#pig welfare improvement
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How the Deep Litter System Transformed Pig Farming in Kajiado
The world of agriculture is continuously evolving, with farmers embracing innovative solutions to enhance productivity, improve animal welfare, and ensure environmental sustainability. In 2023, I had the privilege of collaborating with a dedicated farmer in Kajiado, Kenya, who was running a medium-sized pig farm with 30 sows. Our journey towards transforming his operations ended with the…
#agribusiness success stories#compost from pig litter#cost-effective pig farming#deep litter system#deep litter system benefits#eco-friendly pig farming#environmental stewardship in pig farming#innovative pig farming practices#low maintenance pig farming#nutrient-rich compost#pig farm productivity#pig farm sustainability#pig farming in Kajiado#pig farming innovations#pig health improvement#pig welfare improvement#reducing pig mortality#sustainable agriculture practices#sustainable pig farming#waste management in pig farming
0 notes
Text
I wanted to make so many metaphors from livestock welfare for that post, but didn't feel like catching the associated snarl of feelings and ideas that people have about animal management and food in response, because that's its own kettle of fish. But while I was looking for an easily accessible concept to tap into, I found something really cool.
Let me talk about farrowing rails for a second. When sows give birth to piglets, it's unfortunately rather common for little piglets to get crushed beneath their mother's weight. No one, least of all sows, wants this to happen, but the sow is huge and has to lie down a lot so the piglets can suckle and especially when they are born piglets are almost cartoonishly tiny. They are also not good at moving quickly and anticipating their mother's movements yet. This means that there are often piglet losses from being squished to death.
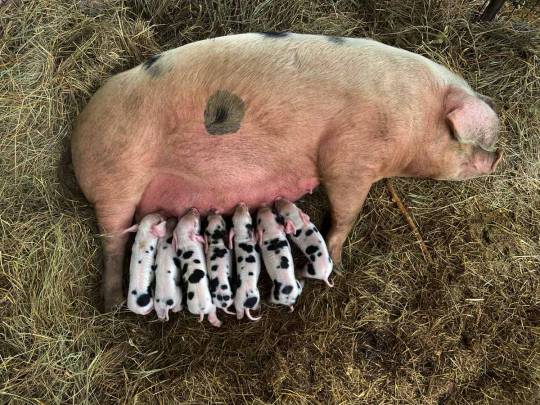

So pig farmers often use a farrowing crate to protect piglets from getting squished. Sows go into it before they give birth and come out either at weaning or when the piglets are big enough that squishing isn't an issue.
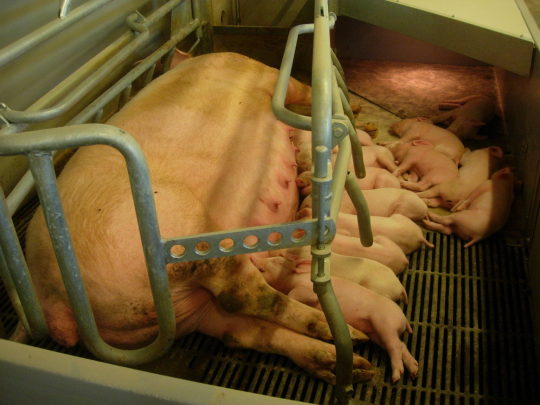
It has slats that piglets can fit between and move around in, so their mothers can't crush them. It's very effective for increasing piglet survival and decreasing these kinds of crushing deaths. But it's really not ideal for the sow for all kinds of reasons that should be obvious. That's a long time to be confined in a small space.
The thing I'm delighted to find is the existence of this site by a couple of agriculture researchers in the UK, which is focused on providing resources and research on ways to allow sows to farrow (give birth) with much less restriction for the animals. There are recommendations for many kinds of operations and pointers to many kinds of evidence - based systems, complete with plans for how to design each system and a list of what each can accomplish for sow, piglets, and caregiving staff.
Each of the options are set up with contact information for the people who designed it and instructions about how to go about finding a system to suit farmers' needs. There's also research sections explaining how we know what welfare provisions improve quality of life for both sow and piglets, plus lists of assurance schemes farmers can use to market their products as ethical to consumers. It's really cool and well designed, and it makes setting up changes in pig operations relatively straightforward and feel easy to do. It's such a nice piece of communication. I like it a lot.
285 notes
·
View notes
Quote
The short answer is that focusing on vegan outreach just doesn’t work. Diet is a core part of a lot of people’s identity, and to a random person walking down the street (or browsing the metaphorical street online), being approached by a vegan activist asking them to “simply” stop eating animals is a major imposition. They’ll probably think the activist is telling them what to do, and most people don’t like being told what to do.1 As a result, even after orgs have spent decades talking to people about veganism and distributed over 30 million pamphlets, the number of vegans and vegetarians per capita has barely changed. Welfare campaigns, like the Shrimp Welfare Project, are different. They cast corporations and the government, rather than individual consumers, as the actors at fault for animal suffering. And by leading with a message focused on suffering and systemic change rather than diet and individual choices, they manage to raise public awareness of factory farming while actually boosting support for the total abolition of animal agriculture. This is true even when they successfully curtail egregious factory farming practices that one might think would catalyze opposition to animal agriculture. Multiple research teams have tested how welfare campaigns affect support for animal product consumption and abolitionism by presenting survey participants with either a news article about a new corporate or government animal welfare policy or a control article. They consistently find that participants who are shown the treatment article say they’re more likely to reduce their consumption of animal products, and sometimes by wide margins. As law professor and researcher Justin Marceau remarked at one of the leading animal advocacy conferences this year, participants in a yet-unpublished study “who learned about the fact of a Prop 12 type [animal welfare] law [in their state] were about twice as likely to think that pigs should have more rights, and to say that they were less likely to eat pig.” For all the good you can do by going vegan — or talking to people you know personally about veganism (as opposed to random people on the street) — you can do even more good by supporting or raising money for corporate and political campaigns to improve farmed animal welfare. Corporate pressure campaigns to stop companies from using eggs laid by hens who are confined in tiny cages can improve between 9 and 120 years of animal life for every dollar spent, while cage-free ballot initiatives improve about 5 years of life per dollar spent, without even accounting for their effect on public opinion. Yesterday’s highlighted charity, the Shrimp Welfare Project, estimates it can help 1,500 shrimp per dollar. If the average person in the United States gave just 1% of their disposable income to effective animal charities or volunteered an equivalent amount of their time, they could help at least hundreds of chickens and thousands of shrimp per year — far more than the average person eats. This point was made, albeit in a more incendiary manner, in a 2007 article by animal rights lawyer and activist Wayne Hsiung titled “Boycott Veganism.” Hsiung argued that the vegan paradigm, focused on diet change, completely obscures the object of the animal protection movement — which is a social and political revolution in ideas about animal rights, rather than just a change in how individual people behave as consumers.
