#signum function graph
Text
youtube
#identity function#constant function#signum function#modulus function#function#graph of identity function#functions#signum function class 11#signum function graph domain and range#constant function graph#signum function graph#graph of signum function#greatest integer function#polynomial function#constant function rule#modulus function graph#constant function example#identity function graph#graph of constant function#Youtube
0 notes
Text
MEXC Global Research: High Performance Public Chain Fantom (FTM) Recommended by Andre Cronje (AC)
Fantom
Fantom is a high-performance public chain based on DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph), which provides services for enterprises and applications, and aims to solve the scalability and processing time of existing blockchain technologies.
Fantom is powered by Lachesis, an advanced DAG-based aBFT consensus algorithm. In Fantom, each transaction information can become a unit, and the units can be connected to each other arbitrarily to verify their validity. Transactions do not need to be packaged together to complete the transaction, thereby increasing transaction concurrency and volume, and realizing instant transactions.
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
If a directed graph cannot start from a vertex and return to that point through several edges, the graph is a directed acyclic graph (DAG in the figure). In other words, it is non-cyclic, meaning it can only carry out the one-way flow of information. Compared to the typical chain design of blockchain, DAG can speed up the transaction speed and scalability.
Lachesis aBFT (LCA algorithm, Asynchronous Byzantine Consensus)
Lachesis is a breakthrough aBFT consensus mechanism developed by Fantom. aBFT consensus stands for “asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant” consensus. When a network is said to be “Byzantine Fault Tolerant”, it means that nodes can still reach an agreement on an ordering of events even if part of the network acts maliciously.
Key properties of Lachesis algorithm:
· Asynchronous: Participants have the freedom to process commands at different times.
· Leaderless: All participants are equal and play no special roles.
· Byzantine Fault-Tolerant: Functional even when up to one-third of faulty nodes and malicious nodes are present.
· Instant: The output transaction of Lachesis can be confirmed in 1-2 seconds.
Unlike Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake (POS) and pBFT, Lachesis nodes do not send blocks to each other. Validators don’t vote on a concrete state of the network; instead, they periodically exchange observed transactions and events with peers.
The event block includes the following information: transaction, smart contract, historical information, and the value of previous transactions.
In general, LCA specifically forms the Lachesis DAG based on the Lachesis protocol. A set of links between event blocks form a DAG, which is a distributed system that stores arbitrary data that cannot be changed. Due to the design of validator node, DAG supports high-speed real-time transactions.
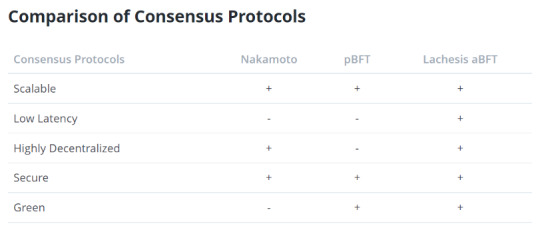
Comparison of different consensus algorithms (Nakamoto consensus, pBFT consensus, Lachesis aBFT)
Opera Mainnet
The blockchain environment built by Fantom is called Opera, in which DApps can be built using smart contracts. The main features are: based on DAG technology that realizes cost-efficiency, integration with Ethereum Virtual Machines (EVMs) and the Solidity programming language.
Opera's technical architecture consists of three layers:
Opera core layer: responsible for large-scale transaction processing;
Opera ware layer: responsible for supporting smart contracts and other functions;
Opera application layer: provides support for third-party DApps
Investor Institutions
Blockwater Capital, Digital Currency Holdings, FBG Capital, Origin X Capital, X Squared, Huobi VC, Signum Capital, One Block Capital, Chainrock, Kosmos Capital, MB Technology, Bibox Fund, Block Tech Capital, Lemniscap Capital, AVA Quest, Lumen, Orichal Partners, FutureMoney Ventures, Block VC, BlockCrafters, SuperChain Capital, Arrington XRP Capital, JRR Crypto, Black Edge Capital, CryptoBazzar, Digital Strategies/Polymath, Zorax Capital, Transference Fund, LinkVC, Nirvana Capital, JD capital, DFund, Danhua Capital, Alameda Research (FTX parent company), BlockTower Capital, HyperChain Capital, etc.
