#lets hope this also means the same successes for ukraine and they can liberate land
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Easter Greetings by the President of Ukraine

youtube
Great People of Great Ukraine!
Today we celebrate a significant holiday — the Resurrection of the Lord. Easter. Easter symbolizes the liberation of the human soul from the slavery of evil and darkness. It symbolizes the victory of goodness and justice, the victory of life over death.
We have been fighting for all of this for 802 days in a row. 802 days of freedom standing up to darkness, valor standing up to terror. 802 days of our resistance, which can be described by the words from the Gospel of John: "The light shines in the darkness, and the darkness has not overcome it…"
The exact same words are dedicated to one of the exhibitions at St. Sophia Cathedral, where I am now. Together, this exhibition and the other works by various Ukrainian artists convey a deep meaning. These are the icons on ammunition boxes. They are saturated with the smoke of our land and the spirit of our people. They are the symbols of great trials and great power that helps us overcome them. Each of these icons is like a divine manifestation, a proof that the heavens are with us, an answer to the question of why Ukrainians have withstood. It is because in the most difficult circumstances and in the darkest times we are able to create light. We can do it on boards scorched by fire and grief, that came from Ukrainian cities and villages exhausted by suffering. We can do this by combining the seemingly incompatible: the war and the Lord, by overcoming evil with faith, overcoming adversity with hope.
When taking a closer look at these icons, one can understand the feelings of our entire nation. It's a mirror that reflects our reality in times of war, the path we have already taken, and this Easter, and our entire present. This is what our amulets look like today. This is how we feel that God is protecting us through the hands of our warriors. This is how we see the protection of the heavenly forces, embodied in the Security and Defense Forces of Ukraine, every Ukrainian who devotes themself to the sacred cause of defending their native land from darkness and evil.
These icons bear the names of heroes who sacrificed their lives to protect us. They showed that Ukrainians kneel only to pray. And never do they kneel in front of invaders and occupiers.
The Bible teaches us to love our neighbor. And the present has shown us the true meaning of this word. When we support and help each other even hundreds of kilometers away from one another. We protect each other. We pray for each other. When we all have become closer to each other, we have become each other's neighbors. And our former neighbor, who was always making us take him for a brother, remains distant from us for centuries. They have broken all the commandments, coveted our house, and come to kill us. The world sees it.
God knows it. And we believe that there is a chevron with the Ukrainian flag on the shoulder of God. Therefore, with such an ally, life will definitely prevail over death.
As we overcome a common path and experience common pain, we are all united today by one common prayer. We pray for all our warriors who are celebrating Easter in the trenches and on the positions. We pray for our warriors of light, who restrain demons in all directions. We pray for those who keep another commandment in their lives: to defend Ukraine. We pray that they all come back alive.
We pray for all our civilians who work hard every day to strengthen our state and ensure that it successfully overcomes evil. We pray for those who live and work for this purpose.
We pray for all our children, for all the boys and girls brave far beyond their years, whose childhood was stolen from them by Russia, but who, despite everything, have not forgotten how to smile and believe in miracles.
We pray for all our mothers and fathers who were robbed of a happy, peaceful aging, and who, despite everything, are holding on and taking care of us.
We pray for all our cities and villages, that should feel the Lord's grace, not the constant terror of evil, and which have black clouds hanging over them, and bombs and missiles coming from those who belong in hell, not in the Ukrainian sky.
We pray for our lands and our people, whose spirit cannot be broken. And we remember the words written in St. Sophia Cathedral above the Oranta image, which came true in our lives: "God is in the midst of the city, and it will not be shaken. God will help it before dawn.”
Today, we are praying for all Ukrainians who are waiting for this dawn and will certainly see it. They will find peace, truth, and God, who will return to the scorched land, the land scarred with craters and trenches. He will return with peace, tranquility, and flowers instead of mines in the fields. He will return with children's laughter instead of the roar of an air alarm. The light that will return to all of our Lord-given land, to all the territories that are temporarily occupied by the devils. God will return to Mariupol. To the slag heaps and the seashores. It has always been so. It will definitely be so. I believe in this every day, especially on this glorious day in this glorious place, the history of which reminds us that neither the Horde invasion, nor the Nazi occupation, nor the Russian terror will be able to wipe us off the face of the Earth.
May the heavens strengthen our will in the battle against thralldom. May they give us courage for new achievements and wisdom to appreciate all that we have already gained. May they give us the strength to maintain unity, and give us unity to enhance our strength. May God grant eternal rest to all those who gave their lives for Ukraine and everlasting peace to their descendants, to all our children and grandchildren, and to all our future generations. They have the sacred right to know what a peaceful Easter in a peaceful Ukraine is.
Today we pray for it and we fight for it.
And the light shines in the darkness...
Happy Easter to all of you, dear Ukrainians!
Christ is risen!
He is risen indeed!
#what a touching and moving greeting#perfect words again after over 800 days of full-scale war#always amazes me how he and his team are able to (still) do this#the shade at russia and all the “russia is your neighbour” people...#also loved the images he painted with his words#god wears a ukraine chevron...#for some reason this easter greeting felt a lot like the on in 2022#maybe because the situation feels so weirdly similiar#lets hope this also means the same successes for ukraine and they can liberate land#i love how he always talks about the “we”#including all of his people#these videos are never about him and praising himself#theyre always about ukraine and its people in the end#a servant of his people i have said it before and i will say it till the end#this man breathes and lives for his country and his country alone#he is committed to it and his goal and only that#ready to sacrify himself if necessary to give them peace and a future#his people and all the kids of ukraine and with this also his kids#he may be small but he is one of the greatest#i always have to think back to that one interview where he said he wants to be of use#he wants to feel needed#he really wants to change something for the better#and he does#and he is needed so so much#even though this is the worst period of his time and he has to give up and sacrify the dearest thing to him#he probably finds his purpose in it#may he find peace and calm afterwards#surrounded by friends and family to grow old#Youtube#volodymyr zelensky
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Celtic Tiger - A Kaiserreich Ireland AAR Chapter 4: Soldiers Are We

“Being Irish, he had an abiding sense of tragedy, which sustained him through temporary periods of joy.” -W.B. Yeats
---
4 January 1939 - Economic Session of the Dail, Dublin, Ireland
Michael Collins had been debating initiatives to help smooth things over with the Ulster Unionists in the North. He had already revitalized plenty of the region’s industrial base, Harland and Wolff and the Short Brothers Aerospace PLC were employing plenty of people in Belfast, but the new American refugees had caused a great deal of cultural friction. The Unionist Party was never particularly quiet about their opinions on the state of affairs, but things were actively getting worse in Northern Ireland.
