#or astrophysics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
holy ship grandma
im turning 14 in two months and ur turning 15 in 1
ikrrr im gonna be a 15 yo grandma and u a 14 yo zygotee
#honestly i cant believe im turning 15#like omgg in just another 4 years i wont be a teen#and after 5 years im gonna be in my fucking twenties#and in literallly 3 years ill have to choose which uni i want to go to#which career i want to have#and deal with rejection (tho not from my fav uni i hope)#and then ill have to get a job#and then the marriage era starts#tho if i ever get married it will onyl be after im in my late twenties or early thirties#but most importantly i dont know if i shud take plain physics#or plain science#or plain bio#or astronomy#or astrophysics#or medicine#or should i leave it all to become a crime investigator like i wanted to when i was 11#god help me lol
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
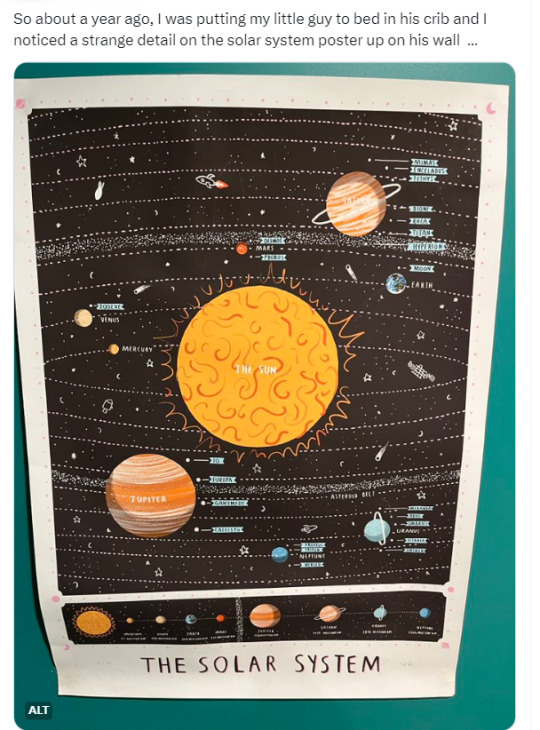


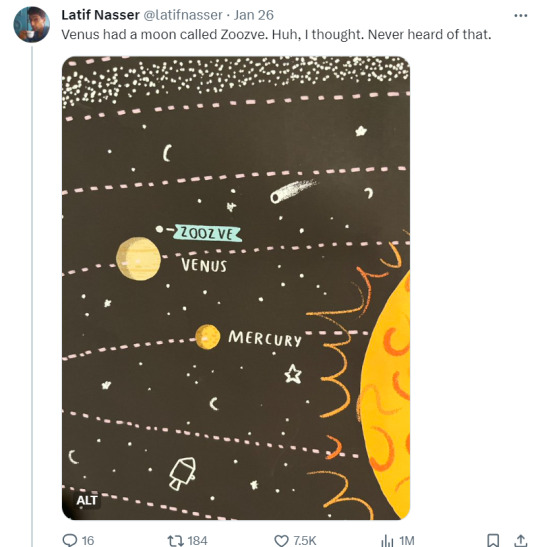
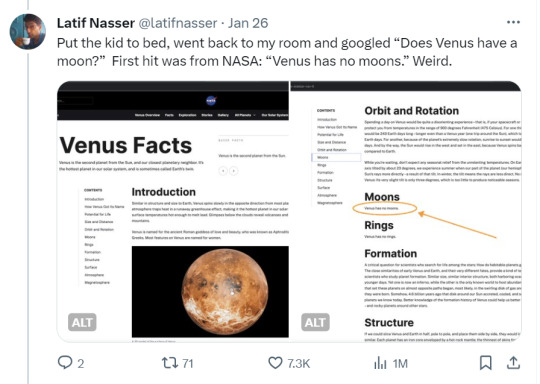
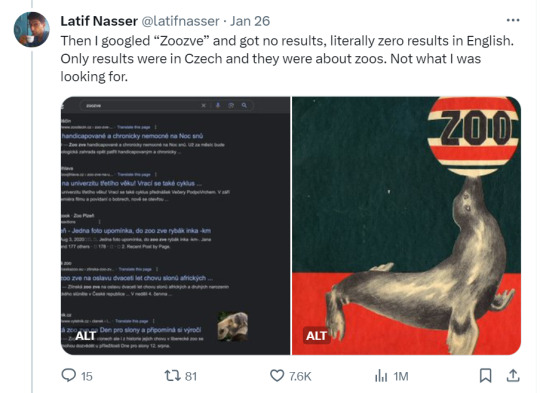
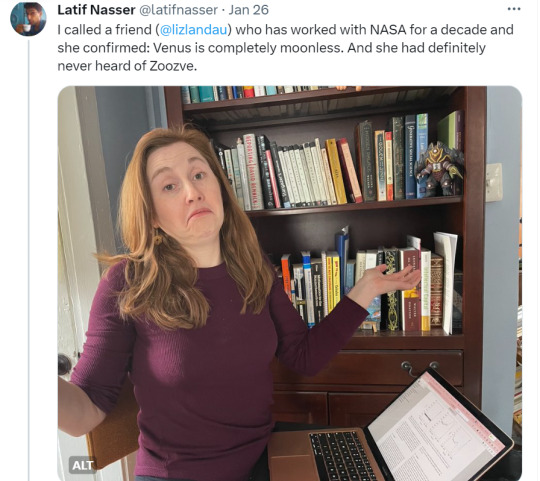

