#myeloperoxidase
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
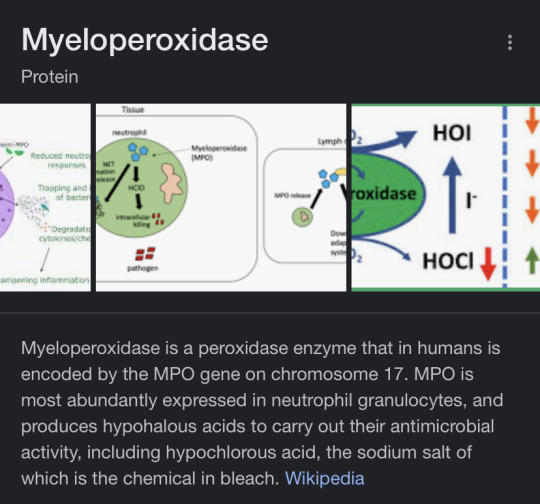
Text
can somebody make a firefox extension that just. removes all images from the webpage. sometimes i'm curious about a gross topic, but i hesitate to look it up because i know i'll have to look at gross pictures.
#tag 5#anyway i knew that pus was usually white bc infection=dead white blood cells#but now also i know the reason it's sometimes green is because certain white blood cells release an antibacterial protein (myeloperoxidase)#which happens to be green
0 notes
Text
Why is pus a little green?
Could be from the presence of a greenish antibacterial protein called myeloperoxidase
produced by some white blood cells
Could be from the pigment pyocyanin
produced by bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa
This kind of pus is foul-smelling -- pus from anaerobic infections can more often have a foul color
Main source: Pus on Wikipedia
0 notes
Text
Leucocyte Myeloperoxidase from Human Sputum
Leucocyte Myeloperoxidase from Human Sputum Catalog number: B2019075 Lot number: Batch Dependent Expiration Date: Batch dependent Amount: 0.5 mg Molecular Weight or Concentration: N/A Supplied as: Powder Applications: a molecular tool for various biochemical applications Storage: 2-8°C Keywords: Leucocyte Myeloperoxidase, Human Sputum Grade: Biotechnology grade. All products are highly pure. All…
0 notes
Text
7 Obat Termahal Sejagat, Ada yang Tembus Rp60 Miliar!

Dalam beberapa tahun terakhir, perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan dan teknologi di bidang kesehatan telah menghasilkan obat-obatan yang tidak hanya inovatif, tetapi juga sangat mahal. Biaya tinggi ini sering kali disebabkan oleh proses penelitian yang panjang, pengembangan yang rumit, dan biaya produksi yang signifikan. Beberapa obat bahkan menembus harga ratusan ribu hingga miliaran rupiah. Berikut adalah tujuh obat termahal di dunia yang mencengangkan, dengan beberapa di antaranya mencapai harga di atas Rp60 miliar.
1. Zolgensma (Nusinersena)
Zolgensma adalah obat yang digunakan untuk mengobati spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), penyakit genetik yang mempengaruhi saraf dan otot. Obat ini dirancang untuk memberikan terapi gen dengan cara mengisi gen SMN1 yang hilang atau tidak berfungsi pada pasien. Zolgensma diproduksi oleh Novartis dan menjadi salah satu obat termahal di dunia, dengan harga sekitar USD 2.125.000 atau sekitar Rp32 miliar per dosis.
Proses pengembangan Zolgensma memakan waktu lebih dari satu dekade dan melibatkan riset yang mendalam. Harga tinggi obat ini dipengaruhi oleh kompleksitas produksi dan pentingnya terapi yang diberikan bagi pasien SMA, di mana pengobatan dini dapat mencegah perkembangan penyakit yang parah.
2. Luxturna (Voretigene Neparvovec)
Luxturna adalah obat terapi gen yang digunakan untuk mengobati penyakit mata genetik yang menyebabkan kebutaan, seperti retinitis pigmentosa. Obat ini juga memerlukan prosedur injeksi ke dalam mata dan dikembangkan oleh Spark Therapeutics. Harganya diperkirakan sekitar USD 850.000 atau sekitar Rp12,8 miliar per pasien.
Luxturna bekerja dengan mengantarkan salinan gen yang berfungsi ke sel-sel retina, memberikan harapan baru bagi pasien yang sebelumnya tidak memiliki pilihan pengobatan. Meskipun harga tinggi, efektivitas Luxturna dalam memperbaiki penglihatan pasien sangat signifikan, sehingga banyak yang menganggapnya sebagai investasi berharga dalam kesehatan mata.
3. Actimmune (Interferon gamma-1b)
Actimmune adalah obat yang digunakan untuk mengobati penyakit langka seperti osteopetrosis dan chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Obat ini bekerja dengan merangsang sistem kekebalan tubuh untuk melawan infeksi. Harga Actimmune bisa mencapai USD 500.000 atau sekitar Rp7,5 miliar per tahun.
