#floral formula of fabaceae
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Mod 2 Botany Sem End
Fabaceae - Pea Family
Classification: Spermatophyta Angiosperms Dicotyledons Polypetalae Calyciflorae Rosales Fabaceae
---
Derivation of Classification:
Spermatophyta: Seed bearing plants.
Angiosperms: Seeds enclosed within a fruit.
Dicotyledons: 1) Tap root system 2) Dorsiventral leaves 3) Reticulate venation 4) Mostly pentamerous flowers 5) Seed with two cotyledons
Polypetalae: 1) Perianth present; differentiated into calyx and corolla 2) Petals free
Calyciflorae: 1) Flowers actinomorphic or zygomorphic 2) Hypogynous, perigynous, or epigynous 3) Cup shaped thalamus called calyx tube may be present 4) Stamens 10-many, inserted on the calyx tube 5) Monocarpellary gynoecium with marginal placentation
Rosales: 1) Leaves alternate and stipulate 2) Flowers bisexual 3) Actinomorphic or zygomorphic 4) Monocarpellary
---
Family:
Distribution: This family includes 600 genera and 12800 species, cosmopolitan distribution.
Habitat: Terrestrial mesophytes. Exceptions: Aeschynomene - hydrophyte Alhagi maurorum - xerophyte
Habit:
Mostly herbs - Pisum spp., Medicago
Few shrubs - Tephrosia, Crotolaria
Some trees - Butea frondosa (aka flame of the forest), Erythrina
Some herbaceous stem climbers/twiners - Dolichos, Clitoria.
Herbaceous tendril chambers - Pisum spp, Lathyrus spp.
Root System: Tap root system with bacterial nodules. These plants are used in crop rotation and as green manure.
Stem: Aerial, erect or climbing, strong or weak, solid, branched, herbaceous or woody, cylindrical or angular, smooth or hairy.
Leaves: Alternate, mostly compound
Unipinnately compound - Clitoria, Tephrosia, Pisum.
Pinnately trifoliate - Dolichos
Palmately trifoliate - Crotolaria
Simple - Crotolaria retusa
Stipulate or Exstipulate, stipules are foliaceous in Lathyrus and Pisum. They take on the function of photosynthesis.
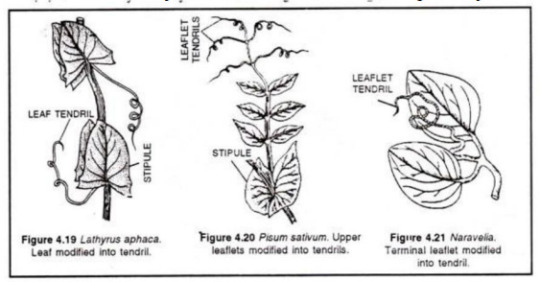
In Pisum the terminal leaflets are modified into tendrils.
In Lathyrus the entire leaf is modified into tendrils.
In Dolichos and Clitoria the leaflets are stipelate.
Leaf is petiolate, pulvinous leaf base, leaflets – ovate, oblong, margin entire, apex acute, obtuse or retuse, pinnately reticulate venation.
In Desmodium gyrans (Indian telegraph plant) the central leaflets exhibit autonomous movements in response to variation in temperature.
Inflorescence: Axillary or terminal, racemose – simple raceme, solitary in Cicer.
Flower: Bracteate, pedicellate, bracteolate (Crotalaria, Clitoria) or ebracteolate (Dolichos, Tephrosia), actinomorphic, zygomorphic, complete, bisexual, hypogynous, pentamerous.
Calyx: 5 sepals, gamosepalous, valvate aestivation and persistent, odd sepal anterior in position.
Corolla: 5 Petals, polypetalous, papilionaceous corolla or butterfly shaped.
The large outermost posteriorly placed petal is called standard/vexillum; it overlaps the two median lateral petals called wings/alae; which in turn overlaps two antero-lateral petals called keel/carina.
Descendingly imbricate aestivation or vexillary.
Androecium: Ten Stamens,
Mostly diadelphous - Tephrosia, Dolichos and Clitoria.
Crotolaria: five long and five short, monoadelphous condition,
Dalbergia spp: 9 stamens, monoadelphous.
Anthers are dithecous, introrse, basifixed, or dorsifixed.
Gynoecium: Simple, monocarpellary. Ovary superior, long cylindrical (Pisum) or laterally compressed (Crotolaria).
Gynophore may be present. Style long, terminal but at the base in Crotolaria it bends ends in hairy stigma.
Fruit: Legume or pod
Seed: Seeds are endospermic
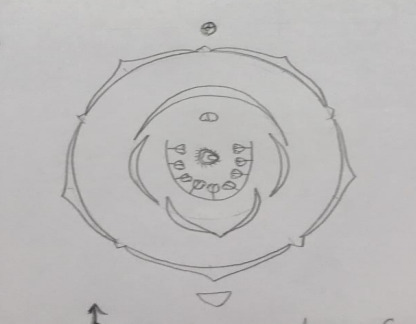
Floral Formula:
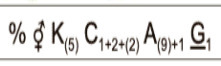
---
Economic Importance:
Most of the crops are used as fodder for cattle.
Pulses: Pisum sativum - Garden pea, Glycine max - Soybean
Vegetables: Phaseolus vulgaris - Kidney bean
Oils: Arachis hypogea - Groundnut
Timber yielding: Dalbergia latifolia – Indian Rosewood,
Indigofera tinctoria – the leaves yield indigo dye used in dyeing and printing cotton and rayon and pigments for paints and ink.
-------------------------------------------------
Embryology in Relation to Taxonomy
Schnarf, a German embryologist, studied the role of embryology in 1931.
The angiosperm embryological characters of importance are: anatropous, double fertilization, triple fusion, post fertilized triploid endosperm, and dicot or monocot conditions.
Embryology in relation to taxonomy can be observed at three levels: above family level, at family level, and at generic level.
---
Above Family Level
1) Caryophyllales
Commonly known as centrospermae
Have trinucleate pollen
Bitegmic crassinucellate ovule
Curved and peripheral embryo
Perisperm with or without endosperm.
2) Helobia
Have helobial type of endosperm
-(a cell wall is laid down between the first two nuclei, after which one half develops endosperm along the cellular pattern and the other half along the nuclear pattern.)-
3) Gentinales
Lack of integumentary tapetum
Have nuclear endosperm
Buddleiaceae and Oleaceae have integuments and cellular endosperm
4) Orchidales
Have an undifferentiated embryo
Very little to no endosperm
---
At Family Level
1) Podostemaceae
Includes perennial aquatic herbs with unique embryo features such as:
Pseudo embryo sac
Bisporic type of embryo sac
Pollen grain in pairs
Tenuinucellate bitegmic ovule
Presence of suspensor
2) Onagraceae
-(THe one where the megaspore divides one less time, only forming 4 nuclei instead of 8)-
Monosporic 4 nucleate, oenothera type embryo sac (with the exception of trapa)
Embryo sac derived from micropylar megaspore of tetrad
Only egg apparatus, 2 synergids, and one polar nucleus form.
Antipodals and one polar nucleus absent.
3) Cyperaceae
Microspore mother cell only gives one funtional microspore
4) Loranthaceae
Actually has 2 sub families, Loranthoideae and Viscoideae
i) Loranthoideae - Triradiate pollen - Polygonum embryo sac - Composite endosperm - Presence of suspensor - Polyembryony
ii) Viscoideae - Spherical pollen - Allium type embryo sac - Non-composite endosperm - Absence of suspensor - Polyembryony - The subfamilies have recently changed to Loranthaceae and Viscaceae respectively
At Generic Level
1) Trapa
Kept under Onagraceae (B&H) and Trapaceae (Englerian)
Evidence for both: -(????)-

