#ribonucleic
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#aging#HealthyAging#HealthCare#Deoxyribonucleic#ribonucleic#rejuvenatedskin#collagen#healthy living#wellness#nutrition#health
0 notes
Text









X X X . X x X . X X X
#ribonucleic acid#RNA#stimblr#my stimboards#slime#paint#multicolor#teal#blue#STEMboard#kidcore#kinda
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
mRNA Translation
-- process of translating sequence of messenger RNA
-- messenger RNA = mRNA
-- turns sequence into amino acids
-- ribosome reads mRNA sequence in groups of three
-- three mRNA letters = codon
-- codons code for an amino acid
-- information begins in the DNA
-- transcribed into messenger RNA
-- translated from messenger RNA to protein
-- information is being transferred from one form to another
-- ribosome travels along the mRNA
-- detects the code as it goes
-- decides what amino acid to add based on the code
-- adds that amino acid to the polypeptide chain
-- this polypeptide chain becomes the protein
.
Patreon
#studyblr#notes#biology#bio#bio notes#biology notes#genetics#genetics notes#transcription#translation#mrna#messenger rna#rna#ribonucleic acid#dna#deoxyribonucleic acid#polypeptides#proteins#making proteins#life science#science#health science#medblr#medical notes#med notes#biochemistry#biochem#biochemistry notes#biochem notes#polypeptide chains
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 1970, it was discovered that the reverse process is also possible, where single-stranded RNA is ultimately transcribed into double-stranded DNA (see figure 25.23).

"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quotes#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#70s#1970s#20th century#rna#ribonucleic acid#dna#deoxyribonucleic acid#transcription#virus#retrovirus
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
For example, if the next codons on a strand of mRNA were -UCU-GGU-GCU-U..., and the first G was deleted, the sequence would become -UCU-GUG-CUU.
"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
0 notes
Photo

https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-rna-therapeutics-market
0 notes
Text
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Therapeutics Market
#Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Therapeutics Market trend#Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Therapeutics Market forcast#Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Therapeutics Market segment#Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Therapeutics Market overview#Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Therapeutics Market growth#Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Therapeutics Market share#Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Therapeutics Market demand
0 notes
Text
Two Idaho lawmakers have introduced a bill to charge those who administer mRNA vaccines with a misdemeanor.
Sen. Tammy Nichols, R-Middleton, and Rep. Judy Boyle, R-Midvale, sponsored HB 154. It was introduced in the House Health & Welfare Committee on Feb. 15 by Nichols. According to the bill text, "A person may not provide or administer a vaccine developed using messenger ribonucleic acid technology for use in an individual or any other mammal in this state."
That person would then be charged with a misdemeanor.
Nichols said during her presentation to the committee, "We have issues this was fast tracked."
Nichols said there is no liability, informed consent or data on mRNA vaccines. She later clarified she was referring to the two COVID-19 vaccines, Pfizer and Moderna.
"I think there is a lot of information that comes out with concerns to blood clots and heart issues," Nichols said.
Rep. Ilana Rubel, D-Boise, questioned Nichols' statement that the vaccines were fast-tracked. She said her understanding was that the vaccines were approved and survived the testing, later approved by the FDA.
Nichols said she is finding it "may not have been done like we thought it should've been done."
"There are other shots we could utilize that don't have mRNA in it," Nichols said.
MRNA is a molecule that assists in making proteins. The COVID-19 vaccines, which are known as mRNA vaccines, help your body make proteins that mimic the COVID virus to help bodies fight off the infection, according to John Hopkins Medicine. MRNA was discovered in the early 1960's, John Hopkins states. Some were used to fight the Ebola virus. Researchers are also currently working to use mRNA to prevent other respiratory viruses.
The bill requires a future vote in the committee to pass onto the House floor for debate.
