#indian oil and gas industry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Indian Oil Corporation
#indian oil corporation#gas station#petrol#petrol pumps#wikipedia#wikipedia pictures#petrol station#fossil fuels#industry#khammam#india#telangana#transportation
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Challenges in Gas Supply During Peak Demand
Due to lack of timely supply, consumers with only one cylinder have to wait for 5-7 days for gas completion The demand for gas increases by about 30 percent in winter, but the common people do not get it on time, the government should facilitate it as soon as possible. – Chandra Thapa, President, Gas Sellers Federation Apart from Nepal Gas, there is no problem, we have issued as many PDOs as…
0 notes
Text
Genocide experts warn that India is about to genocide the Shompen people
Who are the Shompen?
The Shompen are an indigenous culture that lives in the Great Nicobar Island, which is nowadays owned by India. The Shompen and their ancestors are believed to have been living in this island for around 10,000 years. Like other tribes in the nearby islands, the Shompen are isolated from the rest of the world, as they chose to be left alone, with the exception of a few members who occasionally take part in exchanges with foreigners and go on quarantine before returning to their tribe. There are between 100 and 400 Shompen people, who are hunter-gatherers and nomadic agricultors and rely on their island's rainforest for survival.
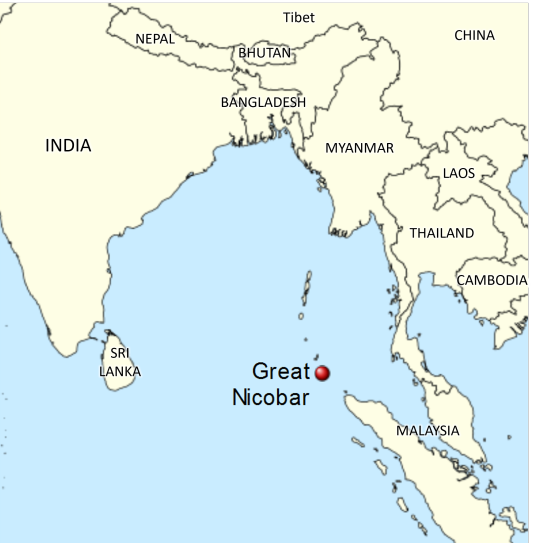
Why is there risk of genocide?
India has announced a huge construction mega-project that will completely change the Great Nicobar Island to turn it into "the Hong Kong of India".
Nowadays, the island has 8,500 inhabitants, and over 95% of its surface is made up of national parks, protected forests and tribal reserve areas. Much of the island is covered by the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve, described by UNESCO as covering “unique and threatened tropical evergreen forest ecosystems. It is home to very rich ecosystems, including 650 species of angiosperms, ferns, gymnosperms, and bryophytes, among others. In terms of fauna, there are over 1800 species, some of which are endemic to this area. It has one of the best-preserved tropical rain forests in the world.”
The Indian project aims to destroy this natural environment to create an international shipping terminal with the capacity to handle 14.2 million TEUs (unit of cargo capacity), an international airport that will handle a peak hour traffic of 4,000 passengers and that will be used as a joint civilian-military airport under the control of the Indian Navy, a gas and solar power plant, a military base, an industrial park, and townships aimed at bringing in tourism, including commercial, industrial and residential zones as well as other tourism-related activities.
This project means the destruction of the island's pristine rainforests, as it involves cutting down over 852,000 trees and endangers the local fauna such as leatherback turtles, saltwater crocodiles, Nicobar crab-eating macaque and migratory birds. The erosion resulting from deforestation will be huge in this highly-seismic area. Experts also warn about the effects that this project will have on local flora and fauna as a result of pollution from the terminal project, coastal surface runoff, ballasts from ships, physical collisions with ships, coastal construction, oil spills, etc.
The indigenous people are not only affected because their environment and food source will be destroyed. On top of this, the demographic change will be a catastrophe for them. After the creation of this project, the Great Nicobar Island -which now has 8,500 inhabitants- will receive a population of 650,000 settlers. Remember that the Shompen and Nicobarese people who live on this island are isolated, which means they do not have an immune system that can resist outsider illnesses. Academics believe they could die of disease if they come in contact with outsiders (think of the arrival of Europeans to the Americas after Christopher Columbus and the way that common European illnesses were lethal for indigenous Americans with no immunization against them).
And on top of all of this, the project might destroy the environment and the indigenous people just to turn out to be useless and sooner or later be abandoned. The naturalist Uday Mondal explains that “after all the destruction, the financial viability of the project remains questionable as all the construction material will have to be shipped to this remote island and it will have to compete with already well-established ports.” However, this project is important to India because they want to use the island as a military and commercial post to stop China's expansion in the region, since the Nicobar islands are located on one of the world's busiest sea routes.
Last year, 70 former government officials and ambassadors wrote to the Indian president saying the project would “virtually destroy the unique ecology of this island and the habitat of vulnerable tribal groups”. India's response has been to say that the indigenous tribes will be relocated "if needed", but that doesn't solve the problem. As a spokesperson for human rights group Survival International said: “The Shompen are nomadic and have clearly defined territories. Four of their semi-permanent settlements are set to be directly devastated by the project, along with their southern hunting and foraging territories. The Shompen will undoubtedly try to move away from the area destroyed, but there will be little space for them to go. To avoid a genocide, this deadly mega-project must be scrapped.”
On 7 February 2024, 39 scholars from 13 countries published an open letter to the Indian president warning that “If the project goes ahead, even in a limited form, we believe it will be a death sentence for the Shompen, tantamount to the international crime of genocide.”
How to help
The NGO Survival International has launched this campaign:
From this site, you just need to add your name and email and you will send an email to India's Tribal Affairs Minister and to the companies currently vying to build the first stage of the project.
Share it with your friends and acquittances and on social media.
Sources:
India’s plan for untouched Nicobar isles will be ‘death sentence’ for isolated tribe, 7 Feb 2024. The Guardian.
‘It will destroy them’: Indian mega-development could cause ‘genocide’ and ‘ecocide’, says charity, 8 Feb 2024. Geographical.
Genocide experts call on India's government to scrap the Great Nicobar mega-project, Feb 2024. Survival International.
The container terminal that could sink the Great Nicobar Island, 20 July 2022. Mongabay.
[Maps] Environmental path cleared for Great Nicobar mega project, 10 Oct 2022. Mongabay.
#shompen#genocide#stop genocide#india#indigenous#indigenous peoples#indigenous rights#human rights#anthropology#stateless nations#end occupation#andaman and nicobar islands#nicobar islands#great nicobar#💬#asia#geopolitics#ecocide#sustainability
23K notes
·
View notes
Text

Are you looking for drilling oil rig workers?
#oil rig workers#drilling oil rig#oil and gas worker#oil and gas staffing#offshore workers#oil and gas industry recruitment#offshore drilling workers#oil & gas workers#indian#bangladeshi#manpower#oil and gas recruitment
1 note
·
View note
Text
"India’s announcement that it aims to reach net zero emissions by 2070 and to meet fifty percent of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030 is a hugely significant moment for the global fight against climate change. India is pioneering a new model of economic development that could avoid the carbon-intensive approaches that many countries have pursued in the past – and provide a blueprint for other developing economies.
The scale of transformation in India is stunning. Its economic growth has been among the highest in the world over the past two decades, lifting of millions of people out of poverty. Every year, India adds a city the size of London to its urban population, involving vast construction of new buildings, factories and transportation networks. Coal and oil have so far served as bedrocks of India’s industrial growth and modernisation, giving a rising number of Indian people access to modern energy services. This includes adding new electricity connections for 50 million citizens each year over the past decade.
The rapid growth in fossil energy consumption has also meant India’s annual CO2 emissions have risen to become the third highest in the world. However, India’s CO2 emissions per person put it near the bottom of the world’s emitters, and they are lower still if you consider historical emissions per person. The same is true of energy consumption: the average household in India consumes a tenth as much electricity as the average household in the United States.
India’s sheer size and its huge scope for growth means that its energy demand is set to grow by more than that of any other country in the coming decades. In a pathway to net zero emissions by 2070, we estimate that most of the growth in energy demand this decade would already have to be met with low-carbon energy sources. It therefore makes sense that Prime Minister Narendra Modi has announced more ambitious targets for 2030, including installing 500 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity, reducing the emissions intensity of its economy by 45%, and reducing a billion tonnes of CO2.
These targets are formidable, but the good news is that the clean energy transition in India is already well underway. It has overachieved its commitment made at COP 21- Paris Summit [a.k.a. 2015, at the same conference that produced the Paris Agreement] by already meeting 40% of its power capacity from non-fossil fuels- almost nine years ahead of its commitment, and the share of solar and wind in India’s energy mix have grown phenomenally. Owing to technological developments, steady policy support, and a vibrant private sector, solar power plants are cheaper to build than coal ones. Renewable electricity is growing at a faster rate in India than any other major economy, with new capacity additions on track to double by 2026...
Subsidies for petrol and diesel were removed in the early 2010s, and subsidies for electric vehicles were introduced in 2019. India’s robust energy efficiency programme has been successful in reducing energy use and emissions from buildings, transport and major industries. Government efforts to provide millions of households with fuel gas for cooking and heating are enabling a steady transition away from the use of traditional biomass such as burning wood. India is also laying the groundwork to scale up important emerging technologies such as hydrogen, battery storage, and low-carbon steel, cement and fertilisers..."
