#best national park in india
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

#ranthambore national park#ranthambore tiger reserve rajasthan#tiger reserve in rajasthan#best national park in india#national parks in india#junglesafariinindia#SafariinIndia#junglesafaribooking#LuxurySafariinIndia
1 note
·
View note
Text
Valley of Flowers National Park: A UNESCO Heritage Gem in Uttarakhand
#adventure trekking in Uttarakhand#best time to visit Valley of Flowers#biodiversity in Himalayas#Chamoli district attractions#Frank S Smythe#Hemkund Sahib trek#Himalayan flora and fauna#Mysterious Himachal tours#nature trails in India#rare Himalayan flowers#trekking in Uttarakhand#UNESCO World Heritage Site Uttarakhand#Uttarakhand hill stations#Valley of Flowers#Valley of Flowers National Park
0 notes
Text
Genocide experts warn that India is about to genocide the Shompen people
Who are the Shompen?
The Shompen are an indigenous culture that lives in the Great Nicobar Island, which is nowadays owned by India. The Shompen and their ancestors are believed to have been living in this island for around 10,000 years. Like other tribes in the nearby islands, the Shompen are isolated from the rest of the world, as they chose to be left alone, with the exception of a few members who occasionally take part in exchanges with foreigners and go on quarantine before returning to their tribe. There are between 100 and 400 Shompen people, who are hunter-gatherers and nomadic agricultors and rely on their island's rainforest for survival.
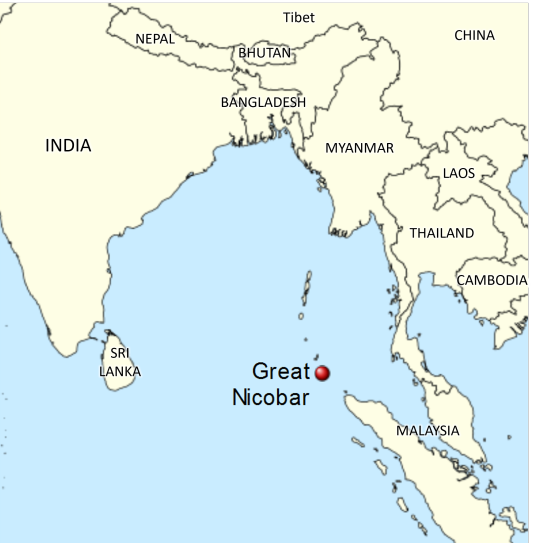
Why is there risk of genocide?
India has announced a huge construction mega-project that will completely change the Great Nicobar Island to turn it into "the Hong Kong of India".
Nowadays, the island has 8,500 inhabitants, and over 95% of its surface is made up of national parks, protected forests and tribal reserve areas. Much of the island is covered by the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve, described by UNESCO as covering “unique and threatened tropical evergreen forest ecosystems. It is home to very rich ecosystems, including 650 species of angiosperms, ferns, gymnosperms, and bryophytes, among others. In terms of fauna, there are over 1800 species, some of which are endemic to this area. It has one of the best-preserved tropical rain forests in the world.”
The Indian project aims to destroy this natural environment to create an international shipping terminal with the capacity to handle 14.2 million TEUs (unit of cargo capacity), an international airport that will handle a peak hour traffic of 4,000 passengers and that will be used as a joint civilian-military airport under the control of the Indian Navy, a gas and solar power plant, a military base, an industrial park, and townships aimed at bringing in tourism, including commercial, industrial and residential zones as well as other tourism-related activities.
This project means the destruction of the island's pristine rainforests, as it involves cutting down over 852,000 trees and endangers the local fauna such as leatherback turtles, saltwater crocodiles, Nicobar crab-eating macaque and migratory birds. The erosion resulting from deforestation will be huge in this highly-seismic area. Experts also warn about the effects that this project will have on local flora and fauna as a result of pollution from the terminal project, coastal surface runoff, ballasts from ships, physical collisions with ships, coastal construction, oil spills, etc.
