#metropoliti
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
About the entanglement of "science" and Empire. About geographic imaginaries. About how Empire appeals to and encourages children to participate in these scripts.
Was checking out this recent thing, from scavengedluxury's beloved series of posts looking at the archive of the Budapest Municipal Photography Company.

The caption reads: "Toys and board games, 1940."
And I think the text on the game-box in the back says something like "the whole world is yours", maybe?
(The use of appeals to science/progress in imperial narratives probably already well-known to many, especially for those familiar with Victorian era, Edwardian era, Gilded Age, early twentieth century, etc., in US and Europe.)
And was struck, because I had also recently gone looking through nemfrog's posts about the often-strange imagery of children's material in late nineteenth- and early twentieth-century US/Europe. And was disturbed/intrigued by this thing:
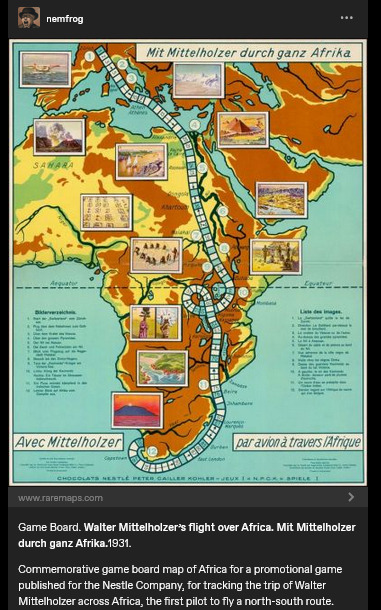
Caption here reads: "Game Board. Walter Mittelholzer's flight over Africa. [...] 1931. Commemorative game board map of Africa for a promotional game published for the N*stle Company, for tracking the trip of Walter Mittelholzer across Africa, the first pilot to fly a north-south route."
Hmm.
"Africa is for your consumption and pleasure! A special game celebrating German achievement, brought to you by the N*stle Company!"
1930s-era German national aspirations in Africa. A company which, in the preceding decade, had shifted focus to expand its cacao production (which would be dependent on tropical plantations). Adventure, excitement, knowledge, science, engineering prowess, etc. For kids!
Another, from a couple decades earlier, this time British.

