#sparkfun
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Rubber Duck Debugging is the method of working through a problem by verbalizing the problem at hand. There is something that happens once you verbalize your problem that makes your brain skirt around the log jam, and jump over to the solution. No really, it works! It turns out, it doesn't matter who you're talking to, the solution follows the action; you might as well be talking to a rubber duck. Try it out if you want: ask any person "what are you stuck on?". While they are describing the problem, 50% of the time you'll see them pause, and then regroup as they realize a solution to the issue they just described. You've been made into a rubber duck. Congrats!
The SparkFun Debugging Duck is a flexible, exceedingly buoyant, clearly fabricated, cognitive device for hardware debugging. Guaranteed to reduce debugging times and increase productivity and conversation. Before you ask your coworker, ask your Debugging Duck "Can I bother you for a minute?".
This is a product that is 50% tongue in cheek, and 50% legit. Ask any engineer and they'll tell you similar stories.
8 notes
·
View notes
Photo
I dont Understand...

Robotics Hand at Vision World Tech Pvt Ltd - Follow for new Updates @visionworldtech 🎯 🌍 - #uav #yuneec #hexacopter #djiinspire1 #quadcopter #miniquad #ironman #robotics #robot #skynet #fpv #drones #aerialphotography #octocopter #robots #djiphantom #arduino #dronepilot #drone #tesla #elonmusk #rcplane #spacex #sparkfun #nasa #mavicpro #2 #staypositive #lawofattraction #3dprinting (at Vision World Tech Pvt. Ltd.) https://www.instagram.com/p/BvOJ59aHmiY/?utm_source=ig_tumblr_share&igshid=1xlx1v8pzqg3q
#uav#yuneec#hexacopter#djiinspire1#quadcopter#miniquad#ironman#robotics#robot#skynet#fpv#drones#aerialphotography#octocopter#robots#djiphantom#arduino#dronepilot#drone#tesla#elonmusk#rcplane#spacex#sparkfun#nasa#mavicpro#2#staypositive#lawofattraction#3dprinting
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text
Quake runs in just 276 kB RAM on the Arduino Nano Matter board
https://community.silabs.com/s/share/a5UVm000000Vi1ZMAS/quake-ported-to-arduino-nano-matter-and-sparkfun-thing-plus-matter-boards?language=en_US
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
This Week in Rust 531
Hello and welcome to another issue of This Week in Rust! Rust is a programming language empowering everyone to build reliable and efficient software. This is a weekly summary of its progress and community. Want something mentioned? Tag us at @ThisWeekInRust on Twitter or @ThisWeekinRust on mastodon.social, or send us a pull request. Want to get involved? We love contributions.
This Week in Rust is openly developed on GitHub and archives can be viewed at this-week-in-rust.org. If you find any errors in this week's issue, please submit a PR.
Updates from Rust Community
Foundation
Q4 2023 Recap from Rebecca Rumbul
Project/Tooling Updates
Ruffle 2023 in review
Four challenges cargo-semver-checks has yet to tackle
rustc_codegen_gcc: Progress Report #29
Roadmap for the Xilem backend in 2024
rust-analyzer changelog #217
pq-sys 0.5.0
What's new in SeaORM 0.12.x
Rust on Espressif chips - January 24 2024
Observations/Thoughts
Making Rust binaries smaller by default
My Best and Worst Deadlock in Rust
Why SQL hang for exactly 940s? TCP and Async Rust!
Making Async Rust Reliable
Identifying Rust’s collect::() memory leak footgun
[video] embassy is now on crates.io
[video] Rust full stack web frameworks have a bright future
[video] Rust Halifax - Rust & Tell #1
[video] Why Rust will keep growing in 2024
Rust Walkthroughs
Using mem::take to reduce heap allocations
Writing your own Rust linter
Using Serde in Rust
Parsing JSON in Rust
Billion-row challenge: Rust walkthrough
Embassy on ESP: Timers
Supporting LoRa on the SparkFun expLoRaBLE Thing Plus with Rust
How to work with !Sized types in Rust
Rocket - logging in the web application
Rocket - access custom configuration in the routes
Testing with tempfiles and environment variables
Research
Profiling Programming Language Learning
Rust-lancet: Automated Ownership-Rule-Violation Fixing with Behavior Preservation
Crate of the Week
This week's crate is apistos, an OpenAPI documentation tool.
Thanks to Romain Lebran for the self-suggestion!
Please submit your suggestions and votes for next week!
Call for Participation; projects and speakers
CFP - Projects
Always wanted to contribute to open-source projects but did not know where to start? Every week we highlight some tasks from the Rust community for you to pick and get started!
Some of these tasks may also have mentors available, visit the task page for more information.
* Ockam - Have a single SqlxDatabase instance per process * Ockam - Improve database migrations to pair sql and rust migration code * Ockam - Make install.sh not fail during upgrade process * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Make cache configuration configurable at runtime * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Implement Code cov for local system using makefile * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Setup code coverage for local tests & CI * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Add domain type for client secret * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Have get_required_value to use ValidationError in OptionExt
If you are a Rust project owner and are looking for contributors, please submit tasks here.
CFP - Speakers
Are you a new or experienced speaker looking for a place to share something cool? This section highlights events that are being planned and are accepting submissions to join their event as a speaker.
If you are an event organizer hoping to expand the reach of your event, please submit a link to the submission website through a PR to TWiR.
Updates from the Rust Project
453 pull requests were merged in the last week
HashMap/HashSet: forward fold implementations of iterators
dead_code treats #[repr(transparent)] the same as #[repr(C)]
fix(rust-analyzer): use new pkgid spec to compare
large_assignments: Lint on specific large args passed to functions
maybe_lint_impl_trait: separate is_downgradable from is_object_safe
never_patterns: Count ! bindings as diverging
never_patterns: typecheck never patterns
pat_analysis: Don't rely on contiguous VariantIds outside of rustc
pattern_analysis: Remove Ty: Copy bound
proc_macro: Add Literal::c_string constructor
single_use_lifetimes: Don't suggest deleting lifetimes with bounds
add #[track_caller] to the "From implies Into" impl
add Ipv6Addr::is_ipv4_mapped
add PatKind::Err to AST/HIR
add help message for exclusive_range_pattern error
add private NonZero<T> type alias
add way to express that no values are expected with check-cfg
added NonZeroXxx::from_mut(_unchecked)?
allow any const expression blocks in thread_local!
always use RevealAll for const eval queries
avoid ICEs in trait names without dyn
consolidate logic around resolving built-in coroutine trait impls
deny braced macro invocations in let-else
detect NulInCStr error earlier
improve let_underscore_lock
improved collapse_debuginfo attribute, added command-line flag
make unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn migrated in edition 2024
restrict access to the private field of newtype indexes
simplify closure_env_ty and closure_env_param
suggest .swap() when encountering conflicting borrows from mem::swap on a slice
undeprecate lint unstable_features and make use of it in the compiler
make MIR pass name a compile-time constant
make stable_mir::with_tables sound
SMIR: make the remaining "private" fields actually private
use an interpreter in MIR jump threading
use implied bounds compat mode in MIR borrowck
validate AggregateKind types in MIR
sandwich MIR optimizations between DSE
cache local DefId-keyed queries without hashing
pack u128 in the compiler to mitigate new alignment
use UnhashMap for a few more maps
fold arithmetic identities in GVN
optimize large array creation in const-eval
implement iterator specialization traits on more adapters
optimize EscapeAscii's Display and CStr's Debug
stabilise bound_map
stabilize round_ties_even
stabilize slice_first_last_chunk
stabilize single-field offset_of!