Advantage
Instant Transaction finality: event blocks are connected and verified with each other, and there is no need to package blocks to improve concurrency and speed.
Low transaction fee: the transaction fee is close to 0. At the same time, 30% of the transaction fee is held by the CSRC (locked hedging), and the remaining 70% of the transaction fee is allocated to the verifier in proportion.
Strong scalability: It supports multiple nodes. The more nodes join, the faster the speed and the greater the scalability. It is compatible with Ethereum EVM virtual machine, etc.
Openness and transparency: open-source code
Tokenomics
Governance token: FTM (currently supports mainnet, ERC20 and BEP20)
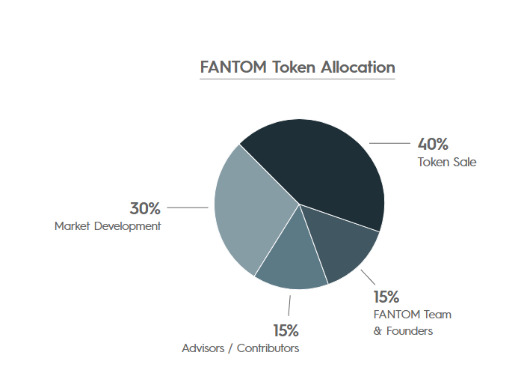
Total: 3.175 billion
Token sale: 40%
Market development: 30%
Advisors and contributors:15%
FANTOM team and founders: 15%
Practical Value
Proof of stake, and hold tobecome the verification node
Transaction fee
Participation in voting governance
Collateral for Fantom’s DeFi suite
Existing risks
DAG technology is not yet mature or recognized in the market
The project is still in the improvement stage, and is pending completion pending
Cash out by investors and team
Public chain ecosystem competition is fierce
Partial Ecosystem Projects
Aggregator SpiritSwap
Token: Spirit
Market value: 15 million USDT
SpiritSwap (SPIRIT) is a one-stop comprehensive trading application on Fantom, which integrates the functions such as trading, lending, IDO, NFT trading, smart pool, and automatic insurance.
Collateral lending Scream
Token: SCREAM
Market value: 17 million USDT
SCREAM is a highly-scalable decentralized lending protocol built and powered by the Fantom Blockchain, and is similar to AAVE and Compound.
Aggregator ZooCoin
Token: ZOO
Market value: /
ZooCoin (ZOO) is a comprehensive trading application on Fantom, which is mainly composed of trading aggregator, K-line chart, NFT market and other functions.
Cross-chain yield aggregator Beefy Finance
Token: BIFI
Market value: 84 million USDT
Beefy Finance (BIFI) is a cross-chain revenue aggregator that can run on multiple chains. Currently, it supports Fantom and BSC chains. By providing users with automated investment strategies through smart contracts and algorithm programs, users can maximize their benefits from various liquidity pools (LP), automatic market making (AMM) projects and other mining and farming projects on Fantom.
Cross-chain stablecoin Curve
Token: CRV
Market value: 872 million USDT
Curve Fi is a cross-chain decentralized stablecoin trading application. Launched in Ethereum as early as January 2020, it enables users to trade between stablecoins with low slippage, low handling fee, and supports cross-chain, including ETH, Polygon, xDai, Fantom and other networks.
DEX platform Spookyswap
Token: BOO
Market value: 80 million USDT
SpookySwap is an automated market-making (AMM) decentralized exchange (DEX) for the Fantom Opera network. Take BOO token as governance token to provide diversified farms, built-in cross-chain bridges, limited price orders and user-centered services.
Cross-chain yield aggregator Popsicle Finance
Token: ICE
Market value: 29 million USDT
Popsicle Finance is a multichain yield optimization platform for Liquidity Providers, which supports automated compound interest to improve capital efficiency. They can automatically provide its users with the highest possible yield on the assets they wish to deploy to liquidity pools.
Cross-chain yield aggregator Graviton
Token: GTON
Market value: 18 million USDT
Graviton is a universal wrapped tokens’ liquidity incentivization solution that provides the technological foundation for seamless cross-chain communication and creates a reward-based economy around wrapped assets. Graviton's diverse infrastructure includes cross-chain bridge aggregators, cross-chain wallets, and LP reward farming products.
