#it must inherently be because it didn’t live up to the glorified version of it in their heads
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Can’t write today because too much of everything is making me angry. Love that for me. Excellent. No notes.
#to the left it’s people being shitty about ao3 again#to the right it’s completely bad faith takes that if someone doesn’t like something#it must inherently be because it didn’t live up to the glorified version of it in their heads#and not because it’s objectively garbage and insulting#sure jan#also obviously all around me is just the world being cruel and unkind but if I expand my anxieties outwards that far#I just go back to bed
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Girls Don’t Want Boys, Girls Want Monsters: Netflix’s The Witcher Review
Finally, the show we deserve.
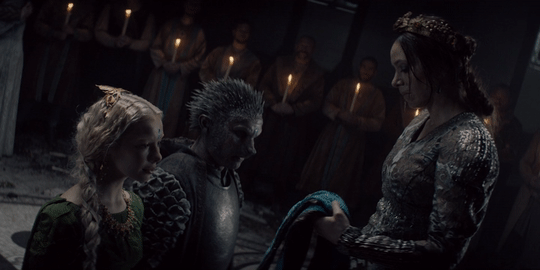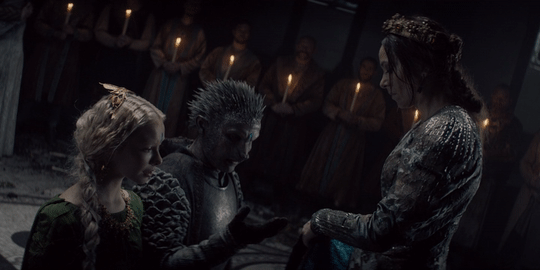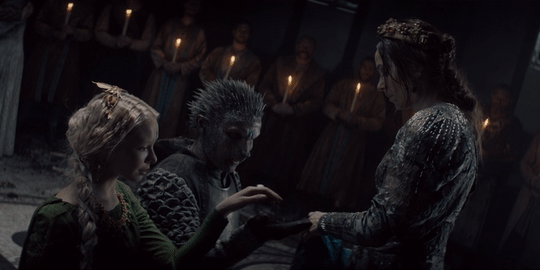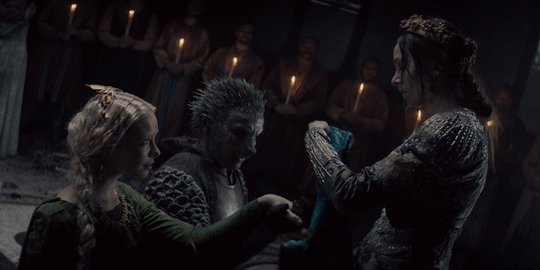
Men get all their superhero power fantasies of kicking villain ass. Finally there’s a story that has that and includes women’s emotional power fantasies about falling in love with monsters who change. It doesn’t treat either as ridiculous or limited by gender, either, since Geralt falls for a monster too and women get to kick ass as well.
Essentially, it’s a story about defeating monsters: often through integration with the shadow, sometimes involving love and connection, sometimes violence, but the violence is never glorified. It’s good.
NB: I’m in the middle of reading the books (in the middle of Blood of Elves so far). I haven’t played the game since video games aren’t really a medium I enjoy. So I’ll make some comparisons since the show covered the two books I’ve read thus far, but please don’t put spoilers for the books below!

Let’s talk my favorite aspect of every story: characters.
Renfri.
Her story was somewhat sanitized from the books (it’s a lot more brutal what happened to Renfri) but well adapted. Both versions--the book and show--depict sincere empathy for our deconstructed Snow White. I loved her dialogue with Geralt, in which Geralt praises her for escaping the huntsman her stepmother hired to kill her, and she laughs and says that she didn’t. He let her go, but not before raping and robbing her. The story never directly answers if the prophecy was true or not; Geralt doesn’t believe it, but a lot of things Geralt doubts turn out to be true. Renfri was supposedly attacking animals as a child; however, the person reporting that is highly unlikely to be unbiased (Stregobor) so is this even true? Did Renfri become a killer because she was horribly abused and left with no other option? (That’s the option that I think seems most likely.)
We can’t know. The Witcher isn’t interested in giving its audience palatable answers. It’s interested in provoking questions. The show gives more answers than do the books, again likely due to the medium, but it still lets these questions linger.
Renfri’s story is not the first one in the books, but it is the first one the show adapts, and that’s a good decision imo. Her story embodies The Witcher’s themes and questions:
By acting the monster, we make monsters out of others.
To defeat monsters, you must be a monster.
What, then, can heal, especially in a world so broken?

Ciri.
Our deconstructed Rapunzel (yes, there are a lot of fairy tale references). As far as her story goes in its adaptation, the addition of Dara was well done. Sadly, no, Dara is not in the books, but his addition gave Ciri an arc beyond merely running in this story.
That said, Ciri in the books is much younger than she is in the show. Which is okay, because Ciri is somewhat emblematic of the future: there’s a lot unknown about her powers, she needs to be protected from everyone trying to grab her and use her powers for themselves. She is Geralt’s destiny, and she is the future of the world of The Witcher.

NB: I can’t discuss Ciri without shouting out to the casting director for casting Pavetta: how did they find an actress who looks so much like Ciri’s actress? It’s almost eerie.

