as most unsolved murders; there just wasn’t any concrete evidence definitively tying any of the big suspects (of which there were many). Two of the prime suspects had DNA evidence at various scenes, but even then not enough of a smoking gun to get a confession or conviction. And considering witness testimonies are often very shakey and unreliable to build a case off of, if police HAD followed up with Pentious, if Helluverse Jack was a powerful elite, any lawyer would have poked holes and discredited his testimony completely.
And that’s another pet peeve I have here; I get that it’s a fictionalized version here, but the idea that Jack was some high-class lord who could just get away with his crimes because he was rich doesn’t hold up under any actual examination of the evidence, and came around in the 1960s. The suspect with the most high-standing was a schoolteacher; all the other suspects were either journalists, sailors, painters, barbers. Even when the case was re-examined in the 80s and compared to more recent killers, they came to the same conclusion. Whoever The Ripper was, he was most likely some antisocial working class guy that already lived on the East End that, for some reason, started murdering prostitutes for sport. Also he was probably left-handed, something the Victorian British Upperclass hated.
This, this, all of this. If you're going to base your character's life and death around Jack the Ripper and have him living in the same neighborhood and witnessing the death of a real human being who actually existed, at least try to act like you gave enough of a shit to open a book.
Also, the idea that Jack the Ripper was some wealthy guy in a sexy black coat and top hat is fun, but it's nonsense and in this case, borderline offensive. He would have stuck out like a sore thumb. In actuality, like you said, Jack the Ripper was probably a normal looking working class guy who could blend in with a crowd and knew his way around the East End.
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Power Of Ley Lines

Ley lines are straight lines or tracks, essentially energy grids that stretch across the earth in every direction. The ancients marked these lines with stone monuments and pagan temples. Our ancient ancestors could feel the magick and power emanating from these lines, so they set up natural sanctuaries and called the intersections of the ley lines sacred places.
If we look at some of the world's most important sites on a map, we can draw straight lines between them. These lines form a grid-like pattern across the entire surface of the planet. Stonehenge, the Great Pyramids of Giza, and Machu Pichu are sacred sites the connect, through the lines, with many other sites, including landmarks like Mt. Everest.
You won't find the ley lines on a typical geographical map or in a history book. They are mostly a topic in occult books or folklore. The contemporary concept was developed by Alfred Watkins in 1921, who believed so strongly in ley lines that he organized a group, that gathered in England and walked the countryside in search of them.
Faerie Paths and Corpse Roads
Spirits often travel the earth along ley lines. In England and throughout Europe there is a concept referred to as a 'corpse road'. A corpse road was a path taken by funerary processions to escort the recently deceased to their final resting place. Terrifying stories are told of supernatural creatures on corpse trails that, more often than not, correspond with ley lines.
Faeries, also known as the Fae, the Fair Folk, or the Sidhe, are known to travel along specified paths as well. There are many stories from Ireland and the British Isles that describe Faerie pathways leading into hills or over Fae bridges. These paths also follow ley lines. People are warned not to ever travel a Fae path during twilight hours (dawn or dusk) or at night, for fear the Faeries would steal them away.
The Importance of Ley Lines Today
Though the concept has ancient roots, ley lines are just as relevant in modern practice and very much affect us. The planet is like a living being, in and of itself. It produces energetic vibrations that we can both feel and interact with, if the conditions are right. The ley lines are like earth's veins; sacred sites where the planet allows us to easily tap into her essence.
Of you feel particularly revitalized after visiting your secret hiking spot, swimming in a body of water, or digging your toes into a patch of dirt or moss, then you know a taste of the potency that comes with being near a ley line.

The Affects of Ley Lines
• If your home is on a ley line, it may make thr energy more intense or chaotic.
• You may not be able to relax and sleeping may be difficult.
• You may experience increased paranormal activity, including apparitions, disembodied voices, and encounters with spirits, Faeries, or elementals.
• If your business is on a ley line, you will most likely notice an increase in energy, positive or negative. Your business may be considered haunted.
• When ley lines intersect, any building located on the intersection will have a constant flow of energy. This will cause supernatural occurrences and regular chaos.
• At ancient/sacred sites on ley lines, you will experience spiritual development, enlightenment, awakenings, visions, feelings of peace, messages from beyond or spiritual downloads.
Discovering Nearby Ley Lines
Finding your local ley lines is easier than one wound expect. Think of any historical landmarks in your area. Native, ancient, and pagan landmarks are excellent starting points, as are caves, rivers/creeks, manmade mounds, burial grounds, etc. The ancient natives were very in tune with nature and knew the lines intimately.
In addition, consider local sites with well-known hauntings, supernatural activity, or legends attached to them. Locations with high paranormal activity are most often on or near a ley line. For example, Gettysburg PA, Washington DC, and further, every state capital are located on ley lines.
Locating a Ley Line
After investigating your local sites and finding possible line spots, it's time to make the journey to confirm it in person. This is a sacred journey and you should prepare as such. Cleanse yourself before traveling to any sacred place so you can be as spiritually pure as possible. This will make the energy from the lines easier to sense. It's also a wise idea to bring along a pendulum or dowsing rods. Once there, be open to any sensation. You may feel nervous or excited.
You can dowse and find which areas have the highest energetic charge, test each place with the pendulum/rods, if they spin or swing vigorously, you are very close to the ley line.

Ley Line Magick
In addition to being excellent places for spirit work and necromancy, the energy of the lines can be harnessed to super charge manifestation. Enlightenment is primary. It should go without saying that visiting a ley line give you divine insight, spiritual downloads, and/or a total spiritual awakening.
Healing is another prominent form of magick performed at ley lines. While there, ask the earth and the spirits to send healing vibrations up through your feet and throughout your entire being. Stand still for a while and feel the healing energy pulse through your body. Few sensations match this potent connection.
Other forms of ley line magick include drawing love, abundance, meditation, grounding, cleansing, and charging. You can perform entire rituals on top of ley lines to add primal power to the working and drastically increase the success rate of your spell.
Ley Lines in the US
• Montana Megaliths, MT
• Pryor Mountains, MT
• Bighorn Medicine Wheel, NY
• Sedona, AZ
• Serpent Mound, OH
• Mount Shasta, CA
• Mount Denali, AK
• Tocobaga Indian Mound, FL
• Uinta Basin, UT
• Chicago, IL (Lake Michigan)
• Yellowstone National Park, WI
• Pine Barrens, NJ

