#import-export data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Unlocking Global Trade Opportunities: The Importance of Import-Export Data Providers

In today’s highly interconnected global economy, having access to accurate and real-time import-export data is crucial for businesses, investors, and governments aiming to stay competitive and make informed decisions. Import-export data provides insights into the flow of goods across borders, offering a clear view of market trends, trade patterns, and the health of global economies. This article explores the importance of import-export data providers, the sources of this data, and how businesses can leverage it to gain a strategic edge in the marketplace.
The Significance of Import-Export Data
1. Driving Business Decisions
Import-export data is a valuable tool for businesses engaged in global trade. By understanding the volume, frequency, and direction of trade flows, companies can make informed decisions about where to expand, which markets to enter, and how to optimize their supply chains. Access to comprehensive trade data enables businesses to anticipate demand, reduce costs, and increase profitability in international markets.
2. Informing Investment Strategies
Investors heavily rely on import-export data to assess market potential and identify lucrative investment opportunities. This data provides key insights into economic trends, the performance of specific industries, and potential risks associated with global trade. With the right data, investors can make more informed choices about where to place their capital, whether in emerging markets or established global trade hubs.
3. Shaping Economic Policies
Governments and policymakers depend on accurate import-export data to assess economic health, set tariffs, negotiate trade agreements, and implement regulatory policies. By understanding trade imbalances and identifying economic trends, policymakers can devise strategies that foster growth, reduce trade deficits, and strengthen national economies.
Sources of Import-Export Data
1. Government Agencies and National Statistical Offices
Many countries collect and publish detailed import-export data through national statistical offices. These agencies compile data on exports, imports, trade balances, and tariffs, offering a detailed picture of a country’s trade dynamics. These insights are essential for businesses seeking to expand internationally, as they provide a granular view of trade patterns and industry-specific trends.
2. International Trade Organizations
Organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) provide comprehensive, global trade data. These organizations aggregate data from member countries and publish reports on worldwide trade flows, offering a macroeconomic view of global commerce. This data helps businesses and policymakers understand how different regions and industries are interconnected.
3. Private Import-Export Data Providers
Private companies that specialize in trade data have emerged as crucial players in the global marketplace. These data providers use advanced technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence to collect and analyze trade data in real-time. They offer businesses customized reports, market forecasts, and predictive analytics that give a competitive edge in international trade.
The Impact on Global Supply Chains
1. Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
Import-export data is a vital tool for businesses looking to build resilient supply chains. By analyzing trade data, companies can monitor potential disruptions, such as changes in import/export regulations, natural disasters, or geopolitical instability. Early insights into these challenges allow businesses to adapt their supply chains to minimize disruptions and ensure continuity of operations.
2. Streamlining Operations
Businesses can optimize their operations by using import-export data to identify reliable suppliers, negotiate better deals, and streamline logistics. Data insights enable companies to reduce transportation costs, find alternate suppliers in case of disruptions, and ensure that inventory levels align with market demand. These efficiency improvements can enhance competitiveness in an increasingly globalized market.
Challenges and Future Trends
1. Data Accuracy and Standardization
One of the biggest challenges with import-export data is ensuring its accuracy and standardization. Differences in reporting standards between countries and industries can lead to discrepancies in the data, making it difficult to draw reliable conclusions. To overcome this, businesses must work with trusted data providers that adhere to high standards of data integrity and transparency.
2. The Role of Blockchain Technology
As global trade becomes more digitized, the potential for blockchain technology to enhance the accuracy and security of import-export data is significant. Blockchain’s decentralized nature allows for secure, transparent transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring the reliability of trade data. With the rise of blockchain, businesses and governments alike can benefit from more trustworthy and efficient trade data solutions.
Conclusion
Import-export data is a cornerstone of international business success, influencing decision-making, investment strategies, and supply chain operations. Accessing high-quality, accurate data from reliable sources empowers businesses to thrive in the global marketplace. As technology continues to evolve, the role of import-export data providers will only grow in importance. Embracing advanced data analytics and emerging technologies like blockchain will help businesses unlock new opportunities, streamline operations, and navigate the complexities of global trade. With the right data at your fingertips, the world’s markets are within reach, and the opportunities are endless.
#trade data#import export data providers#Export-Import Data Providers#role of import-export data providers#Sources of Import-Export Data#importance of import-export data providers#Import-Export Data#Import-Export Trad Data
0 notes
Text
[T]he Dutch Republic, like its successor the Kingdom of the Netherlands, [...] throughout the early modern period had an advanced maritime [trading, exports] and (financial) service [banking, insurance] sector. Moreover, Dutch involvement in Atlantic slavery stretched over two and a half centuries. [...] Carefully estimating the scope of all the activities involved in moving, processing and retailing the goods derived from the forced labour performed by the enslaved in the Atlantic world [...] [shows] more clearly in what ways the gains from slavery percolated through the Dutch economy. [...] [This web] connected them [...] to the enslaved in Suriname and other Dutch colonies, as well as in non-Dutch colonies such as Saint Domingue [Haiti], which was one of the main suppliers of slave-produced goods to the Dutch economy until the enslaved revolted in 1791 and brought an end to the trade. [...] A significant part of the eighteenth-century Dutch elite was actively engaged in financing, insuring, organising and enabling the slave system, and drew much wealth from it. [...] [A] staggering 19% (expressed in value) of the Dutch Republic's trade in 1770 consisted of Atlantic slave-produced goods such as sugar, coffee, or indigo [...].
---
One point that deserves considerable emphasis is that [this slave-based Dutch wealth] [...] did not just depend on the increasing output of the Dutch Atlantic slave colonies. By 1770, the Dutch imported over fl.8 million worth of sugar and coffee from French ports. [...] [T]hese [...] routes successfully linked the Dutch trade sector to the massive expansion of slavery in Saint Domingue [the French colony of Haiti], which continued until the early 1790s when the revolution of the enslaved on the French part of that island ended slavery.
Before that time, Dutch sugar mills processed tens of millions of pounds of sugar from the French Caribbean, which were then exported over the Rhine and through the Sound to the German and Eastern European ‘slavery hinterlands’.
---
Coffee and indigo flowed through the Dutch Republic via the same trans-imperial routes, while the Dutch also imported tobacco produced by slaves in the British colonies, [and] gold and tobacco produced [by slaves] in Brazil [...]. The value of all the different components of slave-based trade combined amounted to a sum of fl.57.3 million, more than 23% of all the Dutch trade in 1770. [...] However, trade statistics alone cannot answer the question about the weight of this sector within the economy. [...] 1770 was a peak year for the issuing of new plantation loans [...] [T]he main processing industry that was fully based on slave-produced goods was the Holland-based sugar industry [...]. It has been estimated that in 1770 Amsterdam alone housed 110 refineries, out of a total of 150 refineries in the province of Holland. These processed approximately 50 million pounds of raw sugar per year, employing over 4,000 workers. [...] [I]n the four decades from 1738 to 1779, the slave-based contribution to GDP alone grew by fl.20.5 million, thus contributing almost 40% of all growth generated in the economy of Holland in this period. [...]
---
These [slave-based Dutch commodity] chains ran from [the plantation itself, through maritime trade, through commodity processing sites like sugar refineries, through export of these goods] [...] and from there to European metropoles and hinterlands that in the eighteenth century became mass consumers of slave-produced goods such as sugar and coffee. These chains tied the Dutch economy to slave-based production in Suriname and other Dutch colonies, but also to the plantation complexes of other European powers, most crucially the French in Saint Domingue [Haiti], as the Dutch became major importers and processers of French coffee and sugar that they then redistributed to Northern and Central Europe. [...]
The explosive growth of production on slave plantations in the Dutch Guianas, combined with the international boom in coffee and sugar consumption, ensured that consistently high proportions (19% in 1770) of commodities entering and exiting Dutch harbors were produced on Atlantic slave plantations. [...] The Dutch economy profited from this Atlantic boom both as direct supplier of slave-produced goods [from slave plantations in the Dutch Guianas, from Dutch processing of sugar from slave plantations in French Haiti] and as intermediary [physically exporting sugar and coffee] between the Atlantic slave complexes of other European powers and the Northern and Central European hinterland.
---
Text above by: Pepijn Brandon and Ulbe Bosma. "Slavery and the Dutch economy, 1750-1800". Slavery & Abolition Volume 42, Issue 1. 2021. [Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#these authors lead by pointing out there is general lack of discussion on which metrics or data to use to demonstrate#extent of slaverys contribution to dutch metropolitan wealth when compared to extensive research#on how british slavery profits established infrastructure textiles banking and industrialisation at home domestically in england#so that rather than only considering direct blatant dutch slavery in guiana caribbean etc must also look at metropolitan business in europe#in this same issue another similar article looks at specifically dutch exporting of slave based coffee#and the previously unheralded importance of the dutch export businesses to establishing coffee mass consumption in europe#via shipment to germany#which ties the expansion of french haiti slavery to dutch businesses acting as intermediary by popularizing coffee in europe#which invokes the concept mentioned here as slavery hinterlands#and this just atlantic lets not forget dutch wealth from east india company and cinnamon and srilanka etc#and then in following decades the immense dutch wealth and power in java#tidalectics#caribbean#archipelagic thinking#carceral geography#ecologies#intimacies of four continents#indigenous#sacrifice zones#slavery hinterlands#european coffee
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Duplex Board Paper Manufacturer