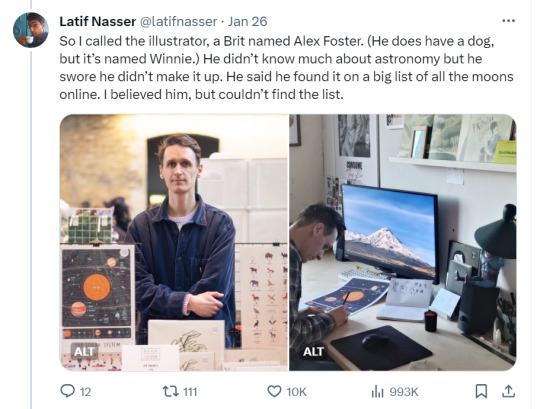

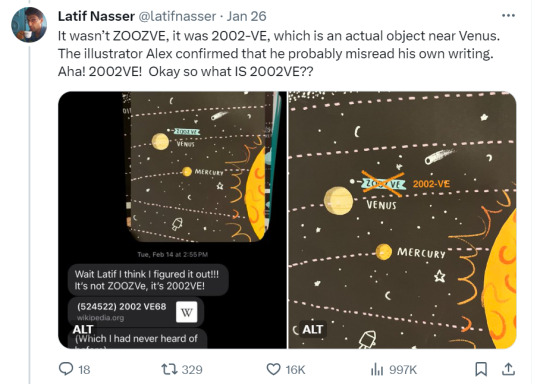


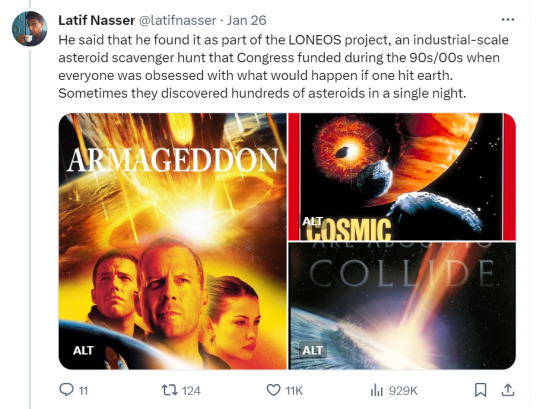
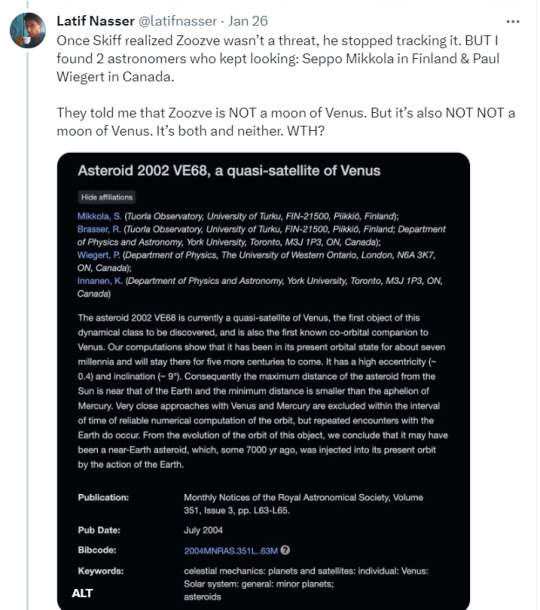
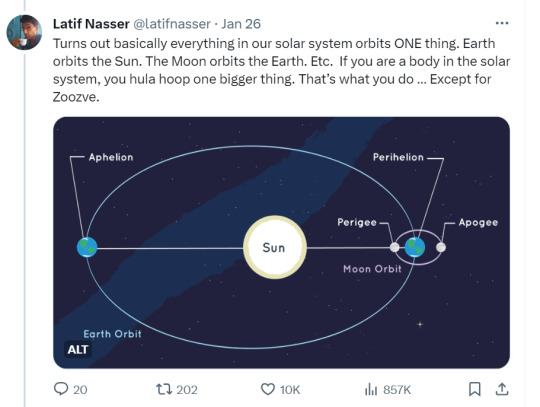