The indigenous people are not only affected because their environment and food source will be destroyed. On top of this, the demographic change will be a catastrophe for them. After the creation of this project, the Great Nicobar Island -which now has 8,500 inhabitants- will receive a population of 650,000 settlers. Remember that the Shompen and Nicobarese people who live on this island are isolated, which means they do not have an immune system that can resist outsider illnesses. Academics believe they could die of disease if they come in contact with outsiders (think of the arrival of Europeans to the Americas after Christopher Columbus and the way that common European illnesses were lethal for indigenous Americans with no immunization against them).
And on top of all of this, the project might destroy the environment and the indigenous people just to turn out to be useless and sooner or later be abandoned. The naturalist Uday Mondal explains that “after all the destruction, the financial viability of the project remains questionable as all the construction material will have to be shipped to this remote island and it will have to compete with already well-established ports.” However, this project is important to India because they want to use the island as a military and commercial post to stop China's expansion in the region, since the Nicobar islands are located on one of the world's busiest sea routes.
Last year, 70 former government officials and ambassadors wrote to the Indian president saying the project would “virtually destroy the unique ecology of this island and the habitat of vulnerable tribal groups”. India's response has been to say that the indigenous tribes will be relocated "if needed", but that doesn't solve the problem. As a spokesperson for human rights group Survival International said: “The Shompen are nomadic and have clearly defined territories. Four of their semi-permanent settlements are set to be directly devastated by the project, along with their southern hunting and foraging territories. The Shompen will undoubtedly try to move away from the area destroyed, but there will be little space for them to go. To avoid a genocide, this deadly mega-project must be scrapped.”
On 7 February 2024, 39 scholars from 13 countries published an open letter to the Indian president warning that “If the project goes ahead, even in a limited form, we believe it will be a death sentence for the Shompen, tantamount to the international crime of genocide.”
How to help
The NGO Survival International has launched this campaign:
From this site, you just need to add your name and email and you will send an email to India's Tribal Affairs Minister and to the companies currently vying to build the first stage of the project.
Share it with your friends and acquittances and on social media.
Sources:
India’s plan for untouched Nicobar isles will be ‘death sentence’ for isolated tribe, 7 Feb 2024. The Guardian.
‘It will destroy them’: Indian mega-development could cause ‘genocide’ and ‘ecocide’, says charity, 8 Feb 2024. Geographical.
Genocide experts call on India's government to scrap the Great Nicobar mega-project, Feb 2024. Survival International.
The container terminal that could sink the Great Nicobar Island, 20 July 2022. Mongabay.
[Maps] Environmental path cleared for Great Nicobar mega project, 10 Oct 2022. Mongabay.
#shompen#genocide#stop genocide#india#indigenous#indigenous peoples#indigenous rights#human rights#anthropology#stateless nations#end occupation#andaman and nicobar islands#nicobar islands#great nicobar#💬#asia#geopolitics#ecocide#sustainability
23K notes
·
View notes
Text
Best Time for Valley of Flowers Trek: A Seasonal Guide
The Valley of Flowers is a breathtaking destination located in the state of Uttarakhand, India. Famous for its vibrant meadows and diverse flora, this stunning valley attracts nature lovers, trekkers, and photographers from around the world. To fully enjoy the beauty of this valley, it’s essential to plan your visit at the right time. In this guide, we will help you determine the best time…
#4 himalayan best monsoon treks in india#best monsoon treks in 2024#best time to visit valley of flowers trek#monsoon trekking#Monsoon treks#national park of flowers#the valley of gods#valley of flowers#valley of flowers trek#valley of flowrs trek in uttarakhand
0 notes
Text
Sanjay Gandhi National Park
Romi: tookmehere do you know an amazing and beautiful big park in Mumbai to explore wildlife? Tookmehere: Yup! Romi you can visit to Sanjay Gandhi National Park it's an amazing park to know about wildlife.
