#iaas vs paas
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How To Choose The Right SaaS App Development Partner?
Visit Website, Glasier Inc.
Our Blogs
Other Services,
erp software development company
hospital management system
Hire Angular Developers
Hire SaaS developer
Hire Flutter Developers
Hire ReactJs Developers
#saas vs paas vs iaas#hire saas developers#hire dedicated resources#hire react#saas vs paas#paas vs saas#iaas vs paas#custom software develpment#hire offshore developers#custom erp software development#custom software solutions#saas solutions examples#saas developers#saas software solutions
1 note
·
View note
Text
How To Choose Between SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS.
Read more Blogs,
Visit Website, Glasier Inc.
Hire SaaS developers
#saas vs paas vs iaas#saas vs paas#iaas vs paas#hire saas developers#custom software develoment#hire dedicated developers#app development company#hire saas developer
1 note
·
View note
Text
SaaS Vs PaaS Vs IaaS Find the Right Cloud Model for Your Business
In todays world anything as a service has become a topic of discussion. We are going to discuss in-depth about SaaS, PaaS Ans IaaS. Popular Examples of SaaS Providers Include BigCommerce, Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox, MailChimp, ZenDesk, DocuSign, Slack, and Hubspot. Popular Examples of PaaS Providers Include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, Force, Apache Stratos, and Adobe Magento Commerce Cloud. Popular Examples of IaaS Providers Include AWS EC2, Rackspace, Google Compute Engine (GCE), Digital Ocean, and Microsoft Azure. To know in detail about the main advantages and Disadvantages of SaaS, IaaS, And PaaS click on the following link to read the full article https://www.careerbright.com/entrepreneur/saas-vs-paas-vs-iaas-discover-the-right-cloud-model-for-your-business
0 notes
Text
What is CaaS? Container-as-a-Service Explained
Content Role and Responsibilities of CAAs What is CaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS? What Is Containers-as-a-Service? CaaS Explained Apiculus by Yotta: Leading the Way in Cloud as a Service For example, starting up a Linux container with an application happens in seconds. If your application was deployed across two VMs, you’d need two OS installations in addition to the space your application took. This…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Cloud App development made easy with Codestore Get free consulting. Contact us from this link:- https://codestoresolutions.com/cloud-app-development/
#app development#mobile app development#custom app development#web app development#cloud development#cloud devops services
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
SaaS-Based vs Cloud-Based: What’s the Difference?
Two terminologies that often get tossed around are saas cloud applications (Software as a Service) and Cloud-Based. While they might seem interchangeable, these terms represent distinct facets of the digital space, each offering a unique set of advantages and applications.
The cloud is a space where data and applications float effortlessly, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. It’s a virtual space that eliminates the need for physical infrastructure, allowing businesses and individuals to store, process, and access their information without the constraints of physical servers.
At its core, Cloud-Based refers to the delivery of computing services – from storage to processing power – over the internet. It is a comprehensive umbrella term encompassing a variety of services, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and, of course, Software as a Service (SaaS).
This offers virtualized computing resources over the internet. Companies can rent virtual machines and other resources rather than investing in and maintaining physical servers.
A level up, PaaS provides a platform allowing developers to build, deploy, and scale applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, or update the software on their devices.
SaaS-Based takes center stage when it comes to delivering specific software applications through the cloud. This means users can access software applications without the hassle of installation, updates, or maintenance. Popular examples include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce.
One of the key advantages of SaaS-Based solutions is accessibility. Users can access applications from any device with an internet connection, fostering collaboration and flexibility.
Forget the days of manual updates. SaaS applications are maintained and updated by the service provider, ensuring users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
SaaS offers scalability on demand. Whether a business is growing rapidly or experiencing a temporary surge, SaaS applications can adapt to changing needs without requiring significant infrastructure investments.
While SaaS-Based and Cloud-Based are interconnected, the difference lies in their scope and application. Cloud-Based serves as the overarching model, providing the infrastructure and platforms, while SaaS-Based refines the experience, focusing specifically on delivering software applications smoothly.
When choosing between the two, it’s crucial to assess your needs. If you’re seeking a complete solution that encompasses infrastructure, platforms, and software, then Cloud-Based might be your go-to. However, if your primary goal is smooth access to specific applications without the burden of maintenance, then SaaS-Based is the star of the show.
