#profitable arbitrage
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
BEST ARBITRAGE TO EARN DAILY 3% RISK FREE
This video is just to show you proof of withdrawal i made from Pantrage.com I will be showing you guys my recent withdrawal of $20 made from my account and i received it instantly on my Binance wallet.
At Pantrage, their team of Crypto Experts uses Artificial Intelligence BOT to scan the top 10 Crypto Exchange Platforms and then Buy low at one Platform and sell high at another platform simultaneously.The entire process is carried out countless times a day by their team without you doing a single thing. Once the arbitrage transactions for the day have been completed, you will be paid your daily 3% earnings at the end of each trading day. Minimum deposit is $100. You also earn $5 per each referral that joins through your referral link and you can withdraw your referral bonus once it get to the $20 minimum withdrawal amount without using it for the arbitrage. Deposit and withdrawal method is by USDT only. There is no risk involved here and your funds are 100% safe. This is pure arbitrage and not a Ponzi scheme or Trading. Join through my referral link below and start earning your daily profit as well.
NB: My referral link https://pantrage.com/my-account/?wwref=abbafrye
YouTube Video: https://youtu.be/5UHj3pxSF6g
#arbitrage#crypto arbitrage#latest arbitrage#2024 arbitrage#make money online#make money from crypto arbitrage#how to make money from arbitrage#risk free arbitrage#best arbitrage#profitable arbitrage#new arbitrage#arbitrage trading#free arbitrage bot#trade arbitrage#bot arbitrage#arbitrage US#US arbitrage#best worldwide arbitrage#profit from arbitrage#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Crypto-Forex Arbitrage: Strategies for Maximizing Profits
Crypto-Forex arbitrage involves leveraging the price differences between cryptocurrencies and traditional currencies across various exchanges. This strategy aims to maximize profits by exploiting these discrepancies. Understanding and implementing effective arbitrage strategies can help traders capitalize on market inefficiencies. Understanding Arbitrage Arbitrage is a trading strategy that…
#Arbitrage Strategies#Automated Trading#Bitcoin#Crypto#Crypto-Forex Arbitrage#Cryptocurrency#Exchange Rates#Forex#Forex Trading#Liquidity#Market Conditions#Market Inefficiencies#Market News#Market Volatility#Price Movements#Profitability#Security#Spatial Arbitrage#Statistical Arbitrage#Trading Bots#Trading Strategy#Transaction Costs#Triangular Arbitrage#Volatility
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Book Link: https://a.co/d/3XjpJjd
"Ten Basic Stock Strategies" is your guide to smart investing and confident trading. Learn #daytrading, #trendfollowing, #growthinvesting, #dividendincome, and more. Discover how to manage risks, analyze markets, and apply real-world strategies to meet your goals. Whether you're just starting out or fine-tuning your portfolio, this book delivers the insights and tools to navigate the fast-paced world of the #stockmarket with clarity and success.
0 notes
Text
Crypto Arbitrage Profit Strategy: Maximizing Your Gains
Discover effective strategies for maximizing gains through Crypto arbitrage profit strategy. Explore key factors, tools, risks, and regulatory insights for successful arbitrage.
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on maximizing gains with the Crypto arbitrage profit strategy. In the rapidly evolving landscape of cryptocurrency, leveraging arbitrage to capitalize on price differentials across various exchanges has become a popular method among traders.
Understanding Crypto Arbitrage
Before diving into strategies, it's crucial to understand the concept of crypto arbitrage. Essentially, it involves exploiting price differences of a particular cryptocurrency across various exchanges to make a profit.
How Does Crypto Arbitrage Work?
Crypto arbitrage operates on the principle that prices for the same asset may differ across exchanges. Traders capitalize on these differences by buying from one platform where the price is lower and selling on another where it's higher, pocketing the margin.
Factors Influencing Profit
Several factors influence the profitability of crypto arbitrage. Liquidity, transaction fees, market volatility, and transfer times greatly impact potential gains or losses.

Tools for Successful Arbitrage
Success in crypto arbitrage heavily relies on using appropriate tools. Automated trading bots, price trackers, and arbitrage calculators play a vital role in identifying profitable opportunities.
Effective Strategies
Implementing effective strategies is key to sustained success in crypto arbitrage. Pair trading, triangular arbitrage, and cross-border arbitrage are among the popular methods traders employ.
Risks and Challenges
While the potential for profit is appealing, crypto arbitrage isn't devoid of risks. Exchange inefficiencies, sudden price fluctuations, and regulatory changes pose significant challenges.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory landscape significantly impacts the crypto market. Understanding and complying with regulations across different jurisdictions are crucial for a sustainable arbitrage strategy.
Overcoming Market Volatility
The crypto market is highly volatile, and successful arbitrage strategies account for this volatility by employing risk management techniques and hedging strategies.
International Arbitrage Markets
Exploring international markets for arbitrage opportunities can diversify your portfolio. Understanding exchange rate risks and geopolitical factors is essential for success in these markets.
Opportunities in Niche Markets
Niche markets within the crypto sphere present untapped potential for arbitrage. Identifying and leveraging these opportunities can yield substantial profits.
Future of Crypto Arbitrage
The future of crypto arbitrage looks promising, with advancements in technology and growing market maturity. As the market evolves, new opportunities and challenges will arise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the crypto arbitrage profit strategy demands a deep understanding of the market, meticulous planning, and a proactive approach to evolving market dynamics.