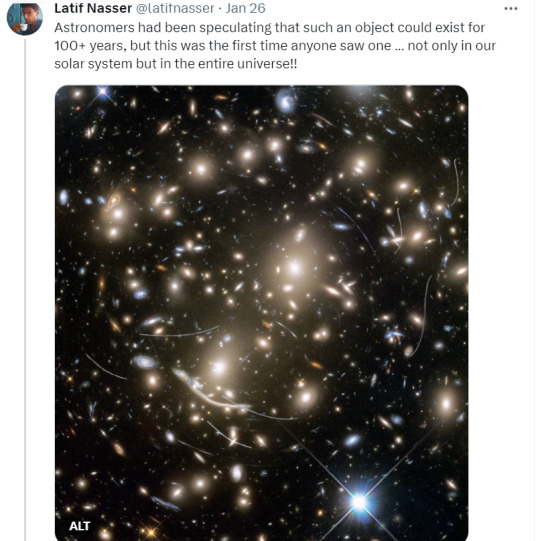


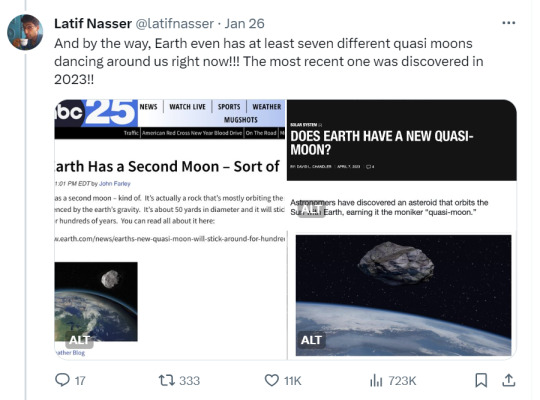

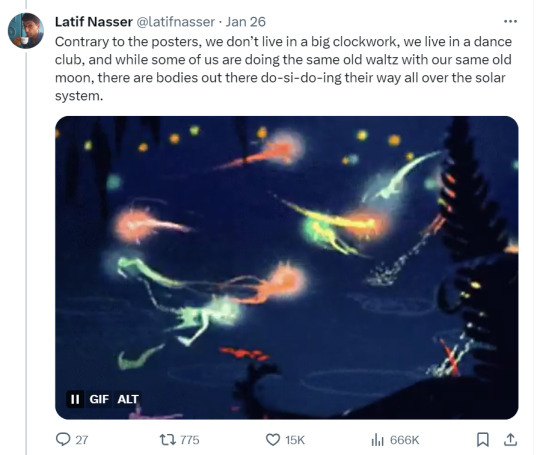
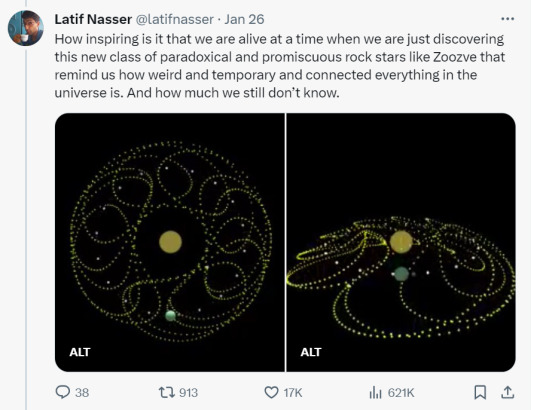