2) Paeonia
Used to be included in Ranunculaceae (characters not present), now in Paeoniaceae
Generative cells are longer and elongated
Embryo sac long and narrow
Seed coat is massive
Germination epigeal
3) Exocarpus (Previously Santalaceace)
Initially placed in Exocarpaceae (under gymnosperms) due to the presence of naked ovules and pollen chamber.
But later it was confirmed to be Santalaceae due to the:
Presence of angiospermic flowers
Polygonum embryo sac
Cellular endosperm
And transverse division in zygote
4) Butomus
Polygonum embryo sac
Other genera of the family Butomaceae process Allium type embryo sac
With the exception of Butomus, all other genera have been transferred to Alismataceae
I'm failing
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Cytotaxonomy
Cytology in relation to taxonomy
The application of cytological data in solving taxonomic problems.
The characteristics of the chromosomes, which have proved to be of taxonomic value include: - Chromosome number - Chromosome size - Chromosome morphology - Chromosome behavior
Chromosome Number: - The chromosome no. is constant and same in all individuals of a species. - It is used as a confirmative property to distinguish a species from members of other species. - Can be divided into: - Separation at species level - Separation at interspecific level - Separation at generic level - Separation at family level - Ex: Monotropa hypoptiys and Monotropa hypophegea are two difference species that are morphologically similar, but they are separated on the bases of chromosome no. - M. hypopitys is hexaploid (2n=48) - M. hypophegea is diploid (2n=16) - It is usually seen that closely related plants, like the different species of a genus, show chromosome numbers with reveal an arithmetic relation with one another.
Aneuploids: - Plants with basic no of chromosome with some addition or deletion of a few chromosomes. - Monosomics: 2n-1, like in Datura - Nullisomics: 2n-2, like in Triticum - Tricomics: 2n+1, like in Wheat - Tetrasomics: 2n+2 chromosome
Chromosome Size: - It has already been discovered that evolutionary development involves in addition to alterations in chromosome number - Ex: Cytologically, Cyclea and Cissampelos are seen to be based on 12, while Stephania shows n=13. It is seen that the number n=13 is characteristic of the tribe Cocculeae, which further shows chromosomes of small size. - Large chromosomes, low chromosome no., and symmetrical karyotype represents a primitive status. - Small chromosomes, high chromosome no., and extreme asymmetry indicates advancement.
Chromosome Morphology: - Karyotype of plants is now very useful for the classification of some plants. - Monocotyledons have larger chromosome no. than dicot. - Woody plants have smaller chromosome no. than herbs. - The position of centromere and satellite is considered in classification: - ex 1: Human chromosomes are divided into 7 groups and sex chromosomes: - ex 2: Also, the shape of metaphase chromosome is considered for classification.