Caption reads: "The "World's globe circler." A game board based on Nellie Bly's travels. 1890." At center, a trumpet, and a proclamation: "ALL RECORDS BROKEN".
Same year that the United States "closed the frontier" and conquered "the Wild West" (the massacre at Wounded Knee happened in December 1890). A couple years later, the US annexed Hawai'i; by decade's end, the US military was in both Cuba and the Philippines. The Scramble for Africa was taking place. At the time, Britain especially already had a culture of "travel writing" or "travel fiction" or whatever we want to call it, wherein domestic residents of the metropole back home could read about travel, tourism, expeditions, adventures, etc. on the peripheries of the Empire. Concurrent with the advent of popular novels, magazines, mass-market print media, etc. Intrepid explorers rescuing Indigenous peoples from their own backwardness. Many tales of exotic allure set in South Asia. Heroic white hunters taking down scary tigers. Elegant Englishwomen sipping tea in the shade of an umbrella, giggling at the elephants, the local customs, the strange sights. Orientalism, tropicality, othering.
I'd lately been looking at a lot of work on race/racism and imperative-of-empire in British scientific and pop-sci literature, especially involving South and Southeast Asia. (From scholars like Varun Sharma, Rohan Deb Roy, Ezra Rashkow, Jonathan Saha, Pratik Chakrabarti.) But I'd also lately been looking at Mashid Mayar's work, which I think closely suits this kinda thing with the board games. Some of her publications:
"From Tools to Toys: American Dissected Maps and Geographic Knowledge at the Turn of the Twentieth Century". In: Knowledge Landscapes North America, edited by Kloeckner et al., 2016.
"What on Earth! Slated Globes, School Geography and Imperial Pedagogy". European Journal of American Studies 16, number 3, Summer 2020.
Citizens and Rulers of the World: The American Child and the Cartographic Pedagogies of Empire, 2022.
Discussing her book, Mayar was interviewed by LA Review of Books in 2022. She says:
[Quote.] Growing up at the turn of the 20th century, for many American children, also meant learning to view the world through the lens of "home geography." [...] [T]hey inevitably responded to the transnational whims of an empire that had stretched its dominion across the globe [recent forays into Panama, Cuba, Hawai'i, the Philippines] [...]. [W]hite, well-to-do, literate American children [...] learned how to identify and imagine “homes” on the map of the world. [...] [T]he cognitive maps children developed, to which we have access through the scant archival records they left behind (i.e., geographical puzzles they designed and printed in juvenile periodicals) [...] mixed nativism and the logic of colonization with playful, appropriative scalar confusion, and an intimate, often unquestioned sense of belonging to the global expanse of an empire [...]. Dissected maps - that is, maps mounted on cardboard or wood and then cut into smaller pieces that children were to put back together - are a generative example of the ways imperial pedagogy [...] found its place outside formal education, in children's lives outside the classroom. [...] [W]ell before having been adopted as playthings in the United States, dissected maps had been designed to entertain and teach the children of King George III about the global spatial affairs of the British Empire. […] [J]uvenile periodicals of the time printed child-made geographical puzzles [...]. [I]t was their assumption that "(un)charted," non-American spaces (both inside and outside the national borders) sought legibility as potential homes, [...] and that, if they did not do so, they were bound to recede into ruin/"savagery," meaning that it would become the colonizers' responsibility/burden to "restore" them [...]. [E]mpires learn from and owe to childhood in their attempts at survival and growth over generations [...]. [These] "multigenerational power constellations" [...] survived, by making accessible pedagogical scripts that children of the white and wealthy could learn from and appropriate as times changed [...]. [End quote.] Source: Words of Mashid Mayar, as transcribed in an interviewed conducted and published by M. Buna. "Children's Maps of the American Empire: A Conversation with Mashid Mayar". LA Review of Books. 11 July 2022.
Some other stuff I was recently looking at, specifically about European (especially German) geographic imaginaries of globe-as-playground:
The Play World: Toys, Texts, and the Transatlantic German Childhood (Patricia Anne Simpson, 2020) /// "19th-Century Board Game Offers a Tour of the German Colonies" (Sarah Zabrodski, 2016) /// Advertising Empire: Race and Visual Culture in Imperial Germany (David Ciarlo, 2011) /// Learning Empire: Globalization and the German Quest for World Status, 1875-1919 (Erik Grimmer-Solem, 2019) /// “Ruling Africa: Science as Sovereignty in the German Colonial Empire and Its Aftermath” (Andrew Zimmerman. In: German Colonialism in a Global Age, 2014) /// "Exotic Education: Writing Empire for German Boys and Girls, 1884-1914". (Jeffrey Bowersox. In: German Colonialism and National Identity, 2017) /// Raising Germans in the Age of Empire: Youth and Colonial Culture, 1871-1914 (Jeff Bowersox, 2013) /// "[Translation:] (Educating Modernism: A Trade-Specific Portrait of the German Toy Industry in the Developing Mass-Market Society)" (Heike Hoffmann, PhD dissertation, Tubingen, 2000) /// Home and Harem: Nature, Gender, Empire, and the Cultures of Travel (Inderpal Grewal, 1996) /// "'Le rix d'Indochine' at the French Table: Representation of Food, Race and the Vietnamese in a Colonial-Era Board Game" (Elizabeth Collins, 2021) /// "The Beast in a Box: Playing with Empire in Early Nineteenth-Century Britain" (Romita Ray, 2006) /// Playing Oppression: The Legacy of Conquest and Empire in Colonialist Board Games (Mary Flanagan and Mikael Jakobsson, 2023)
#mashid mayar book is useful also the Playing Oppression book is open access online if you want#in her article on slated globes mayar also mentions how european maps by 1890s provoked a sort of replete homogenous filling in of globe#where european metropole thought of itself as having sufficiently mapped the planet by now knit into neat web of interimperial trade#and so european apparent knowledge of globe provided apparently enlightened position of educating or subjugating the masses#whereas US at time was more interested in remapping at their discretion#a thing which relates to what we were talking about in posts earlier today where elizabeth deloughrey describes twentieth century US#and its aerial photographic and satellite perspectives especially of Oceania and Pacific as if it now understood the totality of the planet#ecologies#tidalectics#geographic imaginaries#mashid mayar
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hotel Metropole, 42nd Street and Broadway, New York, New York, 1909
333 notes
·
View notes
Text