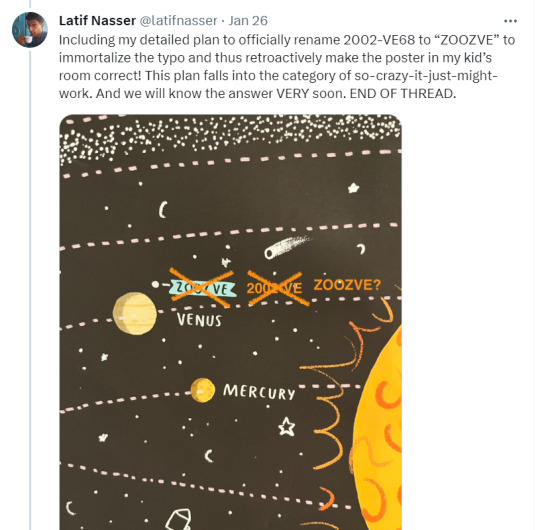
Zoozve, my beloved
#i cannot tell you how much this made me smile just bc it's so full of love#moon#venus#zoozve#long post#sorry about that it's very long but it's very entertaining i hope you enjoy this lil zoozve gem haha#astronomy#astrophysics#space
152K notes
·
View notes
Text


Stellar death
#dddaily4sherin#day 313 i totally did not mess up the day count yesterday#life series#grian#scott smajor#pearlescentmoon#inthelittlewood#goodtimeswithscar#zombiecleo#3rd life smp#last life smp#double life smp#limited life smp#real life smp#mcyt#trafficblr#traffic smp#my art#i had an epiphany after a certain astro class and have been losing it ever since#screw the solar system make them all (dying/dead) stars!!!!!! (and related events)#and I finally got to do it tdy LMASODAOS HOPE U GUYS LIKE THIS IM VERY HAPPY WITH IT >:D#also ppl who knows astronomy/astrophysics feel free to psychoanalyze the hell out of this. i had sm fun assigning them HEHEHE
16K notes
·
View notes
Text


by babaktafreshi
#perseids#shooting stars#night sky#milky way#galaxy#astrophotography#astrophysics#astronomy#meteor#meteor shower#nature#naturecore#curators on tumblr#up
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
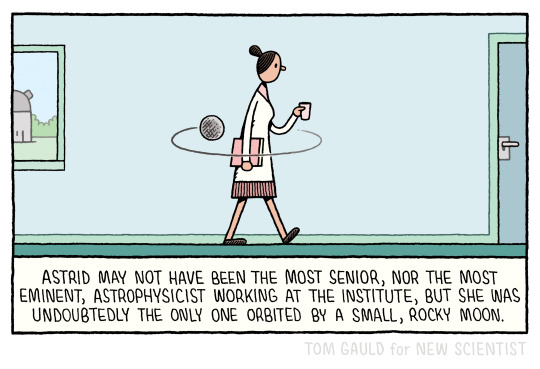
My latest cartoon for New Scientist.
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
Close up of Pluto from the New Horizons space probe.
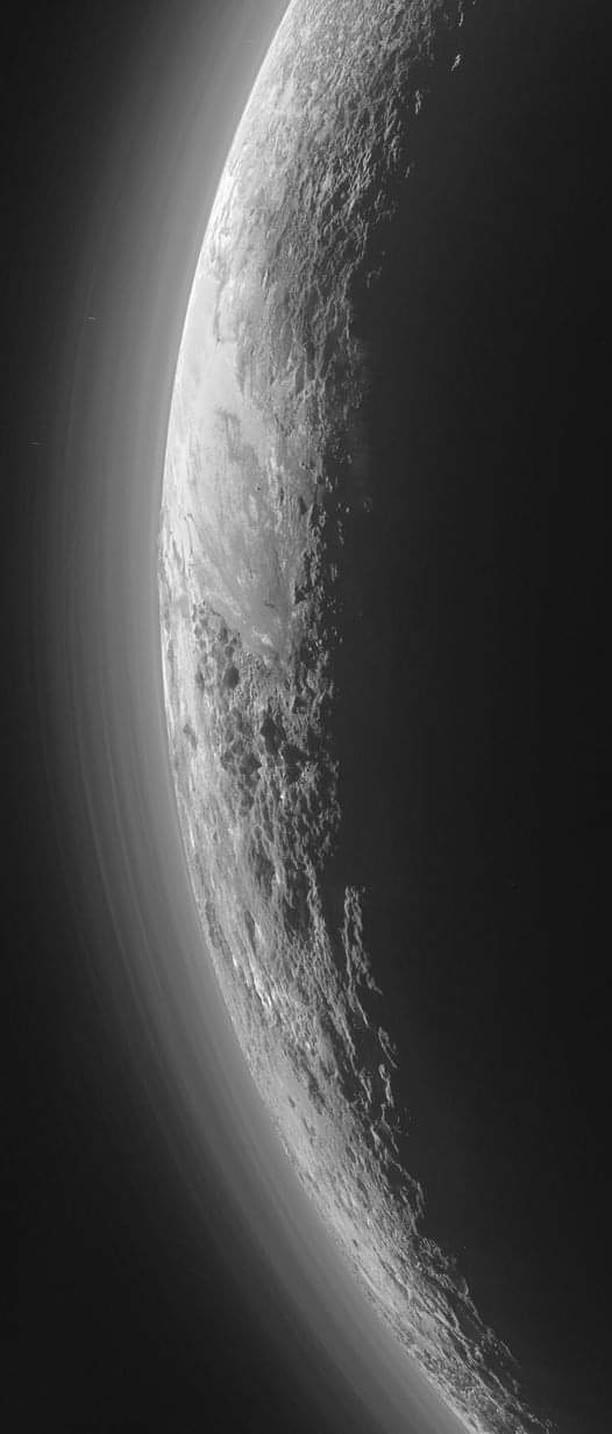