Chromosome Behavior - It provides clues about the cause of sterility and fertility among populations - Structural difference in the paternal chromosome is the main cause for the sterility - If the two sets of paternal chromosomes are homologous, the plants seem to be fertile.
---
Significance of Cytotaxonomy:
The role of cytotaxonomy is very important in taxonomic studies.
Cytotaxonomy is more significant, the process is dealing with the comparative study of chromosome and with this method minute variation among the individuals can be detected.
DNA is present in the every chromosome and the variations in each DNA are responsible for the variation among the individuals, species, genus and everything.
When the differences of physiological variations are too less among the individuals of same species and other higher taxa, Cytotaxonomy is a part of taxonomic biology that deals with the classification of organisms.
Cytotaxonomy classifies these organisms based on their function and cellular (DNA) structure. As the cytologic data are directly derived from nucleus, the seat of hereditary material, they may be used for understanding the evolution and relationships of population.
The characteristics of karyotypes are taxonomically useful where the individual chromosomes are large enough for detailed microscopic observation.
In this branch, another useful taxonomic character is the position of centromere. Meiotic behavior may show heterozygosity of in versions. This may be constant for a taxon, offering further taxonomic evidence.
--------------------------------------------------------------
Chemotaxonomy
The chemical constituents of plants differ from one species to another
They are restricted to certain taxa, making them valuable characters for plant classification.
The classification of plants on the basis of chemical contents is called chemotaxonomy or chemical taxonomy.
The following chemicals are present in plants and accounted for classification:
- Non-protein amino acids
- Phenolics
- Betalins
- Alkoloids
- Terpenoids and Steroids
- Crystals
- Immunological reactions
1) Non-protein Amino Acids
There are 300 non-protein amino acids in plants
Some are restricted to certain groups alone
They are used to classify and distinguish the taxa from others
Ex: Lathyrine in genus Lathyrus
Ex: add one more
2) Phenolics
Derivatives of phenolic compounds
Plants are classified on the basis of specific phenolic compounds.
Ex: Flavonols and methoxy cinnamic acid - herbaceous plants
Ex: Leucoanthocynin - woody plants.
3) Betalins
Derivatives of phenols serving as pigments.
They are present in only 10 families.
Ex: The position of the family Cactaceae was disputed for many years, but on the basis of the presence of betalins, it's position in centrospermae has been confirmed.
4) Alkaloids
Nitrogen containing compounds with a heterocyclic ring.
There are about 5000 different alkaloids in angiosperms.
They are used as a source for plant classification.
Ex: Lupin - Fabaceae
Ex: Tropane - Solanaceae
Ex: Morphine - Papaver somnifer
5) Terpenoids and Steroids
Terpenoids are unsaturated hydrocarbons derived from isoprenes
Ex: Carotenoids, iridoids
Steroids are saturated hydrocarbons with four rings in their structure
Ex: Cucurbitins present in Cucurbitaceae
6) Crystals yay
Some plants have raphide crystals in different parts of their body.
The forms of crystals are used to some extent in the classification of plants.
Ex: Presence and absence of raphides are used in the grouping of plants in the family Rubiaceae
Calcium oxalate crystals are present in the ovary walls of the members of Asteraceae.
7) Immunological Reactions
The storage protein or pollen protein is injected from the plant body to a test animal (usually a mouse or rabbit)
The test animal produces antiserum against the protein
The antiserum is mixed with the plant extract to detect the precipitate formed by antigen-antibody reaction.
The nature and amount of precipitate indicate the relationship of the protein to the plant.
High rate of precipitation indicates closeness of the plants.
Low rate shows that the plants are not related.
This type of study is called serotaxonomy.
Ex: Closeness of Delphinium to Aconitumis has been confirmed by serological studies.
--------------------------------------------------------------
Numerical Taxonomy
Numerical taxonomy or taximetrics is taxonomy which uses mathematical methods to find similarities and differences.
It is based oh phenetic evidences (phenotype) published by Sokal and Sneath in 1963.
Basic aspects:
I) Construction of Taxonomic Groups: - Individuals are selected and their characters are spotted - There is no limitation in the number of characters. - The greater the number, the better the approach (at least 100 characters) - General character analysis
II) Discrimination of Taxonomic Groups: - When groups show a overlapping of characters. - The discrimination between them is done by analysis technique
---
Construction of Taxonomic Groups:
Phenetics: - Based on the similarities between phenetic characters - There is no idea of ancestral relationship - Taxa are connected at different levels according to the overall similarity in the form of a tree diagram called phenogram.
Cladistics: - Based on the relationship between individuals to evolutionary history. - There is a common ancestry - The taxa re connected in a tree called a cladogram.
There are 5 steps in the construction of taxonomic groups: i) Operational Taxonomic Units ii) Unit Characters or Attributes iii) Selection of Unit Characters iv) Estimation of Similarity v) Similarity Matrix
1) Operational Taxonomic Units:
Can be written as OTUs
The basic unit of study in numerical taxonomy
Can be individual, species, genus, family, order, or class based.
OTU is not comparable to formal taxonomic units
Comparison made only with equal rank - Genera are compared with different species - Family with different genera
2) Unit Characters or Attributes:
Characters used in numerical taxonomy are called unit characters
According to Sokal and Sneath 1963- “Taxonomic character which exists in one or more states”
Only the presence or absence of phenetic characters are considered.
Divides into two types:
a) Binary Characters: - Unit characters with two contrasting states - Ex: Presence or absence of trichomes - Ex: Fruits dehiscent or indehiscent - Positive Characters can be denoted as + or 1 - Negative Characters can be denoted as - or 0 - Missing characters are denoted as NC (no comparison)
b) Multistate Characters: - Characters in more than 2 states - Characters coded into number of states: i) Qualitative Multistate Characters: - They contain 3 or more contrasting forms, ex: flower color. - They are analyzed by converting them into a series of binaries. ii) Quantitative Multistate Characters: - Measures size on a continuous scale, ex: Length of leaf/height of plant.
3) Selection of Unit Characters:
According to Sneath & Sokal:
They should come from all parts of an organism
Belong to all stages of the life cycle of organism
Variable characters within the group used
Attention is given to characters related to morphology, physiology, ecology, and the distribution of organism
All characters are given equal value
4) Estimation of Similarity
The resemblance between a pair of OTUs
Similarity- % of characters in which they agree
Dissimilarity- % of characters they do not agree
Can be calculated with:
a) The Coefficient of Association (S):

The number of possible different combination of matches and mismatches of characters of 2 OTUs in a conventional 2x2 table:

b) Coefficient of Correlation (r):

c) The Measurement of Taxonomic Distance between OTUs (d):

5) Similarity Matrix
Simple matching indices found for all OTUs
Similarity arranged in a test table
10x10 similarity matrix for 10 OTUs

3 clusters can be regarded as three phenons
Group of similar organism by numerical method are phenos
Phenos are arranged in phenogram or dendrogram
Since this process of rearrangement is based on visual inspection, it is difficult to achieve with more than 10 OTUs.