Duplex paper board, also known as duplex board, is a type of paperboard or cardboard that is widely used for packaging and printing purposes. It is made by combining two layers of paper, typically made from recycled fibers, with a layer of adhesive in between. This results in a material that is strong, durable, and versatile, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
In India, the manufacture of duplex paper board has been growing steadily in recent years. The country has seen an increase in demand for packaging materials due to the booming e-commerce industry, as well as the growth of various other industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. This has led to a greater need for high-quality packaging materials, including duplex paper board.
One of the key advantages of duplex paper board is its strength and rigidity, which makes it ideal for packaging heavy or fragile items. It also provides a smooth and consistent surface for printing, making it suitable for a wide range of printing and graphic applications. Additionally, duplex paper board is often coated to improve its surface properties, such as smoothness and gloss, further enhancing its suitability for printing and packaging.
The manufacture of duplex paper board in India involves several key processes, including pulping, refining, blending, and coating. The raw materials used in the production of duplex paper board are typically sourced from recycled paper and cardboard, making it an environmentally friendly choice. The manufacturing process also involves the use of advanced machinery and technology to ensure the consistent quality of the final product.
In recent years, the Indian government has also been promoting the use of eco-friendly and sustainable packaging materials, which has further contributed to the growth of the duplex paper board industry in the country. This has led to an increased focus on using renewable resources and reducing the environmental impact of packaging materials, making duplex paper board an attractive option for businesses looking to align with these sustainability goals.
With its strength, versatility, and environmental benefits, duplex paper board is well-positioned to continue being a key player in the packaging and printing industry in India. As the market continues to evolve, it is expected that the manufacture of duplex paper board will continue to thrive and contribute to the country's growing economy.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
In our interconnected world, the exchange of goods and services across borders is crucial for shaping the global economy. Malaysia, a key player in international trade, contributes significantly. Analyzing Malaysia's trade data, including the Importers List and Export Data, provides valuable insights into economic trends, market dynamics, and the global economy's overall health. Explore the article "The Impact of Malaysia Trade Data on the Global Economy" to gain more knowledge.
#export#import#import data#export data#trade data#market research#data driven#global market#global trade data#malaysia#Malaysia Trade Data#Malaysia Importers List#Malaysia Export Data#Data Import Export Data#international trade
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Export Import Products List
Exporting and importing products is a major part of the global economy. In 2022, the value of global merchandise trade was over $28 trillion. This means that businesses and consumers all over the world are exchanging goods and services on a massive scale.