The episode where Geralt finds out about the Law of Surprise and his reaction to Pavetta’s pregnancy is perhaps the only story that I felt was better in the show than in the books (again, this isn’t inherently a quality thing but a medium preference). It added some much-needed hilarity (Geralt’s perfectly-timed “destiny can go f--” *Pavetta vomits* and all he can say is, “fuck”) and gave Geralt an arc.
Geralt.
Mm.

I liked how they handled his character and his struggles with what it means to be a Witcher and/or human. His struggles to understand himself are relatable, and fairly well set-up for future exploration. He’s a foil of Ciri, Yennefer, Jaskier, and Cahir so far, and I’m particularly intrigued by the monster theme and the foiling that is already set up thus with all of the above except Jaskier (who is no monster). Geralt was skeptical about saving the striga for her father, but managed to succeed, and I wonder if he will somehow be able to save himself from his own inner fears/monster by being a father. (Basically, I am curious as to how being Ciri’s de factor dad is going to challenge him.)
Jaskier.

Or, Dandelion, as he’s known in the books. The bard adds some much needed levity to the tale, and as @aspoonofsugar says, he’s pretty much Donkey from Shrek. But he is used fairly well within the story: he shows Geralt even before Ciri and Yennefer enter his life that he has a purpose beyond being a killing machine. In that sense he’s the foil of Renfri (Renfri accomplishes the same, but through violence) in that Geralt saves him and he clearly thinks highly of the Witcher. Jaskier is in some ways humanity in all its paradoxes and foibles, annoying and stupid, kind and clever, funny and truthful, deceptive and respectful.
Cahir.
I’m a sucker for ravens as part of an aesthetic, as well as pretty, tormented bad boys. Yes, I know he’s a character I’m sure will arouse much handwringing and puritanical policing a la his other archetype brothers (Loki, Kylo Ren, Snape, etc). I don’t care. I do think the show made him much darker when compared to the books, but I still expect his arc to go in the same direction as the books. He’s a complicated, conflicted, complex character, and I’m not sorry for feeling empathy for him.
But I am curious about his foiling with Geralt. Both are characters seeking Ciri to fulfill... something, and monstrous in a way (Cahir more for what he does, but there’s a humanity to him as well).

Yennefer.
Finally, my favorite, my baby murder daughter.
Yennefer’s character was fascinating. I appreciated that she’s allowed to want deeply, her own wants, instead of attaching her wants to be whatever the male character desires. She wants to have children. She wants love. She wants to be beautiful. Her desires are traditionally feminine, and the show doesn’t put this down. And she also kicks ass and takes names, she fails, she’s allowed to be angry, to be mean often, to want to learn and to want to be the best.

The show doesn’t punish Yennefer for her ambition. Neither do the books. She experiences consequences, both positive and negative, for her every choice. The show reveals her backstory right away, whereas the books don’t, but again that’s a medium thing. I think both do excellently in setting up Yennefer for our empathy. It doesn’t apologize for her or her wants or actions; it lets her arc and the story itself do the talking.
Yennefer’s not here to be your cautionary tale or your role model. She’s just there to be her and to live.
That is, to an extent, perhaps the best kind of role model.
That doesn’t mean the show did everything in Yennefer’s story justice. I wasn’t thrilled with the adaptation of her first meeting with Geralt--the orgy in the background isn’t in the books and is a very bizarre decision given context. While, I loved Tissaia’s character and her foiling with Yennefer: they are too alike to ever get along, I really didn’t understand the point of Tissaia turning the other girls into slugs in episode 2. It was unsettling and not in the books. It was a heavy-handed metaphor not explained until episode 7 (about treating people as expendable slugs) that didn’t tell us anything we didn’t already know about how the world and Dark!Hogwarts worked. If anything it made the school seem foolishly cackling-mustache evil instead of the true current of darkness within it: manipulation and utilitarianism. As part of effort to control things, that control itself can lead to chaos.
I think the rest of the series set this precise dilemma of a precarious balance between self-control and manipulation/utilitarianism quite well, though (it goes hand-in-hand with the theme of a “lesser evil” to quote Renfri’s story). I’m excited to see this explored more.
Other comments:
When comparing the show to the books as I’ve read so far, I think the show made some smart changes for adapting to a visual medium. For example, Foltest and Adda’s story was adapted as a mystery: what is the monster? Who is the father? Who is the curser? Can the monster be saved? Whereas the book doesn’t do that: you know immediately that the monster is a striga, Foltest is the father, and he wants the striga saved. The answer to who cursed Adda is never clear in the written story either, whereas the show declares it was Ostrit (the book leaves it very much up in the air as to whether it was Ostrit or Adda’s mother). However, the way this particular episode weaves Adda’s story of rebirth with Yennefer’s rebirth was beautifully done. (Foltest is a good dad. We need more good dads in stories; of course, if we had more good dads, we’d have far less stories.) (I’m jesting.)
The dialogue is at times... well it’s not like it’s The Rise of Skywalker levels of “who wrote this???” but it’s not always stellar. Actually, I’d say the quality tends to swing wildly about between clever (episode 4) and just confusing (episode 5). But in general, I think the dialogue issue is representative of the show’s largest issue: it struggles to know when to trust its audience. When should it give details? When should it trust them? When is it spoonfeeding, and when is it just confusing? It tries to walk a fine line and stumbles a bit. It succeeds, however, with the characters as I mentioned earlier with Yennefer, Geralt, and Ciri.