#ley lines#sacred#sacred places#sacred space#magick#witchcraft#manifesation#witch#spiritual journey#spiritual awakening#hiking#nature#nature witch#eclectic#pagan#witchblr#witch community#haunted#haunting#historical sites#history
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
SARS-CoV-2 is now circulating out of control worldwide. The only major limitation on transmission is the immune environment the virus faces. The disease it causes, COVID-19, is now a risk faced by most people as part of daily life.
While some are better than others, no national or regional government is making serious efforts towards infection prevention and control, and it seems likely this laissez-faire policy will continue for the foreseeable future. The social, political, and economic movements that worked to achieve this mass infection environment can rejoice at their success.
Those schooled in public health, immunology or working on the front line of healthcare provision know we face an uncertain future, and are aware the implications of recent events stretch far beyond SARS-CoV-2. The shifts that have taken place in attitudes and public health policy will likely damage a key pillar that forms the basis of modern civilized society, one that was built over the last two centuries; the expectation of a largely uninterrupted upwards trajectory of ever-improving health and quality of life, largely driven by the reduction and elimination of infectious diseases that plagued humankind for thousands of years. In the last three years, that trajectory has reversed.
The upward trajectory of public health in the last two centuries Control of infectious disease has historically been a priority for all societies. Quarantine has been in common use since at least the Bronze Age and has been the key method for preventing the spread of infectious diseases ever since. The word “quarantine” itself derives from the 40-day isolation period for ships and crews that was implemented in Europe during the late Middle Ages to prevent the introduction of bubonic plague epidemics into cities.
Modern public health traces its roots to the middle of the 19th century thanks to converging scientific developments in early industrial societies:
The germ theory of diseases was firmly established in the mid-19th century, in particular after Louis Pasteur disproved the spontaneous generation hypothesis. If diseases spread through transmission chains between individual humans or from the environment/animals to humans, then it follows that those transmission chains can be interrupted, and the spread stopped. The science of epidemiology appeared, its birth usually associated with the 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak in London during which the British physician John Snow identified contaminated water as the source of cholera, pointing to improved sanitation as the way to stop cholera epidemics. Vaccination technology began to develop, initially against smallpox, and the first mandatory smallpox vaccination campaigns began, starting in England in the 1850s.
The early industrial era generated horrendous workplace and living conditions for working class populations living in large industrial cities, dramatically reducing life expectancy and quality of life (life expectancy at birth in key industrial cities in the middle of the 19th century was often in the low 30s or even lower). This in turn resulted in a recognition that such environmental factors affect human health and life spans. The long and bitter struggle for workers’ rights in subsequent decades resulted in much improved working conditions, workplace safety regulations, and general sanitation, and brought sharp increases in life expectancy and quality of life, which in turn had positive impacts on productivity and wealth.
Florence Nightingale reemphasized the role of ventilation in healing and preventing illness, ‘The very first canon of nursing… : keep the air he breathes as pure as the external air, without chilling him,’ a maxim that influenced building design at the time.
These trends continued in the 20th century, greatly helped by further technological and scientific advances. Many diseases – diphtheria, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, etc. – became things of the past thanks to near-universal highly effective vaccinations, while others that used to be common are no longer of such concern for highly developed countries in temperate climates – malaria, typhus, typhoid, leprosy, cholera, tuberculosis, and many others – primarily thanks to improvements in hygiene and the implementation of non-pharmaceutical measures for their containment.
Furthermore, the idea that infectious diseases should not just be reduced, but permanently eliminated altogether began to be put into practice in the second half of the 20th century on a global level, and much earlier locally. These programs were based on the obvious consideration that if an infectious agent is driven to extinction, the incalculable damage to people’s health and the overall economy by a persisting and indefinite disease burden will also be eliminated.
The ambition of local elimination grew into one of global eradication for smallpox, which was successfully eliminated from the human population in the 1970s (this had already been achieved locally in the late 19th century by some countries), after a heroic effort to find and contain the last remaining infectious individuals. The other complete success was rinderpest in cattle9,10, globally eradicated in the early 21st century.
When the COVID-19 pandemic started, global eradication programs were very close to succeeding for two other diseases – polio and dracunculiasis. Eradication is also globally pursued for other diseases, such as yaws, and regionally for many others, e.g. lymphatic filariasis, onchocerciasis, measles and rubella. The most challenging diseases are those that have an external reservoir outside the human population, especially if they are insect borne, and in particular those carried by mosquitos. Malaria is the primary example, but despite these difficulties, eradication of malaria has been a long-standing global public health goal and elimination has been achieved in temperate regions of the globe, even though it involved the ecologically destructive widespread application of polluting chemical pesticides to reduce the populations of the vectors. Elimination is also a public goal for other insect borne diseases such as trypanosomiasis.
In parallel with pursuing maximal reduction and eventual eradication of the burden of existing endemic infectious diseases, humanity has also had to battle novel infectious diseases40, which have been appearing at an increased rate over recent decades. Most of these diseases are of zoonotic origin, and the rate at which they are making the jump from wildlife to humans is accelerating, because of the increased encroachment on wildlife due to expanding human populations and physical infrastructure associated with human activity, the continued destruction of wild ecosystems that forces wild animals towards closer human contact, the booming wildlife trade, and other such trends.
Because it is much easier to stop an outbreak when it is still in its early stages of spreading through the population than to eradicate an endemic pathogen, the governing principle has been that no emerging infectious disease should be allowed to become endemic. This goal has been pursued reasonably successfully and without controversy for many decades.
The most famous newly emerging pathogens were the filoviruses (Ebola, Marburg), the SARS and MERS coronaviruses, and paramyxoviruses like Nipah. These gained fame because of their high lethality and potential for human-to-human spread, but they were merely the most notable of many examples.
Such epidemics were almost always aggressively suppressed. Usually, these were small outbreaks, and because highly pathogenic viruses such as Ebola cause very serious sickness in practically all infected people, finding and isolating the contagious individuals is a manageable task. The largest such epidemic was the 2013-16 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, when a filovirus spread widely in major urban centers for the first time. Containment required a wartime-level mobilization, but that was nevertheless achieved, even though there were nearly 30,000 infections and more than 11,000 deaths.
SARS was also contained and eradicated from the human population back in 2003-04, and the same happened every time MERS made the jump from camels to humans, as well as when there were Nipah outbreaks in Asia.
The major counterexample of a successful establishment in the human population of a novel highly pathogenic virus is HIV. HIV is a retrovirus, and as such it integrates into the host genome and is thus nearly impossible to eliminate from the body and to eradicate from the population (unless all infected individuals are identified and prevented from infecting others for the rest of their lives). However, HIV is not an example of the containment principle being voluntarily abandoned as the virus had made its zoonotic jump and established itself many decades before its eventual discovery and recognition, and long before the molecular tools that could have detected and potentially fully contained it existed.
Still, despite all these containment success stories, the emergence of a new pathogen with pandemic potential was a well understood and frequently discussed threat, although influenza viruses rather than coronaviruses were often seen as the most likely culprit. The eventual appearance of SARS-CoV-2 should therefore not have been a huge surprise, and should have been met with a full mobilization of the technical tools and fundamental public health principles developed over the previous decades.
The ecological context One striking property of many emerging pathogens is how many of them come from bats. While the question of whether bats truly harbor more viruses than other mammals in proportion to their own species diversity (which is the second highest within mammals after rodents) is not fully settled yet, many novel viruses do indeed originate from bats, and the ecological and physiological characteristics of bats are highly relevant for understanding the situation that Homo sapiens finds itself in right now.
Another startling property of bats and their viruses is how highly pathogenic to humans (and other mammals) many bat viruses are, while bats themselves are not much affected (only rabies is well established to cause serious harm to bats). Why bats seem to carry so many such pathogens, and how they have adapted so well to coexisting with them, has been a long-standing puzzle and although we do not have a definitive answer, some general trends have become clear.
Bats are the only truly flying mammals and have been so for many millions of years. Flying has resulted in a number of specific adaptations, one of them being the tolerance towards a very high body temperature (often on the order of 42-43ºC). Bats often live in huge colonies, literally touching each other, and, again, have lived in conditions of very high density for millions of years. Such densities are rare among mammals and are certainly not the native condition of humans (human civilization and our large dense cities are a very recent phenomenon on evolutionary time scales). Bats are also quite long-lived for such small mammals – some fruit bats can live more than 35 years and even small cave dwelling species can live about a decade.
These are characteristics that might have on one hand facilitated the evolution of a considerable set of viruses associated with bat populations. In order for a non-latent respiratory virus to maintain itself, a minimal population size is necessary. For example, it is hypothesized that measles requires a minimum population size of 250-300,000 individuals. And bats have existed in a state of high population densities for a very long time, which might explain the high diversity of viruses that they carry. In addition, the long lifespan of many bat species means that their viruses may have to evolve strategies to overcome adaptive immunity and frequently reinfect previously infected individuals as opposed to the situation in short-lived species in which populations turn over quickly (with immunologically naive individuals replacing the ones that die out).
On the other hand, the selective pressure that these viruses have exerted on bats may have resulted in the evolution of various resistance and/or tolerance mechanisms in bats themselves, which in turn have driven the evolution of counter strategies in their viruses, leading them to be highly virulent for other species. Bats certainly appear to be physiologically more tolerant towards viruses that are otherwise highly virulent to other mammals. Several explanations for this adaptation have been proposed, chief among them a much more powerful innate immunity and a tolerance towards infections that does not lead to the development of the kind of hyperinflammatory reactions observed in humans, the high body temperature of bats in flight, and others.
The notable strength of bat innate immunity is often explained by the constitutively active interferon response that has been reported for some bat species. It is possible that this is not a universal characteristic of all bats – only a few species have been studied – but it provides a very attractive mechanism for explaining both how bats prevent the development of severe systemic viral infections in their bodies and how their viruses in turn would have evolved powerful mechanisms to silence the interferon response, making them highly pathogenic for other mammals.
The tolerance towards infection is possibly rooted in the absence of some components of the signaling cascades leading to hyperinflammatory reactions and the dampened activity of others.
An obvious ecological parallel can be drawn between bats and humans – just as bats live in dense colonies, so now do modern humans. And we may now be at a critical point in the history of our species, in which our ever-increasing ecological footprint has brought us in close contact with bats in a way that was much rarer in the past. Our population is connected in ways that were previously unimaginable. A novel virus can make the zoonotic jump somewhere in Southeast Asia and a carrier of it can then be on the other side of the globe a mere 24-hours later, having encountered thousands of people in airports and other mass transit systems. As a result, bat pathogens are now being transferred from bat populations to the human population in what might prove to be the second major zoonotic spillover event after the one associated with domestication of livestock and pets a few thousand years ago.
Unfortunately for us, our physiology is not suited to tolerate these new viruses. Bats have adapted to live with them over many millions of years. Humans have not undergone the same kind of adaptation and cannot do so on any timescale that will be of use to those living now, nor to our immediate descendants.
Simply put, humans are not bats, and the continuous existence and improvement of what we now call “civilization” depends on the same basic public health and infectious disease control that saw life expectancy in high-income countries more than double to 85 years. This is a challenge that will only increase in the coming years, because the trends that are accelerating the rate of zoonotic transfer of pathogens are certain to persist.