-via IEA (International Energy Agency), January 10, 2022
Note: And since that's a little old, here's an update to show that progress is still going strong:
-via Economic Times: EnergyWorld, March 10, 2023
#india#solar power#renewable energy#green energy#sustainability#wind power#population grown#economic growth#developing economies#renewable electricity#carbon emissions#good news#hope#hope posting
861 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is "interesting," (to use a mild word), because it shows us how trump and his minions are manipulating our thinking toward their imperialistic goals. In this case, the threat to impose tariffs globally on any country that impose tariffs on the US are not intended to generate revenue, but rather are intended to generate increased exports of fossil fuels, in particular, liquified natural gas, from the US to the rest of the world. Who benefits? The fossil fuel industry. Unfuckingbelievable, yet very believable when one considers the source, methodology, motivation.
Excerpt from Bill McKibben's Substack, The Crucial Years:
In the last few days, Taiwan, India and Japan made clear they will be buying exported American LNG in the months and years ahead. Why? Entirely in an effort to hold off tariffs from the Trump administration. As the Japanese prime minister put it,
“We will cooperate to strengthen energy security between the two countries including increasing exports of United States liquefied natural gas to Japan in a mutually beneficial manner.”
Here’s how Bloomberg described the Indian decision-making:
Indian importers are under pressure from the government to reach deals that could smooth relations with Trump, the people said, but they will be looking for the best possible terms before signing any agreements.
Meanwhile, as Sing Yee Ong reports from Taipei
Taiwan is preparing to buy more liquefied natural gas from the US to reduce its trade surplus and potentially avoid higher tariffs.
Oh, and more to come
South Korea, Vietnam and the European Union are among energy buyers trying to appease President Donald Trump — and reduce the threat of tariffs — by looking to increase purchases from the biggest exporter of the super-chilled fuel and largest producer of crude.
I want to highlight these shakedowns, which have mostly been lost amidst the thousand other terrible things the Trump administration has loosed upon the world, because I know that before long Big Oil will be holding them up as evidence that the world needs and wants more fossil fuel. In fact, the world wants to move in entirely the opposite direction: 85% of new electric generation in 2023 came from renewables, and the numbers for 2024 will almost certainly be higher. That, of course, terrifies the fossil fuel industry—which is why they spent record amounts on November’s election. As fracking baron Harold Hamm explained, “We’ve got to do this because it’s the most important election in our lifetime.”
And now they’re getting the payoff: Trump threatens tariffs, and offers to make them go away if they buy some LNG. It’s akin to a protection racket. Pay up, or your windows get broken. It’s not criminal—it’s all entirely legal. It’s just wrong.
This particular protection racket makes no sense for America at large. Forget, for a moment, that LNG is a huge driver of the climate change driving fire and flood (by the time you’ve shipped it overseas it’s far worse even than coal); exporting it in huge quantities also obviously drives up the price for Americans still reliant on fracked gas for heating and cooking. The Energy Information Administration just predicted that natural gas prices will rise 21 percent in the year ahead. Politico did the math
Paul Cicio, president of the Industrial Energy Consumers of America trade association, said U.S. LNG exports are pushing natural gas and electricity prices higher. Every “dollar increase in natural gas costs consumers $34 billion plus about $20 billion in higher electricity cost,” Cicio said in a statement Tuesday. It's “only going to get worse from here as LNG exports increase.”t of the Industrial Energy Consumers of America trade association, said U.S. LNG exports are pushing natural gas and electricity prices higher.
As the Sierra Club points out, Trump’s strategy “makes no sense.” And they’re right—as long as we’re talking about the future of the planet or the cost to American consumers. But that’s not who Trump is thinking about. He’s got one constituency and one only: the Big Oil execs who bankrolled his campaign. For them, this is sweet payback, a 100-1 return on their investment.
And it’s a stark reminder that we have to fight back on the only turf we have: the fact that the sun and wind can deliver the same product as LNG, only more cheaply and much more cleanly. We can’t threaten tariffs to get our way; we can only make the case in such persuasive terms that we start to change the zeitgeist. That’s the point of SunDay project I described last week and that you are going to hear a lot more about. Many thanks to those who went to sunday.earth to help us draw some suns as we prepare for the official launch of this big effort. So many of you took part already. Here’s a beautiful example from the effervescent Ayana Johnson (whose book What If We Get It Right is a document for this tough moment)
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
November 29, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Nov 30, 2024
In 2008, Congress passed and President George W. Bush signed into law an act making the day after Thanksgiving National Native American Heritage Day.
About a month ago, on Friday, October 25, President Joe Biden became the first president to visit Indian Country in ten years when he traveled to the Gila River Indian Community in Maricopa County, Arizona, near Phoenix. Secretary of the Interior Deb Haaland traveled with him. The trip was designed to highlight the investments the Biden-Harris administration has made in Tribal Nations.
At a press gaggle on Air Force One on the way to Arizona, White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre noted that under Biden, Tribal Nations have seen the largest direct federal investment in history: $32 billion from the American Rescue Plan and $13 billion through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to build roads and bridges, bring clean water and sanitation, and build high-speed Internet in Tribal communities.
Jean-Pierre added that First Lady Jill Biden has also championed Native communities, visiting them ten times to highlight investments in youth mental health, the revitalization of Native languages, and to improve access to cancer screening and cancer care in Native communities.
Secretary Haaland, herself a member of the Pueblo of Laguna, agreed that the Biden-Harris administration has brought “transformational change” to Native communities: “electricity on the Hopi Reservation in Arizona for homes that have never had electricity; protecting cultural resources, like salmon, which Pacific Northwest Tribes have depended on for thousands of years; new transportation infrastructure for the Mescalero Apache Nation in New Mexico that will provide a safer travel route and boost their economic development, their local economy; addressing toxic legacy pollution and abandoned oil and gas infrastructure that pollutes our air and water for the Osage Nation in Oklahoma; providing clean drinking water for Fort Peck in Montana.”
“Tribal leaders are experiencing a new era,” Haaland added. “They’re at the table. They’re being consulted.”
When Biden spoke at the Gila Crossing Community School, he said he was there “to right a wrong, to chart a new path toward a better future for us all.” As president of the United States, Biden formally apologized to the Native peoples—Native Americans, Native Hawaiians, Native Alaskans—for the U.S. government policy that forced Native children into federal Indian boarding schools.
The apology comes after the release of an Interior Department study, The Federal Boarding School Initiative, that Secretary Haaland directed the department to undertake in 2021. According to Assistant Secretary of the Interior Bryan Newland, a citizen and former president of the Bay Mills Indian Community (Ojibwe), the initiative was “a comprehensive effort to recognize the troubled legacy of Federal Indian boarding school policies with the goal of addressing their intergenerational impact and to shed light on the traumas of the past.”
The initiative set out to identify federal Indian boarding schools and sites, to identify the children who attended those schools and to identify their Tribal identities, to find marked and unmarked burial sites of the remains of Indian children near school facilities, and to incorporate the viewpoints of those who attended federal Indian boarding schools and their descendants into the story of those schools.
The report looked at the Indian education system from 1819 to 1969 as a whole, bringing together federal funding for religious schools in the early 1800s with later explicitly federal schools and their public school successors during and after the 1930s. But historians generally focus on the period from 1879 to the 1930s as the boarding school era.
In 1879, the government opened the Carlisle Indian Industrial School, a boarding school for American Indian children in Carlisle, Pennsylvania, explicitly designed to separate children from their families and their culture and to train them for menial jobs.
The boarding school era was the brainchild of Army officer Richard Henry Pratt, a Civil War veteran who, in the years after the war, commanded the 10th United States Cavalry, a Black regiment stationed in the American West whose members Indigenous Americans nicknamed the “Buffalo Soldiers.” Pratt fought in the campaigns on the Plains from 1868 through 1875, when he was assigned to oversee 72 Cheyenne, Kiowa, Comanche, Arapaho, and Caddo prisoners of war at Fort Marion in St. Augustine, Florida (now known as the Castillo de San Marcos National Monument).
Many Indigenous prisoners at Fort Marion, taken from the dry Plains to the hot and humid coast of Florida where they were imprisoned in a cramped stone fort, quickly sickened and died. Pratt worked to upgrade conditions and to assimilate prisoners into U.S. systems by teaching them English, U.S. culture, Christianity, and how the American economy worked. He cut their hair, dressed them in military-type uniforms, and urged them to make art for sale to local tourists—it’s from here we get the world-famous collection of ledger art by the artists of Fort Marion—but focused on turning the former warriors and their families into menial workers.
After the Battle of the Little Bighorn in 1876 and the subsequent pursuit and surrender of leading Lakota bands throughout that year and the next, leading to the murder of Crazy Horse in 1877, popular opinion ran heavily toward simply corralling Indigenous Americans on reservations and waiting either for their assimilation or extermination. At the same time, with what seemed to be the end of the most serious of the Plains Wars, Army officers like Pratt had reason to worry that the downsizing of the U.S. Army would mean the end of their careers.
Indigenous survivors of Fort Marion returned home to see that the American government had no real plans for a thriving American Indian populace. There was little infrastructure to link them to the rest of the country to sell their art, and Indian agents rejected tribal members for jobs in favor of white cronies.
But Pratt considered his experiment at Fort Marion a great success, and he came to believe he could make his system work even more thoroughly by using a loophole in the treaties between Plains Tribes and the U.S. government to force Indigenous Americans to assimilate as children. He planned, he said, to “Kill the Indian and save the man.”
Treaties between Plains Indian Tribes and the government required the U.S. government to educate American Indian children—something their parents cared deeply about—but the treaties didn’t actually specify where the schools would be. So Pratt convinced the U.S. Army and officials at the Interior Department to give him the use of the Carlisle Barracks to open an industrial school, designed to teach American Indian children the skills necessary to be servants and menial workers.
In summer 1879, Pratt traveled to western reservations of the Lakotas and Dakotas, primarily, to gather up 82 children to begin his experiment in annihilating their culture from their minds. He forbade the practice of any aspect of Indigenous culture—language, religion, custom, clothing—and forced children to change their names, use English, practice Christianity, and wear clothing that mirrored that of Euro-American children.
