#balloon tipped catheter
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
[Encore] ICU Equipment Deep Dive: A Revisit with Sean Dent
In this episode, we are re-sharing an episode where we sit down with Sean Dent, DNP ACNP APRN, a highly experienced ICU nurse practitioner. We dig deep into the types of equipment you’ll run into in the ICU. These include:
Arterial lines
Different options for monitoring fluid status
Cooling devices
CRRT
Hemodialysis catheters
Impellas and aortic balloon pumps
Internal pacing
Proning devices
These episodes were originally recorded in 2019, but the information is still incredibly relevant today for ICU nurses. This content is for informational purposes only; best practices may have changed.
For ALL of our ICU nursing content: https://www.freshrn.com/critical-care-icu-nursing/
For our free mini-course ICU Drips For Beginners, click here: https://courses.freshrn.com/p/icu-drips-for-beginners
To learn more about our comprehensive ICU prep course, Breakthrough ICU: A Crash Course For New ICU Nurses, click here: https://courses.freshrn.com/p/breakthrough-icu
Learn more about the FreshRN All-Access Pass here - https://courses.freshrn.com/p/membership
To see our latest course catalog (med-surg, ICU, precepting, charge nurse, ortho, cardiac, neuro courses and more), click here: https://courses.freshrn.com/
Get weekly tips, encouragement, stories from the bedside, and more - just for nursing students and new nurses at: https://www.freshrn.com/email-sign-up/
Connect With Me Online!
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FreshRN
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Kati_Kleber
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/Fresh_RN/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/kati_kleber/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@freshrn
Music credit: Keep My Cool by Benj Heard
Check out this episode!
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best Angioplasty Doctor and Surgery in Jaipur – Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao

When it comes to cardiovascular health, few procedures are as critical as angioplasty. In Jaipur, Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao has emerged as a top specialist, known for his expertise in providing cutting-edge angioplasty treatments and delivering high success rates for his patients. With his extensive experience, advanced medical knowledge, and dedication to patient care, Dr. Rao has positioned himself as one of the leading angioplasty doctors in Jaipur. This article explores everything you need to know about angioplasty surgery, Dr. Rao’s expertise, and why his approach stands out in the field.
Understanding Angioplasty: A Lifesaving Procedure
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure aimed at restoring blood flow in the coronary arteries, which are often narrowed or blocked due to atherosclerosis (buildup of plaque). During the procedure, a thin catheter with a small balloon at the tip is inserted into the blocked artery. The balloon is then inflated, widening the artery and allowing for better blood flow. Sometimes, a stent is placed to keep the artery open.
Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao’s approach to angioplasty surgery in Jaipur combines meticulous attention to detail and the latest techniques in interventional cardiology, ensuring high standards of safety and efficacy. His commitment to using advanced technology and minimally invasive methods makes him one of the most sought-after specialists in the region.
Why Choose Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao for Angioplasty Surgery in Jaipur?
1. Exceptional Expertise and Experience
Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao has spent years specializing in interventional cardiology, making him highly skilled in diagnosing and treating complex cardiac issues. His proficiency in angioplasty procedures extends to both routine and high-risk cases, where his attention to patient history, pre-operative conditions, and tailored approach result in successful outcomes.
With a background in top-tier medical institutions and continual training in new techniques, Dr. Rao’s expertise offers patients in Jaipur a world-class solution for their cardiac issues without needing to travel to distant, high-cost facilities.
2. Use of Advanced Technology and Techniques
Dr. Rao’s clinic is equipped with state-of-the-art angioplasty technology, including imaging systems and catheterization labs that allow precise visualization of arterial blockages. He frequently employs drug-eluting stents and advanced intracoronary imaging tools, such as IVUS (Intravascular Ultrasound) and OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography), for a more accurate assessment.
By incorporating these tools, Dr. Rao ensures a minimally invasive approach, reducing complications and shortening recovery time. This approach provides patients with the best of modern interventional cardiology practices right here in Jaipur.
3. Patient-Centric Approach to Treatment
Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao is known not only for his expertise but also for his compassionate and patient-centered care. His team places great emphasis on patient education, making sure that individuals understand every aspect of their angioplasty procedure, including potential risks, benefits, and post-surgery care.
Dr. Rao’s clinic provides comprehensive follow-up support, which is crucial for patients undergoing cardiac procedures. This involves lifestyle counseling, medication management, and regular check-ups to monitor heart health, all tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Who Needs Angioplasty? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Angioplasty is typically recommended for patients experiencing symptoms of coronary artery disease (CAD), such as:
Chest Pain (Angina): Persistent or recurring pain in the chest can indicate blocked arteries.
Shortness of Breath: Reduced blood flow to the heart can cause difficulty in breathing.
Heart Attack: Complete blockage of a coronary artery often requires immediate intervention through angioplasty.
Dr. Rao conducts thorough assessments to determine the severity of coronary artery disease and decides the most appropriate treatment, whether it���s angioplasty, medication, or surgery.
Types of Angioplasty Procedures Performed by Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao
1. Balloon Angioplasty
In this procedure, a small balloon is inflated within the artery to open the blockage. While balloon angioplasty itself does not always involve stent placement, it is often combined with stenting to maintain long-term arterial openness.
2. Stent Placement (Coronary Stenting)
A stent is a small metal or drug-eluting tube that Dr. Rao places in the artery to keep it open post-angioplasty. Drug-eluting stents release medication over time, preventing the artery from narrowing again. This advanced approach ensures better outcomes, particularly in high-risk or repeat cases.
3. Complex Angioplasty Procedures
Dr. Rao also handles complex angioplasty cases, including multivessel angioplasty, left main coronary artery interventions, and chronic total occlusion (CTO) angioplasty. His experience with these advanced techniques is particularly beneficial for patients who have complex blockages that require a sophisticated approach.