Meskipun harga tersebut terlihat tinggi, bagi pasien dengan penyakit langka yang memerlukan perawatan khusus, biaya ini dapat dianggap wajar jika dibandingkan dengan potensi kualitas hidup yang diperoleh. Keberhasilan Actimmune dalam meningkatkan sistem kekebalan tubuh telah membantu banyak pasien dalam menghadapi tantangan penyakit langka.
4. Haffner's Syndrome (Myeloperoxidase deficiency)
Obat yang digunakan untuk mengobati Haffner's Syndrome, sebuah kondisi genetik langka, juga termasuk dalam daftar obat termahal. Biaya perawatan tahunan untuk pasien dengan Haffner's Syndrome bisa mencapai USD 450.000 atau sekitar Rp6,7 miliar.
Penyakit ini mempengaruhi kemampuan tubuh untuk memproduksi enzim myeloperoxidase, yang berfungsi dalam memerangi infeksi. Pasien yang mengalami kondisi ini sangat rentan terhadap infeksi serius, sehingga memerlukan pengobatan yang intensif dan teratur.
5. Soliris (Eculizumab)
Soliris adalah obat yang digunakan untuk mengobati dua penyakit autoimun langka: paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) dan atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS). Dikenal sebagai salah satu obat termahal di dunia, harganya mencapai USD 500.000 atau sekitar Rp7,5 miliar per tahun.
Soliris bekerja dengan menghambat sistem kekebalan tubuh yang berlebihan, sehingga mengurangi risiko komplikasi dari penyakit ini. Meskipun biaya tinggi, Soliris menawarkan harapan bagi pasien yang menderita penyakit autoimun langka yang dapat berakibat fatal.
6. Kymriah (Tisagenlecleucel)
Kymriah adalah terapi sel CAR-T yang digunakan untuk mengobati kanker darah, seperti leukemia limfoblastik akut. Proses pembuatan Kymriah melibatkan pengambilan sel-sel darah pasien, kemudian memodifikasinya di laboratorium untuk meningkatkan kemampuan melawan kanker. Harganya mencapai USD 373.000 atau sekitar Rp5,5 miliar.
Terapi ini memberikan harapan baru bagi pasien kanker yang tidak merespons pengobatan lain. Meskipun biayanya tinggi, keberhasilan Kymriah dalam menyelamatkan nyawa pasien membuatnya sangat berharga.
7. Danyelza (Naxitamab)
Danyelza adalah obat terbaru yang digunakan untuk mengobati neuroblastoma, jenis kanker yang umum terjadi pada anak-anak. Dengan harga sekitar USD 1.200.000 atau sekitar Rp18 miliar, Danyelza menawarkan solusi inovatif dalam pengobatan kanker pada anak.
Obat ini bekerja dengan menargetkan sel-sel kanker dan merangsang sistem kekebalan tubuh untuk melawannya. Meskipun harganya sangat tinggi, potensi Danyelza untuk meningkatkan harapan hidup pasien kanker anak sangat signifikan.
Faktor Penyebab Tingginya Harga Obat
Beberapa faktor yang menyebabkan tingginya harga obat-obatan ini antara lain:
Biaya Riset dan Pengembangan: Proses pengembangan obat memerlukan investasi yang sangat besar dalam penelitian dan pengujian klinis. Seringkali, hanya sedikit obat yang berhasil memasuki pasar setelah melewati tahap penelitian yang panjang.
Regulasi yang Ketat: Persetujuan dari badan regulasi seperti FDA memerlukan standar keamanan dan efektivitas yang tinggi. Hal ini membuat biaya produksi meningkat.
Pasar Terbatas: Beberapa obat hanya tersedia untuk penyakit langka yang mempengaruhi sedikit pasien. Dengan basis pasien yang kecil, harga obat harus cukup tinggi untuk menutupi biaya produksi dan pengembangan.
Inovasi Teknologi: Obat yang menggunakan teknologi canggih, seperti terapi gen atau terapi sel, biasanya memiliki biaya produksi yang lebih tinggi, sehingga mempengaruhi harga jual.
Kesimpulan
Obat-obatan termahal di dunia mencerminkan kemajuan luar biasa dalam bidang medis, tetapi juga menyoroti tantangan yang dihadapi dalam hal aksesibilitas dan biaya. Meskipun biaya tinggi dapat menyebabkan kekhawatiran di kalangan pasien dan penyedia layanan kesehatan, efektivitas dan inovasi yang ditawarkan oleh obat-obatan ini memberikan harapan baru bagi mereka yang menderita penyakit serius dan langka.