Crowded together, many children died of disease; bereft of their family and culture, many died of heartache. Some found their newfound language and lessons tolerable, others ran away. For the next fifty years, the Carlisle model was the central model of government education for Indigenous children, with tens of thousands of children educated according to its methods.
In the 1920s the Institute for Government Research, later renamed the Brookings Institution, commissioned a study funded by the Rockefeller Institute—to make sure it would not reflect government bias—to investigate conditions among Indigenous Americans.
In 1928 that study, called the Meriam Report, condemned the conditions under which American Indians lived. It also emphasized the “deplorable health conditions” at the boarding schools, condemned the schools’ inappropriate focus on menial skills, and asserted that “[t]he most fundamental need in Indian education is a change in point of view.” In 1934 the Indian Reorganization Act reversed the policy of trying to eradicate Tribal cultures through boarding children away from their families, and introduced the teaching of Indian history and culture in federal schools.
But the boarding schools remain a central part of the experience of American Indians since the establishment of the U.S. government in North America, and the Federal Boarding School Initiative recommended that “[t]he U.S. Government should issue a formal acknowledgment of its role in adopting a national policy of forced assimilation of Indian children, and carrying out this policy through the removal and confinement of Indian children from their families and Indian Tribes and the Native Hawaiian Community and placement in the Federal Indian boarding school system.”
It continued: "The United States should accompany this acknowledgment with a formal apology to the individuals, families, and Indian Tribes that were harmed by U.S. policy."
On October 25, 2024, President Joe Biden delivered that apology.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters From An American#American History#native Americans#American Indians#Federal Boarding School Initiative#Indian Children#Indian Reorganization Act#American Heritage Day
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Carbon Pipe Fittings : Astm A234 WPB Pipe Fittings Manufacturers
Introduction:
ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings, also known as carbon steel pipe fittings, have largely become standard parts in many industries. The fitting elements will be used to adapt straight pipe or tubing sections, to maintain different size or shape, and to control the rate of flow of liquids.
Always resistant to strength and versatile, ASTM A234 WPB fittings play a critical role in industries dealing with oil, gas, petrochemicals, and power generation.
What are ASTM A234 WPB Pipe Fittings?
They are used to connect pipes in shapes such as elbows, tees, reducers, and caps. The prime factors that make the use of these fittings highly prevalent are their excellent mechanical properties, like high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion. They are very important in ensuring the integrity and efficiency of piping systems across industries.
Manilaxmi Industrial also supplies Carbon ASTM Pipe Fittings around the globe.
Real-Time Advancements in Industries
Ranging from new manufacturing technologies and materials science to improved performance and reliability, these fittings have carved out a niche in use. Applications of the ASTM A234 WPB carbon steel pipe fitting have greatly improved in the industrial sector.For example, refined heat treatment processes leave behind fittings that are easier to manipulate and work under higher pressure and temperature conditions.
Besides, numerous coating and lining innovations provide improved corrosion resistance and give extended life expectancy.
Manilaxmi Industrial the Indian manufacturers, suppliers, and exporters have been among the most active adopters of these developments to ensure that the country is retained as a main supplier of quality pipe fittings in the global market.
Technology and Need in Various Countries
Demands for ASTM A234 WPB carbon steel pipe fittings are ever-increasing in the global scenario. This demand has been hastened further by the requirement of strong, efficient piping systems in the developing countries and renovated or rejuvenated ones in the developed nations.
Such as setting up power plants and oil refineries. In contrast, developed nations always require update works and servicing of already existing facilities. Equipped with state-of-the-art technology in the manufacturing process, these fittings comply with strict standards that make them very important and cardinal for maintaining efficiency and safety during industrial operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ASTM A234 WPB pipe fittings are the most essential material in the industrial market, possessing qualities of high durability, adaptability, and tolerance toward extreme situations. With relentless development in the manufacturing technologies, further improvements are made in their performances, making them trustworthy for different applications.
#innovation#management#technology#metalfabrication#metalwork#supplychain#manufacturers#exporters#suppliers
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heather Cox Richardson
November 29, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Nov 30
In 2008, Congress passed and President George W. Bush signed into law an act making the day after Thanksgiving National Native American Heritage Day.
About a month ago, on Friday, October 25, President Joe Biden became the first president to visit Indian Country in ten years when he traveled to the Gila River Indian Community in Maricopa County, Arizona, near Phoenix. Secretary of the Interior Deb Haaland traveled with him. The trip was designed to highlight the investments the Biden-Harris administration has made in Tribal Nations.
At a press gaggle on Air Force One on the way to Arizona, White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre noted that under Biden, Tribal Nations have seen the largest direct federal investment in history: $32 billion from the American Rescue Plan and $13 billion through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to build roads and bridges, bring clean water and sanitation, and build high-speed Internet in Tribal communities.
Jean-Pierre added that First Lady Jill Biden has also championed Native communities, visiting them ten times to highlight investments in youth mental health, the revitalization of Native languages, and to improve access to cancer screening and cancer care in Native communities.
Secretary Haaland, herself a member of the Pueblo of Laguna, agreed that the Biden-Harris administration has brought “transformational change” to Native communities: “electricity on the Hopi Reservation in Arizona for homes that have never had electricity; protecting cultural resources, like salmon, which Pacific Northwest Tribes have depended on for thousands of years; new transportation infrastructure for the Mescalero Apache Nation in New Mexico that will provide a safer travel route and boost their economic development, their local economy; addressing toxic legacy pollution and abandoned oil and gas infrastructure that pollutes our air and water for the Osage Nation in Oklahoma; providing clean drinking water for Fort Peck in Montana.”
“Tribal leaders are experiencing a new era,” Haaland added. “They’re at the table. They’re being consulted.”
When Biden spoke at the Gila Crossing Community School, he said he was there “to right a wrong, to chart a new path toward a better future for us all.” As president of the United States, Biden formally apologized to the Native peoples—Native Americans, Native Hawaiians, Native Alaskans—for the U.S. government policy that forced Native children into federal Indian boarding schools.
The apology comes after the release of an Interior Department study, The Federal Boarding School Initiative, that Secretary Haaland directed the department to undertake in 2021. According to Assistant Secretary of the Interior Bryan Newland, a citizen and former president of the Bay Mills Indian Community (Ojibwe), the initiative was “a comprehensive effort to recognize the troubled legacy of Federal Indian boarding school policies with the goal of addressing their intergenerational impact and to shed light on the traumas of the past.”
The initiative set out to identify federal Indian boarding schools and sites, to identify the children who attended those schools and to identify their Tribal identities, to find marked and unmarked burial sites of the remains of Indian children near school facilities, and to incorporate the viewpoints of those who attended federal Indian boarding schools and their descendants into the story of those schools.
The report looked at the Indian education system from 1819 to 1969 as a whole, bringing together federal funding for religious schools in the early 1800s with later explicitly federal schools and their public school successors during and after the 1930s. But historians generally focus on the period from 1879 to the 1930s as the boarding school era.
In 1879, the government opened the Carlisle Indian Industrial School, a boarding school for American Indian children in Carlisle, Pennsylvania, explicitly designed to separate children from their families and their culture and to train them for menial jobs.
The boarding school era was the brainchild of Army officer Richard Henry Pratt, a Civil War veteran who, in the years after the war, commanded the 10th United States Cavalry, a Black regiment stationed in the American West whose members Indigenous Americans nicknamed the “Buffalo Soldiers.” Pratt fought in the campaigns on the Plains from 1868 through 1875, when he was assigned to oversee 72 Cheyenne, Kiowa, Comanche, Arapaho, and Caddo prisoners of war at Fort Marion in St. Augustine, Florida (now known as the Castillo de San Marcos National Monument).
Many Indigenous prisoners at Fort Marion, taken from the dry Plains to the hot and humid coast of Florida where they were imprisoned in a cramped stone fort, quickly sickened and died. Pratt worked to upgrade conditions and to assimilate prisoners into U.S. systems by teaching them English, U.S. culture, Christianity, and how the American economy worked. He cut their hair, dressed them in military-type uniforms, and urged them to make art for sale to local tourists—it’s from here we get the world-famous collection of ledger art by the artists of Fort Marion—but focused on turning the former warriors and their families into menial workers.
After the Battle of the Little Bighorn in 1876 and the subsequent pursuit and surrender of leading Lakota bands throughout that year and the next, leading to the murder of Crazy Horse in 1877, popular opinion ran heavily toward simply corralling Indigenous Americans on reservations and waiting either for their assimilation or extermination. At the same time, with what seemed to be the end of the most serious of the Plains Wars, Army officers like Pratt had reason to worry that the downsizing of the U.S. Army would mean the end of their careers.
Indigenous survivors of Fort Marion returned home to see that the American government had no real plans for a thriving American Indian populace. There was little infrastructure to link them to the rest of the country to sell their art, and Indian agents rejected tribal members for jobs in favor of white cronies.
But Pratt considered his experiment at Fort Marion a great success, and he came to believe he could make his system work even more thoroughly by using a loophole in the treaties between Plains Tribes and the U.S. government to force Indigenous Americans to assimilate as children. He planned, he said, to “Kill the Indian and save the man.”
Treaties between Plains Indian Tribes and the government required the U.S. government to educate American Indian children—something their parents cared deeply about—but the treaties didn’t actually specify where the schools would be. So Pratt convinced the U.S. Army and officials at the Interior Department to give him the use of the Carlisle Barracks to open an industrial school, designed to teach American Indian children the skills necessary to be servants and menial workers.