“We should expand the steel initiative.” Collins had addressed the Dail in the annual IEAA meeting. “Producing steel domestically will allow us to better manage supply shortages in the event that our trade is cut off, and domestic steel production will be invaluable to the factories and shipyards. Belfast has made a compelling point, they have a significant amount of steelworking knowledge and experience that would meet the target goals faster than they would in other regions. Belfast will reclaim her old mantle as our very own Steel City. The Open For Business Initiative has put us significantly in the black this past year, we can afford to invest heavily in steel production in Ulster along with zinc mining in our rural provinces. That should keep us in boom times and diversify our economic base, in case any post-Black Monday bubbles pop.”
Privately, Collins was more concerned with placating the Unionists. They had been complaining that Dublin was largely favored over Belfast, and that the Open for Business Initiative was an attempt to lure away the young workers of Northern Ireland to Dublin where they would lose their culture, and their voices, largely swallowed up by the Catholic voters. Violent crime was steadily rising in Belfast, the victims being either Catholics or American refugees, or reprisal attacks by Catholics. If there was a war, he could not reliably count on Ulster, even in the face of aggression from the Union. That was a pity. That had been the British strategy against Ireland, divide and conquer. Something would have to give very soon, no amount of economic bandaging was going to resolve the core tension within Ulster - they did not see themselves as part of an Irish Republic.
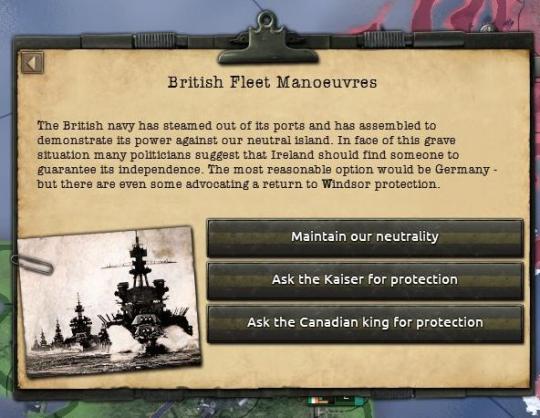
An aide burst into the meeting hall, causing a minor clamor and it took some time to restore order. The aide burst out breathlessly. “The Union, sir, they’re steaming out of port. The RMS Rebecca is going full-speed at our destroyers in the Irish Sea.” The poor fellow could barely complete a full sentence, his stammering professed an almost lack of belief in what was happening.
“Have they declared war?” Collins asked. The Union and Ireland did not have normalized relations, but that did not mean no information passed between the two countries. G2, the Directorate of Military Intelligence routinely monitored diplomatic intentions within Mosley’s government. Of all the espionage work performed by the Directorate, the Union accounted for almost fifty percent of its foreign operations, perhaps even more.
“No, sir. No word.”
What was frightening about Mosley’s intentions was how much sense it made to Collins. Mosley and Deat, despite their opposition to each other, had stressed the urgency of the revolution at their electoral campaigns, and had prosecuted an aggressive foreign policy to export syndicalism to the world. Both had turned inwards, Deat had been particularly violent in his purging of Blum and Gamelin, and they believed now that without dissent, they would not have naysayers and fifth columnists betraying their governments. By all accounts, their countries were ready to stand at the forefront of a global transformation. Yet the results were not successful. France and Britain had been completely humiliated in the Second American Civil War, with Reed about to face a war crimes tribunal. The Commune of France had threatened to annex Savoy only to have Switzerland seek German support and membership within the Reichspakt, and Deat had backed down. A defeat, militarily, within Europe, would be a disaster, evidence of endemic weakness of the Internationale’s new leadership.
Ireland would have been Mosley’s choice for a target. The stunning growth of the Irish economy and rise in the Irish standard of living would be an ideological foe, proof perhaps, that another way would be better. It was close to Britain and far from Mosley’s foes in Germany, Canada, and the United States. Its army and navy were tiny, compared to the Union’s. If they hurried, it could be a fait accompli no matter what any of the other great powers would do.
Collins thought for a moment. Ireland had benefited significantly from its neutrality between Entente and Reichspakt, not the least of which because it hadn’t been drawn into Germany’s wars as it had in Ukraine. The Open for Business Initiative never would have succeeded had Ireland been fully within the German sphere, and trade with the Entente had pacified the Anglophiles in the Centre Party. It was a natural pivot point that Ireland, as the middleman, could profit from. But an invasion of Ireland would see Ireland severely outnumbered in manpower and industrial capacity.
“Get ahold of Admiral O’Muiris, have him mine the Irish Sea. Conduct a full investigation of the radar stations and anti-aircraft batteries, I want them in perfect working condition yesterday. No more drills, our men must go immediately to battle positions. See what we can learn about any invasion plans, put G2 on it; if they’re planning to land, I want to know where so we can put enough guns to turn their landing craft to splinters.” Collins spoke as if it were 20 years ago, as if he was that same man, ready to fight the last time the British refused the demand of Irish independence. “Also, let’s see if there are others as willing to fight for Ireland as we are, start with the Kaiser.”
“And if he isn’t?”
“We look farther then. Look to Canada if you have to.”
“Are you going to invite the Windsors back in?”
“Not for a moment, but sometimes you must deal with devils. ”
---

25 January 1939 - Áras an Uachtaráin, Dublin, Ireland
It was the worst possible news.
The Kaiser had been unable to provide support for Ireland. The Vozhd was threatening the Baltic Duchy and White Ruthenia with his goal of one land for all the Russian people, and Wilhelm II would not abandon them for a western war, especially not one who was not in the Reichspakt. Canada too, could not commit to protecting Ireland, as they were engaged in a large-scale war in India with the Princely Federation. The United States was still deep into Reconstruction, President Garner would not deploy the badly-battered US Army into a foreign campaign when there were still cholera outbreaks and people dying of exposure. They were all perfectly reasonable excuses, but it led Collins to an inescapable conclusion: Ireland was on its own.
No doubt Mosley was jumping for joy. His ambitions would not be curtailed by the major anti-syndicalist factions. Protests certainly arose, even within the Union itself, but Mosley had been able to quell them with daily speeches against Ireland, lambasting the nation for its capitalist economic policies, its embargo of British goods, and the ethnic tensions between Ulster and the rest of Ireland, which Mosley alleged to be inspired by Stephen X and a precursor to the establishment of a Catholic theocratic state. He had harshly criticized Dan McKenna, accusing him and the Thunderbolts of war crimes, summary executions of British volunteers, and torture of Union prisoners; a pointed criticism given that McKenna was soon to return to the United States to give his testimony on Welfare Island and the atrocities that had taken place in the Mississippi Delta.