The Angioplasty Procedure: What to Expect
For patients considering angioplasty, understanding the process can ease anxiety and build confidence:
Pre-Procedure Preparation: Dr. Rao ensures that every patient undergoes a thorough evaluation before the surgery. This may include blood tests, an ECG, or a coronary angiogram.
The Procedure: During angioplasty, Dr. Rao inserts a catheter through a small incision, typically in the arm or groin. Guided by X-ray imaging, he advances the catheter to the blocked artery and inflates the balloon or places a stent to restore blood flow.
Post-Procedure Care: After angioplasty, patients are monitored in a recovery area and usually discharged within a day or two. Dr. Rao provides comprehensive guidance on lifestyle modifications, medications, and follow-up appointments to ensure full recovery.
Advantages of Angioplasty Surgery with Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao
Choosing Dr. Rao for angioplasty in Jaipur offers numerous advantages, including:
Minimally Invasive Technique: This reduces recovery time and the risk of complications.
High Success Rates: Dr. Rao’s vast experience contributes to consistently positive outcomes for his patients.
Quick Recovery and Improved Quality of Life: With angioplasty, patients often notice an immediate improvement in symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
Post-Operative Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
Following angioplasty, Dr. Rao recommends a personalized cardiac rehabilitation plan that includes:
Medications: These may include antiplatelet drugs, beta-blockers, and statins to manage heart health.
Diet and Exercise: Adopting a heart-healthy diet and incorporating regular exercise are critical for long-term success.
Regular Follow-Ups: Dr. Rao schedules routine check-ups to monitor the heart’s performance and catch any signs of re-narrowing early on.
His dedicated follow-up care ensures patients have the support needed to maintain heart health, make necessary lifestyle changes, and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Angioplasty
1. Is angioplasty a permanent solution for coronary artery disease?
Angioplasty significantly improves blood flow, but it does not cure coronary artery disease. Dr. Rao emphasizes lifestyle changes and medication management to prevent future blockages.
2. How long does recovery take after angioplasty?
Most patients can resume normal activities within a week, though Dr. Rao provides individualized advice based on each patient’s condition.
3. What are the risks associated with angioplasty?
While angioplasty is generally safe, there are risks such as artery re-narrowing, bleeding at the catheter site, and, in rare cases, heart attack or stroke. Dr. Rao takes extensive precautions to minimize these risks.
Conclusion
Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao is recognized as a leading angioplasty specialist in Jaipur. His combination of medical expertise, advanced technology, and patient-centered approach makes him the ideal choice for those needing angioplasty. Whether it’s a routine case or a complex, high-risk procedure, Dr. Rao’s patients can count on the highest standards of care and a dedicated team that ensures their well-being throughout the treatment journey.
#dr. ravinder singh rao#best heart expert in jaipur#best heart expert in india#best cardiologist in chandigarh#best cardiologist expert in india#best heart doctor of mitral valve#angioplasty expert in india#best cardiologist expert in jaipur
0 notes
Text
Post-Bypass Angioplasty In Chennai
Understanding Post-Bypass Angioplasty
Post-bypass angioplasty, also referred to as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) following coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is a medical procedure designed to address blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries after bypass surgery. During this procedure, a catheter with a balloon at its tip is inserted into the affected artery, where the balloon is inflated to compress the plaque or blockage and restore blood flow. Stenting is commonly employed to keep the artery open, effectively enhancing blood flow to the heart muscle, alleviating symptoms, and reducing the risk of future cardiac complications.
Causes Leading to Post-Bypass Angioplasty
Several factors can necessitate post-bypass angioplasty, including:
Restenosis: This is the most common cause, where the treated artery narrows again over time due to the body’s healing response, often involving the proliferation of smooth muscle cells.
Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as smoking, a high-fat diet, insufficient physical activity, and chronic stress can contribute to recurrent arterial blockages after angioplasty.
Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk, as the condition can accelerate atherosclerosis and impair the healing process.
Why Choose Dr. M. Kathiresan for Post-Bypass Angioplasty in Chennai
Selecting a highly qualified cardiologist is crucial for successful post-bypass angioplasty. Dr. M. Kathiresan, a renowned interventional cardiologist in Chennai, possesses extensive expertise in performing this procedure. Here are some compelling reasons to consider Dr. M. Kathiresan for your post-bypass angioplasty needs:
Minimally Invasive Techniques: Dr. Kathiresan specializes in advanced techniques that ensure a faster recovery for patients.
Comprehensive Care: From initial consultations to post-operative follow-ups, he provides personalized care throughout the treatment journey.
State-of-the-Art Technology: Utilizing the latest medical equipment, Dr. Kathiresan ensures that each procedure is performed safely and effectively.
Treatment Approach Post-Angioplasty
After post-bypass angioplasty, a comprehensive treatment plan is vital for optimal recovery and long-term heart health. Key components include:
Medications:
Antiplatelet agents: Such as aspirin or clopidogrel to prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of restenosis.
Statins: To lower cholesterol and mitigate atherosclerosis risk.
Beta-blockers: To manage blood pressure and reduce heart workload.
ACE inhibitors or ARBs: To control blood pressure and enhance heart function.
Nitrates: To manage angina.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Smoking Cessation: Stopping smoking is essential for maintaining heart health.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces heart disease risk.
Stress Management: Finding effective stress-reduction strategies, such as yoga or meditation, is essential.
Cardiac Rehabilitation:
Structured exercise programs and educational support aid recovery and promote heart health.
Psychosocial Support:
Emotional support from family, friends, or mental health professionals can be beneficial.
Cost of Post-Bypass Angioplasty in Chennai
The cost of post-bypass angioplasty in Chennai typically ranges from ₹2 lakh to ₹4 lakh. Factors influencing the cost include:
Type of Stent: Drug-eluting stents tend to be pricier; however, they are effective in lowering the risk of re-blockage when compared to bare-metal stents.
