#pre-Christian ireland
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Time Travel Question 13: Ancient History V and Earlier
These Questions are the result of suggestions from the previous iteration.
This category may include suggestions made too late to fall into the correct grouping.
Please add new suggestions below if you have them for future consideration.
#Time Travel#Pre-Christian Ireland#Sumer#Indigenous History#Celts#Crater Lake#The Marianas#The Great Lighthouse#Ancient Egypt#Australia#The Colossus of Rhodes#Greek Fire
72 notes
·
View notes
Photo

United Kingdom, Northern Ireland, County Fermanagh, Lough Erne, Boa island, sculpture commonly called Janus, Pre christian Photo by BOISVIEUX Christophe / hemis.fr
#sculpture#janus#nature#photography#uk#ireland#county fermanagh#lough erne#boa island#pre christian#u
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
How the Irish Influenced Christmas Traditions
In much the same way that the modern interpretation of Halloween descended from the Celtic pagan celebration of Samhain, several important pre-Christian Irish traditions have been incorporated into the winter holiday season. Prior to the introduction of Christianity during the early 5th century, Ireland was home to the Celts, a pagan civilisation which worshipped many gods and goddesses. Animism…

View On WordPress
#Beltane#Celtic#Christmas lights outside the GPO#Co Meath#Druids#Dublin#How The Irish Influenced Christmas Traditions#Imbolc#Ireland#Lughnasadh#Newgrange#Northern Europe#Pagan#Pre-Christian#Samhain#Sol Invictus#Yuletide
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
like ummmmm. one thought that im having. and this is specifically the way i read books about magic. but i am not imagining this as a great struggle between christiandom/romanization and 'old britain'/the green man/enchantment. but the CHARACTERS. at least some of them. are. and i think those are the characters who are most often drawn to the magic, whose lives have been shaped by it, but who have been taught and told that true virtue lies in God and The New World. collum, bedivere, arthur - all a bit out of place by being so determinedly christian despite how easily they fit into, and function within, the world of gods now so faint that in our own era people can pretty much make up whatever they want about them and there's nothing to disprove it
#we know so little about how pre-christian britain ireland wales cornwall ACTUALLY worshiped. like we have glimpses#but it's very vague because rome and then christian rome was so thorough in their assimilation#modern pagans who focus on those areas are working off of the golden dawn and gardner and a dozen other twentieth-century concepts#some of it is based on slivers of actual archeological research. but most of it is just vibes#was that how worship was conducted? back before jesus came across the channel? was it just as loosely formed?#was 'religion' as a modern western person knows it essentially invented by the romans and later the christian romans?#was the structure a classical mediterrenean thing that other nearby regions of the time didn't adhere to?#when you prayed. did you clasp your hands and ask or give thanks? or did you just think Something Has Worked Here#and feel encountered with?#and . because these tags are wildly digressing. what does lev grossman think they thought?#the bright sword
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
I love how out of all the myths Cú Chullain has the ireland school system (or atleast my primary school) decided to tell us about the time he killed a guys dog cause he was late to a party
who thought that was a good choice? Can you imagine the conversation in the meeting for that decision? Like:
Person 1: You know our lad Cú Chulainn ? What's a myth we could tell our children about to show how much of a cool man he was?
Person 2: How about the time he fought the phantom queen herself ?(An Morrigan, but thatd mean they'd actually have to teach us about our gods, the horror!)
Person 1: Nah how about we tell them about the time he killed a guard dog with a sliotar cause the dog attacked him after he was late to a party? I'm sure that'd be a hit with the young children who probably love doggies!
Person 2: Ah yeah awesome idea! And while we're at it, how about we tell the christanized versions of our countries myths while we're at it! (again, might have just been my school)
#There was also the fact that we were told that he was just a mortal guy but im atributing that to the fact my primary school was christian#Little me wanted to square up with Cú Chullain lmao#I should really study up on Pre-Christian ireland again tbh#Tho i'm doing classical studies this year which is Greek and Roman#Basically both the traumatized little girl in me and the mythology nerd in me are angry at capital G god and Christianity as a whole
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