Sokal and Sneath described shaded similarity matrices
The range of similarity is indicated by squares with different densities of shading

Advantages: - Helps in interpretation of wide range of data - Gives better classification - Re-interpretation possible
Disadvantages: - Selection of characters can be difficult - Numerical species recognized by this method are unacceptable
0 notes
Text
Angiosperm Plant Families and their Floral Formula
Angiosperm Plant Families and their Floral Formula
In this tutorial, we have discussed ‘Angiosperm Plant Families and their Floral Formula‘. Flowering plants are described in sequential order of morphological characters, like habit, habitat, root, stem, leaves, inflorescence, flower, fruit, and seed of the plant. On the basis of floral characters, a floral diagram and a floral formula are drawn. By the observed characters, the plant is identified…

View On WordPress
#floral formula of brassicaceae#floral formula of fabaceae#floral formula of liliaceae#floral formula of malvaceae#floral formula of solanaceae
0 notes
Text
PLANT PROFILE: RED CLOVER {TRIFOLIUM PRATENSE}

by Crooked Bear Creek Organic Herbs
Family: Fabaceae
This all-around wellness herb and blood purifier is a key ingredient in herbal blends popularised during the early 1900’s and used in cancer treatment, including Essiac, Dr. Christopher’s Red Clover Combination, and the Hoxsey formula. Red clover has been an Old World symbol for luck and abundance since ancient times. And when it arrived in America with the colonists, its use quickly spread among American Indian tribes.
Description:
This stout clover has deep pink – not red – plump, round flower heads that contain numerous, small, pea-type flowers above a three-leaved bract. The leaves are marked with a single pale chevron. The lax stems trail up to 2 feet, creating a soft green mass.

Preparations Infusion:
Make a strong infusion or tincture of red clover tops, and drink 1/2 to 1 cup two or three times daily. Commercially available red clover preparations include tinctures and concentrated and often standardised extracts {containing consistent amounts of genistein} in capsules and tablets, as well as syrups and elixirs. Follow the package instructions.
Healing Properties:
Red clover flowering tops are a veritable pharmacy, containing many active compounds that reduce inflammation, activate your immune response, and improve liver function. According to traditional medicine, preparations of this herb are effective expectorants, regulate blood flow, and help your body heal skin problems such as eczema, psoriasis, acne, and dermatitis.
Red clover formulas are known as “blood purifiers,” which is likely due to their active chemicals – flavonoids and other compounds are known as phenolics – which act as antioxidants, have anti-inflammatory properties and mild estrogen-like activity, and are stimulating to the liver and bile. Blood purifiers are thought to slowly alter the function of cells and tissues to bring them closer to a normal, healthy function. They are also thought to help create a healthy inner environment for the wellness of your skin, your body’s largest organ. Red clover is a component of many formulas recommended by herbalists to help the body eliminate toxins and fight cancer.
Red clover contains isoflavonoids like genistein, which has been widely studied and is sold in dietary supplements as a natural estrogen alternative.
Safety:
Red clover can be used regularly as a moderately strong tea infusion. Avoid taking it during pregnancy because of its alleged estrogenic effect. Theoretically, red clover preparations may potentiate, or strengthen, the effects of anticoagulant drugs. However, the coumarins in red clover are not like pharmaceutical anti-coagulants {such as dicoumarol or warfarin}, but are much milder in their action.