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of SaaS-Based vs. Cloud-Based is crucial in navigating the digital space.. As technology continues to advance, these terms will undoubtedly evolve, but for now, they remain essential in shaping how we interact with, access, and leverage digital tools and cloud-saas solutions.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Hospital Information Systems (HIS) - Guide
Visit Website, Glasier Inc.
Our Blogs
Other Services,
erp software development company
hospital management system
Hire Angular Developers
Hire SaaS developer
Hire Flutter Developers
Hire ReactJs Developers
#saas vs paas vs iaas#hire saas developers#hire dedicated resources#hire react#saas vs paas#paas vs saas#iaas vs paas#custom software develpment#hire offshore developers#custom erp software development#custom software solutions#saas solutions examples#saas developers#saas software solutions
1 note
·
View note
Text
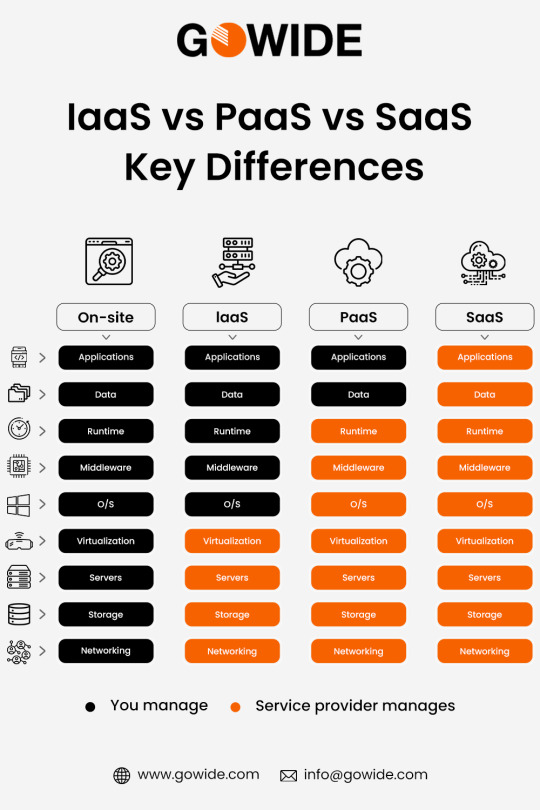
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Key Differences
When choosing a cloud computing model for your business, it’s essential to understand the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
IaaS: You manage the software, data, and runtime, while the provider manages the infrastructure.
PaaS: You manage applications and data; the provider manages the infrastructure and platform.
SaaS: The provider manages everything; you simply use the software.
Choose the model that fits your business needs, whether it’s total control (IaaS), development freedom (PaaS), or ease of use (SaaS).
Know More - https://gowide.com/paas-iaas-and-saas-key-features-and-benefits/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cloud Computing vs Cloud Consulting
Cloud computing and cloud consulting are related but distinct concepts within the broader field of cloud services. Here’s a breakdown of the differences and how each plays a role in the technology landscape:
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the Internet. These services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and more. The main idea is to provide scalable and flexible resources on demand, allowing users to access and use these resources without needing to manage physical hardware or software.
Key Components:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Examples include virtual machines, storage, and networks.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform allowing developers to build, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, accessible via web browsers.
Benefits:
Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
Cost Efficiency: Pay for what you use rather than investing in physical hardware.
Accessibility: Access resources from anywhere with an internet connection.
Maintenance: Providers handle maintenance and updates.
Cloud Consulting
Cloud consulting involves advisory services provided by experts to help organizations plan, implement, and optimize their cloud computing strategies. Consultants assist businesses in understanding how cloud technologies can be applied to meet their specific needs and goals.
Key Components:
Strategy Development: Advising on the best cloud strategy based on an organization’s needs, including choosing between public, private, or hybrid clouds.
Migration Planning: Helping businesses move their data, applications, and workloads to the cloud efficiently and securely.
Architecture Design: Designing cloud solutions that are scalable, secure, and aligned with business objectives.
Optimization: Analyzing and improving cloud performance and cost-efficiency.
Compliance and Security: Ensuring that cloud solutions meet regulatory requirements and have appropriate security measures.
Benefits:
Expertise: Access to specialized knowledge and experience that helps in making informed decisions.
Tailored Solutions: Customized advice and solutions that address specific business challenges and goals.
