#hyperbilirubinemia
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
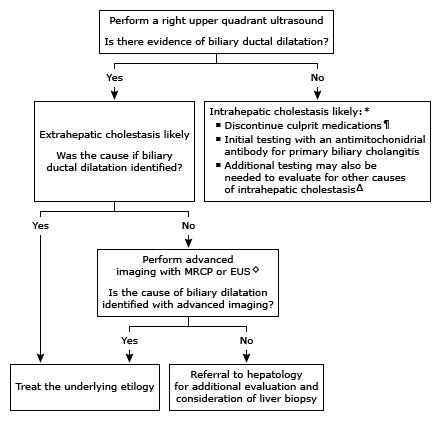
Approach to the evaluation of an asymptomatic adult with elevated alkaline phosphatase and hyperbilirubinemia
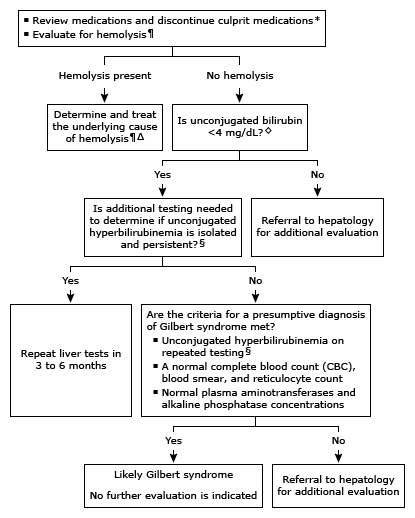
Approach to the evaluation of an adult with isolated unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Classification of hyperbilirubinemia – For clinical purposes, serum bilirubin is fractionated to classify hyperbilirubinemia into one of two major categories: unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia and conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinemia. Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia is characterized by plasma elevation of predominantly unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin. This may be due to the overproduction of bilirubin, impaired bilirubin uptake by the liver, or abnormalities of bilirubin conjugation. In patients with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, both unconjugated and conjugated (direct) bilirubin are elevated. This may be due to hepatocellular disease, impaired canalicular excretion of bilirubin, or biliary obstruction.
●Historical clues – Multiple clues to the etiology of hyperbilirubinemia can be obtained from the history:
•Use of medications, herbal medications, dietary supplements, and recreational drugs
•Significant alcohol consumption (>210 grams of alcohol (15 drinks) per week in males, >140 grams of alcohol (10 drinks) per week in females
•Hepatitis risk factors (eg, travel to endemic areas, blood transfusions prior to 1992, intravenous drug use)
•History of abdominal operations, including gallbladder surgery
•History of inherited disorders, including liver diseases and hemolytic disorders
•HIV status
•Occupational or recreational exposure to toxic substances
•Associated symptoms (eg, fever, right upper quadrant pain, myalgias)
●Laboratory evaluation – Initial laboratory tests include measurements of serum total and unconjugated bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, aminotransferases (aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase), prothrombin time/international normalized ratio, and albumin. Subsequent testing is guided by the predominant pattern of liver injury.
●Additional testing to determine etiology of hyperbilirubinemia based on pattern of liver tests
•Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia and elevated alkaline phosphatase – Elevation of the serum alkaline phosphatase out of proportion to the serum aminotransferases suggests biliary obstruction or intrahepatic cholestasis. Testing in patients with elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase of hepatic origin typically starts with right upper quadrant ultrasonography to assess the hepatic parenchyma and bile ducts (algorithm 1). The absence of biliary ductal dilatation suggests intrahepatic cholestasis.
•Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia and hepatocellular injury – A predominant elevation of serum aminotransferase activity suggests that jaundice is caused by intrinsic hepatocellular disease. The evaluation is based on the degree and pattern of aminotransferase elevation and is discussed in detail separately.
•Isolated unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia – The evaluation of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia typically involves evaluation for hemolytic anemia, drugs that impair hepatic uptake of bilirubin, and Gilbert syndrome (algorithm 2). However, patients with unconjugated bilirubin levels ≥4 mg/dL or abnormal aminotransferases should be referred to a hepatologist for further evaluation and consideration of a liver biopsy.
•Isolated conjugated hyperbilirubinemia – Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia without other routine liver test abnormalities is found in two rare inherited conditions: Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome. Normal levels of serum alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase help distinguish these conditions from disorders associated with biliary obstruction.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bilirubin is Bad for the Brain! Who knew?
We have known for a very long time that bilirubin can cause an encephalopathy leading to acute and chronic clinical impacts, the most severe chronic impacts being kernicterus, a disabling movement disorder and nerve deafness. What seems to be the case is that bilirubin bound to albumin doesn’t cross the blood-brain barrier, and that the BBB, which appears to develop early, and be functional by 20…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Jaundice Meter

A jaundice meter, also known as a transcutaneous bilirubinometer or jaundice detector, is a medical device used to non-invasively measure the level of bilirubin in a patient's skin or subcutaneous tissue. Convenient to browse and delete functions
0 notes
Text
( disclaimer : i made this theory with the intention of making it into a YouTube video so please excuse if that hasn't translated properly as a post on its own. also this contains spoilers for dialtown + the roger dlc, it makes more sense with the context of it anyway. that along with i use all pronouns for Gingi in this post (he/she/they/it) and uh Tw because i do bring up a few sensitive things like suicide and death but also some other things I'm forgetting )
and one last thing is that there are some pieces of information i didn't know so have been left out in this post but i may or may not make a follow up on this if i find enough to talk about
with that in mind : under the cut is my phonegingi and object head theory !! ♡
A while ago I made a poll on my tumblr asking what one of these theories you’d like for me to make a video upon and ‘figuring out what Phonegingi is ‘n’ their anatomy (or just phony anatomy)’ managed to win. It's a blessing in disguise if I'm being honest as the context of what I'm going to explain and set up in this video greatly helps with my Enc0unter and god theory.
So without any further stalling : I think it's best to start with analysing the cryptid.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Analysing Phonegingi :
So it doesn't take a genius to see that Phonegingi isn't like anything we've seen before. Not only does their species not really have an in-game name nor explanation, we also don't see anything else like it running around Dialtown. While there is a slim chance that maybe others like her do exist but we’ve never seen them and / or live in other places of the world, I really do doubt it from other characters' reaction to it alone. Not to even mention that Gingi doesn't have any confirmed origins along with the eggs that it lays and doesn't look anything like him. Obviously the whole ‘egg’ thing is a theory within itself but that's for another day.
Now if we’re going to get to figuring out what this thing is, we should analyse its features. We can see some human-like attributes but the list is rather limited when you take a closer look at him. So to make things a tad bit easier I've analysed some of the physical attributes from its sprites and art shown in game, along with a few not so physical things that are worth pointing out.