There are a wide variety of products that are exported and imported, but some of the most common include:
Agricultural products: This category includes food crops, such as wheat, rice, and corn, as well as livestock and animal products, such as meat, dairy, and eggs.
Chemicals: This category includes a wide range of products, such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and fertilizers.
Electrical machinery and equipment: This category includes products such as generators, motors, and computers.
Food and beverages: This category includes processed foods and drinks, as well as fresh produce.
Machinery and equipment: This category includes products such as machine tools, engines, and construction equipment.
Manufactured goods: This category includes a wide range of products, such as textiles, clothing, and electronics.
Minerals and fuels: This category includes products such as crude oil, natural gas, and coal.
Other goods: This category includes products that do not fall into any of the other categories, such as furniture and toys.
Textiles and clothing: This category includes products such as yarn, fabric, and garments.
Transport equipment: This category includes products such as cars, trucks, and airplanes.
The specific products that are exported and imported vary from country to country. For example, the United States is a major exporter of agricultural products, machinery, and equipment, while China is a major exporter of manufactured goods and electronics.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Export Import Products
There are a number of factors that businesses should consider when choosing which products to export or import. These factors include:
Demand: Is there a strong demand for the product in the target market?
Competition: How much competition is there for the product in the target market?
Profitability: Is the product profitable to export or import?
Regulations: Are there any regulations that restrict the export or import of the product?
Logistics: How will the product be transported to and from the target market?
Benefits of Exporting and Importing Products
There are a number of benefits to exporting and importing products. For businesses, exporting can help to increase sales and profits, and it can also help to diversify the business's customer base. Importing can help businesses to access products that are not available domestically, and it can also help businesses to reduce costs.
For consumers, exporting and importing can help to lower prices and increase the availability of goods. For example, consumers in the United States can buy fresh produce from all over the world, and they can also buy electronics and other manufactured goods at lower prices because of imports.
Conclusion
Exporting and importing products is a vital part of the global economy. It helps businesses to grow and consumers to save money. If you are considering starting an export import business, there are a number of resources available to help you get started.
#Export Import Products List#export import products#export import data#exporter#bussiness#export#import#importers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
(white knuckling my desk while dijkstra's algorithm slinks up slowly behind me, waiting to strike) I Need To Take Pokemon Go Less Seriously
#thinking about a workflow of using ingress intel total conversion community edition (IITC-CE) and tampermonkey as well as PoGOHWH#exporting pokestop/gym data as a JSON file#importing that data back into openstreetmap and using the aformentioned dijkstra's algorithm#to find an optimal route between every pokestop/gym on my university campus#and THEN exporting all that as a shapefile and downloading it on my phone for an on-the-go reference#(all of which i am not going to do)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Truly astonishing to me that Google Calendar still doesn’t have a batch delete feature
#i lament this every day#but no more so than today#when i was like ''i wonder what this huge amount of timestamped data would look like in a calendar''#but accidentally imported one batch of it into my home calendar instead of the one i set up for the data#it's.......so many events#just going to have to export the calendar and delete everything in icalendar#and then start from scratch
1 note
·
View note
Text