Hospital Amenities: Premium facilities may charge higher fees for procedures and post-operative care.
Health Insurance: Most insurance plans cover a significant portion of angioplasty expenses, helping to alleviate financial concerns.
Patients are encouraged to consult hospitals for detailed package information and insurance coverage options.
Overview of the Procedure
Diagnostic Evaluation: Comprehensive assessments through imaging and tests to identify post-bypass issues.
Angioplasty Technique: A catheter is inserted into the blocked artery, and a balloon is inflated to widen it, with potential stent placement to maintain blood flow.
Guidance Technology: Advanced imaging aids precise navigation during the procedure.
Recovery and Monitoring: Patients are closely monitored post-procedure for recovery and potential complications.
Benefits of Post-Bypass Angioplasty
Post-bypass angioplasty offers several advantages, including:
Improved Blood Flow: The primary goal is to restore blood flow through narrowed or blocked grafts, alleviating symptoms like chest pain and enhancing heart function.
Symptom Relief: Patients can experience significant relief from chest pain and shortness of breath, improving their overall quality of life.
Reduced Risk of Future Heart Events: By enhancing blood flow and minimizing blockages, the procedure can lower the risk of future cardiac events, such as heart attacks or the need for repeat bypass surgery.
Risks Associated with Post-Bypass Angioplasty
Although post-bypass angioplasty is generally safe, potential risks include:
Infection: A rare risk at the catheter insertion site.
Bleeding: Minor bleeding may occur at the insertion site, but severe cases are uncommon.
Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may react to the contrast dye used during the procedure.
Steps Involved in Post-Bypass Angioplasty
Catheter Insertion: A catheter with a balloon is inserted through the groin or wrist and guided to the blocked artery.
Balloon Expansion: The catheter's balloon is inflated to expand the artery, facilitating improved blood flow.
Stent Insertion: A stent is typically positioned to maintain the artery's openness and reduce the risk of future blockages.
Post-Procedure Monitoring: Patients are monitored for complications and given medications to prevent clot formation.
This minimally invasive approach provides a quicker recovery compared to repeat bypass surgery.
Conclusion
Post-bypass angioplasty in Chennai is a crucial step in managing patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass surgery. It requires diligent monitoring and follow-up to ensure the procedure's success and the patient's long-term health. Adhering to prescribed medications and lifestyle changes is vital for maintaining the patency of grafts and preventing complications. Regular check-ups, including imaging studies and stress tests, are essential for evaluating cardiac health. Patient education and support play a significant role in promoting a heart-healthy lifestyle. For more details: https://drkathiresan.com/angioplasty-treatment-in-chennai
1 note
·
View note
Text
Urine Catheter Change At Home | Catheter Change At Home
Changing a urinary catheter at home can be done safely with the right preparation and technique. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Supplies Needed:
- New catheter (make sure it's the correct type and size)
- Sterile gloves
- Antiseptic wipes or solution
- Lubricant (if applicable)
- Clean container for the used catheter
- Absorbent pad or towel
- Disposal bag for used materials
Procedure:
1. **Wash Hands:** Begin by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Dry them with a clean towel.
2. **Prepare the Area:** Find a clean, well-lit space. Arrange everything you'll need close at hand.
3. **Put on Gloves:** Wear sterile gloves to maintain cleanliness.
4. **Remove Old Catheter:**
- If it's a balloon catheter, deflate the balloon by using a syringe to draw out the saline.
- Gently pull out the catheter. If you encounter resistance, stop and consult a healthcare professional.
5. **Clean the Area:** Use antiseptic wipes to clean the area around the urethra.
6. **Prepare the New Catheter:**
- If needed, apply lubricant to the tip of the new catheter.
- Ensure that the catheter is sterile and handle it by the end that will not enter the body.
7. **Insert the New Catheter:**
- Gently insert the catheter into the urethra, advancing it until urine begins to flow.
- If it's a balloon catheter, inflate the balloon according to the instructions.
8. **Secure the Catheter:** Use tape or a catheter securing device to keep it in place.
9. **Dispose of Old Materials:** Place the used catheter and gloves in a disposal bag.
10. **Wash Hands Again:** Remove your gloves and wash your hands thoroughly.
Aftercare:
- Monitor for any signs of infection, such as fever, increased pain, or unusual discharge.
- Keep the area clean and dry.
- Observe any further guidance that your healthcare practitioner may provide.
Important Tips:
- Always seek the advice of a medical expert if you have any questions or concerns.
- Make sure to have a backup plan in case of difficulties during the change.
If you're ever unsure about the procedure, don't hesitate to seek help from a healthcare provider. — Carevive Healthcare Pvt. Ltd.
0 notes
Text

Medical Translation: Chinese to English Verification Plan for Shelf Life of Medical Devices
Shelf life refers to the maximum period during which medical device products can maintain their performance specifications and functionality under specified storage conditions. This concept typically applies to single-use products, such as catheters and syringes.