Given this context, it is as important now to maintain the public health principle that no new dangerous pathogens should be allowed to become endemic and that all novel infectious disease outbreaks must be suppressed as it ever was.
The death of public health and the end of epidemiological comfort It is also in this context that the real gravity of what has happened in the last three years emerges.
After HIV, SARS-CoV-2 is now the second most dangerous infectious disease agent that is 'endemic' to the human population on a global scale. And yet not only was it allowed to become endemic, but mass infection was outright encouraged, including by official public health bodies in numerous countries.
The implications of what has just happened have been missed by most, so let’s spell them out explicitly.
We need to be clear why containment of SARS-CoV-2 was actively sabotaged and eventually abandoned. It has absolutely nothing to do with the “impossibility” of achieving it. In fact, the technical problem of containing even a stealthily spreading virus such as SARS-CoV-2 is fully solved, and that solution was successfully applied in practice for years during the pandemic.
The list of countries that completely snuffed out outbreaks, often multiple times, includes Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Bhutan, Cuba, China, and a few others, with China having successfully contained hundreds of separate outbreaks, before finally giving up in late 2022.
The algorithm for containment is well established – passively break transmission chains through the implementation of nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) such as limiting human contacts, high quality respirator masks, indoor air filtration and ventilation, and others, while aggressively hunting down active remaining transmission chains through traditional contact tracing and isolation methods combined with the powerful new tool of population-scale testing.
Understanding of airborne transmission and institution of mitigation measures, which have heretofore not been utilized in any country, will facilitate elimination, even with the newer, more transmissible variants. Any country that has the necessary resources (or is provided with them) can achieve full containment within a few months. In fact, currently this would be easier than ever before because of the accumulated widespread multiple recent exposures to the virus in the population suppressing the effective reproduction number (Re). For the last 18 months or so we have been seeing a constant high plateau of cases with undulating waves, but not the major explosions of infections with Re reaching 3-4 that were associated with the original introduction of the virus in 2020 and with the appearance of the first Omicron variants in late 2021.
It would be much easier to use NPIs to drive Re to much below 1 and keep it there until elimination when starting from Re around 1.2-1.3 than when it was over 3, and this moment should be used, before another radically new serotype appears and takes us back to those even more unpleasant situations. This is not a technical problem, but one of political and social will. As long as leadership misunderstands or pretends to misunderstand the link between increased mortality, morbidity and poorer economic performance and the free transmission of SARS-CoV-2, the impetus will be lacking to take the necessary steps to contain this damaging virus.
Political will is in short supply because powerful economic and corporate interests have been pushing policymakers to let the virus spread largely unchecked through the population since the very beginning of the pandemic. The reasons are simple. First, NPIs hurt general economic activity, even if only in the short term, resulting in losses on balance sheets. Second, large-scale containment efforts of the kind we only saw briefly in the first few months of the pandemic require substantial governmental support for all the people who need to pause their economic activity for the duration of effort. Such an effort also requires large-scale financial investment in, for example, contact tracing and mass testing infrastructure and providing high-quality masks. In an era dominated by laissez-faire economic dogma, this level of state investment and organization would have set too many unacceptable precedents, so in many jurisdictions it was fiercely resisted, regardless of the consequences for humanity and the economy.
None of these social and economic predicaments have been resolved. The unofficial alliance between big business and dangerous pathogens that was forged in early 2020 has emerged victorious and greatly strengthened from its battle against public health, and is poised to steamroll whatever meager opposition remains for the remainder of this, and future pandemics.
The long-established principles governing how we respond to new infectious diseases have now completely changed – the precedent has been established that dangerous emerging pathogens will no longer be contained, but instead permitted to ‘ease’ into widespread circulation. The intent to “let it rip” in the future is now being openly communicated. With this change in policy comes uncertainty about acceptable lethality. Just how bad will an infectious disease have to be to convince any government to mobilize a meaningful global public health response?
We have some clues regarding that issue from what happened during the initial appearance of the Omicron “variant” (which was really a new serotype) of SARS-CoV-2. Despite some experts warning that a vaccine-only approach would be doomed to fail, governments gambled everything on it. They were then faced with the brute fact of viral evolution destroying their strategy when a new serotype emerged against which existing vaccines had little effect in terms of blocking transmission. The reaction was not to bring back NPIs but to give up, seemingly regardless of the consequences.
Critically, those consequences were unknown when the policy of no intervention was adopted within days of the appearance of Omicron. All previous new SARS-CoV-2 variants had been deadlier than the original Wuhan strain, with the eventually globally dominant Delta variant perhaps as much as 4× as deadly. Omicron turned out to be the exception, but again, that was not known with any certainty when it was allowed to run wild through populations. What would have happened if it had followed the same pattern as Delta?
In the USA, for example, the worst COVID-19 wave was the one in the winter of 2020-21, at the peak of which at least 3,500 people were dying daily (the real number was certainly higher because of undercounting due to lack of testing and improper reporting). The first Omicron BA.1 wave saw the second-highest death tolls, with at least 2,800 dying per day at its peak. Had Omicron been as intrinsically lethal as Delta, we could have easily seen a 4-5× higher peak than January 2021, i.e. as many as 12–15,000 people dying a day. Given that we only had real data on Omicron’s intrinsic lethality after the gigantic wave of infections was unleashed onto the population, we have to conclude that 12–15,000 dead a day is now a threshold that will not force the implementation of serious NPIs for the next problematic COVID-19 serotype.
Logically, it follows that it is also a threshold that will not result in the implementation of NPIs for any other emerging pathogens either. Because why should SARS-CoV-2 be special?
We can only hope that we will never see the day when such an epidemic hits us but experience tells us such optimism is unfounded. The current level of suffering caused by COVID-19 has been completely normalized even though such a thing was unthinkable back in 2019. Populations are largely unaware of the long-term harms the virus is causing to those infected, of the burden on healthcare, increased disability, mortality and reduced life expectancy. Once a few even deadlier outbreaks have been shrugged off by governments worldwide, the baseline of what is considered “acceptable” will just gradually move up and even more unimaginable losses will eventually enter the “acceptable” category. There can be no doubt, from a public health perspective, we are regressing.
We had a second, even more worrying real-life example of what the future holds with the global spread of the MPX virus (formerly known as “monkeypox” and now called “Mpox”) in 2022. MPX is a close relative to the smallpox VARV virus and is endemic to Central and Western Africa, where its natural hosts are mostly various rodent species, but on occasions it infects humans too, with the rate of zoonotic transfer increasing over recent decades. It has usually been characterized by fairly high mortality – the CFR (Case Fatality Rate) has been ∼3.6% for the strain that circulates in Nigeria and ∼10% for the one in the Congo region, i.e. much worse than SARS-CoV-2. In 2022, an unexpected global MPX outbreak developed, with tens of thousands of confirmed cases in dozens of countries. Normally, this would be a huge cause for alarm, for several reasons.
First, MPX itself is a very dangerous disease. Second, universal smallpox vaccination ended many decades ago with the success of the eradication program, leaving the population born after that completely unprotected. Third, lethality in orthopoxviruses is, in fact, highly variable – VARV itself had a variola major strain, with as much as ∼30% CFR, and a less deadly variola minor variety with CFR ∼1%, and there was considerable variation within variola major too. It also appears that high pathogenicity often evolves from less pathogenic strains through reductive evolution - the loss of certain genes something that can happen fairly easily, may well have happened repeatedly in the past, and may happen again in the future, a scenario that has been repeatedly warned about for decades. For these reasons, it was unthinkable that anyone would just shrug off a massive MPX outbreak – it is already bad enough as it is, but allowing it to become endemic means it can one day evolve towards something functionally equivalent to smallpox in its impact.
And yet that is exactly what happened in 2022 – barely any measures were taken to contain the outbreak, and countries simply reclassified MPX out of the “high consequence infectious disease” category in order to push the problem away, out of sight and out of mind. By chance, it turned out that this particular outbreak did not spark a global pandemic, and it was also characterized, for poorly understood reasons, by an unusually low CFR, with very few people dying. But again, that is not the information that was available at the start of the outbreak, when in a previous, interventionist age of public health, resources would have been mobilized to stamp it out in its infancy, but, in the age of laissez-faire, were not. MPX is now circulating around the world and represents a future threat of uncontrolled transmission resulting in viral adaptation to highly efficient human-to-human spread combined with much greater disease severity.
While some are better than others, no national or regional government is making serious efforts towards infection prevention and control, and it seems likely this laissez-faire policy will continue for the foreseeable future. The social, political, and economic movements that worked to achieve this mass infection environment can rejoice at their success.
Those schooled in public health, immunology or working on the front line of healthcare provision know we face an uncertain future, and are aware the implications of recent events stretch far beyond SARS-CoV-2. The shifts that have taken place in attitudes and public health policy will likely damage a key pillar that forms the basis of modern civilized society, one that was built over the last two centuries; the expectation of a largely uninterrupted upwards trajectory of ever-improving health and quality of life, largely driven by the reduction and elimination of infectious diseases that plagued humankind for thousands of years. In the last three years, that trajectory has reversed.
The upward trajectory of public health in the last two centuries Control of infectious disease has historically been a priority for all societies. Quarantine has been in common use since at least the Bronze Age and has been the key method for preventing the spread of infectious diseases ever since. The word “quarantine” itself derives from the 40-day isolation period for ships and crews that was implemented in Europe during the late Middle Ages to prevent the introduction of bubonic plague epidemics into cities1.
Rat climbing a ship's rigging. Modern public health traces its roots to the middle of the 19th century thanks to converging scientific developments in early industrial societies:
The germ theory of diseases was firmly established in the mid-19th century, in particular after Louis Pasteur disproved the spontaneous generation hypothesis. If diseases spread through transmission chains between individual humans or from the environment/animals to humans, then it follows that those transmission chains can be interrupted, and the spread stopped. The science of epidemiology appeared, its birth usually associated with the 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak in London during which the British physician John Snow identified contaminated water as the source of cholera, pointing to improved sanitation as the way to stop cholera epidemics. Vaccination technology began to develop, initially against smallpox, and the first mandatory smallpox vaccination campaigns began, starting in England in the 1850s. The early industrial era generated horrendous workplace and living conditions for working class populations living in large industrial cities, dramatically reducing life expectancy and quality of life (life expectancy at birth in key industrial cities in the middle of the 19th century was often in the low 30s or even lower2). This in turn resulted in a recognition that such environmental factors affect human health and life spans. The long and bitter struggle for workers’ rights in subsequent decades resulted in much improved working conditions, workplace safety regulations, and general sanitation, and brought sharp increases in life expectancy and quality of life, which in turn had positive impacts on productivity and wealth. Florence Nightingale reemphasized the role of ventilation in healing and preventing illness, ‘The very first canon of nursing… : keep the air he breathes as pure as the external air, without chilling him,’ a maxim that influenced building design at the time. These trends continued in the 20th century, greatly helped by further technological and scientific advances. Many diseases – diphtheria, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, etc. – became things of the past thanks to near-universal highly effective vaccinations, while others that used to be common are no longer of such concern for highly developed countries in temperate climates – malaria, typhus, typhoid, leprosy, cholera, tuberculosis, and many others – primarily thanks to improvements in hygiene and the implementation of non-pharmaceutical measures for their containment.
Furthermore, the idea that infectious diseases should not just be reduced, but permanently eliminated altogether began to be put into practice in the second half of the 20th century3-5 on a global level, and much earlier locally. These programs were based on the obvious consideration that if an infectious agent is driven to extinction, the incalculable damage to people’s health and the overall economy by a persisting and indefinite disease burden will also be eliminated.