#us politics#news#ktvb#2023#vaccines#vaccine bans#misdemeanor#idaho#HB 154#idaho legislature#Idaho House Health & Welfare Committee#Tammy Nichols#Judy Boyle#mrna vaccines#Ilana Rubel#covid vaccine#coronavirus vaccine#moderna#Pfizer#food and drug administration#trust the science#conservatives#republicans#gop#gop platform#gop policy
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Different types of brain cells could age at different speeds, and that may help explain the development of Alzheimer's disease. Engineers at the University of California San Diego (UCSD) have used cutting-edge technology to analyze the postmortem brains of 14 donors aged over 59, some of whom died with Alzheimer's disease and some of whom did not. The team found that brain cells from the frontal cortex with the most signs of aging and Alzheimer's disease shared a common feature. Their DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) interacted with the genetic 'translator', RNA (ribonucleic acid), in a less intimate way than in healthy brain cells.
Continue Reading.
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
Share to slowly dissolve your followers
176 notes
·
View notes
Text
Propaganda!


The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long strands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression.
Nucleotides are organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver.
#Nucleus#Nucleotides#tournament poll#polls#wikipedia#cells of the human body#science tournament#biochemistry
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Bombshell news today on the vaccine front as AstraZeneca, after admitting its covid jabs cause fibrous clots, is now withdrawing its covid vaccine from the entire world marketplace.
The EU has now revoked authorization for this vaccine, meaning it is now illegal to administer this jab to anyone in the EU.
Meanwhile, an attempted reinfection trial that exposed volunteers to 10,000 times the "dose" of covid deemed necessary to cause infections failed to produce a single infection. The premise of virology as being capable of causing pandemics is a total fraud. And that means vaccines are a fraud, too."
We could not surpass his brevity or logic.
Contrary to what the perpetually gullible Public has been led to believe, The Virus Theory, also known as The Germ Theory, is, and has always remained a theory with as many bits of evidence against it as for it.
While the introduction of any foreign substance does trigger the immune system and if it is a biological entity or molecule will provoke the creation of specific antibodies, that doesn't really prove anything about the nature of what we have come to call "viruses".
All this does is prove things about the immune system and basic mechanisms of immunity, leaving the more basic issue of the Causative Agent in limbo.
Our scientists assure us that viruses, also called "exosomes" are dead, little pinched off particles of DNA and waste products encapsulated in a protein shell.
Can dead things "infect"? Not really.
Think of waste DNA and RNA as Hazmat and the protein shell of a virus as a specially designed waste container with a lid. The protein shell is not alive, but its contents, the degraded bits of deoxy or ribonucleic acid can still replicate, if they get back inside a cell.
And then what have you got?
You've got bits of polluted and degraded foreign DNA or RNA snippets coding for foreign proteins inside your cells.
Those foreign proteins then hit your system like a sledge hammer and provoke your immune response -- which is then misidentified as a "disease".
It can be any disease, depending on the nature of the DNA or RNA contained in the "virus" packet, and the nature of the resulting immune response to whatever foreign proteins are being produced.
Blood clotting factor snippets of DNA or RNA code result in foreign blood clotting factor proteins and your immune system reacts to them, specifically.
Tumor producing snippets of DNA or RNA code result in foreign tumor proteins and your immune system reacts to them, specifically.
Each set of such stimulus-response reactions is different, so, Astrazeneca's "vaccine" loaded with blood clotting factor snippets of RNA (left over from a Department of Defense Experiment during the Iraq War) leads to "fibrous clots" as the foreign blood clotting factor proteins meet your body's immune response.
Depending on what the "payload" of DNA or RNA snippets are, you exhibit different symptoms and appear to have different diseases.
Our cell walls and membranes naturally work to exclude foreign DNA and RNA and keep this intracellular production of foreign proteins from happening, but thanks to Doctor Fauci and other Mad Scientists --- tech-crazed men with no actual brains or hearts --- this natural barrier has purportedly been overcome.
To our universal detriment.
We are calling for an immediate full stop and end of production and injection of all DNA and RNA "vaccines" worldwide.
We are calling for the prosecution and public punishment of all the Corporations responsible for this genocidal crime against humanity, and in the case of this country, the prosecution of the US CONGRESS and its Members, which recklessly and in gross negligence and dereliction of duty agreed to accept the liability for vaccine manufacturers.