I have translated a verification plan for the shelf life of a pressure balloon catheter consisting of over 4,600 words into English, including the following sections:
Purpose
Scope
Product Description
3.1. Product Name
3.2. Intended Use
3.3. Product Classification
3.4. Product Structure
3.5. Main Raw Materials
3.6. Sterilization Method
3.7. Sterilization Parameters
3.8. Packaging Method
3.9. Transportation Methods and Environment
3.10. Model Specifications
Verification Team Members and Responsibilities
Shelf Life Impact Analysis
Test Types and Conditions
6.1. Real-time Stability Testing
6.2. Real-time Stability Testing Conditions
6.3. Simulated Transportation
Sample Size and Test Items
7.1. Determination of Sample Size
7.2. Total Sample Size for Shelf Life
Acceptance Criteria and Testing Methods
8.1. Appearance and End Tip
8.2. Balloon Cross-section
8.3. Dimensions
8.4. Hydrophilicity
8.5. Peak Tensile Strength
8.6. No Leakage
8.7. Catheter Hub
8.8. Balloon Burst Pressure
8.9. Balloon Fatigue
8.10. Balloon Inflation and Deflation Time
8.11. Relationship Between Balloon Diameter and Inflation Pressure
8.12. Integrity of Hydrophilic Coating (Appearance)
8.13. Integrity of Hydrophilic Coating (Particle Shedding)
8.14. Friction of Hydrophilic Coating
8.15. Adhesion of Hydrophilic Coating
8.16. Simulated Use
8.17. Balloon Retraction
8.18. Insoluble Particles
8.19. Pulse Discharge Count
8.20. Electrical Safety
8.21. Sound Output Performance
8.22. Packaging Appearance
8.23. Packaging Seal Leakage
8.24. Packaging Seal Strength
8.25. Five Chemical Tests
8.26. Residue Levels of Ethylene Oxide and 2-Chloroethanol
8.27. Sterility
8.28. Bacterial Endotoxins
Sample Preparation
9.1. Sample Production
9.2. Sample Specifications and Quantities
9.3. Flowchart
Implementation Steps
Result Processing
Test Records
Conclusion
0 notes
Text
Silicone Foley Catheter Online is Made from Silicon Like Material That Never Cause Allergies!
A silicone foley catheter is a medical device that is used to help people who have trouble urinating on their own. It is mainly a thin flexible tube that is inserted into the bladder to drain urine. The catheter is made of silicone which is a soft and flexible material that is gentle on the body. It is a type of urinary catheter and it is designed to stay in the bladder for a period of time and allowing continuous drainage of urine. The catheter has two main parts which is tube and balloon. Tube is the thin and flexible part that goes into the bladder. A small balloon is placed near the tip of the catheter that is inflated once the catheter is in place.
Made from such material that will not cause allergies
The silicone is used because it is soft, is flexible and also gentle on the body. It is also less likely to cause allergies compared to latex. Buying silicone foley catheter online has many benefits. You can shop from home easily without going to a physical store instead. This store offers a wide range of products and brands. You can read customer reviews to make an informed decision properly. You get the product delivered to your entrance. Get to compare prices and features across different stores. By considering these factors and following the tips for safe use one can find the perfect silicone foley catheter online now.

Silicone Foley Catheter Online
Get the best quality suction catheter
Suction catheter is a medical tool that is used to remove mucus and other secretions from the airways. It helps people who have trouble clearing their throat or who cannot cough properly. Suction catheter for sale in Bangalore online can really help you get the best product in affordable price. This online store has got a wide range of such items. So this brings the best chance for you to buy them in an informed manner.
#Silicone Foley Catheter Online#Suction Catheter for Sale in Bangalore#Commode Chair in Bangalore#Bed Back Rest Recliner
0 notes
Text
Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty: A Comprehensive Guide
Balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat aortic stenosis, a condition where the aortic valve becomes narrowed, restricting blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body. This procedure is often recommended for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgical valve replacement, providing significant relief from symptoms and improving quality of life.
Understanding Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis occurs when the aortic valve, which controls blood flow from the heart to the aorta and the rest of the body, becomes narrowed due to calcification or scarring. This condition can lead to symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and fainting. If left untreated, severe aortic stenosis can result in heart failure or sudden cardiac death.
What is Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty?
Balloon aortic valvuloplasty is a procedure designed to relieve the narrowing of the aortic valve. It involves the insertion of a catheter with a balloon at its tip into the femoral artery in the groin, which is then guided to the aortic valve. Once in position, the balloon is inflated to widen the valve opening, improving blood flow and reducing symptoms.
Indications for Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty
BAV is typically recommended for:
High-Risk Surgical Patients: Patients who are considered high-risk for traditional open-heart surgery due to age, frailty, or other medical conditions.
Pediatric Patients: Children with congenital aortic stenosis may undergo BAV as a bridge to future surgical interventions.
Temporary Relief: Adults who need temporary relief from symptoms while waiting for valve replacement surgery.
The Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty Procedure
Preparation: The patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted. Sedation may also be provided to help the patient relax.
Catheter Insertion: A small incision is made in the groin, and a catheter is threaded through the femoral artery up to the aortic valve.
Balloon Inflation: Once the catheter is in place, the balloon at the tip is carefully inflated to stretch the narrowed valve and improve blood flow.
Completion: The balloon is deflated and removed, and the incision site is closed. The procedure typically takes about one to two hours.
Benefits of Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty
Minimally Invasive: BAV is less invasive than open-heart surgery, resulting in shorter recovery times and reduced hospital stays.
Symptom Relief: Many patients experience immediate relief from symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
Bridge to Surgery: For patients awaiting valve replacement, BAV can provide temporary relief and stabilize their condition.
Risks and Considerations
While BAV is generally safe, it is not without risks. Potential complications include:
Valve Re-narrowing: The aortic valve may become narrowed again over time, requiring repeat procedures or valve replacement.
Blood Vessel Damage: There is a risk of damage to the blood vessels during catheter insertion.
Stroke: Though rare, there is a small risk of stroke during the procedure.
Recovery and Follow-Up
After the procedure, patients are typically monitored in the hospital for a day or two before being discharged. Most patients can resume normal activities within a week, though strenuous activities should be avoided for a few weeks. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the condition of the aortic valve and overall heart health.
Conclusion
Balloon aortic valvuloplasty is a valuable option for patients with aortic stenosis who are not candidates for surgery. It offers significant symptom relief with a minimally invasive approach, improving quality of life and providing a bridge to further treatment when necessary. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of aortic stenosis, consult with a cardiologist to determine if BAV is a suitable option for you.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Valve Blockage in the Heart: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Valve blockage in the heart is a serious condition that can significantly impact one's health and quality of life. It occurs when the heart valves, which control the flow of blood through the heart, become obstructed or narrowed. This blog will delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for valve blockage in the heart, providing a comprehensive overview to help you understand this critical health issue.