In summer 1879, Pratt traveled to western reservations of the Lakotas and Dakotas, primarily, to gather up 82 children to begin his experiment in annihilating their culture from their minds. He forbade the practice of any aspect of Indigenous culture—language, religion, custom, clothing—and forced children to change their names, use English, practice Christianity, and wear clothing that mirrored that of Euro-American children.
Crowded together, many children died of disease; bereft of their family and culture, many died of heartache. Some found their newfound language and lessons tolerable, others ran away. For the next fifty years, the Carlisle model was the central model of government education for Indigenous children, with tens of thousands of children educated according to its methods.
In the 1920s the Institute for Government Research, later renamed the Brookings Institution, commissioned a study funded by the Rockefeller Institute—to make sure it would not reflect government bias—to investigate conditions among Indigenous Americans.
In 1928 that study, called the Meriam Report, condemned the conditions under which American Indians lived. It also emphasized the “deplorable health conditions” at the boarding schools, condemned the schools’ inappropriate focus on menial skills, and asserted that “[t]he most fundamental need in Indian education is a change in point of view.” In 1934 the Indian Reorganization Act reversed the policy of trying to eradicate Tribal cultures through boarding children away from their families, and introduced the teaching of Indian history and culture in federal schools.
But the boarding schools remain a central part of the experience of American Indians since the establishment of the U.S. government in North America, and the Federal Boarding School Initiative recommended that “[t]he U.S. Government should issue a formal acknowledgment of its role in adopting a national policy of forced assimilation of Indian children, and carrying out this policy through the removal and confinement of Indian children from their families and Indian Tribes and the Native Hawaiian Community and placement in the Federal Indian boarding school system.”
It continued: "The United States should accompany this acknowledgment with a formal apology to the individuals, families, and Indian Tribes that were harmed by U.S. policy."
On October 25, 2024, President Joe Biden delivered that apology.
—
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Buy SS 304 Blind Flange | Lowest Price in India
SS 304 Blind Flanges are a vital component for industrial piping systems, known for their durability, corrosion resistance, and strength. These flanges, made from stainless steel grade 304, are designed to seal the ends of pipes or valves, making them ideal for industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and more. For businesses in India, finding SS 304 Blind Flanges at the lowest price is essential for minimizing operational costs while ensuring high-quality performance. With a wide range of suppliers offering competitive pricing, it's easier than ever to source these flanges at the best rates.
What is SS 304 Blind Flange?
SS 304 Blind Flanges are flat, circular components used to close off the ends of pipelines, valves, or pressure vessels. Unlike other flanges, the blind flange does not have a central bore, meaning it completely blocks the flow of liquid or gas through the pipe. This makes it useful for isolating sections of a piping system for maintenance, testing, or system shutdowns.
The material used in these flanges—stainless steel grade 304—is an austenitic alloy with high chromium (18%) and nickel (8%) content. This composition gives SS 304 its excellent corrosion resistance, making it a perfect choice for harsh industrial environments where chemicals, moisture, and high temperatures are present.
Benefits of SS 304 Blind Flange
1. Outstanding Corrosion Resistance: The SS 304 Blind Flange’s high chromium content allows it to form a passive layer of chromium oxide on its surface, which prevents rust and corrosion. This makes it ideal for use in chemical processing, oil refineries, water treatment plants, and other industries that deal with corrosive environments.
2. High Strength and Durability: SS 304 Blind Flanges are designed to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures. This makes them suitable for high-pressure applications, including oil and gas pipelines, steam systems, and heavy-duty processing plants. Their durability ensures long-term performance without frequent replacements, reducing maintenance costs.
3. Low Maintenance: Due to its superior resistance to corrosion and wear, SS 304 Blind Flanges require minimal maintenance compared to other materials. This makes them a cost-effective choice for industries where reliable performance and low upkeep are critical.
4. Versatile Applications: SS 304 Blind Flanges are used across a wide range of industries. They are suitable for temporarily sealing off pipelines during repairs or permanently closing off systems. Their versatility makes them valuable in oil and gas, petrochemical, marine, pharmaceutical, food processing, and water treatment industries.
Why Buy SS 304 Blind Flanges in India?
India is home to a vast array of suppliers and manufacturers offering SS 304 Blind Flanges at competitive prices. Buying locally ensures that you have access to high-quality products that meet Indian and international standards, such as ASTM or ASME certifications. Here are a few reasons why purchasing SS 304 Blind Flanges in India makes sense:
1. Cost-Effective Pricing: Indian suppliers offer some of the most competitive prices in the global market for SS 304 Blind Flanges. Whether you're looking to buy in small quantities or bulk, Indian manufacturers provide quality products at reasonable rates, often with the option to negotiate prices for large orders.
2. Fast Delivery and Local Availability: When you buy from Indian suppliers, you benefit from faster delivery times and lower shipping costs, especially for domestic orders. Many suppliers have stock readily available, ensuring that you can meet your project deadlines without delays.
3. Industry-Standard Certifications: SS 304 Blind Flanges manufactured in India often adhere to industry standards such as ASTM, ASME, or DIN. These certifications guarantee that the flanges meet the required quality and performance specifications, ensuring safety and reliability in industrial applications.
4. Bulk Discounts: Many suppliers in India offer discounts on bulk orders, making it more affordable for businesses that need large quantities of SS 304 Blind Flanges. Bulk purchasing not only reduces the unit price but can also lead to savings on transportation and logistics.
Applications of SS 304 Blind Flange
SS 304 Blind Flanges are used in various industrial settings due to their robust and corrosion-resistant properties. Common applications include:
Oil and Gas Industry: SS 304 Blind Flanges are used to close off pipeline sections during repairs or testing, especially in environments where corrosion is a concern.
Chemical Processing: In chemical plants, these flanges are used to block pipes that carry corrosive fluids, ensuring the system remains secure and sealed.
Water Treatment Plants: SS 304 Blind Flanges help in sealing off sections of water pipelines, providing a rust-resistant solution for water treatment facilities.
Marine Applications: Due to their resistance to seawater corrosion, SS 304 Blind Flanges are used in marine environments, including shipbuilding and offshore drilling operations.
Pharmaceutical and Food Industry: The non-reactive and hygienic properties of SS 304 make it an excellent choice for industries that require clean and sterile processing, such as pharmaceuticals and food manufacturing.
Tips for Finding SS 304 Blind Flanges at the Lowest Price in India
1. Compare Multiple Suppliers: When purchasing SS 304 Blind Flanges in India, it’s important to compare prices from several suppliers. This will allow you to find the most competitive pricing while ensuring the quality of the product.
2. Look for Bulk Discounts: If your project requires a large quantity of flanges, ask suppliers about bulk pricing. Many manufacturers offer substantial discounts for large orders, helping you reduce the cost per unit.
3. Check for Certifications: Make sure the supplier offers SS 304 Blind Flanges that meet industry standards like ASTM, ASME, or DIN. Certified products provide assurance that the flange will perform under the required conditions.
4. Negotiate for Better Pricing: Negotiation is common in the industrial supply market. If you’re placing a large order or planning a long-term partnership, don’t hesitate to ask for better terms or discounts.
5. Look for Seasonal or Promotional Offers: Some suppliers may offer seasonal discounts or promotional deals on SS 304 Blind Flanges. Stay on the lookout for such opportunities to get the best value for your money.
#SS304BlindFlange#BuySS304Flange#StainlessSteelFlange#IndustrialFlange#CorrosionResistantFlange#LowestPriceInIndia#PipelineSolutions#OilAndGasFlange#MarineFlange#WaterTreatmentFlange#BuyNow#IndiaFlangeDeals
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Indian Oil Corporation
#indian oil corporation#indianoil#indianoilcorporation#wikipedia#wikipedia pictures#petrol#petrol station#gas station#fossil fuels#industry#oil#transportation#punjab#india#dera bassi
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Economic Impact of Paraffin Dispersant Exports: A Global Perspective
In the modern oil and gas industry, paraffin or wax deposition has emerged as a significant challenge. Paraffin, a naturally occurring hydrocarbon, can solidify in pipelines, tanks, and other equipment, leading to blockages that disrupt production and transportation. The answer to this growing problem lies in the development and export of wax or paraffin dispersants, chemicals designed to mitigate wax build-up by keeping the wax particles suspended in oil.

India has established itself as a key player in the production and export of wax or paraffin dispersants, supplying global markets with these critical chemicals. With the growing demand for oil, especially in emerging economies, the need for these dispersants continues to rise. This blog explores the economic impact of paraffin dispersant exports, with a focus on India’s role as a key manufacturer, exporter, and supplier in the global market.
Understanding the Role of Paraffin Dispersants in the Oil and Gas Industry
Wax build-up in pipelines and storage tanks is a costly and time-consuming issue for oil producers worldwide. Paraffin dispersants, also known as wax dispersants, are chemicals that prevent the solidification of paraffin by dispersing it into smaller particles, allowing it to flow with the crude oil. This significantly reduces the risk of blockages in pipelines, maintains efficient flow, and ensures smoother operations in oilfields.
The demand for paraffin dispersants has increased over the past decade due to the global expansion of oil production, especially in regions with colder climates where paraffin solidification is more likely to occur. As oil exploration and production continue to grow globally, especially in emerging economies like Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia, the need for reliable paraffin dispersants will only increase.
India: A Leading Wax / Paraffin Dispersant Manufacturer
India has become a major hub for the production of wax dispersants. As a wax dispersant manufacturer in India, the country is home to several companies that specialize in producing high-quality paraffin dispersants. These companies have invested heavily in research and development to create efficient and eco-friendly dispersants that meet global standards.
Indian manufacturers benefit from a robust chemical production infrastructure and access to raw materials, making them competitive on the global stage. The strategic geographic location of India also allows for easy access to key markets in Asia, the Middle East, and Africa, where oil production is booming. Companies like Imperial Oilfield Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. have emerged as leaders in the production and export of wax dispersants, driving economic growth through international trade.