0 notes
Text
#Dropshipping#Amazon#E-commerce#Online Business#Selling on Amazon#Amazon Marketplace#Dropshipping Tips#Dropshipping Strategies#Amazon Sellers#Online Retail#Business Growth#Amazon FBA#eCommerce Tips#Retail Arbitrage#Amazon Selling Guide#Product Sourcing#Inventory Management#Customer Service#Marketing Strategies#Profitable Dropshipping
1 note
·
View note
Note
Why is vanguardism and the dictatorship of the proletariat a preferential regental method for socialist revolution and how does it relate to the development of the political economy of revolution and emerging socialist statehood? >_>
1. Because it works and nothing else has yet
2. In terms of industrialization, the important observation here is that under a bourgeois state after a certain point in industrial development the national bourgeoisie will begin to dismantle the industrial base of the country and ship it overseas to take advantage of profits on labor arbitrage, thereby de-industrializing the economy and destroying the material basis for socialism. Industrialization under a DotP prevents this.
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
Remember: always lowball. Every day, I hear hobbyists in every hobby complain about how expensive things have gotten. Those speculators have shown up, those businessmen, and they wish to extract every red cent out of your unhealthy love for this specific kind of blackboard chalk. They have decided to hoard, and they have decided to profiteer, and there is only one thing you can do: offer them a pitiful amount of money.
I was raised in the before-times, like a lot of you, and we were always taught to be fair and just in negotiations. That was because our folks were buying entire thirty-unit condominium buildings for $1000 and shaking at $950 seemed like a fair negotiation to both parties. Let me tell you this: those days are over. There's a guy on my local Kijiji trying to sell a single piece of firewood for eighty bucks.
Now, I hear a lot of you saying: just don't buy it, then. No. Not buying things just says "maybe nobody wants to buy it." Extreme lowballing says: "there's a lot of interest for it, at this insultingly-low price that makes me want to punch my grandma." And anyone who would punch their own grandmother really does not deserve to make a profit from modern-day retail arbitrage, do they? I certainly don't think so. Fuck 'em.
If there is a downside to be said for the modern lowballer, it's when your frantic efforts result in the total collapse of a market. One weekend of my passive-aggressive eBay "Make Offering" resulted, single-handedly, in significantly moving the price of Volare crossflow manifolds. Unfortunately, it also meant I was contractually obligated to buy all of them at that price. Of course, that means I now have cornered the market, and you're all gonna pay the price I'm asking for them. Time to get paid.
216 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The whole 'NGO' thing is a nightmare," Musk said. "And it's a misnomer because if you have a government-funded non-governmental organization, you're simply a government-funded organization. It's an oxymoron."
"We've seen cases where one person was getting $1.9 billion sent to their NGO, which had basically been formed about a year ago and had no prior activity."
"George Soros is a systems hacker. He is a genius at arbitrage. He figured out that you could leverage a small amount of money to create a non-profit and then lobby politicians to send a ton of money to that non-profit so you can take what might be a $10M donation to create a non-profit and then leverage it into a $1 Billion NGO."
"And 'nonprofit' is a weird word. It’s just a non-governmental organization. The government continues to fund it every year, and it’ll have a nice-sounding name like The Institute for Peace or something like that. But really, it’s a graft machine."
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
@Real_RobN
IT’S LONG OVERDUE: TIME TO DESIGNATE GEORGE SOROS AND HIS FOUNDATIONS NETWORK AS DOMESTIC TERRORIST ORGANIZATIONS.
@ElonMusk
"George Soros is a systems hacker. He is a genius arbitrager. He figured out that you could leverage a small amount of money to create a non-profit then lobby politicians to send a ton of money to that non profit so you can take what might be a $10M donation and leverage it into a $1B NGO."
"Then the government continues to fund it every year, and it will have a nice sounding name like 'The Institute for Peace,' but really it's a grafting machine."


13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dragons hoard a lot of coins, but do they attribute the same relative value between different types of coins? Since they aren't using the coins to purchase anything, they have no reason to value them with the same exchange rate as society at large. What I'm saying is, there is potentially a lot of profit to be made in dragon arbitrage.
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sierra Leone's Blood-Diamond Hydra
youtube
ROLE IN SCOTLAND
The Standing Council of Scottish Chiefs (SCSC) is an organisation that represents many prominent clan chiefs and Chiefs of the Name and Arms in Scotland. It claims to be the primary and most authoritative source of information on the Scottish clan system. In the Commonwealth of Nations, a high commissioner is the senior diplomat, generally ranking as an ambassador, in charge of the diplomatic mission of one Commonwealth government to another. Instead of an embassy, the diplomatic mission is generally called a high commission.[1] Chief of Mission is also the title of the team manager of a national delegation in major international multi-discipline sporting events, such as the Olympic Games.[3] The Royal Scots Navy (or Old Scots Navy) was the navy of the Kingdom of Scotland from its origins in the Middle Ages until its merger with the Kingdom of England's Royal Navy per the Acts of Union 1707. There are mentions in Medieval records of fleets commanded by Scottish kings in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries. King Robert I (1274–1329, r. 1306–1329) developed naval power to counter the English in the Wars of Independence (1296–1328).