What is Valve Blockage in the Heart?
Valve blockage in the heart, also known as valvular stenosis, refers to the narrowing of one or more of the heart valves. This condition restricts the blood flow, forcing the heart to work harder to pump blood through the body. The heart has four valves: the aortic, mitral, pulmonary, and tricuspid valves. Each of these can be affected by blockage, leading to various health complications.
Symptoms of Valve Blockage in the Heart
The symptoms of valve blockage in the heart can vary depending on the severity and location of the blockage. Common symptoms include:
. Chest Pain: Often described as a pressure or tightness in the chest, which can be mistaken for angina or heart attack.
. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or when lying down.
. Fatigue: A constant feeling of tiredness and lack of energy.
. Palpitations: Irregular heartbeats or a sensation of the heart skipping beats.
. Swelling: Swelling in the ankles, feet, or abdomen due to fluid buildup.
These symptoms can develop gradually and may not be noticeable until the condition has significantly progressed.
Causes of Valve Blockage in the Heart
Several factors can contribute to valve blockage in the heart, including:
. Congenital Heart Defects: Some people are born with abnormal heart valves that can lead to blockage over time.
. Age-Related Changes: As we age, the heart valves can become thickened and calcified, leading to stenosis.
. Rheumatic Fever: A complication of untreated strep throat that can damage the heart valves.
. Infections: Conditions like endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves, can cause scarring and narrowing.
. Other Health Conditions: High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes can increase the risk of developing valve blockage in the heart.
Diagnosis of Valve Blockage in the Heart
Diagnosing valve blockage in the heart typically involves several tests and procedures:
. Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart that provides images of the heart valves and chambers.
. Electrocardiogram (ECG): A test that measures the electrical activity of the heart and can detect irregularities.
. Chest X-ray: An imaging test that can show the size and shape of the heart and detect fluid in the lungs.
. Cardiac Catheterization: A procedure that involves inserting a catheter into a blood vessel to measure the pressure inside the heart and take detailed images.
Treatment Options for Valve Blockage in the Heart
The treatment for valve blockage in the heart depends on the severity of the condition and the specific valve affected. Common treatment options include:
. Medications: To manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. These may include diuretics, beta-blockers, and anticoagulants.
. Balloon Valvuloplasty: A minimally invasive procedure to widen the narrowed valve using a balloon-tipped catheter.
. Valve Repair: Surgical procedures to repair the damaged valve, which may involve reshaping or removing excess tissue.
. Valve Replacement: In severe cases, the damaged valve may need to be replaced with a mechanical or biological valve.
Preventing Valve Blockage in the Heart
While some risk factors for valve blockage in the heart cannot be controlled, such as age and congenital defects, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
. Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain heart health.
. Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve cardiovascular health and prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
. Managing Chronic Conditions: Keeping conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol under control can reduce the risk of valve blockage.
. Avoiding Tobacco: Smoking and other tobacco use can damage the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of valve blockage.
Valve blockage in the heart is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help you manage this condition effectively. For those seeking reliable information and support, PatientSelfTesting provides comprehensive resources on valve blockage in the heart, helping you stay informed and proactive about your heart health.
0 notes
Text
Angioplasty Specialist Doctor in India for Treatment – Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao

India has become a hub for advanced medical treatments, and Angioplasty Specialist Doctor in India Among the top names in this field is Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao, a leading angioplasty specialist whose expertise in cardiovascular interventions has earned him a reputation for excellence. In this article, we will explore why Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao is the go-to expert for angioplasty in India, delve into the importance of angioplasty as a treatment, and discuss the numerous benefits that patients can expect when seeking his care.
Understanding Angioplasty: A Lifesaving Procedure
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to restore blood flow to the heart by opening blocked or narrowed arteries. This procedure is critical for patients suffering from coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition where plaque buildup restricts blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain, heart attacks, and other serious cardiovascular issues. Angioplasty not only alleviates these symptoms but also significantly reduces the risk of future heart complications.
How Angioplasty Works
During an angioplasty, a catheter with a small balloon at its tip is inserted into the blocked artery. The balloon is then inflated to compress the plaque against the artery walls, creating a wider passage for blood flow. In many cases, a stent—a small wire mesh tube—is placed in the artery to keep it open permanently. This procedure is highly effective, with a success rate of over 90%, making it a preferred treatment option for patients with CAD.
Why Choose Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao for Angioplasty?
Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao is a renowned name in the field of interventional cardiology in India. His vast experience, coupled with a patient-centric approach, makes him one of the most sought-after specialists for angioplasty. Here’s why Dr. Rao stands out:
Extensive Experience and Expertise
With years of experience in performing complex angioplasty procedures, Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao has honed his skills to perfection. He has successfully treated thousands of patients, earning their trust and respect through his dedication and exceptional results. His expertise extends to performing angioplasties in high-risk patients, including those with multiple blockages, chronic total occlusions, and previous failed procedures.
Advanced Techniques and Technology
Dr. Rao is known for adopting the latest techniques and technologies in angioplasty. He is proficient in Rotablation, a specialized procedure used to treat heavily calcified arteries that are resistant to conventional angioplasty. Additionally, he is skilled in performing drug-eluting balloon angioplasty, which uses balloons coated with medication to prevent the re-narrowing of arteries. His commitment to staying at the forefront of medical advancements ensures that his patients receive the best possible care.
Personalized Patient Care
What sets Dr. Rao apart is his unwavering commitment to personalized patient care. He believes that each patient’s condition is unique and requires a tailored treatment approach. Dr. Rao takes the time to thoroughly assess each patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and specific needs before recommending a treatment plan. This individualized approach not only enhances the effectiveness of the procedure but also ensures that patients feel supported and informed throughout their treatment journey.