The Growing Importance of Paraffin Dispersant Exports
As a leading wax dispersant exporter in India, the country plays a critical role in supplying global markets with the chemicals necessary to ensure the smooth operation of oil and gas infrastructure. The export of paraffin dispersants contributes significantly to India’s foreign exchange earnings, supporting the nation’s economy and positioning it as a key player in the global oil and gas supply chain.
India’s wax dispersant exports have found markets in oil-producing countries across the Middle East, Africa, Latin America, and Asia. These regions are experiencing rapid growth in oil exploration and production, leading to an increased demand for chemicals that can enhance operational efficiency. By providing high-quality dispersants at competitive prices, India has established itself as a trusted supplier on the global stage.
Economic Impact of Wax Dispersant Exports on India’s Economy
The economic impact of paraffin dispersant exports on India’s economy is multifaceted. The growth of this industry has created jobs, generated foreign exchange, and driven innovation in the chemical sector. Some key impacts include:
Job Creation: The manufacturing and export of paraffin dispersants have led to job creation in both the chemical production sector and related industries, such as logistics and transportation. This has helped boost local economies, particularly in regions where manufacturing facilities are located.
Foreign Exchange Earnings: As a major wax dispersant exporter in India, the country generates significant foreign exchange earnings. These earnings contribute to the overall economic stability of the nation, supporting investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
Technological Advancements: The increasing demand for high-quality dispersants has encouraged Indian manufacturers to invest in research and development. This has led to innovations in the production of eco-friendly dispersants, enhancing the competitiveness of Indian companies on the global stage.
Trade Relationships: Exporting paraffin dispersants has strengthened India’s trade relationships with oil-producing nations. These relationships open doors to further collaboration and trade opportunities, particularly in related sectors such as oilfield services and equipment.
Diversification of the Economy: The growth of the paraffin dispersant industry helps diversify India’s economy. As the country becomes less reliant on traditional exports like textiles and agriculture, it builds a more resilient economy capable of weathering global economic fluctuations.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Global Wax Dispersant Market
While the global demand for paraffin dispersants is on the rise, there are also challenges that manufacturers and exporters face. These include fluctuating oil prices, environmental regulations, and competition from other global suppliers.
Fluctuating Oil Prices: The price of oil is a major factor influencing the demand for paraffin dispersants. When oil prices drop, oil producers may cut back on production, leading to reduced demand for dispersants. However, when prices rise, production increases, driving up the need for dispersants. Indian manufacturers must be agile and responsive to these market fluctuations to remain competitive.
Environmental Regulations: With increasing global concern about the environmental impact of chemicals used in the oil industry, there is a growing demand for eco-friendly dispersants. Indian manufacturers are investing in the development of biodegradable dispersants to meet these regulatory demands. This presents an opportunity for India to position itself as a leader in the production of environmentally sustainable chemicals.
Competition from Other Suppliers: As a wax dispersant supplier in India, Indian companies face competition from manufacturers in other countries, particularly those in the United States, China, and Europe. To maintain their competitive edge, Indian exporters must continue to focus on quality, cost-efficiency, and customer service.
The Future of India’s Paraffin Dispersant Exports
The future looks bright for India’s paraffin dispersant export industry. As oil production continues to expand globally, especially in regions like Africa and Southeast Asia, the demand for dispersants will rise. Indian manufacturers are well-positioned to meet this demand, thanks to their competitive pricing, innovative solutions, and established trade relationships.
In addition, India’s focus on sustainability and environmentally friendly dispersants will allow the country to capture a growing segment of the market that prioritizes eco-conscious products. By staying ahead of global trends and continuing to invest in research and development, Indian companies can ensure long-term success in the global wax dispersant market.
Conclusion
India’s role as a wax dispersant manufacturer in India, exporter, and supplier is having a significant economic impact both domestically and globally. The country’s ability to produce high-quality paraffin dispersants at competitive prices has positioned it as a trusted supplier in key oil-producing regions. As the global demand for these chemicals continues to grow, India stands to benefit economically from its leadership in this critical sector.
From job creation to foreign exchange earnings, the export of paraffin dispersants is a vital part of India’s economic landscape. By continuing to innovate and meet the demands of the global market, Indian manufacturers will play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of the world’s oil and gas infrastructure.
#Wax / Parrafin Disperssant supplier in India#Wax / Parrafin Disperssant Manufacturer in India#Wax / Parrafin Disperssant exporter in India
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Trumen Technologies Pvt. Ltd.” is an ISO 9001:2015 certified ,Indian based Manufacturer and Exporters of Level and Pressure sensing instruments. We at Trumen is a team of professionals having years of experience in Level and Pressure Instruments manufacturing who understands what customer needs, and try to fulfill those requirements in appropriate time with best Quality.
We have wide range of CE certified product like Radar Level Transmitters, Ultrasonic Level ,Vibrating fork solid level switch, Vibrating fork liquid level switch, Admittance point level switch, Capacitance point level switch, Vibrating rod point level switch, Conductivity point level switch, Capacitive continuous level transmitter, Hydrostatic continuous level transmitter, etc.
Our products used in different industrial applications in various industries like Power and Water, Oil and Gas, Petrochemical, Mining and Metal, Food and Beverages, Cement ,Pharmaceutical and many more. We are regularly supplying our products to NTPC, IOCL,BPCL, BORL, Cipla, Lupin, Cadila healthcare, Praj High Purity Systems , Ultratech Cement, Shree Cement ,Jindal Group ,TATA, Asian Paints, Procter & Gamble, Hindustan Unilever Ltd, Kirloskar, Vedanta, Nestle, Pepsi, BASF, Novartis and many more.
We are regularly exporting our products to USA, UK, South Korea, Italy ,Thailand, Taiwan, UAE, Tanzania, Turkey ,Sri Lanka ,Saudi Arabia , Kuwait ,Malaysia, Sweden, Canada, Egypt , Brazil ,Singapore etc.
Address: 39, Mangal Nagar, Behind Sai Ram Plaza, Near Rajeev Gandhi Circle, AB Road, Indore, Madhya Pradesh 452001
Web: https://trumen.in/
Contact: 0731 497 2065
#VibratingForkLevelSensor
#VibratingForkLevelSwitch
#VibratingRodPointLevelSwitch
#Vibratingrodpointlevelswitchmanufacturersinindia
#Vibratingrodpointlevelswitchsupplierinindia
#TuningForkPointLevelSwitch
#AdmittancePointLevelSwitch
#RotatingPaddleLevelSwitch
#RadarLeveltransmitter
#LevelSensor
#solidlevelswitch
#powderlevelswitch
#limestone
#coalbunker
#PVCpowder
#levelinstruments
#Levelswitch
#levelindicator
#leveltransmitter
#vibratingforklevelswitch#radarleveltransmitter#levelsensor#solidlevelswitch#capacitanceleveltransmitter#levelswitchinindia#levelindicator#rotatingpaddlelevelswitch#cementlevelsensor#vibratingforklevelsensor
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Holidays 8.27
Holidays
Anti-Rent Insurrection Anniversary Day (Delaware)
The Duchess Who Wasn't Day
Film and Movies Day (Russia)
First Kiss Day
Good Sex Day
Harvest’s End (Elder Scrolls)
Hydrogen Balloon Flight Anniversary Day
International Boobs Day (Italy)
International Boxing Day
International Gamecock Day
International Lottery Day
Just Because Day
Karam Puja (Assam, India)
Kiss Me Day
Krakatoa Day
Ladder Day (French Republic)
Lyndon Baines Johnson Day (Texas)
Motorist Consideration Day
National Radio Day (Argentina)
Nativity of Isis (Egyptian Goddess of Fertility)
Oil & Gas Industry Appreciation Day
Petroleum Day
Pharmacy Day (Iran)
Russian Cinema Day
Senior Race Day (Isle of Man)
Tarzan Day
Three-Thousandth Thnork of the Year (Fairy)
World Rock Paper Scissors Day
Food & Drink Celebrations
Crab Soup Day
National Banana Lovers Day
National Peach Day
National Pots de Creme Day
Salo Day (Ukraine)
Independence & Related Days
Declaration of the Rights of Man (Adopted by French Assembly; 1789)
Moldova (a.k.a. Ziua Republicii); from USSR, 1991)
Yungtaria (Declared; 2016) [unrecognized]
4th & Last Tuesday in August
Lammas Fair Day (Ballycastle, Ireland) [Last Tuesday]
Prophetic Prayer Day [4th Tuesday]
Taco Tuesday [Every Tuesday]
Target Tuesday [Every Tuesday]
Tater Tot Tuesday [Every Tuesday]
Tell the Truth Tuesday [4th Tuesday of Each Month]
Teriyaki Tuesday [Last Tuesday of Each Month]
Thai Tuesday [4th Tuesday of Each Month]
Touch-A-Heart Tuesday [Tuesday of Be Kind to Humankind Week]
Transformation Tuesday [Last Tuesday of Each Month]
Trivia Tuesday [Every Tuesday]
Two For Tuesday [Every Tuesday]
Festivals Beginning August 27, 2024
Farm Progress Show (Boone, Iowa) [thru 8.29]
Free Earth Festival (Asprovalta, Greece) [thru 9.2]
Van Wert County Fair (Van Wert, Ohio) [thru 9.2]
Feast Days
Alexandra Nechita (Artology)
Baculus of Sorrento (Christian; Saint)
Caesarius of Arles (Christian; Saint)
Calasanetius (Christian; Saint)
Day Sacred to Consus (God of Graineries; Ancient Rome)
Decuman (Christian; Saint)
Devaki Day (Indian Mother-Goddess; Everyday Wicca)
Euthalia (Christian; Saint)
Feast Day of Pan (Ancient Greece)
Feast of Incandescent Rebellion
Funella Furchester (Muppetism)
Gebhard of Constance (Christian; Saint)
Harris Day (Church of the SubGenius; Saint)
Hugh if Lincoln (Christian; Saint)
Inspiration Day (Starza Pagan Book of Days)
Jeanette Winterson (Writerism)
John of Pavia (Christian; Saint)
Joseph Calasanctius (Christian; Saint)
Juan Fernando Cobo (Artology)
Klebold Day (Church of the SubGenius; Saint)
Little St.Hugh of Lincoln (Christian; Saint)
Lycerius (a.k.a. Glycerius, Lizier; Christian; Saint)
Máel Ruba (a.k.a. Rufus, Malrubius) of Scotland (Christian; Saint)
Man Ray (Artology)
Marcellus and His Companions (Christian; Martyrs)
Margaret the Barefooted (Christian; Saint)
Monica of Hippo (mother of Augustine of Hippo; Christian; Saint) [Alcoholics]
Murray Matisse (Muppetism)
Narnus (Christian; Saint)
Phallogia (Pagan)
Phanourios of Rhodes (Christian; Saint)
Poëmen (a.k.a. Pastor; Christian; Saint)
Rufus and Carpophorus (Christian; Saints)
Stevin (Positivist; Saint)
Syagrius of Autun (Christian; Saint)
Theodore Dreiser (Writerism)
Thomas Gallaudet and Henry Winter Syle (Episcopal Church)
The Threethousandth Thnork of the Year (Shamanism)
Tithi of Sri Sri Madhabdeva (Assam, India)
Udon Day (Pastafarian)
Usuki Stone Buddhas Fire Festival (Japan)
Volturnalia (Festival to the God of Waters & Fountains; Ancient Rome)
Lucky & Unlucky Days
Prime Number Day: 239 [52 of 72]
Shakku (赤口 Japan) [Bad luck all day, except at noon.]