reading about sacral kingship
#in pre-christian ireland specifically#like ok. fine. the king is not only the protector of his people but a mediator between them and the supernatural/ natural world.#cool. the king's reign is intimately linked with the health and the fertility of the land. cool#i Had thought of that previously but this is really giving it form in my mind#also the concept of an áer killing a bad king. incredible. roasts you so hard you die#htoo rambles#this is kind of funny actually because i do think we're in divine right of kings territory#and i HATE fucking divine right of kings#something about this compels me though ngl#(leans into the microphone) this is important in the fair folk au because despite the fact that neil cares about his people#his reluctance to be king poisons the land#and so does his father's hatred#until nature has to step up and restore the balance herself
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Every day I see some new pagan revisionist nonsense. Eostre and Ostara weren't Celtic! Now we're even re-writing stuff that's ALREADY speculative at BEST??? Eostre has nothing to do with st patrick's day! SHE'S A GERMANIC DEITY! SHE WAS IN GERMANY! IF SHE WAS THERE AT ALL! Eostre is not mentioned in any of the Irish mythological cycles and neither is Ostara to the best of my knowledge.
Ostara is a wonderful modern pagan holiday! It may even have very old roots! But it's certainly not an "ancient celtic holiday." Basically I am begging you to fact check yourself before you go posting stuff like "ancient celts celebrated Ostara in Ireland" (where did you even get this info)
#yes i am vague posting but im mad that this JUST KEEPS HAPPENING#ENOUGH!!!!!#do you know how hard it is to dig through the piles and piles of stupid bullshit people make up#to find ANYTHING actually about pre-christian ireland????#witchcraft#witchblr#ostara
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
I appreciate this!
What's funny is that Halloween isn't a pagan holiday that got Christianized. It's far more likely to be the other way around lol. It's a Christian Holiday that Celtic people kinda slapped their traditions onto.
All Saints Day was a pretty big thing for medieval Christians. The catholics love spooky macabre shit. All Saints Day was when you prayed for the holy departed.
It's funny, the most "pagan" elements are actually trick-or-treating, (which started around the 16th-ish century as a practice called Mumming,) and bobbing for apples, which is an old Celtic divination method that became a fun game for family gatherings. All the spooky goth shit in Halloween is from the Catholics.
#i dont always agree with you but i do always enjoy reading your takes and write-ups#unfortunately pre Christian records in Ireland are practically non-existent bc the druids kept an oral tradition#and when monks began writing down Irish myths and legends#they were already being recontextualized around Christian ideals#so we dont really have any truely pre-Christian Celtic/Gaelic stories
8K notes
·
View notes
Note
you’re attacking that neopagan kind of birthstone post about druid plants, but could you please elaborate or at least clarify the explicit trope that is being used that has been historically weaponized?
I used to spend about a good third of my time on this godforsaken website attacking that idea, but sure, I'll do it again. This will be a bit of an effortpost, so I'll stick it under the readmore
There is a notion of 'celts' or Gaels as being magicial and somehow deeply in touch with nature and connected to pre-Christian worldviews that the people who decided to make up the "Celtic tree astrology" used. This is also why Buffy used Irish Gaelic as the language of the demons, why Warhammer uses Gaelic as Elvish, why garbled Scottish Gaelic is used by Wiccans as the basis for their new religious construct, why people call themselves Druids to go an say chants in bad Welsh in Stonehenge, or Tursachan Chalanais, or wherever, etc etc. This stuff is everywhere in popular culture today, by far the dominant view of Celtic language speaking peoples. Made up neopagan nonsense is the only thing you find if you go looking for Gaelic folklore, unless you know where to look, and so on and so on. I could multiply examples Endless, and in fact have throughout the lifespan of this blog, and probably will continue to.
To make a long history extremely brief (you can ask me for sources on specifics, or ask me to expand if you're interested), this is directly rooted in a mediaeval legalistic discussion in Catholic justifications for the expansionist policies of the Normans, especially in Ireland, who against the vigourous protestation of the Church in Ireland claimed that the Gaelic Irish were practically Pagan in practice and that conquest against fellow Christians was justified to bring them in like with the Church. That this was nonsense I hope I don't need to state. Similar discourses about the Gaels in Scotland exist at the same time, as is clear from the earliest sources we have postdating the Gaelic kingdom of Alba becoming Scotland discussing the 'coastal Scots' - who speak Ynglis (early Scots) and are civilised - and the 'forest Scots' (who speak 'Scottis' (Middle Gaelic) and have all the hallmarks of barbarity. This discourse of Gaelic savagery remains in place fairly unchanged as the Scottish and then British crowns try various methods for integrating Gaeldom under the developing early state, provoking constant conflict and unrest, support certain clans and chiefs against others and generally massively upset and destabilise life among the Gaels both in Scotland and Ireland. This campaign, which is material in root but has a superstructure of Gaelic savagery and threat justifying it develops through attempts at assimilation, more or less failed colonial schemes in Leòdhas and Ìle, the splitting of the Gaelic Irish from the Gaelic Scots through legal means and the genocide of the Irish Gaels in Ulster, eventually culminates in the total ban on Gaelic culture, ethnic cleansing and permanent military occupation of large swathes of Northern Scotland, and the destruction of the clan system and therefore of Gaelic independence from the Scottish and British state, following the last rising in 1745-6.
What's relevant here is that the attitude of Gaelic barbarity, standing lower on the civilisational ladder than the Anglo Saxons of the Lowlands and of England, was continuously present as a justification for all these things. This package included associations with the natural world, with paganisms, with emotion, and etc. This set of things then become picked up on by the developing antiquarian movement and early national romantics of the 18th century, when the Gaels stop being a serious military threat to the comfortable lives of the Anglo nobility and developing bourgeoise who ran the state following the ethnic cleansing after Culloden and permanent occupation of the Highlands (again, ongoing to this day). They could then, as happened with other colonised peoples, be picked up on and romanticised instead, made into a noble savage, these perceived traits which before had made them undesirable now making them a sad but romantic relic of an inexorably disappearing past. It is no surprise that Sir Walter Scott (a curse upon him and all his kin) could make Gaels the romantic leads of his pseudohistorical epics at the exact same time that Gaels were being driven from their traditional lands in their millions and lost all traditional land rights. These moves are related. This tradition is what's picked up on by Gardner when he decides to use mangled versions of Gaelic Catholic practice (primarily) as collected by the Gaelic folklorist Alasdair MacIlleMhìcheil as the coating for Wicca, the most influential neo-pagan "religion" to claim a 'Celtic' root and the base of a lot of oncoming nonsense like that Celtic Tree Astrology horseshit that started this whole thing, and give it a pagan coat of paint while also adding some half-understood Dharmic concepts (three-fold law anyone?) and a spice of deeply racist Western Esotericism to the mix. That's why shit like that is directly harmful, not just historically but in the present total blotting out of actually existing culture of Celtic language speakers and their extremely precarious communities today.
If you want to read more, I especially recommend Dr. Silke Stroh's work Gaelic Scotland in the Colonial Imaginary, Dr. Aonghas MacCoinnich's book Plantation and Civility in the North-Atlantic World, the edited collection Mio-rún Mór nan Gall on Lowland-Highland divide, the Gaelic writer known in English as Ian Crichton Smith's essay A real people in a real place on these impacts on Gaelic speaking communities in the 20th century, Dr. Donnchadh Sneddons essay on Gaelic racial ideas present in Howard and Lovecrafts writings, and Dr. James Hunter's The Making of the Crofting Community for a focus on the clearings of Gaels after the land thefts of the late 18th and early 19th century.
@grimdr an do chaill mi dad cudromach, an canadh tu?
285 notes
·
View notes
Text