In the Garden:
Red clover grows wild in open meadows and pastures. {The species name, pratense, means “of the meadows,”}. It loves full sun and rich, fertile, well-drained soil – but it’s not picky. Water it regularly until the plants look big and healthy, and then let it go dry between waterings; this mild drought stress will bring on the flowers. Red clover is a short-lived perennial, but in most areas, you’ll sow it yearly. Treat the seed with inoculant or stratify it, and direct sow in the fall {if you don’t get a snowy winter where you live} or very early spring.
Harvesting Red Clover:
When the blossoms are open and vibrant, pick them by holding them gently and snapping them off with your thumbnail. You can include the triad of leaves just below the flower head. They will brown as they mature, but as long as the browning is less than one-third of the flower, they are still medicinally strong. Collect clover early in the day, when there is only light dew, to help preserve the colour. Keep harvesting every 2 or 3 days to keep the flowers coming. They dry quickly, so keep a close eye on them to avoid over-drying them. Before you store them, press the centres of the flowers to make sure there’s no moisture left. Store in a cool, dark place to keep the colour from fading.
Also, Known As:
Clover
Cow Clover
Meadow Clover
Purple Clover
Red Clover
Additional Information About Red Clover:
The red clover is in a symbiotic relationship with bacteria present in the root nodules, the plant is capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen into the soil, and this enhances the quality of the soil in which it is grown – the primary reason for its use as a rotation crop. Traditionally, a rare four-leaf red clover specimen is believed to bring good luck and children in America love hunting through a patch of red clover for such rare four-leaf specimens of the plant. Folk and herbal medicine make use of the dried red clover flowers in the treatment of different disorders. An expectorant action is attributed to the blossoms of the red clover; disorders such as bronchitis and asthma are treated using the dried flowers. A topical herbal remedy is also made using the red clover, this remedy is believed to speed up the process of healing wounds and other external injuries, red clover is also used in the treatment of skin diseases such as psoriasis and other external conditions. The traditional use of the red clover in gaining relief from menopausal symptoms what is generating current interest in the plant. The red clover has high phytoestrogen content, and browsing animals such as cattle and sheep grazing exclusively or heavily on the red clover often tend to develop fertility problems.
The total content of phytoestrogens in the red clover herb is approximately 0.17 percent of the dry weight per plant. Chemical compounds such as formononetin, the compound genistein, the compound daidzein, and biochanin A. are some of the major compounds present in the herb. A mild estrogen-like effect is displayed by the compound formononetin, the compound biochanin A, the compound daidzein and the genistein compound – that is they tend to mimic the effects of estrogen in the body. Australian herbal marketers have commercially translated the perceived estrogen-like the effect of the plant and turned the red clover into a herbal estrogen supplement, thus, a very widely advertised product called the red clover blossom dietary supplement is now touted as the natural choice for maintaining estrogen in Australia. The phytoestrogen effects of the red clover need to be supported by thorough clinical studies of the plant in the laboratory, such tests are currently on the anvil. Red clover also contains a class of plant-based compounds called isoflavones, these compounds are also present in familiar plant products like soybeans, the isoflavones are believed to be capable of changing the rate of hormone synthesis and are believed to be capable of influencing metabolism in the body, these compounds are also believed to affect intracellular enzymes, they are also known to affect the rate of cell differentiation and production, and may also be involved in the synthesis of biological growth factors in the body.
The possible benefit of using isoflavones in the process of chemoprevention, which is cancer prevention, is also being investigated by an epidemiologist in many Asian countries where a lot of isoflavone-rich soy products are consumed by the majority of the population. The potential need for further investigation and research is suggested by the results obtained from a recent in vitro study, where it was found that the compound biochanin A sourced from red clover seems to inhibit the activation of carcinogenic cell cultures – further studies will doubtless shed a light on this phenomenon.
Methyl salicylate is one compound among the many other chemical compounds present in the volatile oil of the red clover blossoms. The blossoms have also been found to contain small amounts of coumarin derivatives and certain types of cyanogenic glycosides.
The supplementary use of red clover extract in the treatment of symptoms associated with menopausal women has found sudden prominence due to the release of a herbal supplement called Promensil from Australia – this new supplement is meant for the exclusive use of women in any stage of menopause. Each Promensil pill contains 40 mg of the isoflavones, set to a standardized ratio, Promensil was introduced in the US market in 1998. Australian researchers have been responsible for the majority of the research which supports the beneficial nature of red clover based isoflavones. Another red clover based supplement called Trinivin is marketed by the same Australian firm, this pill also contains 40 mg of the standardized isoflavones isolated from the herb, Trinivin is meant for men affected by disease free but enlarged prostates, this product is also sold in the United States. Researchers conducted by the company also indicated that the isoflavones present in red clover and Novogen are able to suppress the hot flashes which periodically affect peri-menopausal women without inducing proliferation in the uterine or endometrial tissue of the body. The ability of the isoflavones present in red clover to keep the blood vessels pliable was also demonstrated in a double-blind and controlled trial published in March 1999 edition of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Applications:
Flowers:
FRESH – The flowers of the red clover can be used in the topical treatment of skin. Red clover flowers can be crushed and applied or rubbed into irritated skin caused by insect bites and stings, the floral poultice will alleviate the pain and speed up healing in the affected area.TINCTURE – A herbal red clover floral tincture can be prepared from the flowers of the plant, this floral tincture can be consumed to treat cases of eczema and psoriasis.COMPRESS – A herbal floral compress can also be prepared from the flowers of the red clover, this can be applied to the affected parts of the body in the treatment of arthritic pains, the compress can also be used to alleviate the symptoms of gout by placing the herbal compress on the affected area.OINTMENT – Red clover floral ointments can also be made for the treatment of lymphatic swellings. This floral ointment can be prepared by covering some fresh red clover flowers in some water and then simmering the water in a slow cooker for a period of forty-eight hours at a stretch. The concoction can then be strained, and the residue evaporated to a semi-dry condition, this can then be combined with an equal amount of a good ointment base. The floral ointment made from red clover blossoms is for topical use only.EYEWASH – The flowers of the red clover can be used in the preparing herbal eyewash from the diluted floral tincture, the dilution ratio can be 20 ml of water or a full eyecup to which 5 – 10 drops of the floral tincture or a well-strained floral infusion must be added. This floral eyewash can be used for disorders such as conjunctivitis and other conditions of the eye.DOUCHE – The floral infusion of the red clover herb can be used to alleviate vaginal itching in the form of a douche.SYRUP – The red clover floral infusion can be boiled down to herbal syrup, this herbal remedy can be used in the treatment of persistent or stubborn, dry coughs.
Indian Tea or Essiac:
3 oz (90 g) red clover flowers
3 oz (90 g) wood sorrel flowers
3 oz (90 g) common burdock root
1 oz (30 g) kelp
1 oz (30 g) slippery elm powder
1 oz (30 g) Canada thistle head
Combine all the plants. Boil 1 t (5 ml) of the mixture in 1 cup (250 ml) water for 5 minutes. Drink 3 cups (750 ml) per day for 1 to 3 months. This is the closest recipe to the original famous North American Indian tea used to fight cancer. It is also an excellent lymphatic and blood depurative.
https://crookedbearcreekorganicherbs.com/2018/03/17/plant-profile-red-clover-trifolium-pratense/
0 notes
Text
IA2 Prep: Botany (Taxonomy)
Fabaceae - Pea Family
Classification:
Spermatophyta
Angiosperms
Dicotyledons
Polypetalae
Calyciflorae
Rosales
Fabaceae
Derivation of Classification:
Spermatophyta: Seed bearing plants.
Angiosperms: Seeds enclosed within a fruit.
Dicotyledons:
1) Tap root system
2) Dorsiventral leaves
3) Reticulate venation
4) Mostly pentamerous flowers
5) Seed with two cotyledons
Polypetalae:
1) Perianth present; differentiated into calyx and corolla
2) Petals free
Calyciflorae:
1) Flowers actinomorphic or zygomorphic
2) Hypogynous, perigynous, or epigynous
3) Cup shaped thalamus called calyx tube may be present
4) Stamens 10-many, inserted on the calyx tube
5) Monocarpellary gynoecium with marginal placentation
Rosales:
1) Leaves alternate and stipulate
2) Flowers bisexual
3) Actinomorphic or zygomorphic
4) Monocarpellary
Family:
Distribution: This family includes 600 genera and 12800 species, cosmopolitan distribution.
Habitat: Terrestrial mesophytes. Exceptions:
Aeschynomene - hydrophyte
Alhagi maurorum - xerophyte
Habit:
Mostly herbs - Pisum spp., Medicago
Few shrubs - Tephrosia, Crotolaria
Some trees - Butea frondosa (aka flame of the forest), Erythrina
Some herbaceous stem climbers/twiners - Dolichos, Clitoria.
Herbaceous tendril chambers - Pisum spp, Lathyrus spp.
Root System: Tap root system with bacterial nodules. These plants are used in crop rotation and as green manure.
Stem: Aerial, erect or climbing, strong or weak, solid, branched, herbaceous or woody, cylindrical or angular, smooth or hairy.
Leaves: Alternate, mostly compound
Unipinnately compound - Clitoria, Tephrosia, Pisum.
Pinnately trifoliate - Dolichos
Palmately trifoliate - Crotolaria
Simple - Crotolaria retusa
Stipulate or Exstipulate, stipules are foliaceous in Lathyrus and Pisum. They take on the function of photosynthesis.