Premieres
The African Queen, by C.S. Forester (Novel; 1935)
A-Lad-In Bagdad (WB MM Cartoon; 1938)
Bill & Ted Face the Music (Film; 2020)
Camouflage (Terrytoons Cartoon; 1943)
A Cat, a Man, and Two Women, by Jun'ichirō Tanizaki (Novella; 1937)
Cat on a Hot Tin Roof (Film; 1958)
The Centaur, by John Updike (Novel; 1963)
Cheaper by the Dozen, by Frank B. Gilbreth Jr. (Novel; 1948)
Cherish, by The Association (Song; 1966)
Circus (Ub Iwerks MGM Cartoon; 1932)
The Dippy Diplomat (Woody Woodpecker Cartoon; 1945)
Dizzy Newsreel (Phantasies Cartoon; 1943)
Dudley Do-Right (Film; 1999)
Egyptian Melodies (Silly Symphony Disney Cartoon; 1931)
El Salón México, by Aaron Copland (Symphonic Composition; 1937)
Fright to the Finish (Fleischer/Famous Popeye Cartoon; 1954)
Games People Play, by Eric Berne (Psychology Book; 1963)
A Ham in a Role (WB LT Cartoon; 1949)
Hamlet 2 (Film; 2008)
Hollywood Graduation (Color Rhapsody Cartoon; 1938)
Hyde and Hare (WB LT Cartoon; 1955)
I’m Gonna Send Your Vote to College (America Rock Cartoon; Schoolhouse Rock; 2002)
In the Heat if the Night, by Pat Benatar (Album; 1979)
Martin (TV Series; 1992)
Mary Poppins (Film; 1964)
Niagara Fools (Woody Woodpecker Cartoon; 1956)
No Code, by Pearl Jam (Album; 1996)
Old Blackout Joe (Phantasies Cartoon; 1942)
Pigmalion, by Jean-Philippe Rameau (Opera/Ballet; 1748)
Presidential Minute, a.k.a. The Campaign Trail (America Rock Cartoon; Schoolhouse Rock; 2002)
Prométhée, by Gabriel Fauré (Tragédie Lyrique (Grand Cantata); 1900)
Rabbit Redux, by John Updike (Novel: 1971) [Rabbit #2]
Roman Holiday (Film; 1953)
The Shepherds Crown, by Terry Pratchet (Novel; 2015) [Discworld #41]
The Simulacra, by Philip K. Dick (Novel; 1964)
South Pole Pals (Chilly Willy Cartoon; 1966)
Spinach vs. Hamburgers (Fleischer/Famous Popeye Cartoon; 1948)
Swing Time (Film; 1936)
Tarzan of the Apes (Novel; 1912)
Ten, by Pearl Jam (Album; 1991)
Toomorrow (Film; 1970)
Vacation Friends (Film; 2021)
Wet Blanket Policy (Andy Panda Cartoon; 1948)
Wholly Smoke (WB LT Cartoon; 1938)
Today’s Name Days
Gebhard, Margareta, Monika, Vivian (Austria)
Anđelka, Bogoljub, Monika (Croatia)
Otakar (Czech Republic)
Gebhardus (Denmark)
Maime, Maimi, Maimo, Maimu (Estonia)
Rauli (Finland)
Monique (France)
Gebhard, Monika, Vivian (Germany)
Arcadia, Arcadios, Fanourios, Liberios, Osios (Greece)
Gáspár (Hungary)
Cesario, Monica, Rocco (Italy)
Jorens, Ragnars, Valdmiers, Žanis (Latvia)
Aušrinė, Cezarijus, Cezaris, Tolvydas (Lithuania)
Roald, Rolf (Norway)
Angel, Angelus, Cezary, Gebhard, Józef, Kalasanty, Małgorzata, Przybymir, Rufus, Teodor (Poland)
Silvia (Slovakia)
Mónica (Spain)
Raoul, Rolf (Sweden)
Caesar, Cesar, King, Kingsley, Lyndon, Sheri, Sherri, Sherry, Sheryl (USA)
Today is Also…
Day of Year: Day 240 of 2024; 126 days remaining in the year
ISO: Day 2 of Week 35 of 2024
Celtic Tree Calendar: Coll (Hazel) [Day 25 of 28]
Chinese: Month 7 (Ren-Shen), Day 24 (Guy-Hai)
Chinese Year of the: Dragon 4722 (until January 29, 2025) [Wu-Chen]
Hebrew: 23 Av 5784
Islamic: 21 Safar 1446
J Cal: 30 Purple; Lastday [30 of 30]
Julian: 14 August 2024
Moon: 37%: Waning Crescent
Positivist: 14 Gutenberg (9th Month) [Vaucanson]
Runic Half Month: Rad (Motion) [Day 5 of 15]
Season: Summer (Day 69 of 94)
Week: 4th Full Week of August
Zodiac: Virgo (Day 6 of 32)
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leaders of the Navajo Nation, a federally-recognized tribe in the southwest, are heavily criticizing the Biden administration for its action last week banning oil and gas leasing impacting their citizens.
In a highly-anticipated action last week, Interior Secretary Deb Haaland finalized a ban on fossil fuel leasing within 10 miles of the Chaco Culture National Historical Park located near San Juan County, New Mexico. While she said the move would protect the sacred and culturally significant site, Navajo leaders have argued it will wreak economic devastation on tribal members who rely on leasing the land for income.
"I really am emotionally distraught for our constituents that have been impacted by this," Brenda Jesus, who chairs Navajo Nation Council's Resources & Development Committee, told Fox News Digital in an interview.
"Since I've entered the legislative body for my Navajo people, I've listened to a lot of constituents out in that area and, you know, it's just emotional distress, psychologically as well, that they've talked about this – it really disturbs me to know how much more of a hardship that these folks are going to be experiencing out there," she said.
On Wednesday, Jesus led a delegation of Navajo tribal leaders who met with lawmakers on Capitol Hill, making their case against the Department of the Interior's (DOI) action and for a compromise solution. The tribe previously backed a five-mile buffer zone to protect the site while ensuring future drilling on oil-rich allotments.
Navajo Nation leaders have also warned that the federal government failed to properly consult them on the action. They said Haaland never seriously considered their compromise solution and potentially neglected her legal duty to protect rights of Navajo allottees.
"The proper government-to-government tribal consultation has never really taken place at all," Jesus told Fox News Digital. "We're just really advocating on behalf of our constituents. That wasn't really considered – tribal sovereignty."
BIDEN ADMIN HIT WITH LAWSUITS FOR HIDING COMMUNICATIONS INVOLVING CABINET SECRETARY’S DAUGHTER
Overall, the ban amounts to a withdrawal of approximately 336,404 acres of public lands from mineral leasing near Chaco Canyon site.
There are currently 53 Indian allotments located in the so-called 10-mile buffer zone around Chaco Canyon, generating $6.2 million per year in royalties for an estimated 5,462 allottees, according to Navajo Nation data. In addition, there are 418 unleased allotments in the zone that are associated with 16,615 allottees.
According to the Western Energy Alliance, an industry group that represents oil and gas producers in the area, Navajo members will lose an estimated $194 million over the 20 years the action is in place.
"A lot of the allottees themselves rely on these royalties for their livelihood," Carlyle Begay, the federal and state government affairs adviser for the Navajo Nation Council, told Fox News Digital. "Instead of providing our communities and these people directly the opportunity to provide for themselves, they are providing no solutions in how these families are going to compensate for these income losses."
In addition, Navajo Nation President Buu Nygren blasted Haaland for announcing the leasing ban on Treaty Day, which celebrates the signing of the 1868 treaty that formally began the government-to-government relationship between U.S. and the Navajo Nation.