Will be adding several more photos to this same post
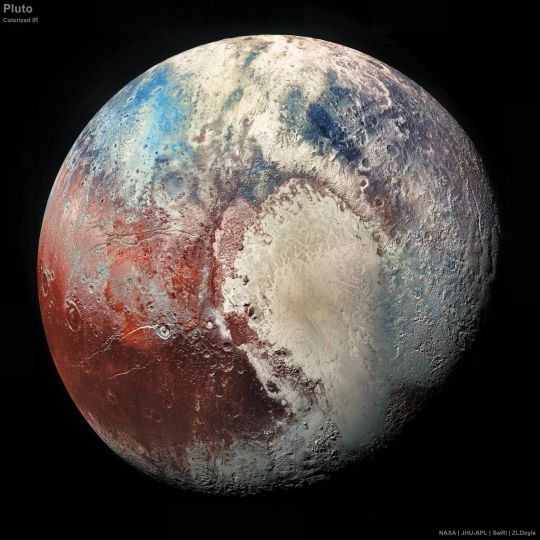
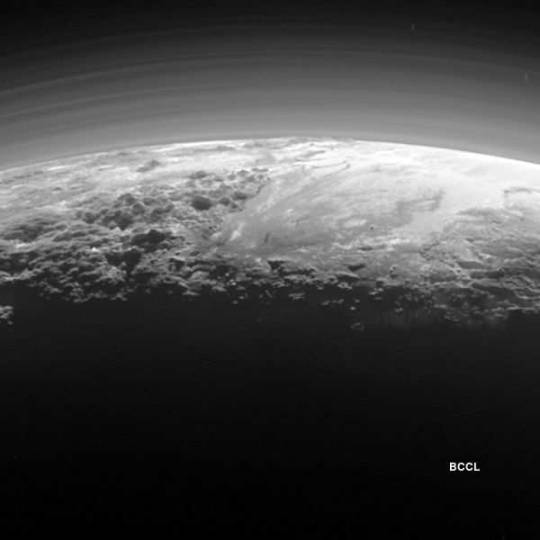