My advice for the show going forward (not that they should definitely listen to me) is to forget Game of Thrones. It’s pretty obvious that this show is a passion project made by people who love The Witcher. I really hope they lean into that aspect instead of into the GoT-replacement aspect (because there are definitely aspects of that, particularly in the mood/aesthetic, tone, and gratuitous nudity--which is not exploitative or disturbing, but it also wasn’t necessary, isn’t in the books, and so felt like pandering).
However, the sheer love for the material still really shines through. They made me care for the characters, they interested me in the world, and they have me hooked for season 2. The showrunners’ excitement for the story and adoration of its characters is contagious, and I hope the show lets this excitement spread.
#the witcher#netflix's the witcher#geralt of rivia#yennefer of vengerberg#cahir#ciri#princess cirilla#hamliet reviews#jaskier#renfri
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
The 12 Worst Ideas Organized Religion Has Unleashed On the World
These dubious concepts advocate conflict, cruelty and suffering.
By Valerie Tarico / AlterNet
April 30, 2018, 10:34 PM GMT
Some of humanity’s technological innovations are things we would have been better off without: the medieval rack, the atomic bomb and powdered lead potions come to mind. Religions tend to invent ideas or concepts rather than technologies, but like every other creative human enterprise, they produce some really bad ones along with the good.
I've previously highlighted some of humanity’s best moral and spiritual concepts, our shared moral core. Here, by way of contrast, are some of the worst. These twelve dubious concepts promote conflict, cruelty, suffering and death rather than love and peace. To paraphrase Christopher Hitchens, they belong in the dustbin of history just as soon as we can get them there.
1. Chosen People –The term “Chosen People” typically refers to the Hebrew Bible and the ugly idea that God has given certain tribes a Promised Land (even though it is already occupied by other people). But in reality many sects endorse some version of this concept. The New Testament identifies Christians as the chosen ones. Calvinists talk about “God’s elect,” believing that they themselves are the special few who were chosen before the beginning of time. Jehovah’s witnesses believe that 144,000 souls will get a special place in the afterlife. In many cultures certain privileged and powerful bloodlines were thought to be descended directly from gods (in contrast to everyone else).
Religious sects are inherently tribal and divisive because they compete by making mutually exclusive truth claims and by promising blessings or afterlife rewards that no competing sect can offer. “Gang symbols” like special haircuts, attire, hand signals and jargon differentiate insiders from outsiders and subtly (or not so subtly) convey to both that insiders are inherently superior.
2. Heretics – Heretics, kafir, or infidels (to use the medieval Catholic term) are not just outsiders, they are morally suspect and often seen as less than fully human. In the Torah, slaves taken from among outsiders don’t merit the same protections as Hebrew slaves. Those who don’t believe in a god are corrupt, doers of abominable deeds. “There is none [among them] who does good,” says the Psalmist.
Islam teaches the concept of “dhimmitude” and provides special rules for the subjugation of religious minorities, with monotheists getting better treatment than polytheists. Christianity blurs together the concepts of unbeliever and evildoer. Ultimately, heretics are a threat that needs to be neutralized by conversion, conquest, isolation, domination, or—in worst cases—mass murder.
3. Holy War – If war can be holy, anything goes. The medieval Roman Catholic Church conducted a twenty year campaign of extermination against heretical Cathar Christians in the south of France, promising their land and possessions to real Christians who signed on as crusaders. Sunni and Shia Muslims have slaughtered each other for centuries. The Hebrew scriptures recount battle after battle in which their war God, Yahweh, helps them to not only defeat but also exterminate the shepherding cultures that occupy their “Promised Land.” As in later holy wars, like the modern rise of ISIS, divine sanction let them kill the elderly and children, burn orchards, and take virgin females as sexual slaves—all while retaining a sense of moral superiority.
4. Blasphemy – Blasphemy is the notion that some ideas are inviolable, off limits to criticism, satire, debate, or even question. By definition, criticism of these ideas is an outrage, and it is precisely this emotion–outrage–that the crime of blasphemy evokes in believers. The Bible prescribes death for blasphemers; the Quran does not, but death-to-blasphemers became part of Shariah during medieval times.
The idea that blasphemy must be prevented or avenged has caused millions of murders over the centuries and countless other horrors. As I write, blogger Raif Badawi awaits round after round of flogging in Saudi Arabia—1000 lashes in batches of 50—while his wife and children plead from Canada for the international community to do something.
5. Glorified suffering – Picture secret societies of monks flogging their own backs. The image that comes to mind is probably from Dan Brown’s novel, The Da Vinci Code, but the idea isn’t one he made up. A core premise of Christianity is that righteous torture—if it’s just intense and prolonged enough–can somehow fix the damage done by evil, sinful behavior. Millions of crucifixes litter the world as testaments to this belief. Shia Muslims beat themselves with lashes and chains during Aashura, a form of sanctified suffering called Matam that commemorates the death of the martyr Hussein. Self-denial in the form of asceticism and fasting is a part of both Eastern and Western religions, not only because deprivation induces altered states but also because people believe suffering somehow brings us closer to divinity.