Risk Mitigation: Identifying potential risks and developing strategies to manage them.
Efficiency: Streamlining cloud adoption processes and optimizing existing cloud investments.
Comparison
Scope:
Cloud Computing: Focuses on the actual delivery and use of cloud services and resources.
Cloud Consulting: Focuses on advising and assisting organizations in adopting and optimizing cloud technologies.
Objective:
Cloud Computing: Provides the infrastructure, platforms, and software needed for cloud-based operations.
Cloud Consulting: Helps businesses navigate their cloud journey, from planning and migration to optimization and compliance.
Audience:
Cloud Computing: Typically involves IT departments and end-users who consume cloud services.
Cloud Consulting: Targets business leaders, IT managers, and organizations seeking expert guidance on cloud strategies.
In summary, cloud computing is about using Cloud Computing services to meet your business needs, while Cloud Consulting is about getting expert advice to make the most of those services. Both are crucial, but they address different aspects of cloud technology.
0 notes
Text
Next - Gen cyber security

Introduction
Welcome and Orientation
Overview of the Next-Gen Cyber Security Skills course in Bangalore
Introduction to instructors and fellow participants
Setting goals and expectations for the course
Module 1: Foundations of Cyber Security
Understanding Cyber Security
Definition and importance of cyber security in today’s world
Current landscape and emerging threats
Cyber Security Terminology
Key terms and concepts crucial for the Bangalore cyber security course
Overview of common attack vectors and defenses
Cyber Security Frameworks and Standards
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
ISO/IEC 27001
CIS Controls and their relevance to Bangalore’s cyber security environment
Module 2: Network Security
Network Security Fundamentals
Basic networking concepts vital for Bangalore cyber security professionals
Understanding firewalls, VPNs, and IDS/IPS
Securing Network Infrastructure
Techniques for network segmentation and isolation
Secure network design and architecture
Wireless Network Security
Wireless security protocols (WPA3, WPA2)
Securing wireless access points in a Bangalore context
Module 3: Application Security
Introduction to Application Security
Common vulnerabilities (OWASP Top Ten)
Secure coding practices essential for Bangalore developers
Web Application Security
Addressing Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and SQL Injection
Integrating secure development lifecycle (SDLC) practices
Mobile Application Security
Addressing mobile-specific threats and vulnerabilities
Best practices for securing mobile apps in the Bangalore market
Module 4: Endpoint Security
Endpoint Protection
Anti-virus and anti-malware solutions
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools
Securing Operating Systems
Hardening Windows and Linux systems
Effective patch management and software updates
BYOD and IoT Security
Managing Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies in Bangalore
Securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices
Module 5: Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Fundamentals of IAM
Authentication vs. Authorization
Identity lifecycle management and its application in Bangalore businesses
Access Control Mechanisms
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Identity Management Solutions
Single Sign-On (SSO) and Federation
Identity as a Service (IDaaS) platforms and their relevance
Module 6: Cloud Security
Cloud Security Basics
Understanding cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
Shared responsibility model for cloud security
Securing Cloud Environments
Best practices for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud in Bangalore
Cloud security posture management
Cloud Compliance and Governance
Regulatory requirements and compliance standards applicable in Bangalore
Data protection and privacy in the cloud
Module 7: Threat Intelligence and Incident Response
Cyber Threat Intelligence
Gathering and analyzing threat data
Using threat intelligence platforms effectively
Incident Response Planning
Developing an incident response plan
Incident detection and analysis
Handling Security Incidents
Containment, eradication, and recovery strategies
Post-incident activities and lessons learned
Module 8: Security Operations and Monitoring
Security Operations Center (SOC)
Roles and responsibilities of SOC teams
Setting up and managing a SOC in Bangalore
Monitoring and Logging
Importance of logging and monitoring
Using SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools
Threat Hunting
Proactive threat hunting techniques
Leveraging advanced analytics and AI for threat detection
Module 9: Compliance and Legal Aspects
Understanding Cyber Security Regulations
Key regulations (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, etc.)