The ambition of local elimination grew into one of global eradication for smallpox, which was successfully eliminated from the human population in the 1970s6 (this had already been achieved locally in the late 19th century by some countries), after a heroic effort to find and contain the last remaining infectious individuals7,8. The other complete success was rinderpest in cattle9,10, globally eradicated in the early 21st century.
When the COVID-19 pandemic started, global eradication programs were very close to succeeding for two other diseases – polio11,12 and dracunculiasis13. Eradication is also globally pursued for other diseases, such as yaws14,15, and regionally for many others, e.g. lymphatic filariasis16,17, onchocerciasis18,19, measles and rubella20-30. The most challenging diseases are those that have an external reservoir outside the human population, especially if they are insect borne, and in particular those carried by mosquitos. Malaria is the primary example, but despite these difficulties, eradication of malaria has been a long-standing global public health goal31-33 and elimination has been achieved in temperate regions of the globe34,35, even though it involved the ecologically destructive widespread application of polluting chemical pesticides36,37 to reduce the populations of the vectors. Elimination is also a public goal for other insect borne diseases such as trypanosomiasis38,39.
In parallel with pursuing maximal reduction and eventual eradication of the burden of existing endemic infectious diseases, humanity has also had to battle novel infectious diseases40, which have been appearing at an increased rate over recent decades41-43. Most of these diseases are of zoonotic origin, and the rate at which they are making the jump from wildlife to humans is accelerating, because of the increased encroachment on wildlife due to expanding human populations and physical infrastructure associated with human activity, the continued destruction of wild ecosystems that forces wild animals towards closer human contact, the booming wildlife trade, and other such trends.
Because it is much easier to stop an outbreak when it is still in its early stages of spreading through the population than to eradicate an endemic pathogen, the governing principle has been that no emerging infectious disease should be allowed to become endemic. This goal has been pursued reasonably successfully and without controversy for many decades.
The most famous newly emerging pathogens were the filoviruses (Ebola44-46, Marburg47,48), the SARS and MERS coronaviruses, and paramyxoviruses like Nipah49,50. These gained fame because of their high lethality and potential for human-to-human spread, but they were merely the most notable of many examples.
Pigs in close proximity to humans. Such epidemics were almost always aggressively suppressed. Usually, these were small outbreaks, and because highly pathogenic viruses such as Ebola cause very serious sickness in practically all infected people, finding and isolating the contagious individuals is a manageable task. The largest such epidemic was the 2013-16 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, when a filovirus spread widely in major urban centers for the first time. Containment required a wartime-level mobilization, but that was nevertheless achieved, even though there were nearly 30,000 infections and more than 11,000 deaths51.
SARS was also contained and eradicated from the human population back in 2003-04, and the same happened every time MERS made the jump from camels to humans, as well as when there were Nipah outbreaks in Asia.
The major counterexample of a successful establishment in the human population of a novel highly pathogenic virus is HIV. HIV is a retrovirus, and as such it integrates into the host genome and is thus nearly impossible to eliminate from the body and to eradicate from the population52 (unless all infected individuals are identified and prevented from infecting others for the rest of their lives). However, HIV is not an example of the containment principle being voluntarily abandoned as the virus had made its zoonotic jump and established itself many decades before its eventual discovery53 and recognition54-56, and long before the molecular tools that could have detected and potentially fully contained it existed.
Still, despite all these containment success stories, the emergence of a new pathogen with pandemic potential was a well understood and frequently discussed threat57-60, although influenza viruses rather than coronaviruses were often seen as the most likely culprit61-65. The eventual appearance of SARS-CoV-2 should therefore not have been a huge surprise, and should have been met with a full mobilization of the technical tools and fundamental public health principles developed over the previous decades.
The ecological context One striking property of many emerging pathogens is how many of them come from bats. While the question of whether bats truly harbor more viruses than other mammals in proportion to their own species diversity (which is the second highest within mammals after rodents) is not fully settled yet66-69, many novel viruses do indeed originate from bats, and the ecological and physiological characteristics of bats are highly relevant for understanding the situation that Homo sapiens finds itself in right now.
Group of bats roosting in a cave. Another startling property of bats and their viruses is how highly pathogenic to humans (and other mammals) many bat viruses are, while bats themselves are not much affected (only rabies is well established to cause serious harm to bats68). Why bats seem to carry so many such pathogens, and how they have adapted so well to coexisting with them, has been a long-standing puzzle and although we do not have a definitive answer, some general trends have become clear.
Bats are the only truly flying mammals and have been so for many millions of years. Flying has resulted in a number of specific adaptations, one of them being the tolerance towards a very high body temperature (often on the order of 42-43ºC). Bats often live in huge colonies, literally touching each other, and, again, have lived in conditions of very high density for millions of years. Such densities are rare among mammals and are certainly not the native condition of humans (human civilization and our large dense cities are a very recent phenomenon on evolutionary time scales). Bats are also quite long-lived for such small mammals70-71 – some fruit bats can live more than 35 years and even small cave dwelling species can live about a decade. These are characteristics that might have on one hand facilitated the evolution of a considerable set of viruses associated with bat populations. In order for a non-latent respiratory virus to maintain itself, a minimal population size is necessary. For example, it is hypothesized that measles requires a minimum population size of 250-300,000 individuals72. And bats have existed in a state of high population densities for a very long time, which might explain the high diversity of viruses that they carry. In addition, the long lifespan of many bat species means that their viruses may have to evolve strategies to overcome adaptive immunity and frequently reinfect previously infected individuals as opposed to the situation in short-lived species in which populations turn over quickly (with immunologically naive individuals replacing the ones that die out).
On the other hand, the selective pressure that these viruses have exerted on bats may have resulted in the evolution of various resistance and/or tolerance mechanisms in bats themselves, which in turn have driven the evolution of counter strategies in their viruses, leading them to be highly virulent for other species. Bats certainly appear to be physiologically more tolerant towards viruses that are otherwise highly virulent to other mammals. Several explanations for this adaptation have been proposed, chief among them a much more powerful innate immunity and a tolerance towards infections that does not lead to the development of the kind of hyperinflammatory reactions observed in humans73-75, the high body temperature of bats in flight, and others.
The notable strength of bat innate immunity is often explained by the constitutively active interferon response that has been reported for some bat species76-78. It is possible that this is not a universal characteristic of all bats79 – only a few species have been studied – but it provides a very attractive mechanism for explaining both how bats prevent the development of severe systemic viral infections in their bodies and how their viruses in turn would have evolved powerful mechanisms to silence the interferon response, making them highly pathogenic for other mammals.
The tolerance towards infection is possibly rooted in the absence of some components of the signaling cascades leading to hyperinflammatory reactions and the dampened activity of others80.
Map of scheduled airline traffic around the world, circa June 2009 Map of scheduled airline traffic around the world. Credit: Jpatokal An obvious ecological parallel can be drawn between bats and humans – just as bats live in dense colonies, so now do modern humans. And we may now be at a critical point in the history of our species, in which our ever-increasing ecological footprint has brought us in close contact with bats in a way that was much rarer in the past. Our population is connected in ways that were previously unimaginable. A novel virus can make the zoonotic jump somewhere in Southeast Asia and a carrier of it can then be on the other side of the globe a mere 24-hours later, having encountered thousands of people in airports and other mass transit systems. As a result, bat pathogens are now being transferred from bat populations to the human population in what might prove to be the second major zoonotic spillover event after the one associated with domestication of livestock and pets a few thousand years ago.
Unfortunately for us, our physiology is not suited to tolerate these new viruses. Bats have adapted to live with them over many millions of years. Humans have not undergone the same kind of adaptation and cannot do so on any timescale that will be of use to those living now, nor to our immediate descendants.
Simply put, humans are not bats, and the continuous existence and improvement of what we now call “civilization” depends on the same basic public health and infectious disease control that saw life expectancy in high-income countries more than double to 85 years. This is a challenge that will only increase in the coming years, because the trends that are accelerating the rate of zoonotic transfer of pathogens are certain to persist.
Given this context, it is as important now to maintain the public health principle that no new dangerous pathogens should be allowed to become endemic and that all novel infectious disease outbreaks must be suppressed as it ever was.
The death of public health and the end of epidemiological comfort It is also in this context that the real gravity of what has happened in the last three years emerges.
After HIV, SARS-CoV-2 is now the second most dangerous infectious disease agent that is 'endemic' to the human population on a global scale. And yet not only was it allowed to become endemic, but mass infection was outright encouraged, including by official public health bodies in numerous countries81-83.
The implications of what has just happened have been missed by most, so let’s spell them out explicitly.
We need to be clear why containment of SARS-CoV-2 was actively sabotaged and eventually abandoned. It has absolutely nothing to do with the “impossibility” of achieving it. In fact, the technical problem of containing even a stealthily spreading virus such as SARS-CoV-2 is fully solved, and that solution was successfully applied in practice for years during the pandemic.
The list of countries that completely snuffed out outbreaks, often multiple times, includes Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Bhutan, Cuba, China, and a few others, with China having successfully contained hundreds of separate outbreaks, before finally giving up in late 2022.
The algorithm for containment is well established – passively break transmission chains through the implementation of nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) such as limiting human contacts, high quality respirator masks, indoor air filtration and ventilation, and others, while aggressively hunting down active remaining transmission chains through traditional contact tracing and isolation methods combined with the powerful new tool of population-scale testing.
Oklahoma’s Strategic National Stockpile. Credit: DVIDS Understanding of airborne transmission and institution of mitigation measures, which have heretofore not been utilized in any country, will facilitate elimination, even with the newer, more transmissible variants. Any country that has the necessary resources (or is provided with them) can achieve full containment within a few months. In fact, currently this would be easier than ever before because of the accumulated widespread multiple recent exposures to the virus in the population suppressing the effective reproduction number (Re). For the last 18 months or so we have been seeing a constant high plateau of cases with undulating waves, but not the major explosions of infections with Re reaching 3-4 that were associated with the original introduction of the virus in 2020 and with the appearance of the first Omicron variants in late 2021.
It would be much easier to use NPIs to drive Re to much below 1 and keep it there until elimination when starting from Re around 1.2-1.3 than when it was over 3, and this moment should be used, before another radically new serotype appears and takes us back to those even more unpleasant situations. This is not a technical problem, but one of political and social will. As long as leadership misunderstands or pretends to misunderstand the link between increased mortality, morbidity and poorer economic performance and the free transmission of SARS-CoV-2, the impetus will be lacking to take the necessary steps to contain this damaging virus.
Political will is in short supply because powerful economic and corporate interests have been pushing policymakers to let the virus spread largely unchecked through the population since the very beginning of the pandemic. The reasons are simple. First, NPIs hurt general economic activity, even if only in the short term, resulting in losses on balance sheets. Second, large-scale containment efforts of the kind we only saw briefly in the first few months of the pandemic require substantial governmental support for all the people who need to pause their economic activity for the duration of effort. Such an effort also requires large-scale financial investment in, for example, contact tracing and mass testing infrastructure and providing high-quality masks. In an era dominated by laissez-faire economic dogma, this level of state investment and organization would have set too many unacceptable precedents, so in many jurisdictions it was fiercely resisted, regardless of the consequences for humanity and the economy.