High Success Rate and Patient Satisfaction
Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao’s high success rate in angioplasty procedures is a testament to his skill and dedication. His patients consistently report significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life after undergoing treatment. Moreover, Dr. Rao’s compassionate approach and clear communication help to alleviate patient anxiety, leading to high levels of satisfaction and trust.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection of coronary artery disease is crucial for preventing serious heart complications. Symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue should not be ignored, as they may indicate the presence of blocked arteries. Regular check-ups and diagnostic tests such as stress tests, echocardiograms, and coronaryangiography can help detect CAD early, allowing for timely intervention.
Angioplasty, when performed at the right time, can prevent the progression of heart disease and reduce the risk of heart attacks. Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and prompt treatment, which can save lives and improve long-term outcomes for patients.
The Recovery Process: What to Expect
Recovery after angioplasty is generally swift, with most patients resuming their normal activities within a few days. Dr. Rao provides detailed post-procedure care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery. These include guidelines on medication management, dietary modifications, physical activity, and follow-up appointments. Patients are also advised to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet, to prevent future complications.
Why India is a Preferred Destination for Angioplasty
India has emerged as a leading destination for medical tourism, particularly for cardiovascular treatments like angioplasty. The country offers world-class healthcare facilities, experienced specialists, and cutting-edge technology at a fraction of the cost compared to Western countries. Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao’s clinic is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities, ensuring that patients receive top-notch care in a comfortable and supportive environment.
Affordability Without Compromise
One of the key reasons why patients from around the world choose India for angioplasty is the affordability of treatment. Despite the lower costs, the quality of care is on par with international standards. Dr. Rao’s clinic offers a range of treatment packages tailored to meet the needs and budgets of different patients, ensuring that everyone has access to life-saving procedures without financial strain.
Seamless Patient Experience
International patients seeking treatment in India benefit from a seamless and well-coordinated experience. Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao’s clinic provides comprehensive support, including assistance with travel arrangements, visa facilitation, accommodation, and post-treatment follow-up. This holistic approach ensures that patients can focus on their recovery without worrying about logistical challenges.
Conclusion
Choosing the right specialist for angioplasty can make a significant difference in the outcome of the procedure. Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao’s unparalleled expertise, commitment to patient care, and use of advanced techniques make him the top choice for angioplasty in India. Whether you are a domestic patient or traveling from abroad, you can trust Dr. Rao to provide the highest standard of care for your heart.
#dr. ravinder singh rao#best heart expert in jaipur#best heart expert in india#angioplasty expert in india#best cardiologist expert in jaipur#best cardiologist expert in india#best cardiologist in chandigarh#best heart bypass surgeon in ahmedabad#best heart doctor of mitral valve
0 notes
Text
Innovative Heart Treatments: What Dr. Rahul Sharma Recommends

Meet Dr. Rahul Sharma: your expert cardiologist in Jaipur, who is dedicated to providing the latest and most effective treatments for heart disease. With advancements in medical technology and a deeper understanding of cardiovascular conditions, innovative treatments have significantly improved patient outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes of heart disease, highlight important points about the condition, discuss various treatment options, and offer prevention tips.
Understanding Heart Disease: Important Points and Causes
Heart Disease Overview
Heart disease encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart, including coronary artery disease, heart rhythm problems, heart infections, and congenital heart defects. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can lead to heart attacks.
Causes of Heart Disease
Heart disease is often caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Key causes include:
Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow.
High Blood Pressure: Can damage blood vessels and lead to heart disease.
High Cholesterol: Excess cholesterol can contribute to plaque formation.
Smoking: Damages the lining of the arteries and accelerates plaque buildup.
Diabetes: Increases the risk of heart disease due to high blood sugar levels.
Obesity: Excess weight increases the burden on the heart.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of exercise can lead to several risk factors for heart disease.
Poor Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can lead to heart disease.
Innovative Treatments for Heart Disease
Medications
Dr. Rahul Sharma, a leading cardiologist in Jaipur, emphasizes the importance of medications in managing heart disease. Statins are commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Antihypertensive medications help control high blood pressure, while antiplatelet agents like aspirin prevent blood clots.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
Also known as angioplasty, PCI is a minimally invasive procedure used to open clogged arteries. A small balloon is inserted and inflated at the site of the blockage, often followed by placing a stent to keep the artery open. This procedure significantly improves blood flow to the heart, reducing the risk of heart attacks.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
CABG is a surgical procedure recommended for patients with severe coronary artery disease. It involves creating a bypass around the blocked arteries using a vessel from another part of the body. This restores normal blood flow to the heart muscle, alleviating symptoms and reducing the risk of heart attacks.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
For patients with severe aortic stenosis, TAVR is an innovative alternative to open-heart surgery. The procedure involves replacing the aortic valve using a catheter inserted through a small incision. TAVR offers a less invasive option with shorter recovery times and reduced complications.
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
Patients at risk of sudden cardiac arrest can benefit from an ICD. This device is implanted under the skin and monitors heart rhythms. If a life-threatening arrhythmia is detected, the ICD delivers an electric shock to restore normal heart rhythm, potentially saving the patient's life.
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT)
CRT is recommended for patients with heart failure and abnormal heart rhythms. It involves implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to both ventricles, synchronizing their contractions. This improves the efficiency of the heart and alleviates heart failure symptoms.
Prevention: How to Reduce the Risk of Heart Disease
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Dr. Rahul Sharma, a renowned cardiologist in Jaipur, stresses the importance of adopting a healthy lifestyle to prevent heart disease. Key recommendations include:
Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking to reduce the risk of heart disease.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limiting alcohol intake to reduce heart disease risk.