Attention all businesses engaged in international trade with Chile! Get access to the most comprehensive Chile import export data available. Our database includes detailed information on the products being imported and exported, their quantities, and their origin and destination. With this data, you can make informed decisions on your import-export strategies, identify potential new markets, and stay ahead of your competition.
For more-
Contact: +16075244100
Mail: [email protected]
Website: https://www.eximpedia.app/global-trade-data/chile
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Are you looking to expand your business into Paraguay? Look no further!
Our Paraguay import export data service provides detailed information on the market trends, top importing and exporting companies, and more. With our data, you will be able to make informed decisions and take advantage of new opportunities in the Paraguay market. Don't miss out - contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help your business grow.
For More Information:-
Email- [email protected]
Website:- https://www.eximpedia.app/global-trade-data/paraguay
Call Us:- +16075244100
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Import Candle Charts from TradingView websites?
youtube
💥S#.Data provides functionality that supports automatic downloading of historical market data from many data sources. But sometimes websites do not provide an API to make the process automatically. Fortunately, in addition to downloading you can import market data from CSV files directly.
💥TradingView is a charting platform and social network used by many traders and investors worldwide to spot opportunities across global markets. The major feature of the website - various historical dataset - that you can download as a csv file for further usage (e.g. - backtesting, analyzing).
💥For the TradingView website, you need a premium subscription to be able to export candles. Let’s look at this process step-by-step to understand how we can import this market data into S#.Data.
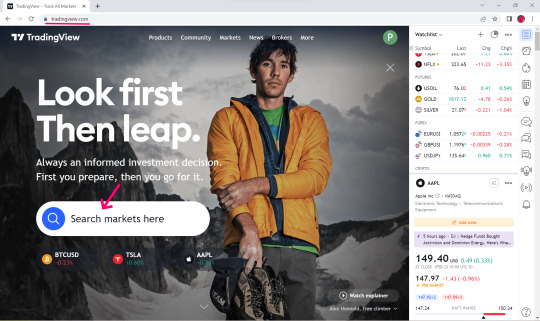
👉Visit TradingView Website.

👉Select Search Market for example NFLX. 👉Click Launch Chart for view.
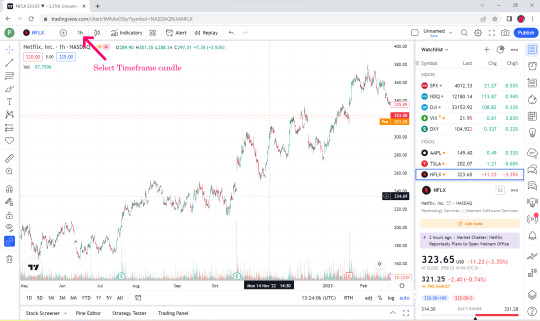

👉Select Time Flame Candle for example 1 hr.
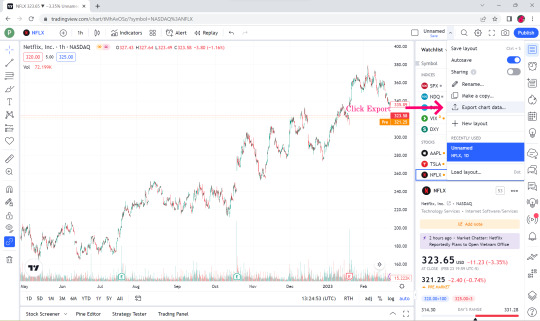
👉Select Export Chart Data.
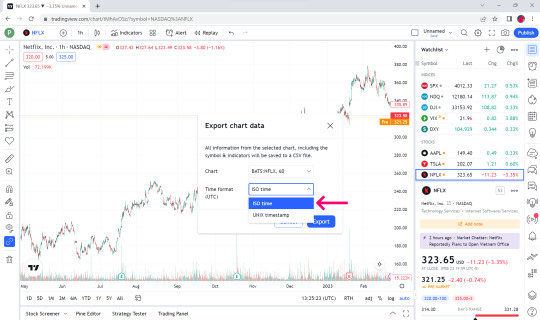
👉In the Time format box, select ISO time.

👉Click Export.

👉Open the downloaded Market data file. You can see that the top bar is date and time, open price, low price, close price, volume and volume MA.
👉S#.Data supports only the first 6 data, the last one volume MA we will not take.
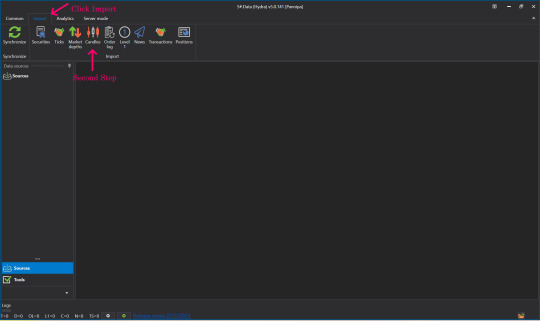
👉Open up your S#.Data Application.
👉Visit our instruction if you doesn't have S#.Data application.
👉How I can get S#.Data
👉Go to S#.Data application, click select import and Click candle.

👉Find the name of the file we just downloaded (btw, you can import by directories as well).
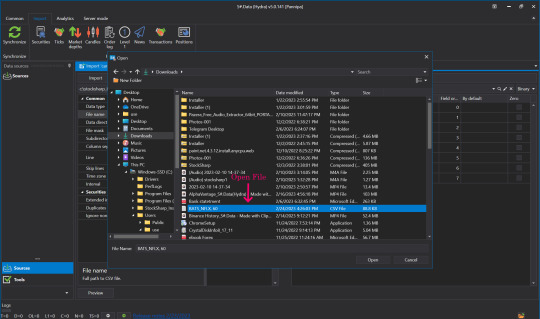
👉Click to select the file that we downloaded, click open.

👉Click to select the time frame to match the timeframe we selected in the file we downloaded initially in the data type field.