None of these social and economic predicaments have been resolved. The unofficial alliance between big business and dangerous pathogens that was forged in early 2020 has emerged victorious and greatly strengthened from its battle against public health, and is poised to steamroll whatever meager opposition remains for the remainder of this, and future pandemics.
The long-established principles governing how we respond to new infectious diseases have now completely changed – the precedent has been established that dangerous emerging pathogens will no longer be contained, but instead permitted to ‘ease’ into widespread circulation. The intent to “let it rip” in the future is now being openly communicated84. With this change in policy comes uncertainty about acceptable lethality. Just how bad will an infectious disease have to be to convince any government to mobilize a meaningful global public health response?
We have some clues regarding that issue from what happened during the initial appearance of the Omicron “variant” (which was really a new serotype85,86) of SARS-CoV-2. Despite some experts warning that a vaccine-only approach would be doomed to fail, governments gambled everything on it. They were then faced with the brute fact of viral evolution destroying their strategy when a new serotype emerged against which existing vaccines had little effect in terms of blocking transmission. The reaction was not to bring back NPIs but to give up, seemingly regardless of the consequences.
Critically, those consequences were unknown when the policy of no intervention was adopted within days of the appearance of Omicron. All previous new SARS-CoV-2 variants had been deadlier than the original Wuhan strain, with the eventually globally dominant Delta variant perhaps as much as 4× as deadly87. Omicron turned out to be the exception, but again, that was not known with any certainty when it was allowed to run wild through populations. What would have happened if it had followed the same pattern as Delta?
In the USA, for example, the worst COVID-19 wave was the one in the winter of 2020-21, at the peak of which at least 3,500 people were dying daily (the real number was certainly higher because of undercounting due to lack of testing and improper reporting). The first Omicron BA.1 wave saw the second-highest death tolls, with at least 2,800 dying per day at its peak. Had Omicron been as intrinsically lethal as Delta, we could have easily seen a 4-5× higher peak than January 2021, i.e. as many as 12–15,000 people dying a day. Given that we only had real data on Omicron’s intrinsic lethality after the gigantic wave of infections was unleashed onto the population, we have to conclude that 12–15,000 dead a day is now a threshold that will not force the implementation of serious NPIs for the next problematic COVID-19 serotype.
UK National Covid Memorial Wall. Credit: Dominic Alves Logically, it follows that it is also a threshold that will not result in the implementation of NPIs for any other emerging pathogens either. Because why should SARS-CoV-2 be special?
We can only hope that we will never see the day when such an epidemic hits us but experience tells us such optimism is unfounded. The current level of suffering caused by COVID-19 has been completely normalized even though such a thing was unthinkable back in 2019. Populations are largely unaware of the long-term harms the virus is causing to those infected, of the burden on healthcare, increased disability, mortality and reduced life expectancy. Once a few even deadlier outbreaks have been shrugged off by governments worldwide, the baseline of what is considered “acceptable” will just gradually move up and even more unimaginable losses will eventually enter the “acceptable” category. There can be no doubt, from a public health perspective, we are regressing.
We had a second, even more worrying real-life example of what the future holds with the global spread of the MPX virus (formerly known as “monkeypox” and now called “Mpox”) in 2022. MPX is a close relative to the smallpox VARV virus and is endemic to Central and Western Africa, where its natural hosts are mostly various rodent species, but on occasions it infects humans too, with the rate of zoonotic transfer increasing over recent decades88. It has usually been characterized by fairly high mortality – the CFR (Case Fatality Rate) has been ∼3.6% for the strain that circulates in Nigeria and ∼10% for the one in the Congo region, i.e. much worse than SARS-CoV-2. In 2022, an unexpected global MPX outbreak developed, with tens of thousands of confirmed cases in dozens of countries89,90. Normally, this would be a huge cause for alarm, for several reasons.
First, MPX itself is a very dangerous disease. Second, universal smallpox vaccination ended many decades ago with the success of the eradication program, leaving the population born after that completely unprotected. Third, lethality in orthopoxviruses is, in fact, highly variable – VARV itself had a variola major strain, with as much as ∼30% CFR, and a less deadly variola minor variety with CFR ∼1%, and there was considerable variation within variola major too. It also appears that high pathogenicity often evolves from less pathogenic strains through reductive evolution - the loss of certain genes something that can happen fairly easily, may well have happened repeatedly in the past, and may happen again in the future, a scenario that has been repeatedly warned about for decades91,92. For these reasons, it was unthinkable that anyone would just shrug off a massive MPX outbreak – it is already bad enough as it is, but allowing it to become endemic means it can one day evolve towards something functionally equivalent to smallpox in its impact.
Colorized transmission electron micrograph of Mpox virus particles. Credit: NIAID And yet that is exactly what happened in 2022 – barely any measures were taken to contain the outbreak, and countries simply reclassified MPX out of the “high consequence infectious disease” category93 in order to push the problem away, out of sight and out of mind. By chance, it turned out that this particular outbreak did not spark a global pandemic, and it was also characterized, for poorly understood reasons, by an unusually low CFR, with very few people dying94,95. But again, that is not the information that was available at the start of the outbreak, when in a previous, interventionist age of public health, resources would have been mobilized to stamp it out in its infancy, but, in the age of laissez-faire, were not. MPX is now circulating around the world and represents a future threat of uncontrolled transmission resulting in viral adaptation to highly efficient human-to-human spread combined with much greater disease severity.
This is the previously unthinkable future we will live in from now on in terms of our approach to infectious disease.
What may be controlled instead is information. Another lesson of the pandemic is that if there is no testing and reporting of cases and deaths, a huge amount of real human suffering can be very successfully swept under the rug. Early in 2020, such practices – blatant denial that there was any virus in certain territories, outright faking of COVID-19 statistics, and even resorting to NPIs out of sheer desperation but under false pretense that it is not because of COVID-19 – were the domain of failed states and less developed dictatorships. But in 2023 most of the world has adopted such practices – testing is limited, reporting is infrequent, or even abandoned altogether – and there is no reason to expect this to change. Information control has replaced infection control.
After a while it will not even be possible to assess the impact of what is happening by evaluating excess mortality, which has been the one true measure not susceptible to various data manipulation tricks. As we get increasingly removed from the pre-COVID-19 baselines and the initial pandemic years are subsumed into the baseline for calculating excess mortality, excess deaths will simply disappear by the power of statistical magic. Interestingly, countries such as the UK, which has already incorporated two pandemic years in its five-year average, are still seeing excess deaths, which suggests the virus is an ongoing and growing problem.
It should also be stressed that this radical shift in our approach to emerging infectious diseases is probably only the beginning of wiping out the hard-fought public health gains of the last 150+ years. This should be gravely concerning to any individuals and institutions concerned with workers and citizens rights.
This shift is likely to impact existing eradication and elimination efforts. Will the final pushes be made to complete the various global eradication campaigns listed above? That may necessitate some serious effort involving NPIs and active public health measures, but how much appetite is there for such things after they have been now taken out of the toolkit for SARS-CoV-2?
We can also expect previously forgotten diseases to return where they have successfully been locally eradicated. We have to always remember that the diseases that we now control with universal childhood vaccinations have not been globally eradicated – they have disappeared from our lives because vaccination rates are high enough to maintain society as a whole above the disease elimination threshold, but were vaccination rates to slip, those diseases, such as measles, will return with a vengeance.
The anti-vaccine movement was already a serious problem prior to COVID-19, but it was given a gigantic boost with the ill-advised vaccine-only COVID-19 strategy. Governments and their nominal expert advisers oversold the effectiveness of imperfect first generation COVID-vaccines, and simultaneously minimized the harms of SARS-CoV-2, creating a reality gap which gave anti-vaccine rhetoric space to thrive. This is a huge topic to be explored separately. Here it will suffice to say that while anti-vaxxers were a fringe movement prior to the pandemic, “vaccination” in general is now a toxic idea in the minds of truly significant portions of the population. A logical consequence of that shift has been a significant decrease in vaccination coverage for other diseases as well as for COVID-19.
This is even more likely given the shift in attitudes towards children. Child labour, lack of education and large families were the hallmarks of earlier eras of poor public health, which were characterized by high birth-rates and high infant mortality. Attitudes changed dramatically over the course of the 20th century and wherever health and wealth increased, child mortality fell, and the transition was made to small families. Rarity increased perceived value and children’s wellbeing became a central concern for parents and carers. The arrival of COVID-19 changed that, with some governments, advisers, advocacy groups and parents insisting that children should be exposed freely to a Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome virus to ‘train’ their immune systems.
Infection, rather than vaccination, was the preferred route for many in public health in 2020, and still is in 2023, despite all that is known about this virus’s propensity to cause damage to all internal organs, the immune system, and the brain, and the unknowns of postinfectious sequelae. This is especially egregious in infants, whose naive immune status may be one of the reasons they have a relatively high hospitalization rate. Some commentators seek to justify the lack of protection for the elderly and vulnerable on a cost basis. We wonder what rationale can justify a lack of protection for newborns and infants, particularly in a healthcare setting, when experience of other viruses tells us children have better outcomes the later they are exposed to disease? If we are not prepared to protect children against a highly virulent SARS virus, why should we protect against others? We should expect a shift in public health attitudes, since ‘endemicity’ means there is no reason to see SARS-CoV-2 as something unique and exceptional.
We can also expect a general degradation of workplace safety protocols and standards, again reversing many decades of hard-fought gains. During COVID-19, aside from a few privileged groups who worked from home, people were herded back into their workplaces without minimal safety precautions such as providing respirators, and improving ventilation and indoor air quality, when a dangerous airborne pathogen was spreading.
Can we realistically expect existing safety precautions and regulations to survive after that precedent has been set? Can we expect public health bodies and regulatory agencies, whose job it is to enforce these standards, to fight for workplace safety given what they did during the pandemic? It is highly doubtful. After all, they stubbornly refused to admit that SARS-CoV-2 is airborne (even to this very day in fact – the World Health Organization’s infamous “FACT: #COVID19 is NOT airborne” Tweet from March 28 2020 is still up in its original form), and it is not hard to see why – implementing airborne precautions in workplaces, schools, and other public spaces would have resulted in a cost to employers and governments; a cost they could avoid if they simply denied they needed to take such precautions. But short-term thinking has resulted in long-term costs to those same organizations, through the staffing crisis, and the still-rising disability tsunami. The same principle applies to all other existing safety measures.
Worse, we have now entered the phase of abandoning respiratory precautions even in hospitals. The natural consequence of unmasked staff and patients, even those known to be SARS-CoV-2 positive, freely mixing in overcrowded hospitals is the rampant spread of hospital-acquired infections, often among some of the most vulnerable demographics. This was previously thought to be a bad thing. And what of the future? If nobody is taking any measures to stop one particular highly dangerous nosocomial infection, why would anyone care about all the others, which are often no easier to prevent? And if standards of care have slipped to such a low point with respect to COVID-19, why would anyone bother providing the best care possible for other conditions? This is a one-way feed-forward healthcare system degradation that will only continue.
Finally, the very intellectual foundations of the achievements of the last century and a half are eroding. Chief among these is the germ theory of infectious disease, by which transmission chains can be isolated and broken. The alternative theory, of spontaneous generation of pathogens, means there are no chains to be broken. Today, we are told that it is impossible to contain SARS-CoV-2 and we have to "just live with it,” as if germ theory no longer holds. The argument that the spread of SARS-CoV-2 to wildlife means that containment is impossible illustrates these contradictions further – SARS-CoV-2 came from wildlife, as did all other zoonotic infections, so how does the virus spilling back to wildlife change anything in terms of public health protocol? But if one has decided that from here on there will be no effort to break transmission chains because it is too costly for the privileged few in society, then excuses for that laissez-faire attitude will always be found.
And that does not bode well for the near- and medium-term future of the human species on planet Earth.
(Follow the link for more than 100 references and sources)
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aziraphale’s secret investigation and overlooked Clues