Our ancestors lived in a world in which pain came unbidden, and people had very little power to control it. An aspirin or heating pad would have been a miracle to the writers of the Bible, Quran, or Gita. Faced with uncontrollable suffering, the best advice religion could offer was to lean in or make meaning of it. The problem, of course is that glorifying suffering—turning it into a spiritual good—has made people more willing to inflict it on not only themselves and their enemies but also those who are helpless, including the ill or dying (as in the case of Mother Teresa and the American Bishops) and children (as in the child beating Patriarchy movement).
6. Genital mutilation – Primitive people have used scarification and other body modifications to define tribal membership for as long as history records. But genital mutilation allowed our ancestors several additional perks—if you want to call them that. Infant circumcision in Judaism serves as a sign of tribal membership, but circumcision also serves to test the commitment of adult converts. In one Bible story, a chieftain agrees to convert and submit his clan to the procedure as a show of commitment to a peace treaty. (While the men lie incapacitated, the whole town is then slain by the Israelites.)
In Islam, painful male circumcision serves as a rite of passage into manhood, initiation into a powerful club. By contrast, in some Muslim cultures cutting away or burning the female clitoris and labia ritually establishes the submission of women by reducing sexual arousal and agency. An estimated 2 million girls annually are subjected to the procedure, with consequences including hemorrhage, infection, painful urination and death. – In the list of religion’s worst ideas, this is the only one that appears to be in its final stages. Only some Hindus (, goddess of power) and some Muslims (, Feast of the Sacrifice) continue to ritually slaughter sacrificial animals on a mass scale. Hindu scriptures including the Gita and Puranas forbid ritual killing, and most Hindus now eschew the practice based on the principle of ahimsa, but it persists as a residual of folk religion.
7. Blood sacrifice – In the list of religion’s worst ideas, this is the only one that appears to be in its final stages. Only some Hindus (during the Festival of Gadhimai, goddess of power) and some Muslims (during Eid al Adha, Feast of the Sacrifice) continue to ritually slaughter sacrificial animals on a mass scale. Hindu scriptures including the Gita and Puranas forbid ritual killing, and most Hindus now eschew the practice based on the principle of ahimsa, but it persists as a residual of folk religion.
When our ancient ancestors slit the throats of humans and animals or cut out their hearts or sent the smoke of sacrifices heavenward, many believed they were literally feeding supernatural beings. In time, in most religions, the rationale changed—the gods didn’t need feeding so much as signs of devotion and penance. The residual child sacrifice in the Hebrew Bible (yes, it is there) typically has this function. Christianity’s persistent focus on blood atonement—the notion of Jesus as the be-all-end-all lamb without blemish, the final “propitiation” for human sin—is hopefully the last iteration of humanity’s long fascination with blood sacrifice.
8. Hell – Whether we are talking about Christianity, Islam or Buddhism, an afterlife filled with demons, monsters, and eternal torture was the worst suffering the Iron Age minds could conceive and medieval minds could elaborate. Invented, perhaps, as a means to satisfy the human desire for justice, the concept of Hell quickly devolved into a tool for coercing behavior and belief.
Most Buddhists see hell as a metaphor, a journey into the evil inside the self, but the descriptions of torturing monsters and levels of hell can be quite explicit. Likewise, many Muslims and Christians hasten to assure that it is a real place, full of fire and the anguish of non-believers. Some Christians have gone so far as to insist that the screams of the damned can be heard from the center of the Earth or that observing their anguish from afar will be one of the pleasures of paradise.
9. Karma – Like hell, the concept of karma offers a selfish incentive for good behavior—it’ll come back at you later—but it has enormous costs. Chief among these is a tremendous weight of cultural passivity in the face of harm and suffering. Secondarily, the idea of karmasanctifies the broad human practice of blaming the victim. If what goes around comes around, then the disabled child or cancer patient or untouchable poor (or the hungry rabbit or mangy dog) must have done something in either this life or a past one to bring their position on themselves.
10. Eternal Life – To our weary and unwashed ancestors, the idea of gem encrusted walls, streets of gold, the fountain of youth, or an eternity of angelic chorus (or sex with virgins) may have seemed like sheer bliss. But it doesn’t take much analysis to realize how quickly eternal paradise would become hellish—an endless repetition of never changing groundhog days (because how could they change if they were perfect).
The real reason that the notion of eternal life is such a bad invention, though, is the degree to which it diminishes and degrades existence on this earthly plane. With eyes lifted heavenward, we can’t see the intricate beauty beneath our feet. Devout believers put their spiritual energy into preparing for a world to come rather than cherishing and stewarding the one wild and precious world we have been given.
11. Male Ownership of Female Fertility – The notion of women as brood mares or children as assets likely didn’t originate with religion, but the idea that women were created for this purpose, that if a woman should die of childbearing “she was made to do it,” most certainly did. Traditional religions variously assert that men have a god-ordained right to give women in marriage, take them in war, exclude them from heaven, and kill them if the origins of their offspring can’t be assured. Hence Catholicism’s maniacal obsession with the virginity of Mary and female martyrs.
As we approach the limits of our planetary life support system and stare dystopia in the face, defining women as breeders and children as assets becomes ever more costly. We now know that resource scarcity is a conflict trigger and that demand for water and arable land is growing even as both resources decline. And yet, a pope who claims to care about the desperate poor lectures them against contraceptionwhile Muslim leaders ban vasectomies in a drive to outbreed their enemies.