👉Setting S#.filed from the Security and Board fields.
👉By default put the Instruments Code that we downloaded. For example NFLX in the Security slot in the instrument board e.g. BATS by default.
👉Enter numbers 0-5 in the date box and so on. Remember - numeration started from 0, not from 1.

👉Skip lines Row 1 cause it contains data columns description.
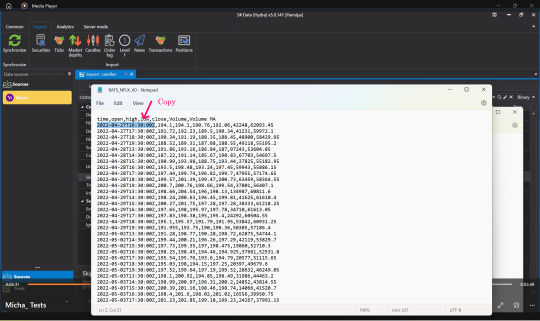
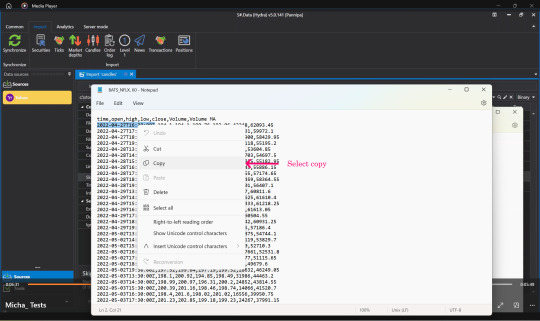
👉Open the file that we downloaded again, select Copy, time, date that we started downloading Market Data.
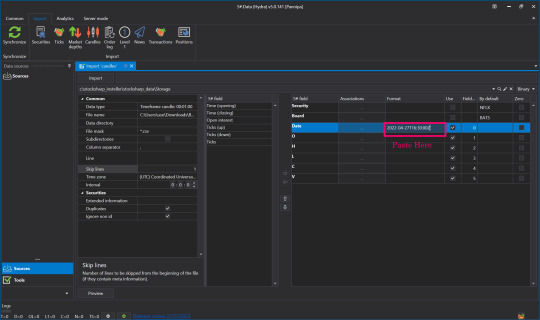
👉Press Paste in the Date Format field.
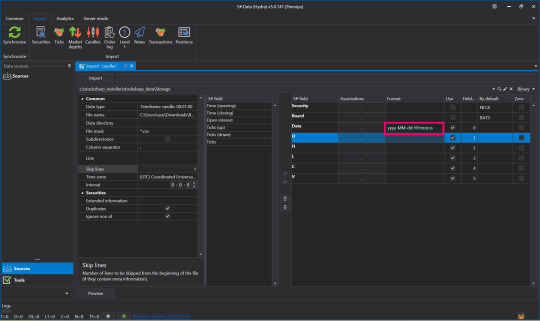
👉Change Numbers to Code Letters By yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss You can read more about format on Microsoft website

👉Once everything is entered correctly, click Preview to double check before importing.
👉When the screen shows this page, there is no problem.
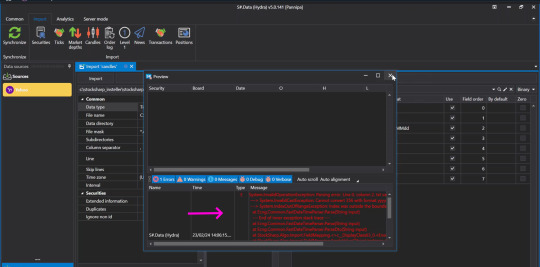
👉But if you press Preview and the screen appears like this, check the details that you have entered again to see if there is any mistake, correct it and press Preview again.
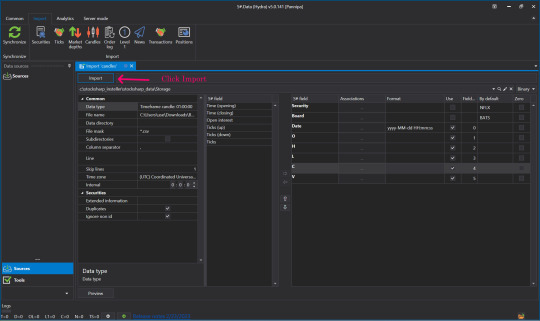
👉Once it's verified and there are no problems, press Import.
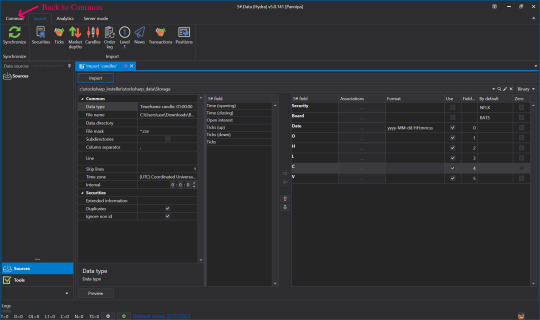
👉When done, click Back to go to Common.
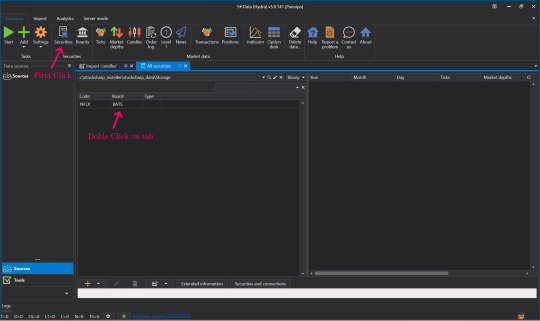
👉Click on our Security.
👉Click on Instrument Tab to view market Data.