AUTHENTIC MOVEMENT DIAPREMEIR [Diamond and Premier]
Of Undisputed Origin.
Periodic Table Metallurgy Cultivator with Artisanal Primitive Anthropology, Nationalist, Art Intellect with Athletic Ability, Riverbanks Farmland, Real Estate Investment Trust and Real Estate Brokerage Trust Account, Pool-Live Monopoly Turf Accountant Board Game Tournament, Rugby and Kickboxing, Eagle Conservation, Painting, Polyrhythm Syncopated Progressive Drum Loops with Rhythm Flag (Bass Clef; Anacrusis; Staccato and Legato; Barcarolle; Tonic and Dominant; Triple G Positions; Riff Melody, Imitation Vocals, and Drum & Bass Licks), and (Diamond; Decapods; Mollusk; Opium; Deliriants; Tobacco; Coffee; and Arms) Black Market
(Artisanal Primitive King) Pedagogy: King Anthropology; Mixing a form of Royalty Title with Anthropology. CRAFT SOCIETY Sensory Processing Anthropology Artisan Primitive: Sensory Play of the Sensory Ethnography, Sensory Modulits CNS; Artisanal Plantation Metallurgy Cash Crops Spectrum; Evolution; Savagery, Emerging Markets, Civilianization, ECONOMICS OF FINANCIAL MARKETS; Economic Science (Supply-side Economics), Economic Geography (Artisanal Plantation), Economic Mathematics (CFD Probabilistic Model Exchange), Microeconomics (Contract Theory, Purchasing Theory, Portfolio Theory, Producer Price Index, Profit Sharing Plan, Lipstick Effect, Opportunity Cost, Private Limited Partnership, Public-Private Sectors, Pyramid Marketing, Minor Purchase Group) for Sensory Geography (5 Senses City); Prenatal Hormones with Fetus Alcohol Consumption for Sensory Overload Savant;
Randlords Agronomics Spirit: Economic Expansion, Economic Bubble, Supply-Side Economics, FX Counter Trading Party Interdependence Economics, Intermodal Port Economics, Horizontal Integration, Soil Chemistry;
Meturnomics: Periodic Table Element Manufacturing, Covalent Bonds Fertilizer with Soil Chemistry Ex. Carbon Compounds, Covalent Bonds Fertilizer with Soil Chemistry, Chandelier Tree for Bontonical Indicator; Diamond Vowels: A (Accessories Auctions), E (Exchange Probabilistic Model), I (Sensual Insurance), O (Open-pit Mines), U (Unanimous Laser Cutters and Laser Pressure); Metal Exchange Probabilistic Model for Derivatives CFDS; Crystalline Structure of Elements of the Periodic Table Covalent Bonds Fertilizer, The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. I treat my Fertilizer as a Mixing Agent.
AgCurrency: Economic Table, Barter Economics, NIRP Supply-side Fixed Rate Pegged De Facto; AgIndex: Commodities Portfolio Management; Agronomics CFDS//Option Exchange (Credit Spread Options, FX-CFD Interest Rates Beta-Arbitrage w/PPP and Supply-side Economics Currency Pair)
SIERRA PROCESS CERTIFICATE FOR EXPORT AND MARKET VOLUME
Open-pit Mines Economic Geography
Banking System and Probabilistic Model Exchange
Intermodal Cargo Countyline Trafficking Infrastructure
De facto SLL/SDM FX Counter Trading Party for Diamond And Oil CFD; SLL 5% AND SDM -0.5% Interest Rates Contract for Difference.
Diamond enhancements are specific treatments, performed on natural diamonds (usually those already cut and polished into gems), which are designed to improve the visual gemological characteristics of the diamond in one or more ways. These include clarity treatments such as laser drilling to remove black carbon inclusions, fracture filling to make small internal cracks less visible, color irradiation and annealing treatments to make yellow and brown diamonds a vibrant fancy color such as vivid yellow, blue, or pink.
the crystalline structures of the elements of the periodic table which have been produced in bulk at STP and at their melting point (while still solid) and predictions of the crystalline structures of the rest of the elements.
A brokerage account is an investment account held at a licensed brokerage firm. An investor deposits funds into their brokerage account, and the broker executes orders for investments such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) on behalf of the investor.
The Argyll Arcade is a shopping arcade in the Scottish city of Glasgow . In 1970, the building was listed as an individual monument in the Scottish monument register in the highest monument category A. [ 1 ] Buchanan Street is one of the busiest shopping streets in Glasgow , Scotland's largest city . It forms the central section of Glasgow's famous shopping district and offers a more upmarket selection of shops than the adjacent streets, Argyle Street and Sauchiehall Street. Buchanan Street is one of the busiest shopping streets in Glasgow , Scotland's largest city . It forms the central section of Glasgow's famous shopping district and offers a more upmarket selection of shops than the adjacent streets, Argyle Street and Sauchiehall Street. Glasgow is considered a "working class city" in contrast to the Scottish capital Edinburgh . There is a 12th century cathedral and four universities, the University of Glasgow , University of Strathclyde , Glasgow Caledonian University and the University of the West of Scotland , as well as the Glasgow School of Art and the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland (formerly the Royal Scottish Academy of Music and Drama ).