implement strict integer operations that panic on overflow
core: introduce split_at{,_mut}_checked
un-hide iter::repeat_n
fix deallocation with wrong allocator in (A)Rc::from_box_in
use bool instead of PartialOrd as return value of the comparison closure in {slice,Iterator}::is_sorted_by
regex: make Input::new guard against incorrect AsRef implementations
cargo-rustdoc: use same path by output format logic everywhere
cargo: use pkgid spec in in JSON messages
cargo: remap common prefix only
cargo doc: add a heading to highlight "How to find features enabled on dependencies"
cargo: inherit jobserver from env for all kinds of runner
cargo: fix precise-prerelease tracking link
cargo: go back to passing an empty values() when no features are declared
cargo: improve GitHub Actions CI config
rustdoc: Allows links in headings
rustdoc: hide modals when resizing the sidebar
rustfmt: check that a token can begin a nonterminal kind before parsing it as a macro arg
rustfmt: add config option generated_marker_line_search_limit
clippy: blocks_in_conditions: do not warn if condition comes from macro
clippy: default_numeric_fallback: improve const context detection
clippy: no_effect_underscore_binding: _ prefixed variables can be used
clippy: unused_io_amount captures Ok(_)s
clippy: add suspicious_open_options lint
clippy: correctly handle type relative in trait_duplication_in_bounds lint
clippy: don't emit derive_partial_eq_without_eq lint if the type has the non_exhaustive attribute
clippy: find function path references early in the same lint pass
clippy: fix FP on semicolon_if_nothing_returned
clippy: fix multiple_crate_versions to correctly normalize package names to avoid missing the local one
clippy: fix warning span for no_effect_underscore_binding
clippy: respect #[allow] attributes in single_call_fn lint
clippy: improve wording and fix dead link in description of arc_with_non_send_sync lint
rust-analyzer: add "One" import granularity
rust-analyzer: add a new config to allow renaming of non-local defs
rust-analyzer: goto type actions for notable trait hovers
rust-analyzer: show additional value information when hovering over literals
rust-analyzer: show notable implemented traits on hover
rust-analyzer: add error recovery for use_tree_list parsing
rust-analyzer: fix panic when extracting struct from enum variant
rust-analyzer: fix progress reporting getting stuck
rust-analyzer: handle SelfParam better in "Inline call"
rust-analyzer: include for construct in convert to guarded return conditions
rust-analyzer: infer OUT_DIR when workspace root contains a symlink
rust-analyzer: make value_ty query fallible
rust-analyzer: parse macro_rules as macro name
Rust Compiler Performance Triage
This week saw a bunch of regressions caused by correctness fixes and in general doing more work in the compiler. These were offset by many improvements (especially around hashing in the compiler) that improved performance by ~2% across a large number of benchmarks. Don't get too excited about the large 45+% wins though, these were only for tiny benchmarks like helloworld. They were caused by a change in Cargo which introduces stripping of debug symbols from Rust release binaries by default, and in turn also improves compilation time for small crates.
Triage done by @kobzol. Revision range: f9c2421a..d6b151fc
Summary:
(instructions:u) mean range count Regressions ❌ (primary) 0.7% [0.2%, 1.5%] 11 Regressions ❌ (secondary) 2.2% [0.2%, 9.9%] 26 Improvements ✅ (primary) -3.2% [-47.5%, -0.2%] 191 Improvements ✅ (secondary) -7.9% [-46.5%, -0.1%] 123 All ❌✅ (primary) -3.0% [-47.5%, 1.5%] 202
4 Regressions, 4 Improvements, 9 Mixed; 4 of them in rollups 48 artifact comparisons made in total
Full report here
Approved RFCs
Changes to Rust follow the Rust RFC (request for comments) process. These are the RFCs that were approved for implementation this week:
No RFCs were approved this week.
Final Comment Period
Every week, the team announces the 'final comment period' for RFCs and key PRs which are reaching a decision. Express your opinions now.
RFCs
No RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Tracking Issues & PRs
[disposition: close] Add a default flag for enum documentation
[disposition: merge] impl From<&[T; N]> for Cow<[T]>
[disposition: merge] Tracking Issue for array_methods
Language Reference
No Language Reference RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Unsafe Code Guidelines
No Unsafe Code Guideline RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
New and Updated RFCs
eRFC: Iterate on and stabilize libtest's programmatic output
Call for Testing
An important step for RFC implementation is for people to experiment with the implementation and give feedback, especially before stabilization. The following RFCs would benefit from user testing before moving forward:
No RFCs issued a call for testing this week.
If you are a feature implementer and would like your RFC to appear on the above list, add the new call-for-testing label to your RFC along with a comment providing testing instructions and/or guidance on which aspect(s) of the feature need testing.
Upcoming Events
Rusty Events between 2024-01-24 - 2024-02-21 🦀
Virtual
2024-01-24 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | WeAreDevelopers Community
WeAreDevelopers LIVE - Rust Day
2024-01-25 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-01-25 | Virtual (Linz, AT) | Rust Linz
Rust Meetup Linz - 36th Edition
2024-01-25 | Virtual (Mexico City, DF, MX) | Rust MX
Iniciando 2024 con Rust
2024-01-28 | Virtual (Wrocław, PL) | Stacja IT Wrocław
Wprowadzenie do języka Rust
2024-01-30 | Virtual | Bevy Game Development
Bevy Meetup #1
2024-01-30 | Virtual (Buffalo, NY, US) | Buffalo Rust User Group
Buffalo Rust User Group
2024-01-30 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Last Tuesday
2024-01-31 | Virtual (Cardiff, UK) | Rust and C++ Cardiff
Rust for Rustaceans Book Club launch!
2024-02-01 | Virtual + In Person (Barcelona, ES) | BcnRust
12th BcnRust Meetup - Stream
2024-02-01 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust Hack n Learn | Mirror: Rust Hack n Learn
2024-02-03 | Virtual + In-person (Brussels, BE) | FOSDEM 2024
FOSDEM Conference: Rust devroom - talks
2024-02-03 | Virtual (Kampala, UG) | Rust Circle
Rust Circle Meetup
2024-02-04 | Virtual | Rust Maven
Web development with Rocket - In English
2024-02-07 | Virtual (Indianapolis, IN, US) | Indy Rust
Indy.rs - with Social Distancing
2024-02-08 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-02-08 | Virtual (Nürnberg, DE) | Rust Nüremberg
Rust Nürnberg online
2024-02-10 | Virtual (Wrocław, PL) | Stacja IT Wrocław
Rust – budowanie narzędzi działających w linii komend
2024-02-13 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Second Tuesday
2024-02-15 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust Hack n Learn | Mirror: Rust Hack n Learn
2024-02-21 | Virtual (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
Europe
2024-01-24 | Zagreb, HR | impl Zagreb for Rust
Rust Meetup 2024/01: WebGPU intro using Rust
2024-01-25 | Augsburg, DE | Rust Meetup Augsburg
Augsburg Rust Meetup #5: Async Part2 and Async in action
2024-01-25 | Vienna, AT | Rust Vienna
Rust Vienna Meetup - January - Blockchains and Data Pipelines
2024-02-01 | Hybrid (Barcelona, ES) | BcnRust
12th BcnRust Meetup
2024-02-03 | Brussels, BE | FOSDEM '24
FOSDEM '24 Conference: Rust devroom - talks | Rust Aarhus FOSDEM Meetup
2024-02-03 | Nürnberg, BY, DE | Paessler Rust Camp 2024
Paessler Rust Camp 2024
2024-02-06 | Bremen, DE | Rust Meetup Bremen
Rust Meetup Bremen [1]
2024-02-07 | London, UK | Rust London User Group
Rust for the Web — Mainmatter x Shuttle Takeover
2024-02-08 | Bern, CH | Rust Bern
Rust Bern Meetup #1 2024 🦀
North America
2024-01-24 | Austin, TX, US | Rust ATX
Rust Lunch - Fareground
2024-01-27-28 | Calgary, AB, CA | Rust Calgary
Harnessing Rust for Real-World Problems hackathon: Day 1
Harnessing Rust for Real-World Problems hackathon: Day 2
2024-01-25 | Mountain View, CA, US | Mountain View Rust Meetup
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
2024-01-30 | Cambridge, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Harvard Square Rust Lunch
2024-02-07 | Brookline, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Coolidge Corner Brookline Rust Lunch, Feb 7
2024-02-12 | Minneapolis, MN, US | Minneapolis Rust Meetup
Minneapolis Rust: Open Source Contrib Hackathon & Happy Hour
2024-02-13 | New York, NY, US | Rust NYC
Rust NYC Monthly Mixer
2024-02-13 | Seattle, WA, US | Cap Hill Rust Coding/Hacking/Learning
Rusty Coding/Hacking/Learning Night
2024-02-15 | Boston, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Back Bay Rust Lunch, Feb 15
2024-02-15 | Seattle, WA, US | Seattle Rust User Group
Seattle Rust User Group Meetup
Oceania
2024-02-06 | Perth, WA, AU | Perth Rust Meetup Group
Rust Feb 2024 Meetup
If you are running a Rust event please add it to the calendar to get it mentioned here. Please remember to add a link to the event too. Email the Rust Community Team for access.
Jobs
Please see the latest Who's Hiring thread on r/rust
Quote of the Week
The functional ML roots of the language, Graydon's first Rust compiler was written in OCaml, shine through, influencing it right from the start.
It's not "C++ but better".
It's Haskell standing on Lisp's shoulders, hiding in C's coat to sneak into PRDCTN. (The fancy nightclub where all the popular language's hang out)
– tris on his "No Boilerplate" Youtube channel
Thanks to PrototypeNM1 for the suggestion!
Please submit quotes and vote for next week!
This Week in Rust is edited by: nellshamrell, llogiq, cdmistman, ericseppanen, extrawurst, andrewpollack, U007D, kolharsam, joelmarcey, mariannegoldin, bennyvasquez.
Email list hosting is sponsored by The Rust Foundation
Discuss on r/rust
1 note
·
View note
Photo
sharing something like this...