In Pisum the terminal leaflets are modified into tendrils.
In Lathyrus the entire leaf is modified into tendrils.
In Dolichos and Clitoria the leaflets are stipelate.
Leaf is petiolate, pulvinous leaf base, leaflets – ovate, oblong, margin entire, apex acute, obtuse or retuse, pinnately reticulate venation.
In Desmodium gyrans (Indian telegraph plant) the central leaflets exhibit autonomous movements in response to variation in temperature.
Inflorescence: Axillary or terminal, racemose – simple raceme, solitary in Cicer.
Flower: Bracteate, pedicellate, bracteolate (Crotalaria, Clitoria) or ebracteolate (Dolichos, Tephrosia), actinomorphic, zygomorphic, complete, bisexual, hypogynous, pentamerous.
Calyx: 5 sepals, gamosepalous, valvate aestivation and persistent, odd sepal anterior in position.
Corolla: 5 Petals, polypetalous, papilionaceous corolla or butterfly shaped.
The large outermost posteriorly placed petal is called standard/vexillum; it overlaps the two median lateral petals called wings/alae; which in turn overlaps two antero-lateral petals called keel/carina.
Descendingly imbricate aestivation or vexillary.
Androecium: Ten Stamens,
Mostly diadelphous - Tephrosia, Dolichos and Clitoria.
Crotolaria: five long and five short, monoadelphous condition,
Dalbergia spp: 9 stamens, monoadelphous.
Anthers are dithecous, introrse, basifixed, or dorsifixed.
Gynoecium: Simple, monocarpellary. Ovary superior, long cylindrical (Pisum) or laterally compressed (Crotolaria).
Gynophore may be present. Style long, terminal but at the base in Crotolaria it bends ends in hairy stigma.
Fruit: Legume or pod
Seed: Seeds are endospermic
Floral Formula: ?? how-

Economic Importance:
Most of the crops are used as fodder for cattle.
Pulses: Pisum sativum - Garden pea, Glycine max - Soybean
Vegetables: Phaseolus vulgaris - Kidney bean
Oils: Arachis hypogea - Groundnut
Timber yielding: Dalbergia latifolia – Indian Rosewood,
Indigofera tinctoria – the leaves yield indigo dye used in dyeing and printing cotton and rayon and pigments for paints and ink.

------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chemotaxonomy
The chemical constituents of plants differ from one species to another
They are restricted to certain taxa, making them valuable characters for plant classification.
The classification of plants on the basis of chemical contents is called chemotaxonomy or chemical taxonomy.
The following chemicals are present in plants and accounted for classification:
- Non-protein amino acids
- Phenolics
- Betalins
- Alkoloids
- Terpenoids and Steroids
- Crystals
- Immunological reactions
1) Non-protein Amino Acids
There are 300 non-protein amino acids in plants
Some are restricted to certain groups alone
They are used to classify and distinguish the taxa from others
Ex: Lathyrine in genus Lathyrus
Ex: add one more
2) Phenolics
Derivatives of phenolic compounds
Plants are classified on the basis of specific phenolic compounds.
Ex: Flavonols and methoxy cinnamic acid - herbaceous plants
Ex: Leucoanthocynin - woody plants.
3) Betalins
Derivatives of phenols serving as pigments.
They are present in only 10 families.
Ex: The position of the family Cactaceae was disputed for many years, but on the basis of the presence of betalins, it's position in centrospermae has been confirmed.
4) Alkaloids
Nitrogen containing compounds with a heterocyclic ring.
There are about 5000 different alkaloids in angiosperms.
They are used as a source for plant classification.
Ex: Lupin - Fabaceae
Ex: Tropane - Solanaceae
Ex: Morphine - Papaver somnifer
5) Terpenoids and Steroids
Terpenoids are unsaturated hydrocarbons derived from isoprenes
Ex: Carotenoids, iridoids
Steroids are saturated hydrocarbons with four rings in their structure
Ex: Cucurbitins present in Cucurbitaceae
6) Crystals yay
Some plants have raphide crystals in different parts of their body.
The forms of crystals are used to some extent in the classification of plants.
Ex: Presence and absence of raphides are used in the grouping of plants in the family Rubiaceae
Calcium oxalate crystals are present in the ovary walls of the members of Asteraceae.
7) Immunological Reactions
The storage protein or pollen protein is injected from the plant body to a test animal (usually a mouse or rabbit)
The test animal produces antiserum against the protein
The antiserum is mixed with the plant extract to detect the precipitate formed by antigen-antibody reaction.
The nature and amount of precipitate indicate the relationship of the protein to the plant.
High rate of precipitation indicates closeness of the plants.
Low rate shows that the plants are not related.
This type of study is called serotaxonomy.
Ex: Closeness of Delphinium to Aconitumis has been confirmed by serological studies.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Embryology in relation to taxonomy
Schnarf, a German embryologist, studied the role of embryology in 1931.
The angiosperm embryological characters of importance are: anatropous, double fertilization, triple fusion, post fertilized triploid endosperm, and dicot or monocot conditions.
Embryology in relation to taxonomy can be observed at three levels: above family level, at family level, and at generic level.
Above Family Level
1) Caryophyllales
Commonly known as centrospermae
Have trinucleate pollen
Bitegmic crassinucellate ovule
Curved and peripheral embryo
Perisperm with or without endosperm.
2) Helobia
Have helobial type of endosperm
-(a cell wall is laid down between the first two nuclei, after which one half develops endosperm along the cellular pattern and the other half along the nuclear pattern.)-
3) Gentinales
Lack of integumentary tapetum
Have nuclear endosperm
Buddleiaceae and Oleaceae have integuments and cellular endosperm
4) Orchidales
Have an undifferentiated embryo
Very little to no endosperm
At Family Level
1) Podostemaceae
Includes perennial aquatic herbs with unique embryo features such as:
Pseudo embryo sac
Bisporic type of embryo sac
Pollen grain in pairs
Tenuinucellate bitegmic ovule
Presence of suspensor
2) Onagraceae
-(THe one where the megaspore divides one less time, only forming 4 nuclei instead of 8)-
Monosporic 4 nucleate, oenothera type embryo sac (with the exception of trapa)
Embryo sac derived from micropylar megaspore of tetrad
Only egg apparatus, 2 synergids, and one polar nucleus form.
Antipodals and one polar nucleus absent.
3) Cyperaceae
Microspore mother cell only gives one funtional microspore
4) Loranthaceae
Actually has 2 sub families, Loranthoideae and Viscoideae
i) Loranthoideae
Triradiate pollen
Polygonum embryo sac
Composite endosperm
Presence of suspensor
Polyembryony
ii) Viscoideae
Spherical pollen
Allium type embryo sac
Non-composite endosperm
Absence of suspensor
Polyembryony
The subfamilies have recently changed to Loranthaceae and Viscaceae respectively
At Generic Level
1) Trapa
Kept under Onagraceae (B&H) and Trapaceae (Englerian)
Evidence for both: -(WTF DOES THIS MEAN)-