12. Bibliolatry (aka Book Worship) – Preliterate people handed down their best guesses about gods and goodness by way of oral tradition, and they made objects of stone and wood, idols, to channel their devotion. Their notions of what was good and what was Real and how to live in moral community with each other were free to evolve as culture and technology changed. But the advent of the written word changed that. As our Iron Age ancestors recorded and compiled their ideas into sacred texts, these texts allowed their understanding of gods and goodness to become static. The sacred texts of Judaism, Christianity and Islam forbid idol worship, but over time the texts themselves became idols, and many modern believers practice—essentially—book worship, also known as bibliolatry.
“Because the faith of Islam is perfect, it does not allow for any innovations to the religion,” says one young Muslim explaining his faith online. His statement betrays a naïve lack of information about the origins of his own dogmas. But more broadly, it sums up the challenge all religions face moving forward. Imagine if a physicist said, “Because our understanding of physics is perfect, it does not allow for any innovations to the field.”
Adherents who think their faith is perfect, are not just naïve or ill informed. They are developmentally arrested, and in the case of the world’s major religions, they are anchored to the Iron Age, a time of violence, slavery, desperation and early death.
Ironically, the mindset that our sacred texts are perfect betrays the very quest that drove our ancestors to write those texts. Each of the men who wrote part of the Bible, Quran, or Gita took his received tradition, revised it, and offered his own best articulation of what is good and real. We can honor the quest of our spiritual ancestors, or we can honor their answers, but we cannot do both.
Religious apologists often try to deny, minimize, or explain away the sins of scripture and the evils of religious history. “It wasn’t really slavery.” “That’s just the Old Testament.” “He didn’t mean it that way.” “You have to understand how bad their enemies were.” “Those people who did harm in the name of God weren’t real [Christians/Jews/Muslims].” Such platitudes may offer comfort, but denying problems doesn’t solve them. Quite the opposite, in fact. Change comes with introspection and insight, a willingness to acknowledge our faults and flaws while still embracing our strengths and potential for growth.
In a world that is teeming with humanity, armed with pipe bombs and machine guns and nuclear weapons and drones, we don’t need defenders of religion’s status quo—we need real reformation, as radical as that of the 16th Century and much, much broader. It is only by acknowledging religion’s worst ideas that we have any hope of embracing the best.
Valerie Tarico is a psychologist and writer in Seattle, Washington, and the founder of Wisdom Commons. She is the author of "Trusting Doubt: A Former Evangelical Looks at Old Beliefs in a New Light" and "Deas and Other Imaginings." Her articles can be found at valerietarico.com.
27 notes
·
View notes
Link
“These twelve dubious concepts promote conflict, cruelty, suffering and death rather than love and peace.
1. Chosen People –The term “Chosen People” typically refers to the Hebrew Bible and the ugly idea that God has given certain tribes a Promised Land (even though it is already occupied by other people). But in reality many sects endorse some version of this concept. The New Testament identifies Christians as the chosen ones. Calvinists talk about “God’s elect,” believing that they themselves are the special few who were chosen before the beginning of time. Jehovah’s witnesses believe that 144,000 souls will get a special place in the afterlife. In many cultures certain privileged and powerful bloodlines were thought to be descended directly from gods (in contrast to everyone else).
Religious sects are inherently tribal and divisive because they compete by making mutually exclusive truth claims and by promising blessings or afterlife rewards that no competing sect can offer. “Gang symbols” like special haircuts, attire, hand signals and jargon differentiate insiders from outsiders and subtly (or not so subtly) convey to both that insiders are inherently superior.
2. Heretics – Heretics, kafir, or infidels (to use the medieval Catholic term) are not just outsiders, they are morally suspect and often seen as less than fully human. In the Torah, slaves taken from among outsiders don’t merit the same protections as Hebrew slaves. Those who don’t believe in a god are corrupt, doers of abominable deeds. “There is none [among them] who does good,” says the Psalmist. Islam teaches the concept of “dhimmitude” and provides special rules for the subjugation of religious minorities, with monotheists getting better treatment than polytheists. Christianity blurs together the concepts of unbeliever and evildoer. Ultimately, heretics are a threat that needs to be neutralized by conversion, conquest, isolation, domination, or—in worst cases—mass murder.
3. Holy War – If war can be holy, anything goes. The medieval Roman Catholic Church conducted a twenty year campaign of extermination against heretical Cathar Christians in the south of France, promising their land and possessions to real Christians who signed on as crusaders. Sunni and Shia Muslims have slaughtered each other for centuries. The Hebrew scriptures recount battle after battle in which their war God, Yahweh, helps them to not only defeat but also exterminate the shepherding cultures that occupy their “Promised Land.” As in later holy wars, like the modern rise of ISIS, divine sanction let them kill the elderly and children, burn orchards, and take virgin females as sexual slaves—all while retaining a sense of moral superiority.
4. Blasphemy – Blasphemy is the notion that some ideas are inviolable, off limits to criticism, satire, debate, or even question. By definition, criticism of these ideas is an outrage, and it is precisely this emotion–outrage–that the crime of blasphemy evokes in believers. The Bible prescribes death for blasphemers; the Quran does not, but death-to-blasphemers became part of Shariah during medieval times.The idea that blasphemy must be prevented or avenged has caused millions of murders over the centuries and countless other horrors. As I write, blogger Raif Badawi awaits round after round of flogging in Saudi Arabia—1000 lashes in batches of 50—while his wife and children plead from Canada for the international community to do something.