All About Imbolc
Imbolc, also known as Imbolg, celebrated on February 1st, marks the halfway point between the winter solstice and the spring equinox in early Ireland and Scotland, and also signified the beginning of the first signs of spring after all the harsh winter days. Originally a pagan holdiay in pre-Christian times, there is little in writing about the historic traditions and customs, although many historians believe it revolved around the Celtic Goddess Brigid, lambing season, and cleansing due to observed ancient poetry.
Brigid is a Goddess and daughter of the father-God of Ireland, Dagda. She is associated with quite a few things depending on the sources, but universally associated with wisdom and poetry. Other associations of hers are blacksmithing, protection, domesticated animals, childbirth, fire, and healing. She was also known as a protector of the home and the family.
Once Christianity arose, it is believed that the Goddess was syncretized with the Irish Saint Brigid by Christian monks due to the many overlapping associations. This caused Imbolc to quickly turn into St. Brigids Day and the next day into Candlemas with the rising Christian popularity, enmeshing the holiday associations together.
Today, many people have mixed the traditions and melded many associations from both religious and cultural history to celebrate their own unique way. Common ways to celebrate are making a Brigid's Cross, welcoming Brigid into the home, having a feast in her honor, cleaning the home and oneself, visiting a holy well, and in some parts of the world they still hold festivals and processions carrying a representation of Brigid. Many pagans nowadays are using associations of hers and their connection with nature to create their own ways to celebrate, however, and you can absolutely celebrate however you feel called to do so.
Imbolc Associations:
Colors - white, gold or yellow, green, and blue
Food - milk, butter, cheese, seeds and grains, breads, herbs, blackberries, oat porridge, wild onion and garlic, honey
Animals - sheep and lambs, swans, cows, burrowing and hibernating animals
Items - candles, corn dolls, Brigid's cross, fires, snowdrops and white flowers, crocuses and daffodils, flower crowns
Crystals - amethyst, garnet, ruby, quartz, bloodstone
Other - lactation, birth, feasting, farm preparation, cleansing and cleaning, the sun, poetry and creative endevours, smithing, water
Ways To Celebrate Imbolc:
make a Brigid's cross
light candles
have a feast
bake bread
plan your spring garden
leave an offering for Brigid
make a corn doll
craft a flower crown
clean your home
take a cleansing bath
make something out of metal
have a bonfire
look for the first signs of spring
make your own butter or cheese
do divination work and seek wisdom
write a poem
#magical#magic#magick#witch#witchy#pagan#paganism#witchblr#imbolc#imbolg#brigid#st brigid#candlemas#holiday#baby witch#witch tips#sabbat#wheel of the year#wiccan#celtic#gaelic#history#brigit#beginner witch#witchcraft#witchcore#cottage witch#hedge witch#green witch#eclectic witch
566 notes
·
View notes
Text