Penting bagi pemerintah, perusahaan farmasi, dan pemangku kepentingan lainnya untuk bekerja sama dalam menciptakan sistem kesehatan yang berkelanjutan dan terjangkau, sehingga semua pasien dapat memperoleh akses kepada pengobatan yang mereka butuhkan tanpa terbebani oleh biaya yang sangat tinggi. Diskusi mengenai harga obat dan regulasi yang ada harus terus dilakukan untuk memastikan bahwa kemajuan dalam penelitian dan pengembangan obat tidak hanya bermanfaat bagi segelintir orang, tetapi dapat diakses oleh semua lapisan masyarakat.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Myeloperoxidase Alters Lung Cancer Cell Function to Benefit Their Survival
Pubmed: http://dlvr.it/SvDwNz
0 notes
Text
Biosensors, Vol. 13, Pages 662: A Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Hypochlorite and Lipid Droplets to Monitor Oxidative Stress
Mitochondria are valuable subcellular organelles and play crucial roles in redox signaling in living cells. Substantial evidence proved that mitochondria are one of the critical sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and overproduction of ROS accompanies redox imbalance and cell immunity. Among ROS, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is the foremost redox regulator, which reacts with chloride ions in the presence of myeloperoxidase (MPO) to generate another biogenic redox molecule, hypochlorous acid (HOCl). These highly reactive ROS are the primary cause of damage to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), #RNA (ribonucleic acid), and proteins, leading to various neuronal diseases and cell death. Cellular damage, related cell death, and oxidative stress are also associated with lysosomes which act as recycling units in the cytoplasm. Hence, simultaneous monitoring of multiple organelles using simple molecular probes is an exciting area of research that is yet to be explored. Significant evidence also suggests that oxidative stress induces the accumulation of lipid droplets in cells. Hence, monitoring redox biomolecules in mitochondria and lipid droplets in cells may give a new insight into cell damage, leading to cell death and related disease progressions. Herein, we developed simple hemicyanine-based small molecular probes with a boronic acid trigger. A fluorescent probe AB that could efficiently detect mitochondrial ROS, especially HOCl, and viscosity simultaneously. When the AB probe released phenylboronic acid after reacting with ROS, the product AB–OH exhibited ratiometric emissions depending on excitation. This AB–OH nicely translocates to lysosomes and efficiently monitors the lysosomal lipid droplets. Photoluminescence and confocal fluorescence imaging analysis suggest that AB and corresponding AB–OH molecules are potential chemical probes for studying oxidative stress. https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6374/13/6/662?utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes
Text
Honestly, you might be onto something here. Myeloperoxidase is one of the first enzymes that to-be-neutrophils promyelocytes produce. It’s one of the components of azure granules, which are first granules that neutrophils get. Monocytes, and consequentially, macrophages also have this enzyme, but in far lower concentration than neutrophils. This could explain why macrophages are white, but not AS pale as neutrophils. Also, no other granulocyte has this enzyme which could be the reason why basophils , eosinophils and mast cells don’t have super pale complexion.
However, IRL, this enzyme is green. It has heme ion and it’s the reason why your snot is greenish in color during infections. So, maybe it’s not that. But it’s a cool theory!
I GOT IT. I KNOW WHY THE WHITE BLOOD CELLS ARE PASTY WHITE BOYS.
It was right in front of us all along.
They contain a chemical that’s also in bleach. Bleach makes things white…
They literally are bleached.
12 notes
·
View notes
Link
Avail best offer on Myeloperoxidase test home collection Near Me from CNC Pathlab at the affordable Myeloperoxidase test In Delhi, Myeloperoxidase test Cost Price in Delhi
0 notes
Text
TheHorse.com | 12 August, 2020
...
Richardson’s team compared the effects of firocoxib (a COX-2-selective NSAID) and phenylbutazone (a nonselective NSAID) on gastric ulceration in adult horses. They used fecal myeloperoxidase (MPO, a protein released during acute inflammation) as a marker of lower GI tract injury.
They randomly assigned 10 adult horses to one of each of the treatment groups (firocoxib administered at 0.1 mg/kg once a day or phenylbutazone administered at 4.4 mg/kg once a day) and five horses to a control group that received a placebo treatment. The team administered treatments for 10 days and collected fecal samples on Days 0, 10, and 20. They also scoped the horses for gastric ulcers on Days 0 and 10.
In looking at the results, horses in both treatment groups had significantly higher squamous gastric ulceration scores (in the upper region of the stomach) than the horses in the control group at Day 10. Similarly, both treatments resulted in significantly more ulcers in the glandular (bottom) portion of the stomach than in controls. However, said Richardson, on Day 10 horses receiving phenylbutazone had significantly more severe glandular ulcers than the horses given firocoxib.
She also noted that fecal MPO increased with both treatments but was only statistically significant in the horses given phenylbutazone. Because MPO is derived from neutrophils, the type of white blood cell involved in NSAID-induced intestinal injury in other species, these results suggest that GI disease caused by administration of NSAIDs is neutrophil-driven in the horse, said Richardson.
So while both phenylbutazone and firocoxib induced GI inflammation and injury, glandular ulcers were more severe and fecal MPO levels greater in the horses receiving phenylbutazone. These results suggest that firocoxib’s effects were less severe, said Richardson.
Please follow the link above for the full article which contains additional information on NSAIDs.
#equine science#equine health#equine welfare#equine med#musculoskeletal#nsaid#equine gastric ulcers#stomach ulcers
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Polyclonal Antibody to Human Myeloperoxidase
Polyclonal Antibody to Human Myeloperoxidase Catalog number: B2018825 Lot number: Batch Dependent Expiration Date: Batch dependent Amount: 0.25 mL Molecular Weight or Concentration: N/A Supplied as: Powder Applications: a molecular tool for various biochemical applications Storage: 2-8°C Keywords: Polyclonal Antibody to Human Myeloperoxidase Grade: Biotechnology grade. All products are highly…
0 notes
Text
7 Obat Termahal Sejagat, Ada yang Tembus Rp60 Miliar!

Dalam beberapa tahun terakhir, perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan dan teknologi di bidang kesehatan telah menghasilkan obat-obatan yang tidak hanya inovatif, tetapi juga sangat mahal. Biaya tinggi ini sering kali disebabkan oleh proses penelitian yang panjang, pengembangan yang rumit, dan biaya produksi yang signifikan. Beberapa obat bahkan menembus harga ratusan ribu hingga miliaran rupiah. Berikut adalah tujuh obat termahal di dunia yang mencengangkan, dengan beberapa di antaranya mencapai harga di atas Rp60 miliar.
1. Zolgensma (Nusinersena)
Zolgensma adalah obat yang digunakan untuk mengobati spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), penyakit genetik yang mempengaruhi saraf dan otot. Obat ini dirancang untuk memberikan terapi gen dengan cara mengisi gen SMN1 yang hilang atau tidak berfungsi pada pasien. Zolgensma diproduksi oleh Novartis dan menjadi salah satu obat termahal di dunia, dengan harga sekitar USD 2.125.000 atau sekitar Rp32 miliar per dosis.
Proses pengembangan Zolgensma memakan waktu lebih dari satu dekade dan melibatkan riset yang mendalam. Harga tinggi obat ini dipengaruhi oleh kompleksitas produksi dan pentingnya terapi yang diberikan bagi pasien SMA, di mana pengobatan dini dapat mencegah perkembangan penyakit yang parah.
2. Luxturna (Voretigene Neparvovec)
Luxturna adalah obat terapi gen yang digunakan untuk mengobati penyakit mata genetik yang menyebabkan kebutaan, seperti retinitis pigmentosa. Obat ini juga memerlukan prosedur injeksi ke dalam mata dan dikembangkan oleh Spark Therapeutics. Harganya diperkirakan sekitar USD 850.000 atau sekitar Rp12,8 miliar per pasien.
Luxturna bekerja dengan mengantarkan salinan gen yang berfungsi ke sel-sel retina, memberikan harapan baru bagi pasien yang sebelumnya tidak memiliki pilihan pengobatan. Meskipun harga tinggi, efektivitas Luxturna dalam memperbaiki penglihatan pasien sangat signifikan, sehingga banyak yang menganggapnya sebagai investasi berharga dalam kesehatan mata.
3. Actimmune (Interferon gamma-1b)
Actimmune adalah obat yang digunakan untuk mengobati penyakit langka seperti osteopetrosis dan chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Obat ini bekerja dengan merangsang sistem kekebalan tubuh untuk melawan infeksi. Harga Actimmune bisa mencapai USD 500.000 atau sekitar Rp7,5 miliar per tahun.
Meskipun harga tersebut terlihat tinggi, bagi pasien dengan penyakit langka yang memerlukan perawatan khusus, biaya ini dapat dianggap wajar jika dibandingkan dengan potensi kualitas hidup yang diperoleh. Keberhasilan Actimmune dalam meningkatkan sistem kekebalan tubuh telah membantu banyak pasien dalam menghadapi tantangan penyakit langka.
4. Haffner's Syndrome (Myeloperoxidase deficiency)
Obat yang digunakan untuk mengobati Haffner's Syndrome, sebuah kondisi genetik langka, juga termasuk dalam daftar obat termahal. Biaya perawatan tahunan untuk pasien dengan Haffner's Syndrome bisa mencapai USD 450.000 atau sekitar Rp6,7 miliar.
Penyakit ini mempengaruhi kemampuan tubuh untuk memproduksi enzim myeloperoxidase, yang berfungsi dalam memerangi infeksi. Pasien yang mengalami kondisi ini sangat rentan terhadap infeksi serius, sehingga memerlukan pengobatan yang intensif dan teratur.
5. Soliris (Eculizumab)
Soliris adalah obat yang digunakan untuk mengobati dua penyakit autoimun langka: paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) dan atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS). Dikenal sebagai salah satu obat termahal di dunia, harganya mencapai USD 500.000 atau sekitar Rp7,5 miliar per tahun.
Soliris bekerja dengan menghambat sistem kekebalan tubuh yang berlebihan, sehingga mengurangi risiko komplikasi dari penyakit ini. Meskipun biaya tinggi, Soliris menawarkan harapan bagi pasien yang menderita penyakit autoimun langka yang dapat berakibat fatal.
6. Kymriah (Tisagenlecleucel)
Kymriah adalah terapi sel CAR-T yang digunakan untuk mengobati kanker darah, seperti leukemia limfoblastik akut. Proses pembuatan Kymriah melibatkan pengambilan sel-sel darah pasien, kemudian memodifikasinya di laboratorium untuk meningkatkan kemampuan melawan kanker. Harganya mencapai USD 373.000 atau sekitar Rp5,5 miliar.
Terapi ini memberikan harapan baru bagi pasien kanker yang tidak merespons pengobatan lain. Meskipun biayanya tinggi, keberhasilan Kymriah dalam menyelamatkan nyawa pasien membuatnya sangat berharga.
7. Danyelza (Naxitamab)
Danyelza adalah obat terbaru yang digunakan untuk mengobati neuroblastoma, jenis kanker yang umum terjadi pada anak-anak. Dengan harga sekitar USD 1.200.000 atau sekitar Rp18 miliar, Danyelza menawarkan solusi inovatif dalam pengobatan kanker pada anak.
Obat ini bekerja dengan menargetkan sel-sel kanker dan merangsang sistem kekebalan tubuh untuk melawannya. Meskipun harganya sangat tinggi, potensi Danyelza untuk meningkatkan harapan hidup pasien kanker anak sangat signifikan.
Faktor Penyebab Tingginya Harga Obat
Beberapa faktor yang menyebabkan tingginya harga obat-obatan ini antara lain:
Biaya Riset dan Pengembangan: Proses pengembangan obat memerlukan investasi yang sangat besar dalam penelitian dan pengujian klinis. Seringkali, hanya sedikit obat yang berhasil memasuki pasar setelah melewati tahap penelitian yang panjang.
Regulasi yang Ketat: Persetujuan dari badan regulasi seperti FDA memerlukan standar keamanan dan efektivitas yang tinggi. Hal ini membuat biaya produksi meningkat.
Pasar Terbatas: Beberapa obat hanya tersedia untuk penyakit langka yang mempengaruhi sedikit pasien. Dengan basis pasien yang kecil, harga obat harus cukup tinggi untuk menutupi biaya produksi dan pengembangan.
Inovasi Teknologi: Obat yang menggunakan teknologi canggih, seperti terapi gen atau terapi sel, biasanya memiliki biaya produksi yang lebih tinggi, sehingga mempengaruhi harga jual.
Kesimpulan
Obat-obatan termahal di dunia mencerminkan kemajuan luar biasa dalam bidang medis, tetapi juga menyoroti tantangan yang dihadapi dalam hal aksesibilitas dan biaya. Meskipun biaya tinggi dapat menyebabkan kekhawatiran di kalangan pasien dan penyedia layanan kesehatan, efektivitas dan inovasi yang ditawarkan oleh obat-obatan ini memberikan harapan baru bagi mereka yang menderita penyakit serius dan langka.
Penting bagi pemerintah, perusahaan farmasi, dan pemangku kepentingan lainnya untuk bekerja sama dalam menciptakan sistem kesehatan yang berkelanjutan dan terjangkau, sehingga semua pasien dapat memperoleh akses kepada pengobatan yang mereka butuhkan tanpa terbebani oleh biaya yang sangat tinggi. Diskusi mengenai harga obat dan regulasi yang ada harus terus dilakukan untuk memastikan bahwa kemajuan dalam penelitian dan pengembangan obat tidak hanya bermanfaat bagi segelintir orang, tetapi dapat diakses oleh semua lapisan masyarakat.
0 notes
Text
Tablets for sugar control |JRK's D-CO-D Tablets
JRK’s D-Co-D tablets, tablets for sugar control scientifically proven to reduce the co-morbidities of diabetes. JRK’s D-Co-D tablets, tablets for sugar control protects vital organsfrom high blood glucose. These tablets for sugar control reduces the risk of co-morbidities and multiple organ dysfunctions. Tablets for sugar controlboosts first line of immunity by improving the phagocytosis thus prevents infections. DCOD tablets decrease myeloperoxidase enzyme thereby reduce the chance of inflammatory and cardiovascular diseases.JRK’s D-Co-D tablets, tablets for sugar controltested on Liver cells, skeletal muscle cells, Nerve cells, pancreatic cells, Lipocytes, kidney cells and neuroblast cells. Did not affect any of the above organ cells –Safe for long term use.JRK’s D-Co-D tablets, tablets for sugar controlreduces alpha amylase, alpha glucosidase and thus control post prandial blood glucose levels.JRK’s D-Co-D tablets, tablets for sugar controlincreases Glucose utilization and metabolism. JRK’s D-Co-D tablets, tablets for sugar control suppress myeloperoxidase activity- protect from cardiac & inflammatory diseases. DCOD tablets boosts immunity and prevents infections.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Nanotechnology, A Promising Tool to Combat the Pitfalls of The Phenolic Transport across Blood- Brain Barrier-Juniper Publishers

Abstract
The growing interest in natural polyphenols during the last years is aimed to identify new applications to these natural compounds of biological interest, as well as to design new uses in the field of health care. In this regard, to date, it has been demonstrated a wide range of positive health effects for phenolic compounds, being most research studies focused on the anti-oxidant, anti- inflammatory, anti-microbial, and anti-aging effects, while the biological potential demonstrated for these compounds have led to search for specific applications in the field of neurodegenerative diseases. Indeed, brain related diseases factors like antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, as well as proteins defibrillation and mitochondrial regulation have been pointed as the advantages of the use of all kind of phenolics. However, the transport of these molecules to can be prevented by specific biological barriers developed to protect these sensible structures. In this short review, the effects of phenolic compounds described in nervous tissues and cells, has been studied, as well as the downsides of their use, and how nanotechnology can help to provide new valuable alternatives to get enhanced biological impacts despite de constraint represented by the blood-brain barrier.