As shown I've decided to point out its green skin, six nipples, somewhat human body and tail. Some non visible attributes being how she can lay eggs, consume gravel and roadkill just fine, glans that burst when stressed(i forgot to add these two when making this) and teeth. two more noteworthy things being the fact he can speak proper English on top of hallucinations, but these are somewhat irrelevant as of now.
And for the sake of argument, I won't be taking the typewriter and phone heads into consideration as it's been proven by Gingi on multiple occasions that it had made it themselves and along with how it can change just complicates things. That's the same reason why I also won't be taking the scars into consideration as he was most likely not born with them (also it does change on occasion. No shade dogman) But don't worry as we shall return to it once it’s fully figured out what this thing is made up of.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Analysing Phonegingi : The green skin
Now I feel as if we should start off with one of the most important things with Phonegingi, and one of the most prominent ones at that. That being the bright green hue of its skin, perhaps we could even describe it as being fluorescent. Obviously the claim on its own sounds quite outlandish until we take a look at what could have possibly caused this.
Now there are many things that cause green skin in nature such as hyperbilirubinemia and layered chromatophores within the skin but one main detail i feel like is worth mentioning is that while Phonegingi does have certain reptilian like moments, simplifying judging by looks alone it is worthy to note that it appears to be a mammal of some sorts. Or a creature who's mostly covered in skin. This may seem somewhat irrelevant unless you remember that there aren't any naturally occurring mammals within nature with green skin. So maybe it isn't natural. And maybe this could be from lead.
While from the surface this seems rather outlandish, it is notable to say that there have been many instances where people had gotten their skin punctured by such things made from lead, leading to a long lasting green mark upon their skin. And the reason I bring this all up is in one of the endings for the Roger DLC we hear from Mingus herself that she's been putting lead into Dialtown’s lake. Presumably being the one within the forest. The same first that Phonegingi is from. Now I am no scientist but perhaps the led from the lake somehow found itself into its system though one of the main scars upon her body caused the green pigmentation. That or perhaps even radiation.
Side note here, my original theory was that this was entirely radiation until I looked into it a tad more. But we still have much to discuss with radiation as a topic.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Analysing Phonegingi : six nipples / eggs
I was honestly pretty stumped when it came to this point, obviously this is one of the main features of Gingi and on paper wouldn’t seem all too bad but when we consider the whole egg laying thing this really throws a wrench into everything until we consider the possibility that perhaps that Phonegingi is more than one animal biologically.
Now obviously I'm not going to sit here and act like I'm all too sure about what exactly these animals are just yet but I do have a contender. That being the platypus. Or that's what i would say because google lied to me about them having nipples. Apparently they only have mammary gland ducts to feed their young but perhaps Gingi’s genes somehow got broken so this being had to insert itself into his system, it’s an interesting look upon this but perhaps it's caused by something else. That I shall explain in a different post if enough people care for me to look into it. Either way : at least we now have a current solution for the eggs too
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Analysing Phonegingi : tail / eating gravel and roadkill / teeth
So now that we've managed to identify one of the beings that makes up Phonegingi, that being the platypus, we still have a few things that are left still in the air. But it's very simply solved when we consider that the other animal that Gingi is made up of is perhaps an alligator.
One of the main attributes of this is probably its teeth, such teeth that Gingi has been canonically confirmed to have from under his face. Such as within text and achievement art. Also another ability of the alligator is the fact that it has been proved to be able to process such things like rock and fresh dead animals, two things that Gingi has also been confirmed to eat without much struggle.
And one final thing to add on, we can also note Gingi’s tail from being from an alligator if it wasn't for how it goes from hairless to having hair on the tip along with it sometimes not being shown at all. That mainly being in model edits of the character so perhaps it's not worth noting.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Analysing Phonegingi : glans that burst when stressed
This one is quite the new development to say the least, I'm going to be honest when I say that I almost completely missed this as it's only a thing within one of the endings of the Roger DLC. Due to this I am quite honestly clueless, but I was able to find one thing that links back to the platypus point of this theory. Obviously this is quite different but male platypuses do produce venom connected to hollow spurs on the pack of their legs, but other than that I am honestly stumped so I hope that somebody can help me w this.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Analysing Phonegingi : putting together everything to come to a conclusion
Now with this information we can come to the conclusion that somehow a platypus, alligator and a human came together and created Phonegingi. For how they combined : If we look at the real world for just a moment there have been actual real life mutations that have led to rats growing features of humans. Although all of these examples are strictly manmade and have never occurred in nature, leading me to think Phonegingi didn't just happen. Although radiation could also be an option. While I plan on speaking about the human in particular that Gingi took over, I feel it would only be logical to now take a look at object heads to get a better understanding on how exactly Gingi is able to function.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out object heads:
So now we start with the big one. Some may know that dogman has been very useful with helping us figure this out. Okay I am being sarcastic for the most part but this doesn't change the fact that he actually has given us quite a few hints on how this works.
One main thing we can reference is that within Randy’s route we know that object heads aren't fully wires, but rather are a mixture of organic and mechanical parts. And to quote the hound himself : ‘they have layers’. This could simply be a metaphor or an actual explanation but with this man we don't know. I personally think of this as maybe there is a shell that is around the remaining parts of the head that the object head is placed on top of, making object head transfers much easier.

Also he had said within the past that phony’s have an ‘adaptor’ of sorts, so that does help a lot despite humans not being born with them as seen here One more thing I would also like to add before we go in depth about the methods of being dialed ; it is very likely that the technological parts of these objects gain their power from the body, just to clear that up. Either way : I think we should go over all of the different kinds of objects' heads. That being ones given to normies, born object heads and animals n such who are simply born with them.

︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out object heads: normies to objects
This part of my theory was by far the easiest but still wasn't quite that simple, obviously there aren't any real life examples of this happening so we are kinda making this one up along the way.
One of the main things to keep in mind is that when the dialup happened it happened practically overnight. That means that this progress had to be somewhat quick and considering how little flaws that come with having an object head that aren't exclusive to having an object head, there has to be a clear method to do this. So i propose a possible example for how to do this type of surgery:
The skin would be removed from the face, then the musicales before the bones. Making sure to keep the nerves, veins and brain within place. Then a small incision is made within the neck around these parts to not damage them, this being the base for where the adaptor would be placed on the head. But with this a small hole would be left in the neck to be used as a man-made mouth. (this was wrote b4 knowing its in the base of the head so forgive me) Within this process the olfactory nerve is also connected to this hole or slightly above it from out of the adaptor to retain smell. Moving onto the main head now, the back and front of the object is connected and wires from the phone are connected to certain parts of the brain so it has control with whatever object it may be without having to touch it. For the eyes, the photoreceptors are salvaged and turned into optical receptors with small holes in the head to remain eyesight. And finally, the inner ear is changed for a speaker with a microphone on the outside that picks up on a digital signal that transfers to the speaker inside then back to the brain as sound. With that done the case is closed up with whatever object it is being placed on top.