Collins had established the Mosley Gan Mosley program on 2RN in response, with Irish comedians regularly mocking Mosley’s wild proclamations and providing evidence against his more spurious claims. Collins ensured that the broadcasts were transmitted on a wide band toward the British Isles, focusing on Scotland and Wales as the Autonomists had chafed under Mosley’s centralization and embrace of British nationalism. Collins directed the program to emphasize Mosley’s speeches as expressions of old British imperialism in the hopes of creating public unrest at home. He wondered if it was working at all, or if he was simply trying to give everyone a laugh before the end.
The days after the German and Canadian refusal had been a tense form of limbo. The An tAerchór only had a few fighter planes with limited training, nothing compared to the British Republican Air Force. Sending up pilots would be risky, and casualties would be high. The An tSeirbhís Chabhlaigh was only slightly better off. The cruisers and destroyers were unlikely to match the British Navy in naval combat, but the submarines could pose a serious threat, and advances in naval mines would help cause further casualties among the landing craft. There was no getting around it, the Irish did not have the ability to contest the seas and so would be forced to repel the invasion with their ground forces. Civilians had been preparing for the coming disaster with air raid drills. Last-minute preparations for war were almost all that Collins could hope for, war would come, and Ireland would be alone.

“To ensure the liberation of the working class from the chains of oppressive and exploitative political and economic systems in the pursuit of global peace has been the compelling and continuing mission of the Socialist Union of Britain. To cultivate friendly relationships with nations likewise dedicated to the emancipation of those enslaved peoples and continue to progress toward the prosperity of mankind has always been the foundation of our foreign policy.
Wherefore the government of Michael Collins has engaged and continues to engage in an economic and political system within the Republic of Ireland that deprives the Irish Worker of the fruits of his labor and depends upon his continued shackling to the dictates of Capital in violation of the Internationale Declaration of Human Rights. In pursuit of its goals against the working class, the Irish Republican government has illegally prohibited the Irish Worker to establish a political party to advance their interests in violation of the 1925 Irish Constitution’s declaration of freedom of association by banning the Labour Party.
The Socialist Union of Britain, in defense of the Irish Worker, therefore demands the reformation of the Irish government to that of a Regional Provincial Workers Council to be directly administered under the oversight of the Trades Union Congress and in accordance with the laws and principles of the Socialist Union of Britain.”
Yet, instead of an immediate declaration of war, Mosley had elected to send words, much to Collins's surprise. For a moment, the Taioseach wondered why Mosley had even bothered, such was the extent of his demands. Perhaps it was to spare himself a war while the Internationale conserved their fighting strength for other targets, or perhaps it was a compromise asked by France. Maybe Mosley thought that Ireland would surrender and he could one-up Deat who had failed to have his ultimatum obeyed. As he had read the words, Collins had almost torn the paper in anger, and among the ministers he had invited to the closed session, he had seen similar expressions on their faces. They may have disagreed on everything else, but not on this.
“The Republic of Ireland will not submit to the colonial dictates of Oswald Mosley. We consider these demands completely illegitimate and a violation of the sovereignty of the independent Republic of Ireland and the government recognized by the Irish people. The Irish Republic is a free and independent nation, and shall not surrender to the British yoke that has for centuries defined the history of Ireland with cruelty and deprivation. We demand the unequivocal cessation of all hostilities against the Republic of Ireland, the immediate removal of British ships from Irish territorial waters, and the abrogation of all demands and claims against the island of Ireland. We also call on the Third Internationale to condemn such a demand and reconsider their relationship with an aggressive nation dedicated to a mission of subjugation.”
Collins was sure that would get Mosley’s anger up. His support of the Anti-Colonialist movement could not abide a direct challenge by naming him the colonist that his government had spoken so long about overthrowing. The Union fixated upon proving that they were not the old British Empire, that they were a modern, just triumph over backward authoritarianism. Questioning the Union’s place in the Internationale was sure to cause some stir as well. South America had long spoken against European colonialism, and Chile had considered itself a bastion of colonial liberation within the continent. Even though Chile had not joined the Internationale, their success in Latin America and their support of Britain and France’s mission had mattered greatly within left-wing intellectual circles; it was their testament against accusations of colonialism. Robbing Mosley of Chilean support could cause unrest at home and with other syndicalist nations like Burma, and perhaps end his expansionist ambitions on Ireland.

Collins was only half-right. None of the major syndicalist nations saw fit to criticize Mosley, neither Chile, nor Burma, nor France, nor the Socialist Republic of Italy in Torino had seen fit to condemn Mosley’s action, nor was any independent comment from the Third Syndicalist Internationale forthcoming, at least not any that Collins had seen or heard. What was true is that Mosley was furious. He had read the Irish response out loud in the Trade Union Congress, and had immediately moved for a declaration of war. It had not been a request, not that any would oppose him after his centralizing purges in ‘37 and ‘38, but the British people were fired up. The declaration of war had been delivered, and almost immediately, planes began flying overhead, and the air raid sirens gave their low bleak wail. For a moment, Collins was certain that he could hear them as a banshee’s wail, and wondered whose death warrant he had just signed.
---
28 March 1939 - Command Bunker, Dublin, Ireland
It had been months since the declaration of war, and bombing missions had been flown against Ireland daily. The anti-aircraft guns and radar stations did their part, but the Union still commanded the skies. They had prioritized strategic bombing, hitting factories, port facilities, and coastal fortresses, but any target would do in a pinch. Each day, Collins made sure to hear the casualty counts, and each day he would address the nation by radio, encouraging them to continue to fight on. Every man, woman, and child had been doing their part. The Union had done a good job choking the imports of steel in an attempt to starve the Irish industrial machine. Air raid shelters had been a regular part of construction during the massive push for industrialization, and for that Collins had been grateful for what foresight he had. Even one life saved was worth it, but thousands had been spared being killed or maimed in a night raid or building collapse. That was small comfort, because fewer people dying still meant people were dying on his watch, soldiers and civilians alike.