Compliance requirements for organizations in Bangalore
Legal Considerations in Cyber Security
Data breach laws and notification requirements
Intellectual property and cyber crime laws
Auditing and Assessment
Conducting security audits and assessments
Preparing for compliance audits
Module 10: Capstone Project and Certification
Capstone Project
Real-world scenario-based project
Applying learned skills to solve complex problems
Exam Preparation
Review of key concepts and practice exams
Tips and strategies for passing the certification exam
Certification and Next Steps
Receiving course completion certificate
Exploring advanced certifications and career paths
Conclusion and Course Wrap-Up
Final Q&A Session
Addressing any remaining questions
Sharing additional resources and tools
Networking and Alumni Community
Joining the course alumni network
Continued learning and professional development opportunities in Bangalore
This Next-Gen Cyber Security course in Bangalore will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in the evolving field of cyber security
0 notes
Text
Cloud Computing provides integrated application & network to business solutions. It provides numerous design & deliver digital services to customers. Business needs cloud computing because of high performance, Advanced security, Efficitue cost, Scalability & flexibility etc. To choose the right cloud module there are some features, Business requirements, Budget, and Technical Expertise. If you want to get a clear idea about SaaS Vs PaaS Vs IaaS: Choose Right for Your Business, then explore our article.
0 notes
Text
Optimize Public Cloud Security with 10 Tips

Public Cloud Security
The first commercial cloud launched 20 years ago, and Public Cloud security has exploded. They take for granted the many ways public cloud-related services like Instagram, Netflix, Gmail, and others pervade their lives.
Small startups and major organizations use public cloud computing models for flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. IDC predicts $1.35 trillion in public cloud provider investment by 2027.
The top 10 corporate use cases show how a Public Cloud security underpins contemporary business and drives digital transformation.
What is public cloud?
Public clouds allow customers to pay-per-use computing resources from a third-party vendor via the internet. Public clouds also let enterprises automatically scale computation and storage resources to their requirements.
How does public cloud work?
Cloud service providers (CSPs) execute customer workloads in massive physical data centers in public cloud computing. A self-service API interface created and allotted virtual resources to tenants in multi-tenant Public Cloud security settings. Multi-tenant hosting lets cloud service providers optimize data center and infrastructure usage to provide prices lower than company-owned data centers.
Cloud service providers also maintain hardware and offer high-speed network connection for application and data access. They handle server, operating system, networking, and other infrastructure virtualization to optimize public cloud data center resources. For instance, virtualization may divide a single server into many virtual servers serving various customers.
Public Cloud Service
Every major public cloud provider updates and maintains their infrastructure and uses the strongest data protection and security standards to avoid data breaches.
Cloud security technologies like IAM, DLP, and SIEM are also available.
Finally, a SLA encompasses public cloud service performance, availability, and management and specifies the CSP-client relationship.
Public cloud models
Hundreds of managed services and tools are available from cloud providers in four categories. Most major firms employ all four services to construct a contemporary IT cloud computing infrastructure.
Cloud-hosted application software is available on-demand as SaaS.
PaaS provides hardware, software, and infrastructure for app development, operating, and management.
IaaS provides basic computation, network, and storage services in the cloud.
The cloud provider handles provisioning, scaling, scheduling, and patching in serverless computing.
Public cloud advantages
Companies using public cloud solutions may get these benefits:
Use pay-per-usage or subscription pricing to cut hardware and on-premises infrastructure costs.
Efficiency: Use what you paid for to save resources.
Automate capacity addition for traffic spikes.
Scalability: Scale up or scale out to increasing workloads.
Access cutting-edge technologies like AI, edge computing, and the IoT.
Be more predictable with continuing operations expenditures to reduce IT spending.
Team collaboration: Use public cloud resources from anywhere and have real-time team communication for quicker results.
With automated backup and disaster recovery, reduce downtime and protect data.
Sustainability: Reduce your carbon impact by improving energy efficiency using CSP.
Public vs private vs hybrid cloud vs multicloud
Other cloud deployment methods include private, hybrid, and multicloud, each with its own benefits. Single-tenant cloud infrastructure deployed on-premises at a company’s location is called a private cloud. Dedicated cloud providers or third-party infrastructure may host private clouds. Financial, government, and healthcare enterprises with sensitive data and strict regulatory or security needs should use private clouds.
Hybrid clouds combine on-premises, private, and public cloud computing environments to offer a flexible managed IT architecture.
Businesses now employ multicloud and hybrid cloud environments to connect to numerous Public Cloud security providers. Companies may avoid vendor lock-in and choose the finest cloud services with a multicloud strategy. Large companies choose hybrid multiclouds because they have the greatest control over workload deployment and scaling.