Now obviously this is just a very early draft of this part of the theory. I am aware there are a few characters that contradict this theory such as Abel, Stabby and Shooty or Craig so i may change this part of my theory at another point in time.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out object heads: born object heads
This is also pretty easy to figure out as dogman has actually answered this question before, as claimed here the hound has stated that after the dialup fetuses are born with thinner heads to make the process of dialing easier. although this still raises a few questions.

One of the first ones is if after birth they’re given the similar type procedure as normies, as that is the only solution I can think of. obviously there is the question of how this works outside of hospitals but if i tried to figure that out this post would be too long so it’s probably going to be a very boring post in itself.
The second question is asking how the head is altered in that way. my proposal for how and why is possibly genetic mutations caused by chemicals that would have been taken by pregnant mothers back during the dialup. These could possibly serve as a generational mutation to prevent normie children from happening. not an ideal answer but I'm sure i can put a tad bit more research into this later.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out object heads: animal object heads
While I do believe this is somewhat irrelevant for this part, I do think it’s worth mentioning and possibly solving. Unlike humans who aren’t born with them, animals and such are. and if you know almost anything about biology you’d know that animals don’t really have the means to have non organic heads without human intermittent so i think I've finally came to a solution to my final point
I believe there is a possibility that animals, bugs and whatnot have object heads created out of bone that simply mimic what they’re supposed to be. Due to the existence of horns and such we do know that this kind of thing can exist. but other than this there aren’t many alternatives
the only reason i bring this up is for my theory it is known that Gingi is an animal so perhaps it could fit into the category of this but due to the whole ‘i made it myself’ line from them it’s very quick to dismiss
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out how Gingi is made:
So now that we know or well have a somewhat understanding of how object heads function, that begs the question of how did Phonegingi have this information? How did such a primitive creature gain the knowledge of creating such a complicated head that mirrors the one of the former president that he had never seen before? This is where I propose the idea that maybe the human part of Phonegingi actually belonged to somebody before. That somebody being Milton r Wallace
Okay, I feel like I should explain myself a tad. I know it's quite an outlandish idea but it does explain quite a lot. After all ; it is quite a coincidence there is so much mystery around this character and no instance of him being mentioned in the game. I mean if there was a scene where he was mentioned and Gingi just said ‘oh yeah that’s me’ it would be pretty underwhelming. Jokes aside, Milton’s body being the human part of Gingi does explain one too many things such as the seemingly male anatomy, probably the scar on his chest, hallucinations along with connections to Callum, how he would know how to make their object head and even why he’s in the woods in the first place.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out how Gingi is made: scars on the body
I'll start by adding on to my scars as I feel like the male anatomy speaks for itself. Not to mention I promised to return to this so I am now. So let's take a look at the scars that we can see.
Visibly on the chest and right shoulder we can see two wounds. The one upon the shoulder is a supposed bruise from a gorilla bite (although i got this off the wiki and don’t remember this line from the game so feel free to correct me) and the one upon the chest looking like a gaping wound that was stitched up in a familiar fashion to their head. Since we know that Phonegingi made their head itself it is a possibility that he stitched up this wound upon her chest in a similar way but we cant be sure as it’s never acknowledged.
Second point I would like to add is that on multiple occasions Gingi has been called ‘blue blooded’ but these wounds have a more yellowish brown hue to them rather than the blue that you’d assume. Why is this important? Well if you've ever had the displeasure of seeing dried blood you’d know it eventually changes to a brown colour overtime. Now it doesn't take a genius to know that since the man died around 60 years ago his blood would have been heavily deoxygenated. Perhaps being the reason why when reanimated as Phonegingi his blood was blue form the same lack of oxygen.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out how Gingi is made: hallucinations and Callum connection
This part is a lot more simple to explain, while i am aware of these things only really occurring due to the cough stirrup consumed by it, i find it oddly strange that these things occur in the way that they do especially since presumably before meeting Mingus in bigfoot’s route, Gingi was never even aware of Callum's existence. Plus I don't feel like the hound would add these hallucinations just to write them off as nothing. Maybe somewhere in Gingi’s scrambled brain he had these memories from his previous life leak though.
Additionally, while Milton being Gingi helps the Callum connection ; it also explains why he would be able to identify Mingus as a cat. For us it would be pretty simple but we need to keep in mind that in Dialtown all organic beings have object heads so Phonegingi would have only ever really seen cats with these heads. While this could be written off as her seeing one within a textbook or something I find that incredibly hard to believe considering they’re confirmed to be illiterate. It could also just be a joke not meant to be looked into like this but it definitely could explain.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out how Gingi is made: making the object head
This part of the theory is actually what led me to believing that Milton could be Gingi as he would be one of the only characters who had a physical resemblance to it as far as we know along with having access to that knowledge. Considering we see Gingi make their phone head similar to Callum, maybe he was shown the pattern by Cal when explaining the dialup close to the end of their friendship. Same thing could be said for the typewriter variant of them, probably mirroring Marla’s head since the typewriter head was based upon her along with there being hints of them two having a platonic relationship but since she is sadly as mysterious as him so we may never know.
Either way, since Phonegingi presumably came from the woods it wouldn't make sense for them to make an object head within there. Especially since Theoroar had it in captivity in their early years so it wouldn't make sense for Gingi to create an object head with other animals while caged. If i may even say, i personally struggle to wrap my head around why Gingi would decide to conform with their head considering she certainly does not conform by wearing clothes.

Oh alright.
Either way, I have two options why this would even be the case. The first option is that he was found by Mingus who forced this change upon them so they made the object head. But this doesn't make sense within the context of chapter 3 where Mingus hints at discovering Gingi for the first time. After all; Mingus would probably have just gotten rid of it earlier if that. So for the second option, which is much darker mind you, but perhaps their face could have been heavily mutilated by Milton’s early death along with the decades of rotting that he had to improvise by fixing it with a head made in the way that he had remembered from Callum. This also explains why it's a tad bit different from the norm too since Gingi’s brain would have been a tad bit screwed with this too. Either way, I'll let you decide what option works best with you.
Also a side note; i did actually consider Marla as a possible candidate for Gingi but there was one too many plot holes such as her dying of old age so her body would look a lot different, a lack of any comment by Mingus talking about Marla and her most likely getting a proper burial from somewhere that isn't the woods.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Figuring out how Gingi is made: why he would be in the woods
Speaking of being in the woods, I have a small idea for why Milton’s body would wind up being there. As far as we know basically every single person who knew him wouldn't have been around, plus as of making this post he has no confirmed family so it's hard to say. Perhaps his body was simply thrown into the woods? I suppose it would be irregular to do that but considering who Milton was it would make sense that this act would be covered up and simply not addressed at all. Perhaps even respecting him enough to dig him a proper grave would attract unwanted attention along with the fact that there are just not enough people who would care for him enough.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
Putting this all together :
With that all being said. Let me summarize all the information that I've proposed so far. We have theorized that Phonegingi has the DNA of a platypus and alligator that has been combined with the body of the former vice president, having some form of lead poisoning from the lake and radiation that has combined these creatures together. There are two questions left now, the first one being just how did these creatures find their way into the woods to combine with the body, and the second and by far the most important one being just how did this creature come to fruition.