Bullaun ('Bowl') Pre-Christian Stone, Newton Stewart Museum, Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland
Found in a field near Kirkcowan, south-west of Newton Stewart.
Bullaun stones are found in Ireland and Baltic countries and are thought to be pre-Christian, but are also seen outside churches. White quartz pebbles, incised with crosses, have been found in some examples.
The water in the bowl was considered to have healing properties. Some bullauns may have been used as grinding stones.
#bullaun#stonework#stone carving#archaeology#relic#sacred#ancient living#ancient cultures#ancient craft#stones#sacred water#Scotland#Newton Stewart#dumfries and galloway
119 notes
·
View notes
Text
Time Travel Poll Winner Second Round Match Up 6:
These Questions are the winners from the previous iteration.
Please add new suggestions below, if you have them, for future consideration.
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did Christianity Steal From Paganism? Yes... No... It's Complicated. Part 2: Vikings
Tis the season so I figured I'd talk about the topic that's been the subject of debate for a long time, most recently with the 2024 Olympics. I will be discussing the visual aspect of these religions, not the theological aspects.
Short answer: Yes
Long answer: No
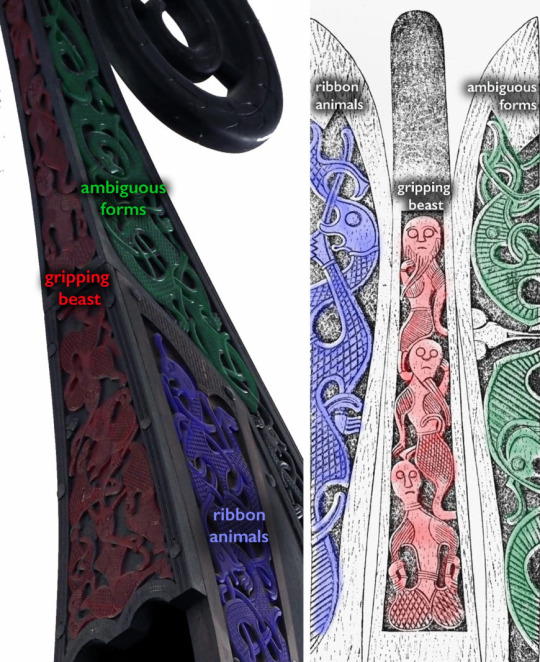
Let's get into it: The Viking era is from 800-1050 AD and can be divided into seven parts based off the style of visual art that was popular. The first style is called the Oseberg style (775-800 AD) and would be the basis of all the Viking styles of art after it. It was made of three forms that were derived from Pagan pre-Viking art: ribbon animals, gripping beasts, and ambiguous forms. You can see it on the bow of the ship below; the ship dates to the 9th century and was found in a burial mound in Tønsberg, Norway. Remember these forms because they're going to be important later.