2) Paeonia
Used to be included in Ranunculaceae (characters not present), now in Paeoniaceae
Generative cells are longer and elongated
Embryo sac long and narrow
Seed coat is massive
Germination epigeal
3) Exocarpus (Previously Santalaceace)
Initially placed in Exocarpaceae (under gymnosperms) due to the presence of naked ovules and pollen chamber.
But later it was confirmed to be Santalaceae due to the:
Presence of angiospermic flowers
Polygonum embryo sac
Cellular endosperm
And transverse division in zygote
4) Butomus
Polygonum embryo sac
Other genera of the family Butomaceae process Allium type embryo sac
With the exception of Butomus, all other genera have been transferred to Alismataceae
WHAT DOES ANY OF THIS MEAN? IDK.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Red and the White of Clover

by Crooked Bear Creek Organic Herbs
Red Clover {Trifolium pratense}
Family: Fabaceae
This all-around wellness herb and blood purifier is a key ingredient in herbal blends popularised during the early 1900s and used in cancer treatment, including Essiac, Dr. Christopher’s Red Clover Combination, and the Hoxsey formula. Red clover has been an Old World symbol for luck and abundance since ancient times. And when it arrived in America with the colonists, its use quickly spread among American Indian tribes.

Description:
This stout clover has deep pink – not red – plump, round flower heads that contain numerous, small, pea-type flowers above a three-leaved bract. The leaves are marked with a single pale chevron. The lax stems trail up to 2 feet, creating a soft green mass.

Preparations Infusion:
Make a strong infusion or tincture of red clover tops, and drink 1/2 to 1 cup two or three times daily. Commercially available red clover preparations include tinctures and concentrated and often standardised extracts {containing consistent amounts of genistein} in capsules and tablets, as well as syrups and elixirs. Follow the package instructions.
Healing Properties:
Red clover flowering tops are a veritable pharmacy, containing many active compounds that reduce inflammation, activate your immune response, and improve liver function. According to traditional medicine, preparations of this herb are effective expectorants, regulate blood flow, and help your body heal skin problems such as eczema, psoriasis, acne, and dermatitis.
Red clover formulas are known as “blood purifiers,” which is likely due to their active chemicals – flavonoids and other compounds are known as phenolics – which act as antioxidants, have anti-inflammatory properties and mild estrogen-like activity, and are stimulating to the liver and bile. Blood purifiers are thought to slowly alter the function of cells and tissues to bring them closer to a normal, healthy function. They are also thought to help create a healthy inner environment for the wellness of your skin, your body’s largest organ. Red clover is a component of many formulas recommended by herbalists to help the body eliminate toxins and fight cancer.
Red clover contains isoflavonoids like genistein, which has been widely studied and is sold in dietary supplements as a natural estrogen alternative.
Safety:
Red clover can be used regularly as a moderately strong tea infusion. Avoid taking it during pregnancy because of its alleged estrogenic effect. Theoretically, red clover preparations may potentiate, or strengthen, the effects of anticoagulant drugs. However, the coumarins in red clover are not like pharmaceutical anti-coagulants {such as dicoumarol or warfarin} but are much milder in their action.