On Boycotting Veganism - by Glenn
1 note
·
View note
Text
Blood sports including ‘goose pulling’ and attempting to decapitate roosters will in future only be allowed using animals that died a natural death. ‘Goose pulling’ used to involve hanging a goose with a greased head from a beam and getting somebody on horseback to try and pull its head off. Consuming live fish is now also being banned. The sale of animals on a market or on the public highway is also banned. Sheep, goats and pigs can no longer be slaughtered at home either any more.
These are only some of the raft of new measures that Flemish animal welfare minister Ben Weyts (N-VA) has brought together in the new Animal Welfare Codex that replaces what the minister called the "outdated Animal Welfare Act", which originated almost 40 years old.
"For the first time, animals are officially being recognised as living beings with feelings, specific needs and intrinsic value. It follows that they must be properly protected. The Flemish Codex greatly expands that protection. We have literally completely rewritten the code" Minister Weyts notes
Every police zone will now get a designated animal welfare officer. In this way animal welfare will be monitored more closely. Chicken farms will have to give animals even more space. A complete switch from chicken in cages to free-range aviary systems will have to be made.
There will also be stricter rules for dolphinariums. This will affect the Boudewijn Sea Park in Bruges, the only dolphinarium in Flanders. It will be allowed to have a maximum of six dolphins. That's the number the park has at the minute. If one of these dies, the park will be allowed to replace it on condition it improves welfare and provides an outdoor pool from 1 January 2027 onwards.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Where to buy LED lighting for pig barns in Canada
If you're looking to buy high-performance agricultural LED lighting for pig barns in Canada, JW LED offers a trusted solution tailored to agricultural environments. Our products are specifically engineered to meet the lighting demands of swine facilities, enhancing both energy efficiency and animal welfare.
Request a quote on our website JW LED. From swine farrowing areas to poultry houses and dairy milking parlours, our selection includes low and high bay fixtures, vapour-tight lights, and essential accessories such as frosted lenses and mounting hardware. These purpose-built agricultural LED lighting solutions deliver optimal light levels and spectrum control, supporting livestock health, improving behavioural conditions, and helping regulate circadian rhythms. As a dedicated agricultural LED lighting manufacturer, we prioritize reliability and performance, offering lighting technologies backed by industry research and developed with the evolving needs of livestock producers in mind.
Whether you're outfitting a new barn or upgrading an existing facility, JW LED provides durable, efficient, and research-driven lighting solutions designed to perform in Canada's demanding agricultural environments.
0 notes
Text
Exposing the Hidden Realities of Factory Farming: A Comprehensive Look into Animal Cruelty Practices in the Czech Agricultural Industry
The website by the Humane Foundation is a comprehensive resource that sheds light on the multifaceted issues associated with factory farming. It delves into the ethical, environmental, and societal impacts of industrial agriculture, advocating for more humane and sustainable practices.
The Plight of Animals in Factory Farming
Factory farming, or industrial agriculture, is characterized by large-scale operations that prioritize efficiency and profit over animal welfare. Animals such as cows, pigs, chickens, and fish are often kept in confined spaces, leading to physical and psychological distress. The website details the conditions these animals endure, including overcrowding, lack of natural light, and limited access to the outdoors. Such environments can lead to the development of abnormal behaviors and increased susceptibility to diseases.
For instance, dairy cows are frequently subjected to repeated cycles of impregnation and milking, leading to physical exhaustion. Pigs are often confined in gestation crates that restrict movement, and chickens may be kept in battery cages with little room to spread their wings. These practices raise significant ethical concerns about the treatment of sentient beings in the pursuit of food production.
Environmental Consequences
Beyond animal welfare, factory farming has profound environmental implications. The website highlights how intensive animal agriculture contributes to deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Large tracts of forests are cleared to create space for livestock or to grow feed crops, leading to habitat loss and decreased biodiversity.
Moreover, the concentration of animal waste can contaminate water sources, affecting both human and aquatic life. Methane emissions from ruminant animals like cows significantly contribute to climate change. These environmental challenges underscore the need for more sustainable agricultural practices.
Human Health and Societal Impacts
The repercussions of factory farming extend to human health and societal well-being. The overuse of antibiotics in animal agriculture can lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a threat to public health. Additionally, the close quarters in which animals are kept can facilitate the spread of zoonotic diseases, increasing the risk of pandemics.
Economically, small-scale farmers often struggle to compete with large industrial operations, leading to the decline of rural communities. The website also discusses the psychological toll on workers in factory farms, who may experience trauma from participating in the slaughter and processing of animals.
Advocacy and Alternatives
The Humane Foundation advocates for a shift towards more ethical and sustainable food systems. They promote plant-based diets as a means to reduce reliance on factory-farmed animal products. The website offers resources on vegan nutrition, recipes, and guides to help individuals transition to plant-based eating.
Furthermore, the organization encourages policy changes to improve animal welfare standards and environmental regulations. They support initiatives that provide subsidies for sustainable farming practices and education programs to raise awareness about the impacts of factory farming.
Taking Action
Individuals can play a role in addressing the issues associated with factory farming. By making informed food choices, supporting local and sustainable agriculture, and advocating for policy reforms, consumers can contribute to a more humane and environmentally friendly food system. The website provides actionable steps, including petitions, community events, and educational materials, to empower individuals to make a difference.
The website cruelty.farm/cs by the Humane Foundation is a comprehensive resource that sheds light on the multifaceted issues associated with factory farming. It delves into the ethical, environmental, and societal impacts of industrial agriculture, advocating for more humane and sustainable practices.
The Plight of Animals in Factory Farming
Factory farming, or industrial agriculture, is characterized by large-scale operations that prioritize efficiency and profit over animal welfare. Animals such as cows, pigs, chickens, and fish are often kept in confined spaces, leading to physical and psychological distress. The website details the conditions these animals endure, including overcrowding, lack of natural light, and limited access to the outdoors. Such environments can lead to the development of abnormal behaviors and increased susceptibility to diseases.