The Vikings started coming into contact with Christian Anglo Saxon (modern day English) missionaries in the 700-800s, but they had little effect. The missionaries were well received by the kings but when their Pagan chieftains threatened to rescind their support, the missionaries were sent away. Another example of that is in 878 AD, the Christian king of the Anglo Saxons, Alfred the Great of Wessex, and the Pagan king of the Vikings, Guthrum the Old, were at war. King Alfred ended up winning and as part of the peace treaty, Guthrum had to get baptized into Christianity. He did so but maintained his Pagan worship and did not implement Christianity.
Besides the kings, common people had also started to slowly assimilate to Christianity. Christians had a rule that they couldn't trade with Pagans so Pagan Vikings began primsigning. Primsigning is an old Norse word meaning "to make the sign of the cross," the way to show you followed Christian beliefs before converting all the way through baptism. Even though they weren't being baptized and were still practicing Paganism, primsigning was enough for Christians to feel comfortable trading with them and brought the Vikings more into the world of Christianity.
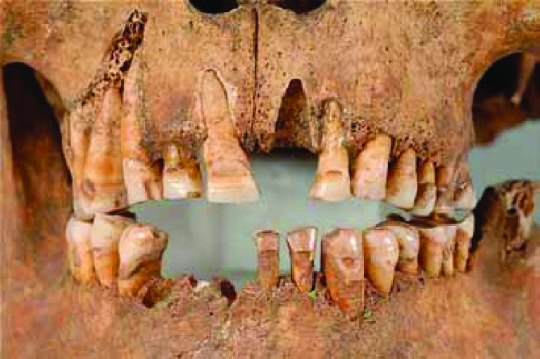
An interesting example of this is in Kopparsvik, Sweden, where a large number of Viking individuals were buried in a prone position from 900-1050 AD. This is completely different from traditional Pagan Viking burials: there were no grave goods, no animal sacrifices, no mighty ships. Typically, a prone position is a sign of showing humility towards God and all the figures had notches carved into their teeth (below). Historians theorize that they used the notches to secretly signal to Christian merchants that they were also Christian to get discounts while not being alienated from their Pagan communities.
The coin below is from ~921 AD. It's a Viking coin from York, England and wonderfully shows the mixing of Pagan and Christian iconography. Coins like this typically had the name of the Viking king engraved on them but this one has "St. Peter." However, it also depicts the hammer of Thor on both the head (left) and reverse (right). It really demonstrates the visual mixing of religions.


Sometime between 940-1000 AD, the cross below was made. It was found in St Andrew's Church, Andreas, Isle of Man (between England and Ireland), and is another great example of the combination of Pagan and Christian art. On one side (left) it depicts Odin with one of his ravens fighting the wolf Fenrir at Ragnarök. The other side (right) depicts Christ triumphing over Satan. Both of these are stories of good vs evil and depict a god triumphing at the end of days. It would have drawn attention to the theological similarities between Christianity and Norse Paganism, making it easier for people to conflate the differing theologies.

Remember the Oseberg style from before? We're going to revisit it. By the 900s, Viking art was being done in the Mamman style; the ribbon animals and gripping beasts had combined into an icon called the Great Beast. The Great Beast was a symbol of power and strength, frequently put on longships and other Pagan items. In 986 AD, Viking King Bluetooth, a recent convert to Christianity, had the jelling stone below erected in honor of his deceased parents. On one side, he included a Great Beast; this was to show the strength and nobility of his parents and the nation they ruled. On the other side, he put an image of Christ Triumphant. This makes sense for a cenotaph as the promise of a resurrection is a comfort in the face of death. But the combination of a Pagan symbol of strength and an image of Christ is very interesting; it's doing more than pointing out the similarities between the two religions, it's uniting both Pagan and Christian subjects under his rule and proudly displaying the two different sources of the Viking's strength.