When I was about to go outside, I received a call from my grandfather. I wondered why my grandpa called so early today. It might be something urgent. On the phone, the old man was relieved: “I finally called you. My phone is broken and now I know. I said why you haven’t called me for so long. Is there something wrong? Is TYC’s teeth better? "I haven’t had time to answer. . It was warm and guilty, and I was really busy recently, and my usual habit of calling my grandfather once a week was affected. No matter how busy you are in the future, remember to call your family if you are outside… #djiphantom4 #djiglobal #uav #3drobotics #djiinspire1 #quadcopter #miniquad #djiphantom3 #robotics #robot #aerialphotography #fpv #drones #hexacopter #octocopter #djiphantom #arduino #hobbyking #drone #multirotor #dronephotography #rcplane #spacex #sparkfun #adafruit #nasa #raspberrypi #mavicpro #skynet #blackmirror https://www.instagram.com/p/CGtawHAHTwT/?igshid=1rey1qj8wmy9v
#djiphantom4#djiglobal#uav#3drobotics#djiinspire1#quadcopter#miniquad#djiphantom3#robotics#robot#aerialphotography#fpv#drones#hexacopter#octocopter#djiphantom#arduino#hobbyking#drone#multirotor#dronephotography#rcplane#spacex#sparkfun#adafruit#nasa#raspberrypi#mavicpro#skynet#blackmirror
1 note
·
View note
Text
Global External Plug-In Adapters Market: Technological Advancements and Market Dynamics 2025–2032
Global External Plug-In Adapters Market Research Report 2025(Status and Outlook)
The global External Plug-In Adapters Market size was valued at US$ 3.67 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 5.94 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 5.6% during the forecast period 2025-2032
Our comprehensive Market report is ready with the latest trends, growth opportunities, and strategic analysis https://semiconductorinsight.com/download-sample-report/?product_id=95822
MARKET INSIGHTS
The global External Plug-In Adapters Market size was valued at US$ 3.67 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 5.94 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 5.6% during the forecast period 2025-2032.
External plug-in adapters are power supply units that convert alternating current (AC) from electrical outlets to direct current (DC) required by electronic devices. These adapters come in various types including AC/AC, AC/DC, and DC/DC configurations, serving diverse applications from consumer electronics to industrial equipment. Key product categories include wall adapters, desktop adapters, and travel adapters designed for different voltage and power requirements.
The market growth is driven by increasing adoption of portable electronic devices, growing demand for energy-efficient power solutions, and expansion of IoT infrastructure. While the Asia-Pacific region dominates production, North America and Europe lead in innovation with stricter energy efficiency standards. However, the market faces challenges from integrated power solutions in newer devices and increasing regulatory pressures on electronic waste. Major players like Delta Electronics, MEAN WELL, and TDK-Lambda continue to invest in compact, high-efficiency designs to meet evolving market needs.
List of Key External Plug-In Adapter Companies Profiled
3M Touch Systems (U.S.)
4D Systems (Australia)
AAEON Technology (Taiwan)
Adafruit Industries (U.S.)
Advantech (Taiwan)
American Power Conversion (U.S.)
Analog Devices (U.S.)
TDK-Lambda Americas (U.S.)
Triad Magnetics (U.S.)
Universal Microelectronics (U.S.)
SparkFun Electronics (U.S.)
MEAN WELL (Taiwan)
Inventus Power (U.S.)
Segment Analysis:
By Type
AC/DC Adapters Dominate the Market Due to Ubiquitous Use in Consumer Electronics
The market is segmented based on type into:
AC/AC
AC/DC
DC/DC
Others
By Application
Communication Products Lead the Market Due to Rapid Digitalization and IoT Expansion
The market is segmented based on application into:
Communication products
Laptops
Broadcasting equipment
Medical devices
Others
By Power Rating
Medium Power Range (50W-100W) Segment Holds Significant Share in Industrial Applications
The market is segmented based on power rating into:
Low power (below 50W)
Medium power (50W-100W)
High power (above 100W)
By Form Factor
Wall Plug-in Variants Remain Most Popular Due to Space Efficiency
The market is segmented based on form factor into:
Wall plug-in
Desktop
Others
Regional Analysis: Global External Plug-In Adapters Market
North America The North American market is characterized by high consumer demand for energy-efficient external plug-in adapters, driven by strict regulatory standards like the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) efficiency mandates. The region holds a 32% share of the global market, primarily due to rapid technological advancements in USB-C and GaN (Gallium Nitride) based adapters. Leading manufacturers such as American Power Conversion and Triad Magnetics are investing in compact, fast-charging solutions to cater to the rising demand for portable electronics. While the U.S. dominates, Canada is also witnessing steady growth due to increasing adoption in IT & telecom sectors. However, supply chain disruptions and tariff policies have moderately impacted pricing trends.
Europe Europe’s market is shaped by rigorous environmental policies under the EU Ecodesign Directive, which enforces energy efficiency benchmarks for external power adapters. The region accounts for approximately 28% of global sales, with Germany, France, and the UK leading in demand. European consumers prioritize eco-design certifications like Energy Star and ErP compliance. The shift towards wireless charging and universal adapter compatibility has spurred R&D investments by companies like TDK-Lambda Americas and Analog Devices. However, economic uncertainties, including inflation and energy crises, have led to cautious spending in the commercial sector, slightly slowing market expansion.
Asia-Pacific Asia-Pacific dominates the global market with a 42% revenue share, fueled by massive electronics manufacturing hubs in China, Japan, and South Korea. China alone contributes over 30% of global adapter production, supported by cost-efficient labor and strong supply chain networks. The region benefits from growing laptop and smartphone penetration, with India and Southeast Asia emerging as high-growth markets due to rapid urbanization. While price sensitivity drives demand for budget-friendly AC/DC adapters, premium GaN-based products are gaining traction in developed economies like Japan. Challenges include inconsistent regulatory standards across countries and intellectual property concerns in manufacturing.
South America The South American market remains niche but is expanding at a steady CAGR of 6.8%, primarily driven by increasing digitalization in Brazil and Argentina. Demand is concentrated in urban centers for communication devices and laptops, though economic instability has limited large-scale investments. Import dependency on Chinese-manufactured adapters creates pricing volatility, while local assembly initiatives are gradually emerging. The lack of stringent efficiency regulations compared to North America or Europe results in a higher share of non-certified, low-cost adapters. Nevertheless, partnerships between global brands like MEAN WELL and regional distributors are improving product accessibility.
Middle East & Africa This region shows promising but uneven growth, with the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa accounting for 70% of the regional market. Infrastructure development and rising FDI in tech sectors are driving demand for reliable power adapters in enterprise and consumer applications. While high disposable incomes in GCC countries support premium adapter sales, price-sensitive African markets rely on refurbished or generic products. Market fragmentation and counterfeit products pose significant challenges, though initiatives like the UAE’s Energy Efficiency Strategy are encouraging standardized adoption. Long-term opportunities lie in renewable energy-compatible adapters as solar power gains momentum across Africa.
MARKET DYNAMICS
The global data center market expansion, driven by cloud computing and AI workloads, presents a significant opportunity for high-performance external power solutions. Modern hyperscale data centers require thousands of precisely regulated power supplies for networking equipment and edge computing devices. The power adapter segment for data center applications is expected to reach $3.2 billion by 2026, with demand focusing on reliability, efficiency, and intelligent power management features. Leading manufacturers are developing specialized adapters with remote monitoring capabilities and load balancing functions to address this growing niche.
Developing economies in Southeast Asia, Africa and Latin America offer substantial expansion opportunities as electrification rates improve and disposable incomes rise. These regions exhibit compound growth rates 2-3 times higher than mature markets, driven by first-time electronics buyers and infrastructure development. Manufacturers are establishing localized production facilities and distribution networks to capitalize on this demand while navigating varying regional voltage standards and plug configurations. Strategic partnerships with local retailers and telecom providers are proving effective in accessing these growth markets.
The external power adapter industry continues grappling with semiconductor shortages and logistical bottlenecks that extend lead times by 8-12 weeks compared to pre-pandemic levels. Critical components like power ICs and capacitors face allocation constraints, forcing manufacturers to redesign products with alternative components. This component substitution process adds validation costs and risks performance variations. The situation is particularly challenging for smaller manufacturers lacking the purchasing power to secure stable component supplies through long-term contracts.
Expanding environmental directives regarding hazardous substances and recyclability are adding compliance complexity. New regulations require detailed material disclosures and impose restrictions on certain chemicals used in adapter manufacturing. Meeting these requirements while maintaining competitive pricing represents a key challenge, with environmental compliance costs estimated to add 7-10% to overall product costs. Manufacturers must balance these requirements against the need to deliver affordable products in price-sensitive market segments.
The market is highly fragmented, with a mix of global and regional players competing for market share. To Learn More About the Global Trends Impacting the Future of Top 10 Companies https://semiconductorinsight.com/download-sample-report/?product_id=95822
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
What is the current market size of Global External Plug-In Adapters Market?
Which key companies operate in Global External Plug-In Adapters Market?
What are the key growth drivers?
Which region dominates the market?
What are the emerging trends?