5. Glorified suffering – Picture secret societies of monks flogging their own backs. The image that comes to mind is probably from Dan Brown’s novel, The Da Vinci Code, but the idea isn’t one he made up. A core premise of Christianity is that righteous torture—if it’s just intense and prolonged enough–can somehow fix the damage done by evil, sinful behavior. Millions of crucifixes litter the world as testaments to this belief. Shia Muslims beat themselves with lashes and chains during Aashura, a form of sanctified suffering called Matam that commemorates the death of the martyr Hussein. Self-denial in the form of asceticism and fasting is a part of both Eastern and Western religions, not only because deprivation induces altered states but also because people believe suffering somehow brings us closer to divinity.
Our ancestors lived in a world in which pain came unbidden, and people had very little power to control it. An aspirin or heating pad would have been a miracle to the writers of the Bible, Quran, or Gita. Faced with uncontrollable suffering, the best advice religion could offer was to lean in or make meaning of it. The problem, of course is that glorifying suffering—turning it into a spiritual good—has made people more willing to inflict it on not only themselves and their enemies but also those who are helpless, including the ill or dying (as in the case of Mother Teresa and the American Bishops) and children (as in the child beating Patriarchy movement).
6. Genital mutilation – Primitive people have used scarification and other body modifications to define tribal membership for as long as history records. But genital mutilation allowed our ancestors several additional perks—if you want to call them that. In Judaism, infant circumcision serves as a sign of tribal membership, but circumcision also serves to test the commitment of adult converts. In one Bible story, a chieftain agrees to convert and submit his clan to the procedure as a show of commitment to a peace treaty. (While the men lie incapacitated, the whole town is then slain by the Israelites.)
In Islam, painful male circumcision serves as a rite of passage into manhood, initiation into a powerful club. By contrast, in some Muslim cultures cutting away or burning the female clitoris and labia ritually establishes the submission of women by reducing sexual arousal and agency. An estimated 2 million girls annually are subjected to the procedure, with consequences including hemorrhage, infection, painful urination and death.
7. Blood sacrifice – In the list of religion’s worst ideas, this is the only one that appears to be in its final stages. Only some Hindus (during the Festival of Gadhimai) and some Muslims (during Eid al Adha, Feast of the Sacrifice) continue to ritually slaughter sacrificial animals on a mass scale. Hindu scriptures including the Gita and Puranas forbid ritual killing, and most Hindus now eschew the practice based on the principle of ahimsa, but it persists as a residual of folk religion.
When our ancient ancestors slit the throats on humans and animals or cut out their hearts or sent the smoke of sacrifices heavenward, many believed that they were literally feeding supernatural beings. In time, in most religions, the rationale changed—the gods didn’t need feeding so much as they needed signs of devotion and penance. The residual child sacrifice in the Hebrew Bible (yes it is there) typically has this function. Christianity’s persistent focus on blood atonement—the notion of Jesus as the be-all-end-all lamb without blemish, the final “propitiation” for human sin—is hopefully the last iteration of humanity’s long fascination with blood sacrifice.
8. Hell – Whether we are talking about Christianity, Islam or Buddhism, an afterlife filled with demons, monsters, and eternal torture was the worst suffering that Iron Age minds could conceive and medieval minds could elaborate. Invented, perhaps, as a means to satisfy the human desire for justice, the concept of Hell quickly devolved into a tool for coercing behavior and belief.
Most Buddhists see hell as a metaphor, a journey into the evil inside the self, but the descriptions of torturing monsters and levels of hell can be quite explicit. Likewise, many Muslims and Christians hasten to assure that it is a real place, full of fire and the anguish of non-believers. Some Christians have gone so far as to insist that the screams of the damned can be heard from the center of the Earth or that observing their anguish from afar will be one of the pleasures of paradise.
9. Karma – Like hell, the concept of karma offers a selfish incentive for good behavior—it’ll come back at you later—but it has enormous costs. Chief among these is a tremendous weight of cultural passivity in the face of harm and suffering. Secondarily, the idea of karma can sanctify the broad human practice of blaming the victim. If what goes around comes around, then the disabled child or cancer patient or untouchable poor (or the hungry rabbit or mangy dog) must have done something in this or a previous life to bring their position on themselves.
10. Eternal Life – To our weary and unwashed ancestors, the idea of gem encrusted walls, streets of gold, the fountain of youth, or an eternity of angelic chorus (or sex with virgins) may have seemed like sheer bliss. But it doesn’t take much analysis to realize how quickly eternal paradise would become hellish—an endless repetition of never changing groundhog days (because how could they change if they were perfect).
The real reason that the notion of eternal life is such a bad invention, though, is the degree to which it diminishes and degrades existence on this earthly plane. With eyes lifted heavenward, we can’t see the intricate beauty beneath our feet. Devout believers put their spiritual energy into preparing for a world to come rather than cherishing and stewarding the one wild and precious world we have been given.