0 notes
Text
Dazonn Travels on an unforgettable journey to Uttarakhand's best national parks. Explore Jim Corbett, Rajaji, and Valley of Flowers at your own pace. Encounter diverse wildlife and stunning scenery on our guided tours. Experience the true beauty of Uttarakhand with us. Book now for an adventure you'll never forget.For more details visit our website or Contact us now: 896-872-7340
0 notes
Text
Kaziranga National Park Wildlife Photography Tour/Workshop
https://www.jayantaguhaphotography.com/kaziranga-wildlife-photography-tour

#wildlife#wildlife photography#indian wildlife#wild#nature#best indian wildlife photographer#bird#indian wildlife photographer#indian wildlife safari#nature photography#one horned rhino#kaziranga photo tour#kaziranga#kaziranga national park#safari india#safari#safari trex dinosaur biganimals cowvideos fatanimals funnyanimals#safri tour
0 notes
Text

Best National Parks in India
Discover India's best National Parks, a testament to the country's diverse wildlife and breathtaking landscapes. From Kaziranga's rhinos to Jim Corbett's tigers, these parks offer captivating encounters with nature.
0 notes
Text
The Best time for Jungle Safari
#TheBesttimeforJungleSafari #BandhavgarhNationalPark #PenchNationalPark#TadobaAndhariTigerReserve #KanhaNationalPark #SatpuraNationalPark #PugdudeeSafaris #SafariPackage #NationalPark #MadhyaPradesh #Maharashtra #Wildlife #WildlifePackage #FamilyHoliday #SummerHoliday #AdlerTours #adlertourssafaris #adlertoursandsafaris #TravelAgent #Rajkot #Gujarat #India #Asia Visit our Website for more…

View On WordPress
#Adler Tours#Adler Tours & Safaris#Adler Tours and Safaris#Asia#Bandhavgarh National Park#family Holidays#Gujarat#India#Kanha National Park#National Park#Pench National Park#Pugdudee Safaris#Rajkot#Safari Packages#Satpura National Park#Summer Holidays#Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve#The Best Time for Jungle Safari#Travel#Wildlife Safaris
0 notes
Text





Luxury Resorts at Ranthambore National Park book your dream resort in ranthambore safari booking
#best national park in india#best tiger reserve in india#ranthambore national park#national parks in india#tiger reserve in rajasthan#tiger reserves in india#ranthambore tiger reserve rajasthan#ranthambore national park tiger safari#resort#traveling#tourism#tour package
0 notes
Link
Embark on a tour of North East India. Places to visit in North East India are full of misty mountains, serene valleys, cascading waterfalls, etc.
#Kaziranga National Park#Best places to visit in North East India#Places to visit in North East India#Top places to visit in North East India
0 notes
Text
Har Ki Dun Trek - Explore 500 Years of Cultural Heritage
#best summer treks in India#cultural trek in Uttarakhand#easy-moderate trek in Uttarakhand#Govind Ballabh Pant National Park#Har Ki Dun trek#Har Ki Dun trekking routes#Har Ki Dun valley#Mysterious Himachal trekking tours#Swargarohini massif#trekking in Garhwal Himalayas
0 notes
Text
Brian Tyler Cohen (12.30.2024):
As this volatile year nears its end, most of the talk being hurled around the incoming administration is minimally focused on plans for the country’s future, for better or for authoritarianism. Instead, it remains trained on MAGA’s adolescent civil war between Trump’s most vocal supporters and his co-president, Elon Musk. Musk’s honeymoon in the MAGA-sphere—though destined to combust—appears to be ending weeks before the administration has officially launched. While most of us were celebrating our holidays, Elon was holed up in some supervillain cyber vehicle, waging a fight with the very people whose voices and ideologies he spent months amplifying.
Trump created the problem, as is his way, by proposing the appointment of Srinam Krishnan, a Silicon Valley venture capitalist with whom Musk has consulted closely, as his senior policy advisor on AI. Putting forth Krishnan is apparently more outrageous than choosing an alleged sex offender and financial mismanager for defense secretary; a woman who’s been enthusiastically green-lit by the Kremlin for director of national security; or an anti-vaxxer (who dumped a bear he intended to eat in Central Park) to lead health and human services. But Krishnan caused the crater within MAGA this holiday season…because he’s a naturalized American citizen who was born in India and recruited here because of his tech expertise.
He’s remained here thanks to our H1B program, which offers visas to highly skilled foreign workers. Such a laudable program, which celebrates American values and could have been deftly supported, was instead publicly advocated for by Musk via increasingly hysterical posts capped with awkward attempts at wedging in sports references.