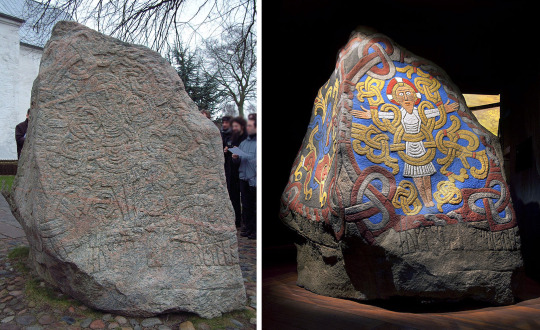
I can't end this without also talking about architecture. The last Viking art style is called the Urnes style and it's primarily because of the church below. It was built in 1132 AD in Urnes, Norway and is a stave church, meaning the whole thing was built without any nails!! The entire thing is self-supporting wood made using the post and lintel system. It's a Chrisitan church but has Pagan iconography on the sides: the last version of the Great Beast (right) and Pagan runes. It's fascinating how a Christian place of worship is decorated and protected by Pagan icons, once again showing the combination of visual cultures and methods of thought.

So, the answer everyone is looking for is NO.
The Christians didn't steal anything from the Pagans, they made an association. They produced art in the style that was popular and followed the artistic trends of the time. Christian and Pagan imagery was produced in the same medium and combined until Paganism was phased out over hundreds of years. They saw similar gods and iconography and combined them to make a message that was understandable to all audiences.
Happy Yule! Happy Winter Solstice!
Further reading:
Smarthistory – Art of the Viking Age
BBC - History - Ancient History in depth: Viking Religion
The Vikings and Christianity | History of Christian Vikings – Sons of Vikings
Treaty of Wedmore - Wikipedia
Manx runestones - Wikipedia
Prone Burials and Modified Teeth at the Viking Age Cemetery of Kopparsvik - Historische Beratung Dr. Matthias Toplak
Ancient Viking Art - Medievalists.net
Gamla Uppsala - Wikipedia
#i tried to include both academic and general further readings#this is very simplified bc i'm trying to give a general overview#yule#artist talk#ancient art#pagan witch#paganism#pagan#paganblr#christianity#norse paganism#celtic paganism#norse mythology#celtic mythology#norse art#celtic art#scandinavian folklore#scandinavian mythology#thor#odin#jesus christ#norse heathen#heathenism#winter solstice
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Reference: 5 Symbols
for your next poem/story (pt. 3)
CAULDRON

In understanding symbols, sometimes it is useful to simply look at the shape and see what it resembles.
The traditional cauldron represents nothing so much as the belly of a pregnant woman and, unsurprisingly, it is an important female symbol all over the world.
The circular shape of the cauldron gives another clue; the circle is a symbol of never-ending life and regeneration, and these themes recur repeatedly in stories containing cauldron symbolism.
The way the cauldron is used also gives a hint about its symbolic meaning.
Things are put into the cauldron, heated, and something different is taken out; the basic ingredients are transformed.
Therefore, the cauldron also symbolizes germination and transformation.
Traditionally, cauldrons have three legs:
The number 3 in this instance represents the triple aspect of the Great Goddess, or the three fates.
Shakespeare alludes to this when the three Weird Sisters—arguably the most famous witches in literature—cook up trouble at the beginning of Macbeth.
In pre-Christian literature, countless legends feature magical cauldrons, and it may be because of this that the cauldron has its witchy associations.
Celtic tales tell of cauldrons that contain an unending supply of food or of knowledge.
The dead are frequently thrown into a magical Cauldron of Rebirth and climb out the next day, alive once more.
Mythical warriors and heroes who died in battle are restored to life in this way.
Ceridwen (one of the most powerful witches in all of Celtic mythology and is typically depicted as simultaneously a mother and a wise woman) had a cauldron full of inspiration and magical powers.
In India, a magic life-giving food, called Soma, was brewed in three huge bottomless cauldrons.
In Greece, there are tales in which an ordeal of initiation involves the person boiling in a cauldron, but after the rite, the initiate emerges with magical powers, including the gift of immortality.
CHNOUBIS

The Chnoubis is a hybrid creature, with the head of a lion and the tail of a serpent.
It was carved onto stones for use as an amulet, providing protection against poisons in particular.
Amulets featuring the Chnoubis date back to the first century and it is supposed that this odd-looking creature may be related to Abraxas, whose image was used in a similar way.
CLADDAGH

The Claddagh is a popular symbol, often incorporated into the design of rings.
Traditionally used as a wedding ring, it is so-called because it was originally made in a Galway fishing village of the same name in 17th century Ireland.
However, the elements of the design are much older, stretching back into pre-Christian Celtic history.
The Romans had a popular ring design, the Fede, which featured clasped hands.
“Fede” means “fidelity.”
The Claddagh symbol features a heart held by a pair of hands.
A crown usually surmounts the heart.
These features represent love, friendship, and loyalty.
CORNUCOPIA

Also called the Horn of Plenty, the cornucopia is often depicted in paintings and on friezes where it symbolizes the notion of boundless abundance, as flowers, fruits, sheaves of wheat, and other produce spill out of a hollow horn or a twisting basket woven in the shape of the horn.
The origin of the cornucopia is found in the Greek myth of Amalthea.
Amalthea fed the infant Zeus a drink of goat’s milk and was given the brimming goat’s horn as a reward.
Sometimes the infant Zeus is depicted being fed the milk from the horn itself.
The Cornucopia, as a symbol of a bounteous harvest, is also associated with Ceres, the Goddess of corn, and also with Fortuna, Goddess of good fortune.
CROSSROADS

In fairy stories and myths, it is often at the crossroads where mischief awaits, usually in the form of other-worldly spirits.
Effectively, the crossroads symbolizes the intersection of two paths, making four potential routes, and a place where a decision must be made, not only practically, but metaphorically too.
The X of the crossroads marks a spot where two worlds meet.
The origins of this story go back to African folklore, where a deity called Esu was the guardian of the crossroads.
When Christianity took over, these old Gods were, quite literally, demonized, and Esu was transformed into the Devil.
Hecate, too, personified as the Queen of the Witches, was called the Goddess of the Crossroads.
In Celtic mythology, corpses belonging to those considered “unholy” were buried at crossroads in order to prevent them coming back to life and because the crossroads was a Gate to the Otherworld. Gibbets were placed at crossroads for the same reason.
Source ⚜ More: On Symbols ⚜ Writing Notes & References
#writing reference#symbolism#symbols#writeblr#halloween#spilled ink#dark academia#witchblr#literature#writers on tumblr#writing prompt#poetry#poets on tumblr#writing inspiration#creative writing#light academia#writing inspo#writing ideas#mythology#folklore#writing resources
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
90% of the time I'm like "the only reason why the medieval Irish material seems bizarre is because it isn't taught as part of the standard humanities curriculum -- Greek Mythology is just as bizarre, you're just USED to it, stop reducing this stuff to Lol That's So Weird", but then I do have to be like. "Anyway the postulated father god of the postulated pre-Christian Irish pantheon, if ever such a thing existed in a uniform way, creates a zombie apocalypse in one text that allows him to become king of Ireland and his wife is a crow (part time) that commits crimes and castrates a Viking warlord (who has a really messy family life btw). He also has a xylophone made out of corpses in another text." and I have to be like. "Okay, so maybe the Irish texts ARE a little bit. Out there. On occasion."
#for what it's worth though there's still a REASON for these things#the scribes weren't putting them in because Lol Funny#but also...yeah.#Zeus could never#irish mythology#the mythological cycle#the dagda#i should clarify: they weren't JUST putting them in because Lol Funny
193 notes
·
View notes
Text