The first one is easy, some may know that platypuses and alligators aren't native to Wisconsin but we need to remember that these creatures could be found within a zoo. And would you look at that, in Dialtown we do have a zookeeper, the same zookeeper that found Phonegingi mind you. It is possible that Theoroar decided to dump these two within the woods for whatever reason and they somehow wound up next to the corpse and got mixed up. I understand this isn't a perfect explanation, but it is somewhat logical for now.
Now onto my second point, it isn't as clear but I feel like I've found a solution for how this creature came to life. It doesn't take a genius to know that Milton is dead, meaning even if these animals mutated them it still would leave her dead so it's hard to figure out but I still feel like I have a solution. If you remember I did state that Phonegingi came together as one could possibly be man made so perhaps this same person brought their freakish creation to life. And perhaps that person is none other than enc0unter but this post is getting too long.
︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶⠀୨♡୧⠀︶︶︶ ⊹ ︶︶︶
I apologize for leaving this theory on a cliff hanger but this post is getting long and i have a lot more to say about Gingi and enc0unter. As stated in the same poll from the beginning I will be making a whole different theory / analysis about that stuff. With that being said, please let me know your opinions on this theory and if you'd like me to make the enc0unter one or a part 2 when i have the time. so yeah thanks for going though the effort to read this whole thing!! it means a lot
#//if i get the time i will still make a video but i dont know#//espically since i plan on going on hiatus soon#dialtown#dialtown phone dating sim#dial town#dialtown theory#theory#phonegingi#gingi dialtown#dialtown gingi#milton r wallace#dialtown milton#milton dialtown#writing posting#yap posting#+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++#<- mr kitty put his head on the keyboard
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Let's talk about risk factors for neonatal jaundice, which is found in >80% of newborn babies and usually resolves in 1-2 weeks as the infant feeds and poops. However, a small percentage of babies develop hazardous hyperbilirubinemia (TSB≥30) --> brain damage from bilirubin crossing the blood-brain barrier (aka kernicterus). Visual assessment of significant jaundice does not reliably correlate with high total serum bilirubin levels! Therefore all newborns should be screened 24-48 hours after birth or before discharge, whichever is sooner. Both transcutaneous and serum bilirubin levels are reliable screening tools, although if a TcB is close to the treatment threshold, it should be checked with a TsB.
Source: https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/150/3/e2022058859/188726/Clinical-Practice-Guideline-Revision-Management-of
Image: "Intensive phototherapy Our area has as a very high level of newborn jaundice, which is sometimes fatal. The treatment is phototherapy for less severe cases, exchange blood transfusion for the more serious ones. This special, intense blue phototherapy lamp (NeoBLUE) was donated by Natus Medical, Inc. with the assistance of Henk J. Vreman, Ph.D., at Stanford University Dept. of Pediatrics. (ECWA Evangel Hospital, Jos, Nigeria)" ~California pediatrician Mike Blyth, Flickr, CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Recitation in neonatal class in Pediatrics..
Dr: *presented a case of breastfeeding hyperbilirubinemia* So is this pathologic or physiologic?
C: It's physiologic because the breastmilk contains the enzyme for bilirubin deconjugation back to indirect bilirubin.
Dr: Someone did his readings. So how do you manage the patient?
C: Stop breastfeeding
Dr: 🤦🏻♀️
Dr: Okay so what is that complication seen in babies with hyperbilirubinemia being treated with phototherapy?
C: *doesn't know the answer, while we whisper the answer Bronze syndrome*
C: *confidently* Brown syndrome
Dr: Neonates have more fat than adults, what do you call that fat?
E: Baby fat?
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Playing scrabble
Grover: I'm going to put down R, P, and E to make PER Percy: I'm going to add H and Y to your per to make HYPER Annabeth: I'm going to add 4 I's, L, R, U, 2 B's, 2 A's, N, and M to your HYPER to make HYPERBILIRUBINEMIA
#percy jackon and the olympians#pjo hoo toa#percy pjo#grover pjo#annabeth chase#percy jackson#percy and annabeth#rick riordan
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global Kernicterus Treatment Market Analysis 2024: Size Forecast and Growth Prospects
The kernicterus treatment global market report 2024 from The Business Research Company provides comprehensive market statistics, including global market size, regional shares, competitor market share, detailed segments, trends, and opportunities. This report offers an in-depth analysis of current and future industry scenarios, delivering a complete perspective for thriving in the industrial automation software market.
Kernicterus Treatment Market, 2024 report by The Business Research Company offers comprehensive insights into the current state of the market and highlights future growth opportunities.
Market Size - The kernicterus treatment market size has grown steadily in recent years. It will grow from $2.88 billion in 2023 to $2.98 billion in 2024 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.4%. The growth in the historic period can be attributed to improvements in neonatal care practices, increased awareness among healthcare professionals, government initiatives for maternal and child health, research funding and clinical trials, collaborations in medical research..
The kernicterus treatment market size is expected to see steady growth in the next few years. It will grow to $3.29 billion in 2028 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.6%. The growth in the forecast period can be attributed to continuous medical education programs, global health policies and initiatives, patient advocacy and support groups, international collaboration in pediatric research, government funding for neonatal health.. Major trends in the forecast period include advancements in neonatal jaundice monitoring technologies, introduction of phototherapy devices with enhanced features, development of bilirubin-reducing medications, focus on home-based phototherapy solutions, implementation of bilirubin nomograms and guidelines, integration of telehealth for remote monitoring..
Order your report now for swift delivery @ https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/kernicterus-treatment-global-market-report
Scope Of Kernicterus Treatment Market The Business Research Company's reports encompass a wide range of information, including:
1. Market Size (Historic and Forecast): Analysis of the market's historical performance and projections for future growth.
2. Drivers: Examination of the key factors propelling market growth.
3. Trends: Identification of emerging trends and patterns shaping the market landscape.
4. Key Segments: Breakdown of the market into its primary segments and their respective performance.
5. Focus Regions and Geographies: Insight into the most critical regions and geographical areas influencing the market.
6. Macro Economic Factors: Assessment of broader economic elements impacting the market.
Kernicterus Treatment Market Overview
Market Drivers - The prevalence of neonatal jaundice is driving the growth of the kernicterus treatment market going forward. Neonatal jaundice, also known simply as jaundice in newborns, is a common and typically harmless condition characterized by the yellowing of a baby's skin and the whites of their eyes. Kernicterus treatment is commonly used for neonatal jaundice; it manages the symptoms and provides supportive care. This procedure removes blood from the baby and replaces it with blood with a lower bilirubin level, improving the affected child's quality of life. For instance, in August 2023, according to reports published by the National Library of Medicine, a US-based biomedical library, globally, about 1.1 million babies each year develop severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia (neonatal jaundice). Furthermore, in February 2021, according to ClinMed International Library, a US-based publishing company, it was estimated that at least 114,000 infants die yearly from neonatal hyperbilirubinemia (neonatal jaundice). Therefore, the prevalence of neonatal jaundice is expected to propel the growth of the kernicterus treatment market.