Related Reports:
https://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/network-set-top-box-market-strategic.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/digital-set-top-box-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/5g-base-station-microwave-dielectric.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/automotive-magnetic-sensor-market-cost.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/holographic-diffraction-grating-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/electronic-grade-silicon-wafer-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/silicon-epitaxial-wafer-market-value.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/annealed-silicon-wafer-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/computer-power-supplies-market-revenue.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/power-supply-unit-psu-market-innovation.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/automotive-cockpit-domain-control-unit.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/global-vehicle-ecus-and-dcus-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/global-automotive-ecuelectronic-control.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/global-vehicle-electronic-control-units.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/07/global-automotive-ecus-and-dcus-market.html
CONTACT US: City vista, 203A, Fountain Road, Ashoka Nagar, Kharadi, Pune, Maharashtra 411014 [+91 8087992013] [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Resistor Calculator: The Smart Way to Choose the Right Resistor
In electronics, precision and efficiency go hand-in-hand. One of the most common—and important—components in any circuit is the resistor. Whether you're adjusting current levels, dividing voltage, or protecting a component, selecting the correct resistor value is critical. This is where a resistor calculator comes into play. It’s a simple yet powerful digital tool that takes the guesswork out of resistor selection.

What Is a Resistor Calculator?
A resistor calculator is an online or app-based tool designed to help users quickly find resistor values, decode resistor color bands, and perform resistance-based calculations. It is especially helpful for decoding the color bands printed on traditional axial resistors and for calculating required resistance using Ohm’s Law.
There are several types of resistor calculators, including:
Color Code Calculators: Decode 4, 5, or 6-band resistor values based on band colors.
Ohm’s Law Calculators: Calculate resistance, voltage, or current when two of the three variables are known.
Power Rating Calculators: Determine how much power a resistor will dissipate based on voltage and resistance.
Why You Need a Resistor Calculator
1. Simplifies Resistor Selection: With just a few inputs, you can determine exactly which resistor you need for your project. No need to memorize color code charts or perform manual calculations.
2. Saves Time: Instead of digging through datasheets or conversion tables, you get instant results. It’s especially useful when prototyping or troubleshooting on the fly.
3. Reduces Mistakes: It's easy to misread a color band or miscalculate resistance, especially when working under pressure. A resistor calculator ensures your values are correct and consistent.
4. Accessible for Everyone: Whether you're a student learning basic electronics or an engineer designing advanced circuits, resistor calculators make complex calculations accessible and understandable.
How It Works
Let’s say you have a resistor with color bands: brown, black, orange, and gold. Instead of figuring out what those mean manually, simply input the band colors into a color code calculator. It will tell you that the resistor is 10,000 ohms (10kΩ) with a ±5% tolerance.
If you're designing a circuit and want to power an LED with a 5V supply and limit current to 20mA, just resistor color code chart voltage and current into an Ohm’s Law calculator. It will give you the required resistor value: 250 ohms.
Where to Find Resistor Calculators
There are many reliable tools online from websites like Digi-Key, Mouser, All About Circuits, and SparkFun. Many of these platforms also offer free mobile apps that you can use offline—perfect for field work or classroom labs.
Final Thoughts
A resistor calculator may seem like a small part of your electronics toolkit, but it plays a big role in improving accuracy, saving time, and enhancing the design process. Whether you’re building a simple blinking LED circuit or a complex embedded system, using a resistor calculator ensures that your project is built on a solid foundation.
0 notes
Text
Next-Gen Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensors: Market Outlook & Innovations Through 2032

Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market was valued at USD 89.4 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 148.6 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2032.
Get Full Report:
Market Overview
global Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market was valued at USD 89.4 million in 2024 and is expected to grow significantly, reaching USD 148.6 million by 2032. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2032.
This report presents a comprehensive examination of the market, offering a detailed view that spans from high-level industry trends to specific segment analyses. It explores the evolving competitive landscape, assesses the impact of technological developments, and identifies both the challenges and growth opportunities shaping the future of this sector.
Through a combination of data-driven insights and strategic perspectives, this report serves as a valuable resource for industry stakeholders, including manufacturers, investors, analysts, consultants, and business leaders planning to enter or expand within this market.
Key Market Trends
Increased Use in Medical Devices The flexibility and sensitivity of these sensors make them ideal for medical diagnostics and continuous patient monitoring.
Industrial Automation Growth The adoption of automation technologies across sectors has spurred demand for precise and reliable sensor solutions.
Advancements in Wearable and Flexible Electronics Innovation in flexible electronics is integrating piezo sensors into next-generation consumer and industrial devices.
Rising Defense Sector Adoption Military applications for these sensors include surveillance, vibration sensing, and advanced combat systems.
Ongoing R&D Investment Continuous research aims to enhance sensor performance, miniaturization, and durability.
Regional Market Insights
North America remains a strong market, with high demand driven by the rapid expansion of electric vehicles, 5G infrastructure, and renewable energy technologies. The United States leads this region in terms of market share and technological adoption.
Europe is witnessing steady growth, fueled by automotive electrification, sustainable energy initiatives, and supportive regulatory policies. Germany, with its advanced manufacturing base, plays a pivotal role in the region’s development.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the global market, thanks to large-scale production capabilities in China and Japan. The increasing penetration of EVs, advanced semiconductors, and telecommunications infrastructure continues to drive demand in this region.
South America is emerging as a growing market, particularly in Brazil, where investment in clean energy and electric mobility is accelerating adoption. In the Middle East and Africa, gradual but consistent growth is expected, primarily due to national programs focusing on renewable energy and electric vehicle infrastructure. Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are at the forefront of this development.
Get a Free Sample Report:
Market Segmentation
By Type
Surface Sensors
Implant Sensors
By Application
Industrial
Defense
R&D Laboratories
Technical Education
Medical
By Region
North America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
South America
Middle East & Africa
Key Companies
TE Connectivity
SparkFun Electronics
E-Touch
Market Drivers
Rising Demand for Lightweight and Flexible Electronics Especially in healthcare and consumer devices.
Industrial Automation Need for high-performance sensing in automated systems is expanding.
Health Monitoring Technologies Wearables and patient care devices are increasingly adopting piezo sensors.
Market Restraints
High Production Costs Advanced manufacturing methods lead to higher unit costs.
Durability Issues in Harsh Conditions Sensor degradation can occur under extreme environments, limiting industrial usage.
Integration Complexity Existing systems may require adaptation, slowing adoption.
Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
Despite current limitations, several promising opportunities are on the horizon. Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific, offer immense potential for expansion due to rapidly growing healthcare and electronics sectors. The development of application-specific, customizable sensor solutions also provides an avenue for differentiation and value creation. Furthermore, as the Internet of Things (IoT) and wearable technology continue to gain traction globally, demand for lightweight, flexible sensors is expected to surge.
At the same time, competition from alternative sensing technologies such as MEMS and capacitive sensors may challenge market share. Regulatory and compliance complexities, especially in defense and healthcare applications, can slow time-to-market for new products. Additionally, global supply chain disruptions continue to pose risks to raw material availability and production schedules.
Key Benefits of This Report
Covers all key drivers, restraints, opportunities, and trends
Provides historical, current, and future market values (USD)
Highlights high-growth regions and segments
Includes strategies of major players
Offers a clear overview through charts and tables
Enables better strategic planning and competitor benchmarking
Features value chain analysis and market dynamics
Backed by 6-month post-sales analyst support
Why Purchase This Report?
Stay informed with the latest market data and forecasts
Gain insights into emerging trends and opportunities
Make informed decisions with concise, actionable insights
Copy data directly into presentations and strategy documents
Identify regions and segments offering fastest growth and ROI
Need Customization?
Our team is ready to customize the report to meet your specific business goals. For tailored research, additional data, or specific regional insights, contact our sales team today.