Instagram
Remember her appreciation?
#Tait rhymes with hat#Good times#Outlander#Starfury Conventions#The Highlanders 7#Hilton Metropole#19-21 July 2024#Birmingham England#20 July 2024#Instagram
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Karácsonynak elment az esze! Azt állítja a Föld forog a nap körül!
62 notes
·
View notes
Text

just kiss me slow
#photography#analog#photographers on tumblr#la vie en rose#original photographers#analog photography#photooftheday#la vie est belle#original photography blog#photography on tumblr#la vita è bella#la vie boheme#la dolce vita#indie#retro#girly#vintage#bohostyle#bohemian#boho#bohochic#aesthetic#beograd#belgrade#tasmajdan#srbija#serbia#hotel#metropol#autumn
30 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Alice Brasser, “Metropole”, oil on canvas, 2022. Dutch artist based in Haarlem, the Netherlands.
#alice brasser#metropole#2022#oil on canvas#oil painting#painting#art#dutch artist#landscape#cityscape#metropolis#night city#grid#city lights#nightview#urban#blues#night sky#mountains#summer#contemporary art
17 notes
·
View notes
Text

Loretta Young and Tyrone Power in Cafe Metropole c.1937
#1937#tyrone power#loretta young#cafe metropole#actor#vintage actress#actress#classic actor#classic actress#vintage actors#hollywood#classic hollywood#golden age of hollywood#old hollywood glamour#vintage hollywood
20 notes
·
View notes
Photo
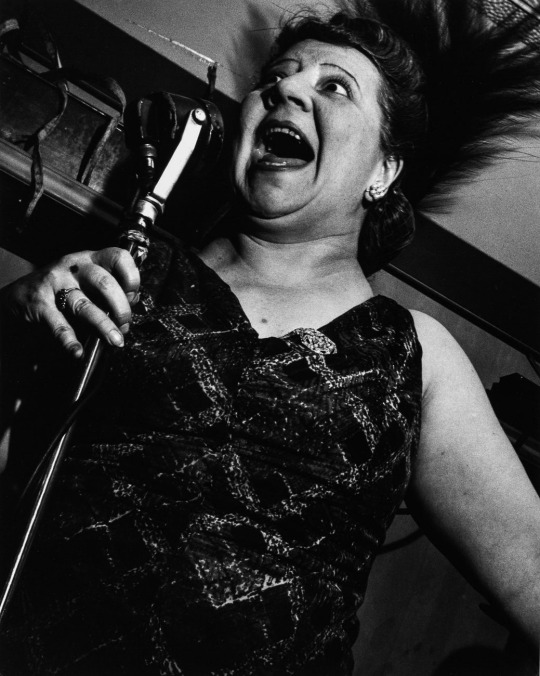

Lisette Model. Singer at the Cafe Metropol. New York. 1946
I Am Collective Memories • Follow me, — says Visual Ratatosk
#BW#Black and White#Preto e Branco#Noir et Blanc#黒と白#Schwarzweiß#retro#vintage#Lisette Model#Singer#Cafe Metropol#New York#1946#1940s#40s#portrait#肖像#画像#retrato#Porträt
35 notes
·
View notes
Photo
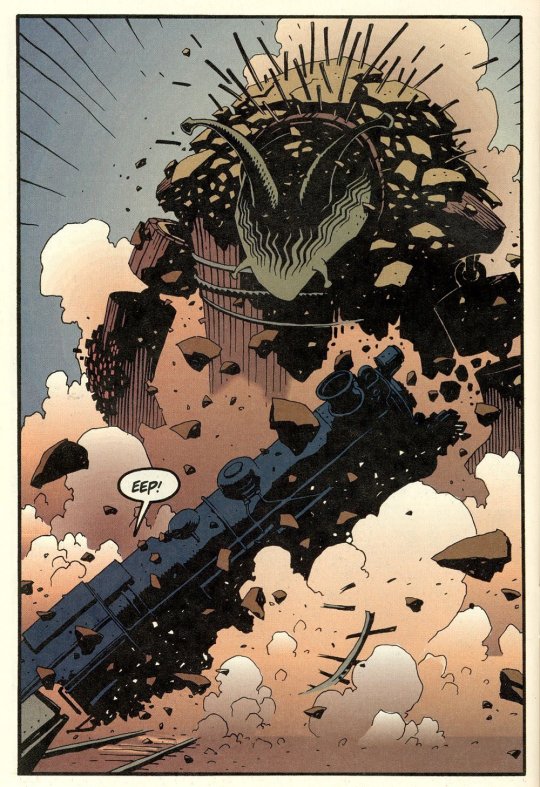