Let them have the liability for all this expense and disruption and death -- individually, personally, and with 100% commercial liability.
And may no bank dare to give them as much as a peso of our credit. They were not acting "for" us or in our favor when they did this, and they do not deserve any indemnification or insurance at public cost.
The UN CORPORATION has promoted war instead of stopping it, and has contributed to this genocide through its WHO organization. We see no reason for its continued existence, much less any treaty empowering it in any way.
We call for the immediate liquidation of the UN CORPORATION and WHO, both, and an end to any further discussion of a sea "treaty" among the guilty corporations to grant any purported powers possessed by any corporation to either entity.
#youtube#ados#blacklivesmatter#blackvotersmatters#donald trump#joe biden#naacp#blackmediamatters#blackvotersmatter#news
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Marvels of Biological Macromolecules: The Molecular Machinery of Life (Part 3)
Nucleotide Structure: The Building Blocks
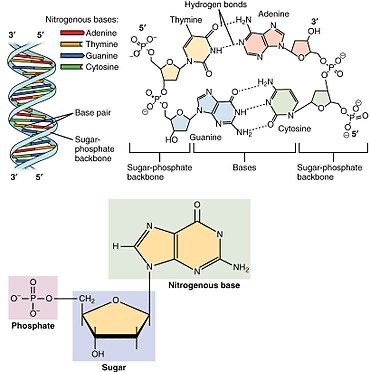
Nucleotides, the monomers of nucleic acids, consist of three fundamental components:
1. Phosphate Group (PO4): Provides a negatively charged backbone for the nucleic acid strand.
2. Pentose Sugar: In DNA, it's deoxyribose; in RNA, it's ribose. The sugar moiety forms the framework of the nucleotide.
3. Nitrogenous Base: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) in DNA, and Uracil (U) in RNA. These bases are responsible for the genetic code.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): The Repository of Genes
DNA is a double-stranded helical molecule, with each strand composed of a linear sequence of nucleotides. It encodes the genetic information necessary for an organism's development, growth, and functioning. The Watson-Crick base pairing rules—A with T and C with G
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): The Repository of Genes
DNA is a double-stranded helical molecule, with each strand composed of a linear sequence of nucleotides. It encodes the genetic information necessary for an organism's development, growth, and functioning. The Watson-Crick base pairing rules—A with T and G with C—ensure DNA's complementary and faithful replication.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): From DNA's Blueprint to Protein Synthesis
RNA plays diverse roles in the cell, including serving as a messenger (mRNA) for protein synthesis, a structural component of ribosomes (rRNA), and an adapter molecule (tRNA) that brings amino acids to the ribosome during translation. Unlike DNA, RNA is often single-stranded and contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
Genome Organization and Chromosomes
Genomic DNA is organized into chromosomes within the cell nucleus. These structures enable efficient storage, replication, and transmission of genetic information during cell division and reproduction.
Replication and Transcription
DNA replication ensures the faithful duplication of genetic material during cell division, while transcription converts DNA into RNA, providing a template for protein synthesis.
Translation
The cellular machinery, composed of ribosomes and tRNA, reads the mRNA code and assembles amino acids into polypeptides during translation, ultimately forming functional proteins.
Genetic Code
The genetic code, a triplet code of nucleotide sequences (codons), dictates a protein's sequence of amino acids. It is nearly universal, with only minor variations across species.
Epigenetics
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, regulate gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence, pivotal in development and cell differentiation.
Macromolecular interactions are the essence of cellular life. Within the complex microcosm of a cell, countless molecules engage in precise and choreographed dances, forming intricate networks that govern every facet of biology. These interactions, governed by the principles of biochemistry, are the foundation upon which life's processes are built.
Amino Acids: The Building Blocks
Proteins are composed of amino acids organic molecules that contain an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side chain (R group). There are 20 different amino acids, each with a unique side chain that confers specific properties to the amino acid.
Primary Structure: Amino Acid Sequence
The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. The genetic information in DNA encodes the precise arrangement of amino acids.