👉Now let's see what data was imported. Click Candles.
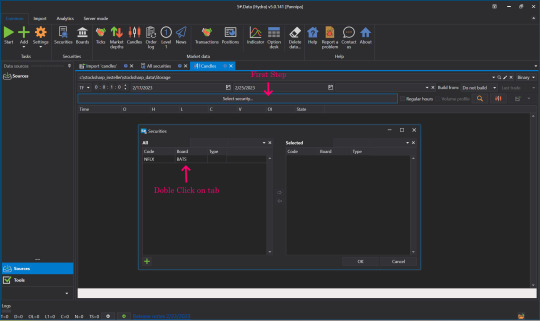
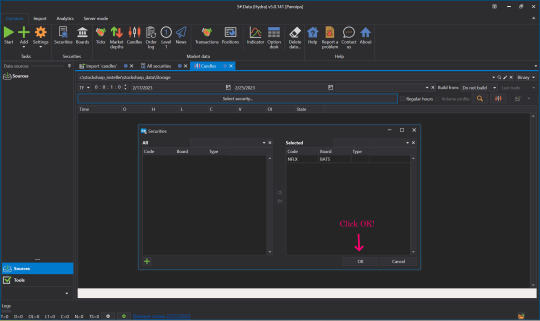
👉Select Security, select the Instrument to view by double-clicking the Instrument Tab, move it to the right side and click OK.

👉Select date and time frame.

👉Click View Market data.
👉Click View Candle Chart to see our candles as a chart.

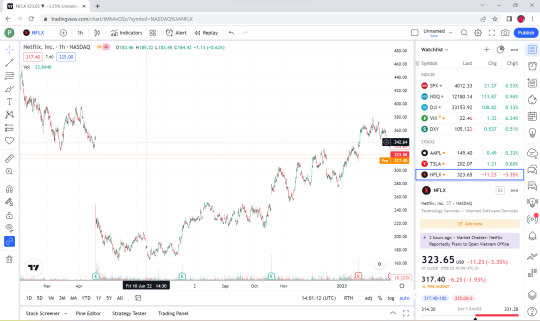
👉This is a Candle Chart comparison between the Chart that was in TradingView website before it was downloaded and the downloaded Chart rendered in S#.Data application.
💥💥Now you know how to import from a CSV file. To make this process you no need to use only limited websites like TradingView. S#.Data supports any format of CSV files that you can download from a variety of sources and websites.
💥Hope this blog is interesting for you. Please comment us what you interesting to know more about S#.Data. We will try to write our next posts.
Sources : StockSharp.com
#downloading of historical market data#import market data#charting platform#export candles#trading view#backtesting#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Is Customs Data Different from Other Trade Data?