Like his co-president, Elon doesn’t handle criticism with a notable amount of grace.
Naturally, he was backed up by his fellow unelected co-chair of the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), Vivek Ramaswamy, who tweeted a tirade that delved into misplaced parenting advice while referencing shows like Saved by the Bell and Family Matters, to really drive home his point that…well, that remains unclear.
[...] Safe to assume that this fight is not going to end well. Or end at all. This is a hill that Elon will die on, for obvious reasons: He’s a former H1B visa immigrant who owns businesses that, no doubt, rely on H1B visa recipients to function. But it’s also a hill that the original MAGA faithful (you know, those who attempted a coup on our Capitol before the oligarchs became part of Trump’s traveling circus) will die on. Trump’s agenda is “America First.” His campaign handed out “Deport Them All” signs at rallies. So they were both fooled. The MAGA loyalists will take it worse, once they recognize (if they haven’t already) that they unwittingly installed into power an unelected foreign oligarch who’s going to use Trump to expand immigration programs that they hate. And there’s nothing they can do about it; Elon is the de facto president. Which is not to suggest that he is in a position of triumph. Remember, Musk is a sad little man who so desperately craves the rousing approval of the MAGA base that he spent the better part of a year nurturing them and doing performative jumping jacks for their applause. He needs their adulation; his ego depends on it. And now he’s facing off with those he presumed would be his footsoldiers. Perhaps he is only now becoming fully aware that they are immovable racists who were happy to accept financial help but don’t actually agree with his worldview. They want to elevate white Americans and no one else. So…nobody wins.
I sincerely hope this goes without saying, but the H1B program is an invaluable channel. We should absolutely bring the best and brightest talent to the United States. If we don’t welcome them here, that talent goes to other countries. In other words, there’s an “America First” incentive to continue investing in such programs. Of course, MAGA doesn’t care. For them, that brand is about promoting white Americans. It’s not concerned with helping the nation as a whole.
Brian Tyler Cohen gives an excellent breakdown on the MAGA-on-MAGA feud over H1-B Visas.
#MAGA on MAGA Violence#Elon Musk#Donald Trump#H1B Visas#Srinam Krishnan#Trump Administration II#Vivek Ramaswamy#Matt Gaetz#Laura Loomer
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
KATHMANDU, Nepal—When Kumar Paudel turned on the TV in August 2016 and saw former Prime Minister Kirti Nidhi Bista giving an interview from his home, it wasn’t the content of the conversation that caught his attention. It was the massive tiger pelt hanging on Bista’s wall.
At the time, Paudel, a conservationist based in Kathmandu, was traveling around Nepal’s prisons to conduct interviews with incarcerated individuals as part of his research into why people commit wildlife crime. Although there are few official statistics on wildlife crime in Nepal, researchers believe that the country is a key hub in the region for wildlife trafficking, one that serves as an important transit route between India and China.
Nepal has some of the strictest wildlife crime laws in the world, but they are unevenly enforced: While the country’s poor languish in prison for their involvement in the trade, the rich and powerful illegally flaunt exotic skins as showpieces.
Paudel is deeply aware of this disparity. Between 2016 and 2017, he interviewed 116 prisoners convicted for wildlife crime, mostly in the rhinoceros trade. Some had been part of international wildlife trafficking syndicates; many others were driven by economic desperation or were not sure why they had been arrested. More than half of them lived below the poverty line, and 75 percent came from Indigenous communities.
“Prosecution is mainly targeted at poor and vulnerable communities in the global south who are not often at the helm of driving international illegal wildlife trade,” Paudel said when I met him in December at a small forested patch amid Kathmandu’s urban sprawl. The 33-year-old conservationist had a scientist’s curiosity, his attention ensnared by every insect and plant, and his wardrobe was unselfconscious outdoor nerd: trekking shoes, baggy pants, safari jacket.
After Bista’s interview aired, Paudel decided to take matters into his own hands. Bista hadn’t been prime minister since 1979, but he was emblematic of Nepal’s elite. Paudel sought legal action to rectify Nepal’s double standard in enforcing wildlife crime. Finally, in May 2023, Nepal’s Supreme Court ruled that the government must enforce its conservation laws and seize illegal wildlife parts. The verdict marks a significant victory for conservation, but Nepal’s entrenched power structures and deep-seated inequality mean that this is only a first step in supporting both vulnerable communities and conservation efforts in the country.