Remember this frame from Good Omens S02E06? Apparently Aziraphale had been using the empty carton box brought by Jim to store things in. It became a new home to at least two out of three “Lost Quartos” — the supposedly lost Shakespeare plays briefly but hilariously mentioned in the Good Omens book — as well as a very mysterious legal document.
Thought probably half of the Good Omens analysts here, including the ever so wonderful @fuckyeahgoodomens, who managed to find some information about the deceased John Gibson from New Cumnock (1855 - 1905).
Unfortunately the most interesting thing about this early 20th century provincial postmaster was his youngest child James (1894 - 1973), a quite famous stage (West End!) and film actor immortalized on screen in The Master of Ballantrae (1962), Witch Wood (1964) and Kidnapped (1963).
After that particular discovery the fandom-wide search seemingly led nowhere and the topic died a premature death.

And I almost figured it out seven months ago.
“But Yuri, you’re so clever. How can somebody as clever as you be so stupid?”, you probably want to shout across a busy London street at this point. Well, let me tell you. Much like Aziraphale, I'm blindingly intelligent for about thirty seconds a day. I do not get to choose which seconds and they are not consecutive.
Only tonight the stars have aligned in an ineffable way.
For those of you who don’t follow this account, some time ago I’ve realized that John Gibson isn’t the only testator whose estate was being investigated by Aziraphale right before The Whickber Street Traders and Shopkeepers Association monthly meeting.
If you watch S2 finale closely enough, you should notice that Crowley not only stress cleans Aziraphale’s bookshop — he also goes through the books and papers on his desk between the last three angels leaving the bookshop and Maggie and Nina’s intervention. A seemingly permanent arrangement of the props post-shooting, visible in detail both on Radio Times tour and SFX magazine photo shoot, sheds even more light on this detail.