Eddy Current in “Playing With Coal” Written by Ted McKeever Art by Mike Mignola and Ted McKeever
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
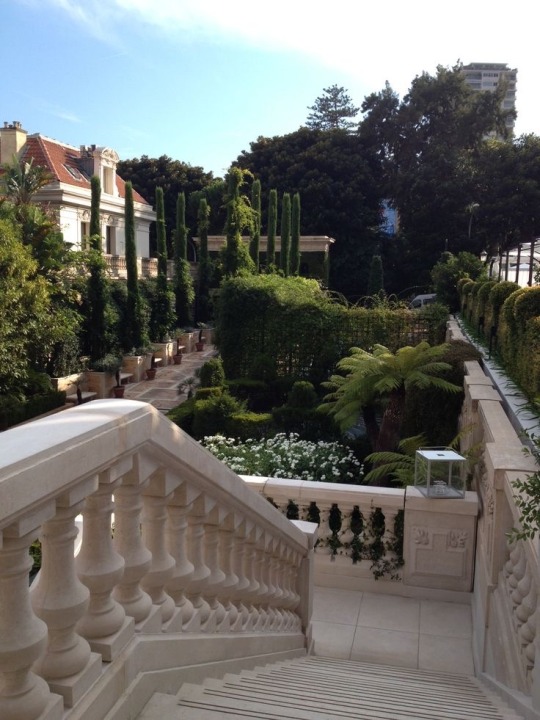

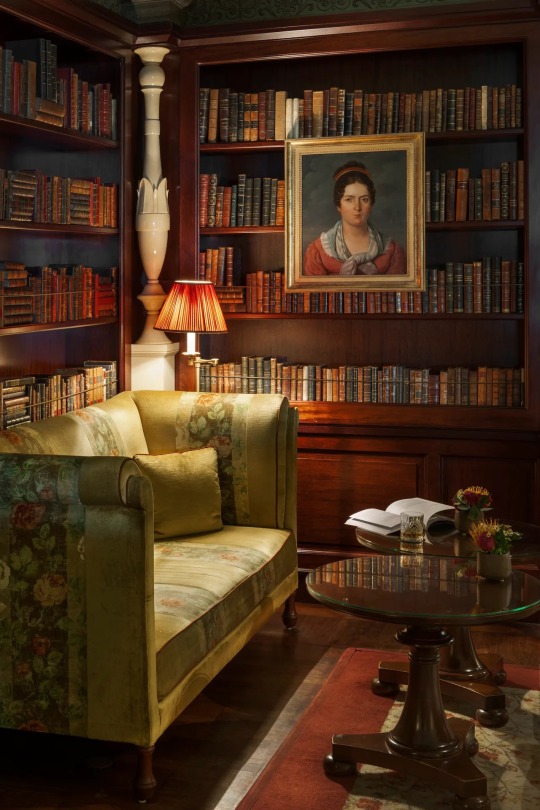
#hotel metropole#monte carlo#Monaco#cypress trees#greenery#land#steps#stairs#travel#traveling#riviera#French riviera
86 notes
·
View notes
Text