Market Trends - Major institutes operating in the kernicterus treatment market are developing innovative technological products, such as wearable devices to monitor jaundice accurately, that help gain a competitive advantage. A wearable device is a small, flexible patch placed on the body according to the treatment requirement. For instance, in March 2021, Yokohama National University, a Japan-based university, designed the first-ever wearable device to accurately monitor jaundice, a yellowing of the skin due to increased bilirubin levels in the blood that can result in severe medical conditions in infants. This wearable sensor for infants can constantly measure bilirubin to achieve the intricate balance of administering the accurate amount of blue light required to neutralize the correct bilirubin levels. Moreover, it is a small, flexible patch that is placed on the infant's chest, and it transmits data to a smartphone or computer, where doctors or parents can monitor it. Also, it is more accurate and convenient than traditional methods of monitoring jaundice, such as blood tests.
The kernicterus treatment market covered in this report is segmented –
1) By Treatment: Phototherapy, Intravenous Immunoglobulins (IVIG), Blood Transfusion, Medication, Other Treatments 2) By Symptoms: Jaundice, Unusual Eye Movements, Vomiting, Fever, Poor Feeding, Apnoea, Irritability, Seizures, Sleepiness, Other Symptoms 3) By Dosage: Injection, Solution, Other Dosages 4) By End-Users: Clinic, Hospital, Other End-Users
Get an inside scoop of the kernicterus treatment market, Request now for Sample Report @ https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/sample.aspx?id=13470&type=smp
Regional Insights - North America was the largest region in the kernicterus treatment market in 2023. The regions covered in the kernicterus treatment market report are Asia-Pacific, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, North America, South America, Middle East, Africa.
Key Companies - Major companies operating in the kernicterus treatment market report are Pfizer Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd , Merck and Co. Inc., AbbVie Inc., Bayer AG, Novartis AG, AstraZeneca plc., Abbott Laboratories, Sanofi SA, GlaxoSmithKline plc, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Johnson and Johnson Private Limited, Baxter International Inc., Grifols S.A, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd., Alembic Pharmaceuticals Limited, Lupin Pharmaceuticals Inc., CSL Limited, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Cipla Inc., Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Octapharma Brasil Ltda, Kedrion S.p.A, Biotest AG, Wockhardt Ltd., Mylan N.V., Cadila Healthcare Ltd., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., China Biologic Products Holdings Inc.
Table of Contents 1. Executive Summary 2. Kernicterus Treatment Market Report Structure 3. Kernicterus Treatment Market Trends And Strategies 4. Kernicterus Treatment Market – Macro Economic Scenario 5. Kernicterus Treatment Market Size And Growth ….. 27. Kernicterus Treatment Market Competitor Landscape And Company Profiles 28. Key Mergers And Acquisitions 29. Future Outlook and Potential Analysis 30. Appendix
Contact Us: The Business Research Company Europe: +44 207 1930 708 Asia: +91 88972 63534 Americas: +1 315 623 0293 Email: [email protected]
Follow Us On: LinkedIn: https://in.linkedin.com/company/the-business-research-company Twitter: https://twitter.com/tbrc_info Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TheBusinessResearchCompany YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC24_fI0rV8cR5DxlCpgmyFQ Blog: https://blog.tbrc.info/ Healthcare Blog: https://healthcareresearchreports.com/ Global Market Model: https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/global-market-model
0 notes
Text
Bilitool tells you at what level transcutaneous bilirubin you should check a serum bilirubin and at what level you should do phototherapy.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Baby’s Yellow Skin? Causes of Newborn Jaundice
https://womenworldmagazine.com/babys-yellow-skin-causes-of-newborn-jaundice/
Baby’s Yellow Skin? Causes of Newborn Jaundice
What is Newborn Jaundice?
Jaundice in newborns, also known as neonatal jaundice, is a common condition, caused by hyperbilirubinemia (excess production of serum bilirubin). Bilirubin is an orange-yellow pigment formed in the liver by the normal breakdown of old red blood cells (RBCs).
Neonatal jaundice is characterized by turning the infant’s skin and eye color to yellowish and it is the most common cause of readmission for newborn babies.
What are the Causes of Newborn Jaundice?
Elevation in bilirubin in newborns may be due to several reasons:
Their liver may not be fully developed, especially among preterm newborns, therefore, the metabolism of bilirubin would be slower.
Premature babies may have feeding and digesting difficulties, resulting in insufficient milk intake.
Newborns have a shorter lifespan of RBCs, and higher concentration of RBBs, leading to a higher production rate of bilirubin than adults.
They may have delayed first tar-like stools (meconium), resulting in increased intestinal reabsorption of bilirubin.
Sickle cell anemia may create abnormal shapes of red blood cells.
ABO or Rh incompatibility between the mother and baby, resulting in increased breakdown of the baby’s RBCs, thus elevated bilirubin levels. This type needs medical intervention. The sooner the treatment, the better the results are.
Other causes include medical conditions like rubella, cystic fibrosis, and hypoxia.
What are the Types of Newborn Jaundice?
1. Physiological Jaundice:
Physiological Jaundice is the most common type, especially in the first week of life. The newborn’s immature liver is often the cause of this type, resulting in excess bilirubin. However, it is mild, transient, and resolves without treatment. It usually resolves on its own when the liver matures without causing any complications.
2. Breastfeeding Jaundice:
This type of jaundice occurs in neonates that are breastfed. It usually presents during the first one to two weeks after birth and often resolves spontaneously, however, it may persist for 8 to 12 weeks of life.
The etiology of breast milk jaundice is not well known, nevertheless, it may occur due to reasons in the breast milk itself. Also, genetic mutations in the newborn may be present. Insufficient intake of breast milk and dehydration can also be risk factors, as well. It is recommended to continue breastfeeding to reduce its risk.
3. Breast Milk Jaundice:
This type differs from breastfeeding jaundice and occurs in well-fed newborns, often after the second weeks of life, and may last for a few weeks. It is usually harmless. The mechanism leading to breast milk jaundice is poorly understood; it may be due to substances in the mother’s milk that increase intestinal reabsorption of bilirubin.
How is Newborn Jaundice Diagnosed?
Physical examination of signs includes checking the baby’s skin and eye color changing to yellow within the first 72 hours of birth.
Blood levels of bilirubin must be tested through a bilirubinometer and a blood sample.