Regular Health Screenings
Regular check-ups with a cardiologist in Jaipur can help detect and manage risk factors early. Dr. Rahul Sharma recommends routine screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes. Early intervention can prevent the progression of heart disease and improve outcomes.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
Adequate Sleep
Getting 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night is crucial for heart health. Poor sleep can increase the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Medication Adherence
For those prescribed medications for heart disease or risk factors, adhering to the treatment plan is essential. Skipping doses or stopping medications without consulting a healthcare provider can lead to adverse outcomes.
Conclusion
Meet Dr. Rahul Sharma: your expert cardiologist in Jaipur, who is committed to providing cutting-edge treatments and personalized care for heart disease patients. Understanding the causes, recognizing important points, exploring innovative treatments, and adopting preventive measures can significantly improve heart health. For those seeking comprehensive cardiac care, visiting JaipurCardiologist.com can provide valuable resources and expert guidance. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can lead healthier lives and reduce the risk of heart disease.
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to Urine Tube, Feeding Tube, and Ryles (NGT) Tube Insertion at Home

In recent years, home healthcare has become an increasingly viable option for many individuals needing medical assistance. Among the procedures that can now be safely performed at home are the insertion of urine tubes, feeding tubes, and Ryles (nasogastric or NGT) tubes. While these procedures may initially seem daunting, with proper preparation and guidance, they can be managed effectively in the comfort of one’s home. This guide will provide detailed information on each type of tube insertion, including the necessary steps, equipment, and safety considerations.
Urine Tube Insertion at Home
Urinary catheterization involves placing a catheter into the bladder to drain urine. This procedure is commonly required for individuals with urinary retention, chronic urinary tract infections, or those who are bedridden. Here are the steps to insert a urine tube at home:
Equipment Needed:
Sterile catheter (size as recommended by a healthcare provider)
Sterile gloves
Lubricant (preferably water-soluble)
Antiseptic solution
Sterile drainage bag
Towel or absorbent pad
Syringe (if using a Foley catheter)
Sterile water (if using a Foley catheter)
Procedure:
Preparation: Wash your hands thoroughly and wear sterile gloves. Lay the patient in a comfortable, flat position, with legs slightly apart. Place a towel or absorbent pad under the patient’s buttocks to keep the area clean.
Cleaning: Clean the genital area with antiseptic solution. For males, retract the foreskin (if uncircumcised) and clean from the tip of the penis outward. For females, spread the labia and clean from front to back.
Lubrication: Lubricate the catheter tip generously to ensure smooth insertion and reduce discomfort.
Insertion: Gently insert the catheter into the urethra. For males, hold the penis perpendicular to the body and insert the catheter slowly until urine starts to flow. For females, spread the labia and insert the catheter into the urethral opening. Once urine begins to flow, insert the catheter about an inch further to ensure it is properly positioned in the bladder.
Inflation (Foley Catheter): If using a Foley catheter, inflate the balloon with the prescribed amount of sterile water using a syringe. This will keep the catheter in place.
Attachment: Connect the catheter to the sterile drainage bag, ensuring it is securely attached and positioned below the bladder to allow gravity to assist in drainage.
Secure: Tape the catheter to the thigh (for males) or to the abdomen (for females) to prevent pulling and ensure comfort.
Monitoring: Regularly check the catheter and drainage bag for signs of blockage or infection, and ensure the area remains clean and dry.
Feeding Tube Insertion at Home
Enteral feeding tubes are used to provide nutrition to individuals who cannot eat by mouth, have difficulty swallowing, or need nutritional supplementation. These tubes can be placed through the nose (nasogastric) or directly into the stomach (gastrostomy). This section will focus on nasogastric (NG) feeding tube insertion.
Equipment Needed:
Nasogastric (NG) tube
Lubricant (water-soluble)
pH test strips or an aspirating syringe
Adhesive tape or securing device
Stethoscope
Glass of water with a straw
Towel or absorbent pad
Procedure:
Preparation: Wash your hands thoroughly and wear sterile gloves. Ensure the patient is sitting up at a 45-90 degree angle. Place a towel or absorbent pad under their chin.
Measuring the Tube: Measure the length of the NG tube by holding the tip at the patient's nose and extending it to the earlobe, then down to the xiphoid process (bottom of the sternum). Mark this length on the tube.
Lubrication: Lubricate the first 2-3 inches of the tube with water-soluble lubricant.
Insertion: Gently insert the tube into one nostril and advance it slowly towards the back of the throat. Encourage the patient to swallow or drink water as you advance the tube. This helps the tube pass more easily into the esophagus.
Confirmation: Once the tube is inserted to the marked length, confirm placement by aspirating a small amount of stomach content and testing its pH (should be acidic, typically less than 5). Alternatively, use a stethoscope to listen for a whooshing sound in the stomach when a small amount of air is injected through the tube.
Securing the Tube: Secure the tube to the patient's nose with adhesive tape or a securing device. Make sure it is comfortable and does not pull on the nostril.
Feeding: Attach the feeding bag or syringe and begin the feeding as prescribed. Ensure the patient remains in an upright position for at least 30 minutes after feeding to prevent aspiration.
Ryles (NGT) Tube Insertion at Home
Ryles tube or nasogastric tube (NGT) insertion is similar to the NG feeding tube but may be used for different purposes such as decompression, medication administration, or sampling gastric contents. The procedure is nearly identical, but it’s essential to understand its specific uses and considerations.
Equipment Needed:
Nasogastric (NG) tube
Lubricant (water-soluble)
pH test strips or an aspirating syringe
Adhesive tape or securing device
Stethoscope
Glass of water with a straw
Towel or absorbent pad
Suction equipment (if required)
Procedure:
Preparation: Wash your hands thoroughly and wear sterile gloves. Position the patient sitting up at a 45-90 degree angle. Place a towel or absorbent pad under their chin.
Measuring the Tube: Measure the length of the tube as described in the feeding tube insertion section. Mark the tube at this point.