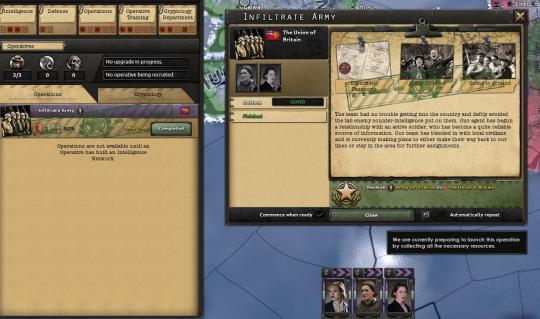
G2 had conducted countless missions against the Union. Infiltrating the Army and Marine Corps were a top priority, any landing or invasion plans were a high priority for their agents. It had been a difficult endeavor, but Nancy Stewart, a Union turncoat who had lost her family members in Mosley’s purges and had been recruited to G2 as a local asset, had outdone herself. She had spoken to an overworked member of base security, stolen his keys and identification card, and had snuck it to her colleagues after drugging the man’s gin and dragging him home posing as his girlfriend. From there, Nancy and Rachael O’Brien, who had been recruited from the Cumann na mBan as part of Collins’s efforts to recruit sabotage experts for the Irish intelligence services, had been able to copy the plans all night before sneaking out the next morning, returning everything that they had left before their victim recovered from his night. The plans had been scheduled for late June, to land in the Clew Bay and Killary Harbor, on the west of Ireland.

Surprise was the Union’s primary goal, the territory in that region was a difficult landing, but if the Union soldiers were able to land and fortify, they could use the terrain to repulse an attack, perhaps even establish a breakout while forces had to cross the River Shannon and potentially seize Irish fortifications. The Republican Army was not concentrated in County Mayo, the likely destination would be on the east coast and it was there that they fortified with machine guns and artillery. The Union elected to launch from Cornwall, with a diversionary operation from Liverpool and the Isle of Man. Admiral O’Muiris elected to keep a defensive posture in a double-bluff; he didn’t want to risk any of his few ships on pursuing the Republican feint but kept his ships close to make it seem that he had not known about the Galway-Mayo landings. He didn’t like it, but if they could push back the attack, it might force Mosley to abort his attempt.
Tom Barry had stationed his men in Sligo and Galway city, waiting for forward observers to spot the landings on the western coast. The 1st Armored Division and the 2nd ‘Spearhead’ infantry would strike from Galway, while a mobilized force of cavalry Gardai would strike from surprise from the northeast. The 1st Thunderbolts were given the most difficult position, to fight a pre-dawn attack against the northern landing. Once they had attacked and cleared the beaches, they would march south and attack the main landing zone where the beaches were longer and flatter, supporting the most landing forces. Collins had hoped that he could bombard the beaches to oblivion, pinning the British invasion force soon after it had landed, and destroying their landing craft so they could not retreat.
The landings were commanded by Thomas Wintringham, who had decided to primarily use regular army forces. He had petitioned Mosley for more men, but as that would have compromised the Welsh and Cornwall defensive region, so he was forced to call upon the West Lowlands Home Guard to fill out the invasion. In the middle of the night, the British had attempted to make the landings, but the currents had taken several of the landing craft off course to Galway, where a general alarm had been sounded and the landing craft subject to a heavy barrage. The anti-aircraft turrets weren’t able to be redirected toward the sea, but the river defenses on the Claddagh had utilized static artillery and machine gun pillboxes to create killzones, and the ports within Galway city had been blockaded.

The mobilized Gardai Síochána and the 1st Thunderbolts moved to their northern position, and Barry began to push with a combined infantry and armor push toward the main landing zones. As it was a night landing, the Republican Air Force was unable to provide air support to its invasion zones. The Thunderbolts had marched all night and shot the Mayo landing forces to pieces as they arrived, keeping in contact with radio and light signals, before turning south to attack the main landing point. The 1st Armored advanced rapidly with light tanks before abruptly turning. Ground forces commanders, thinking that the Irish attack had been aborted because the tanks had outpaced their infantry, had attempted a shock charge to attack the Irish armor when they were out of position. Having advanced quickly, Barry closed the net, attacking with the South Mayo Flying Column and the 2nd Spearhead Division as the light tanks returned to repair the damage they had sustained during the light engagement. The ambush had taken the Union forces completely by surprise, and they were scattered, allowing Tom Maguire to push forward with his native Mayo forces and the Dublin Rifles toward the beach landings.
Continuing his hard push, Barry repeatedly probed the Union lines on the beaches, following up weakpoints with infiltration tactics and strongpoints with a withering suppressive barrage of artillery fire. Admiral Richard Boyle, commanding the U-Boats, attacked as the sun began to give visibility, sinking supply ships and troop transports. As the British Republican Air Force began to fly to support their mission, they had found the beaches to be a disaster area, littered with dead Union soldiers and destroyed Union equipment. The Union soldiers had fought tenaciously, but ultimately could not break out of the beachhead. As the hours stretched on, eventually the divisions surrendered. The first invasion of Ireland had been successfully repulsed.
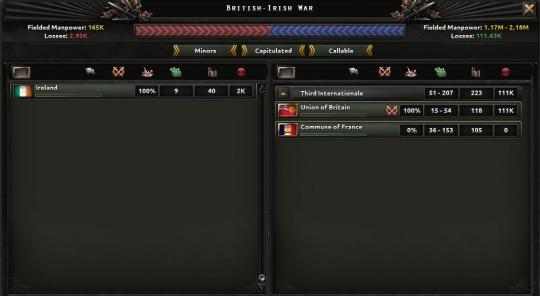
Collins hadn’t been able to sleep, and paced in his command center the night of the march no matter what he tried. Mulcahy had opted to handle the long wait and let Collins try to get a few hours of sleep on a cot, but neither man believed that such a thing could really happen. When the news had come, Collins had listened to Maguire’s report almost dumbfounded, as if he expected to be woken up at any time. A complete success on all fronts, the British invasion had been foiled, and Irish casualties had been exceptionally low. Killed and wounded, Ireland had suffered just short of 3,000 casualties, roughly evenly split among the divisions in theater. The Union had suffered over 111,000 killed or captured in the failed raid, and what few weren’t captured were isolated and fleeing for their lives in the Irish countryside. It had been an overwhelming victory.
“My God, we certainly gave them a bloody nose.” Mulcahy, just as stunned as Collins himself, nodded approvingly.
“Then let us hope all it takes is a bloody nose.” Collins replied glumly.