Keywords: Phenolic compounds; Nervous system; Blood-brain barriers; Bioavailability; Bassive transport; Bioactivity
Introduction
For several decades, it has been experienced a growing interest in natural phenolic compounds as bioactive molecules present in edible and non-edible plant material with potential effects on human health. The main goal of this trend is to find new applications to these natural compounds of biological interest and design new uses for them in the field of medical treatments [1-3]. Indeed, to date it has been demonstrated a wide range of positive health effects for phenolic compounds, being most research studies focused on the anti-oxidant, antiinflammatory, anti-microbial, and anti-aging effects. In the last years, the biological potential demonstrated for phenolic compounds have led to the interest in assessing their effects in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases [2-6].
Discussion
Proved facts on the neuroprotective effects of phenolic compounds
Several studies have contributed to establish a link between phenolic compounds and neuroprotection, revealing their potential against aging and neurodegenerative diseases [4,5]. In this regard, it is required to notice that there are innumerous possible patho physiological mechanisms related with neurodegeneration, even though the major pathways already identified are neuro- inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and protein misfolding, all of them susceptible to be affected by the presence of polyphenol [4,7,8]. However, despite the plethora of mechanisms responsible for neurodegeneration, oxidative damage to neuron molecules, and decreased cellular antioxidant species, such as glutathione in the brain, are major aspects of most common neurological diseases [4,8,9]. For instance, dopaminergic neurons of the central nervous system are susceptible to oxidative stress, turning oxidative stress into a risk factor for nigral substance degeneration. In this frame, polyphenols are recognized on their antioxidant particularities, while their presence in neurons has been related with lower levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [8]. However, radical scavenging is not the only biological activity of phenolics, which besides working as antioxidants, are also competent to increase the activity and expression of enzymes with antioxidant power. Hence, the endogenous glutathione system, one of the most important antioxidant defense of the organism, can also be boosted by polyphenols, according to previous works in vitro and in vivo [8-10]. In addition, polyphenols also contribute to diminish the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines in brain therapeutic models, such as IL-1β, TNF-α, 1L-4, 1L-6, and 1L-10 [10-12]. Resveratrol has been shown capable to decrease the level of nitrite and the expression of myeloperoxidase, an enzyme that, during microglial respiration, produces hypochlorous acid and tyrosyl radical that are cytotoxic to pathogens, but also to cells [13] Some polyphenols have shown the ability to prevent protein fibrillization, by promoting the clearance of aggregates and oligomers, thus stimulating the cell autophagic pathways [8] which proves once more their neuroprotective actions. Regarding this, for instance, phenolic compounds from green tea have been characterized on their fibril-destabilizing properties in neurological diseases. Hence, resorting to several in vitro studies, it has been demonstrated that epigallocatechin gallate and quercetin can prevent growth and aggregation of amyloidogenic a-synuclein and reduce their levels in the hippocampus and the striatum [14-16]. Mitochondrial disturbances can also be responsible for the damage observed in neurological diseases. Indeed, the loss of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential triggers mechanisms of apoptosis in dopaminergic neurons. In this sense, polyphenols have been noticed as competent to enhance mitochondrial function by increasing the ATP production, while lower ROS and lactate production [17,18].