For instance, dairy cows are frequently subjected to repeated cycles of impregnation and milking, leading to physical exhaustion. Pigs are often confined in gestation crates that restrict movement, and chickens may be kept in battery cages with little room to spread their wings. These practices raise significant ethical concerns about the treatment of sentient beings in the pursuit of food production.
Environmental Consequences
Beyond animal welfare, factory farming has profound environmental implications. The website highlights how intensive animal agriculture contributes to deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Large tracts of forests are cleared to create space for livestock or to grow feed crops, leading to habitat loss and decreased biodiversity.
Moreover, the concentration of animal waste can contaminate water sources, affecting both human and aquatic life. Methane emissions from ruminant animals like cows significantly contribute to climate change. These environmental challenges underscore the need for more sustainable agricultural practices.
Human Health and Societal Impacts
The repercussions of factory farming extend to human health and societal well-being. The overuse of antibiotics in animal agriculture can lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a threat to public health. Additionally, the close quarters in which animals are kept can facilitate the spread of zoonotic diseases, increasing the risk of pandemics.
Economically, small-scale farmers often struggle to compete with large industrial operations, leading to the decline of rural communities. The website also discusses the psychological toll on workers in factory farms, who may experience trauma from participating in the slaughter and processing of animals.
Advocacy and Alternatives
The Humane Foundation advocates for a shift towards more ethical and sustainable food systems. They promote plant-based diets as a means to reduce reliance on factory-farmed animal products. The website offers resources on vegan nutrition, recipes, and guides to help individuals transition to plant-based eating.
Furthermore, the organization encourages policy changes to improve animal welfare standards and environmental regulations. They support initiatives that provide subsidies for sustainable farming practices and education programs to raise awareness about the impacts of factory farming.
Taking Action
Individuals can play a role in addressing the issues associated with factory farming. By making informed food choices, supporting local and sustainable agriculture, and advocating for policy reforms, consumers can contribute to a more humane and environmentally friendly food system. The website provides actionable steps, including petitions, community events, and educational materials, to empower individuals to make a difference.
0 notes
Text
How I Improved My ENVIRONMENTAL ACTIVISM In One Day

Factory Breeding: Threats to animals, people, and the environment In today's world, factory breeding has become the main way of producing meat, dairy products and eggs. However, this industrial approach aims to meet the growing demand for animal products, raising considerable concerns about wells, human health and the environment. Animal welfare concerns Factory farms often prioritize efficiency and profits on the disadvantages of animal welfare. Animals are often restricted in overcrowded rooms, restricting natural behavior and causing stress. For example, pigs are stored in pregnancy boxes, which prevent the pregnancy boxes from turning, leading to physical and psychological stress. Chickens and turkeys are housed in a quarter, with some receiving painful interventions such as beak trimming to prevent stress-related attacks. Dairy cows are exposed to intensive milk schemes, leading to health problems such as mastitis. Even fish in aquaculture systems suffer from poor water quality and high mortality due to overcrowding The meaning of human health Overuse of antibiotics on factory farms to prevent disease in overcrowding contributes to an increase in antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a serious risk to public health. Furthermore, the stress and unsanitary conditions in these companies could lead to the outbreak of zoonotic diseases that could be transferred to humans by animals, as observed in the previous pandemic. Environmental impact Breeding in factories has greatly contributed to environmental degradation. The concentration of many animals in small rooms leads to waste accumulation and contamination of the air, soil and water. This pollution can damage local ecosystems and contribute to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases such as methane. Furthermore, the industry consumes a large amount of water and land, leading to deforestation and habitat loss Ethical and Social Considerations
The ethical effects of factory breeding go beyond cruelty to animals. Industry practices often ignore wells of employees who may be exposed to dangerous situations or low wages. Municipalities near factory farms can suffer from pollution and poor quality of life. Furthermore, marketing living things raises moral questions about how animals are treated. Sustainable alternatives Treating factory color-related problems requires a multifaceted approach. Political reform: Implementing and enforceing stricter environmental and animal welfare regulations could undermine some of the harmful effects of the industry. Consumer decisions: Decisions on the sourcing of vegetable or animal products from ethical and sustainable farms can promote the demand for better practices. Education and Advocacy: Recognizing the impact of factory breeding allows people to make healthy decisions and drive change. Reevaluating our food system and prioritizing compassion and sustainability, we can work towards a future that respects the health of our animals, people and planets.
Environmental activism
0 notes
Text
The Rise of Preventative Care in Animal Healthcare: Trends to Watch
The animal healthcare market has undergone significant transformation in recent years, driven by advancements in veterinary science, growing pet ownership, and an increasing focus on animal health and welfare. As the global population of pets and livestock continues to rise, the demand for innovative healthcare solutions for animals has surged. This, in turn, has led to the rapid growth of the animal healthcare industry, which encompasses pharmaceuticals, vaccines, diagnostics, and other healthcare products designed to improve the well-being of animals.

This article explores the key trends shaping the animal healthcare market, the factors influencing its growth, and the future outlook for the sector.
1. Growing Demand for Pet Healthcare
One of the primary drivers of the animal healthcare market is the increasing ownership of pets, particularly in developed countries. As more people view pets as family members, they are becoming more invested in ensuring the health and longevity of their animals. This shift in mindset has led to a significant increase in pet healthcare spending, particularly for companion animals such as dogs, cats, and birds.
Pet owners are increasingly seeking out advanced veterinary care, including diagnostic testing, vaccinations, and specialty treatments for conditions such as cancer, arthritis, and diabetes. The growing trend of pet humanization, where pets are treated as family members, has also led to an increased demand for high-quality food, supplements, and grooming products, all of which contribute to overall animal health.
2. Livestock Health and Disease Management
In addition to companion animals, livestock health remains a critical component of the animal healthcare market. Livestock farming is a vital part of the global food supply chain, and ensuring the health and productivity of animals such as cattle, poultry, and pigs is essential to maintaining food security. As such, farmers and agricultural producers are increasingly turning to advanced veterinary products to manage diseases, prevent infections, and improve animal productivity.
Vaccination programs for livestock are crucial for preventing the spread of infectious diseases such as foot-and-mouth disease, avian influenza, and swine flu. Furthermore, the use of antibiotics, antiparasitic drugs, and other treatments helps maintain healthy herds and flocks. However, there is growing concern about the overuse of antibiotics in livestock, which has led to the rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). This has prompted the development of more targeted treatments and alternative therapies, which are expected to play a key role in the future of livestock healthcare.
3. Advancements in Veterinary Pharmaceuticals and Vaccines
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in research and development to create innovative veterinary medicines and vaccines. These advancements are aimed at addressing a wide range of animal diseases and health conditions, from infectious diseases to chronic illnesses and conditions related to aging.
In particular, the development of monoclonal antibodies, gene therapies, and other biologics is transforming the landscape of veterinary medicine. These treatments offer more effective solutions for diseases that were once difficult to treat, such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and certain viral infections. Moreover, advancements in gene editing technologies hold the potential to enhance the development of vaccines and therapies tailored to specific animal species or breeds.
In addition to pharmaceuticals, the growing use of diagnostics is playing a crucial role in the early detection and management of animal health conditions. Veterinary diagnostics, including imaging, blood tests, and molecular diagnostics, allow for more accurate and timely identification of diseases, which in turn leads to better treatment outcomes and improved overall animal health.
4. Increased Focus on Preventive Healthcare
Preventive healthcare has become a significant focus in the animal healthcare market, as both pet owners and livestock producers recognize the importance of early intervention in managing animal health. Preventive measures such as routine vaccinations, parasite control, and regular health check-ups help minimize the risk of disease outbreaks and improve the overall quality of life for animals.
For pets, preventive care often includes annual wellness exams, vaccinations, dental care, and nutritional support. Many veterinary clinics are now offering wellness plans that allow pet owners to bundle preventive services at discounted rates, encouraging regular visits and proactive health management.
For livestock, preventive measures such as biosecurity protocols, vaccination programs, and parasite control are critical to ensuring healthy herds and flocks. By preventing diseases before they occur, farmers can reduce the need for costly treatments and minimize the risk of widespread outbreaks that could have devastating consequences for both animal health and the economy.
5. Digitalization and Technological Integration
The integration of technology into animal healthcare is another key trend reshaping the market. Digital tools and platforms are enabling veterinary professionals to provide better care, improve diagnostic accuracy, and streamline operations. Telemedicine, for example, is becoming an increasingly popular option for pet owners, allowing them to consult with veterinarians remotely and access expert advice from the comfort of their homes.
Additionally, wearables and smart collars are becoming more common in the pet care industry. These devices track an animal’s activity levels, monitor vital signs, and even detect early signs of illness. Such innovations are not only improving animal health but are also enhancing the overall experience for pet owners, who can gain more insight into their animals' well-being and make more informed decisions about their care.
In livestock farming, the use of IoT (Internet of Things) technology and farm management software is helping farmers monitor animal health in real-time. Sensors placed on animals can collect data on temperature, heart rate, and movement, alerting farmers to potential health issues before they become serious problems.
6. Regulatory and Sustainability Considerations
As the animal healthcare market continues to evolve, regulatory considerations and sustainability are becoming increasingly important. Governments around the world are implementing stricter regulations to ensure the safety and efficacy of veterinary products, including medicines, vaccines, and feed additives. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and other national agencies are playing a critical role in shaping the market by setting standards for product approval, labeling, and safety.
Sustainability is also a growing concern, particularly in the livestock sector. The environmental impact of farming practices, including the use of antibiotics, has led to calls for more sustainable and eco-friendly solutions. This includes the development of alternative treatments, such as plant-based medicines and vaccines that reduce the environmental footprint of animal healthcare.
7. Market Challenges
Despite the positive growth trends, the animal healthcare market faces several challenges. One of the most significant challenges is the rising cost of veterinary care, which can be a barrier to access for some pet owners, particularly in developing regions. Additionally, there are concerns about the increasing prevalence of counterfeit veterinary products, which pose a serious threat to animal health and safety.
Another challenge is the growing concern about antimicrobial resistance (AMR), particularly in livestock. The overuse of antibiotics in animal farming has contributed to the emergence of drug-resistant pathogens, which is a global health threat. Efforts to combat AMR include stricter regulations on antibiotic use, the development of alternative therapies, and greater awareness among farmers and healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
The animal healthcare market is poised for continued growth as demand for advanced veterinary products and services rises. With a growing focus on preventive care, technological integration, and sustainable practices, the industry is expected to evolve rapidly in the coming years. However, addressing challenges such as the rising cost of care, regulatory compliance, and antimicrobial resistance will be crucial for ensuring the continued success and sustainability of the sector.
As pet ownership continues to rise and livestock farming faces increasing pressure to improve productivity and animal welfare, the animal healthcare market is set to play a pivotal role in ensuring the health and well-being of animals around the world. The future of animal healthcare looks bright, with innovation and collaboration driving the industry forward.
0 notes
Text
Farm Animal Advocacy
Farm animal advocacy is the practice of promoting better treatment and protection for animals raised on farms, such as cows, pigs, chickens, and sheep. These animals are often kept in large-scale, industrial farming systems where their welfare is not prioritized. Advocates work to raise awareness about these issues and encourage more humane farming methods, dietary changes, and stronger legal protections.
Why It Matters
Farm animals are sentient beings capable of feeling pain, fear, and joy. However, in many modern agricultural systems, they face severe confinement, lack of veterinary care, and stressful living conditions. For example:
Chickens are often kept in cages so small they cannot spread their wings.
Pigs may be kept in crates that prevent them from turning around.
Calves are separated from their mothers shortly after birth in the dairy industry.
Advocacy aims to reduce this suffering and promote systems that respect the animals’ well-being.
What Farm Animal Advocates Do
Farm animal advocates use a variety of strategies to create change, including:
Education: Teaching the public about animal welfare issues through documentaries, articles, and social media.
Policy and legislation: Working to pass laws that ban cruel practices, such as the use of battery cages or gestation crates.
Corporate outreach: Pressuring food companies to adopt better animal welfare standards.
Promoting plant-based diets: Encouraging consumers to reduce or eliminate animal products from their diets.
Achievements So Far
Thanks to advocacy efforts:
Many major food companies have committed to phasing out cage systems.
Several countries and states have passed laws to protect farm animals.
The popularity of plant-based food options has grown rapidly, giving consumers more ethical choices.
How You Can Help
Anyone can support farm animal advocacy by:
Reducing or eliminating meat, dairy, and eggs from your diet.
Supporting companies that follow higher welfare standards.
Sharing information to help others learn about animal welfare.
Supporting organizations that advocate for farm animals.
Conclusion
Farm animal advocacy is about creating a kinder, more compassionate world. By taking action, we can help improve the lives of billions of animals and build a food system that aligns with our values of empathy and respect.
0 notes
Text
Swine Feed Market: Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of Pork Production and Sustainability
The swine feed market has evolved considerably in recent years, driven by factors such as technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, environmental concerns, and global economic conditions. As the global pork industry continues to grow, the demand for efficient and sustainable swine feed solutions is also on the rise. With an increasing focus on animal health, nutrition, and cost-effective production, several trends are shaping the future of the swine feed market.

1. Growing Demand for High-Quality Swine Feed
The demand for high-quality swine feed is expected to increase as producers aim to enhance productivity, improve feed conversion ratios, and optimize the overall health and welfare of pigs. Consumers are becoming more discerning about the quality of the meat they consume, with a focus on traceability, animal welfare, and sustainability. This is prompting the feed industry to invest in higher-quality ingredients and advanced nutritional formulations that improve the overall health and yield of pigs.
To address these consumer demands, swine feed producers are turning to specialized formulations that focus on optimal growth, disease resistance, and overall health. For example, adding probiotics, prebiotics, and functional ingredients to swine feed helps maintain gut health, reduce the use of antibiotics, and improve feed efficiency. The future of the swine feed market is likely to be driven by innovations in ingredient sourcing and feed formulations that prioritize animal welfare and sustainability.
2. Focus on Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Feed Solutions
Sustainability is at the forefront of the global food production industry, and the swine feed market is no exception. As environmental concerns grow, the industry is facing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint, improve resource efficiency, and adopt more eco-friendly feed production practices.
The rising costs of raw materials and concerns about the environmental impact of traditional livestock farming have prompted the exploration of alternative, sustainable feed ingredients. For instance, the use of insect meal, algae-based proteins, and plant-based sources of protein is gaining traction. These alternative ingredients offer sustainable solutions while reducing the reliance on conventional animal feed sources such as soybean and fishmeal.
Furthermore, innovations in feed formulation and production processes are helping to reduce the environmental impact of swine farming. Precision feeding techniques, which involve monitoring and adjusting nutrient intake for individual animals, are becoming more popular. These practices allow for more efficient feed use, reducing waste and improving the overall sustainability of swine farming.
3. Technological Advancements in Feed Production
The future of the swine feed market will be heavily influenced by technological advancements in feed production. With the advent of smart farming technologies and digital tools, producers can now monitor and optimize every aspect of the feeding process, from formulation to delivery.
One of the key technological innovations shaping the market is the development of precision feeding systems. These systems use sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning to assess the nutritional needs of individual pigs and adjust their feed intake accordingly. By ensuring that each pig receives the optimal amount of nutrients, these technologies help improve growth rates, reduce feed waste, and enhance overall efficiency.
In addition, blockchain technology is being explored for its potential to improve traceability and transparency in the swine feed supply chain. Blockchain can help track the sourcing and movement of feed ingredients, ensuring that producers and consumers alike can verify the quality and sustainability of the feed products.
4. Rising Demand for Organic and Non-GMO Feed
Consumer demand for organic and non-genetically modified organisms (GMO) products has been rising steadily, and this trend is influencing the swine feed market. More producers are opting for organic or non-GMO feed to cater to the growing number of health-conscious consumers who are concerned about the long-term effects of GMOs and synthetic chemicals.
Organic swine feed, which is produced without the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified crops, is becoming a popular choice among producers seeking to meet consumer demands for cleaner, more natural food sources. As a result, there is a growing market for organic feed ingredients, such as organic grains and soybeans, as well as natural additives like herbs and essential oils that support animal health.
5. Increased Focus on Disease Prevention and Animal Health
The swine feed market is also evolving in response to the growing emphasis on animal health and disease prevention. Pigs are vulnerable to various diseases, including viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections, which can significantly impact productivity and profitability. As a result, there is an increased focus on incorporating functional ingredients into swine feed that help boost immunity, prevent diseases, and improve overall health.
Vaccines, probiotics, and antimicrobial peptides are some of the key additives gaining popularity in swine feed formulations. These ingredients are designed to support the gut microbiome, enhance immune responses, and reduce the need for antibiotics, which are facing increasing scrutiny due to their contribution to antimicrobial resistance. The development of such health-promoting feed ingredients will be crucial in meeting the growing demand for safer, healthier pork products.
6. Market Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
As the swine feed industry becomes increasingly competitive, consolidation and strategic partnerships are expected to play a significant role in shaping the market's future. Larger feed manufacturers are likely to acquire smaller, specialized companies to expand their product portfolios and gain access to new technologies, ingredients, and markets.
At the same time, strategic partnerships between feed manufacturers, ingredient suppliers, and technology providers will help drive innovation in the industry. These collaborations will enable the development of cutting-edge feed solutions that address both the nutritional needs of pigs and the sustainability requirements of modern farming.
Conclusion
The swine feed market is poised for significant transformation in the coming years. As consumer demand for high-quality, sustainable, and health-focused products continues to rise, the industry will need to adopt innovative technologies, alternative feed ingredients, and advanced nutritional strategies. With a strong emphasis on sustainability, animal welfare, and disease prevention, the future of the swine feed market will be driven by a combination of consumer preferences, technological advancements, and environmental considerations.
0 notes
Text
What Are the Latest Innovations in the Vegetarian Food for Pets Market?

Vegetarian Food for Pets Market: Growth Trends and Industry Analysis
The vegetarian food for pets market is poised for substantial growth, fueled by increasing awareness of sustainability, ethical concerns, and pet health benefits. As consumer preferences shift towards plant-based alternatives, key players are focusing on innovation, collaborations, and expanding their product portfolios to capture this evolving market segment.
The global Vegetarian Food for Pets Market size was valued at approximately USD 15.66 billion in 2023 and is expected to witness significant expansion. The market is projected to grow from USD 17.31 billion in 2024 to USD 38.5 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.51% during the forecast period (2025–2032). The rise in demand for plant-based pet food is driven by factors such as growing pet humanization trends, rising concerns over pet health, and increasing awareness about environmental sustainability.
Market Drivers
Growing Pet Humanization: Pet owners are treating pets as family members and are opting for healthier, plant-based food options.
Rising Vegan and Vegetarian Diet Trends: The increasing adoption of plant-based diets among humans is influencing pet food choices.
Concerns Over Animal Welfare: Ethical considerations regarding traditional meat-based pet food are driving market growth.
Environmental Sustainability Awareness: Reduced carbon footprint and sustainability concerns are encouraging plant-based pet food consumption.
Health Benefits for Pets: Improved digestion, reduced allergies, and longer lifespan associated with vegetarian diets are appealing to pet owners.
Key Market Dynamics
The market is witnessing increased R&D investments from pet food manufacturers to enhance the nutritional profile of vegetarian pet food.
Strict government regulations on pet food labeling and safety are influencing product formulation.
High production costs and concerns regarding the complete nutritional adequacy of vegetarian pet food are potential market restraints.
Key Market Opportunities
Product Innovations: Companies are investing in plant-based proteins such as pea protein, lentils, and soy to improve nutrition.
E-commerce Expansion: The growing online retail sector offers opportunities for global reach and accessibility.
Customized Pet Diets: Rising demand for personalized pet nutrition opens avenues for tailor-made vegetarian pet food.
Partnerships and Mergers: Collaborations with veterinarians and nutrition experts are aiding the development of superior formulations.
Browse Report - Explore the report's contents, sections, and key insights by browsing through its detailed information.
Market Segmentation
By Pet Type:
Dogs – Largest segment due to their high adoption rate of plant-based diets.
Cats – A growing segment despite their obligate carnivorous nature, with supplements enhancing their diet.
Other Pets – Includes rabbits, guinea pigs, and exotic pets increasingly fed vegetarian diets.
By Product Type:
Dry Pet Food – Most popular due to convenience and longer shelf life.
Wet Pet Food – Gaining traction for its palatability and ease of consumption.
Treats & Supplements – High demand driven by pet owners seeking additional nutrition benefits.
By Distribution Channel:
Online Stores – Rapidly expanding due to ease of availability and variety.
Pet Specialty Stores – Continue to dominate due to customer trust and product variety.
Supermarkets/Hypermarkets – Growing segment owing to the increasing preference for one-stop shopping.
Segment Insights
Vegetarian Food for Pets Market insights are that dogs lead the market due to their adaptability to plant-based diets, with owners seeking high-protein, grain-free options.
Dry pet food dominates the market, but wet food and supplements are growing as pet owners focus on balanced nutrition.
Online sales are surging due to direct-to-consumer models and subscription-based services.
Recent Developments
Vegetarian Food for Pets Market growth is that leading companies are launching innovative plant-based formulas enriched with essential amino acids.
Increased mergers and acquisitions among key players to expand market reach.
Government regulations are focusing on nutritional adequacy standards for plant-based pet food.
Key Players
Wild Earth
V-dog
Halo Pets
Benevo
Ami Pet Food
Bramble Pets
Petaluma
The Honest Kitchen
Soopa Pets
Yarrah Organic Pet Food
Regions Covered
North America – Largest market due to high pet adoption rates and increasing vegan trends.
Europe – Significant growth owing to strict animal welfare regulations and sustainable food practices.
Asia-Pacific – Fastest-growing region due to rising disposable income and increased pet ownership.
Latin America & Middle East – Emerging markets with growing awareness about pet nutrition.
Discover more Research Reports of WiseGuy:
Global Wrap Snack Cake Market Research Report: By Type (Single-Serve Wrap Snack Cakes, Multi-Serve Wrap Snack Cakes), By Filling (Fruit, Cream, Chocolate, Caramel, Nut Butter), By Frosting (Cream Cheese Frosting, Buttercream Frosting, Ganache Frosting, Marshmallow Frosting), By Packaging (Individual Packaging, Multi-Pack Packaging, Bulk Packaging), By Distribution Channel (Supermarkets and Hypermarkets, Convenience Stores, Online Retailers, Specialty Food Stores) and By Regional (North America, Europe, South America, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa) - Forecast to 2032.
Global Zhacai Market Research Report: By Preservation Method (Fresh, Vacuum-packed, Canned, Fermented), By Type (Green Zhacai, White Zhacai, Yellow Zhacai), By End-Use Industry (Food and Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, Agriculture), By Distribution Channel (Traditional Markets, Supermarkets and Hypermarkets, Online Platforms, Food Service) and By Regional (North America, Europe, South America, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa) - Forecast to 2032.
Global Wheat Bran Oil Market Research Report: By Application (Food, Animal Feed, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, Industrial), By Extraction Method (Cold-Pressing, Hot-Pressing, Solvent Extraction), By Composition (High in Fiber, Rich in Protein, Contains Antioxidants, Anti-inflammatory Properties), By Distribution Channel (Direct Sales, Retail Sales, Online Platforms, Foodservice Industry) and By Regional (North America, Europe, South America, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa) - Forecast to 2032.
About WiseGuy :
Wise Guy Reports is pleased to introduce itself as a leading provider of insightful market research solutions that adapt to the ever-changing demands of businesses around the globe. By offering comprehensive market intelligence, our company enables corporate organizations to make informed choices, drive growth, and stay ahead in competitive markets.
Sales: +162 825 80070 (US) | +44 203 500 2763 (UK)
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.wiseguyreports.com/
#Vegetarian Food For Pets Market share#Vegetarian Food For Pets Market size#Vegetarian Food For Pets Market trends#Vegetarian Food For Pets Market growth
0 notes
Text
Controversial or Outdated Themes Fairground Games.

While fairground games are meant to be fun and entertaining, some have come under scrutiny due to outdated themes, cultural insensitivity, or ethical concerns.
Controversial Fairground Games Include: "Dunk the Clown" / "Dunk the Fool" (Controversy: Sometimes, these games include clowns or people who hurl insults at participants, which can encourage bullying behavior.) , "Hit the Blackface" / Racist Carnival Games (Historical)" (Controvery: These games were blatantly racist and have been rightfully banned.), Goldfish in a Bag (Live Animal Prizes) (Controversy: Many animals die shortly after being won due to stress, poor handling, or lack of proper care. Animal welfare groups have pushed for bans on live animal prizes.), "Shoot the Red Star" (Rigged Shooting Games) Controversy: Many of these games are intentionally rigged, with weak BB guns or indestructible paper, making it nearly impossible to win fairly, "Test Your Strength" (Misleading Strength Testers) Controversy: Some versions have been accused of being rigged, where only certain mallets or hidden adjustments allow the bell to ring. "Chase the Greased Pig" (Live Animal Games – Historical) Controversy: Considered inhumane as it causes stress and potential injury to the animals. "Midget Tossing" / "Dwarf Throwing" (Banned in Most Places) Controversy: Exploitive and dehumanizing. Rightfully banned in most parts of the world. "Throw the Ball at the Prisoner" (Historical). Controversy: Humiliating and abusive, eventually replaced with more lighthearted dunk tank variations.
Everything in the above are outdated fairground games, that i found during my research when I looked at controversial games. The Ones above are banned, But I still wanted to list them to show what i have found.
Outdated Fairground Games Include: Coconut Shy - Some versions have been accused of being rigged with heavier coconuts or soft balls, making them unwinnable., Shooting Gallery with Real Guns (Historical) - Replaced with safer airsoft or laser versions due to safety concerns. "Guess Your Weight" - Can be uncomfortable or embarrassing for participants, especially in modern times where body positivity is a concern. Fat Lady" or "Freak Show" Attractions - Seen as exploitative and unethical. Cigarette or Cigar Prizes (Historical) - Now banned due to health risks and regulations.
Everything above are outdated aspects of Fairground rides. Like the controversial list, these are only listed because these are what i found in my research when I looked at controversial and outdated fairground games in this genre. I probably won't use this genre for my final project, but I wanted to post this to show that i have looked at Fairground games, even controversial ones.
These days fairground games are more improved and many outdated and controversial fairground games have been phased out or modernized to be more ethical, fair, and inclusive. Games today focus on fun, skill, and entertainment without reinforcing harmful stereotypes or mistreating animals.
I think when looking into this genre, I will look into how things have improved since then, rather than the controversies.
0 notes
Text
Top 10 Countries Enforcing Stricter Animal Welfare Standards for Bacon Farming
Introduction In recent years, there has been a growing concern over animal welfare standards in livestock farming, particularly in bacon production. Various countries have taken significant steps to enforce stricter animal welfare regulations, aiming to improve the living conditions of pigs and ensure humane treatment throughout the supply chain. This report will delve into the top 10 countries…
0 notes
Text
Livestock Flooring Market: A Deep Dive into Materials, Technologies, and Market Opportunities
The livestock flooring market size is estimated at USD 1.76 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2.16 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2025 to 2030. Livestock flooring is a specialized solution designed to offer a safe, hygienic and comfortable environment for animals within agricultural operations. This aspect becomes an important part of today's farming as it supports animal welfare, minimizes health risks, and increases productivity. There exist various materials, including concrete, rubber, plastic, and metal, in livestock flooring systems to meet the needs of different animals such as cattle, pigs, and poultry.
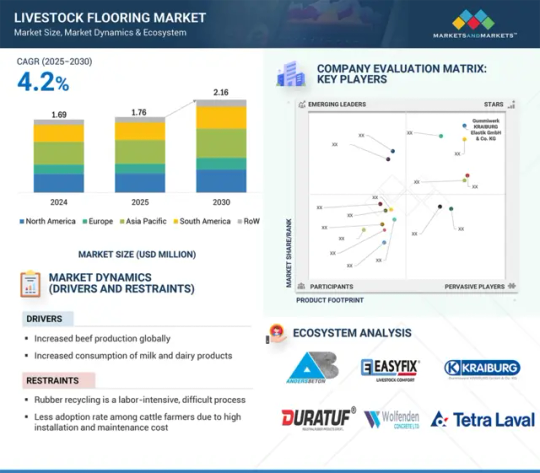
The global demand for meat, milk, and eggs has been driving steady growth in the livestock flooring market. Improvements in farming practices have increased the desire of animal farmers to invest in efficient, durable, easy-to-maintain flooring solutions to maximize their operations, while government measures encouraging hygiene and sustainable farming activities are also increasing market expansion. The integration of new technologies, like IoT-enabled flooring for real-time monitoring, is also changing the industry, so livestock flooring becomes a critical component of agricultural advancements across the globe.
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=103349855
The concrete segment is having the largest share within the material type sector of the livestock flooring market.
Concrete takes the largest market share based on material type as it is relatively strong, and cheap in the market and accessible everywhere. The robustness of concrete enables it to handle massive loads with time and the daily wear of massive animals like cows and pigs. Concrete is extensively used in dairy farms, swine housing, and feedlots, where firm, stable flooring for the animal will ensure its safety and productivity.
Low maintenance requirements and adaptability to different livestock housing establishments fuel the growth of concrete flooring. Moreover, its customization with grooves or non-slip coatings enhances the texture, giving improved grip, which helps prevent injuries in animals. Concrete can be associated well with automated cleaning systems that improve hygiene and biosecurity, factors that are crucially adopted in modern livestock farms. These benefits associated with the cost-effective nature of concrete are the reasons it becomes the dominant choice for large-scale livestock farming across the globe.
The panel series segment holds significant market share in the livestock flooring market.
Panel series products hold a significant market share in the livestock flooring market due to their durability, versatility, and animal comfort benefits. These products, primarily made of rubber, are designed to provide superior cushioning and support, reducing stress on animals' joints and improving overall welfare. Their slip-resistant and shock-absorbing properties make them ideal for housing cattle, pigs, and other livestock, ensuring safety and productivity.
Rubber panel flooring is favored for its ease of installation, low maintenance, and long lifespan, which contribute to cost savings for farmers. Additionally, its non-porous surface promotes better hygiene by minimizing bacterial growth and facilitating efficient cleaning. With growing awareness of animal welfare and demand for sustainable solutions, panel series rubber flooring continues to be in the market, offering reliable and eco-friendly options for modern farming operations.
Make an Inquiry: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Enquiry_Before_BuyingNew.asp?id=103349855
North America has a significant share in the livestock flooring market.
North America holds a significant share in the livestock flooring market, driven by the region's advanced agricultural infrastructure, high livestock production, and focus on animal welfare. The United States and Canada are key contributors, with strong demand for innovative and durable flooring solutions that enhance productivity and ensure animal comfort.
Prominent players like Animat (Canada) and J&D Manufacturing (US) lead the market with cutting-edge products, including rubber mats, designed to improve hygiene, reduce injuries, and support efficient waste management. The region's commitment to adopting modern farming practices and sustainability further drives the demand for high-quality flooring materials. Additionally, government support for agricultural advancements and the presence of well-established livestock farms reinforces North America's dominant position in the global livestock flooring market.