---
“To conclude, what I witnessed in my almost-two years of volunteer service within the Second American Civil War was commitment in its best and worst forms. The Federal government, armed forces, and civilians of the United States had acted in devotion to their government and their mission, preserving their country and Constitution. Its reverse was true of its foes, a commitment to the annihilation of those who did not fit within their vision.” -Daniel McKenna, closing remarks, Denver Trials
McKenna didn’t belong here. Mosley had tried to invade his homeland. Every man was needed to fight. It was only a direct order from Michael Collins that had sent him to the United States. “We need foreign support more than we need one more general. The Thunderbolts will be well-led, you have my word. If the truth can come out about what had happened in New York, then we can push for further support. Your actions may help the war effort far more than back here in the homeland.”
McKenna thought the idea was sound, but he wasn’t seeing it pan out. Foreign support wouldn’t be pouring in, what had happened in the United States was already known and rationalized away. It was closure for the Americans, perhaps, but abstract notions of justice being punished hardly mattered when real Irish men and women were dying from British bombs. He had gone because he was a soldier and that meant obeying the orders of his commander-in-chief. McKenna had hoped that he could give a quick testimony and return, but he had been approached by the Irish-American Aid Association to give speeches to raise funds to donate supplies for Ireland. The United States was still recovering, but there were plenty of descendants from the Irish diaspora who were willing to donate food, money, and weapons to the Irish cause. That was something at least, some good had to come from this excursion.
McKenna remained in Denver as the tribunal judges deliberated their verdict. Reporters had hounded him the second he stepped out of his hotel until the second he stepped back in, even preventing him from enjoying any meals, calling them a bunch of cicadas in private. However, he was surprised to meet the reporter that he had met in New York covering the Denver Trials. Ruth Sofer had become a minor celebrity for her coverage of Welfare Island, and had resolved to write about the victims and perpetrators of the Second Civil War. “In my view, anything less would be cowardly, and I’ve been told I have an ironclad heart.“ Over dinner, Sofer interviewed McKenna, not only asking him further about Welfare Island, but telling him what she had learned in interviewing members of the Union State and Combined Syndicates who had been guilty of categorical atrocity, and what could have motivated them to do such a thing. It had sickened McKenna to his stomach, but no battle was too difficult for a soldier, and he obeyed his orders.
McKenna had wanted to return to Ireland quickly, but felt compelled to stay to help Sofer until she had finished her manuscript. Her book, Superfluous People, was a chilling examination of the systems of the two rebel movements within the Second American Civil War, their conceptions of a new transformation of reality in a form of secular millenarianism. Most of the second section of the book detailed the rationalizations regarding those to be left out of the new world, and the philosophies of the movements that originated these rationalizations, and the appeals both real and imagined that gave strength to these movements. The third and final section detailed the jump from theory to practice, exhaustively compiled through interviews of ground-level commanders that oversaw these eliminations in action. Notably, Sofer expounded at length on the Federal government in permitting Jim Crow legislation in the South as the foundation for groups like the Silver Legion.
Once the manuscript had been completed, only then did McKenna, hitching a ride on a supply ship from the Irish-American Aid Association, return home, to take up the command of his Thunderbolts once again.
---
12 June 1939 - Forward Command Post, Carrick-On-Shannon
After the failed invasion of Connacht, Mosley had blamed the militia system of the Trade Union Congress, finding the failure of the invasion to principally be the fault of the militia system’s poor organization. To Mosley, the inability of the Union Army to probably organize into a coherent and effective fighting force prevented them from successfully managing the Irish counter-attack until the greater numbers of the British army could land. Mosley dissolved the militias and established a more formalized military with an established central command structure. Officers could no longer be elected by fellow soldiers, Mosley had instead integrated soldier assent via the promotion board and mandated promotion in part on merit and ability to accomplish objectives.

Mosley also reached out to the Communards across the Channel. Deat had not supported Mosley’s invasion of Ireland initially, but he was eager to demonstrate the prowess of the Communard Army. He had anticipated Mosley seeking help, but had thought it would have been more for occupation duties, and had planned for landing from Brittany to land in County Cork on the southern side of Ireland in the middle of August. The initial attacks were mere probing attempts, to see the Munster defenses and better analyze how best to invade Ireland. The weather conditions were right on the 15th of August. Unlike the earlier British invasion, the Communard elected on a daylight landing so their airpower could support the ground invasion. The increased visibility meant the Fenian Rams were able to find the French landings, sinking several troop transports and escort vessels and sinking before the destroyers and naval bombers could attack. Despite the navy’s efforts, French forces were also able to land at Baltimore and in a pasture in County Wexford after being shelled by Irish Republican forces in Waterford. The Dublin Rifles and 3rd ‘Black Badgers’ Division attacked in the Battle of the Sheepfold, where the lack of cover led to high casualties on both sides. The Baltimore landings fared little better, the rocky and open ground provided little cover, and the Irish forces were hard-pressed until reinforcements were trucked in from Limerick.

The landings had similarly failed, though Deat had committed few forces and his troops were far more successful than Mosley’s initial foray. Deat had demanded that Wintringham coordinate with the Communard army for a joint invasion of Connacht. Collins had been able to repulse the Communard landings because his forces, not pressured on multiple fronts, had been able to relieve each other. Overwhelming numerical force would be able to do what smaller forces could not. As Ireland was considered Union territory and the Commune required most of its divisions along the border with the Kaiserreich, the Union would supply most of the manpower for the invasion, although the supreme commander would be from the Communard Army. Union and Communard planes and ships would combine for the endeavor, to support landings from County Claire to Sligo.
The larger invasion force did succeed in its goals. Mosley’s centralization efforts had restructured the militias into an effective and organized fighting force. By standardizing equipment and radio procedures, the Union had been able to break through at Clew Bay, getting off the exposed beach. The Donnelly Division had been scattered, and the French were able to land in County Mayo and attack Sligo after a ferocious onslaught of terror bombing. The initial objectives only sought to reach the River Shannon, as the fortifications made crossing the river a daunting task. The Union took Galway after three days of fighting, Irish Republicans had retreated to the forests and hills outside of the urban centers. After five days, almost the entire province of Connacht was under Communard control. In Sligo and Galway, the Irish tricolor was lowered from the city halls and replaced with the hammer and torch of the Union of Britain, and the Internationale was sung.
The Internationale also executed Irish Republican prisoners. A captain of the 1st Thunderbolts was singled out as a particularly grave offender, accused of having committed war crimes against Union volunteers in Philadelphia during the Second American Civil War. During his impromptu tribunal hearing, he loudly denied the charges against him, demanded hard evidence be presented instead of “self-serving lies from a nation of cowards,” and accused the Internationale of being mass murderers, imperialists, and “the bootlicking spawn of Oliver Cromwell,” disrupting the impromptu tribunal to the point where it was impossible to convene any proper hearing. During the occupation of Connacht, hundreds of civilians were executed. Some were executed for supporting Irish Republican partisan activity or giving supplies to holdout forces, some were members of the Catholic clergy, some others for not turning over foodstuffs to the Internationale army, and yet others were executed after being identified as business owners or landlords by native Irish socialists. The accused were given drumhead trials, their property seized, and hanged from lamposts.