Constraints to the biological action of polyphenols in the nervous tissues
Despite all the studies aimed at characterizing in vitro and in vivo the benefits of phenolic compounds, there are several biological limits that interfere with the beneficial properties of these compounds, preventing the direct extrapolation of the results retrieved, so far, on biological activity to the pathophysiology of the nervous system [19]. One of the main obstacle for the biological action of phenolics in cells is their bioavailability. In this regard, the amount of phenolic compounds that reaches the cells is conditioned by the physiochemical properties of the compounds, their interaction with food matrix, and the response to the gastrointestinal tract conditions, which means that in most cases, the concentration available is significantly lower to that administrated and, even, to that tested upon in vitro characterizations [8,12,20]. Moreover, a high proportion of phenolic compounds are esterified in glycoside or polymeric forms. This entails that they are poorly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, rapidly metabolized upon phase I and II metabolism, and excreted by both urine and bile [4,12,21,22]. This implies that, since the phenolic compounds bioactivity is mostly executed by their metabolites, as a result of the modifications triggered upon the gastrointestinal digestion, it could appear metabolites less effective as antioxidants than the original compounds [23,24]. Despite the evident effect of the factors discussed above, the main obstacle to take advantage of the biological potential of polyphenolic compounds in the nervous system is the final concentrations reached in the cells that for most compounds is not sufficient to trigger operative reactions capable to restore physiological condition of the nervous cells [4]. This is mainly due to the barriers existent between the central nervous system and the environments surrounding it [25]. In this concern, the most selective barrier is represented by the blood- brain barrier that constitutes a dynamic interface between the peripheral tissues and the central nervous system. Blood- brain barrier maintains normal brain function, preserving the homeostatic conditions for nervous cells, required to work appropriately and also shield them against invading organisms and damaging elements [26-28]. This barrier is primarily constituted of endothelial cells connected by adherent tight junctions and functions as a physical, metabolic/enzymatic, transport, and immunological barriers [25,27].
The main difficulties that the phenolic compounds find to cross to the blood-brain barrier are the endothelium of brain microvessles and multidrug resistance-associated proteins. Despite this, some phenolic compounds, such as anthocyanins and curcumin, are able to pass through in a lipophilicity- dependent way, while others cross the blood-brain barrier by a mechanism of phosphorylation/dephosphorylation that regulate their passage (quercetin), but the mechanisms of transport into the blood-brain barrier are still relatively unknown [4,29] and the administration of compounds of interest to develop their biological action in these cells deserve to be explored towards the description of new alternatives.
Nanotechnology contribution to bioavailability of phenolic compounds in brain cells
The drawbacks drawn related to polyphenols bioavailability in cells of the central nervous system led to an interesting field of studies to find new ways to overcome those pitfalls and thus, to take advantage of the biological properties of phenolic compounds. Nanotechnology seems to be a valuable contributor to give response to these constraints, and more specifically nanoparticles. These are promising and versatile delivery systems to transport compounds into remote areas of the body, like the brain [25-27]. Usually nanoparticles size range between 1 and 100nm and can have a natural or synthetic origin [25] Synthetic nanoparticles are manufactured using two basic methods: top-down and bottom-up. The first consists in size- reduction by mechanical processes to shrunk big materials to nano-scale, while the second one consists in the aggregation of diverse nanoparticles [18]. Among the different materials used to obtain nanoparticles it can be stressed poly (ethylenimine), poly (alkylcanonaacrylates) poly (amidoamine) dendrimers, poly (s-caprolactone), poly (lactic-co- glycolic acid), polyesters (poly(lactic acid), and inorganic materials like gold and silica [18,25-29].
The commodities and the nanoparticles obtained from them must be nontoxic, biodegradable, and biocompatible, be featured by a prolonged blood circulation time, and be stable, avoiding aggregation and dissociation [18]. These carriers can transport compounds by adsorbing, entrapping or bounding covalently to them [30,31]. The properties of nanoparticles make them a promising system to deliver biologically active compounds into brain, due to the possibility of modifying size, shape, hydrophobicity, surface charge, chemistry, and coating. In this connection, addressing appropriately these features, according to the characteristics of the bioactive molecule and the target tissue were their activity is desired can contribute to enhance the transport of phenolic compounds to the brain and thus, to improve their stability, while circulating, controlling the release of the compound through the blood-brain barrier [25,33].
Nanoparticles improve the solubility of phenolics by encapsulating them, and also protect the compounds from degradation in he gastrointestinal tract. Besides that, and maybe the most important feature of including polyphenols in nanoparticles is that they are able to enhance the absorption of the phenolic compound in brain cells either by disrupting the tight junction of the blood-brain barrier or promote the direct intake by endocytosis [18,25]. Regardless of all that some factors still need to be further studied to make nanoparticles even more helpful in the transport of bioactive compounds to brain cells. Factors like pH, ions, and enzymes, among others, can negatively modulate the properties of the nanoparticles and their delivery as well.
Conclusion
Phenolic compounds from all sorts of plants have been long studied regarding their potential use as bioactive agents. In brain related diseases there are a large amount of evidence that points towards the several potential uses of phenolic compounds as treatments for those diseases. Factors like antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, as well as proteins defibrillation and mitochondrial regulation, have been pointed as the advantages of the use of all kind of phenolics. Otherwise, the transport of those molecules to cells and tissues, where they can be helpful, can be very complicated or even impossible and, in most cases, this situation is responsible for the loss of important properties of metabolites from phenolic compounds. Nano carriers present themselves as an innovating solution that can help to diminish in a great extent the pitfall of phenolic compounds bioavailability, specially concerning the central nervous system. Thus, although nanotechnology seems to contribute to promising solutions, additional studies should be made in order to make nano carriers even more resistant and suitable for the transport of a growing number of phenolic compounds, which might be helpful to combat neurodegenerative disabling illness.