The close-ups published after S2 release are legible enough to refer us to a much more prominent historical figure, Josiah Wedgwood (1730 – 1795) — an English potter, entrepreneur and abolitionist. Founding the Wedgwood company in 1759, he developed improved pottery bodies by systematic experimentation, and was the leader in the industrialisation of the manufacture of European pottery.

Long story short, I transcribed the handwritten pages abandoned on Aziraphale’s desk, found out the source and the full text of what could be identified as Wedgwood’s last will and testament, took a walk to visit his Soho workshop, and proceeded to write a lengthy meta analysis about it.
I was today’s years old when I realized that there’s something else connecting those two dead British men.


The Scottish Post Office Directory of 1903 recorded John Gibson from New Cumnock as a “stationer and china dealer” (above) operating from the shop located in the town’s post office building.
Indeed, a close look at his post office shop window in the Henderson Building (below, bottom left) reveals an artful display of fine china and pottery next to postcards printed by Gibson.

There are multiple ways to connect this surprising link with possible S3 plot points, obviously, but it’s getting late, so let’s just name the two most important ones.
You’ve probably heard of the Holy Grail, maybe from Monty Python or Good Omens S01E03 1941 flashback. Depending on the version of the story, if can be a cup, a chalice, a bowl, or a saucer — but almost always a dish or a vessel connected personally, physically and metaphysically to Jesus (unless you’re partial to Wolfram von Eschenbach’s idea that the Grail was a stone, the sanctuary of the neutral angels who took neither side during Lucifer's rebellion).

A slightly more obscure dish related to the Son of God appears in the sixteenth chapter of the Book of Revelation as a vital part of His Second Coming. The Seven Bowls (or cups, or vials) of God’s Wrath are supposed to be poured out on the wicked and the followers of the Antichrist by seven angels:
Then I heard a loud voice from the temple telling the seven angels, “Go and pour out on the earth the seven bowls of the wrath of God.” So the first angel went and poured out his bowl on the earth, and harmful and painful sores came upon the people who bore the mark of the beast and worshiped its image.
The second angel poured out his bowl into the sea, and it became like the blood of a corpse, and every living thing died that was in the sea.
The third angel poured out his bowl into the rivers and the springs of water, and they became blood. And I heard the angel in charge of the waters say, “Just are you, O Holy One, who is and who was, for you brought these judgments. For they have shed the blood of saints and prophets, and you have given them blood to drink. It is what they deserve!” And I heard the altar saying, “Yes, Lord God the Almighty, true and just are your judgments!”
The fourth angel poured out his bowl on the sun, and it was allowed to scorch people with fire. They were scorched by the fierce heat, and they cursed the name of God who had power over these plagues. They did not repent and give him glory.
The fifth angel poured out his bowl on the throne of the beast, and its kingdom was plunged into darkness. People gnawed their tongues in anguish and cursed the God of heaven for their pain and sores. They did not repent of their deeds.
The sixth angel poured out his bowl on the great river Euphrates, and its water was dried up, to prepare the way for the kings from the east. And I saw, coming out of the mouth of the dragon and out of the mouth of the beast and out of the mouth of the false prophet, three unclean spirits like frogs. For they are demonic spirits, performing signs, who go abroad to the kings of the whole world, to assemble them for battle on the great day of God the Almighty. (“Behold, I am coming like a thief! Blessed is the one who stays awake, keeping his garments on, that he may not go about naked and be seen exposed!”) And they assembled them at the place that in Hebrew is called Armageddon.
The seventh angel poured out his bowl into the air, and a loud voice came out of the temple, from the throne, saying, “It is done!” And there were flashes of lightning, rumblings, peals of thunder, and a great earthquake such as there had never been since man was on the earth, so great was that earthquake. The great city was split into three parts, and the cities of the nations fell, and God remembered Babylon the great, to make her drain the cup of the wine of the fury of his wrath. And every island fled away, and no mountains were to be found. And great hailstones, about one hundred pounds each, fell from heaven on people; and they cursed God for the plague of the hail, because the plague was so severe.

#good omens#good omens meta#good omens analysis#aziraphale#aziraphale’s bookshop#set design#good omens props#the good omens crew is unhinged#john gibson#josiah wedgwood#fine china#pottery#holy grail#seven bowls#second coming#yuri is doing her thing
86 notes
·
View notes
Text



Barrington Hall
Hi guys!!
I'm sharing Barrington Hall. This is the 21st building for my English Collection and inaugurating the red brick collection.
I decorated most of the house ground floor, for reference.
History of the house:
The Barrington family, long-established in Essex since the Conquest, initially resided at Old Barrington Hall. This estate, shown on a 1624 map, included substantial structures, orchards, fish ponds, and brickyards. However, in 1564, they moved to the Priory at Hatfield Broad Oak, signaling their ascent as country gentry. Throughout the late 16th and early 17th centuries, the family engaged in legal disputes over rights to Hatfield Forest with the Rich family, eventually securing a portion of the forest.
Sir Francis Barrington played a significant role in government, receiving a baronetcy in 1622. The family also had investments in New England and Ireland during this period. Despite their growing wealth, the Priory required repairs by 1700 and was demolished, causing the Barringtons to relocate to Great Waltham. The family seat at Hatfield Broad Oak was eventually rebuilt in the 1730s by John Shales Barrington, although he left it unfinished, leading to his reclusive life.
In the 19th century, George Alan Clayton Lowndes acquired the estate and made extensive neo-Jacobean renovations to the house and gardens, which were lauded in contemporary publications. After multiple ownership changes, including the purchase by A.H. Gosling in 1907, the property was later sold to the British Livestock Company and is now owned by CPL Aromas plc. The original parkland has been divided, with only 12 hectares surrounding the house remaining as part of the current estate. The landscape includes notable trees such as ancient oaks, as well as remnants of historic avenues and garden features.
More history: https://www.francisyork.com/blog/barrington-hall-a-palatial-georgian-mansion-one-hour-from-london














House file:
Location: Essex, England
Material: red brick
Style: Neo-Jacobean
Date: 1624 + remodelings
This house fits a 50x50 lot, but it coulf fit a 50x40 if you lose the garden.




I only decorated some of the important rooms. All the rest of the house is up to your taste to decor.
Hope you like it.
You will need the usual CC I use:
all Felixandre cc
all The Jim
SYB
Anachrosims
Regal Sims
King Falcon railing
The Golden Sanctuary
Cliffou
Dndr recolors
Harrie cc
Tuds
Lili's palace cc
Please enjoy, comment if you like the house and share pictures of your game!
Follow me on IG: https://www.instagram.com/sims4palaces/
@sims4palaces
Ealry acces: November 20
DOWNLOAD: https://www.patreon.com/posts/barrington-hall-113325949
#sims 4 architecture#sims 4 build#sims4#sims 4 screenshots#sims4building#sims 4 historical#sims4play#sims4palace#sims 4 royalty#ts4#ts4 download#ts4 screenshots#ts4 simblr#ts4 gameplay#the sims 4#sims 4#simblr#sims4 build#sims 4 gameplay#thesims4#sims 4 cc
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