Trophy hunting in Nepal dates back at least to the reign of Jung Bahadur Rana in the 19th century. British visitors embarked on trips to the region to hunt and collect exotic wildlife, including rhinos, tigers, and elephants. These expeditions weren’t mere hunting outings or camping adventures; they were elaborate demonstrations of wealth, authority, and diplomacy.
Nepali monarchs orchestrated extensive hunting expeditions to curry favor with the British. These encounters provided fertile ground for negotiating political interests and strengthening cultural ties, all while showcasing the monarchy’s authority over its natural riches.
These “hunting diplomacy” expeditions were enormous. Photographic records of the hunts are perhaps the best evidence we have that they drove megafauna across the subcontinent to endangered status and near extinction, from the Bengal tiger to the one-horned rhinoceros and the Indian elephant.
Nepal has come a long way since then. The country completely banned hunting in 1972. The following year, it enacted the National Parks and Wildlife Conservation Act, which provides a comprehensive legal framework for the management of Nepal’s natural resources and biodiversity. The act authorizes the government to designate national parks, wildlife reserves, and conservation areas, as well as zones where hunting is allowed under strict regulation. (Today, hunting is only allowed in the Dhorpatan Hunting Reserve. All other hunting, even for bushmeat, is illegal, though subsistence hunting is still relatively common.)
The act also makes it illegal to use, sell, or distribute wildlife without permission, and it states that any individual in possession of wildlife parts must get a permit after acquiring them by disclosing their source. (This also applies to parts acquired before 1973.)
Despite these efforts, the country’s hunting legacy left its mark, and threats to wildlife continue to grow—including climate change, rapidly expanding human populations, the illegal wildlife trade, and a resurgence in poaching. In addition, the 1973 act isn’t always enforced; for instance, according to the director general of Nepal’s Department of National Park and Wildlife Conservation, no one has ever sought to obtain a permit for any wildlife parts.
The illegal wildlife trade is rampant in Southeast Asia, where the gap between rich and poor creates both poachers and markets. In Nepal, the illegal wildlife trade largely operates covertly, and some of the product is used for manufacturing traditional medicines. But a portion of the trade meets the demand for extravagant decor. Some pelts have been exhibited in public spaces such as banks, markets, and even government offices.
Many Nepalis have been imprisoned for their involvement in the trade. (Despite poor data, researchers have found that from 2011 to 2015, there were 830 wildlife-related arrest cases reported in the country.) They fall into the trap of trafficking to support their families and spend decades paying the price.
“We are expendable and poor and desperate for money,” said Bir Bahadur Tamang, who served 15 years in prison for smuggling wildlife parts. “There are many like us.”
Tamang was born and raised in the village of Kalika on the rim of Chitwan, Nepal’s first national park. Tigers, rhinos, leopards, spotted deer, and wild buffalo roam there, along with elephants that come to graze when the plains are dry. Several Indigenous communities have been living beside these dense forests for centuries.
I first met Tamang last December outside his home in Kalika. With a hint of guilt, Tamang recalled supplying bags to masked ringleaders—whom he called “big people”—in the trade network that were full of rhino horns and pangolin scales (both of which are classic ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine), as well as tiger skin.
One morning, Tamang and six of his friends were arrested for conspiring to smuggle wildlife parts. None of them could afford to post bail, he said, and there was never a trial. Some died in prison due to physical ailments and inadequate medical treatment.
Tamang was released from prison in 2016, but as a former felon, he faces a world of poverty, hazards, and guilt. He struggles to make a living, often existing hand-to-mouth without a stable income or basic necessities. Tamang said that finding work has been challenging due to his criminal record and a spinal injury from poor confinement conditions. He is often psychologically distressed, haunted by nightmares of his time in prison, and fearful of entering the jungles that surround his home. “I’m taking it one day at a time,” he said.
As Paudel put it, when a poor person illegally kills a tiger, the full weight of the law is applied. But when a prime minister illegally owns a dead tiger, it is permitted.
Yet showcasing wildlife is harmful, too: It normalizes the trade and adds to its appeal as a status symbol. This is why, starting in 2016, Paudel lobbied for government action. First, he reported instances of illegal wildlife parts displayed in Kathmandu to different government bodies. But authorities warned him to keep quiet, and he said that some even threatened to end his career by withholding approval for his conservation and research permits.
After running in vain from one department to another for two years, Paudel made little progress. So in May 2018, Paudel filed a petition to Nepal’s Supreme Court with the help of environmental lawyer Padam Bahadur Shrestha. The petition demanded that the government urgently conduct investigations into the private possession of wildlife parts, seize illegal parts and prosecute those who own them, and maintain records on legally held wildlife parts. This includes parts used in medicines, trophies, and displays.
After five years of deferrals, the Supreme Court ruled in Paudel’s favor. It also mandated that the government implement additional measures to combat wildlife crime, including better educating the public on the wildlife possession laws and confiscating wildlife parts for educational and research purposes.
The verdict means anyone displaying trophies without the right permits is in trouble. Penalties can include fines of roughly $7,400 and up to 15 years in prison. Courts may confiscate wildlife parts for evidence, research, or destruction, and offenders can also face penalties such as asset forfeiture and bans on further wildlife-related activities. This applies to all offenders, regardless of their socioeconomic status. “Ensuring justice isn’t about favoring one group over another,” Paudel said. “It’s about equitable treatment and holding everyone accountable under the law.”
Bista, who died in 2017, did not live to see the ruling in the case, which was spurred in part by his own decor.
For now, it’s unclear whether the government will have the desire—or ability—to enforce the law. Part of this comes down to Nepal’s history. For most of the 20th century, Nepal was ruled by a monarch who held all executive power and enjoyed absolute immunity. After the 1973 act, all wildlife trophies seized by the authorities were handed over to the Royal Palace and were often displayed in public as a symbol of royal splendor, according to Sindhu Prasad Dhungana, director general of the Department of National Parks and Wildlife Conservation. The monarchy was abolished in 2008, but wildlife parts are still displayed and used in some private households of Nepal’s elite, often without any consequences.
“The lingering effects of royal impunity still resonate in the present,” Dhungana said.
According to Shrestha, the attorney who helped Paudel with his petition, powerful Nepalis often manipulate the investigation process to evade punishment. “The inconsistent application of laws within Nepal points to a glaring deficiency in our legal system: It fails to dissuade criminals, resulting in rampant impunity,” he explained.
The new rules are expected to go into effect later this year, but it will take time for officials to establish a process for investigating and certifying wildlife trophies. Although the Ministry of Forests and Environment will be responsible for this initiative, the specific details will only be determined after the full text of the verdict is released in the coming months.
Dhungana believes it will be challenging to implement the new law. “Many possessions are displayed flouting the law, but it is nearly impossible to enter every house and investigate,” he said. “One cannot presume people who have wildlife on their walls are criminals and the same ones participating in the current wildlife trade.”
Paudel, for his part, has found relief in the ruling, which marks the end of a long journey for him. He believes the decision will go far in safeguarding Nepal’s biodiversity by addressing the problem at its source: “True justice will prevail only when governments and their law enforcement agencies hold accountable those who drive the demand for illegal wildlife trade.”
Still, Paudel knows that many challenges lie ahead. “Dealing with the past is complex,” he said. “But we must find ways to make the law equitable in the future and adhere to the court’s order.”
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sanjay Gandhi National Park is one of the biggest and most beautiful parks located in Mumbai. The park consists of thousands of trees, different species of animals, and many amazing yet interesting places to explore. One of the main attractions of the park is the Kanheri Caves. The cave is very old, and it is where people of the ancient period used to live.
0 notes
Text
Explore the untamed beauty of India's top 10 national parks! From the royal Bengal tigers of Jim Corbett to the lush Western Ghats of Periyar, each park is a sanctuary of biodiversity. Immerse yourself in the wonders of nature and witness India's diverse wildlife in their natural habitats. For more information, visit our website: or Contact us now:+1-888-216-7282.
#national park#National Parks in india#Best National Parks in india#Name of National Parks in india#10 National Parks in india
0 notes