11. Male Ownership of Female Fertility – The notion of women as brood mares or children as assets likely didn’t originate with religion, but the idea that women were created for this purpose, that if a woman should die of childbearing “she was made to do it,” most certainly did. Traditional religions variously assert that men have a god-ordained right to give women in marriage, take them in war, exclude them from heaven, and kill them if the origins of their offspring can’t be assured. Hence Catholicism’s maniacal obsession with the virginity of Mary and female martyrs. Hence Islam’s maniacal obsession with covering the female body. Hence Evangelical promise rings, and gender segregated sidewalks in Jerusalem and orthodox Jewish women wearing wigs over shaved heads in New York.
As we approach the limits of our planetary life support system and stare dystopia in the face, defining women as breeders and children as assets becomes even more costly. We now know that resource scarcity is a conflict trigger and that demand for water and arable land is growing even as both resources decline. And yet, a pope who claims to care about the desperate poor lectures them against contraception while Muslim leaders ban vasectomies in a drive to outbreed their enemies.
12. Bibliolatry (aka Book Worship) – Preliterate people handed down their best guesses about gods and goodness by way of oral tradition, and they made objects of stone and wood, idols, to channel their devotion. Their notions of what was good and what was Real and how to live in moral community with each other were free to evolve as culture and technology changed. But the advent of the written word changed that. As our Iron Age ancestors recorded and compiled their ideas into sacred texts, these texts allowed their understanding of gods and goodness to become static. The sacred texts of Judaism, Christianity and Islam forbid idol worship, but over time the texts themselves became idols, and many modern believers practice—essentially—book worship, also known as bibliolatry.
“Because the faith of Islam is perfect, it does not allow for any innovations to the religion,” says one young Muslim explaining his faith online. His statement betrays a naïve lack of information about the origins and evolution of his own dogmas. But more broadly, it sums up the challenge all religions face moving forward. Imagine if a physicist said, “Because our understanding of physics is perfect, it does not allow for any innovations to the field.” Adherents who think their faith is perfect, are not just naïve or ill informed. They are developmentally arrested, and in the case of the world’s major religions, they are anchored to the Iron Age, a time of violence, slavery, desperation and early death.
Ironically, the mindset that our sacred texts are perfect betrays the very quest that drove our ancestors to write those texts. Each of the men who wrote part of the Bible, Quran, or Gita took his received tradition, revised it, and offered his own best articulation of what is good and real. We can honor the quest of our spiritual ancestors, or we can honor their answers, but we cannot do both.
Religious apologists often try to deny, minimize, or explain away the sins of scripture and the evils of religious history. “It wasn’t really slavery.” “That’s just the Old Testament.” “He didn’t mean it that way.” “You have to understand how bad their enemies were.” “Those people who did harm in the name of God weren’t real [Christians/Jews/Muslims].” Such platitudes may offer comfort, but denying problems doesn’t solve them. Quite the opposite, in fact.
Change comes with introspection and insight, a willingness to acknowledge our faults and flaws while still embracing our strengths and potential for growth. In a world that is teeming with humanity, armed with pipe bombs and machine guns and nuclear weapons and drones, we don’t need defenders of religion’s status quo—we need real reformation, as radical as that of the 16th Century and much, much broader. It is only by acknowledging religion’s worst ideas that we have any hope of embracing the best.”
Valerie Tarico is a psychologist and writer in Seattle, Washington.
https://valerietarico.com/2015/01/20/religions-dirty-dozen-12-really-bad-religious-ideas-that-have-made-the-world-worse/
384 notes
·
View notes
Text
You can have anything you want, as long as you work hard enough
TW: Mental illness, eating disorder, body dysmorphia
Maximise the 10 percent of your brain that goes unused! Do you know how much can be achieved in just one minute alone? Follow your dreams! If you want something, go get it! Anything is possible as long as you work hard enough! There are no shortcuts! Be an astronaut! Be a millionaire! Be a professor! Live in a lavish apartment! Be a genius! Stop wasting time! Unleash your potential! The sky’s the limit! NEVER give up!
Yep, being hardworking, motivated and resilient are important and admirable traits that everyone should strive to incorporate into their endeavours. But let’s be real—shit just isn’t so simple, as much as society tries to tell us that this is the foolproof formula for “success” and for “anything you want to have”, “anything you want to be”. I would even venture to say that internalising this without awareness and mindfulness can be toxic, especially when you’re dealing with mental health issues.
I can’t account for everyone’s experience, so I shall speak from my own.
The first time I tried to lose weight, I started dieting and employed an exercise regime. It seemed as innocent as it could be. How else would one try to lose weight? There was nothing unhealthy or bad about it. In fact, quite the opposite. I was on my way to achieving a new body and I was working towards the version of myself that I could be proud of. The version of myself that I could show off to society and say—“Hey, look! I achieved this all through my own hard work!” I didn’t like something about myself, and I was going to take steps to change it. I wanted something, and I was going to get it. Just like society said I should. And so I did.
But I very quickly fell into the downward spiral of body dysmorphia and eating disorders. Each time I felt that I wasn’t losing weight, I would tell myself that I just needed to try harder, to work harder, to be willing to sacrifice more. Eat less. Run more. Not enough. Eat lesser. Run even more. Not enough. EAT EVEN LESSER! EXERCISE EVEN MORE! YOU CAN BE ANYTHING YOU WANT AS LONG AS YOU WORK HARD ENOUGH! Before I knew it, I was kneeling over the toilet bowl, gagging myself and puking out all the food that I believed I didn’t deserve, food that I had eaten because I was actually starving. I ended up with chronic digestive problems, a foul temper, a severely distorted sense of what a “proper meal” was and worst of all—lots and lots of shame and guilt for failing to achieve the waif-thin body I so badly wanted. I believed it was just because I didn’t work hard enough. I believe it was because there was something about me that was inherently inferior.