The best public cloud uses
Top 10 ways firms use public cloud computing to save money, innovate, and expand.
Public Cloud Storage
1.Holding
Technology as-a-service and storage capacity in public cloud storage assist enterprises avoid the capital expenditures of constructing and maintaining in-house storage. In the event of a natural catastrophe, outage, or other emergency, cloud storage provides redundancy by keeping firm data on many devices.
2.Dynamic resource allocation
A Public Cloud security lets enterprises grow resources as needed. With a public cloud, a seasonal e-commerce business may swiftly increase its online offerings. They may scale down during normal sales and just pay for capacity during peak times.
3.Building and testing
Instead of the costly and time-consuming waterfall process, a public cloud environment is excellent for building and testing new apps. In minutes, developers may establish public cloud-based VM testing environments. Developers may quickly remove testing environments.
4.Apps and DevOps on the cloud
The public cloud provides cloud-native apps using microservices, which are essential to DevOps. Developers create containerized apps once and deploy them anywhere using DevOp tools to streamline cloud-native development and quick software delivery.
5.Low-coding
Low-code software has a graphical user interface with drag-and-drop functionality to automate development. Low-code platforms empower ordinary “citizen” developers to build apps. Low code speeds up the creation of websites, mobile applications, plugin integration, and cloud-based next-gen technologies like AI and ML.
6.Analytics
Mobile phones, the IoT, and other smart gadgets generate more data than ever, forcing firms to analyze it faster. The employment of sophisticated analytic tools on huge, diversified big data collections is vital to commercial success. Enterprises can make quicker data-driven decisions and improve customer experiences in real time and at scale using public cloud computing and networking infrastructure.
7.Hybrid multicloud strategy
Public cloud is key to hybrid multicloud. Organizations may choose where to execute workloads and pick the finest CSP services by combining public cloud services with private cloud or on-premises infrastructure. Financial institutions may prefer to test and develop new apps on the public cloud while putting fraud-sensitive and regulated workloads on a private cloud hosted by a specialized CSP.
8.Generative AI
For real-time, scalable data processing, generative AI requires the cloud for computation, storage, and networking. Companies may use public cloud providers to obtain data and processing capacity from several distant data centers for generative AI workloads.
9.Edge Computing
Enterprise applications may get quicker insights, reaction times, and bandwidth by moving data sources like mobile phones, sensors, IoT devices, and local edge servers closer to them. For example, edge devices monitor power grid activities to prevent energy waste. Connections to centralized public clouds or edge data centers synergize edge services with public clouds. Only relevant data is usually handled at the edge. Processing less vital data in a major public cloud data center frees up computer resources for low latency.
10.Quantum Computing
Solving complicated issues using computer hardware, algorithms, and quantum physics is quantum computing. Quantum computing for business is still in its infancy, but companies in processing-intensive fields like chemistry, biology, healthcare, and finance are starting to use it. Public cloud service companies now rent quantum machines, allow developers to construct utility-scale quantum algorithms and applications, and more.
IBM public clouds
Enterprise-grade platforms that provide high-performance, secure, and compliant cloud environments are needed to fully use public clouds. The full-stack IBM Cloud platform supports mission-critical workloads with over 170+ Public Cloud security solutions to reduce third- and fourth-party risk, enhance time to value, and minimize TCO.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#publiccloudsecurity#cloudcomputing#serverlesscomputing#ibmcloud#hybridclo#ai#news#technews#govindhtech#technology
0 notes
Text
13.3
Laurent Antonczak Guest lecture
UCC expectations
Difference between client and customer
Talk the same language as management - how to do this?
Digital economy
What technologies do you think will be the next big game changer? What radical changes are on the horizon?
SaaS -
PaaS -
IaaS - infrastructure as service
You manage vs vendor manages
Working out definitions -
Is innovation always related to markets and business?
Exploitation?
Diffusion ? Can you explain this a bit further?
How are you guys innovating your stories?
Who: what - how - why
What is your value proposition? What are you giving to your user/audience? What do you want to solve, address,
Who are you talking to?
When do you think user/customers journey starts? Can you elaborate on different types of touch points? Delivery options?
Importance of understanding systems?
How do you weave the same stories through different aspects of the user journey? From awareness to becoming a customer/user?