Related Research Reports:
https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/12-inch-semiconductor-silicon-wafer-market/
https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/global-gesture-sensor-market/
https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/iris-recognition-access-control-system-market/
https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/thermistor-temperature-sensor-market-2/
Contact us:
+91 8087992013
#marketing#Globalflexibleleadpiezomarket#Globalflexibleleadpiezomarketforecast#Globalflexibleleadpiezomarketoutlook#Globalflexibleleadpiezomarketanalysis#Globalflexibleleadpiezomarketfutureoutlook#Globalflexibleleadpiezomarketkeytrends
0 notes
Link
[ad_1] The launch of the Raspberry Pi Pico 2 marks a significant upgrade from its predecessor, the Raspberry Pi Pico. by Blade November 13, 2024 4:30 pm UTC 8 Favorited Favorite 0 Back in August, Raspberry Pi launched the Raspberry Pi Pico 2 with the onboard RP2350 microcontroller. At the same time, SparkFun came out with the SparkFun Pro Micro - RP2350. Both sold out quickly and it took some time to get them back in stock. Now that we have healthy stock of both the Pico 2 and the Pro Micro - RP2350 we thought we'd go through the technical differences between Raspberry Pi's RP2350 and its predecessor, the RP2040. Overview of the RP2040 The RP2040 chip, introduced in January of 2021 alongside the original Raspberry Pi Pico, was a groundbreaking entry into the microcontroller market by Raspberry Pi. It featured: Dual-core ARM Cortex-M0+: Operating at 133 MHz, the RP2040 provided ample power for a variety of embedded applications. 264kB of SRAM: Sufficient memory for lightweight applications and real-time tasks. 2MB of Flash memory: Provided ample storage for most embedded projects. 30 GPIO Pins: Including programmable IO (PIO) for flexible, custom peripherals. USB 1.1 Device and Host Support: Allowing for basic connectivity options. 2 × Programmable IO (PIO) blocks, 8 state machines total: Enabling custom peripheral implementations such as SD Card and VGA. These features made the RP2040 an excellent choice for hobbyists and professionals alike, offering an affordable platform for a wide range of applications. See Full RP2040 Datasheet Products offering the RP2040 SparkFun Pro Micro - RP2040 In stock DEV-18288 The SparkFun Pro Micro RP2040 is a low-cost, high performance board with flexible digital interfaces featuring the Raspberry … 3 Raspberry Pi Pico In stock DEV-17829 The Raspberry Pi Pico is a low-cost, high-performance microcontroller board with flexible digital interfaces featuring the ne… 3 Overview of the RP2350 The RP2350, the heart of the Raspberry Pi Pico 2, builds upon the strengths of the RP2040 while introducing several enhancements: Dual ARM CortexM33 and Hazard3 RISC-V Processors at 150 MHz: A significant boost in clock speed, offering improved performance for more demanding applications. Users can select two processors to run on boot. 520kB of SRAM: An increase in memory, supporting more complex operations and larger datasets. Up to 16 MB of external QSPI flash/PSRAM: Accessible via optional second chip-select catering to applications that require more extensive codebases or data logging. 30-48 GPIO Pins (depending on model): Expanding the I/O options, offering more flexibility in interfacing with external hardware. 12 Programmable IO (PIO) state machines: Increasing the number of custom peripheral implementations that can be run simultaneously. Optional RISC-V Cores: Unique to the RP2350, users can choose between dual ARM Cortex-M33 cores and dual Hazard3 RISC-V cores, offering flexibility in architecture choice. Advanced Security Features: Includes Arm TrustZone for Cortex-M, signed boot, 8kB of antifuse OTP for key storage, SHA-256 acceleration, a hardware TRNG, and fast glitch detectors, providing robust security options for professional-grade applications. The RP2350’s advanced security features and dual-core, dual-architecture capability highlight its suitability for professional and industrial applications, while still retaining the accessibility and affordability that made the original Raspberry Pi Pico so popular. See Full RP2350 Datasheet Products offering the RP2350 SparkFun Pro Micro - RP2350 In stock DEV-24870 The SparkFun RP2350 Pro Micro provides a powerful development platform in our compact Pro Micro form factor built around the… 5 Raspberry Pi Pico 2 In stock DEV-26124 Raspberry Pi Pico development board featuring the RP2350 Cortex M processor with dual RISC-V Hazard3 cores. 1 Key Differences To provide a clearer view of the advancements, here’s a comparison table highlighting the main differences of the RP2040 and RP2350 chips: Feature RP2040 RP2350 Processor Dual-core ARM Cortex-M0+ at 133 MHz ARM® Cortex® M33 processors and two Hazard3 RISC-V processors at 150 MHz (user-selectable for dual-cores) SRAM 264kB 520kB (in 10 banks) Internal Flash Memory 2MB 0/2MB (model dependent) GPIO Pins 30 30—48 USB Support USB 1.1 Device and Host USB USB 1.1 controller and PHY, with host and device support Programmable IO (PIO) 8 state machines 12 state machines Security Features No security features Arm TrustZone, signed boot, 8kB antifuse OTP, SHA-256 acceleration, hardware TRNG, glitch detectors Performance and Security Implications The increase in clock speed from 133 MHz to 150 MHz in the RP2350 translates to a noticeable performance boost, particularly beneficial in real-time applications. The optional RISC-V cores offer flexibility in processing architecture, catering to various application needs. Additionally, the enhanced security features make the RP2350 suitable for applications requiring robust protection against tampering and unauthorized access. Conclusion The RP2350 chip offers significant upgrades over the RP2040, making it a strong candidate for more demanding embedded applications. Whether you’re developing a new project or looking to upgrade an existing one, the enhancements in performance, memory, I/O options, security, and architectural flexibility make the Raspberry Pi Pico 2 a compelling choice moving forward. [ad_2] Source link
0 notes
Text
Global Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market to Reach US$ 148.6 Million by 2032

Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market Analysis:
The global Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market size was valued at US$ 89.4 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 148.6 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 6.6% during the forecast period 2025-2032
Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market Overview
This report provides a deep insight into the global Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor market covering all its essential aspects. This ranges from a macro overview of the market to micro details of the market size, competitive landscape, development trend, niche market, key market drivers and challenges, SWOT analysis, value chain analysis, etc. The analysis helps the reader to shape the competition within the industries and strategies for the competitive environment to enhance the potential profit. Furthermore, it provides a simple framework for evaluating and accessing the position of the business organization. The report structure also focuses on the competitive landscape of the Global Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market, this report introduces in detail the market share, market performance, product situation, operation situation, etc. of the main players, which helps the readers in the industry to identify the main competitors and deeply understand the competition pattern of the market. In a word, this report is a must-read for industry players, investors, researchers, consultants, business strategists, and all those who have any kind of stake or are planning to foray into the Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor market in any manner.
Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Key Market Trends :
Rising Adoption in Medical Devices Flexible lead piezo film sensors are increasingly used in medical applications for patient monitoring and diagnostics due to their flexibility and sensitivity.
Growth in Industrial Automation Industries are integrating these sensors in automated systems for precise motion detection and control, boosting demand.
Advancements in Flexible Electronics Innovations in flexible and wearable electronics are driving the integration of piezo film sensors into new product designs.
Expansion in Defense Applications Defense sectors are utilizing these sensors for surveillance, vibration monitoring, and advanced weaponry systems.
Increased Research & Development Activities Continuous R&D efforts focus on improving sensor durability, accuracy, and miniaturization to expand applications.
Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market Regional Analysis :
https://semiconductorinsight.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/download-34_11zon-1.png
North America:Strong demand driven by EVs, 5G infrastructure, and renewable energy, with the U.S. leading the market.
Europe:Growth fueled by automotive electrification, renewable energy, and strong regulatory support, with Germany as a key player.
Asia-Pacific:Dominates the market due to large-scale manufacturing in China and Japan, with growing demand from EVs, 5G, and semiconductors.
South America:Emerging market, driven by renewable energy and EV adoption, with Brazil leading growth.
Middle East & Africa:Gradual growth, mainly due to investments in renewable energy and EV infrastructure, with Saudi Arabia and UAE as key contributors.
Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market Segmentation :
The research report includes specific segments by region (country), manufacturers, Type, and Application. Market segmentation creates subsets of a market based on product type, end-user or application, Geographic, and other factors. By understanding the market segments, the decision-maker can leverage this targeting in the product, sales, and marketing strategies. Market segments can power your product development cycles by informing how you create product offerings for different segments. Key Company
TE Connectivity
SparkFun Electronics
E-Touch
Market Segmentation (by Type)
Surface
Implant
Market Segmentation (by Application)
Industry
Defense
R&D Laboratories
Technical Education
Medical
Drivers
Increasing Demand for Lightweight and Flexible Sensors The need for lightweight, flexible, and thin sensors in electronics and healthcare is a major growth driver.
Rising Industrial Automation Automation in manufacturing and process industries requires precise sensing technologies, boosting market demand.
Growth in Healthcare Monitoring Systems Flexible piezo film sensors are favored in wearable health devices, increasing their adoption in the medical sector.
Restraints
High Production Costs The complex manufacturing process of flexible piezo film sensors leads to higher costs, limiting widespread adoption.
Limited Durability in Harsh Environments Some sensor materials may degrade under extreme conditions, restricting use in certain industrial applications.
Technological Complexity Integrating these sensors with existing systems can be challenging, hindering fast market penetration.
Opportunities
Expansion into Emerging Markets Growing electronics and healthcare sectors in Asia-Pacific offer lucrative opportunities for market expansion.
Development of Customized Sensor Solutions Tailoring sensors for specific applications can open new revenue streams for manufacturers.
Integration with IoT and Wearable Devices The rise of IoT and wearable tech creates strong demand for flexible sensors in consumer electronics and fitness monitoring.
Challenges
Competition from Alternative Sensing Technologies Other sensor types like MEMS and capacitive sensors compete for market share, challenging growth.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues Stringent regulations in medical and defense applications can slow down product approvals and adoption.
Supply Chain Disruptions Global supply chain issues can impact the availability of raw materials and components, affecting production timelines.