The point isn’t that I should have had a qualified nutritionist and trainer to help me achieve my goals. The point isn’t that people should never try to lose weight, or that people who have successfully done so don’t deserve to be celebrated.
The point is that I had pre-existing body dysmorphia, and I didn’t know it. The point is that I had pre-existing mental health problems that would make the sheer act of losing weight completely unsuitable for me. The point is that losing weight isn’t for everyone, and just because it isn’t for someone, it doesn’t mean that the person is weak, lazy, not hardworking enough or just a failure. (I don’t want to say that the point is that I had a healthy BMI and didn’t need to lose weight, because that invalidates the people who don’t have a medically acceptable BMI but who have their own reasons for not losing weight.)
The funniest thing? I actually attempted the same thing a couple of years after. Again, it was because I believed that I just needed to try harder. That I needed to be resilient. I was as miserable as could be, and the second attempt left me with detrimental effects even more chronic than the first—exactly because of how much “harder” I was “working”.
After the second episode, I made a decision to swear off dieting and specific weight-loss endeavours, because things had come to a point where I knew that doing so would be unwise and toxic, specifically for someone like me. I’ve felt so much healthier ever since. I work out and eat right mostly for the sake of health and fitness, instead of for obsessing over a certain body type (although I do still suffer from bouts of body dysmorphia). I am proud of myself for that.
The funny thing is that society would hardly ever look at my experience and go, “HOLY SHIT!! YOU’RE AMAZING!! YOU GAVE UP TRYING TO LOSE WEIGHT!! CONGRATS!!” But just look at media and see how many people are glorified for smashing their fitness goals and for achieving a completely new body. Because THAT is a simplistic, conspicuous reflection of hard work, dedication and success. THAT fits into society’s narrative of “work hard and you’ll succeed. And success should be something that we all can SEE. When you do succeed, we’ll give you our stamp of approval for being brilliant. If you don’t, then try harder and come back again.”
Now, now, I’m not saying that society SHOULD and MUST celebrate anything and everything. I’m not saying that society should be a mind-reader and necessarily see and understand all the nuances and specific cases surrounding the discourse of “hard work”. But I do think it is a pathology that we are all so obsessed with achieving tangible things, showing off tangible things, and validating tangible things. I do think it is a pathology that we are only prepared to celebrate the act of 24/7 hustling. Especially when you’re suffering from mental illness, the shame and guilt of falling anything outside of that standard can really do a huge number on you. And so it’s important to open our eyes. It’s important for me to open MY eyes.
The story of my body dysmorphia and eating disorder is only but an anecdote for illustrative purposes. I can go on for forever illustrating my perfectionist and over-ambitious toxicity over all the years that I have lived. But what I really want to say is this:
When you suffer from mental illness, or in fact just dealing with SHIT in general, sometimes the greatest and most brilliant thing you can do is literally just getting out of bed and getting dressed. I’m speaking from my condition of falling into low-functioning states after every few days of being high-functioning. Being motivated and active is literally a constant struggle and fight for me. And often the shame comes in not simply BEING a motivated and active person. The shame comes in not even accomplishing “simple” tasks, and even more so in not achieving “great things”. But shouldn’t this constant fight and these relentless attempts, in themselves, be a testament to resilience and hard work?
On another note, I value my time for slacking, chilling, “wasting time” and napping, because it is personally vital for me to restore my mental, emotional, physical, spiritual and intellectual energy. It shouldn’t be shamed and mocked for being “useless” and for being a sign of weakness. It allows one time and space to observe life and to reflect, as well as to live and to experience. Not everything has to be done for a tangible achievement, end-goal or social validation. Not everything has to be calculated and planned. Not every minute has to be maximised and stretched thin. Not all greatness is achieved in being famous, rich, popular, having numerous tangible skills and hobbies or academic accolades. Sometimes the biggest, wisest and most practical dream you have is staying alive, supporting yourself and loving the people around you. And that can be fucking great and a mean fucking feat for some!
Society teaches us to work hard and to be well-rounded over-achievers. Those who fall within that standard are idolated and glorified. But does society teach us to manage our expectations? Does society teach us to achieve things on our very own terms, according to our very own standards? Does society teach us the value of idling? Does society teach us to just simply breathe and to LIVE? Is any of that any less worthy of celebration and admiration? Is any of that any less worthy of pride?
With all that said, I am in no way saying that I have completely come out of the trap and am no longer privy to these feelings of insecurity, guilt, shame, inadequacy, inferiority and anxiety. There is always that fear that I don’t deserve to validate myself and my own greatness, because it might sound like crumbs of consolation and free passes thrown around for people with mental illness. But it isn’t and it shouldn’t be. Nobody knows what I have gone through and how hard I’ve worked to be where I am today, especially when I haven’t had anything fancy to shout about or to brag. Writing this is more of an act of reflection and a practice in mindfulness. And I hope reading this has done the same for you.
#mental health#mental illness#eating disorder#bulimia#anorexia#ednos#society#media#culture#hard work#success#mindfulness#awareness
0 notes