In the world of international trade, businesses rely on various types of data to make informed decisions, optimize supply chains, and assess market opportunities. Among the many data sources, customs data stands out due to its detailed nature and its role in ensuring compliance with international trade regulations. However, customs data is often compared to other types of trade data, such as shipment data, import/export data, and trade statistics. While these data sets are interconnected, each serves a distinct purpose and provides unique insights. Understanding how customs data differs from these other trade data types is crucial for businesses looking to leverage this information for growth and competitive advantage.
What Is Customs Data?
Customs data refers to the detailed records of goods being imported and exported across a country’s borders, as captured by customs authorities. This data includes information on the type and volume of goods, the countries involved in trade, customs duties, tariff classifications, and businesses participating in the transactions. Customs data is typically collected and verified by customs departments to ensure compliance with trade laws, tariffs, and regulations.
How Customs Data Differs from Other Trade Data
Focus on Compliance and Regulation: Customs data is primarily concerned with ensuring that goods comply with the laws and regulations of the countries involved in the trade. This includes verifying that imports and exports adhere to tariff classifications, meet safety and quality standards, and are subject to the appropriate taxes and duties. Unlike other types of trade data, which might focus on broader market trends or business relationships, customs data offers a more formal record of each transaction’s legal and regulatory compliance.In contrast, import/export data often focuses on business-specific details such as the identity of the importer/exporter, the products being traded, and the trade volume, but does not necessarily include information about the regulatory framework for those goods.
Level of Detail and Specificity: Customs data is highly detailed. It includes not just the product and quantity of trade, but also the Harmonized System (HS) code used to classify each product, information on the customs duties applied, and the precise legal descriptions of goods. This makes it invaluable for understanding the specificities of trade flows. In comparison, shipment data is typically more focused on logistics, such as the movement of goods through ports, shipping timelines, and tracking information, without going into the regulatory details.Import/export data, while crucial for understanding trade relationships, may lack the same level of granularity. For example, it might tell you the name of a company importing a product and the volume of imports, but it won’t necessarily include details on how that product is classified under national or international trade laws.
Data Sources and Scope: Customs data is usually collected by government agencies responsible for overseeing the entry and exit of goods at national borders, such as customs and border protection services. It is often made publicly available by governments or through third-party platforms. The data is legally mandated and is designed to support government agencies in enforcing trade policies.On the other hand, shipment data is typically provided by logistics companies and freight forwarders. This data tracks the physical movement of goods and provides insights into delivery times, ports of entry, and shipping routes, but it doesn’t focus on the compliance or regulatory aspects of trade.
Use in Risk Management and Forecasting: Customs data is especially valuable for businesses in risk management and forecasting. Because customs data captures the duties, tariffs, and regulatory compliance involved in each transaction, it helps businesses assess the cost and risk factors associated with their global trade activities. For example, businesses can track tariff changes, evaluate potential delays due to customs inspections, and ensure they are meeting compliance requirements. This helps mitigate risks associated with fines, delays, or trade restrictions.In contrast, trade statistics might offer high-level insights into market trends and trade volumes but typically lack the depth of regulatory data that customs data provides. Import/export data offers insight into who is trading what with whom, but it doesn’t capture the finer details of the regulatory landscape, which is essential for planning and risk assessment.
Utility for Competitive Intelligence: Customs data offers a significant advantage for competitive intelligence because it not only identifies the goods being traded but also provides insights into the companies involved in these transactions. Businesses can analyze customs data to monitor their competitors’ activities, identify their key suppliers and buyers, and track the goods they are importing or exporting. This level of insight allows businesses to identify gaps in the market, potential opportunities for partnerships, and strategies for positioning their products.While import/export data also reveals which companies are trading in particular markets, it typically does not provide insights into competitors’ supply chain strategies or regulatory compliance practices, which can be crucial for making strategic business decisions.
Conclusion
While customs data is a subset of trade data, it stands out due to its focus on compliance, regulatory detail, and the granularity of the information it provides. Unlike shipment data, which focuses on logistics, or trade statistics, which offer high-level market insights, customs data delivers the precise, legally mandated information necessary to navigate the complexities of global trade. For businesses looking to manage risk, understand market dynamics, and gain a competitive edge, customs data is an invaluable resource.
0 notes
Text
Explore India's soybean production, export trends, leading exporters, HS codes, and tips for success in global markets. Get insights and data to grow your soybean exports from India business effectively.
#soybean export from india#soybean export data#soybean hs code#export of soybean from india#india soybean export#soybean export data from india#soybean export india#soybean exporters in india#soybean exporters#soybean import export data
0 notes
Text
How Can Colombia Import Data and Export Data Enhance Your Business Strategy?