Twitter


Twitter
Remember not to blink…
#Tait rhymes with hat#Good times#Outlander#Starfury Conventions#The Highlanders 7#Hilton Metropole#19-21 July 2024#Birmingham England#20 July 2024#Twitter#Thanks sunsetmagic85
24 notes
·
View notes
Text




tyrone power playing around with his monocle while pretending to be a displaced russian prince in café metropole (1937)
#in turning these scenes into gifs i dropped some frames but the slightly stuttering sped-up effect suits the comedy#movies#1930s#cinema#screwball comedy#old hollywood#tyrone power#film#cafe metropole#comedy#gif#movie gifs#romance#romantic comedy#1930s movies
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finding Bo-Katan fans that despise Satine is so ???? Bo-Katan would hate your ass 😭
#bo katan kryze#satine kryze#like the entire point of bo katan’s character is she realizes how badly she fucked up and was brainwashed by a shitty fascist guy#She Helped Ruin Mandalore At It’s Peak and Helped Kill Her Sister#wanting her to stay some one dimensional villain is crazy#Pre Viszla wasnt a good leader or a good man?? He was violent and foolish and made deals with sith genociders#Bo Katan and Pre Viszla didn’t help metropolize Mandalore or make it a respectable planet/put on the galactic map#Satine did that#and she was The Only One to do that out of thousands of years for the Mandalorians#the only other person that accomplished this was fucking Tarre Viszla#that’s why Pre wanted to take her kingdom#because he Knew he would never be able to do that on his own and he knows it and it infuriates him
13 notes
·
View notes
Text











Frigorifero d'Arte
Dolce&Gabbana - Smeg, Metropol, Milano, 14-17 aprile 2016
Smeg Spa, Guastalla 2016, 18 pagine a colori, 15x21cm
euro 25,00
email if you want to buy [email protected]
Dolce&Gabbana e Smeg hanno unito le loro forze per un progetto unico che unisce le conoscenze come eccellenze del Made in Italy. Le capacità tecnologiche di Smeg si associano allo stile inconfondibile di Dolce&Gabbana. Il progetto si sviluppa sul frigorifero Fab 28, prodotto in 100 pezzi unici, ognuno dipinto a mano dagli artigiani Siciliani nello stile del Carretto Siciliano, ceramiche, pupi e molto altro. Una selezione di questi frigoriferi d’arte è stata presentata al Metropol a Milano durante il Salone Internazionale del Mobile 2016, che si è svolto dal 12 al 17 Aprile.
25/05/24
#Dolce&Gabbana#Smeg#frigorifero d'arte#Metropol Milano#Salone Mobile 2016#fashionbooksmilano#designbooksmilano
16 notes
·
View notes
Note
How would the food supply chain work for city states in in places like Ancient Greece and more recently, the Italian City States? Would they control agricultural land, or would they have to buy food from nearby (or perhaps not so nearby) agricultural regions? What measures would they take in times of war to avoid having their food supply cut off?
Great question!
To answer "How would the food supply chain work for city states," I would answer by answering your other question "Would they control agricultural land, or would they have to buy food from nearby (or perhaps not so nearby) agricultural regions?" by saying: it's both.
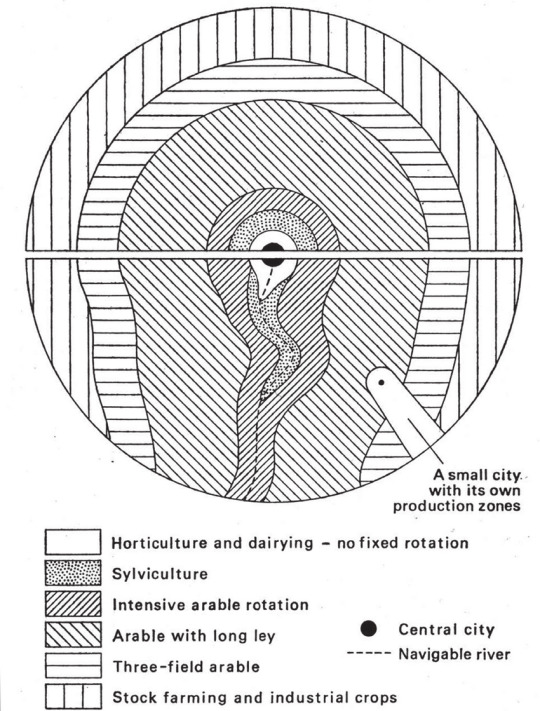
Paradigmatically, a city-state consists of a metropole (the city in question) and the periphery (subordinated lands and territories under the city's control). (Or metropolis and hinterland, if you prefer). To further break this down, the periphery consists of a mix of different lands, including both overseas colonies and tributaries, conquered (and thus lesser and weaker) city-states and their peripheries, and the agricultural hinterland around the metropole. To take just this last category, we can think of the relationship between Athens and Attica, Rome and Latium, Venice and the Mestre and Veneto (everyone always focuses on Venice's overseas empire, but it's rarely remembered that Venice at its height basically controlled all of northeastern Italy and fought Milan for northcentral and parts of northwestern Italy), or Florence and (eventually all of) Tuscany.
How far that agricultural hinterland extended beyond the city's walls depended a lot on transportation technology. Brett Devereaux has very good (but lengthy) explanations of the difficulties of overland grain trade here and here, but the TLDR is that, as a rough rule of thumb, "the price of grain doubles every hundred miles it is moved overland." Those kind of price increases aren't really affordable, so I think if you're looking for a rough rule of thumb, a hundred miles is probably a good maximum radius for an agricultural hinterland, whereas the minimum radius is probably around 7-12 miles (based on medieval urban regulations for agricultural markets), which was roughly how far a cart could travel in a day.
However, certain factors can change the effective radius of the hinterland:
The more and better roads you have, carts can move faster and come from more directions/places, which effectively expands that cart/day radius.
If the city is on a river (and this is one of the main reasons why most historic cities were on rivers, if they weren't on coasts), you can use river-barges to transport grain. Sail-barges could travel 14 miles an hour in good winds, and tow- or pole-barges could do 10-40 miles a day (depending on whether they were going upriver or downriver). Moreover, because of buoyancy, barges can carry much heavier loads than carts, which makes them much more eficient in transporting bulk goods like grain.
Finally, the population density and degree of urbanization matters, because it raises the possibility of making partial trips, because smaller population centers will act as local metropoles and more efficiently bring in grain from rural areas allowing for more efficient routes; also, higher density and urbanization allows for the creation of a network of granaries that allow you to store grain along the way so that you can make partial trips rather than covering the whole distance from the city to the very edge of the periphery.
However, the hinterland usually wasn't enough on its own to supply the city-state, but the same advantages of wind-speed and buoyancy also meant that a long-distance overseas grain trade was absolutely viable in both the Ancient and Medieval worlds. So for example, Greek city-states would draw on grain from southern France, southern Italy and Sicily, the Black Sea, and Anatolia; much of Rome's grain supply came from North Africa and Egypt; and so on. Moreover, as Fernand Braudel points out, the interconnected grain trade of the Mediterranean was the indispensable foundation for southern European urbanism from the Middle Ages through to the Early Modern period, and the geospatial dynamics of that system did not really change that much until the invention of the steam engine.