Acknowledgement
This work was partisally supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness (MEIC) through Research Projects AGL2016-75332-C2-1-R and RTC-201658362. RDP was sponsored by a Postdoctoral Contract (Juan de la Cierva de Incorporation ICJI2015- 25373) from the Ministry of Economy, Industry, and Competitiveness of Spain. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
To read more articles in JOJ Sciences
Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojs/index.php
For more Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers
Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/journals.php
1 note
·
View note
Text
Überblick über die Rolle von Neutrophilen bei systemischen Autoimmun- und autoinflammatorischen Erkrankungen In einem aktuellen Nature Reviews Immunologie In einer Zeitschriftenstudie bewerten Forscher die Rolle von extrazellulären Neutrophilenfallen (NETs) bei systemischen Autoimmun- und autoinflammatorischen Erkrankungen. Lernen: Extrazelluläre Neutrophilenfallen bei systemischen Autoimmun- und autoinflammatorischen Erkrankungen. Bildquelle: Luca9257 / Shutterstock.com Hintergrund Neuere Forschungen haben gezeigt, dass Neutrophile, insbesondere NETs, die bei Aktivieru... #Adenosin #Adenosin_Deaminase_Mangel #Akne #Antikörper #Apoptose #Arginin #Arthritis #Autoimmunerkrankung #Autoimmunität #B_Zelle #Behinderung #BLUT #Blutgefäße #Chemikalien #Citrullin #DNA #EIWEISS #Entzündung #Ex_vivo #Forschung #Gefäßsystem #Gen #Genexpression #Haut #Herz #Histone #Immunologie #Immunsystem #Interferon #Interleukin #Intrazellulär #Kinder #Lunge #Lupus #Lupus_erythematodes #Mutation #Myeloperoxidase #Nekrose #Neutrophile #Peptide #Pyoderma_Gangraenosum #Rezeptor #Rheumatoide_Arthritis #Stoffwechsel #Syndrom #Systemische_Autoimmunerkrankung #Systemischer_Lupus_erythematodes #tumor #Tumornekrosefaktor #Vaskulitis #Zelle #Zelltod #Zytokine
#DiseaseInfection_News#Medical_Research_News#Medical_Science_News#Molecular_Structural_Biology#News#Adenosin#Adenosin_Deaminase_Mangel#Akne#Antikörper#Apoptose#Arginin#Arthritis#Autoimmunerkrankung#Autoimmunität#B_Zelle#Behinderung#BLUT#Blutgefäße#Chemikalien#Citrullin#DNA#EIWEISS#Entzündung#Ex_vivo#Forschung#Gefäßsystem#Gen#Genexpression#Haut#Herz
0 notes
Link
Apocynin Is Not an Inhibitor of Vascular NADPH Oxidases but an Antioxidant
Abstract
A large body of literature suggest that vascular reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidases are important sources of reactive oxygen species. Many studies, however, relied on data obtained with the inhibitor apocynin (4′-hydroxy-3′methoxyacetophenone). Because the mode of action of apocynin, however, is elusive, we determined its mechanism of inhibition on vascular NADPH oxidases. In HEK293 cells overexpressing NADPH oxidase isoforms (Nox1, Nox2, or Nox4), apocynin failed to inhibit superoxide anion generation detected by lucigenin chemiluminescence. In contrast, apocynin interfered with the detection of reactive oxygen species in assay systems selective for hydrogen peroxide or hydroxyl radicals. Importantly, apocynin interfered directly with the detection of peroxides but not superoxide, if generated by xanthine/xanthine oxidase or nonenzymatic systems. In leukocytes, apocynin is a prodrug that is activated by myeloperoxidase, a process that results in the formation of apocynin dimers. Endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells failed to form these dimers and, therefore, are not able to activate apocynin. Dimer formation was, however, observed in Nox-overexpressing HEK293 cells when myeloperoxidase was supplemented. As a consequence, apocynin should only inhibit NADPH oxidase in leukocytes, whereas in vascular cells, the compound could act as an antioxidant. Indeed, in vascular smooth muscle cells, the activation of the redox-sensitive kinases p38-mitogen-activate protein kinase, Akt, and extracellular signal–regulated kinase 1/2 by hydrogen peroxide and by the intracellular radical generator menadione was prevented in the presence of apocynin. These observations indicate that apocynin predominantly acts as an antioxidant in endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells and should not be used as an NADPH oxidase inhibitor in vascular systems.
#Apocynin#family medicine#integrative medicine#herbal medicine#cardiology#cardiovascular disease#free radicals#anti-inflammatory#anti-aging#fav#print this off later#immunology#antioxidants#acetovanillone
6 notes
·
View notes