"The Secretary’s action undermines our sovereignty and self-determination," Nygren said in a statement. "Despite my concerns and denunciation, the Department of Interior has moved forward, which is highly disappointing. Secretary Haaland’s decision impacts Navajo allottees but also disregards the tribe’s choice to lease lands for economic development."
NATIVE AMERICAN TRIBES DEPENDENT ON FOSSIL FUEL RESOURCES RIP BIDEN ADMIN FOR DOUBLE STANDARD
He added that the decision "jeopardizes future economic opportunities" and places thousands of Navajo allottees in "dire financial constraints."
Troy Eid, a lawyer who represents Navajo Nation allottees and a former U.S. attorney who was appointed to chair the federal Indian Law and Order Commission, said his clients were prepared to file a lawsuit against Haaland over the action.
"These are among some of the poorest zip codes in the United States. The secretary has decided to steal their mineral rights and it is theft," Eid told Fox News Digital in an interview. "These are rights that were guaranteed to them by federal law in the Hoover administration and the very opening months of the Roosevelt administration – these allotments."
"This order to withdraw land in violation of a Navajo Nation compromise that has been out there for at least two and a half years to come up with a buffer zone that will work for everybody is absolutely outrageous," he continued. "The secretary chose to do this on Treaty Day, our Navajo Nation holiday. She's looking at a lawsuit that I think she's going to have to take very seriously."
While DOI stated Friday that the action won't impact existing leases or production on those leases, Eid and other opponents of the buffer zone said it would indirectly make Indian-owned allotments worthless.
Because drilling on the Navajo allotments requires horizontal crossings that pass through federal land impacted by the ban, the action effectively ends all drilling in the area, he said.
NATIVE AMERICAN TRIBE CONDEMNS BIDEN ADMIN EFFORT TO BAN OIL, GAS LEASING ON LANDS
"If they ban land development on all federal land, you can't have any more continued developments on our parcels. You wind that down, they would get lease payments for the duration of the leases that they have now, but they could no longer get royalties under what she's done," Eid told Fox News Digital.
"The bulk of the compensation that they earn right now – they, the allottees – from their mineral rights are royalties paid by the companies that are developing the oil and have been, for the most part, since the 1950s. There won't be any new development," he added. "There'll be no economic reason or ability for companies to develop the land."
The allotments date back to the early 1900s, when the federal government awarded them to Navajo citizens as a consolation when the tribe's territory was downsized.
Republican lawmakers, meanwhile, said Haaland's action was part of the Biden administration's broader climate change agenda and argued Chaco Canyon is already protected. Rep. Harriet Hageman, R-Wyo., who chairs a House panel on Indian affairs, said it represented a "taking" of tribal lands and vowed congressional action.
"This afternoon I had the opportunity to meet with Navajo tribal leaders and discuss Chaco Canyon and Secretary Haaland’s radical activist decision to create an arbitrary buffer zone around this national park," Hageman told Fox News Digital on Wednesday, "a decision that should rightfully lie with Congress, not the Department of Interior."
"This buffer amounts to a taking of Navajo land, creating economic hardship that will ultimately take money away from much-needed education, medical and infrastructure projects – an estimated $1 billion in revenue," she continued. "The secretary has made this cruel decision without ever speaking with tribal leaders or allottees. We will do whatever we can to stop this taking – whether through my subcommittee or the upcoming appropriations process."
The DOI declined to comment.
#nunyas news#that's puttin them in a pickle#gonna piss people off no matter what now#should have just left things as they were#could blame trump then I think
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
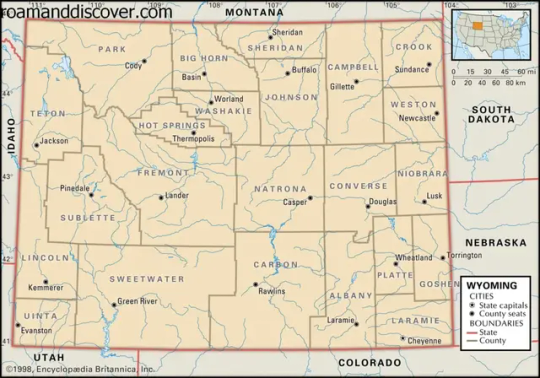
Wyoming

Welcome to Wyoming, the Cowboy State, where you can experience both adventure and tranquility. Wyoming is known for its wide-open spaces, where you can see the stars at night and breathe fresh air during the day. It is a state that is rich in history, culture, and natural wonders, making it a perfect destination for travelers who want to explore the wild and scenic side of the United States. Wyoming has a fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. The state was home to various Native American tribes, including the Shoshone, Arapaho, and Crow, and played an essential role in the fur trade and westward expansion during the 19th century. Wyoming became a territory in 1868 and a state in 1890, making it the 44th state in the Union. When it comes to geography, Wyoming is a stunning state that boasts diverse landscapes, including the Rocky Mountains, rolling hills, and wide-open plains. It is the ninth-largest state in the country, with a total land area of 97,818 square miles. Located in the western United States, Wyoming shares borders with Montana, South Dakota, Nebraska, Colorado, Utah, and Idaho. Wyoming is abundant in natural resources, such as coal, natural gas, and oil, which drive the state's economy. The state is also known for its tourism industry, which offers visitors a chance to explore famous national parks like Yellowstone, Grand Teton, and Devil's Tower. Wyoming has a rich culture that is influenced by western heritage, Native American traditions, and modern art and music. Whether you are interested in hiking, fishing, skiing, or just relaxing in nature, Wyoming has something to offer people of all ages and interests. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about Wyoming, from its history and geography to its culture and tourism. So, pack your bags, and let's begin our journey through Wyoming! Wyoming is a state located in the western United States. It is known for its stunning natural beauty, with vast plains, majestic mountains, and iconic national parks. The state's name is derived from the Delaware Indian word "Maughwauwama," which means "large plains." Wyoming has a rich history that includes Native American tribes, fur trappers, and the Oregon Trail. The area was originally inhabited by various Native American tribes, including the Shoshone, Arapaho, and Cheyenne tribes. In the early 19th century, fur trappers ventured into the region in search of valuable pelts. The Oregon Trail, a historic wagon route, played a significant role in the westward expansion of the United States, passing through Wyoming. Geographically, Wyoming is characterized by its diverse landscapes. The state is home to the Great Plains, which stretch across the eastern part of Wyoming, offering vast open spaces and a rich agricultural heritage. In contrast, the western part of the state is dominated by the Rocky Mountains, including the iconic Grand Tetons and the Wind River Range. These mountain ranges provide breathtaking scenery and endless opportunities for outdoor recreation. One of the state's most famous attractions is Yellowstone National Park, the world's first national park. Yellowstone is renowned for its geysers, hot springs, and abundant wildlife. The park is home to iconic features such as Old Faithful, a geyser that erupts with remarkable predictability, and the Grand Prismatic Spring, a vibrant and mesmerizing natural wonder. Wyoming also boasts several other national parks and recreation areas, including Grand Teton National Park and Bighorn Canyon National Recreation Area. These protected areas offer opportunities for hiking, camping, fishing, and wildlife viewing. The state's commitment to conservation and preserving its natural habitats is evident in its efforts to protect endangered species such as the black-footed ferret and the grizzly bear. Wyoming's economy is diverse, with industries such as energy, tourism, agriculture, and mining playing significant roles. The state is a leading producer of coal, natural gas, and wind energy. Its natural beauty and outdoor recreational opportunities attract visitors from around the world, contributing to the tourism industry. Agriculture, including cattle ranching and crop production, is also an important sector of Wyoming's economy. Throughout the state, you can explore Wyoming's cultural heritage, which includes its Native American tribes and cowboy traditions. Museums, festivals, and events celebrate the state's culture and history. Famous individuals from Wyoming, such as former Vice President Dick Cheney and renowned artist Jackson Pollock, have made significant contributions to politics and the arts. Whether you're seeking outdoor adventure, cultural exploration, or simply a glimpse of the stunning natural beauty, Wyoming offers a wealth of experiences. From its majestic mountains to its vibrant plains, this state is a treasure waiting to be discovered.
1. History of Wyoming
Wyoming, a state located in the western United States, has a fascinating history that encompasses Native American tribes, fur trappers, and the Oregon Trail. The early inhabitants of Wyoming were Native American tribes such as the Shoshone, Arapaho, and Cheyenne. These tribes have inhabited the region for thousands of years, leaving behind a rich cultural heritage. During the 19th century, Wyoming became a significant area for fur trapping, attracting explorers and traders. The fur trade played a crucial role in the state's early economy and brought European settlers to the region. However, it was the Oregon Trail that truly shaped Wyoming's development. The Oregon Trail served as a major route for pioneers heading westward during the mid-1800s, bringing thousands of settlers to the area. Wyoming's history is also intertwined with the expansion of the United States. The state witnessed conflicts between Native American tribes and the U.S. government, including the Battle of Little Bighorn, where Lakota Sioux and Cheyenne warriors defeated General George Custer's forces. Wyoming's history also includes the establishment of military outposts and the development of the transcontinental railroad, which played a crucial role in connecting the East and West coasts of the United States. Today, Wyoming's rich history is celebrated through various museums, historical sites, and events that showcase the state's cultural heritage. Visitors can explore the Oregon Trail Historic Sites, visit the Fort Laramie National Historic Site, or learn about Native American history at the Wind River Indian Reservation. Wyoming's history is a testament to the resilience and spirit of the people who have shaped the state into what it is today.