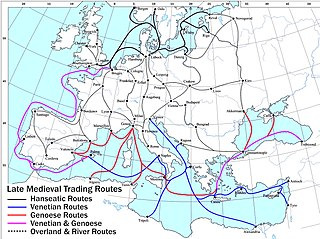
To answer your final question - "What measures would they take in times of war to avoid having their food supply cut off?" - it was usually by a mix of metropolis/hinterland logistics and long-distance trade. A well-organized city-state would have granaries set up both in the city and in the more urbanized areas of the periphery and would have contingency plans to harvest and transport as much grain as possible to the city to use as reserves in a time of crisis. (You'll note that this leaves the periphery in a really bad situation in times of crisis, and this prioritization of the metropole over the periphery is one of the main reasons why it sucked to be in the periphery, which is why there was so much competition over who got to be the metropole and why there were so many rebellions on the peirphery.)
At the same time, if the city-state had naval supremacy over its enemies, it could pretty much indefinitely hold out against its enemies as long as it could maintain a lifeline to the sea. This is why Athens was able to hold out against Sparta for so long during the Pelopennesian War, why Constantinople won so many of its sieges, and why Venice was able to take on most of Europe and still come out on top most of the time.
#history#ancient history#medieval history#renaissance history#city-states#metropole#periphery#metropolis#hinterland#logistics#economic history#medieval economics
65 notes
·
View notes
