#siecle
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

PRIMA PAGINA Le Figaro di Oggi domenica, 16 febbraio 2025
#PrimaPagina#lefigaro quotidiano#giornale#primepagine#frontpage#nazionali#internazionali#news#inedicola#oggi levet#abandonner#sort#cest#certaine#idee#gastronomie#roquefort#siecle#fierte#francaise#militaire#nord#diable#etoiles#nouvel#dune#municipales#veut#changer#mode
0 notes
Photo
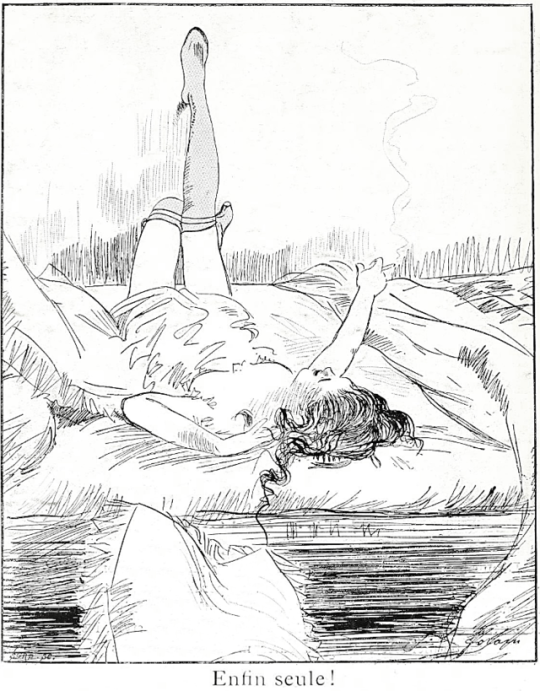

Enfin Seule! (Finally Alone) by Jean-Louis Forain in Le Courrier Français, ca. 1890
#fin de siècle#1890s#victorian#jean-louis forain#comics#illustration#1890#victorian era#fin de siecle
14K notes
·
View notes
Text

Bettye Jordan Young, B. Jordan Young, Inc., Hollywood, California
100 Designers' Favorite Rooms, 1994
#vintage#interior design#home#vintage interior#architecture#home decor#style#1990s#living room#fin de siecle#New York#apartment#French#Baroque#portrait#antique#motif#desk#sculpture
516 notes
·
View notes
Text



Sascha Schneider, 1905.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
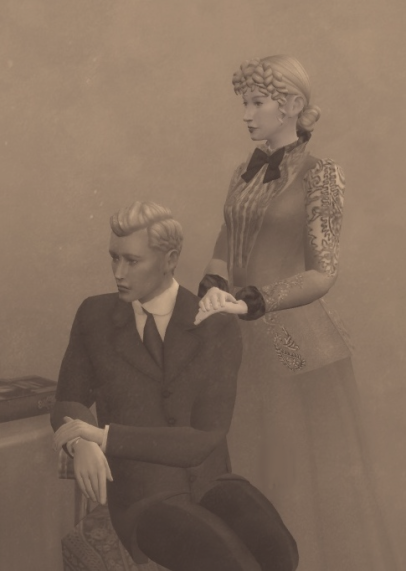

Les Nouveaux Riches
Gregory and Bertha Landgraab, 1890
190 notes
·
View notes
Text

From the outside you appear comfortable and relaxed. By prioritizing your work-life balance in your daily schedule you have witnessed success to come into your life without the need to sacrifice anything along the way. Enjoy your rewards today.
#Fin De Siecle Kipper#kipper deck#kipper card reading#kipper card reader#kipper karten#kipper reader#kipper reading#divination#fortune telling#fortune teller#message for the collective#gay pagan
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
For those who struggle reading today's wall of references, maybe audio will be more your speed! Check out this very nice reading of the chapter over at The Siecle--and enjoy the wealth of hyperlinked annotations!
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
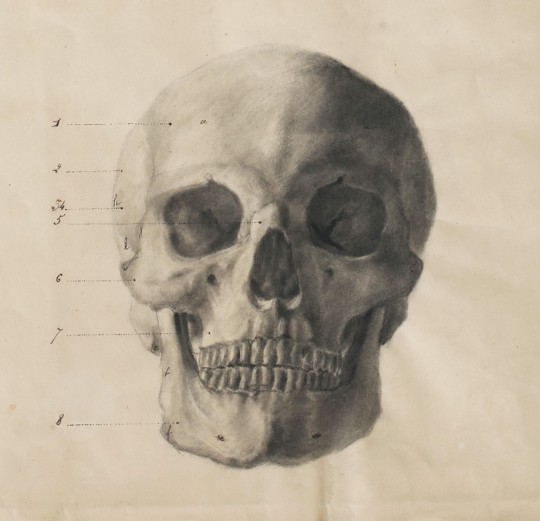
#art#drawing#sketching#chalk drawing#ecole francaise du xixe siecle#dessin d anatomie#french school#19th century#human anatomy#skull#anatomical drawing
127 notes
·
View notes
Text

William Luker Jr., A Dining Room in Notting Hill Square, from W. J. Loftie's Kensington: Historical and Picturesque, 1888, ink and wash.
#william luker jr#william luker#w j loftie#kensington#london#1880s#pen and ink#wash#victorian#victorian era#victorian decor#fin de siecle#decorative arts#english art#english design#decor#interior design#design#architecture#victorian architecture#art#painting#art history#drawing#domestic interior#illustration#dogs in art#victorian artist
8 notes
·
View notes
Photo

PRIMA PAGINA Le Figaro di Oggi sabato, 15 febbraio 2025
#PrimaPagina#lefigaro quotidiano#giornale#primepagine#frontpage#nazionali#internazionali#news#inedicola#oggi levet#abandonner#sort#cest#certaine#idee#gastronomie#roquefort#siecle#fierte#francaise#militaire#nord#diable#etoiles#nouvel#dune#municipales#veut#changer#mode
0 notes
Text
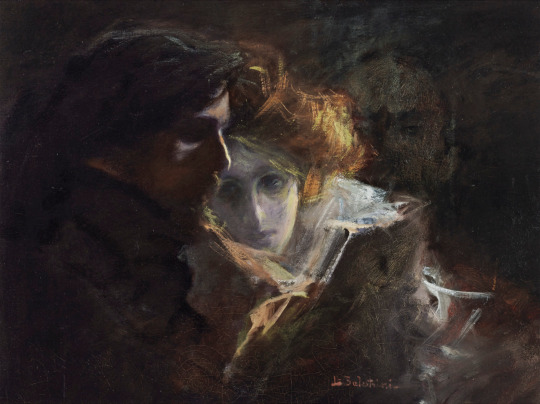




Lionello Balestrieri - Beethoven, Die Kreuzer Sonata. Preliminary studies, the final painting (that brought him fame and fortune) and the artist in his studio, all around 1900.
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lying in my sickbed taking a sketchy OTC opioid tincture (kratom seltzer) for my chronic respiratory ailment while the tinny strains of Ravel can be heard over the radio from an adjoining room. Fin-de-siecle lifestyle is BACK
#I use 'fin-de-siecle' VERY loosely don't @ me of all people about the timeline of the radio lmao#Periodicity is for punchlines ONLY
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

‘Fairy tales from folk lore’ by Hershel Williams; illustrated by M.H. Squire. Published 1908 by Moffat, Yard & Company, New York.
via
66 notes
·
View notes
Photo

1890
348 notes
·
View notes
Text

47 notes
·
View notes
Video
Risqué Edwardian postcard by totallymystified
#postcard#streetwalkers#ladies of the night#Edwardian#illustration#retro#vintage#nostalgia#fin-de-siecle#la belle époque#flickr
8 notes
·
View notes