Origins of the Headless Horseman legend
Despite the legend of Sleepy Hollow being one of the oldest American written horror stories, the origin behind the Headless Horseman is a lot older and originates in Europe.
Washington Irving first published the legend of Sleepy Hollow between 1819-1820. In this story, it is explained that the Headless Horseman was a German mercenary soldier, a Hessian hailing from the German state Hessen, who unfortunately lost his head during the revolutionary war after being hit by a canon ball to the face. It is interesting that Irving chose for a German origin for the Horseman in a Dutch town as both Germany and the Netherlands have legends of headless horsemen, talking decapitated heads, ghost riders in the dark that have its origins in pre-Christian times.
Here are some examples of the headless horseman myth from different countries in Europe:
Netherlands: The belief in the wild hunt was once quite important in pre-Christian times, it's in fact the origin of the modern Dutch holiday of Sinterklaas which was introduced in the USA as Santa Clause. As the days shorten and winter arrives, the Germanic God Wodan, or in some instances the Goddess Hel/Holle, rides through the sky followed by a horde of the undead. Anyone unfortunate enough to see the riders in the sky, would soon die and join the hunt. To please the hunt, people began to give offerings to the God Wodan and his horse Sleipnir, placing carrots in shoes, this tradition is still being done in the Netherlands until this very day. I am myself a Germanic Pagan and I honour the wild hunt by making offerings to Wodan and his horse and blowing the midwinter horn.
There is also a Dutch medieval song 'Heer Halewijn', the origins of which are assumed to be older, an oral tradition before being written down around the 15th century. This song tells the tale of a princess set out to meet Halewijn who in turn ends up being a murderer who decapitates women in the forest. The princess manages to decapitate Halewijn instead and takes his head with her to her father the king, Halewijn's decapitated head however continues to talk to the princess.
Ireland: In Irish folklore, the Dullahan is a headless evil entity who rides a horse while carrying his head under his arm. This spectre is perhaps the most famous and classic example of the visual origin of the Headless Horseman. Not only does the Dullahan carry his own head, he also wields a whip made out of a human spine. Whenever the Dullahan halts his horse, a death will happen by calling out that person's name. Some say that the Dullahan is the spirit of Crom Dubh, a Celtic deity who was worshiped by means of human sacrifices.
There is also the Cóiste Bodhar, a strange headless entity who drives a black coach. Bodhar is a harbinger of death who arrives to announce the passing of a relative or a loved one, quite similar to the grim reaper.
Wales: Now the country of Wales is home to quite a few headless mysteries. One of the more famous stories tells about a headless woman: 'Fenyw heb un pen' who eerily also rides a horse without a head. Another story tells of how Bryn Hall was haunted by a headless horseman until the horseman pointed towards a body which turned out to be the dead body of an illegimate child of Bryn Hall. This version of the Headless Horseman seems to have been more benign, rather than being a harbinger of death or a crazed killer.
Germany: Germany is also home to several Headless Horseman legends and is of course the home country of Irving's version of the Headless Horseman. Most of Germany's legends originate from the Rhineland area and were part of a morality tale. Many of these Headless Horsemen were doomed men, being punished for their sins on earth so they had to wander until they had atoned for their sins. Sometimes these Headless men would perform good deeds, most times however they would kill victims, not by decapitation but simply by touching them. Both Germany and the Netherlands believed in the Wild Hunt legend and it is alleged that many of these Headless Horsemen have their origin in the pagan wild hunt.
England: England also has several legends concerning Headless Horsemen, one of these is part of the legend of Arthur, the Green Knight. This knight challenged one man in Arthur's court to strike him down with his axe but the Green Knight warned the man he would strike the man back later in a year. As promised, the knight got decapitated, picked up his head and later decapitated the man whom he challenged. Another headless horseman legend originates from the Dartmoor area, nothing much is known about this legend other than that people have seen a headless man riding around the countryside.
In the end, the Headless Horseman has its origins in both Celtic and Germanic mythology and new versions of the legend keep on popping up throughout history, either as a bringer/omen of death or as a killer waiting for his unfortunate victims. Seldomly is the Headless Horseman a benign person helping people in need.
The legend found its way to the USA thanks to Dutch, Irish, English and German settlers and was immortalized by Washington Irving in his 1820 story 'the legend of Sleepy Hollow'. Washington Irving himself probably based the story on the old Dutch and German stories as he was familiar with them thanks to his travels. The retellings of German folktakes 'Volksmärchen der Deutschen, 1783 was especially a big source of inspiration for Washington Irving.
27 notes
·
View notes