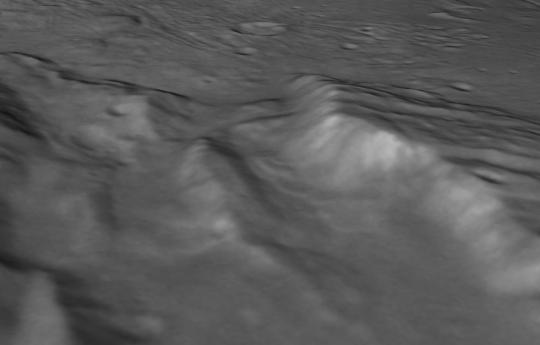

#astronomy#nasa#astronomers#universe#astrophotography#nasa photos#nasawebb#astrophysics#outer space#hubble space telescope#astrology#astronomy photography#astronomy picture of the day#astro observations#astro notes#astro community#astrography#our universe#nebula#pluto#planets#planet#nasa picture of the day#goddard space flight center#galaxies#galaxy#spacecraft#new horizons#space exploration#space
20K notes
·
View notes
Text
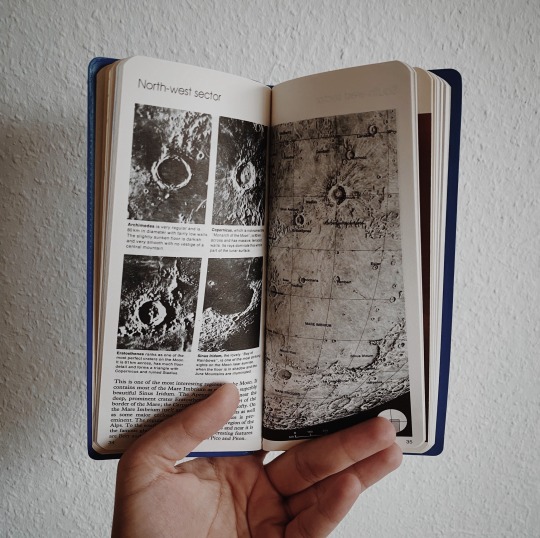
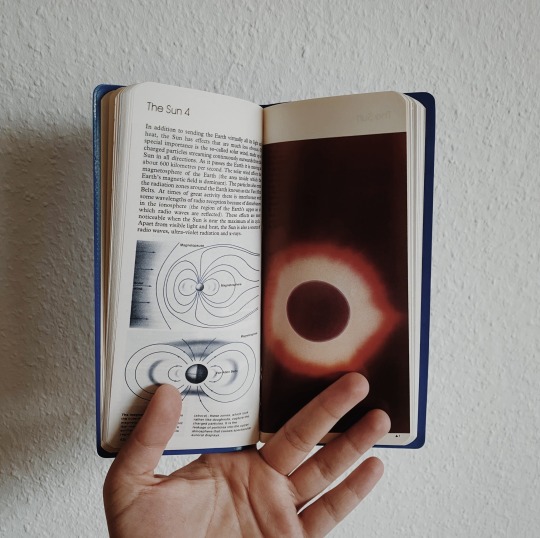
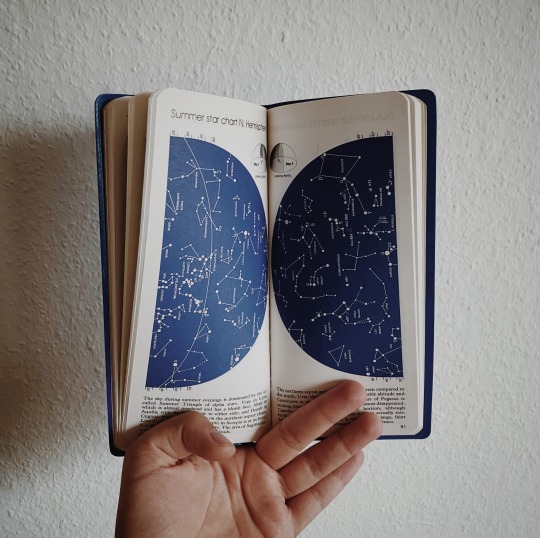






bought this gem secondhand and can’t get over how stunning it is 🪐 reblog is okay, don’t repost/use
#my photos#space science#study space#space#outer space#astronomy#science#stem#stemblr#astrophysics#books#book cover#bookworm#booklover#bookaddict#bookaholic#book aesthetic#bookblr#book blog#studyblr#academia#stem academia#stem aesthetic#light academia#light academia aesthetic
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
NASA is serious
Also NASA:

I love NASA
3K notes
·
View notes
Text


1. The November Meteors, chromolithograph from the Trouvelot Astronomical Drawings, 1882 - 2. Leonid Meteor Storm seen in November 1833, from the Bilderatlas der Sternenwelt.
#art#stars#astrophysics#night#aesthetic#science#meteor#meteor shower#chromolithograph#1833#astronomy#1882#1888#tale#paintings
3K notes
·
View notes
Text








Images to Celebrate NASA’s Chandra 25th Anniversary
These images, which all include data from Chandra, demonstrate how X-ray astronomy explores all corners of the universe. By combining X-rays from Chandra with other space-based observatories and telescopes on the ground, as many of these images do, astronomers can tackle the biggest questions and investigate long-standing mysteries across the cosmos.
On July 23, 1999, the space shuttle Columbia launched into orbit carrying Chandra, which was then the heaviest payload ever carried by the shuttle. With Commander Eileen Collins at the helm, the astronauts aboard Columbia successfully deployed Chandra into its highly elliptical orbit that takes it nearly one-third of the distance to the Moon.
X-rays are an especially penetrating type of light that reveals extremely hot objects and very energetic physical processes. Many fascinating regions in space glow strongly in X-rays, such as the debris from exploded stars and material swirling around black holes. Stars, galaxies, and even planets also give off X-rays that can be studied with Chandra.
NASA/SAO/CXC
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

colored them in !! for funsies
#really really like how dazai’s skirt came out#im not going to lie this is the messiest coloring i think ive like ever done#sorry if it looks strange i used a bunch of new textures + colors but also didnt render a lot#ok ive been HARD procrastinating on studying off i go now to learn all of astrophysics in one day#bungou stray dogs#bsd#bungo stray dogs#bungou stray dogs fanart#dazai osamu#chuuya nakahara#soukoku#soukouku#kokoart
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
I need people to understand that Uranium is an eldritch horror
I'm not talking about radiation, or nuclear weapons, or anything that you can do with uranium, I mean its mere existence on Earth is a reminder of cosmic horrors on a scale you can barely conceive of.
When a nuclear power plant uses Uranium to boil water and spin steam turbines to keep the lights on, they're unleashing the fossilized energy of the destroyed heart of an undead star.
Allow me to elaborate:
In the beginning, there were hydrogen and helium. The primordial fires of the Big Bang produced almost exclusively the two lightest elements, along with a minuscule trace of lithium. It was a start, but that's not much to build a universe out of. Fortunately, the universe is full of element factories. We call them "stars".
Stars are powered by nuclear fusion, smooshing light elements together to make heavier elements, and releasing tremendous amounts of energy in the process, powering the star and making it shine. This goes on for millions to billions of years depending on the stars mass (although not how you might think, the bigger stars die young), the vast majority of that time spent fusing hydrogen into yet more helium. Eventually, the hydrogen in the core starts to run low, and if the star is massive enough it starts to fuse helium into carbon, then oxygen, neon, and so on up through successively heavier elements.
There's a limit to this though:

This chart shows how much energy is released if you were to create a given element/isotope out of the raw protons and neutrons that make it up, the Nuclear Binding Energy. Like in everyday life, rolling downhill on this chart releases energy. So, starting from hydrogen on the far left you can rapidly drop down to helium-4 releasing a ton of energy, and then from there to carbon-12 releasing a fair bit more.
But, at the bottom of this curve is iron-56, the most stable isotope. This is the most efficient way to pack protons and neutrons together, and forming it releases some energy. But once its formed, that's it. You're done. Its already the most stable, you can't get any more energy out of it, and in fact if you want to do anything to it and make it into a different element you're going to have to put energy in.
So, when a massive star's core starts to fill up with iron, the star is doomed. Iron is like ash from the nuclear fire that powers stars, its what's leftover when all the fuel is used up. When this happens, the core of the star isn't producing energy and can't support itself anymore and catastrophically collapses, triggering a supernova explosion which heralds the death of the star.
What kind of stellar-corpse gets left behind depends again on how massive the star is. If its really big, more than ~30 times the mass of the sun and its probably going to form a black hole and whatever was in there is gone for good. But if the star is a bit less massive, between 8-25 solar masses, it leaves behind a marginally less-destroyed corpse.
The immense weight of the outer layers of the star falling down on the core compresses the electrons of the atoms into their nuclei, resulting in them reacting with protons and turning them all into neutrons, which creates a big ball of almost pure neutrons a couple miles across, but containing the entire mass of the star's core, 3-5 sun's worth.
This is the undead heart of the former star: a neutron star.
If, like many stars, this one wasn't alone but had a sibling, it can end up with two neuron stars orbiting each other, like a pair of zombies acting out their former lives. If they get close enough together, their intense gravity warps the fabric of spacetime as they orbit, radiating away their orbital energy as gravitational waves, slowing them down and bringing them closer together until they eventually collide.
The resulting kilonova explosion destroys both of the neutron stars, most likely rendering the majority of what's left into a black hole, but not before throwing out a massive cloud of neutron-rich shrapnel. This elder-god blood-splatter from the collision of the undead hearts of former stars contains massive nuclei with hundreds to thousands of neutrons, the vast majority of which are heinously unstable and decay away in milliseconds or less. Most of their decay products are also unstable and decay quickly as well, eventually falling apart into small enough clusters to be stable and drift off into the universe becoming part of the cosmic dust between the stars.
However,
Some of the resulting massive elements are merely almost stable. They would like to decay, but for quantum-physics reasons decaying is hard and slow for them, so they stick around much longer than you might expect. Uranium is one such element, with U-238 having a half-life of around 4.5 billion years, about the same as the age of the Earth, and its spicier cousin U-235 which still has a respectable 200 million year half life.
These almost-stable isotopes were only able to be created in the fiery excess of energy in a neutron star collision, and are the only ones that stick around long enough to carry a fraction of that energy to the era where hairless apes could figure out that a particular black rock made of them was emitting some kind of invisible energy.
So as I said at the beginning, Uranium is significant because it stores the fossilized energy of the destroyed heart of an undead star, and we can release that energy at will if we set it up just right.
When you say it like that, is it any shock that the energy in question will melt your face off and rot your bones from the inside if you stay near it too long?
#nuclear physics#nucleosynthesis#stellar nucleosynthesis#neutron star#uranium#radiation#supernova#kilonova#cosmic horror#physics#science#space#astrophysics#stars#stellar evolution
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Black Hole Friday Deals!

Get these deals before they are sucked into a black hole and gone forever! This “Black Hole Friday,” we have some cosmic savings that are sure to be out of this world.
Your classic black holes — the ultimate storage solution.
Galactic 5-for-1 special! Learn more about Stephan’s Quintet.
Limited-time offer game DLC! Try your hand at the Roman Space Observer Video Game, Black Hole edition, available this weekend only.
Standard candles: Exploding stars that are reliably bright. Multi-functional — can be used to measure distances in space!
Feed the black hole in your stomach. Spaghettification’s on the menu.
Act quickly before the stars in this widow system are gone!
Add some planets to your solar system! Grab our Exoplanet Bundle.
Get ready to ride this (gravitational) wave before this Black Hole Merger ends!
Be the center of attention in this stylish accretion disk skirt. Made of 100% recycled cosmic material.
Should you ever travel to a black hole? No. But if you do, here’s a free guide to make your trip as safe* as possible. *Note: black holes are never safe.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#astronomy#telescope#Roman Space Telescope#black holes#galaxies#cosmology#astrophysics#stars#galaxy#Hubble#Webb#space#exoplanets#science#physics#comic#comics#comic art
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
i find it so unfair that i cant do all the science. like what do you MEAN I can't study bio and chem and biochem and atrophysics and physics and geology and climate science. what do you MEAN i have a limited lifespan and need to get out of school at some point to get a job. i want to collect the science fields like pokemon, this isn't fair
#minty's crystals#science#biology#chemistry#physics#astrophysics#astronomy#stem#I'm literally such a nerd but i want to learn EVERYTHING i want to be the MASTER OF SCIENCE#also i wanna be famous for it#something something nobel prize something something cover of time magazine#academia#chaotic academia
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
by nasachandraxray


#nasa#space#astrophotography#astronomy#christmas#xmas#merry christmas#star cluster#aesthetic#astrophysics#christmas star cluster#curators on tumblr#up
1K notes
·
View notes