Key Benefits of This Market Research:
Industry drivers, restraints, and opportunities covered in the study
Neutral perspective on the market performance
Recent industry trends and developments
Competitive landscape & strategies of key players
Potential & niche segments and regions exhibiting promising growth covered
Historical, current, and projected market size, in terms of value
In-depth analysis of the Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market
Overview of the regional outlook of the Flexible Lead Piezo Film Sensor Market:
Key Reasons to Buy this Report:
Access to date statistics compiled by our researchers. These provide you with historical and forecast data, which is analyzed to tell you why your market is set to change
This enables you to anticipate market changes to remain ahead of your competitors
You will be able to copy data from the Excel spreadsheet straight into your marketing plans, business presentations, or other strategic documents
The concise analysis, clear graph, and table format will enable you to pinpoint the information you require quickly
Provision of market value (USD Billion) data for each segment and sub-segment
Indicates the region and segment that is expected to witness the fastest growth as well as to dominate the market
Provides insight into the market through Value Chain
Market dynamics scenario, along with growth opportunities of the market in the years to come
6-month post-sales analyst support
Customization of the Report In case of any queries or customization requirements, please connect with our sales team, who will ensure that your requirements are met.
0 notes
Text
Persistent Storage in Zephyr: Saving Data to Files
Introduction
In this series of blog posts introducing The Zephyr Project RTOS, we have primarily concentrated on Zephyr internals and infrastructure. Recall that Zephyr wants to be a leading RTOS for devices with limited resources that are connected. To guarantee a platform that is secure, dependable, and vendor-neutral, Zephyr incorporates open-source and security best practices.

I'll demonstrate how to make an application in Zephyr to store data on a microSD card in this blog post. Even though the majority of embedded systems today can upload sensor data via the internet, the connection might be erratic. There are two benefits to having a microSD card. It can be expanded, to start. A micro-SD card of one size can be changed for a larger one, but onboard RAM and flash storage are fixed. Second, a desktop computer can be used to access data from a microSD card.
Hardware
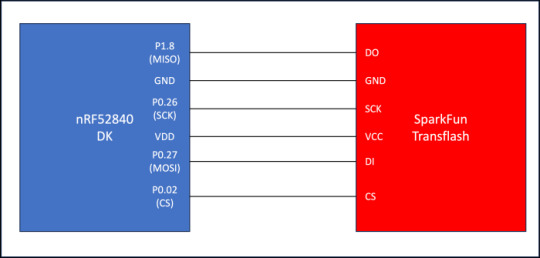
This blog post will use the Nordic nRF52840 development kit (https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Development-hardware/nrf52840-dk). We will connect the nRF52840 development kit to the SparkFun microSD Transflash Breakout board (https://www.sparkfun.com/products/544). Any microSD card from a reputable vendor will suffice.
The following diagram shows the connections between the SparkFun microSD module and the nRF52840 development kit:
Embedded Software
We will go over the pertinent parts of the embedded software that interface with the SD card in this section. First, we can use West to get Zephyr v3.5 by running the following command: $> west init -m <a href="https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr">https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr</a> --mr v3.5.0 zephyrproject$> cd zephyrproject$> west update
Second, we can clone the repository that contains our test application: $> git clone https://github.com/mabembedded/zephyr-sd-spi.git
Third, we need to make sure that the exFAT scheme—which is Windows' default—is used to format our SD card. Lastly, we can open a terminal interface and use the USB connection to connect the nRF52840 development kit to our PC. We can build and flash the application by executing the following commands: $> cd zephyr-sd-spi$> cmake –preset build$> west build && west flash
We should see the following output in the terminal interface: *** Booting Zephyr OS build zephyr-v3.5.0 ***[00:00:00.402,770] <inf> sd: Maximum SD clock is under 25MHz, using clock of 24000000Hz[00:00:00.414,215] <inf> main: Block count 384503808Sector size 512Memory Size(MB) 187746Disk mounted.Listing dir /SD: ...[DIR ] System Volume Information[FILE] test_data.txt (size = 13)Successfully mounted SD cardmain - successfully created file
If we plug in the SD card to our PC and open it up in File Explorer, we should see “test_data.txt” with the string “hello world!” on the first line, as seen below:
Kconfig
The following relevant Kconfig options are enabled in the “prj.conf” file, with a description of each:
CONFIG_DISK_ACCESS: This option allows for the disk access subsystem.
CONFIG_FILE_SYSTEM: This option allows for the filesystem subsystem.
CONFIG_FAT_FILESYSTEM_ELM: This option instructs Zephyr to use the “ELM” FAT FS implementation, found on http://elm-chan.org/.
CONFIG_FS_FATFS_MOUNT_MKFS: This option instructs Zephyr to create a disk with a FAT filesystem if none is found.
CONFIG_FS_FATFS_EXFAT: This option enables the exFAT partition scheme.
CONFIG_DISK_DRIVER_SDMMC: This option enables the SD/EMMC driver.
CONFIG_SPI: This option enables the SPI subsystem.
CONFIG_GPIO: This option enables the GPIO subsystem.
Devicetree Overlay
Additionally, there are two reasons why we must create a Devicetree overlay. The nRF52840 development kit's pins for the SPI connection to the SparkFun Transflash breakout board must first be updated. Secondly, we need to tell the application firmware that an SD card is plugged in. As indicated below, we must first add a new entry to the pinctrl block in order to update the SPI pins: &pinctrl { custom_spi: custom_spi { group1 { psels = <NRF_PSEL(SPIM_SCK, 0, 26)>, <NRF_PSEL(SPIM_MOSI, 0, 27)>, <NRF_PSEL(SPIM_MISO, 1, 8)>; }; };};
Then, we need to update the SPI block in the overlay with our custom pinctrl (and also add the GPIO for the CS line): &spi1 { status = "okay"; pinctrl-0 = <&custom_spi>; pinctrl-1 = <&custom_spi>; pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep"; cs-gpios = <&gpio0 2 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;...
The following needs to be added in the “spi1” node to inform the application of the existence of the SD card: ... sdhc0: sdhc@0 { compatible = "zephyr,sdhc-spi-slot"; reg = <0>; status = "okay"; label = "SDHC_0"; mmc { compatible = "zephyr,sdmmc-disk"; status = "okay"; }; spi-max-frequency = <24000000>; };};
Application Source
With the Devicetree Overlay and Kconfig installed, we can go over the implementation step-by-step. To make sure our program can accurately read the files on the SD card, I made two helper functions. The prototype for the first function, "lsdir," is as follows:staticintlsdir(constchar *path);
This function prints all of the directories and files contained in a given path when it receives it as input. The second function, "mount_sd_card," makes use of "lsdir." The following tasks are carried out by this function:
Initializes the underlying disk via “disk_access_init.”
Retrieves the number of sectors via “disk_access_ioctl” with “DISK_IOCTL_GET_SECTOR_COUNT” as a parameter.
Retrieves the sector size via “disk_access_ioctl” with “DISK_IOCTL_GET_SECTOR_SIZE” as a parameter.
Prints the total space of the SD card using the information retrieved above.
Mounts the SD card. If the SD card was successfully mounted, the function lists the files and directories at the root of the SD card. If not, the function tries to mount again.
In "main," "mount_sd_card" is used as the first function. It initializes the "fs_file_t" data structure, which is displayed below, upon success. Every subsequent file operation will make use of the data structure.structfs_file_t data_filp;fs_file_t_init(&data_filp);
The "fs_unlink" function is then used to remove "test_data.txt" from the SD card's root, if it exists. The following line creates a new file named "test_data.txt" and opens it for writing: fs_open(&data_filp, "/SD:/test_data.txt", FS_O_WRITE | FS_O_CREATE);
Finally, the following lines are used to write “hello world!” to the file that was created: sprintf(file_data_buffer, "hello world!\n");ret = fs_write(&data_filp, file_data_buffer, strlen(file_data_buffer));fs_close(&data_filp);
Summary
In this blog post, we demonstrated how to mount a microSD card, write data to it, and create a new file on the microSD card using a Zephyr application. Devices in the field that need to periodically write data to off-board memory can benefit from the lessons learned from such an application, particularly in situations where Internet access may be intermittent. We will continue our journey of writing a custom BLE application that runs on Zephyr in the upcoming blog post!
If you're looking to enhance your embedded systems with advanced storage capabilities like microSD integration or custom BLE applications, Silicon Signals is here to help. Our team specializes in hardware design, software development, and integration of cutting-edge solutions using Zephyr and other RTOS platforms.
👉 Contact Us Today to explore how we can elevate your projects with tailored embedded systems solutions!
0 notes
Text
Arduino Projects
Arduino is a microcontroller platform made to facilitate hardware integration and programming. Each of its boards, including the Arduino Uno, Nano, and Mega, is designed to meet a distinct set of requirements. When used in conjunction with the Arduino IDE, users may easily write, upload, and execute code.
Users can design projects ranging from basic LED blinkers to intricate robotics and Internet of Things systems thanks to the platform's extensive library of sensors, modules, and components.
Top Arduino Project Ideas
System for Home Automation
An Arduino with a smartphone app can be used to control lights, fans, and other appliances. Your system can become more intelligent and energy-efficient by integrating sensors like temperature or motion detectors.
The weather station
Construct a personal weather station to track air pressure, temperature, and humidity. You can gather data using sensors like the DHT11 and BMP180, show it on an LCD screen, or post it online for remote access.