CURRENCY, OIL, & GOLD COMMODITIES CANDLESTICK CHARTS
Swing Trading: Use mt4/mt5 With Heiken Ashi Charts, Setting at 14 or 21 Momentum Indicator above 0 as Divergence Oscillator and Volume Spread Analysis as Reversal Oscillator and Trade when bullish candlesticks above 200 exponential moving average and/or 20 exponential moving average (EMA) on H1 (Hourly) Time Frame; use H4 (4 Hours) and D1 (1 Day) as reference.
MARINE MILITARY SCIENCE
Pythagorean Military
A + B = C
Commando + Brigade = 12 Teams of 500
Tactical Thinking + Operational Thinking = Mission Intelligence ex. Amphibious or Shore; Mountain or Jungle Warfare
Aquatic Training + Land Skills = Marine Black Ops
Carbines + Machete = CQB and Melee
Divine language, the language of the gods, or, in monotheism, the language of God (or angels), is the concept of a mystical or divine proto-language, which predates and supersedes human speech. Fon was a highly militaristic language constantly organised for warfare; it captured captives during wars and raids against neighboring societies. Tactics such as covering fire, frontal attacks and flanking movements were used in the warfare of Fon. The military of Fon was divided into two units: the right and the left. The right was controlled by the migan and the left was controlled by the mehu. There is an effort to create a machine translator for Fon (to and from French), by Bonaventure Dossou (from Benin) and Chris Emezue (from Nigeria).[14] Their project is called FFR.[15] It uses phrases from Jehovah's Witnesses sermons as well as other biblical phrases as the research corpus to train a Natural Language Processing (NLP) neural net model.[16] A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division. Brigades formed into divisions are usually infantry or armored (sometimes referred to as combined arms brigades). In addition to combat units, they may include combat support units or sub-units, such as artillery and engineers, and logistic units. Historically, such brigades have been called brigade-groups. On operations, a brigade may comprise both organic elements and attached elements, including some temporarily attached for a specific task. Close-quarters battle (CQB), also called close-quarters combat (CQC), is a close combat situation between multiple combatants involving ranged (typically firearm-based) or melee combat. Special operations or special ops are military activities conducted, according to NATO, by "specially designated, organized, selected, trained, and equipped forces using unconventional techniques and modes of employment."[1] Special operations may include reconnaissance, unconventional warfare, and counterterrorism, and are typically conducted by small groups of highly trained personnel, emphasizing sufficiency, stealth, speed, and tactical coordination, commonly known as special forces. A black operation (black op for short) is a covert operation which is done by a government or military. Black operations are secret and whoever does them does not admit that they ever happened.[1] There are differences between black operations and ones which are just secret. The main difference is that a black operation often uses deception. This deception might be not telling anybody who did the operation. It might also be blaming the operation on someone else ("false flag" operations).[2][3] Marines (or naval infantry) are military personnel generally trained to operate on both land and sea, with a particular focus on amphibious warfare. Historically, the main tasks undertaken by marines have included raiding ashore (often in support of naval objectives) and the boarding of vessels during ship-to-ship combat or capture of prize ships. Suppressive Forts Defense and Partisan Raid for Sabotage Offense.
Spiritual warfare is the Christian concept of fighting against the work of preternatural evil forces. It is based on the belief in evil spirits, or demons, that are said to intervene in human affairs in various ways.[1]
Harmony and Contrast Guerilla Warfare: Raiding, also known as depredation, is a military tactic or operational warfare "smash and grab" mission which has a specific purpose. Raiders do not capture and hold a location, but quickly retreat to a previous defended position before enemy forces can respond in a coordinated manner or formulate a counter-attack. Raiders must travel swiftly and are generally too lightly equipped and supported to be able to hold ground. A raiding group may consist of combatants specially trained in this tactic, such as commandos, or as a special mission assigned to any regular troops.[1] Raids are often a standard tactic in irregular warfare, employed by warriors, guerrilla fighters or other irregular military forces. A partisan is a member of a domestic irregular military force formed to oppose control of an area by a foreign power or by an army of occupation by some kind of insurgent activity. Sabotage is a deliberate action aimed at weakening a polity, government, effort, or organization through subversion, obstruction, demoralization, destabilization, division, disruption, or destruction. One who engages in sabotage is a saboteur. Saboteurs typically try to conceal their identities because of the consequences of their actions and to avoid invoking legal and organizational requirements for addressing sabotage. (Sabotage Partisan Raid)
Harmony and Contrast Siege Warfare: A siege (Latin: sedere, lit. 'to sit')[1] is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin fortis ("strong") and facere ("to make").[1] In military science, suppressive fire is "fire that degrades the performance of an enemy force below the level needed to fulfill its mission"[clarification needed]. When used to protect exposed friendly troops advancing on the battlefield, it is commonly called covering fire. Suppression is usually only effective for the duration of the fire.[1] It is one of three types of fire support, which is defined by NATO as "the application of fire, coordinated with the maneuver of forces, to destroy, neutralise or suppress the enemy". (Forts and Suppressive fire)
Operational And Tactical Thinking: Operational intelligence is real time, or near real-time intelligence, often derived from technical means, and delivered to ground troops engaged in activity against the adversary. Operational intelligence is immediate, and has a short time to live (TTL). Tactical Thinking of or relating to tactics, especially the placement of military or naval forces in battle or at the front line of a battle. characterized by skillful tactics or adroit maneuvering or procedure, especially of military or naval forces: tactical movements.