In the Garden:
Red clover grows wild in open meadows and pastures. {The species name, pratense, means “of the meadows,”}. It loves full sun and rich, fertile, well-drained soil – but it’s not picky. Water it regularly until the plants look big and healthy, and then let it go dry between waterings; this mild drought stress will bring on the flowers. Red clover is a short-lived perennial, but in most areas, you’ll sow it yearly. Treat the seed with inoculant or stratify it, and direct sow in the fall {if you don’t get a snowy winter where you live} or very early spring.
Harvesting Red Clover:
When the blossoms are open and vibrant, pick them by holding them gently and snapping them off with your thumbnail. You can include the triad of leaves just below the flower head. They will brown as they mature, but as long as the browning is less than one-third of the flower, they are still medicinally strong. Collect clover early in the day, when there is only light dew, to help preserve the colour. Keep harvesting every 2 or 3 days to keep the flowers coming. They dry quickly, so keep a close eye on them to avoid over-drying them. Before you store them, press the centres of the flowers to make sure there’s no moisture left. Store in a cool, dark place to keep the colour from fading.
Also, Known As:
Clover
Cow Clover
Meadow Clover
Purple Clover
Red Clover
Additional Information About Red Clover:
The red clover is in a symbiotic relationship with bacteria present in the root nodules, the plant is capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen into the soil, and this enhances the quality of the soil in which it is grown – the primary reason for its use as a rotation crop. Traditionally, a rare four-leaf red clover specimen is believed to bring good luck and children in America love hunting through a patch of red clover for such rare four-leaf specimens of the plant. Folk and herbal medicine make use of the dried red clover flowers in the treatment of different disorders. An expectorant action is attributed to the blossoms of the red clover; disorders such as bronchitis and asthma are treated using the dried flowers. A topical herbal remedy is also made using the red clover, this remedy is believed to speed up the process of healing wounds and other external injuries, red clover is also used in the treatment of skin diseases such as psoriasis and other external conditions. The traditional use of the red clover in gaining relief from menopausal symptoms what is generating current interest in the plant. The red clover has high phytoestrogen content, and browsing animals such as cattle and sheep grazing exclusively or heavily on the red clover often tend to develop fertility problems.
The total content of phytoestrogens in the red clover herb is approximately 0.17 percent of the dry weight per plant. Chemical compounds such as formononetin, the compound genistein, the compound daidzein, and biochanin A. are some of the major compounds present in the herb. A mild estrogen-like effect is displayed by the compound formononetin, the compound biochanin A, the compound daidzein and the genistein compound – that are they tend to mimic the effects of estrogen in the body. Australian herbal marketers have commercially translated the perceived estrogen-like the effect of the plant and turned the red clover into an herbal estrogen supplement, thus, a very widely advertised product called the red clover blossom dietary supplement is now touted as the natural choice for maintaining estrogen in Australia. The phytoestrogen effects of the red clover need to be supported by thorough clinical studies of the plant in the laboratory, such tests are currently on the anvil. Red clover also contains a class of plant-based compounds called isoflavones, these compounds are also present in familiar plant products like soybeans, the isoflavones are believed to be capable of changing the rate of hormone synthesis and are believed to be capable of influencing metabolism in the body, these compounds are also believed to affect intracellular enzymes, they are also known to affect the rate of cell differentiation and production, and may also be involved in the synthesis of biological growth factors in the body.
The possible benefit of using isoflavones in the process of chemoprevention, which is cancer prevention, is also being investigated by an epidemiologist in many Asian countries where a lot of isoflavone-rich soy products are consumed by the majority of the population. The potential need for further investigation and research is suggested by the results obtained from a recent in vitro study, where it was found that the compound biochanin A sourced from red clover seems to inhibit the activation of carcinogenic cell cultures – further studies will doubtless shed a light on this phenomenon.
Methyl salicylate is one compound among the many other chemical compounds present in the volatile oil of the red clover blossoms. The blossoms have also been found to contain small amounts of coumarin derivatives and certain types of cyanogenic glycosides.
The supplementary use of red clover extract in the treatment of symptoms associated with menopausal women has found sudden prominence due to the release of an herbal supplement called Promensil from Australia – this new supplement is meant for the exclusive use of women in any stage of menopause. Each Promensil pill contains 40 mg of the isoflavones, set to a standardized ratio, Promensil was introduced in the US market in 1998. Australian researchers have been responsible for the majority of the research which supports the beneficial nature of red clover based isoflavones. Another red clover based supplement called Trinivin is marketed by the same Australian firm, this pill also contains 40 mg of the standardized isoflavones isolated from the herb, Trinivin is meant for men affected by disease free but enlarged prostates, this product is also sold in the United States. Researchers conducted by the company also indicated that the isoflavones present in red clover and Novogen are able to suppress the hot flashes which periodically affect peri-menopausal women without inducing proliferation in the uterine or endometrial tissue of the body. The ability of the isoflavones present in red clover to keep the blood vessels pliable was also demonstrated in a double-blind and controlled trial published in March 1999 edition of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Applications:
Flowers:
FRESH – The flowers of the red clover can be used in the topical treatment of skin. Red clover flowers can be crushed and applied or rubbed into irritated skin caused by insect bites and stings, the floral poultice will alleviate the pain and speed up healing in the affected area.TINCTURE – An herbal red clover floral tincture can be prepared from the flowers of the plant, this floral tincture can be consumed to treat cases of eczema and psoriasis.COMPRESS – An herbal floral compress can also be prepared from the flowers of the red clover, this can be applied to the affected parts of the body in the treatment of arthritic pains, the compress can also be used to alleviate the symptoms of gout by placing the herbal compress on the affected area.OINTMENT – Red clover floral ointments can also be made for the treatment of lymphatic swellings. This floral ointment can be prepared by covering some fresh red clover flowers in some water and then simmering the water in a slow cooker for a period of forty-eight hours at a stretch. The concoction can then be strained, and the residue evaporated to a semi-dry condition, this can then be combined with an equal amount of a good ointment base. The floral ointment made from red clover blossoms is for topical use only.EYEWASH – The flowers of the red clover can be used in the preparing herbal eyewash from the diluted floral tincture, the dilution ratio can be 20 ml of water or a full eyecup to which 5 – 10 drops of the floral tincture or a well-strained floral infusion must be added. This floral eyewash can be used during disorders such as conjunctivitis and other conditions of the eye.DOUCHE – The floral infusion of the red clover herb can be used to alleviate vaginal itching in the form of a douche.SYRUP – The red clover floral infusion can be boiled down to herbal syrup, this herbal remedy can be used in the treatment of persistent or stubborn, dry coughs.
Indian Tea or Essiac:
3 oz (90 g) red clover flowers
3 oz (90 g) wood sorrel flowers
3 oz (90 g) common burdock root
1 oz (30 g) kelp
1 oz (30 g) slippery elm powder
1 oz (30 g) Canada thistle head
Combine all the plants. Boil 1 t (5 ml) of the mixture in 1 cup (250 ml) water for 5 minutes. Drink 3 cups (750 ml) per day for 1 to 3 months. This is the closest recipe to the original famous North American Indian tea used to fight cancer. It is also an excellent lymphatic and blood depurative.
Looking for Red Clover Tincture? Anne’s Backyard Herbal LLC has just what you are looking for; from Red Clover Tincture to other wonderful, healthy glycerites, lip balms, and so much more.
https://goodwitcheshomestead.com/2019/03/17/the-red-and-the-white-of-clover/
0 notes