MWW Artwork of the Day (12/6/24) John Piper (British, 1903-1992) Skelton Church, Yorkshire (1948) Oil on canvas. 63.5 x 76.2 cm. Private Collection
"Skelton Church, Yorkshire" is a prime example of the artist's famous architectural paintings, the late 1940s being a period which Anthony West marks as his most productive years. Piper is celebrated not only for painting some of Britain's best buildings but for capturing their historical and individual characteristics. Piper's aesthetic is often abstracted, so that his recording is not a straight-forward rendition but is more an expression of how a British citizen would feel seeing the destruction. Piper depicted the horrors of war at home painting a picture of life during conflict.
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sapphic vampire fiction mini reviews, ranked from least favorite to most:
House of Hunger: Bland characters, a story that barely scratches the surface of the implications of its premise, and a central relationship with nothing underpinning it make for an aimless story with a climax that hits like a limp noodle. If the dynamic between a vampire and her indentured maid appeals to you, try The Wicked and the Willing instead.
An Education in Malice: For a Carmilla retelling, the titular character really lacks bite. Laura at least has some interesting contradictions in her, and De Lafontaine could be quite compelling if we saw things through her eyes, but the central relationship isn't built on a lot, and Carmilla herself is really disappointingly bland. The prose comes off as overwrought and melodramatic in the first act, and the constant leaning on poetry feels gratuitous, but it picks up steam and becomes appropriately gripping by the one-third mark, and it carries the book enough that I had an enjoyable but rather shallow experience. I struggle to think of a reason to recommend this over In the Roses of Pieria, which plays with similar thematic and aesthetic elements much more adeptly. Also, it's a pet peeve of mine when a story makes a point to establish a specific historical era for its setting but has characters that feel utterly modern.
The Deathless Girls: This book does a much better job with its sense of time and place, and the characters and their motivations are quite strong. I only rate this one low on this list because the main characters don't actually deal with vampirism as a condition until the very end of the book. On its surface, the premise might seem quite similar to A Dowry of Blood, but there's actually very little thematic or narrative overlap.
Ex-Wives of Dracula: An excellent exploration of the queer teenage experience in conservative small town ~2015 USA along with some pretty novel twists on vampire and horror movie tropes. Strong, vibrant characters with a rich, messy, and compelling relationship carry a solid mystery plot and some pretty pointed critiques of its setting, but the actual climax and resolution don't quite hold up to the quality of the rest. Also I simply must warn anyone who didn't grow up in the time and place this book explores about the profound and casual bigotry and nastiness of that setting, which this book replicates to a T.
The Wicked and the Willing: A thrilling and compelling dark romantic drama centered on a British vampire in 1920s Singapore, her newly hired and desperate to escape poverty personal maid, and her majordomo who is struggling to keep her conscience under control after years of aiding and abetting her mistress's dark appetites. Extremely strong character writing pairs with deft exploration of themes of colonialism, entitlement, class divisions, sexism, and the ways in which certain types of status can and cannot afford one leeway to be nonconforming in other ways. Intermixes diagetic and non-diagetic BDSM very organically also, if that's your thing.
In the Roses of Pieria: Rich prose dripping with atmosphere follows an obscure academic as she digs into a series of ancient correspondences and discovers a millenia spanning love story between two vampires. The character writing is solid, if not quite as impressive as some other entries on this list, but the quality of the prose more than elevates it. The text makes elegant and powerful references to Sappho throughout, and the whole experience is heady and compelling in ways that I struggle to describe in greater detail. Funnily enough, the vampires are the least interesting part of the world building. This one has a sequel coming, and I can't wait.
A Dowry of Blood: A darkly enchanting epistolary novel that takes the form of letters written by the first of Dracula's wives to him as she attempts to make peace with killing him. She unpicks a delicious and horrifying knot of feeling and history as she revisits their millenia together, recounting and reckoning with the manipulations and abuses that defined the good times and the bad. The characters are evocative and rich, the narrative voice by turns sparse, longing, furious, contemplative, and mournful, and the story simply springs to life. It accomplishes an incredible amount in approximately 200 pages, and I absolutely cannot recommend this one enough.
#the wlw review#im sure there are countless more sapphic vampire stories#but these are the ones ive read#ignoring a few outliers that don't really explore vampirism
97 notes
·
View notes
Text
Youtube Essays Shill Post
I'm getting close to 1000 subscribers so I'm gonna make a shill post for my channel. I make videos on independent RPGs (no D&D/Pathfinder etc), highlighting narrative moves, the intersection of mechanics and themes, and analyzing them in parallel with books, movies, and game theory. I've had a really great crop of essays this year, and I bet at least one of them will do it for you:
###
youtube
Spire RPG & Babel: The Monstrosity of Empire, the Necessity of Violence (52 min)
I read Spire: The City Must Fall in parallel with RF Kuang's Babel: An Arcane History, and try to make the connection between Spire's worldbuilding and the British Empire's historical methods of extracting labor and resources from its colonized subjects. I'm especially proud of how I work through the ways in which Spire's Drow are treated as commodities, emulating how Britain's most valuable resource was human beings, and discuss why there's not an alternative available to the Drow except for violent uprising.
youtube
Heart RPG, Annihilation, and Sangfielle: Brainworms all the Way Down (38 min)
I follow the themes of compulsion, infection, and dissemination of a supernatural intelligence that I found both in Heart : The City Beneath and in Jeff Vandermeer's Annihilation. It's kind of gross, but if you like reading about parasites, strange urges, and transformations that destroy the self, you'll probably be into this. I also make a few references to Friends at the Table's Sangfielle season, if you're a FATT fan.
youtube
Apocalypse Keys and Desperation to Belong (15 min)
Apocalypse Keys is a really interesting game, but it's also the most emotional game I read this year? It's all about heartbreak, longing, and trying to hold on to the people you love, even though you know you'll lose them in the end. The essay is also very much tied up in my feelings on diaspora, faith, and what it's like to be excluded, except for the home you make for yourself. It's also like, undeniably queer in a way I think a lot of folks will relate to.
youtube
The Endings of Hellwhalers and the Fewness of the Saved (28 min)
Okay I actually talk about being an ex-Catholic a lot, but this is my most explicitly religiously-inspired essay. I compare the text of Hellwhalers and its interpretations of Christian hell to the actual Catholic doctrines of hell, including the sermon that eventually made me break away from the Church altogether. If you like whales and religious trauma, please check this out.
###
Please consider taking a look at my channel! I hate having to beg for viewers, but there's just no other way to build an audience, and I'm really proud of the work I've done this year!
215 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm not Jewish and haven't read the Torah, but I have seen Jewish ppl say that even the Torah doesn't claim Jewish people are Indigenous to Israel. Abraham was born in modern day Iraq and finds Israel, in which there are people already there.
Also, other countries were considered to build Israel on, like Guyana and Australia, but the British landed on Palestine
Jewish people ARE historically and biblically indigenous to the Holy Land. There is no doubt about this and I don't think removing their indigeneity is gonna do any of us good.
However, Jewish people are not the FIRST people to have settled in the land of Canaan, many indigenous groups did exist there from the beginning, such as the Midianites, Philistines (not related to Palestinians) Hittites, Moabites and etc. Interestingly enough, Abraham (a) was a Canaanite himself, so Arabs and Israelites do share a common ancestry through Ishmael (a) and Isaaq (a) respectively. This is attested in Islamic manuscripts as well. With that said, I'm not gonna go through religious texts, because they aren't exactly helpful as a historical source. Most secular sources attest the fact that there was an Israelite kingdom, however, it does not correspond to the borders of today's settler state. The difference is that there was already a group of people that had settled in the holy land for 1400 years and have lives side by side with the Jewish and Christian people, these people are indigenous to that land, so for a group of people to come back centuries later and throw these natives out of their homes is simply not right.
But I think it's important that Jewish people aren't the only people who are indigenous, Samaritans are also indigenous and have remained so even before the Arab conquest. While they don't consider themselves Jewish, despite following the Mosaic laws, they are not given the same rights as their Jewish counterparts.
218 notes
·
View notes
Text




HENRY CAVILL | Saudi Arabia - Oct. 2023
During his visit to the AlBalad area in HistoricJeddah, British actor Henry Cavill expressed his admiration for the area's most prominent monuments and historical buildings while touring the iconic landmarks. - via @jeddahalbalad.sa
271 notes
·
View notes
Note
what does your username mean?
Cat ghost.
As child. Would go to library, to look at books about creatures, with a pen and notepad. Or sit before a television watching "nature" documentary stuff, with a pen and notepad. Was fixated on habitats. The context. Did not like to isolate an individual creature from the wider ecological community. This led to interest in geography, distribution range maps. Was aware that, in popular perception, some creatures were strongly associated with a particular place. "Lion is an African animal. Tiger is an Asian animal." Allegedly. And other stereotypes (many of them, I would later come to learn, due to chauvinism, exoticism, Orientalism, colonialism, etc.). Came across a kind of large textbook on wild cats. Saw the historical distribution maps. Only a few centuries ago, tigers were in Anatolia, the Caucasus, near the shores of the Black Sea. Was intrigued. From the middle of the twentieth century onward, the lion and cheetah were so closely associated with Africa, where like over 99% of their range was located. And yet. There remains a small remnant population of nearly-extinct Asiatic lions far away within India''s borders. And there remains a small remnant population of nearly-extinct Asiatic cheetahs within Iran's borders. And all that space, in between, where both cats were now extinct. Only 100 years ago, tiger, lion, leopard, and cheetah all lived generally near each other, still, in eastern Anatolia, near Mesopotamia, etc. And now, only a few dozen wild native cheetah remain on the entire continent of Asia.
"Cheetah". The word for this cat is from South Asia. Through Hindi, from Sanskrit.
"What happened?" I read on. Cheetahs were present within the national borders of what is now India, along with tigers, lions, and leopards. By the 1500s, there was a tradition in South Asia, where some in the Mughal aristocracy enjoyed using cheetahs as companions in sport hunting. The cats would be captured in the wild, and then trained, and then brought along on royal hunts. The cat was the star athlete, goaded into chasing down prey, for the entertainment of the hunting party. There are elaborate paintings, commissioned by Mughal courts and some now displayed in collections of European museums, depicting trained cheetah hunts. It has since been popularly said that Akbar was particularly fond of cheetahs. (Akbar the Great was the "emperor" who is credited often for consolidating Mughal state power across India, solidifying regional power by building administrative systems/structures in India ["forging an empire out of fiefdoms"] that would later eventually be manipulated and overtaken by the British Empire. According to some tellings of the historical narrative.)
Accurate or not, it was said that at any one time, Akbar possessed one thousand cheetahs. A vast royal menagerie. The names of several of the most celebrated cheetahs are still known. In some stories, when he was still young, Akbar was presented with a gift. His very first cheetah: Fatehbaz.
This disturbed me. A child, reading this book, I was upset by the idea of such a vast menagerie of wild animals. Large wild animals, with great need for food, space, enrichment. I was upset by the exploitation of captive wild animals as displays of aristocratic wealth, not just in the Mughal state(s), but also those menageires and exhibitions elsewhere, both earlier and later in time: the royal hunts of Assyrian kings, the Roman arenas, Charlemagne's elephants, European circuses.
So, as a child, I imagined that Fatehbaz resisted the captivity. Like in a daydream, a fantasy. I imagined a royal menagerie breaking free from restraint. I imagined elephants and rhinos and tigers and lions and leopards and jackals and crocodiles. I imagined the beasts attacking an emperor's court. But there are now less than one hundred cheetahs which survive in the wild in Asia. And when Mughal statecraft gave way to European statecraft, when Britain moved into South Asia, the bounty hunting specifically targeted big cats. And, meanwhile, the cats were confronted indirectly with habitat destruction, commodity crop monocultures, industrial-scale resource extraction. So I came to imagine the ghosts of cats. The ghost of a cheetah like Fatehbaz on the Indus plain. The ghost of a jaguar in the Sonoran desert. The ghost of a lion on the Mediterranean coast. The ghost of a tiger on the Amu Darya shore beyond Bukhara, where even the Aral Sea itself has vanished.
125 notes
·
View notes