2. Geography and Climate
Wyoming, located in the western United States, boasts a diverse geography that offers breathtaking natural beauty. From the expansive Great Plains to the majestic Rocky Mountains, the state is a haven for outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers alike. One of Wyoming's most notable geological formations is Yellowstone National Park. This iconic national park is home to mesmerizing geysers, such as the famous Old Faithful, which erupts with stunning precision. The park also features the Grand Prismatic Spring, a vibrant and captivating natural wonder with its vivid colors and unique microbial life. In addition to Yellowstone, Wyoming is also known for the Grand Tetons. These towering mountains offer awe-inspiring vistas and countless hiking trails for adventurers to explore. Whether you're an experienced hiker or a casual nature enthusiast, the Grand Tetons are sure to leave you in awe of their grandeur. When it comes to climate and weather, Wyoming experiences a range of conditions throughout the year. The state's high elevation and continental climate contribute to its distinct weather patterns. Summers are generally warm with mild temperatures, while winters can be harsh and snowy, especially in the mountainous regions. Overall, Wyoming's geography and climate offer a unique and captivating experience for visitors. Whether you're exploring the vast plains, hiking through the majestic mountains, or marveling at the geological wonders, the state's natural beauty is sure to leave a lasting impression. 2.1 Natural Wonders Wyoming is a treasure trove of natural wonders, and at the top of the list is Yellowstone National Park. Established in 1872, it holds the distinction of being the world's first national park. Spanning over 2.2 million acres, this vast wilderness is a paradise for nature lovers and adventure seekers alike. Yellowstone National Park is renowned for its mesmerizing geysers, hot springs, and bubbling mud pots. The most famous geyser in the park is the iconic Old Faithful. As its name suggests, Old Faithful erupts with remarkable predictability, shooting a column of scalding water high into the sky. Witnessing this natural spectacle is truly awe-inspiring. But the wonders of Yellowstone don't end with geysers. The park is also home to an incredible array of wildlife, including grizzly bears, wolves, elk, and bison. Exploring the park's vast network of trails, you might come across these majestic creatures in their natural habitat. Keep your camera ready for those breathtaking encounters. Aside from Yellowstone, Wyoming boasts other natural wonders that will leave you spellbound. The Grand Prismatic Spring, located in Yellowstone, is a sight to behold. Its vivid colors, ranging from deep blue to vibrant orange, are a result of the presence of heat-loving microorganisms. This kaleidoscope of hues is a testament to the wonders of nature's artistry. Whether you're a nature enthusiast, a wildlife lover, or simply seeking adventure, Wyoming's natural wonders will captivate your senses and leave you with memories that will last a lifetime. 2.1.1 Old Faithful One of the most famous attractions in Yellowstone is the Old Faithful geyser. This natural wonder has captivated visitors for decades with its predictable eruptions and stunning displays of power. But what makes Old Faithful so reliable? The science behind Old Faithful's eruptions lies in its unique geological features. Deep beneath the Earth's surface, there is a reservoir of superheated water. As this water rises to the surface, it encounters a narrow and constricted channel known as the geyser's plumbing system. This channel acts as a natural pressure cooker, trapping the water and steam until the pressure becomes too great, causing the geyser to erupt. Unlike other geysers, Old Faithful has a remarkably consistent eruption pattern. It erupts approximately every 90 minutes, shooting water and steam up to 180 feet in the air. This predictability is what earned it the name "Old Faithful." Early explorers and settlers in the area were amazed by its reliability, and it became a popular destination for tourists. Today, visitors from around the world gather around Old Faithful, eagerly awaiting its next eruption. The geyser's eruptions are not only a spectacle to behold but also a reminder of the incredible forces at work beneath the Earth's surface. It serves as a testament to the dynamic nature of Yellowstone National Park and the wonders of nature. 2.1.2 Grand Prismatic Spring The Grand Prismatic Spring is a natural wonder that never fails to mesmerize visitors with its vibrant colors and unique microbial life. Located in Yellowstone National Park, this spring is a sight to behold. The striking hues of blue, green, yellow, and orange create a stunning visual display that is truly breathtaking. But what makes the Grand Prismatic Spring so colorful? The answer lies in the geological processes that occur beneath the surface. This spring is a hot spring, which means that it is heated by geothermal energy from the Earth's interior. As the hot water rises to the surface, it brings with it minerals and microorganisms. The vibrant colors of the Grand Prismatic Spring are a result of these microorganisms. The water contains different types of bacteria and algae, each thriving in different temperature zones. The colors are a reflection of the specific temperature conditions and the pigments produced by the microorganisms. The outer edges of the spring are cooler, creating an environment suitable for orange and yellow bacteria. As the water gets hotter towards the center, it becomes ideal for green and brown bacteria. The combination of these different colors creates the mesmerizing rainbow-like effect that is characteristic of the Grand Prismatic Spring. In addition to its stunning colors, the Grand Prismatic Spring is also home to a unique microbial ecosystem. The microorganisms living in the spring play a crucial role in the ecosystem by converting the mineral-rich water into organic matter. This process supports the growth of other organisms, such as insects and birds, creating a delicate balance of life. Visiting the Grand Prismatic Spring is a truly awe-inspiring experience. As you walk along the boardwalk that surrounds the spring, you can witness the beauty of nature's artistry up close. The vibrant colors, the steam rising from the water, and the sound of bubbling geothermal activity all combine to create a sensory feast. So, if you ever find yourself in Wyoming, make sure to visit the Grand Prismatic Spring. It is a testament to the wonders of the natural world and a reminder of the incredible geological processes that shape our planet. 2.2 Mountain Ranges Wyoming is blessed with the presence of several breathtaking mountain ranges, making it a paradise for outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers. Two of the most prominent mountain ranges in the state are the Grand Tetons and the Wind River Range. These majestic peaks offer not only awe-inspiring beauty but also a plethora of recreational opportunities. The Grand Tetons, located in the northwestern part of Wyoming, are a sight to behold. Rising abruptly from the surrounding plains, these rugged peaks create a dramatic backdrop for the picturesque Jackson Hole valley. Hiking enthusiasts can explore a network of trails that traverse the mountains, offering stunning vistas and the chance to spot wildlife such as elk, moose, and even grizzly bears. The Grand Tetons also provide excellent opportunities for rock climbing, with their challenging granite faces attracting climbers from all over the world. The Wind River Range, located in western Wyoming, is another mountain paradise waiting to be discovered. Spanning over 100 miles, this range is home to more than 40 peaks exceeding 13,000 feet in elevation, including Wyoming's highest point, Gannett Peak. Hikers and backpackers can embark on multi-day adventures through the Wind River Range, exploring pristine alpine lakes, cascading waterfalls, and lush meadows. The range also offers world-class fishing opportunities, with its numerous lakes and rivers teeming with trout. In addition to hiking and fishing, these mountain ranges provide a playground for a wide range of outdoor activities. Mountain biking, horseback riding, and camping are popular pursuits in both the Grand Tetons and the Wind River Range. During the winter months, snow enthusiasts can enjoy skiing, snowboarding, and snowshoeing in the snowy wonderland of these mountains. Whether you are seeking solitude and serenity or adrenaline-pumping adventures, the mountain ranges of Wyoming have something for everyone. So lace up your hiking boots, pack your fishing rod, and get ready to immerse yourself in the natural beauty and endless possibilities of the Grand Tetons and the Wind River Range.
3. Wildlife and Conservation
Wyoming is a paradise for wildlife enthusiasts, offering a diverse range of species and habitats. The state is home to iconic animals such as bison, elk, wolves, and bears, making it a haven for nature lovers and wildlife photographers. From the vast open plains to the rugged mountain ranges, Wyoming's natural landscapes provide a perfect habitat for these magnificent creatures. Conservation efforts play a crucial role in preserving Wyoming's rich biodiversity. The state recognizes the importance of protecting its natural habitats and has implemented various initiatives to ensure the survival of its wildlife. These efforts include the establishment of protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife refuges, where animals can thrive undisturbed. Yellowstone National Park, located primarily in Wyoming, is a prime example of successful conservation. It is not only home to a diverse range of wildlife but also serves as a sanctuary for endangered species. The park's unique ecosystem, which includes geothermal features and abundant food sources, supports a thriving population of animals. Preserving Wyoming's natural habitats is not only essential for the survival of its wildlife but also for maintaining the ecological balance. The state's diverse ecosystems provide crucial services, such as water filtration, carbon sequestration, and pollination, which are vital for human well-being. By protecting Wyoming's natural habitats, we ensure that future generations can continue to enjoy the beauty and wonder of its wildlife. It is our responsibility to be good stewards of the land and to support conservation efforts that safeguard the state's natural heritage. So, whether you're a wildlife enthusiast, a nature lover, or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of the natural world, Wyoming is a destination that should be on your bucket list. Explore its stunning landscapes, encounter its diverse wildlife, and witness firsthand the importance of conservation in preserving our planet's precious resources.

Bison 3.1 Yellowstone National Park Yellowstone National Park is a world-renowned natural wonder located primarily in Wyoming, but also extending into Montana and Idaho. Established in 1872, it holds the distinction of being the first national park in the United States and is widely considered the birthplace of the national park system. What makes Yellowstone truly remarkable is its unique ecosystem, which is home to a diverse range of plant and animal species. The park boasts an incredible array of wildlife, including grizzly bears, wolves, elk, bison, and many others. Visitors to Yellowstone have the opportunity to witness these magnificent creatures in their natural habitat, making it a sanctuary for both wildlife and nature enthusiasts. The park's ecosystem is shaped by various natural features, such as the famous geysers and hot springs. The most iconic of these is the legendary Old Faithful geyser, which erupts with remarkable regularity, captivating visitors with its spectacular displays. Other notable geothermal features include the Grand Prismatic Spring, known for its vibrant colors and unique microbial life. However, Yellowstone National Park also faces numerous challenges. One of the primary concerns is the delicate balance of its ecosystem. The park's wildlife populations must be carefully managed to ensure their long-term survival. Additionally, the park grapples with issues such as invasive species, habitat degradation, and the impact of climate change. Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes