#copd diagnosis treatment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Copd Awareness: Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Tips
Delve into COPD Awareness: Chronic lung diseases like emphysema & chronic bronchitis caused by smoking. Symptoms include coughing & shortness of breath.
To know more: https://lalithachestandskinhospital.com/blog/copd-awareness-types-causes-symptoms-and-prevention-tips/
chest specialist doctor,best lung doctor in Karimnagar,good pulmonologist near me,breathing problem specialist doctor,copd diagnosis treatment,pulmonologist hospital near me,chronic obstructive pulmonary treatment

#chest specialist doctor#best lung doctor in Karimnagar#good pulmonologist near me#breathing problem specialist doctor#copd diagnosis treatment#pulmonologist hospital near me#chronic obstructive pulmonary treatment
0 notes
Text
#Sudden shortness of breath#Dyspnea causes#Asthma attacks#Heart failure symptoms#Pulmonary embolism treatment#Pneumonia breathing issues#COPD exacerbation#Anxiety shortness of breath#Panic attacks and breathing#Allergic reactions anaphylaxis#Obesity and breathing problems#Respiratory infections#ARDS causes#Shortness of breath emergency#Breathing difficulties#When to seek medical help for breathlessness#Emergency shortness of breath#Breathing problems solutions#Breathing exercises for anxiety#Shortness of breath diagnosis#health & fitness
1 note
·
View note
Text
Ultimate Guide to Respiratory Tract Infections: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Evidence-Based Treatments for URTIs and LRTIs
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections (URTIs) Introduction Respiratory tract infections (RTIs) encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the upper and lower respiratory tracts. They are common ailments that cause significant global morbidity and economic loss. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about RTIs, from symptoms and diagnosis to evidence-based treatments and…
#Acute Bronchitis#Acute Bronchitis Management Guidelines#Bronchiolitis#Clinical Scores for Strep Throat#COPD Exacerbation#COPD Exacerbation Causes and Solutions#COVID-19 Symptoms#COVID-19 vs Influenza Symptoms#How to Treat Sinusitis and Pharyngitis#Lower Respiratory Tract Infections#Pharyngitis#Pneumonia#Pneumonia Diagnosis and Care#Respiratory Tract Infections#Respiratory Tract Infections Treatment#RSV Symptoms and Treatment#Sinusitis
0 notes
Text

Explore cutting-edge COPD treatment options. Stay informed with new developments in COPD care.
0 notes
Note
I wanna know ur HCs for Mod AU jayvik 💕
OOOO this is an interesting one because I usually don't indulge in most modern aus of anything, but I shall try.
ask me about arcane!
Both are graduate students at the academy. Both double-majored in Engineering for undergrad, but Jayce's is Mechanical and Electrical, and Viktor's is Mechanical and Chemical. They are in graduate school for Mechanical Engineering, though. Over-achievers, they are. The school is equivalent to MIT. Or is MIT, technically, if you want to make it USA-centered.
They met in a Thermodynamics class (yes, i had to look up types of classes for this lmao) and became fast friends because everyone else around them was extremely obnoxious and very annoying. They started dating two semesters before Viktor graduated, three before Jayce graduated.
For a few semesters, everyone thought they would be rivals, because they were always trading spots in GPA rankings and scores. Everyone thought the tension they were catching was academic hatred, until a library assistant caught them making out in a study room, and then everyone in the engineering school collectively went "ohhhhh"
Both are at the academy on scholarship, Jayce has a few for welding competitions and even some money from art competitions, and Viktor's schooling is being paid for from essays and whatever grants he can get his hands on. Both are determined to have very little student loans. Viktor is also a graduate assistant to the dean of engineering (similar to canon) which pays for his portion of housing (with Jayce).
Jayce has been offered spots on sports teams all the time. He does not know how to explain he has the coordination of a baby deer on ice. He likes to work out, but it's mostly for long days in the labs and blacksmithing he does, which is something he likes to be traditional for. His excuse is that his schooling and work take up too much time for sports.
Viktor is also an international student, having transferred from his home-country university his sophomore year. He and Jayce (who moved to the city when he was 15 from out of the country) related on this very fast.
Sky, Mel and Elora are all apart of the international student club with Viktor. They are all besties. Caitlyn and Vi are Jayce's friends from home (Caitlyn is his "cousin" and he teases Vi, the GF, all the time) and Catvi are undergrad students. All of them like to meet at the "secret" coffeeshop on campus (aka the one people can never find, because it's in the back of an office building).
Jayce and Viktor organized a sit-in when the campus president and campus board (not Dean of Engineering Heimerdinger) routed money from programs that helped campus-accessibility for students with disabilities to a new stadium. It lasted twenty days, five members quit the board, and the money was routed back to fixing elevators, automatic doors, and providing more covered benches.
Jayce was student-class president his junior year, but stopped working on the student council when it took too much time away from Viktor and his friends. Viktor is thankful for it. (Jayce also ran away screaming from the guys trying to get him to rush for frats).
Both want to start their own company when they graduate, focusing on public health and progress, with things like air and water purifiers, teaming up with medical companies for robotic prosthetics, lung + heart mechanical help.
Viktor got sick the winter between his graduation and what was supposed to be the start of grad school. He was diagnosed with severe acute asthma, pneumonia, but just barely avoided a COPD diagnosis with treatment. He was in the hospital for a month and a half, now takes breathing treatments a few days a week, and goes to doctor appointments once a month.
Jayce was so worried, he almost had to delay his own graduation. Viktor managed to convince him to get it together in time to pass with good marks and keep his spot in his grad cohort, while Viktor had to delay his grad school start by a semester, rather than in the spring like he planned. This is why they are in the same cohort, because Viktor had to start later than planned. (Jayce secretly likes that they have all their classes together, even if he's sad for the reason why).
im sure ill have more at some point, bc it is a little interesting!
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
14 Common Lung Diseases

Introduction
Lung diseases represent some of the most severe health threats globally. The rise of industrialization, environmental pollution, and tobacco usage significantly contribute to the prevalence of these diseases. This article, outlines the most common lung diseases, their symptoms, causes, and treatments.
1. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens. It poses a significant risk to the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and those with chronic conditions but can also affect healthy individuals. Pneumonia can be classified based on the causative agent, such as bacterial pneumonia (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae), viral pneumonia (e.g., influenza virus), or fungal pneumonia (e.g., Pneumocystis jirovecii).
Symptoms
Fever
Cough with sputum
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Sweating and shaking chills
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (less common)
Diagnosis Diagnosis of pneumonia typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures. Blood tests may also be conducted to identify the causative agent.
Treatment Depending on the cause, treatments may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia.
Antiviral medications for viral pneumonia.
Antifungal therapies for fungal pneumonia. Supportive care such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and manage pain can also alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to provide intravenous antibiotics, oxygen therapy, or mechanical ventilation.
2. Bronchitis
Bronchitis involves the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It can be acute, often following colds or the flu, or chronic, usually resulting from smoking or long-term exposure to irritants like pollution or dust.
Symptoms
Persistent cough (productive or dry)
Sputum production (clear, white, yellowish-gray, or green)
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Slight fever and chills
Chest discomfort
Diagnosis Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, where a doctor listens to the patient’s lungs with a stethoscope. Additional tests, such as a chest X-ray, sputum tests, or pulmonary function tests, may be conducted to rule out other conditions like pneumonia or asthma.
Treatment
Acute bronchitis: Symptomatic treatment includes rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers and cough medications. Inhalers or nebulizers may be prescribed to ease breathing.
Chronic bronchitis: Management may involve bronchodilators, steroids, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Smoking cessation and avoiding lung irritants are crucial for treatment.
3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a progressive, irreversible disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways, primarily due to smoking, environmental pollutants, or long-term exposure to respiratory irritants. COPD includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, conditions that often coexist and lead to airflow obstruction.
Symptoms
Chronic cough
Sputum production
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities
Wheezing
Chest tightness
Frequent respiratory infections
Fatigue
Unintended weight loss (in advanced stages)
Diagnosis COPD is diagnosed through a combination of patient history, physical examination, and spirometry, a test that measures the amount of air a person can exhale and how quickly they can do so. Chest X-rays, CT scans, and arterial blood gas analysis may also be used.
Prevention and Treatment Preventive measures include:
Smoking cessation
Vaccinations (influenza and pneumococcal vaccines)
Reducing exposure to lung irritants
Treatments involves;
Bronchodilators to relax the muscles around the airways
Inhaled steroids to reduce airway inflammation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs
Oxygen therapy for severe cases
Surgery (e.g., lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplant) in advanced cases
4. Lung Cancer
Lung cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the lung tissues. Major risk factors include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, exposure to carcinogens (e.g., asbestos, radon), and genetic predisposition.
Types
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Often linked to heavy smoking, SCLC is aggressive and spreads quickly.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): More common and includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Symptoms
Persistent cough
Chest pain
Weight loss
Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
Shortness of breath
Hoarseness
Bone pain (in advanced stages)
Headache (if cancer spreads to the brain)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves imaging tests (chest X-rays, CT scans, PET scans), sputum cytology, and tissue biopsy. Molecular testing may be done to identify specific genetic mutations that can be targeted with specific treatments.
Treatment
Surgery to remove the tumor or part of the lung
Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells
Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors
Targeted drug therapies to attack specific genetic changes in cancer cells
Immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer
5. Pleurisy
Pleurisy, or pleuritis, is the inflammation of the pleura, the tissue lining the lungs and chest cavity. It can be caused by infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal), injuries, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), or other underlying conditions.
Symptoms
Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens with breathing, coughing, or sneezing
Shortness of breath
Cough
Fever (if infection is present)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a physical examination, chest X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans, and blood tests to identify the underlying cause. Thoracentesis, a procedure to remove and analyze pleural fluid, may be performed.
Treatment Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial infections
Antiviral medications for viral infections
Anti-inflammatory medications (e.g., NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
Pain management with medications
Thoracentesis to drain excess fluid from the pleural space
6. Pulmonary Embolism
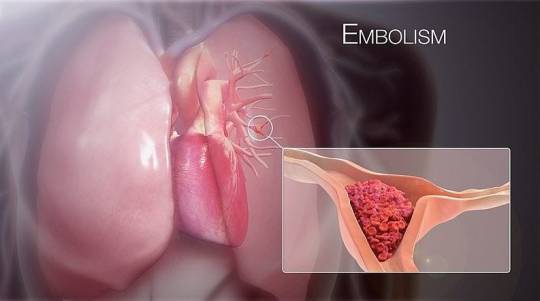
A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot, usually originating in the legs (deep vein thrombosis), travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow and causing tissue damage. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgery, cancer, and certain genetic conditions.
Symptoms
Sudden shortness of breath
Chest pain (may be sharp and worsen with deep breathing or coughing)
Cough (sometimes with bloody sputum)
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Lightheadedness or dizziness
Leg pain or swelling (if DVT is present)
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves imaging tests such as chest X-rays, CT pulmonary angiography, and ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scans. D-dimer blood tests and ultrasound of the legs may also be conducted.
Treatment Immediate treatment includes:
Anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent further clotting
Thrombolytics (clot-dissolving medications) for severe cases
Surgical or catheter-based procedures to remove the clot
Long-term anticoagulation therapy to prevent recurrence
7. Pulmonary Edema
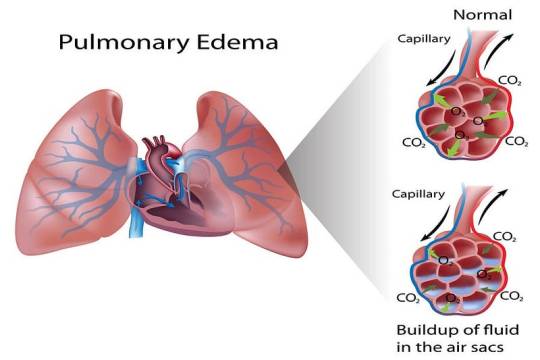
Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of fluid in the lung alveoli, making breathing difficult. It can result from heart failure (cardiogenic pulmonary edema), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or exposure to high altitudes (non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema).
Symptoms
Difficulty breathing (dyspnea), especially when lying down
Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
Wheezing or gasping for breath
Coughing up frothy, pink-tinged sputum
Excessive sweating
Cyanosis (bluish skin or lips)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves physical examination, chest X-rays, and blood tests. Echocardiography and pulmonary artery catheterization may be used to determine the underlying cause and severity.
Treatment Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause and may include:
Diuretics to remove excess fluid
Medications to improve heart function (for cardiogenic pulmonary edema)
Supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation
Treating underlying conditions such as infections or high altitude exposure
8. Pulmonary Fibrosis
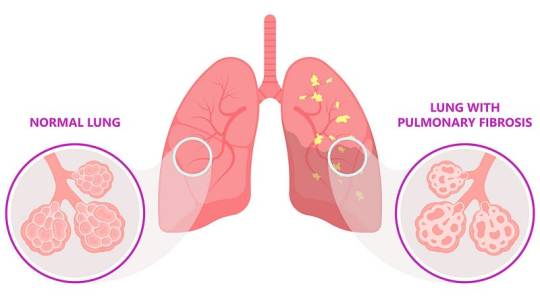
Pulmonary fibrosis is the thickening and scarring of lung tissue, leading to reduced oxygen absorption. Causes include chronic exposure to environmental pollutants, infections, genetic factors, and autoimmune diseases (e.g., scleroderma).
Symptoms
Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
Persistent dry cough
Fatigue
Unexplained weight loss
Aching muscles and joints
Clubbing (widening and rounding) of the fingertips or toes
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, imaging tests (chest X-rays, high-resolution CT scans), pulmonary function tests, and sometimes lung biopsy. Blood tests may be used to identify underlying autoimmune diseases.
Treatment While there is no cure for pulmonary fibrosis, treatments focus on symptom management and slowing progression:
Medications such as pirfenidone and nintedanib to slow disease progression
Oxygen therapy
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Lung transplant in severe cases
9. Pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is a lung disease caused by inhaling dust particles, such as asbestos, silica, or coal dust, leading to lung scarring. It is a type of occupational lung disease commonly seen in miners, construction workers, and industrial workers.
Symptoms:
Chronic cough
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Progressive loss of lung function
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed occupational history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess the extent of lung damage.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Avoiding further exposure to dust
Medications to manage symptoms, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids
Respiratory therapies
Pulmonary rehabilitation
10. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
PAH is a form of high blood pressure affecting the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. It can be idiopathic, familial, or associated with other conditions such as connective tissue diseases, congenital heart disease, or chronic liver disease.
Symptoms
Breathing difficulties (dyspnea), especially during physical activities
Dizziness or fainting (syncope)
Chest pain
Fatigue
Swelling in the ankles, legs, and abdomen (edema)
Cyanosis (bluish lips and skin)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves echocardiography, right heart catheterization, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Blood tests and pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess lung and heart function.
Treatment Treatment strategies include:
Medications to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, such as endothelin receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, and prostacyclin analogs
Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
Oxygen therapy
Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots
In severe cases, surgical procedures such as atrial septostomy or lung transplant
11. Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, leading to thick, sticky mucus buildup in the lungs and other organs. This results in frequent infections, respiratory issues, and digestive problems.
Symptoms
Persistent cough with thick mucus
Recurrent lung infections
Wheezing or shortness of breath
Poor growth and weight gain in children
Salty-tasting skin
Severe constipation
Frequent greasy, bulky stools
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves genetic testing, sweat chloride tests, and newborn screening. Pulmonary function tests, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures may also be conducted to assess lung health.
Treatment Management includes:
Medications to thin mucus, antibiotics to treat infections, and bronchodilators to open airways
Chest physiotherapy to clear mucus
Enzyme supplements and high-calorie diets to manage digestive issues
Newer therapies targeting the underlying genetic defect, such as CFTR modulators
12. Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
RDS primarily affects premature infants due to a lack of surfactant, a substance necessary to keep the lungs open and facilitate gas exchange. Risk factors include premature birth, maternal diabetes, and multiple births.
Symptoms
Rapid, shallow breathing
Grunting sounds while breathing
Nasal flaring
Chest retractions (pulling in of the chest muscles)
Cyanosis (bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves clinical assessment, chest X-rays, and blood gas analysis to measure oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Prenatal tests can also help identify at-risk pregnancies.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Surfactant replacement therapy to improve lung function
Mechanical ventilation or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) to support breathing
Oxygen therapy
Supportive care such as fluids and nutrition
13. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is characterized by the growth of granulomas (small clusters of inflammatory cells) in the lungs and other organs, likely as an immune response to unknown triggers. The exact cause remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Symptoms
Dry cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Fatigue
Fever
Swollen lymph nodes
Skin lesions (e.g., erythema nodosum)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests. Biopsy of affected tissues may be performed to confirm the presence of granulomas.
Treatment While sarcoidosis is often self-limiting and may resolve without treatment, severe cases may require:
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Immunosuppressive medications (e.g., methotrexate, azathioprine)
Antimalarial drugs (e.g., hydroxychloroquine) for skin lesions
Regular monitoring and follow-up care to manage chronic cases
14. Asthma
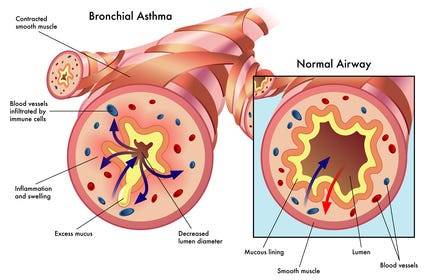
Definition and Causes: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways, causing episodes of wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, often triggered by allergens, exercise, cold air, or respiratory infections. Genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development.
Symptoms
Wheezing
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Coughing, especially at night or early morning
Increased mucus production
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests (spirometry, peak flow measurement). Allergy testing and chest X-rays may also be conducted to identify triggers and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Management includes:
Avoiding known triggers
Inhalers (bronchodilators for quick relief, corticosteroids for long-term control)
Long-term control medications (e.g., leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta agonists)
Immunotherapy (allergy shots) for severe allergies
Asthma action plans to manage symptoms and prevent attacks
Conclusion
Lung diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. Preventive measures such as avoiding smoking, reducing exposure to environmental pollutants, and timely vaccinations can significantly reduce the risk of developing many of these diseases. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by lung diseases. For personalized medical advice and treatment, consult with healthcare professionals.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Email us: [email protected] for professional guidance.
#medical students#nursing school#nursing student#assignment help#medicine#medical university#medical school#medical student#studying#studyspo#student#student life#college student#study inspiration#study blog#academic writing#writters on tumblr#online writing#do my online class
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dysautonomia;
Dysautonomia is a medical condition that affects the Autonomic Nervous System, which is responsible for regulating the automatic functions of the body, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, kidney function, and more. People with dysautonomia may experience difficulty in controlling these systems, leading to symptoms like lightheadedness, fainting, abnormal heart rates, and unstable blood pressure. Dysautonomia can manifest in different forms.
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is a condition that affects an estimated 1 out of 100 teenagers, and including adult patients, it impacts a total of 1,00,000 to 3,000,000 Americans. POTS can cause various symptoms such as lightheadedness, fainting, rapid heartbeat, chest pains, shortness of breath, upset stomach, shaking, exercise intolerance, heat intolerance, temperature sensitivity, and more. Although POTS affects women more commonly, men can also get it. Despite appearing healthy on the outside, researchers compare the disability seen in POTS to the disability seen in conditions such as COPD, congestive heart failure, and kidney disease.
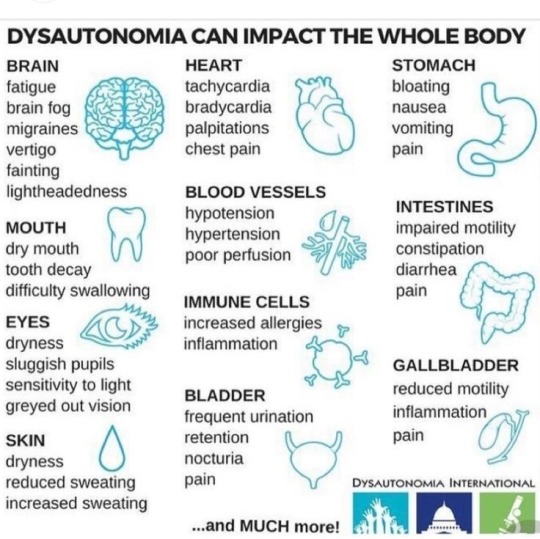
Dysautonomia and POTS can be challenging to treat, and the effectiveness of treatment may vary depending on the expertise of your local medical staff. There are some home remedies that may help alleviate some of the symptoms and triggers associated with these conditions. However, it is important to understand that these remedies may not completely cure Dysautonomia or POTS, and their effectiveness may vary from person to person.
Pots is supposed to be more common than MS or Parkinson’s so why is that some have never heard of it ?

It can take an average of 4-7 years to get proper diagnosis. Because of being misdiagnosed or how most symptoms can be linked to other illnesses. Lots of tests is involved and it just becomes and exhausting time period of wanting answers and fighting to be seen or heard by others.
Pots affects everyone differently so not all pots patients will faint and just because pots is postural doesn’t mean lying down will make symptoms better.
Did you know there are 15 different types of Dysautonomia and all should be taken seriously! No matter how it affects the person it’s a serious illness and it should never be brushed off!! Not only does the illness bring a variety of symptoms but also impacts your life in ways you’d never imagined.
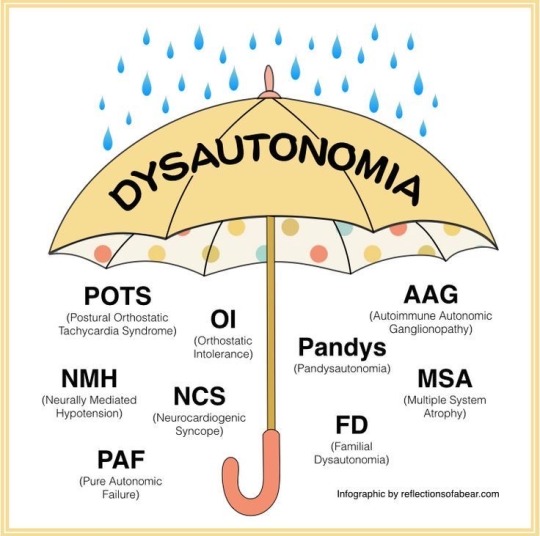
* some of the different types of Dysautonomia 🩵🩵
We shouldn’t have to look sick to get the proper care, treatment and support!
I’m finally comfortable sharing my pots journey and even though I’m nervous and scared about it I can’t wait because while I’m sharing my story I plan to raise awareness on not only pots but als as well. Another illness/disease that impacted my life. I plan to share how much my life has changed since I was diagnosed with pots. I also hope this reaches other chronic illnesses warriors and can show that you can still have a beautiful life even though we have a certain illness.
If you want to know more
intsagram: rebeljennigaines_
TikTok: jennigaines101
February 24th I’ll be participating in my first ever polar plunge and leading up to the big day I plan on sharing my pots journey and how this illness has affected my life! If you have any questions feel free to ask.
🩵🩵🫶🏻💪🏻 no one fights alone!






#potsie#potswarrior#potsawareness#dysautonomia#Dysautonomiaawareness#Dysautonomiawarrior#strongertogether#your not alone
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Going through questions:
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends exercise interventions to prevent falls in community-dwelling adults ≥65 years of age who are at increased risk for falls (B recommendation). Falls occur at least once annually in approximately 30% of community-dwelling adults 65 years or older, and the USPSTF recommendation is based on studies that demonstrated improved fall-related outcomes for patients who participated in exercise programs.
Most evidence included group exercise, but supervised individual interventions also appeared to be of benefit. Gait, balance, and functional training; resistance training; flexibility work; and endurance training all appeared to be effective for reducing falls.
Other interventions associated with a reduction in falls or fall-related fractures include an annual fall risk assessment, assistive devices such as grab bars or walkers, and environmental assessment and modifications such as the removal of trip hazards from the home. However, the evidence for in-home assessment of environmental hazards is less robust.
There is no evidence for psychological evaluation in the prevention of falls. The USPSTF recommends against vitamin D supplementation to prevent falls in community-dwelling adults ≥65 years of age in those who are not known to have osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency (D recommendation).

Above image:
The pearly, papular appearance of this patient’s growth and the overlying telangiectasia makes the most likely diagnosis a nodular basal cell carcinoma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common cutaneous malignancy. The incidence increases with age and occurs most commonly in Fitzpatrick skin types 1 and 2. The tumors appear most frequently on the face, scalp, ears, and neck, and less frequently on the torso and extremities. In-office dermoscopy may make the branching blood vessels or telangiectasias characteristic of basal cell carcinoma easier to see. In pigmented basal cell carcinomas, dermoscopy can highlight pigmented globules or other areas of abnormal deposition not easily seen without a dermatoscope. Basal cell carcinoma can be locally destructive but rarely metastasizes.
A 55-year-old male with a 40-pack-year smoking history comes to your office with the results of spirometry he had at a health fair. He quit smoking 1 year ago. He does not have any cough, dyspnea, wheezing, or sputum production, but he is concerned that the spirometry results show an FEV1/FVC ratio of 0.65 and an FEV1 of 70% of predicted, which indicates mild to moderate airflow obstruction.
Based on the best available evidence, which one of the following should you recommend in order to prevent the development of symptomatic airflow obstruction?
Answer: No treatment
There is no evidence from randomized, controlled trials to show that treating asymptomatic individuals who have mild to moderate airflow obstruction on spirometry prevents future respiratory symptoms or reduces subsequent declines in lung function. Partly for this reason, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and joint guidelines issued by the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, and European Respiratory Society recommend against screening for COPD in asymptomatic adults. Regardless of the results of this patient’s spirometry testing, treatment should not be initiated in the absence of symptoms. Detailed history-taking would be appropriate to detect patients who have limited their activity in order to avoid symptoms. A long-acting anticholinergic, a long-acting β-agonist (LABA), an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS), and combination therapy with an ICS and a LABA would not be recommended for this patient.
Family physicians are often required to manage dyspnea and evaluate common office spirometry results. The American Thoracic Society recommends complete pulmonary function testing with diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) measurement when office spirometry suggests a restrictive pattern, which is defined as an FVC less than 80% of predicted. This level of pulmonary function testing gives further information about gas exchange and lung volumes, allowing a more definitive diagnosis.
The 6-minute walk test is used to evaluate the treatment response for known cardiopulmonary disease. Bronchoprovocation testing helps identify asthma triggered by allergens or exercise when office spirometry is normal.
Pearly papules of the penis are a benign, normal anatomic variant and are not sexually transmitted. They are dome-shaped, skin-colored papules 1–4 mm in size with a ring-like distribution around the corona of the glans penis, more commonly found along the dorsal side of the corona. They are present in up to 15%–40% of males. They most commonly occur in late puberty and early adulthood. Circumcised males have a lower incidence. The differential diagnosis includes condyloma acuminata; Tyson glands, which are modified sebaceous glands in a parafrenular distribution; or molluscum contagiosum.
Angiokeratomas are well-circumscribed red or blue papules that are 1–6 mm in size. Genital warts are raised masses that can be pearly and smooth or have a rough, cauliflower-like appearance, and are not confined to the penile corona. Lichen nitidus consists of discrete, hypopigmented, 1-mm papules that are not confined to the corona and can also occur on the upper extremities and abdomen. Squamous cell carcinoma may be endophytic (ulcerated) or exophytic (thickened skin or wart-like growths that can progress to a large, irregularly shaped, fungating mass).
Adhesive capsulitis is characterized by worsening shoulder pain that is hard to localize. The underlying pathology is contraction of the glenohumeral capsule resulting in decreased active and passive range of motion. It is an idiopathic condition but has an increased prevalence in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism. Adhesive capsulitis is often self-limited but can persist for years in some patients. Nonsurgical treatment options include physical therapy, oral or intra-articular corticosteroids, acupuncture, and hydrodilatation.
Osteoarthritis is more common among older patients and typically develops more chronically than the subacute presentation of adhesive capsulitis. There is often a history of trauma, previous surgery, or repetitive work. Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions can be acute (e.g., sustained during a fall on an outstretched hand) or chronic (e.g., in throwing athletes or other high-risk professions). Passive range of motion may be sustained. Infraspinatus tendinopathy may show pain with resisted external rotation. It may also arise due to acute injury or chronic repetitive overuse. Supraspinatus tendinopathy may present with normal strength but positive impingement testing as well as a positive Jobe test or empty can test.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

The best Pulmonologist in Chhattisgarh at Vidya Hospital can give the patient world-class diagnosis and treatment for all sorts of lung diseases like asthma, tuberculosis, and COPD. State-of-art facilities make it the ultimate destination to achieve advanced care to the reservoir of patients in the region.
0 notes
Text
pulmonologist in hyderabad | Sreshta Sri Kamala Hospitals

If you are looking for pulmonologist in Hyderabad, Sreshta Sri Kamala Hospitals is home to its own cadre of pulmonologists who have specific expertise in treating a broad spectrum of respiratory ailments. Having quite a number of expert pulmonologists with a great wealth of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the lung, including asthma, COPD, pneumonia, tuberculosis, and sleep apnea, the hospital employs even advanced diagnostic methods for diagnosis including pulmonary function tests, CT scans, and chest X-rays, and offers customized treatment regimes that take into consideration the particular needs of each and every patient. Their treatment enjoys different indications, varying from chronic conditions to acute respiratory diseases. Sreshta Sri Kamala Hospital specialists promise to lessen your breath-related maladies and enhance your quality of life.
Sreshta Sri Kamala Hospitals ameliorates care in lung health and forms alliances with other specialists, each looking after a patient in totality.Moreover, it has set in place an implemented preventive arm of programs for lung function maintenance and for respiratory disease prevention. Provision of inpatient and outpatient services is made possible, quite comfortably, under one roof. When faced with respiratory problems, the Sreshta Sri Kamala Hospitals provide the highest quality respiratory care in Hyderabad to enhance your respiratory health and quality of life.
0 notes
Text
Copd Awareness: Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Tips
Delve into COPD Awareness: Chronic lung diseases like emphysema & chronic bronchitis caused by smoking. Symptoms include coughing & shortness of breath.
To Know More: https://lalithachestandskinhospital.com/blog/copd-awareness-types-causes-symptoms-and-prevention-tips/

#chest specialist doctor#best lung doctor in Karimnagar#good pulmonologist near me#breathing problem specialist doctor#copd diagnosis treatment#pulmonologist hospital near me#chronic obstructive pulmonary treatment
0 notes
Text
listen, I think it should be said: I'm so proud of him for quitting. Is it a bit late? Yeah. It's always a bit late. But he did it anyway. David Lynch is a creature of strict habit, and giving up something that is so comforting and consistent in his life must have been very difficult for him. David Lynch has smoked obsessively, and passionately for the vast majority of his, let's face it, fairly long life. It's something that was central to his creative habits, which, as we all know, can be pretty strange, and are very, VERY consistent. And his art is incredibly important to him. I'm so glad he has his meditation practices to help him with this.
I'm so proud of him, and I want to say, if David Lynch's obsessive autistic ass can do it, so can you. Do it today, because I've seen what happens when you put it off, and it's not pretty.
My father smoked like a chimney until he could no longer get out of bed. COPD was his initial diagnosis, but of course, it didn't stop there. His cancer was slow, and vicious, and years of prolonged oxygen depravation slowly eroded his mind. He was slowly dying for most of my life, and if I'm being honest, I'm still not quite sure when he stopped being the father I remember, but by the time he died he was a completely different man. A man who chose cigarettes over life. Over walking his daughter down the aisle, over caring for his wife when she needed multiple surgeries, over seeing sunrises, and smelling flowers, and eating lasagna, and a million other small delights the world offers. It turned him into a man who refused treatment, because he didn't want to live without them. It turned him into a liar, who told his family he quit smoking three years before he died. He would go for "walks" and twice, one of us had to go rescue him when he fell down from lack of oxygen, and hold him up while we walked home, holding him close enough to smell the fresh cigar smoke. More than once, he completely forgot that I worked at the dollar store, and came in to buy cigarettes and would panic when he saw me at the register, and buy a pack of batteries. When he died, I found a small box of unopened packs of batteries under his bed. Ultimately, my father let his habit consume him.
Don't be like my father,
be like David Lynch,
Even if it's a little late,
Don't let the cigarettes win.


744 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lung Specialist in Hyderabad – Expert Respiratory Care at Udai Omni Hospital
Lung diseases can significantly impact one’s quality of life, making it essential to seek expert medical care from a qualified lung specialist in Hyderabad. At Udai Omni Hospital, we offer world-class respiratory care with a team of experienced pulmonologists dedicated to diagnosing, managing, and treating a wide range of lung conditions. If you are looking for the best lung specialist in Hyderabad, Udai Omni is the ultimate choice for comprehensive respiratory health solutions.

Why Choose Udai Omni Hospital for Lung Care?
Udai Omni Hospital is known for providing advanced pulmonary care using cutting-edge technology, experienced specialists, and patient-centric treatment approaches. Here’s why our hospital is the preferred choice:
Highly Qualified Pulmonologists – Our team comprises the top lung specialists in Hyderabad, with vast experience in treating complex lung disorders.
State-of-the-Art Facilities – We utilize advanced diagnostic tools, including pulmonary function tests (PFTs), bronchoscopy, sleep studies, and imaging for accurate diagnosis.
Personalized Treatment Plans – Each patient receives customized treatment based on their specific condition and health history.
Comprehensive Respiratory Care – From preventive measures to intensive care treatment, we provide holistic solutions for all lung-related issues.
Common Lung Conditions Treated at Udai Omni Hospital
Our expert lung specialists in Hyderabad provide specialized care for various respiratory conditions, including:
1. Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the airways, leading to breathing difficulties. Our specialists offer advanced asthma management plans, including medication, lifestyle adjustments, and inhaler therapy.
2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a progressive lung disease that causes breathing difficulties. Our specialists offer the latest treatments, including bronchodilators, pulmonary rehabilitation, and oxygen therapy, to improve lung function.
3. Lung Infections (Pneumonia, Tuberculosis, Bronchitis)
Respiratory infections like pneumonia and tuberculosis require accurate diagnosis and specialized treatment. Udai Omni Hospital has dedicated infection management programs to provide the best care.
4. Sleep Apnea & Other Sleep Disorders
If you suffer from snoring, breathing difficulties during sleep, or daytime fatigue, our lung specialists conduct sleep studies and CPAP therapy to treat conditions like sleep apnea effectively.
5. Lung Cancer
Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for lung cancer patients. Our hospital provides multidisciplinary cancer treatment, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgical interventions.
6. Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
ILD includes conditions like pulmonary fibrosis that cause lung scarring and breathing issues. Our specialized ILD clinics provide the latest treatments, including anti-fibrotic therapies and pulmonary rehabilitation.
7. Occupational Lung Diseases
People exposed to environmental pollutants, chemicals, or allergens may develop lung diseases related to their occupation. Our hospital offers comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services for occupational lung disorders.
Advanced Diagnostic & Treatment Facilities
At Udai Omni Hospital, we use cutting-edge technology to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment for all lung conditions. Our facilities include:
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) – To evaluate lung capacity and function.
Bronchoscopy – A minimally invasive technique to examine and treat airway diseases.
High-Resolution CT Scans – For accurate lung disease diagnosis.
Sleep Study Labs – To diagnose and manage sleep-related breathing disorders.
Oxygen Therapy & Ventilator Support – For patients with severe lung conditions.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Lung Care
At Udai Omni Hospital, our lung specialists work closely with other specialists, including:
Thoracic Surgeons – For advanced surgical interventions.
Critical Care Experts – For managing respiratory emergencies in the ICU.
Oncologists – For lung cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Physiotherapists – To help patients regain lung function through pulmonary rehabilitation programs.
Emergency & ICU Support for Respiratory Issues
Respiratory emergencies can occur at any time, and timely intervention is crucial. Udai Omni Hospital provides 24/7 emergency care and ICU support to handle critical respiratory conditions. Our dedicated respiratory ICU ensures that patients with severe breathing difficulties receive immediate and effective treatment.
Book an Appointment with the Best Lung Specialist in Hyderabad
If you are experiencing breathing difficulties, persistent cough, chest pain, or any lung-related issues, don’t wait! Consult the best lung specialist in Hyderabad at Udai Omni Hospital today.
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive COPD Treatment in Thane: A Guide to Managing the Disease Effectively
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that obstructs airflow, making it difficult to breathe. It is commonly caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke, air pollution, or occupational dust. People with COPD experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, persistent cough, and chest tightness. As the disease progresses, it can severely affect a person’s quality of life. However, with the right treatment, the progression of COPD can be slowed down, and symptoms can be managed effectively.
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with COPD and resides in or around Thane, seeking the right medical care is crucial. Dr. Hrushikesh Vaidya, a renowned pulmonologist specializing in COPD treatment in Thane, offers personalized treatment plans designed to manage the condition and improve your breathing and overall health.
Understanding COPD: Symptoms and Risk Factors
COPD is a progressive disease that leads to irreversible damage in the lungs. The primary risk factor for COPD is smoking, though long-term exposure to harmful pollutants, genetics, and respiratory infections can also play a role. Common symptoms include:
Chronic cough: A persistent cough that may produce mucus.
Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activities.
Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when breathing.
Fatigue: Constant tiredness and lack of energy.
As the disease progresses, symptoms may worsen, and individuals may experience frequent flare-ups. This makes early diagnosis and effective treatment crucial for managing the disease.
The Role of COPD Treatment in Thane
Managing COPD involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. While there is no cure for COPD, early intervention can significantly improve quality of life and slow the disease’s progression.
1. Diagnosis and Assessment
Proper diagnosis is the first step in managing COPD. Dr. Hrushikesh Vaidya provides thorough assessments, which typically include:
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): To assess lung function and the severity of airflow obstruction.
Chest X-rays and CT scans: To rule out other lung diseases and examine the extent of lung damage.
Blood tests: To check for low oxygen levels and other underlying conditions.
Early diagnosis is key to receiving the appropriate treatment and avoiding unnecessary complications.
2. Personalized Treatment Plans
Dr. Vaidya takes a personalized approach to treating COPD. Treatment options vary depending on the stage of the disease and the patient’s individual needs. Common treatment methods include:
Medications: Inhalers containing bronchodilators and steroids help relieve symptoms by opening up airways and reducing inflammation. Long-acting medications may also be prescribed for more severe cases.
Oxygen Therapy: For patients with advanced COPD, supplemental oxygen may be recommended to help maintain adequate oxygen levels.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A structured program involving exercise, nutrition counseling, and breathing techniques can help improve lung function and quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications: Quitting smoking is the most important change a person can make to slow the progression of COPD. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and avoiding lung irritants are essential steps in managing the disease.
3. Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
COPD is a chronic condition that requires ongoing monitoring. Dr. Vaidya ensures that all his patients receive regular follow-ups to monitor lung function and adjust treatment plans as needed. This proactive approach can prevent flare-ups and complications, which are common in COPD patients.
Why Choose Dr. Hrushikesh Vaidya for COPD Treatment in Thane?
Dr. Hrushikesh Vaidya is a trusted pulmonologist with extensive experience in treating COPD. Here’s why he is the preferred choice for COPD treatment in Thane:
Specialized Expertise: Dr. Vaidya has specialized knowledge in diagnosing and managing COPD, making him well-equipped to handle even the most complex cases.
Comprehensive Care: From diagnosis to treatment and follow-up care, Dr. Vaidya provides a holistic approach to managing COPD.
Patient-Centered Approach: Dr. Vaidya believes in tailoring treatment plans to meet the specific needs of each patient, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Cutting-Edge Facilities: Dr. Vaidya practices in a well-equipped clinic with access to the latest diagnostic tools and treatment options to ensure optimal care.
Conclusion
COPD can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right treatment, it is possible to live a full and active life. If you or a loved one is suffering from COPD, it is important to consult a qualified pulmonologist who can offer the best care. Dr. Hrushikesh Vaidya, with his expertise in COPD treatment in Thane, is committed to providing the highest quality care to help manage your condition effectively. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and lifestyle changes can all play a vital role in improving your quality of life with COPD.
0 notes
Text
Best Pulmonology Hospital in India | Lung Treatment in India
HCG Hospitals is recognized as one of the best pulmonology hospitals in India, offering specialized care for various respiratory conditions. Their team of experienced pulmonologists provides comprehensive services, including diagnosis and treatment of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), allergies, lung cancer, tuberculosis, and sleep-related disorders like obstructive sleep apnea.
Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools such as high-definition video bronchoscopy and pulmonary function testing, they ensure accurate assessments and personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. HCG Hospitals is committed to enhancing respiratory health and overall quality of life through expert care and state-of-the-art technology.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Sanjivini Super Speciality Hospital offers expert diagnosis and treatment for pleural effusion with advanced care.
0 notes