When the news out of Connacht reached Collins, he ordered an effort to retake the lost province. That night, Richard Mulcahy, Hugo MacNeill, and Tom Barry outlined their combined plan to surround and eliminate the invaders, called Operation Execution Ground. A night march along the Atlantic Way from Derry to Sligo led by Barry and Maguire, a march north along the River Shannon toward Sligo for Dublin forces, and the main force pushing up toward Galway from their previous positions in Munster led by MacNeill. The Thunderbolts and Black Badgers, the elite infantry units of the Irish Republican Army, would bloody the Commune in Sligo, while the 2nd Spearheads would seize and destroy stockpiles and command posts that led from Sligo to the Mayo landing points, preventing resupply. Police volunteers from the Gardai offered to help encircle the Communards while the Union forces faced the main infantry force southeast of Galway. It left Belfast and Dublin critically exposed, only their naval minefields and garrison forces would protect them.
Cathal Brugha, already getting old, volunteered to lead any home guard for Dublin. Unafraid of any invasion, he insisted that regulars and volunteers support the Irish Republican Army. With a pistol in hand, he gave a stirring speech, that he would defend the Four Courts by himself if it meant that the interlopers were driven from Irish soil. Collins and Brugha took a photo of themselves, pistols in hand, standing on the steps of the Dail, saying that all Irish citizens young and old can do their part for the fight.
Liam Lynch commanded the infantry coming from the south. When he had seen the bodies in Galway, he told the troops under his command that they were not obligated to “be kind to those who have shown us their cruelty.” Both in Sligo and Galway, the Irish Republican Army ordered heavy shellings on enemy positions followed by aggressive charges. The cavalry forces and the Spearheads moved along the shore, attacking supply lines and cutting off avenues of retreat. To complete the encirclement, the Thunderbolts moved to the west, hoping to break the Communard forces first so that they would flee east into hostile territory rather than west toward the Union.
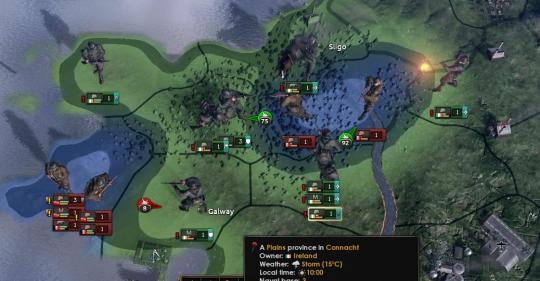
A G2 agent, masquerading as a sympathetic Irish turncoat, made contact with the Communard forces in their forward positions by the River Shannon. Carrying mock orders, G2 successfully tricked the Communard forces into believing that the Irish had seized radio equipment and were attempting to trick them into thinking that they were attacking their landing sites in an attempt to move them out of their defensive positions and ambush them. The Communards didn’t leave for several hours until communications were severed entirely, exposing the ruse. The extra time proved invaluable to the Irish Republican Army, who were able to complete their encirclement before ordering an attack from all sides. Without radio communications, and surrounded on all sides, the Communard forces were shot to pieces. Only the units hunting the partisans to the west were able to successfully rendezvous with Union forces, the rest, after a ferocious battle, surrendered en masse.
The Union forces opted to abandon Galway early, and establish a strong position near their landing zones with Communard forces that had been ambushed in the forests to the west of Sligo. Lynch continued to push aggressively with his infantry, issuing Pervetin rations to the infantry under his command to sustain the attack. As Lynch turned to support the French encirclement, the Union returned to attack the city, revealing their earlier retreat as a ruse to attack while the Irish before their armies could get into position. The Donnelly Division, who had tried to hold Galway, were almost completely destroyed as a fighting unit, losing almost half of their fighting force. A relief effort from the Spearheads was the only thing to save Galway from being overrun.

Only after the Communard Army was defeated did the army regroup and push toward Clew Bay. In the same position that the previous invasion failed, the Union and Communard forces fought a desperate defense. Eventually, the Internationale’s forces were ground down as they began to run out of ammunition and wounds began to take their toll. The news of the murdered civilians and POW’s had enraged the Irish Republican Army, and the Internationale’s landing zone was subject to intense bombardment that, in the words of one private: “seemed to be the devil’s own hand reaching out with one fell swoop to wreak his evil upon the world.” With little in the way of functional radio equipment, surrender was only possible at night when a desperate signals operator flashed Morse code using a spotlight to communicate surrender.
The aftermath of the invasion of Connacht was tragic. Prisoners were marched in chains to prisons in the center of the country, and many officers and enlisted both were sent to firing squads if they were found to have had a hand in executing Irish civilians or in stealing food from non-combatants. Confessions were broadcast around the world about what had happened in Connacht, with the Internationale virulently denying the charges, accusing the Irish of fabricating war crimes to inflame public support and justify their unjust executions of prisoners of war. Collins had barely heard the figures - eight thousand Irish soldiers had been killed or wounded, while the enemy had suffered 179,000. Most of them had been Union soldiers, about 115,000, while France had taken around 75,000. The numbers were one thing, but his people were executed by a foreign power on Irish soil. It was the subjugation of Ireland all over again. Even if they had taken back their territory, how much more would it cost? The Internationale had six times the industrial capacity and fielded far more men. Even now, there had been no indication that Deat would abandon the fight or Mosley call for a truce. Perhaps they would drown Ireland in blood, if they couldn’t have it for themselves.
---
30 June 1939 - Special Joint Session of Congress, Washington D.C., United States of America

“If you will not fight for the Irish, help the Irish fight.” -Eamon “Dev” de Valera
If there was one good thing to come out of the failed invasion of Ireland, it’s that the world finally seemed to wake up to Ireland’s plight. Eamon de Valera had gone to the United States to lobby for more support, and he had been received warmly by President Garner. Warm regards, however, hadn’t translated to what Dev had actually sought, a threat from the United States to back down or face war. The Gallup polls had been encouraging: 47 percent of Americans favored unqualified economic and materiel support to include shipments of food and oil to Ireland, which went up to 57 percent when the responses included “provided it does not enter us into the war.” Most opposition had come from the thought that America still required all of its strength to rebuild, but estimates had been heartening, support for Ireland wouldn’t threaten American recovery, or so the economic analysts had said. There had been much pain suffered by the United States, but it was on the road to recovery. Major Longist guerrilla networks that were uncovered in the Lousiana bayous had been broken up, and the last remnants of the socialist resistance had been killed or arrested among the factory wreckage of Chicago’s industrial district. It was heartening to see America recovering so quickly.