How is Newborn Jaundice Treated?
In most cases, neonatal jaundice resolves spontaneously. Mild hyperbilirubinemia often returns to normal as the newborn’s liver completes development. Additionally, continuous breastfeeding encourages bowel movement, which helps eliminate excess bilirubin.
Phototherapy (light therapy) is commonly used in cases of high or persistent elevation in bilirubin levels. It is a method of treatment using ultraviolet light on the baby’s skin to help break down bilirubin, usually taking one to two days.
In rare cases, blood transfusion may be recommended if phototherapy does not work and bilirubin levels need to be reduced quickly.
0 notes
Link
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a medical condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes. This yellow discoloration is caused by an elevated level of bilirubin in the blood, a condition known as hyperbilirubinemia. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment that is produced during the normal breakdown of red blood cells. Typically, the liver processes bilirubin, which is then excreted in bile. However, when there is an excess of bilirubin or if the liver is unable to process it effectively, jaundice occurs. This condition can be indicative of underlying health issues such as liver disease, hemolytic anemia, or bile duct obstruction. Jaundice is prevalent in newborns but can affect individuals of all ages. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for jaundice is essential for effective management and prevention of potential complications associated with this condition. Types of JaundiceSymptoms of JaundiceCauses of JaundiceDiagnosis of JaundiceTreatment of JaundiceHow to Prevent JaundiceComplications of JaundiceConclusion Types of Jaundice Jaundice can be classified into three primary types based on the underlying causes and the location of the bilirubin processing disruption: pre-hepatic, hepatic, and post-hepatic jaundice. Pre-Hepatic Jaundice: Pre-hepatic jaundice occurs before bilirubin is transported to the liver. It is usually caused by conditions that lead to an increased breakdown of red blood cells, resulting in an excess production of bilirubin. Common causes include hemolytic anemias, such as sickle cell anemia and thalassemia, and conditions like malaria or autoimmune disorders. In pre-hepatic jaundice, the liver is typically functioning normally, but it becomes overwhelmed by the large amount of bilirubin it needs to process. Hepatic Jaundice: Hepatic jaundice arises from problems within the liver itself. These issues can be due to liver diseases that impair the liver’s ability to process and excrete bilirubin. Common causes include hepatitis (both viral and alcoholic), cirrhosis, liver cancer, and genetic disorders like Gilbert’s syndrome or Crigler-Najjar syndrome. In hepatic jaundice, the liver’s impaired function leads to an accumulation of bilirubin in the blood. Post-Hepatic Jaundice: Post-hepatic jaundice, also known as obstructive jaundice, occurs when there is an obstruction in the bile ducts that prevents bilirubin from being excreted into the digestive tract. This obstruction can be caused by gallstones, tumors, strictures, or inflammation of the bile ducts (cholangitis). In post-hepatic jaundice, bilirubin that has been processed by the liver is unable to reach the intestines, leading to its buildup in the bloodstream. Each type of jaundice has distinct underlying causes and mechanisms, making accurate diagnosis essential for effective treatment. Identifying the type of jaundice is critical in determining the appropriate medical intervention and addressing the root cause of the bilirubin imbalance. Symptoms of Jaundice Jaundice manifests through a range of symptoms, primarily caused by elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood. While the hallmark sign of jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and eyes, various other symptoms can accompany this condition, depending on the underlying cause. Here are the primary symptoms associated with jaundice: Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes: The most noticeable symptom of jaundice is a yellow tint to the skin and the sclera (whites of the eyes). This yellowing can vary in intensity, depending on the level of bilirubin in the blood. Dark Urine: Bilirubin excreted through the urine can cause it to appear dark brown or tea-colored. This symptom often precedes the yellowing of the skin and eyes. Pale Stools: Normal stool color is brown due to bile pigments. In jaundice, especially post-hepatic jaundice, stools may become pale or clay-colored due to the lack of bile entering the digestive tract. Itchy Skin: High levels of bilirubin can cause intense itching (pruritus). This itching can be particularly uncomfortable and persistent, often occurring before visible jaundice. Fatigue: General fatigue and weakness are common symptoms, especially in cases where jaundice is caused by liver disease or other systemic conditions. Abdominal Pain: Pain or discomfort in the abdomen, particularly in the upper right quadrant, can occur. This is often related to liver or gallbladder issues. Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting can accompany jaundice, particularly in cases of liver disease or bile duct obstruction. Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss can occur in chronic jaundice cases, particularly when caused by underlying liver disease or malignancy. Fever: A fever may be present if the jaundice is due to an infection such as hepatitis or cholangitis. Swelling: Swelling in the legs and abdomen (ascites) can occur, particularly in chronic liver disease or cirrhosis. These symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the jaundice. If any of these symptoms are observed, it is crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and intervention can help manage the condition effectively and prevent complications. Causes of Jaundice Jaundice results from the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, leading to its deposition in tissues. This accumulation can occur due to various underlying conditions, broadly categorized into pre-hepatic, hepatic, and post-hepatic causes. Here’s a detailed look at these causes: Pre-Hepatic Causes: Pre-hepatic jaundice is due to the excessive production of bilirubin, often resulting from the rapid breakdown of red blood cells. Common pre-hepatic causes include: Hemolytic Anemias: Conditions such as sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, and hereditary spherocytosis lead to the premature destruction of red blood cells. Infections: Diseases like malaria can cause significant hemolysis. Autoimmune Disorders: Autoimmune hemolytic anemia involves the immune system attacking red blood cells. Blood Transfusion Reactions: Mismatched blood transfusions can lead to the destruction of donor red blood cells. Hepatic Causes: Hepatic jaundice arises from conditions that directly affect the liver’s ability to process and excrete bilirubin. These include: Hepatitis: Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E) and alcoholic hepatitis cause inflammation and damage to liver cells. Cirrhosis: Chronic liver damage from various causes, including long-term alcohol use and hepatitis, leads to scarring and impaired liver function. Liver Cancer: Primary liver cancer or metastases can disrupt liver function. Genetic Disorders: Conditions like Gilbert’s syndrome and Crigler-Najjar syndrome affect the liver’s ability to process bilirubin. Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Certain medications and toxins can damage the liver. Post-Hepatic Causes: Post-hepatic jaundice, or obstructive jaundice, is due to blockages in the bile ducts that prevent bilirubin from being excreted into the digestive tract. Causes include: Gallstones: These can obstruct the bile ducts, preventing bile flow. Tumors: Tumors in the bile ducts, pancreas, or nearby structures can cause obstruction. Biliary Strictures: Narrowing of the bile ducts due to inflammation or injury. Cholangitis: Inflammation and infection of the bile ducts can block bile flow. Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas can obstruct the bile ducts. Other Contributing Factors Neonatal Jaundice: Newborns often develop jaundice due to immature liver function and increased bilirubin production. This is usually temporary but needs monitoring. Genetic Conditions: Some inherited conditions, like Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome, affect bilirubin metabolism. Understanding the specific cause of jaundice is crucial for appropriate treatment. Diagnostic tests, including blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes liver biopsies, are used to determine the underlying cause and guide management. Diagnosis of Jaundice Diagnosing jaundice involves a series of steps to determine the underlying cause and assess the severity of the condition. A comprehensive approach includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and a variety of diagnostic tests. Medical History Symptoms: The doctor will ask about the onset, duration, and progression of symptoms such as yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, pale stools, itching, fatigue, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Risk Factors: Information about risk factors such as alcohol use, drug use, exposure to hepatitis, recent travel, family history of liver disease, and blood transfusions is gathered. Medications: A review of current and recent medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, is essential. Physical Examination Skin and Eyes: Examination for yellow discoloration. Abdomen: Checking for liver enlargement, tenderness, or masses. Other Signs: Assessment for signs of chronic liver disease such as spider angiomas, palmar erythema, and ascites. Laboratory Tests Complete Blood Count (CBC): Helps detect hemolysis, infection, or other blood disorders. Liver Function Tests (LFTs): Measures levels of liver enzymes (ALT, AST), bilirubin (total and direct), and other substances to evaluate liver health. Prothrombin Time (PT): Assesses blood clotting ability, which can be impaired in liver disease. Serum Bilirubin Levels: Measures the amount of bilirubin in the blood. Hepatitis Panel: Tests for viral hepatitis (A, B, C, etc.). Autoimmune Markers: Tests for autoimmune liver diseases such as autoimmune hepatitis or primary biliary cholangitis. Imaging Studies Ultrasound: A non-invasive method to visualize the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts. It helps identify obstructions, gallstones, and liver abnormalities. CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the liver and bile ducts to detect tumors, cysts, and other structural abnormalities. MRI and MRCP: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) offer detailed images of the liver and bile ducts. HIDA Scan: A nuclear imaging test to evaluate bile flow through the liver and bile ducts. Specialized Tests Liver Biopsy: A sample of liver tissue is taken to diagnose liver disease, evaluate liver damage, and identify conditions such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or cancer. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A procedure to diagnose and treat conditions of the bile ducts, including obstructions and strictures. Genetic Testing Genetic Tests: Performed if a hereditary condition such as Gilbert’s syndrome or Crigler-Najjar syndrome is suspected. Accurate diagnosis of jaundice requires a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and managing the condition effectively. Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent complications and improve outcomes. Treatment of Jaundice The treatment of jaundice depends on its underlying cause. Managing jaundice effectively requires addressing the root condition that is causing the bilirubin buildup. Here are the main treatment approaches based on the type of jaundice: Pre-Hepatic Jaundice: Pre-hepatic jaundice is usually caused by excessive breakdown of red blood cells. Treatment focuses on managing the underlying cause of hemolysis. Blood Transfusions: In cases of severe anemia. Medications: For treating conditions like malaria or autoimmune disorders. Iron Supplements: If iron deficiency is contributing to hemolysis. Management of Genetic Disorders: Specific treatments for conditions like sickle cell anemia or thalassemia, including folic acid supplements and potential bone marrow transplants. Hepatic Jaundice: Hepatic jaundice is due to liver dysfunction. Treatment aims to manage liver disease and restore liver function. Antiviral or Antibacterial Medications: For viral or bacterial hepatitis. Alcohol Cessation Programs: For alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis. Medications to Reduce Liver Inflammation: For conditions like autoimmune hepatitis. Liver Transplant: In cases of severe liver failure or cirrhosis. Supportive Care: Including a balanced diet, hydration, and avoiding liver-toxic substances. Management of Genetic Disorders: Specific treatments for genetic liver conditions like Wilson’s disease (copper chelation therapy). Post-Hepatic Jaundice: Post-hepatic jaundice is caused by an obstruction in the bile ducts. Treatment focuses on relieving the obstruction. Surgical Removal of Gallstones: Cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) or endoscopic procedures to remove stones. ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): To remove bile duct obstructions, place stents, or perform biopsies. Surgery: For tumors causing obstruction. Treatment of Pancreatitis: Managing inflammation of the pancreas to relieve bile duct pressure. General Supportive Measures Hydration and Nutrition: Ensuring proper hydration and a balanced diet to support liver function and overall health. Avoidance of Alcohol and Certain Medications: To prevent further liver damage. Regular Monitoring: Blood tests and imaging studies to monitor liver function and bilirubin levels. Phototherapy: Used primarily in newborns with jaundice, where blue light helps break down bilirubin in the skin. The treatment of jaundice is multifaceted, focusing on the underlying cause while providing supportive care to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Early diagnosis and targeted treatment are crucial for effective management and improving patient outcomes. If you suspect jaundice, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly for appropriate evaluation and treatment. How to Prevent Jaundice Preventing jaundice involves adopting lifestyle changes, practicing good health habits, and taking preventive measures to avoid conditions that can lead to bilirubin accumulation. Here are some strategies to prevent jaundice: Healthy Lifestyle Choices Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid excessive consumption of fatty foods, processed foods, and sugary beverages. Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help maintain liver function and overall health. Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limit alcohol intake to reduce the risk of liver disease. Follow guidelines for safe drinking, and avoid binge drinking. Vaccination Hepatitis Vaccination: Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B. These vaccines are effective in preventing viral hepatitis, a common cause of liver damage and jaundice. Safe Practices Avoid Sharing Needles: To prevent hepatitis B and C infections, avoid sharing needles or any equipment that can transmit bloodborne pathogens. Safe Sexual Practices: Use condoms and practice safe sex to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections that can lead to hepatitis. Medications and Supplements Use Medications Responsibly: Follow prescription guidelines and avoid overusing medications that can harm the liver. Always inform your doctor about all the medications and supplements you are taking. Avoid Unnecessary Supplements: Some herbal supplements and over-the-counter medications can be toxic to the liver. Use supplements only under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Regular Medical Check-Ups Routine Screening: Regular check-ups and liver function tests can help detect liver issues early. Early intervention can prevent the progression of liver disease. Manage Chronic Conditions: If you have conditions like diabetes, obesity, or hypertension, manage them effectively to reduce the risk of liver disease. Occupational and Environmental Safety Avoid Exposure to Toxins: Be cautious of exposure to harmful chemicals at work or in the environment. Use protective equipment and follow safety guidelines to minimize exposure to liver-damaging substances. Prevent Hemolysis Genetic Counseling: For those with a family history of hemolytic anemias, genetic counseling can help understand and manage the risk. Avoid Triggers: People with conditions like G6PD deficiency should avoid certain foods and medications that can trigger hemolysis. Healthy Weight Management Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which can cause liver damage and jaundice. Engage in regular physical activity and maintain a healthy weight. Neonatal Jaundice Prevention For newborns, some specific measures can help prevent severe jaundice: Adequate Feeding: Ensure that newborns are well-fed, as frequent feeding helps excrete bilirubin. Monitoring: Monitor newborns for signs of jaundice, especially within the first week of life. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications. While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of jaundice, adopting healthy lifestyle practices, getting vaccinated, using medications responsibly, and avoiding exposure to toxins can significantly reduce the risk. Regular medical check-ups and managing underlying health conditions are also crucial in preventing jaundice and maintaining overall liver health. If you have risk factors for liver disease or other conditions that could lead to jaundice, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized preventive strategies. Complications of Jaundice Jaundice itself is a symptom rather than a disease, indicating an underlying issue with bilirubin metabolism. If the underlying cause of jaundice is not identified and treated promptly, several complications can arise, some of which can be severe. Here are the potential complications associated with jaundice: Kernicterus Description: Kernicterus is a form of brain damage that occurs in newborns with severe jaundice due to high levels of unconjugated bilirubin crossing the blood-brain barrier. Symptoms: Symptoms include lethargy, poor feeding, high-pitched crying, muscle rigidity, and seizures. Outcomes: If untreated, kernicterus can lead to permanent neurological damage, developmental delays, hearing loss, and cerebral palsy. Chronic Liver Disease Description: Chronic liver conditions such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease can progress and cause long-term damage if jaundice is not managed. Symptoms: Symptoms include persistent fatigue, swelling in the legs and abdomen (ascites), easy bruising, and confusion. Outcomes: Complications of chronic liver disease include liver failure, which may necessitate a liver transplant. Biliary Cirrhosis Description: Prolonged bile duct obstruction can lead to biliary cirrhosis, where scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue due to chronic inflammation. Symptoms: Symptoms include jaundice, itching, abdominal pain, and fatty deposits in the skin. Outcomes: Biliary cirrhosis can lead to liver failure and increased risk of liver cancer. Sepsis Description: Severe infections, particularly in cases of cholangitis (bile duct infection), can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection. Symptoms: Symptoms include high fever, chills, rapid heart rate, confusion, and low blood pressure. Outcomes: Sepsis requires immediate medical treatment and can lead to organ failure and death if not promptly managed. Pancreatitis Description: Obstruction of the bile ducts can cause inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), leading to severe abdominal pain and digestive issues. Symptoms: Symptoms include severe upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Outcomes: Chronic pancreatitis can lead to malabsorption, diabetes, and persistent pain. Gallstones and Biliary Colic Description: Gallstones causing bile duct obstruction can lead to biliary colic and recurrent episodes of severe pain. Symptoms: Symptoms include intense pain in the upper right abdomen, nausea, and vomiting. Outcomes: Recurrent gallstones can lead to chronic pain and complications like cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder). Hepatic Encephalopathy Description: In severe liver disease, toxins that are normally removed by the liver can accumulate in the bloodstream and affect brain function. Symptoms: Symptoms include confusion, memory loss, personality changes, and in severe cases, coma. Outcomes: Hepatic encephalopathy can be life-threatening and requires immediate treatment. Coagulopathy Description: Liver dysfunction can impair the production of clotting factors, leading to coagulopathy, a condition where blood does not clot properly. Symptoms: Symptoms include easy bruising, frequent nosebleeds, prolonged bleeding from cuts, and heavy menstrual periods. Outcomes: Severe coagulopathy can lead to significant blood loss and complications from bleeding. The complications of jaundice can be severe and life-threatening if the underlying cause is not promptly addressed. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial in preventing these complications. Regular medical check-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and proper management of underlying conditions can significantly reduce the risk of developing jaundice and its associated complications. If jaundice or its symptoms are observed, seeking medical attention immediately is essential for effective management and prevention of adverse outcomes. Conclusion In conclusion, jaundice is a visible sign of underlying health issues involving the liver's ability to process bilirubin, a waste product from the breakdown of red blood cells. It manifests as yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, often accompanied by other symptoms depending on the cause. Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various tests to identify the underlying condition causing jaundice. Treatment focuses on addressing the specific cause, whether it's related to liver dysfunction, bile duct obstruction, or excessive red blood cell breakdown. This may include medications, lifestyle changes, surgical procedures, and supportive care. Prevention strategies include vaccination against hepatitis, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding toxins, and managing underlying health conditions. Early detection and intervention are crucial to prevent complications such as chronic liver disease, neurological damage in newborns (kernicterus), and other serious health issues associated with prolonged jaundice. In managing jaundice, prompt medical attention and adherence to treatment recommendations play key roles in improving outcomes and minimizing the impact on overall health. Search here
0 notes
Text
Guide to Hyperbilirubinemia: Elevated billirubin levels
This blog post is written with an intent to breakdown and simplify hyperbilirubinemia for an avergae medical studenty. What is Hyperbilirubinemia? Hyperbilirubinemia occurs when bilirubin levels in your blood become elevated beyond normal ranges. There are two main types: Unconjugated (Indirect) Hyperbilirubinemia Marked by elevated total bilirubin with < 15% direct bilirubin Often presents…
0 notes
Text
담즙 과다분비 원인 치료법 효과적인 관리 및 예방 전략
담즙 과다분비 원인 치료법 효과적인 관리 및 예방 전략 담즙 과다분비 원인 치료법 효과적인 관리 및 예방 전략담즙 과다분비(hyperbilirubinemia) 원인 간 질환담즙 과다분비(hyperbilirubinemia) 원인 담도 폐쇄담즙 과다분비(hyperbilirubinemia) 원인 적혈구 파괴 증가 (용혈성 빈혈)담즙 과다분비(hyperbilirubinemia) 원인 대사성 질환담즙 과다분비(hyperbilirubinemia) 원인 임신 관련담즙 과다분비(hyperbilirubinemia) 원인 약물 부작용담즙 과다분비(hyperbilirubinemia) 원인 기타 원인담즙 과다분비(hyperbilirubinemia) 원인 진단 및 관리 담즙 과다분비는 다양한 원인에 의해 발생할 수 있으며,…
#Crigler-Najjar 증후군#Dubin-Johnson 증후군#Gilbert 증후군#간 질환#담도 폐쇄#담즙 과다분비#담즙 과다분비 관리#담즙 과다분비 원인#담즙 대사#대사성 질환#소화기 건강#약물 부작용#용혈성 빈혈#임신성 담즙정체
0 notes
Text

Q. At what gestational age is it safe to use ceftriaxone in newborns?
.
.
.
.
.
A. We don't use ceftriaxone until at least 44 weeks post-menstrual age (40 weeks = full term + 4 weeks = neonate) because of biliary sludging and the fact that CTX competes with bilirubin for carrying space on albumin, leading to increased serum levels of bilirubin and the risk of jaundice and kernicterus (=permanent brain damage secondary to hyperbilirubinemia).
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: what it is, causes and how to treat it - https://storelatina.com/?p=111729
0 notes