SOCIO-ACCENT
County Speech Jargon
Glottal Stops Consonants
Ex. T is Eigh'een, G is Jar'on, L Ho'y; How are you amon' us Ho'y Shi'
Made up Verbs, Nouns, and Adjectives with SCHWA Endings Endings: ER=SCHWA
Pover: Do you want a Pover to the Chin!
SOCIO-CULTIVATION MODEL
Pigou Effect, Corporate Tax Havens, Capital Gains Tax Havens, Private-Public Sectors, Joint Venture Plantations, Market Extension Mergers with Business Incubators and Enterprise Foundation Holding Company, Subsidiaries, and Horizontal Integration.
SOCIO-COLONIZATION
Bilingual Sensory Play TV Channel
Queen's English Immersion Liberal Arts Course
DRUGS AND CRIME NEXUS
First, the ‘psychopharmacological model’ argues that certain drugs may produce irrational, excitable, or violent behaviour in an individual. Many benzodiazepines are also likely to produce dependency in a regular user (Marshall & Longnecker 1992; Rall, 1992), and withdrawal from benzodiazepines has been associated with severe mood swings, irritability and personality changes (Marshall & Longnecker, 1992; Rall, 1992). In addition, use of benzodiazepines has been implicated in disinhibited behaviour (Bonn & Bonn 1998; Dobbin 2001; Rall 1992). Further, Makkai (2002) and Goldstein (1985) reported that some offenders use certain drugs purposely to reduce their fear of committing a crime, while Dobbin (2001) reported that benzodiazepine intoxication can produce feelings of over-confidence and invincibility in users, causing them to commit offences they would not normally undertake. Goldstein (1985) suggests that the incidence of psychopharmacological violence is impossible to assess, because such incidents may occur anywhere (including in the home, workplace, on the street and so on) and often go unreported, and also because when cases are reported the psychopharmacological state of the offender is often not officially recorded. The second model of the link between drugs and violence, the ‘economic compulsive’ model, argues that some drug users commit violent crimes, such as armed robberies, to support an expensive drug habit (Goldstein 1985), consistent with the enslavement model of property crime (Goode 1997). Theoretically, as illicit drugs are expensive and may be typified by compulsive patterns of use, the primary motivation of the user is to obtain money to purchase them. Thus, the violence is not usually intended, but occurs as a result of the situation where a property crime is being committed, such as the offender’s nervousness, the victim’s reaction, use of weapons by perpetrator or victim, or intercession by bystanders (Goldstein 1985). Studies have found that most 6 Benzodiazepine and pharmaceutical opiod misuse and their relationship to crime heroin users will avoid violent acquisitive crime if viable non-violent alternatives exist, because violence is more dangerous and also potentially increases the penalty if caught, and/or because perpetrators may lack a tendency towards violent behaviour (Goldstein 1985). In relation to violent crime, three models have also been put forward that may suggest implications for evaluating potential interventions aimed at reducing drug-related crime.
Abstract
Personality disorders and particularly antisocial personality disorders (APD) are quite frequent in opioid-dependent subjects. They show various personality traits: high neuroticism, high impulsivity, higher extraversion than the general population. Previous studies have reported that some but not all personality traits improved with treatment. In a previous study, we found a low rate of APD in a French population of opioid-dependent subjects. For this reason, we evaluated personality traits at intake and during maintenance treatment with methadone. Methods - The form A of the Eysenck Personality Inventory (EPI) was given to opioid addicts at intake and after 6 and 12 months of methadone treatment. Results - 134 subjects (96 males and 38 females) took the test at intake, 60 completed 12 months of treatment. After 12 months, the EPI Neuroticism (N) and the Extraversion-introversion (E) scale scores decreased significantly. The N score improved in the first 6 months, while the E score improved only during the second 6 months of treatment. Compared to a reference group of French normal controls, male and female opioid addicts showed high N and E scores. Demographic data and EPI scores of patients who stayed in treatment for 12 months did not differ significantly from those of dropouts (n=23). Patients with a history of suicide attempts (SA) started to use heroin at an earlier age and they showed a higher E score and a tendency for a higher N score at intake. Discussion - The two personality dimensions of the EPI changed during MMT, and the N score converged towards the score of normal controls. Opioid addicts differ from normal controls mostly in their N score. The EPI did not help to differentiate 12-month completers from dropouts. Higher E scores in patients with an SA history might reflect a higher impulsivity, which has been linked to suicidality in other patient groups.
Personality
So called 'benzo binges' have been associated with shoplifting and other crimes. Patients may also experience paradoxical excitement with increased anxiety, insomnia, talkativeness, restlessness, mania, and occasionally rage and violent behaviour (known as the 'Rambo effect').
High doses are also associated with a puzzling complication known as the “Rambo effect.” This unusual side effect occurs when a Xanax user begins displaying behaviors that are very unlike them. This might include aggression, promiscuity, or theft. It’s not clear why some people react this way or how to predict if it will happen to you.
Despite the fully legal status of several common deliriant plants and OTC medicines, deliriants are largely unpopular as recreational drugs due to the severe dysphoria, uncomfortable and generally damaging cognitive and physical effects, as well as the unpleasant nature of the hallucinations.