Food and medical supplies, unarmed and flagged as humanitarian aid vessels, had already sailed to Ireland mostly without problems. The Union Navy demanded the right to search the ships, but Collins had threatened that if humanitarian food aid to Ireland was cut, the first people to starve would be the prisoners taken during the failed invasion. Dev had hoped to acquire more significant war support than mere food aid. Even basic equipment was starting to run bare in the depots, and bombing raids had started to take their toll on the factories. America had the industrial capacity needed to supply the Irish war effort, if it could only turn on the taps, an endless river of artillery, planes, and ships could flood the Irish Republican Army with everything it needed to fight the war.
Harry Hopkins had drawn up a bill with considerable bipartisan support, one that he hoped could both provide vital jobs for a recovering America as well as helping Ireland. Ireland could receive oil and war materiel on credit, to be returned when the war was concluded unless “the return of the equipment is made impossible due to use or damage.” Dev had asked Hopkins just how anyone was expected to return spent ammunition or artillery shells after they had been fired, answered with a simple chuckle.
Dev gave a rousing speech in the halls of the US Congress, and had specifically asked for the German and Canadian ambassadors to be invited to the session as well so that he might be able to address the Entente and the Reichspakt together. The pictures of what had happened in Connacht had risen the ire of many Americans, and shouts of “Remember Welfare Island” had frequently been shouted at pro-Ireland rallies.
“We are a small nation, and in our young history as an independent republic we have never once acted with aggression toward another nation, whether stronger or weaker. In our history we have been the victims of aggression, not its perpetrator. We have now come to yet another chapter in the long history of struggle, a new foe empowered by an industrial war that far surpasses the Weltkrieg. We have stood strong, taken with calm courage and confidence in our people, that our nation will endure. We know full well that we cannot demand any other to stand beside us, or ask that their fathers, husbands, or sons do so in their stead. We ask only that you remember Ireland, a land who with tearful hearts had her sons and daughters leave her fleeing the horrors of famine and destitution, and who welcomed many of America’s sons and daughters fleeing the horrors of war and deprivation. We ask that you remember a land with blue rivers choked with blood and oil and green fields burnt and stained red. We ask you, America, such a vast and mighty nation, to remember a nation that could be swallowed by most of your own constituent states. We ask that you remember the injustice being wrought upon her, and we ask that you remember the words of your Benjamin Franklin, about how a great nation may be reduced to a lesser one. We know firsthand how difficult the path of justice is, but acting justly has its reward.”
Transcripts of the speech, personally written by de Valera, were delivered to the Canadian and German ambassadors, with slight modifications. Instead of referencing Benjamin Franklin, Dev had referenced British and German liberal thinkers. The Canadian speech had omitted about how Ireland had a long history of oppression, instead focusing upon Union aggression wishing to expel people from their homeland. These speeches were eventually collected together, with the German Foreign Minister secretly praising de Valera for the craft of tailoring his message to his audience. The response had been beyond what de Valera had hoped. In Germany, Kaiser Wilhelm had declared the German Empire recognized the plight of Ireland, and had promised shipments of materiel protected by the Kaiserliche Merchant Marine. In Canada, the Tories were emboldened, accusing the sitting Prime Minister MacKenzie King of not doing enough to support the effort to reclaim the Home Isles, and that Ireland was fighting the Union just as the Entente had been fighting against the Totalists in the Bharatiya Commune in India. With overwhelming support, the Canadian Parliament authorized shipments of weapons to Ireland, emboldening the hawks in the Entente to push for Reclamation Day. Argentina, preparing for its own war with Chile, had independently recognized Ireland’s plight, and offered several large field guns every month to help keep the Irish in the war effort.
The shipments were invaluable, and protected by convoy systems, most of the promised aid had landed in Cork and Galway. A reporter was on hand and took a picture of marching Irish soldiers wearing the German stahlhelm and carrying the Lee-Enfield rifle. The quartermasters had difficulty initially in supplying troops in the field, as German and Canadian rifles used different calibers and parts were often not interchangeable. Eventually, units were marked as “Grey” or “Blue” by the nationality of the loaned equipment. Speaking for the cameras, Collins was in high spirits, stating: “This is the turning point in this war. The Internationale knows that it has not cowed us. While we seek a just peace and an end to hostilities, we are capable of fighting this war forever, and this commitment proves it. Neither the Reichspakt nor the Entente would provide supplies to a nation that was doomed; they would not extend credit to a nation whose defeat was inevitable. We are committed as ever before, because we know that we have already won this war.”
Privately, Collins was less enthusiastic, but he had to keep the faith. Every soldier was doing so, and Collins could do nothing less, because he was still a soldier through and through.
---
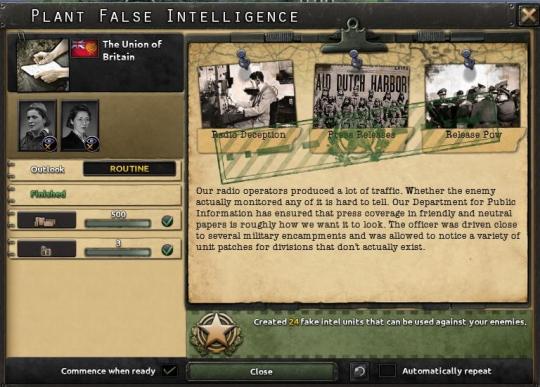
17 August 1939 - G2 Headquarters, Dublin, Ireland
The new supplies were put to use almost immediately, as the Union had attempted a quick invasion at Leinster before the Irish Republican Army could field an effective response. Army engineers had not been idle, the An Balla program had established an extensive array of coastal fortresses facing the Irish Sea. Fielding only 10 divisions, the Union attack only achieved anysuccess at the earlier French landing sites in Wexford, but an aggressive counter-attack by Richard Mulcahy had achieved great results. As much as Collins didn’t like it, ceding the landing grounds to the invaders and then attacking them after they had landed was far more productive than attempting to engage them at sea. Poorly supplied and out of place, they could be driven back to the sea, and the landing crafts weren’t able to pick many back up, if at all. The casualty counts had to be discouraging for the Internationale. 2RN had made sure to broadcast the figures of killed and captured every day toward the Union, to help spread fear and discouragement among the Union’s public. They didn’t have the strength to attack the Union directly, if they were going to win they had to make the cost unbearable, and prayed that the enemy called it quits first.