Top Livestock Flooring Companies:
The report profiles key players such as The Tetra Laval Group (Switzerland), Anders Concrete (Belgium), Wolfenden Concrete Limited (UK), Agri & Industrial Rubber Ltd. (Ireland), Gummiwerk KRAIBURG Elastik GmbH & Co. KG (Germany), Bioret Agri (France), Animat Inc (Canada), Nooyen group (Netherlands), Agri-Plastics (Canada), J&D Manufacturing (US), Agriprom (Netherlands), Legend Rubber Inc. (Canada), Kapoor Mats and Steel (India), Vikas Rubbers (India), and MIK INTERNATIONAL GmbH & Co. KG (Germany).
#Livestock Flooring Market#Livestock Flooring#Livestock Flooring Market Size#Livestock Flooring Market Share#Livestock Flooring Market Growth#Livestock Flooring Market Trends#Livestock Flooring Market Forecast#Livestock Flooring Market Analysis#Livestock Flooring Market Report#Livestock Flooring Market Scope#Livestock Flooring Market Overview#Livestock Flooring Market Outlook#Livestock Flooring Market Drivers#Livestock Flooring Industry#Livestock Flooring Companies
0 notes
Text
Exposing the Hidden Realities of Factory Farming: A Comprehensive Look into Animal Cruelty Practices in the Czech Agricultural Industry
The website by the Humane Foundation is a comprehensive resource that sheds light on the multifaceted issues associated with factory farming. It delves into the ethical, environmental, and societal impacts of industrial agriculture, advocating for more humane and sustainable practices.
The Plight of Animals in Factory Farming
Factory farming, or industrial agriculture, is characterized by large-scale operations that prioritize efficiency and profit over animal welfare. Animals such as cows, pigs, chickens, and fish are often kept in confined spaces, leading to physical and psychological distress. The website details the conditions these animals endure, including overcrowding, lack of natural light, and limited access to the outdoors. Such environments can lead to the development of abnormal behaviors and increased susceptibility to diseases.
For instance, dairy cows are frequently subjected to repeated cycles of impregnation and milking, leading to physical exhaustion. Pigs are often confined in gestation crates that restrict movement, and chickens may be kept in battery cages with little room to spread their wings. These practices raise significant ethical concerns about the treatment of sentient beings in the pursuit of food production.
Environmental Consequences
Beyond animal welfare, factory farming has profound environmental implications. The website highlights how intensive animal agriculture contributes to deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Large tracts of forests are cleared to create space for livestock or to grow feed crops, leading to habitat loss and decreased biodiversity.
Moreover, the concentration of animal waste can contaminate water sources, affecting both human and aquatic life. Methane emissions from ruminant animals like cows significantly contribute to climate change. These environmental challenges underscore the need for more sustainable agricultural practices.
Human Health and Societal Impacts
The repercussions of factory farming extend to human health and societal well-being. The overuse of antibiotics in animal agriculture can lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a threat to public health. Additionally, the close quarters in which animals are kept can facilitate the spread of zoonotic diseases, increasing the risk of pandemics.
Economically, small-scale farmers often struggle to compete with large industrial operations, leading to the decline of rural communities. The website also discusses the psychological toll on workers in factory farms, who may experience trauma from participating in the slaughter and processing of animals.
Advocacy and Alternatives
The Humane Foundation advocates for a shift towards more ethical and sustainable food systems. They promote plant-based diets as a means to reduce reliance on factory-farmed animal products. The website offers resources on vegan nutrition, recipes, and guides to help individuals transition to plant-based eating.
Furthermore, the organization encourages policy changes to improve animal welfare standards and environmental regulations. They support initiatives that provide subsidies for sustainable farming practices and education programs to raise awareness about the impacts of factory farming.
Taking Action
Individuals can play a role in addressing the issues associated with factory farming. By making informed food choices, supporting local and sustainable agriculture, and advocating for policy reforms, consumers can contribute to a more humane and environmentally friendly food system. The website provides actionable steps, including petitions, community events, and educational materials, to empower individuals to make a difference.
The website cruelty.farm/cs by the Humane Foundation is a comprehensive resource that sheds light on the multifaceted issues associated with factory farming. It delves into the ethical, environmental, and societal impacts of industrial agriculture, advocating for more humane and sustainable practices.
The Plight of Animals in Factory Farming
Factory farming, or industrial agriculture, is characterized by large-scale operations that prioritize efficiency and profit over animal welfare. Animals such as cows, pigs, chickens, and fish are often kept in confined spaces, leading to physical and psychological distress. The website details the conditions these animals endure, including overcrowding, lack of natural light, and limited access to the outdoors. Such environments can lead to the development of abnormal behaviors and increased susceptibility to diseases.
For instance, dairy cows are frequently subjected to repeated cycles of impregnation and milking, leading to physical exhaustion. Pigs are often confined in gestation crates that restrict movement, and chickens may be kept in battery cages with little room to spread their wings. These practices raise significant ethical concerns about the treatment of sentient beings in the pursuit of food production.
Environmental Consequences
Beyond animal welfare, factory farming has profound environmental implications. The website highlights how intensive animal agriculture contributes to deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Large tracts of forests are cleared to create space for livestock or to grow feed crops, leading to habitat loss and decreased biodiversity.
Moreover, the concentration of animal waste can contaminate water sources, affecting both human and aquatic life. Methane emissions from ruminant animals like cows significantly contribute to climate change. These environmental challenges underscore the need for more sustainable agricultural practices.
Human Health and Societal Impacts
The repercussions of factory farming extend to human health and societal well-being. The overuse of antibiotics in animal agriculture can lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a threat to public health. Additionally, the close quarters in which animals are kept can facilitate the spread of zoonotic diseases, increasing the risk of pandemics.
Economically, small-scale farmers often struggle to compete with large industrial operations, leading to the decline of rural communities. The website also discusses the psychological toll on workers in factory farms, who may experience trauma from participating in the slaughter and processing of animals.
Advocacy and Alternatives
The Humane Foundation advocates for a shift towards more ethical and sustainable food systems. They promote plant-based diets as a means to reduce reliance on factory-farmed animal products. The website offers resources on vegan nutrition, recipes, and guides to help individuals transition to plant-based eating.
Furthermore, the organization encourages policy changes to improve animal welfare standards and environmental regulations. They support initiatives that provide subsidies for sustainable farming practices and education programs to raise awareness about the impacts of factory farming.
Taking Action
Individuals can play a role in addressing the issues associated with factory farming. By making informed food choices, supporting local and sustainable agriculture, and advocating for policy reforms, consumers can contribute to a more humane and environmentally friendly food system. The website provides actionable steps, including petitions, community events, and educational materials, to empower individuals to make a difference.
0 notes