Secondary Structure: Folding Patterns
Proteins don't remain linear; they fold into specific three-dimensional shapes. Secondary structures, such as α-helices and β-sheets, result from hydrogen bonding between nearby amino acids along the polypeptide chain.
Tertiary Structure: Spatial Arrangement
The tertiary structure is the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein, determined by interactions between amino acid side chains. These interactions include hydrogen bonds, disulfide bridges, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions.
Quaternary Structure: Multiple Polypeptide Chains
Some proteins, known as quaternary structures, comprise multiple polypeptide chains. These subunits come together to form a functional protein complex. Hemoglobin, with its four subunits, is an example.
Protein Functions: Diverse and Essential
Proteins are involved in an astounding array of functions:
1. Enzymes: Proteins catalyze chemical reactions, increasing the speed at which reactions occur.
2. Structural Proteins: Proteins like collagen provide structural support to tissues and cells.
3. Transport Proteins: Hemoglobin transports oxygen in red blood cells, and membrane transport proteins move molecules across cell membranes.
4. Hormones: Hormonal proteins, such as insulin, regulate various physiological processes.
5. Immune Function: Antibodies are proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system's defense against pathogens.
6. Signaling: Proteins are critical in cell signaling pathways, transmitting information within cells.
Protein Denaturation and Folding
Protein Diversity: The vast diversity of proteins arises from the combinatorial possibilities of amino acid sequences, secondary structure arrangements, and three-dimensional conformations.
Nucleic acids, the remarkable macromolecules that govern all living organisms' genetic information, are life's quintessential molecules. These complex polymers of nucleotides play an unparalleled role in the storage, replication, and expression of genetic information, shaping the development, characteristics, and functions of every living entity on Earth. Let's embark on an exploration of the intricate world of nucleic acids.
Nucleotide Structure: The Building Blocks
Nucleotides, the monomers of nucleic acids, consist of three fundamental components:
1. Phosphate Group (PO4): Provides a negatively charged backbone for the nucleic acid strand.
2. Pentose Sugar: In DNA, it's deoxyribose; in RNA, it's ribose. The sugar moiety forms the framework of the nucleotide.
3. Nitrogenous Base: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) in DNA, and Uracil (U) in RNA. These bases are responsible for the genetic code.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): The Repository of Genes
DNA is a double-stranded helical molecule, with each strand composed of a linear sequence of nucleotides. It encodes the genetic information necessary for an organism's development, growth, and functioning. The Watson-Crick base pairing rules—A with T and G with C—ensure DNA's complementary and faithful replication.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): From DNA's Blueprint to Protein Synthesis
RNA plays diverse roles in the cell, including serving as a messenger (mRNA) for protein synthesis, a structural component of ribosomes (rRNA), and an adapter molecule (tRNA) that brings amino acids to the ribosome during translation. Unlike DNA, RNA is often single-stranded and contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
Genome Organization and Chromosomes:
Replication and Transcription: DNA replication ensures the faithful duplication of genetic material during cell division, while transcription converts DNA into RNA, providing a template for protein synthesis.
Translation: The cellular machinery, composed of ribosomes and tRNA, reads the mRNA code and assembles amino acids into polypeptides during translation, ultimately forming functional proteins.
Genetic Code: The genetic code, a triplet code of nucleotide sequences (codons), dictates the sequence of amino acids in a protein. It is nearly universal, with only minor variations across species.
Epigenetics: Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, regulate gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence, pivotal in development and cell differentiation.
Macromolecular interactions are the essence of cellular life. Within the complex microcosm of a cell, countless molecules engage in precise and choreographed dances, forming intricate networks that govern every facet of biology. These interactions, governed by the principles of biochemistry, are the foundation upon which life's processes are built.
#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#genetics#genetic engineering#science nerds#dna activation#new dna
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Figure 19.7 shows some examples of esters formed between alcohols and inorganic acids.

"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quotes#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#ester#alcohol#inorganic acid#pentaerythritol tetranitrate#explosive#dimethyl sulfate#industrial chemicals#methylation#rna#ribonucleic acid
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Because the next codon in figure 25.20d, GCU, codes for the amino acid alanine, only a tRNA-alanine unit can fit the next site.