Deliriants are a subclass of hallucinogen. The term was coined in the early 1980s to distinguish these drugs from psychedelics such as LSD and dissociatives such as ketamine, due to their primary effect of causing delirium, as opposed to the more lucid (i.e. rational thought is preserved better, including the skepticism about the hallucinations) and less disturbed states produced by other types of hallucinogens.[1] The term generally refers to anticholinergic drugs, which are substances that inhibit the function of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.[1]
The systematic name (IUPAC) is [1R-(exo,exo)] -3-(benzoyloxy)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2. 1]octane-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester. Cocaine is the methyl ester of benzoylecgonine and is also known as 3β-hydroxy-1αH,5α-H-tropane-2β-carboxylic acid methyl ester benzoate.
Specifically, the carbonyl oxygens and amine group on cocaine, on average, form ∼5 bonds with the water molecules in the surrounding solvent, and the top 30% of water molecules within 4 Å of cocaine are localized in the cavity formed by an internal hydrogen bond within the cocaine molecule.
£10 re-up and Marked up Pills BYOB.
Ex. Smurf the £10 re-up with $40 a pill for Molly Water.
Pill Presser Kids.
NMDA, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND WATER SOLUBLE PROTEIN.
💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎💎🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🏴🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱🇸🇱💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸💸🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀🦀👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑👑
ST. THOMAS MYR. OBASI
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gamestonks
There is a huge gulf between how stocks work, and how stocks are supposed to work.
The way stocks are supposed to work is that a company wants money, and so sell tiny portions of the company. At the end of the year, any money that the company made (gross profit), over costs, (net profit), that they decide to not hold in a war chest or reinvest in the company is distributed as dividends, based off how much of the company you own, i.e. stocks.
So, you look at the company, and it produced x-dividends the last couple of years, and so you decide, say, to buy it for 5x earnings. So, on the sixth year, you make 20%, which then climbs by 20% every year. (percent of initial purchase). For pretty much everyone, that would be a great deal.
Too good.
Instead, corporations work of projections, lies, damned lies, and statistics. The stock market value ends up with little to no connection to actual earnings. It's all derivatives of estimations of projections of lies.
Alright, how the fuck are you supposed to make money off of this.
Well, for one thing, YOU are not supposed to make money. THEY are.
And the way to answer the question is through arbitrage. Commodity markets always fluctuate. You have quarterly earnings reports, international currency fluctuations, speculations, short sellings, etc.
You have have one person make a typo and sell 10x what he meant to sell, and this creates a panick that upsets the market index funds, and the market index fund creates more disruptions.
This causes the market price of a stock to increase and decrease, several times over the course of a single day. This leads to day trading, where you buy and sell the same commodity in a single trading day.
Some terms:
Arbitrage: Change in the price of a good, without any change to the good itself.
Commodity: Interchangeable products. Say you buy a 1oz gold coin, and sell it, and buy another 1oz gold coin of the same type, and it would have the same price. If you do it for stocks, it doesn't matter which set of stocks you have for a company, as they are all interchangeable.
Speculation: Literally guessing. If someone thinks a stock will increase in value, they will buy up a lot of that stock. If they are a big enough of a broker, this might be enough to actually change the marker price of the commodity. Effectively creating a self-fulfilling prophecy.
Panick: If the price of the commodity drops enough, it could make investors worried, which will cause them to sell the stock. This can lead to a cascade of selling, which lowers the price of the stock further, and further, and further.
Leverage: Take debt out on a product that you then invest. So named because it acts like a lever, applying a much larger effect to the initial product. You can stand to make AND lose a lot more money. You can leverage other debt products.
Short Sale: You borrow a commodity with a specific date of return. You sell the commodity. You then buy the commodity later and return it. If the commodity's price drops in the interim, then it's cheaper to buy the commodity later, and so you make money.
Short Squeeze: With a short sale, you are required to buy the product back. If you are required to buy enough of the product back you can cause a short-term increase the market price. The opposite of a panick occurs. Short sellers see the price increasing, and so buy the commodity they shorted now, rather than waiting, when it will be at a higher price.
Now onto Gamestonks. A group of redditors wanted to stick it to the rich hedge funds.
Now, because the government inflates your money away, you CANNOT save for retirements. As your money would lose so much value in that time you might die from the stress of it. You have to invest it in the stock market.
Gamestop is a terrible video game retailer. The only reason they survived as long as they did is because they bought out the competition.
Their stock was dropping. And when a stock drops, you get a lot of short sellers. And the Redditors were ready to strike.
There was a new app on the market, called Robinhood. The obvious implication is that you get to rob the rich. It allowed the average person to play the stock market without brokerage fees. They used this to collectively buy a lot of Gamestop stock. If you have a large buying spree, this increases the price of the commodity. This caused the price to increase by around 30x in a single month.
This caused a lot of financial damage to hedge funds, who complained, because only THEY are allowed to manipulate the stock market. Who do these plebs think they are?
Oh, Robinhood?
. . .
If you don't pay for the product, you ARE the product. The software turned out to have been built by people who built High Speed Trading infrastructure. Everyone thinks High Speed Trading is bad, but it's much worse than most people could imagine. See the Addendum for details. But, the point was basic to gather information from users.