0 notes
Text
IIT JEE preparation tips for Calculus. What you should know
This article will be one of the very important IIT JEE preparation tips. It is Calculus.
Calculus continued to be my favorite subject in JEE. This is the best, the most logical and the most beautiful topic for me. This subject has it her beauty. It is a mixture of everything: coordinates of geometry, algebra, vector, and the rest. And this is the fact why I am interested in the calculus. It’s extremely important from the point of engineering.

Here is the syllabus of the Calculus Syllabus defined by IIT JEE
Function:
It creates the foundation of calculus. Understand this concept well; otherwise learning Calculus will become very difficult for you. The most common questions are:
Find a domain and range for a particular Function: students here make some very silly mistake
Understanding one-one and onto function.
Drawing the graph and find the number of intersections of two or more functions
To study this chapter, learn drawing graphs. This will help you a lot.
Practice more problems with finding a domain/domain. There are few tips to crack JEE mains such as:
No negative number inside the square root.
There is no division to zero
Never put zero or any negative number in the logarithmic
Base of log is not equal to 1 or zero or negative.
You hope to know these basic terms. It is a good practice to check the answer for available options.
Limits :
the most important part. The whole calculus is based on the chapter limit. Mastering this Chapter is very important. Use it as much as you can. You can also try to learn the expansion series, but I could not avoid it because most of the problem with the expansion can be solved if you know the rules and practiced them rigorously. That is why I never needed expansion. However, it is recommended not to forget the exponential and logarithmic series.
The questions in this chapter are usually simple and easy. All you have to do is start from zero upon zero or infinite upon infinite form to an appropriate value. Most of the questions will be solved using L’hospital rule.
I should also mention that there will be a lot of variety.
IIT JEE preparation tips for Continuity:
Another important Chapter. Questions in this chapter can be solved if you accurately and quickly draw graph of the function. Continuous Chapter have many interesting and important functions, such as greatest integer function, signum etc. Understand and apply them.
Differentiation :
one of the simplest chapters. It does not take much effort. Learn to distinguish: division rules, product rules, chain rule, implicit differentiation, exponential and logarithmic differentiation, a higher level of derivatives. Practice enough questions.
Application Of Derivatives :
the most important chapter because most of the questions relate to this subject. Rolle’s sentence, Lagrange’s Mean Value theorem(LMVT), the concept of maxima & minima, increasing and decreasing functions, inflection points, and so on.
They are really important. Answer all questions from these topics. Prepare to see the most JEE problems on this topic. If you are weak, do something about it before you have problems. Basically, this is a mixture of all the previous chapters in calculus, and JEE is the application of concepts.
IIT JEE preparation tips for Integration:
a very simple chapter but you will not find many questions about integrals IIT JEE. There are several formula for memory in this chapter. Formulas are very important because it will save you a lot of time in the exam.
Definite integrals:
the most important chapter of the integral calculus. There are many questions in this chapter. The majority of questions are based on the properties of definite integrals, and not just the calculation of limits on Indefinite Integration.
Practice enough questions on this topic.
Differential equations:
a fairly simple and interesting chapter. Do a lot of practice. And do not forget the formulas they are really important. You will learn different methods to solve standard differential equations and discover the application topic.
0 notes
Link
Free education is the right of every student. Ashish Kumar – Let’s Learn is providing deep and detailed explanations of full syllabus, all important questions, all important examples and all NCERT solutions for Class 11 Maths through videos on YouTube Channel as well as Blogs and PDFs on website.
Students can learn through videos and blogs and can ask their doubts on Website’s Discussion panel or on YouTube’s Comments Page. Students will also be provided notes, assignments, books and various other educational resources in electronic forms like PDFs, Docs, mp4 etc., which will help them to prepare for CBSE Class 12 Board Exams but more importantly for their upcoming life’s adventures.
You can easily access all chapters with NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths on this page: https://www.ashishkumarletslearn.com/cbse/class-11/maths/
Following are summaries of chapter wise syllabus recommended by CBSE for Class 11 mathematics students with their YouTube as well as Website links.