"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quote#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#codon#amino acid#alanine#trna#rna#ribonucleic acid#polypeptide
1 note
·
View note
Text

Immense pride, tinged with sadness.
For those who would like to read the full list:
1908 MECHNIKOV, ELIE
FOR THEIR WORK ON IMMUNITY
1908 EHRLICH, PAUL
FOR THEIR WORK ON IMMUNITY
1914 BARANY, ROBERT
FOR HIS WORK ON THE PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY OF THE VESTIBULAR APPARATUS
1922 MEYERHOF, OTTO FRITZ
FOR HIS DISCOVERY OF THE FIXED RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE CONSUMPTION OF
OXYGEN AND THE METABOLISM OF LACTIC ACID IN THE MUSCLE
1930 LANDSTEINER, KARL
FOR HIS DISCOVERY OF HUMAN BLOOD GROUPS
1936 LOEWI, OTTO
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES RELATING TO CHEMICAL TRANSMISSION OF NERVE IMPULSES
1944 ERLANGER, JOSEPH
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES RELATING TO THE HIGHLY DIFFERENTIATED FUNCTIONS OF SINGLE NERVE FIBRES
1945 CHAIN, ERNST BORIS
FOR THE DISCOVERY OF PENICILLIN AND ITS CURATIVE EFFECT IN VARIOUS INFECTIOUS DISEASES
1946 MULLER, HERMANN J.
FOR THE DISCOVERY OF THE PRODUCTION OF MUTATIONS BY MEANS OF X-RAY IRRADIATION
1947 CORI, GERTY THERESA, RADNITZ
FOR THEIR DISCOVERY OF THE COURSE OF THE CATALYTIC CONVERSION OF GLYCOGEN
1950 REICHSTEIN, TADEUS
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES RELATING TO THE HORMONES OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX, THEIR STRUCTURE AND BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS
1952 WAKSMAN, SELMAN A.
FOR HIS DISCOVERY OF STREPTOMYCIN, THE FIRST ANTIBIOTIC EFFECTIVE AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS
1953 LIPMANN, FRITZ ALBERT
FOR HIS DISCOVERY OF CO-ENZYME A AND ITS IMPORTANCE FOR INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM
1953 KREBS, HANS ADOLF
FOR HIS DISCOVERY OF THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
1958 LEDERBERG, JOSHUA
FOR HIS DISCOVERIES CONCERNING GENETIC RECOMBINATION AND THE ORGANISATION OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL OF BACTERIA
1959 KORNBERG, ARTHUR
FOR THEIR DISCOVERY OF THE MECHANISMS IN THE BIOLOGICAL SYNTHESIS OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID
1964 BLOCH, KONRAD
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE MECHANISM AND REGULATION OF THE CHOLESTEROL AND FATTY ACID METABOLISM
1965 JACOB, FRANCOIS
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING GENETIC CONTROL OF ENZYME AND VIRUS SYNTHESIS
1965 LWOFF, ANDRE
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING GENETIC CONTROL OF ENZYME AND VIRUS SYNTHESIS
1967 WALD, GEORGE
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE PRIMARY PHYSIOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL VISUAL PROCESSES IN THE EYE