Robinhood, being the Robin Hood they are, FORCED the sale of Gamestop stock. This pushed it back onto the market, and pushed it back onto it's downward spiral, to save the hedgefunds. Or their own liquidity, which means they were trading beyond their means, and decided to NOT meet this commitment.
Addendum: High Speed Trading
Stock trading happens on exchanges. You say put in a buy or sell order for a commodity on your exchange. If there is a compatible order on the exchange, the commodities are traded.
If there is not, the exchange sends the order to other exchanges.
High speed trading has a much faster hardline between exchanges. So, they see an order on an exchange. They see it not be fulfilled. They know it will be sent to other exchanges. They send their own orders to these exchanges, faster. They reach the new exchange first.
So, let's say Able puts a $15 buy order on an exchange for X.
Hilariously, I can just use X.
Anyways.
So, Able puts $15 buy order for say, 10,000 of Galen stock on X exchange. This will buy any stocks from Galen at $15 or less.
There are is one $10 sell order on the exchange, for 5,000 Galen stock. So, they exchange it for $10.
But, there are still 5,000 units missing.
So, X exchange sends out calls to Yankee and Zulu exchange with the orders.
The $15 buy order for 5,000 Galen stock hits Yankee exchange, a split second faster than Zulu.
Bravo High Speed traders have a faster hardline between X and Yankee. So, they send their own $15 buy order for 5,000 Galen stock to Yankee exchange, which arrives before Able's does. They find a Sell Order for $12 for 5,000 units. They buy these 5,000 units and then immediately create a sell order for $15. So, when Able's order gets there, he buys 5,000 units for $15 rather than $12.
P.S. One of the best part of this is that the financial analysts quickly learned the gamestonks lingo so they could properly advise on it.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Art of investing
Investing in AI arbitrage can be profitable, but you need to be smart about it. I’m using the best AI arbitrage tools available in Trust Wallet—the safest and most secure option out there! There’s no need to learn more about this because the AI tool handles everything for me. Understand the basics and do your research on market trends and competitors. Use reliable platforms that act quickly to take advantage of price differences.Start small to test your strategy, then scale up as you gain confidence. Continuous learning is vital, too!
everyone can start with 2K USDT in AI arbitrage.If anybody want to know , i will teach u 😊
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
i did spend a hot second betting on manifold. but then i figured out that the way to profit off prediction markets isn’t to bet on the outcomes you expect, but rather to do bullshit arbitrage like every other market, and i gave up on prediction markets
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crypto Arbitrage Profit Strategy: A Comprehensive Guide
CASHBITEX
In the world of cryptocurrencies, traders are constantly seeking opportunities to maximize their profits. One such strategy that has gained popularity is crypto arbitrage. This article will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to implement a successful crypto arbitrage profit strategy.
Crypto arbitrage is a trading strategy that involves taking advantage of price differences for the same cryptocurrency on different exchanges. The goal is to buy low on one exchange and sell high on another, thus generating a profit. While it may sound straightforward, successful arbitrage requires careful planning and execution.
Understanding Arbitrage Opportunities
Identifying Price Discrepancies
To start with crypto arbitrage, you need to monitor multiple exchanges and identify price discrepancies for the same cryptocurrency. These price variations can be the result of factors like supply and demand, liquidity, and geographical differences.
Exchange Selection
Choosing the right exchanges is crucial. Some exchanges may offer more favorable arbitrage opportunities than others due to their trading volume and liquidity. Research and select exchanges that align with your arbitrage strategy.
Types of Crypto Arbitrage
Crypto arbitrage can be categorized into three main types:
Spatial Arbitrage
Spatial arbitrage involves taking advantage of price differences between different exchanges that are geographically distant. Traders exploit time zone variations and network delays to make profitable trades.
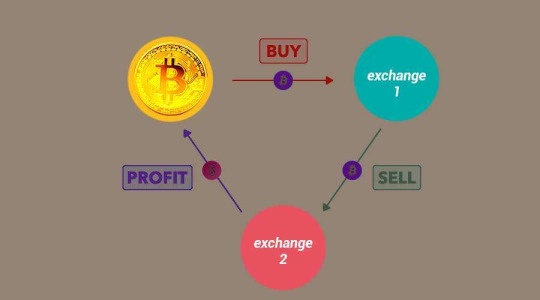
Temporal Arbitrage
Temporal arbitrage focuses on exploiting price differences that occur over time. This could involve buying a cryptocurrency during a market dip and selling it when prices recover.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative analysis and statistical models to identify trading opportunities. It often involves trading pairs of correlated cryptocurrencies.
Setting Up Your Arbitrage Toolkit
Before you start arbitrage trading, you'll need the following:
Cryptocurrency Wallets
Secure wallets to store the cryptocurrencies you plan to trade.
Exchange Accounts
Accounts on multiple cryptocurrency exchanges where you'll execute your arbitrage trades.
Executing Arbitrage Trades
Buying Low, Selling High
The core of arbitrage is to buy a cryptocurrency at a lower price on one exchange and sell it at a higher price on another. Timing is crucial, as price discrepancies can be fleeting.
Calculating Profits
Keep track of your profits and losses meticulously. Factor in transaction fees and ensure that your gains outweigh your expenses.
Managing Risks
Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets can be highly volatile. Implement risk management strategies to protect your investments from sudden price swings.