Unit-I: Sets and Functions
1. Sets:
Sets and their representations. Empty set. Finite and Infinite sets. Equal sets. Subsets. Subsets of a set of real numbers especially intervals (with notations). Power set. Universal set. Venn diagrams. Union and Intersection of sets. Difference of sets. Complement of a set. Properties of Complement.
2. Relations & Functions:
Ordered pairs. Cartesian product of sets. Number of elements in the Cartesian product of two finite sets. Cartesian product of the set of reals with itself (upto R x R x R). Definition of relation, pictorial diagrams, domain, co-domain and range of a relation. Function as a special type of relation. Pictorial representation of a function, domain, co-domain and range of a function. Real valued functions, domain and range of these functions, constant, identity, polynomial, rational, modulus, signum, exponential, logarithmic and greatest integer functions, with their graphs. Sum, difference, product and quotients of functions.
3. Trigonometric Functions:
Positive and negative angles. Measuring angles in radians and in degrees and conversion from one measure to another. Definition of trigonometric functions with the help of unit circle. Truth of the identity sin2x+cos2x=1, for all x. Signs of trigonometric functions. Domain and range of trigonometric functions and their graphs. Expressing sin (x±y) and cos (x±y) in terms of sinx, siny, cosx & cosy and their simple applications. Deducing identities. Identities related to sin2x, cos2x, tan2x, sin3x, cos3x and tan3x. General solution of trigonometric equations of the type siny = sina, cosy = cosa and tany = tana.
Unit-II: Algebra
4. Principle of Mathematical Induction:
Process of the proof by induction, motivating the application of the method by looking at natural numbers as the least inductive subset of real numbers. The principle of mathematical induction and simple applications.
5. Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations:
Need for complex numbers, especially √ , to be motivated by inability to solve some of the quadratic equations. Algebraic properties of complex numbers. Argand plane and polar representation of complex numbers. Statement of Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, solution of quadratic equations (with real coefficients) in the complex number system. Square root of a complex number.
6. Linear Inequalities:
Linear inequalities. Algebraic solutions of linear inequalities in one variable and their representation on the number line. Graphical solution of linear inequalities in two variables. Graphical method of finding a solution of system of linear inequalities in two variables.
7. Permutations and Combinations:
Fundamental principle of counting. Factorial n. (n!) Permutations and combinations, derivation of formulae for and and their connections, simple applications.
8. Binomial Theorem:
History, statement and proof of the binomial theorem for positive integral indices. Pascal’s triangle, General and middle term in binomial expansion, simple applications.
9. Sequence and Series:
Sequence and Series. Arithmetic Progression (A. P.). Arithmetic Mean (A.M.) Geometric Progression (G.P.), general term of a G.P., sum of n terms of a G.P., infinite G.P. and its sum, geometric mean (G.M.), relation between A.M. and G.M. Formulae for the following special sums.
Unit-III: Coordinate Geometry
10. Straight Lines:
Brief recall of two dimensional geometry from earlier classes. Shifting of origin. Slope of a line and angle between two lines. Various forms of equations of a line: parallel to axis, point -slope form, slope intercept form, two-point form, intercept form and normal form. General equation of a line. Equation of family of lines passing through the point of intersection of two lines. Distance of a point from a line.
Unit-IV: Calculus
13. Limits and Derivatives:
Derivative introduced as rate of change both as that of distance function and geometrically. Intuitive idea of limit. Limits of polynomials and rational functions trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic functions. Definition of derivative relate it to scope of tangent of the curve, derivative of sum, difference, product and quotient of functions. Derivatives of polynomial and trigonometric functions.
#ncert solutions for class 11 maths#ncert solutions#class 11 maths#sequences and series#limits and derivatives#Calculus#class 11 maths ncert solutions chapter 10#class 11 maths straight lines#straight lines#binomial theorem#permutation and combination#linear inequalities#ashish kumar lets learn#ashish kumar
0 notes
Text
CBSE Class 11th Math Syllabus
CBSE Class 11th Math Syllabus
Course Structure

Sets and Functions
1. Sets - (20) Periods
Sets and their representations. Empty set. Finite and Infinite sets. Equal sets. Subsets. Subsets of a set of real numbers especially intervals (with notations). Power set. Universal set. Venn diagrams. Union and Intersection of sets. Difference of sets. Complement of a set. Properties of Complement.