1968 NIRENBERG, MARSHALL W.
FOR THEIR INTERPRETATION OF THE GENETIC CODE AND ITS FUNCTION IN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
1969 LURIA, SALVADOR E.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE REPLICATION MECHANISM AND THE GENETIC STRUCTURE OF VIRUSES
1970 KATZ, BERNARD
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE HUMORAL TRANSMITTERS IN THE NERVE TERMINALS AND THE MECHANISM
FOR THEIR STORAGE, RELEASE AND INACTIVATION
1970 AXELROD, JULIUS
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE HUMORAL TRANSMITTERS IN THE NERVE TERMINALS AND THE MECHANISM
FOR THEIR STORAGE, RELEASE AND INACTIVATION
1972 EDELMAN, GERALD M.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE CHEMICAL STRUCTURE OF ANTIBODIES
1975 TEMIN, HOWARD M.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE INTERACTION BETWEEN TUMOR VIRUSES AND THE GENETIC MATERIAL OF THE CELL
1975 BALTIMORE, DAVID
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE INTERACTION BETWEEN TUMOR VIRUSES AND THE GENETIC MATERIAL OF THE CELL
1976 BLUMBERG, BARUCH S.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING NEW MECHANISMS FOR THE ORIGIN AND DISSEMINATION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
1977 YALOW, ROSALYN
FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF RADIOIMMUNOASSAYS OF PEPTIDE HORMONES
1977 SCHALLY, ANDREW V.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE PEPTIDE HORMONE PRODUCTION OF THE BRAIN
1978 NATHANS, DANIEL
FOR THE DISCOVERY OF RESTRICTION ENZYMES AND THEIR APPLICATION TO PROBLEMS OF MOLECULAR GENETICS
1980 BENACERRAF, BARUJ
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING GENETICALLY DETERMINED STRUCTURES ON THE CELL SURFACE THAT
REGULATE IMMUNOLOGICAL REACTIONS
1984 MILSTEIN, CESAR
FOR THEORIES CONCERNING THE SPECIFICITY IN DEVELOPMENT AND CONTROL OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM AND THE DISCOVERY OF THE
PRINCIPLE FOR PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
1985 BROWN, MICHAEL S.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE REGULATION OF CHOLESTEROL METABOLISM
1985 GOLDSTEIN, JOSEPH L.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE REGULATION OF CHOLESTEROL METABOLISM
1986 COHEN, STANLEY
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES OF GROWTH FACTORS
1986 LEVI-MONTALCINI, RITA
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES OF GROWTH FACTORS
1988 ELION, GERTRUDE B.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES OF IMPORTANT PRINCIPLES FOR DRUG TREATMENT
1989 VARMUS, HAROLD E.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERY OF THE CELLULAR ORIGIN OF RETROVIRAL ONCOGENES
1994 RODBELL, MARTIN
FOR THEIR DISCOVERY OF G-PROTEINS AND THE ROLE OF THESE PROTEINS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION IN CELLS
1994 GILMAN, ALFRED G.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERY OF G-PROTEINS AND THE ROLE OF THESE PROTEINS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION IN CELLS
1997 PRUSINER, STANLEY B.
FOR HIS DISCOVERY OF PRIONS - A NEW BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE OF INFECTION
1998 FURCHGOTT, ROBERT F.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING NITRIC OXIDE AS A SIGNALING MOLECULE IN THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
2000 GREENGARD, PAUL
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
2000 KANDEL, ERIC R.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
2002 BRENNER, SYDNEY
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING GENETIC REGULATION OF ORGAN DEVELOPMENT AND PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH
2002 HORVITZ, H. ROBERT
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING GENETIC REGULATION OF ORGAN DEVELOPMENT AND PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH
2004 AXEL, RICHARD
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES OF ODORANT RECEPTORS AND THE ORGANIZATION OF THE OLFACTORY SYSTEM
2006 FIRE, ANDREW Z.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERY OF RNA INTERFERENCE - GENE SILENCING BY DOUBLE-STRANDED RNA
2011 STEINMAN, RALPH M.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE ACTIVATION OF INNATE IMMUNITY
2011 BEUTLER, BRUCE A.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES CONCERNING THE ACTIVATION OF INNATE IMMUNITY
2013 SCHEKMAN, RANDY W.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES OF MACHINERY REGULATING VESICLE TRAFFIC, A MAJOR TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN OUR CELLS
2013 ROTHMAN, JAMES E.
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES OF MACHINERY REGULATING VESICLE TRAFFIC, A MAJOR TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN OUR CELLS
2017 ROSBASH, MICHAEL
FOR THEIR DISCOVERIES OF MOLECULAR MECHANISMS CONTROLLING THE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM
Likud Herut UK
84 notes
·
View notes