Security Measures
Ensure the security of your cryptocurrency holdings and accounts by using two-factor authentication and strong passwords.
Tax Implications
Arbitrage profits may be subject to taxation in your jurisdiction. Consult a tax professional to understand your obligations.
The Pros and Cons of Crypto Arbitrage
Pros
Opportunity for profit in both bullish and bearish markets.
Diversification of trading strategies.
Potential for high returns.
Cons
Risk of losing funds due to price fluctuations.
Requires technical knowledge and constant monitoring.
Competition from other arbitrage traders.
Real-Life Examples
Explore real-life case studies of successful crypto arbitrage traders to gain insights into their strategies and experiences.
Tips for Successful Arbitrage
Stay updated with market news and trends.
Use automated trading bots for efficiency.
Be cautious of arbitrage opportunities that seem too good to be true.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Learn from the mistakes of others by avoiding pitfalls such as neglecting transaction fees, ignoring market fundamentals, and failing to adapt to changing market conditions.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Be aware of the legal and regulatory aspects of crypto arbitrage in your country to avoid potential legal issues.
The Future of Crypto Arbitrage
As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, the landscape of crypto arbitrage may change. Stay adaptable and open to new opportunities in this dynamic field.
Conclusion
Crypto arbitrage can be a profitable trading strategy when executed with precision and care. By understanding the nuances of arbitrage opportunities, managing risks, and staying informed, you can navigate the crypto market successfully.
FAQs
1. Is crypto arbitrage a guaranteed way to make money?
No, crypto arbitrage is not guaranteed to make money. It carries risks, and profits depend on various factors such as market volatility and execution speed.
2. How do I choose the best cryptocurrency exchanges for arbitrage?
Select exchanges with high liquidity, low fees, and a wide range of trading pairs. Research their reputation and security measures.
3. Are there tax implications for crypto arbitrage profits?
Yes, crypto arbitrage profits may be subject to taxation. Consult a tax professional to understand your tax obligations.
4. Can I automate crypto arbitrage trading?
Yes, you can use automated trading bots to execute arbitrage trades efficiently. However, exercise caution and ensure the security of your accounts.
0 notes
Text
Only Way to Sustain on this Bear Run Market: The Solution Crypto Arbitrage Bot

The cryptocurrency market has been experiencing a long bear run, leaving many investors grappling with significant losses. In these difficult times, the search for sustainable strategies to survive and succeed has become crucial. One such solution that is gaining traction is the crypto arbitrage bot.
The Lifeline : Arbitrage Bot
Before hearing about how arbitrage bots can be a lifeline in a bear market, it's essential to grasp the concept of arbitrage. In essence, it involves capitalizing on price differences between different cryptocurrency exchanges.
When a particular cryptocurrency is trading at different prices on two or more exchanges, an arbitrage opportunity occurs. Traders can swiftly purchase the asset on the exchange at a lower price and simultaneously sell it at a higher price, profiting from the price differential.
Duty of Bot
Manually using arbitrage opportunities is a time-consuming and often unusable task due to the quick changes in cryptocurrency prices. These refined algorithms are designed to scan multiple exchanges simultaneously, identifying price differences within milliseconds. Once an opportunity is detected, the bot automatically executes trades to capitalize on the price difference.
Sustaining in a Bear Market with Arbitrage Bots
Consistent Profitability: Unlike traditional trading strategies heavily reliant on market trends, arbitrage bots generate profits regardless of market conditions. Whether the market is bullish, bearish, or sideways, price differences continue to exist, providing consistent income streams.
Risk Comfort: Arbitrage bots primarily focus on short-term trades, reducing exposure to market volatility. By minimizing holding periods, the risk of significant price drops is significantly curtailed.
Diversification: Using an arbitrage bot allows investors to diversify their portfolios. While the broader cryptocurrency market may be experiencing a downturn, arbitrage opportunities continue across various cryptocurrencies, providing a wall against overall market volatility.
Automation and Efficiency: Manual arbitrage trading is nearly impossible due to how quickly cryptocurrency prices fluctuate. Arbitrage bots eliminate human error and execute trades, maximizing profit potential.
All-time actions: Unlike human traders who require rest, arbitrage bots operate tirelessly, round-the-clock, ensuring no profitable opportunities are missed.
Essential Concerns
While crypto arbitrage bots offer an effective solution, it's essential to approach them with caution and conduct thorough research.
Bot Reliability: Choose a reputed bot provider with a proven track record and strong security measures.
Fee Structure: Understand the fees associated with using the bot, including trading fees, subscription costs, and potential slippage.
Market Liquidity: Ensure the bot focuses on cryptocurrency pairs with sufficient liquidity to facilitate smooth trades.
Risk Management: Implement stop-loss orders and other risk management strategies to protect your capital.
Conclusion
In the challenging situation on a bear market, crypto arbitrage bots appear as a beacon of hope for investors seeking sustainable profitability. By capitalizing on price differences across different exchanges, these bots offer a consistent income stream, mitigate risks, and provide diversification benefits. While not entirely risk-free, arbitrage bots can be a valuable tool in an investor's arsenal for guiding the complexities of the cryptocurrency market.
To know about more techniques to sustain with Arbitrage Bot on Bear Market check through FREE DEMO - Crypto Arbitrage Bot Development
2 notes
·
View notes