Robot That Avoids Obstacles
This well-liked project for robotics novices is teaching a robot to use ultrasonic sensors to navigate around obstacles.
Intelligent Plant Monitoring System
An Arduino-based monitoring system that measures temperature, light intensity, and soil moisture can help you keep your plants healthy. Even when it's time to water your plants, it may let you know.
Alarm System with Arduino
Create an Arduino-powered alarm system with a buzzer, keypad, and motion sensors to increase security. For workplace or home security, this project is perfect.
Pet Feeder with Automation
Construct a pet feeder that automatically delivers food depending on a weight sensor reading or at predetermined intervals.
Internet of Things Door Lock
Create a smart door lock that you can operate from a distance using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi by integrating an Arduino with an RFID scanner or fingerprint sensor.
Make Your Own Game Console
Convert an Arduino board with basic buttons and a display into a vintage game console.
How to Get Started with Arduino Projects
Select the appropriate board:
Choose an Arduino board based on the needs of your project. The Arduino Uno is an excellent place to start for the majority of novices.
Assemble the parts:
Determine the sensors, actuators, and other parts your project needs. A wide range of Arduino-compatible components are available on websites like Adafruit, SparkFun, and Amazon.
Set up the Arduino IDE:
Install the Arduino IDE by downloading it from Arduino.cc. You can develop code and upload it to your board using this software.
The universe of creativity and invention is unlocked by Arduino projects. Arduino offers the resources and network to realize your ideas, whether you want to study robotics, automate your house, or develop a ground-breaking technology.
Explore the world of Arduino now and unleash your creative side! Do you have a favorite idea for an Arduino project? Tell us about it in the comments section below.
To know more, click here.
0 notes
Text
Arduino what now??
This project is SUPPOSED to open doors and insights into the world of makerspaces and coding through the Arduino circuit board. Right now it's making me want to pull my hair out and drink way more Diet Dr. Pepper than I need.
This is the code from example circuit #3. I learned that if i anything is out of place- IT WILL NOT WORK!! This is the rainbow circuit...
/*
Example sketch 03
RGB LED
Make an RGB LED display a rainbow of colors!
Hardware connections:
An RGB LED is actually three LEDs (red, green, and blue) in
one package. When you run them at different brightnesses,
the red, green and blue mix to form new colors.
Starting at the flattened edge of the flange on the LED,
the pins are ordered RED, COMMON, GREEN, BLUE.
Connect RED to a 330 Ohm resistor. Connect the other end
of the resistor to Arduino digital pin 9.
Connect COMMON pin to GND.
Connect GREEN to a 330 Ohm resistor. Connect the other end
of the resistor to Arduino digital pin 10.
Connect BLUE to a 330 Ohm resistor. Connect the other end
of the resistor to Arduino digital pin 11.
This sketch was written by SparkFun Electronics,
with lots of help from the Arduino community.
Visit http://www.arduino.cc to learn about the Arduino.
Version 2.0 6/2012 MDG
*/
// First we'll define the pins by name to make the sketch
// easier to follow.
// Here's a new trick: putting the word "const" in front of a
// variable indicates that this is a "constant" value that will
// never change. (You don't have to do this, but if you do, the
// Arduino will give you a friendly warning if you accidentally
// try to change the value, so it's considered good form.)
const int RED_PIN = 9;
const int GREEN_PIN = 10;
const int BLUE_PIN = 11;
// This variable controls how fast we loop through the colors.
// (Try changing this to make the fading faster or slower.)
int DISPLAY_TIME = 100; // In milliseconds
void setup()
{
// Here we'll configure the Arduino pins we're using to
// drive the LED to be outputs:
pinMode(RED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(GREEN_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BLUE_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
// In this sketch, we'll start writing our own functions.
// This makes the sketch easier to follow by dividing up
// the sketch into sections, and not having everything in
// setup() or loop().
// We'll show you two ways to run the RGB LED.
// The first way is to turn the individual LEDs (red, blue,
// and green) on and off in various combinations. This gives you
// a total of eight colors (if you count "black" as a color).
// We've written a function called mainColors() that steps
// through all eight of these colors. We're only "calling" the
// function here (telling it to run). The actual function code
// is further down in the sketch.
mainColors();
// The above function turns the individual LEDs full-on and
// full-off. If you want to generate more than eight colors,
// you can do so by varying the brightness of the individual
// LEDs between full-on and full-off.
// The analogWrite() function lets us do this. This function
// lets you dim a LED from full-off to full-on over 255 steps.
// We've written a function called showSpectrum() that smoothly
// steps through all the colors. Again we're just calling it
// here; the actual code is further down in this sketch.
showSpectrum();
}
// Here's the mainColors() function we've written.
// This function displays the eight "main" colors that the RGB LED
// can produce. If you'd like to use one of these colors in your
// own sketch, you cancopy and paste that section into your code.
void mainColors()
{
// Off (all LEDs off):
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(BLUE_PIN, LOW);
delay(1000);
// Red (turn just the red LED on):
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(BLUE_PIN, LOW);
delay(1000);
// Green (turn just the green LED on):
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BLUE_PIN, LOW);
delay(1000);
// Blue (turn just the blue LED on):
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(BLUE_PIN, HIGH);
delay(1000);
// Yellow (turn red and green on):
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BLUE_PIN, LOW);
delay(1000);
// Cyan (turn green and blue on):
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BLUE_PIN, HIGH);
delay(1000);
// Purple (turn red and blue on):
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(BLUE_PIN, HIGH);
delay(1000);
// White (turn all the LEDs on):
digitalWrite(RED_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(GREEN_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BLUE_PIN, HIGH);
delay(1000);
}
// Below are two more functions we've written,
// showSpectrum() and showRGB().
// showRGB() displays a single color on the RGB LED.
// You call showRGB() with the number of a color you want
// to display.
// showSpectrum() steps through all the colors of the RGB LED,
// displaying a rainbow. showSpectrum() actually calls showRGB()
// over and over to do this.
// We'll often break tasks down into individual functions like
// this, which makes your sketches easier to follow, and once
// you have a handy function, you can reuse it in your other
// programs.
// showSpectrum()
// This function steps through all the colors of the RGB LED.
// It does this by stepping a variable from 0 to 768 (the total
// number of colors), and repeatedly calling showRGB() to display
// the individual colors.
// In this function, we're using a "for() loop" to step a variable
// from one value to another, and perform a set of instructions
// for each step. For() loops are a very handy way to get numbers
// to count up or down.
// Every for() loop has three statements separated by semicolons:
// 1. Something to do before starting
// 2. A test to perform; as long as it's true,
// it will keep looping
// 3. Something to do after each loop (usually
// increase a variable)
// For the for() loop below, these are the three statements:
// 1. x = 0; Before starting, make x = 0.
// 2. x < 768; While x is less than 768, run the
// following code.
// 3. x++ Putting "++" after a variable means
// "add one to it". (You can also use "x = x + 1")
// Every time you go through the loop, the statements following
// the loop (those within the brackets) will run.
// And when the test in statement 2 is finally false, the sketch
// will continue.
void showSpectrum()
{
int x; // define an integer variable called "x"
// Now we'll use a for() loop to make x count from 0 to 767
// (Note that there's no semicolon after this line!
// That's because the for() loop will repeat the next
// "statement", which in this case is everything within
// the following brackets {} )
for (x = 0; x < 768; x++)
// Each time we loop (with a new value of x), do the following:
{
showRGB(x); // Call RGBspectrum() with our new x
delay(10); // Delay for 10 ms (1/100th of a second)
}
}
// showRGB()
// This function translates a number between 0 and 767 into a
// specific color on the RGB LED. If you have this number count
// through the whole range (0 to 767), the LED will smoothly
// change color through the entire spectrum.
// The "base" numbers are:
// 0 = pure red
// 255 = pure green
// 511 = pure blue
// 767 = pure red (again)
// Numbers between the above colors will create blends. For
// example, 640 is midway between 512 (pure blue) and 767
// (pure red). It will give you a 50/50 mix of blue and red,
// resulting in purple.
// If you count up from 0 to 767 and pass that number to this
// function, the LED will smoothly fade between all the colors.
// (Because it starts and ends on pure red, you can start over
// at 0 without any break in the spectrum).
void showRGB(int color)
{
int redIntensity;
int greenIntensity;
int blueIntensity;
// Here we'll use an "if / else" statement to determine which
// of the three (R,G,B) zones x falls into. Each of these zones
// spans 255 because analogWrite() wants a number from 0 to 255.
// In each of these zones, we'll calculate the brightness
// for each of the red, green, and blue LEDs within the RGB LED.
if (color <= 255) // zone 1
{
redIntensity = 255 - color; // red goes from on to off
greenIntensity = color; // green goes from off to on
blueIntensity = 0; // blue is always off
}
else if (color <= 511) // zone 2
{
redIntensity = 0; // red is always off
greenIntensity = 255 - (color - 256); // green on to off
blueIntensity = (color - 256); // blue off to on
}
else // color >= 512 // zone 3
{
redIntensity = (color - 512); // red off to on
greenIntensity = 0; // green is always off
blueIntensity = 255 - (color - 512); // blue on to off
}
// Now that the brightness values have been set, command the LED
// to those values
analogWrite(RED_PIN, redIntensity);
analogWrite(BLUE_PIN, blueIntensity);
analogWrite(GREEN_PIN, greenIntensity);
}
3. The pictures that follow are the Arduino Board and the first successful code...A BLINKING LIGHT!!


4. The husband and I decided we would play around with creating the "Love Meter". It has not worked yet but here is our first attempt!

5. This video is of the first code the "blinking light". I was pretty excited that it worked the first time!
6. My post only allows for one video so text it is! When I first started this project, I opened the box and saw all the pieces and became overwhelmed. You'd think as someone who literally works as an Instructional Technologist I would have been a little more excited. I got to work on reading ALL about the materials and their functions. The starter guide book has been my best friend and YouTube. the husband may have helped when the tears began to start. 😂
7. Really I was just learning about the pieces and the mechanics of each piece and the coding examples. I read the user manual, looked at examples, and watched YouTube videos to help me through the process. Through lots of frustration, trial and error, and time, I was able to successfully download the software, get the light to blink and create the rainbow light circuit. Well, put the pieces and wires where they go and run the code provided. Learning how to actually "code" is going to be my greatest challenge.
0 notes
Link
[ad_1] This Friday, we take a look back on 2024 to see the best products, videos, blogs, and more! Favorited Favorite 0 As another year comes to a close, we at SparkFun can't help but look back at all we've accomplished in 2024. From groundbreaking new products that pushed the boundaries of what's possible, to insightful tutorials and engaging videos that empowered makers of all levels, 2024 has been a year of growth, learning, and shared passion for electronics. In this week's "Look Back at 2024" post, we're taking a moment to celebrate the highlights. Join us as we revisit our most popular product releases, delve into the blog posts and tutorials that sparked the most interest, and relive the captivating moments captured in our videos. Whether you're a seasoned engineer, a curious beginner, or simply someone who appreciates the magic of electronics, we invite you to reminisce with us and discover something new along the way. 2024's Top Products SparkFun RTK mosaic-X5 28 available GPS-23748 Unleash centimeter-level GPS accuracy with SparkFun's RTK mosaic-X5. Web interface, RINEX logging, WiFi / Ethernet, rugged de… 4 This year saw the release of some truly exceptional tools for makers, engineers, and robotics enthusiasts. Leading the pack was the SparkFun RTK Torch and the SparkFun RTK mosaic-X5, a dynamic duo that brought high-precision GPS within reach of everyday projects. The RTK Torch, with its easy-to-use interface and centimeter-level accuracy, proved invaluable for navigation, surveying, and even autonomous vehicle development. Meanwhile, the RTK mosaic-X5 offered a powerful, compact solution for integrating RTK capabilities for base station designs. These products redefined what's possible with affordable, accessible GPS/GNSS technology. But we didn't stop there! The SparkFun Optical Tracking Odometry Sensor - PAA5160E1 (Qwiic) opened up a world of possibilities for robotics and motion tracking with its ability to accurately measure displacement and speed. This tiny sensor, easily integrated with its Qwiic compatibility, allowed for precise navigation in robots and detailed motion detection in interactive projects. For those interested in exploring the world of robotics education and research, the Experiential Robotics Platform (XRP) - DIY Kit proved to be a strong option for XRP users, providing a hands-on learning experience for building and programming robots. Cellular connectivity became more accessible than ever with the SparkFun Digi XBee® Cellular Kit, simplifying the process of adding cellular communication to projects for remote monitoring, data logging, and IoT applications. And let's not forget the SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout - NEO-F10N, SMA, which offered a versatile and high-performance solution for integrating GNSS capabilities into various projects. For those seeking advanced sensing capabilities, the SparkFun Pulsed Coherent Radar Sensor - Acconeer XM125 (Qwiic) provided a powerful tool for detecting objects, measuring distances, and even monitoring human vital signs. Last but certainly not least, the PINECIL Soldering Iron Kit equipped makers with a reliable and affordable soldering solution for bringing their electronic creations to life. 2024's Top Blogs Carbon Dioxide Sensing: PAS vs NDIR vs TVOC January 31, 2024 Raising your Buzzer Projects to the Next Level February 22, 2024 ENGINEERS HATE HIM: LOCAL MAN DISCOVERS 5 TECH SECRETS THEY DON’T WANT YOU TO KNOW April 1, 2024 SparkFun DataLogger: The Easiest Way to Log and Push Data to Your Favorite IoT Platform April 19, 2024 LiDAR, Radar, and PCR: What's The Difference? April 25, 2024 Rocky Mountain RepRap Recap May 23, 2024 Can ChatGPT Successfully Develop a SparkFun Product? May 15, 2024 Local Pickup At SparkFun HQ Is Back! August 19, 2024 This year, our blog was full of insightful articles, helpful tutorials, and thought-provoking explorations of technology. From practical guides to in-depth analyses, we covered a wide range of topics that we hoped would resonate with you. One of the highlights was a series of articles focused on enhancing everyday projects. "Raising your Buzzer Projects to the Next Level" provided makers with creative techniques and coding tips to transform simple buzzers into sophisticated sound generators. We also delved into the world of sensor technology with articles like "LiDAR, Radar, and PCR: What's The Difference?", which demystified these powerful sensing modalities and explored their unique applications. We went a little tongue and cheek with "ENGINEERS HATE HIM: LOCAL MAN DISCOVERS 5 TECH SECRETS THEY DON’T WANT YOU TO KNOW", which offered a lighthearted look at some common engineering misconceptions. Our blog also served as a platform for sharing valuable insights from industry events, as seen in the "Rocky Mountain RepRap Recap", which provided a glimpse into the exciting world of 3D printing and open-source hardware local to SparkFun HQ. We even explored the potential of artificial intelligence with "Can ChatGPT Successfully Develop a SparkFun Product?", a thought-provoking experiment that examined the role of AI in the creative process. Beyond the technical realm, we celebrated the return of in-person interactions with "Local Pickup At SparkFun HQ Is Back!", a heartwarming announcement that reconnected us with our local community. And for those eager to explore the world of data logging and IoT, "SparkFun DataLogger: The Easiest Way to Log and Push Data to Your Favorite IoT Platform" offered a comprehensive guide to our user-friendly data logging solutions. Finally, "Carbon Dioxide Sensing: PAS vs NDIR vs TVOC" blog provided a deep dive into the various technologies used for measuring CO2 levels. 2024's Top Tutorials How to Play Mulitple Buzzers at Once This tutorial demonstrates the SparkFun Qwiic Buzzer's ability to control multiple buzzers simultaneously by playing a 3-part arrangement of a segment of the Super Mario Bros Theme! Calibrating Your Odometry Sensor In this tutorial, we will cover how to calibrate your Qwiic Optical Tracking Odometry Sensor (or "OTOS") with Arduino and Python Examples. Our tutorial section this year was a treasure trove of knowledge, guiding makers through exciting projects and equipping them with valuable skills. From harnessing the power of Odometry sensors for precise motion tracking in "Calibrating Your Odometry Sensor" to unlocking the creative potential of alphanumeric displays in "Moving Beyond the Ordinary With the Qwiic Alphanumeric Display", we helped to empower you to push the boundaries of your projects. We delved into the intricacies of sensor fusion with "IMU Data to Motion: Tutorial for Translating Sensor Data into Real-World Movement", helping makers bridge the gap between raw sensor data and meaningful motion control. For those seeking to add a touch of auditory flair to their creations, "How to Play Multiple Buzzers at Once" provided the tools and techniques to orchestrate a symphony of sounds. We took a look at the vibrant world of color sensing with "Detecting Colors with the SparkFun Tristimulus Color Sensor", enabling makers to build projects that respond to the nuances of light and color. "How To Take Multiple RFID Readings Simultaneously" unlocked the potential of RFID technology for advanced tracking and identification applications. For those with a thirst for adventure, "GeoFence Treasure Hunt With Artemis Global Tracker" combined the thrill of a treasure hunt with the precision of GPS technology. And finally, "Display Distance Measurements On an OLED" provided a practical guide to visualizing sensor data on sleek and compact OLED displays. 2024's Top Videos [embed]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=videoseries[/embed] Our videos this year were also packed with exciting product showcases! Don't miss our deep dives into the Optical Tracking and Odometry Sensor, the Pro Micro 2350, the RTK EVK, the RTK Torch, and the RTK mosaic-X5. We even assembled a playlist for you to check them all out! That's it for this week and 2024. As always, we can't wait to see what you make! Shoot us a tweet @sparkfun, or let us know on Instagram, Facebook or LinkedIn. Please be safe out there, be kind to one another! Happy New Year from all of us here at SparkFun Electronics! Never miss a new product! [ad_2] Source link
0 notes
Text
I guarantee you Lil Wayne would adore the MicroMod RP2040 from SparkFun electronics🤩

0 notes