Q1: What is Colombia Import Data, and Why Should Businesses Care About It?
Colombia import data is a collection of detailed records about goods brought into Colombia from various countries. This data typically includes information like the type of products, HS codes, shipment dates, importers' names, and countries of origin. It plays a pivotal role for businesses that want to understand the Colombian market dynamics, assess demand, and identify key players.
For instance, Colombia import data helps international exporters find potential buyers within Colombia. Companies can also use this data to analyze the competition, understand pricing trends, and identify high-demand products in sectors such as machinery, electronics, or agriculture.
Q2: How Does Colombia Customs Data Support Trade Analysis?
Colombia Customs Data comprises comprehensive records maintained by Colombian customs authorities. It includes both import and export transactions, detailing:
Product descriptions
HS codes
Values of shipments
Importers and exporters
Ports of entry or exit
By analyzing Colombia Customs Data, businesses can uncover valuable trade insights, like identifying profitable products, top trading partners, and customs procedures specific to Colombia. It also ensures businesses comply with local regulations, minimizing delays or penalties.
Q3: What Information Does Colombia Shipment Data Provide?
Colombia Shipment Data offers a granular look at trade activities, focusing on shipment details. This includes:
Shipment origins and destinations
Dates of shipping and delivery
Freight values
Carrier details
For businesses, analyzing Colombia shipment data helps in planning logistics efficiently. For instance, a company importing raw materials can use shipment data to optimize transit times, identify reliable shipping partners, and reduce supply chain costs.
Q4: Why is Colombia Trade Data Essential for Businesses?
Colombia trade data is a treasure trove of insights into the country's import and export activities. It provides a macro view of trade flows and reveals patterns that can guide strategic decision-making. Here’s how:
Understand Market Trends: Identify growing sectors in Colombia, such as renewable energy or pharmaceuticals.
Evaluate Global Trade Relations: Discover which countries are Colombia's top trading partners.
Identify Opportunities: Pinpoint products or industries with untapped potential.
For example, businesses exporting coffee-related machinery to Colombia can study trade data to understand demand cycles and adjust their marketing strategies accordingly.
Q5: What is Colombia Export Data, and Who Can Benefit From It?
Colombia export data provides detailed records of goods shipped out of Colombia to international markets. This data includes information like product categories, exporting companies, and destinations.
Colombia export data is particularly useful for:
Buyers: To identify and connect with reliable Colombian suppliers.
Exporters: To understand competition and optimize their operations.
Market Analysts: To predict demand for Colombian goods in global markets.
For example, a company sourcing fresh flowers might use Colombia export data to evaluate exporters’ reliability based on their shipment history and delivery timelines.
Q6: How Can Colombia Importer Data Help Foreign Businesses?
Colombia importer data is a subset of trade data that focuses on companies importing goods into Colombia. This data is invaluable for exporters looking to enter the Colombian market. It helps:
Identify Key Buyers: Exporters can find companies already importing their products.
Assess Importing Trends: Understand what products are being imported and in what quantities.
Target Marketing Efforts: Focus on industries with high demand for specific products.
For instance, a food exporter can use importer data to identify retailers or wholesalers specializing in processed foods.
Q7: Why is Colombia Exporter Data Important for Buyers?
Colombia exporter data highlights the major exporters in the country and their trading patterns. This data helps international buyers:
Evaluate Exporters: Check the credibility of potential suppliers based on their shipment history.
Negotiate Better Deals: Use shipment volume and frequency data to negotiate favorable terms.
Expand Supplier Base: Find new exporters to diversify sourcing.
For example, an importer of Colombian coffee can use exporter data to compare suppliers based on export volumes and shipment destinations.
Q8: How Can Companies Use Colombia Suppliers Data Effectively?
Colombia suppliers data is particularly valuable for companies looking to establish or enhance their supply chains. With this data, businesses can:
Compare suppliers for pricing and quality.
Assess reliability based on export performance.
Find suppliers in niche markets, such as organic or eco-friendly products.
For instance, a fashion retailer sourcing leather goods can use suppliers' data to find ethical suppliers in Colombia specializing in sustainable practices.
Q9: What Insights Can Colombia Buyers Data Offer Exporters?
Exporters seeking to expand their presence in Colombia need to know who their potential customers are. Colombia buyers data helps exporters:
Identify active buyers in their product category.
Understand purchasing patterns and volumes.
Create targeted marketing campaigns.
For example, a medical equipment manufacturer can use buyers' data to identify hospitals and clinics in Colombia actively purchasing similar products.
Q10: What Are the Main Benefits of Analyzing Colombia Customs Export Data?
Colombia customs export data is a critical tool for exporters, buyers, and researchers. Here are its benefits:
Forecast Demand: Predict global demand for Colombian goods like coffee, flowers, and minerals.
Analyze Competitors: Study competitors’ export volumes and destinations.
Find Emerging Markets: Identify new opportunities for expanding export operations.
By leveraging export data, businesses can align their strategies with market demand and improve their competitiveness.
Q11: What Are the Challenges in Using Colombia Trade Data?
While Colombia trade data is highly beneficial, it does come with some challenges:
Data Overload: Sorting through massive amounts of information can be overwhelming.
Accuracy Issues: Ensuring data is up-to-date and error-free is critical.
Complex Analysis: Understanding trade patterns requires expertise in data analytics.
To overcome these challenges, businesses often rely on specialized trade intelligence platforms or consultants.
Q12: Where Can You Access Reliable Colombia Customs Data?
To access high-quality Colombia Customs Data, businesses can turn to:
Government Portals: Official trade and customs websites.
Data Providers: Companies offering detailed and processed trade data.
Industry Reports: Research firms publishing Colombia-specific trade insights.
Choosing the right data source ensures you get accurate, timely, and actionable information for your business needs.
Q13: What Tools Can You Use to Analyze Colombia Trade Data?
Modern trade data analysis relies on advanced tools, such as:
Data Analytics Platforms: Software like Tableau and Power BI.
Custom Dashboards: Provided by trade intelligence firms.
AI Tools: For predictive analysis and trend forecasting.
These tools help businesses extract actionable insights and make informed decisions quickly.
Q14: How Can Small Businesses Leverage Colombia Trade Data?
Small businesses often face resource constraints, but Colombia trade data can level the playing field. Here's how:
Find niche markets with low competition.
Identify affordable suppliers or trustworthy buyers.
Use data to negotiate better terms with partners.
For example, a startup importing eco-friendly packaging materials can use trade data to discover reliable Colombian suppliers.
Q15: How Does Colombia Trade Data Foster Economic Growth?
By providing transparency and insights into trade flows, Colombia trade data benefits businesses and the overall economy. It fosters:
Increased foreign investments.
More efficient trade policies.
Enhanced global competitiveness for Colombian exporters.
Governments and businesses alike use trade data to drive innovation and boost growth.
Conclusion
Whether you’re a global exporter, local importer, or researcher, understanding Colombia import data, Colombia Customs Data, and Colombia export data is essential for success. With the right tools and insights, you can tap into Colombia’s thriving trade ecosystem, build strategic partnerships, and stay ahead in the competitive market.
#Colombia import data#Colombia Custom import data#Import data Colombia#Colombia import shipment data#Colombia Importer data#Colombia Buyers Data#Colombia Customs Data#Colombia Shipment Data#Colombia Trade Data#Colombia export data#Colombia exporter data#Colombia custom export data#export data Colombia#Colombia export shipment data#Colombia suppliers Data
0 notes
Text
Embarking on Malaysia's import journey? Navigate the intricacies of the country's import landscape with confidence using our "10 Tips for Navigating Malaysia’s Importers List." From understanding regulatory nuances to leveraging online directories and attending trade shows, these insights are your key to forging successful trade relations. Whether you're a seasoned importer or a newcomer, these tips will empower you to make informed decisions and establish fruitful partnerships in Malaysia's dynamic market.
#export#trade data#export data#import#import data#marketresearch#internationaltrade#datadriven#globaltrade#globaltradedata#malaysia#export import data#Malaysia Importers List#Malaysia Export Data#Malaysia Import Data
2 notes
·
View notes