G2 had launched their most audacious campaign yet in an attempt to deter the Internationale’s invasion of Ireland given the new shipments. The new Argentinian cannons had included several decoy pieces meant to be installed on mock forts to draw fire away from real artillery pieces; a technique that was invaluable in their conflict with Chile to cause the enemy to expose their position for no gain. G2 had opted to go further, and opted to make an entire phantom army. The radio office had highlighted that the expanded conscription laws, increased volunteerism in support for the war effort, and new shipments of equipment from the Great Powers had finally allowed Ireland to double the size of their armies. Dan McKenna, freshly returned from the United States, would lead this new army with the 1st Thunderbolts at its head. Taking advantage of young, patriotic artists, G2 designed inflatable tanks and prop equipment to be used for staged photo ops. To properly seed the information, G2 designed the ‘public’ news to be disseminated through the public radio waves in Ireland itself and friendly countries, including a few foreign divisions signing on for adventure and the chance to fight syndicalism. Ireland couldn’t directly claim to receive foreign volunteers, that would undoubtedly run afoul of their foreign partners, but “expatriates” would be invaluable, drawing on the formation of the United States Refugee Brigades during the Second Civil War. G2 had expertly designed one division of British emigres in Ireland electing to “fight the syndicalist menace that the crown itself would not” called the Blue Lions, and a division of German emigres called the Iron Wolves whose goal was to secure “a peaceful future for the Irish Republic and the German Empire both.” McKenna had drawn upon his experience with the Volunteer Brigades to help design the false brigades, combined with the intelligence division’s Army Department to establish a formalized command structure complete with unit patches, fake pay records, and even a speech given to the new army by McKenna himself.
To make sure that the Union got it, Ireland elected to release a few wounded POW’s back to the Union after ensuring that they had overheard the information while they were in convalescence. Not sure of how much each man could remember, G2 had made sure to release multiple POW’s. Collins himself had made the offer, suggesting that as a humanitarian gesture, certain prisoners who were well enough to be moved could be released in order to free up hospital beds for other wounded individuals. Collins had instructed his negotiators to push for a payment in gold, but to back down if pressed. Mosley had thought he had secured a win, but Collins was the man with the last laugh. The news of the new Irish army, primarily stationed in Leinster, gave Mosley reason to pause, and instead he focused his attention upon County Kerry, hoping to secure Munster and establish a secure foundation to offload more Internationale troops with a short naval trip after a successful invasion.

The trap had worked perfectly. Collins had ordered general evacuations to ensure civilians would be able to flee, and had ordered the armies to wait until the enemy had landed in order to attack. On the day of the attack, Collins had ordered the An tAerchór to fly and contest the skies from the Internationale with the new delivery of fighters and close air support aircraft from the United States. The Irish pilots were not well-trained, but had been drilled extensively on formation flying for air superiority missions. The surprising attack blindsided the Republican Air Force, who had grown lax in their patrols due to their dominance over the skies since the beginning of the early war. Now with the aircraft to match the Communard and Republican Air Forces, the Irish were able to wrest control of the airspace over the Irish island and attack enemy bombers. Casualties were highest among the Air Force, many of whom were outmatched by the more experienced enemy pilots, but the surprising victory and establishment of further control had further enraged the Commune of France, who elected not to pursue “any Irish ventures” further. They had returned to focus on their Alpine Warfare program, and reinforce their borders with Germany and Spain, recalling their forces from the British Isles and reminding Mosley of the greater mission against the Reichspakt. Half a million casualties in a short campaign, multiple failed invasions only useful for teaching lessons on how to repulse the Entente when the French had elected to cross the Mediterranean; a true waste in every sense of the word. While the war was not ended, the Internationale had decided on other priorities. With Ireland in control of her skies and her territorial waters, they had held on, and they had won.
---

23 September 1939 - Áras an Uachtaráin, Dublin, ireland
According to the poets, autumn was the time of loss, from the possibilities of summer into the chill of winter. The poets had not seen fit to think of Ireland in that summer of 1939, where the possibilities of summer were to be bombed by a Syndie plane or executed for failing to turn over their food and valuables to an invader. Yet Ireland’s salvation was no balm, an end to war. On the 9th of September, Deat’s Communard government demanded the return of Elsaß-Lothringen, calling it Alsace-Lorraine, and flew over German airspace to drop leaflets in both French and German detailing their grievances. The Kaiser had refused the audacious demand, claiming that the territory had been German territory for over fifty years. The next day, the Commune of France had declared war on the Kaiserreich, with the Union of Britain joining. The Socialist Republic of Italy, already in a border war with the Kingdom of Two Sicilies, joined the Internationale, and King Ferdinando II responded by joining the Reichspakt. On the 10th of September, Savinkov, declaring the necessity to liberate the Russian people from German subjugation and second-class citizen status, declared war on White Ruthenia, the Baltic Duchy, the Polish-Lithuianian Commonwealth, and Germany itself. On the 15th of September, the Entente declared war on the Union of Britain, the Commune of France, and the Socialist Republic of Italy, citing the illegitimate nature of the governments there, and prepared their invasions. Finally, on the 20th of September, the Empire of Japan, citing pan-Asian ideals and the need to liberate the Far East from Western Dominance, declared war on German Indochina in addition to their ongoing wars in China.
Ireland was no longer the focal point on the world stage, but the rest of the world would feel the fires of war that the Irish had borne, and the fires would burn hotter and brighter than any the world had ever seen. Collins wondered who had been listening to his wish
---
Diplomatic Moves in Ireland
Show of Force
Ireland Abandoned
Britain Demands Annexation
Mosley Declares War
Infiltrating the Army
Come Weal or Woe!
Ambush in Connacht
Casualties - First Invasion
French Landings in Southern Ireland
Casualties - Second Invasion
French Forces Encircled in Connacht
Casualties - Third Invasion
Irish Soldiers with Canadian Rifles and German Helmets
G2 Invents a Fake Army
Casualties - Final Count of the Irish War
Alsace Ultamatum
Alright then, 1939 is down. It’s the longest chapter so far, with the Second Weltkrieg having begun, all the Great Powers (except the US) at war. It’s a more successful tale of Czechoslovakia in 1938 combined with some Battle of Britain and some Operation Fortitude. Let me know what you think
24 notes
·
View notes