- Rescripting using chat gpt for different platforms
Point of view statement



0 notes
Text
Traditional Data Centers vs. Cloud: Navigating the Digital Infrastructure Landscape
Introduction -
Businesses must continually make important decisions on their IT infrastructure in the quickly changing world of technology. Making the decision to switch to cloud computing solutions or remain in traditional data centres is one of the biggest decisions they face. Making an informed decision requires a grasp of the subtle differences between the two possibilities, each of which has advantages and disadvantages.
Traditional Data Centers: The Tried and Tested Workhorses
Enterprise IT infrastructures have traditionally been supported by traditional data centres. These on-premises facilities are located within an organization's walls and contain physical servers, storage arrays, networking hardware, and cooling systems.
Pros:
Control and Security: With data stored on-site, organizations have full control over security measures and compliance protocols, ensuring data sovereignty and confidentiality.
Predictable Performance: By managing their own hardware and software stack, organizations can fine-tune performance according to their specific requirements, ensuring consistent and predictable levels of performance.
Compliance: Traditional data centres enable organizations to adhere to industry-specific compliance regulations by keeping sensitive data within their premises, ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
Cons:
Capital Expenditure: A traditional data centre's construction and upkeep involve a large initial infrastructure investment, which covers hardware acquisition, setup fees, and continuing maintenance expenditures.
Scalability Challenges: It can be difficult and time-consuming to scale traditional data centres to handle increasing workloads or unexpected demand spikes; new hardware purchases and infrastructure modifications are frequently needed.
Maintenance overhead: The daily administration, upkeep, and troubleshooting of an organization's data centre infrastructure is their responsibility. This can be a resource-intensive task that takes time away from important company operations.
Cloud Computing: The Game-Changer in IT Infrastructure
Cloud computing, which provides on-demand scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, has completely changed how businesses use and manage IT resources. Numerous services, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), are accessible through cloud solutions. These are the main advantages and difficulties:
Pros:
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing allows organizations to scale resources up or down dynamically in response to changing demand, enabling optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Cost Savings: Cloud solutions operate on a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for upfront capital expenditure and enabling organizations to pay only for the resources they consume, resulting in cost savings and improved financial predictability.
Agility and Innovation: Cloud computing accelerates innovation by providing access to a vast array of services, tools, and technologies that enable rapid development, deployment, and iteration of applications.
Cons:
Security and Compliance Concerns: Entrusting sensitive data to third-party cloud providers raises concerns about data security, privacy, and compliance with industry regulations, necessitating robust security measures and compliance certifications.
Vendor Lock-In: Depending heavily on a single cloud provider may lead to vendor lock-in, limiting organizations' flexibility and portability between different cloud platforms.
Performance and Latency: Cloud solutions rely on internet connectivity, which may introduce latency and performance issues, particularly for applications with stringent latency requirements or data sovereignty concerns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
In the end, several variables, such as the organization's budget, performance requirements, scalability demands, and compliance obligations, will determine whether traditional data centres or cloud computing is preferable. Many businesses use a hybrid strategy, combining cloud and on-premises resources to strike the best possible balance between cost, scalability, and control. You may make well-informed judgments that promote innovation, efficiency, and growth in the digital age by comprehending the advantages and disadvantages of each strategy and matching them with your company's aims and objectives.
In conclusion, a variety of criteria, such as the organization's budget, performance requirements, scalability needs, and compliance duties, influence the decision between traditional data centres and cloud alternatives. Scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness are offered by cloud solutions, while control and security are provided by traditional data centres. Many businesses use a hybrid strategy, combining cloud and on-premises resources to strike the best possible balance between cost, scalability, and control. In the end, choosing the best IT infrastructure plan to support corporate growth and innovation in the digital age depends on knowing the particular requirements of the company.
Additionally, numerous people can view the data simultaneously thanks to this technology. This expedites and simplifies work. You may handle your data in real-time from any remote part of the world with the help of Madman Technologies, they are the best Cloud Computing and DC migration services in India.
You can google our website and contact us over the phone — madmantechnologies.ai@gmail.com
Contact details — 9625468776
#cloud services#cloud computing#it services#information technology#it sector#it company#traditional data centers#it products#itservices#technology#it technology#it solutions#artificial intelligence#video conferencing#wifi#data center#information consultancy#cloudcomputing
0 notes