2. Relations & Functions (20) Periods
Ordered pairs. Cartesian product of sets. Number of elements in the Cartesian product of two finite sets. Cartesian product of the set of reals with itself (upto R x R x R). Definition of relation, pictorial diagrams, domain, co-domain and range of a relation. Function as a special type of relation. Pictorial representation of a function, domain, co-domain and range of a function. Real valued functions, domain and range of these functions, constant, identity, polynomial, rational, modulus, signum, exponential, logarithmic and greatest integer functions, with their graphs. Sum, difference, product and quotients of functions.
3. Trigonometric Functions (20) Periods

Unit-II: Algebra
1. Principle of Mathematical Induction (10) Periods
Process of the proof by induction, motivating the application of the method by looking at natural numbers as the least inductive subset of real numbers. The principle of mathematical induction and simple applications.
2. Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations (15) Periods
Need for complex numbers, especially √-1 , to be motivated by inability to solve some of the quardratic equations. Algebraic properties of complex numbers. Argand plane and polar representation of complex numbers. Statement of Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, solution of quadratic equations (with real coefficients) in the complex number system. Square root of a complex number.
3. Linear Inequalities (15) Periods
Linear inequalities. Algebraic solutions of linear inequalities in one variable and their representation on the number line. Graphical solution of linear inequalities in two variables. Graphical method of finding a solution of system of linear inequalities in two variables.
4. Permutations and Combinations (10) Periods
Fundamental principle of counting. Factorial n. (n!) Permutations and combinations, derivation of formulae for npr and ncr and their connections, simple applications.
5. Binomial Theorem (10) Periods
History, statement and proof of the binomial theorem for positive integral indices. Pascal's triangle, General and middle term in binomial expansion, simple applications.
6. Sequence and Series (10) Periods

Unit-III: Coordinate Geometry
1. Straight Lines (10) Periods
Brief recall of two dimensional geometry from earlier classes. Shifting of origin. Slope of a line and angle between two lines. Various forms of equations of a line: parallel to axis, point-slope form, slope-intercept form, two-point form, intercept form and normal form. General equation of a line. Equation of family of lines passing through the point of intersection of two lines. Distance of a point from a line.
2. Conic Sections (20) Periods
Sections of a cone: circles, ellipse, parabola, hyperbola, a point, a straight line and a pair of intersecting lines as a degenerated case of a conic section. Standard equations and simple properties of parabola, ellipse and hyperbola. Standard equation of a circle.
3. Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry (10) Periods
Coordinate axes and coordinate planes in three dimensions. Coordinates of a point. Distance between two points and section formula.
Unit-IV: Calculus
1. Limits and Derivatives (30) Periods
Derivative introduced as rate of change both as that of distance function and geometrically.
Intuitive idea of limit. Limits of polynomials and rational functions trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic functions. Definition of derivative relate it to scope of tangent of the curve, derivative of sum, difference, product and quotient of functions. Derivatives of polynomial and trigonometric functions.
Unit-V: Mathematical Reasoning
1. Mathematical Reasoning -- (10) Periods
Mathematically acceptable statements. Connecting words/ phrases - consolidating the understanding of "if and only if (necessary and sufficient) condition", "implies", "and/or", "implied by", "and", "or", "there exists" and their use through variety of examples related to real life and Mathematics. Validating the statements involving the connecting words, difference among contradiction, converse and contrapositive.
Unit-VI: Statistics and Probability
1. Statistics -- (15) Periods
Measures of Dispersion: Range, Mean deviation, variance and standard deviation of ungrouped/grouped data. Analysis of frequency distributions with equal means but different variances.
2. Probability (15) Periods
Random experiments; outcomes, sample spaces (set representation). Events; occurrence of events, ‘not’, ‘and’ and ‘or’ events, exhaustive events, mutually exclusive events, Axiomatic (set theoretic) probability, connections with other theories of earlier classes. Probability of an event, probability of ‘not’, ‘and’ and ‘or’ events.



Read the full article
0 notes