Lubrication: Apply water-soluble lubricant to the first few inches of the tube.
Insertion: Insert the tube gently into one nostril, advancing it towards the back of the throat. Encourage the patient to swallow or drink water to facilitate the passage of the tube into the esophagus.
Confirmation: Verify the placement by aspirating stomach contents and checking the pH or using a stethoscope to listen for the characteristic whooshing sound when air is injected.
Securing the Tube: Secure the tube to the patient’s nose with adhesive tape or a securing device, ensuring it is comfortable and stable.
Functionality: If the Ryles tube is for decompression, connect it to the suction equipment and set it to the prescribed level. For medication administration or gastric sampling, follow the healthcare provider's instructions.
Safety Considerations
Regardless of the type of tube being inserted, certain safety considerations must be adhered to:
Hygiene: Maintaining a sterile environment is critical to prevent infections. Always wash hands thoroughly and use sterile gloves and equipment.
Comfort: Be gentle and patient, ensuring the comfort of the patient throughout the procedure. Lubrication is essential to minimize discomfort.
Monitoring: Regularly check the placement and condition of the tube. Look for signs of infection, blockage, or displacement. Contact a healthcare professional if there are any concerns.
Training: It is crucial to receive proper training from a healthcare provider before attempting these procedures at home. Many organizations offer training sessions and resources for caregivers.
Emergency: Have a plan in place for emergencies. Know when to seek immediate medical assistance if complications arise.
Conclusion
Home healthcare procedures such as urine tube, feeding tube, and Ryles tube insertion can significantly improve the quality of life for patients who require these interventions. While these procedures may seem intimidating at first, with adequate preparation, training, and adherence to safety protocols, they can be successfully managed at home.
The key to successful home insertion of these tubes lies in thorough understanding, careful preparation, and continuous monitoring. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and training. By following these guidelines, caregivers can provide essential medical care in the comfort and privacy of home, promoting better health outcomes and improved patient comfort.
0 notes
Text
Angioplasty in Nagpur
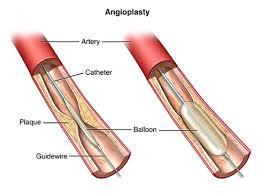
Dr Manish Juneja, best cardiologist in Nagpur. He has done 5091+ angioplasty.
Read More: Angioplasty in Nagpur
Coronary angioplasty, or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a non-surgical procedure that opens blocked heart arteries to improve blood flow. Heart specialists in Nagpur are capable of treating the same with utmost precision and expertise, making it particularly safe to have heart problems treated in Nagpur. A balloon-tipped catheter is threaded through the vessel at the site of damage, and then inflated to widen that section of the artery so blood can flow more easily. Sometimes, a stent is placed to keep the artery open and prevent additional blockages. Advanced medical equipment and experienced cardiologists in Nagpur help these known patients to get excellent treatment for their coronary artery disease, which further helps improve the quality of life, and overall heart condition.
0 notes
Text
Transforming Diabetic Foot Treatment in India: Dr. Gaurav Gangwani’s Interventional Approach
INTRODUCTION
"Diabetic foot treatment in India: Dr. Gaurav Gangwani's use of peripheral angioplasties offers minimally invasive solutions, enhancing recovery and preventing amputations."

The Challenge of Diabetic Foot Complications
Diabetes is a pervasive health issue in India, affecting millions of people. One of the most severe complications associated with diabetes is the development of diabetic foot conditions, including ulcers and gangrene. These conditions can lead to significant morbidity and, in severe cases, may necessitate amputation. Traditional surgical treatments, while effective in some cases, come with high risks and long recovery periods.
Dr. Gaurav Gangwani: Leading the Way with Peripheral Angioplasties
Dr. Gaurav Gangwani, a renowned interventional radiologist based in Mumbai, is pioneering the use of peripheral angioplasties to treat diabetic foot and gangrene, steering a new course in diabetic foot care in India. His expertise and innovative approach have made significant strides in treating these severe complications, emphasizing limb preservation and rapid wound healing.
What is Peripheral Angioplasty?
Peripheral angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open blocked or narrowed arteries, typically those in the legs or feet. The procedure involves the insertion of a balloon-tipped catheter into the affected artery, which is then inflated to restore blood flow. In some cases, a stent may also be placed to keep the artery open.
Advantages of Peripheral Angioplasty Over Surgery
Minimally Invasive Unlike major surgical interventions, peripheral angioplasty does not require large incisions. This minimally invasive nature significantly reduces the risk of infection and other surgical complications.
Rapid Wound Healing Restoring blood flow is critical for wound healing. Peripheral angioplasty effectively improves blood circulation to the affected areas, promoting faster and more effective healing of diabetic foot ulcers and reducing the likelihood of gangrene progression.
Preventing Major Amputations By improving blood flow and promoting healing, peripheral angioplasty plays a crucial role in limb preservation. This procedure can often prevent the need for major amputations, which are a common and devastating consequence of severe diabetic foot complications.
Shorter Recovery Time Patients undergoing peripheral angioplasty typically experience much shorter recovery times compared to those who undergo surgical treatments. This allows patients to return to their daily activities more quickly, enhancing their overall quality of life.
Reduced Hospital Stay The procedure usually requires only a short hospital stay, sometimes less than 24 hours, which not only reduces healthcare costs but also minimizes the patient’s exposure to hospital-associated risks.
Dr. Gangwani’s Role in Advancing Diabetic Foot Care
Dr. Gangwani’s work in peripheral angioplasties is a beacon of hope for many diabetic patients in India. His commitment to using interventional radiology for limb preservation highlights the potential of modern medical techniques to combat the severe consequences of diabetes. Through his pioneering efforts, Dr. Gangwani not only improves the lives of his patients but also contributes to the broader understanding and acceptance of less invasive treatments for complex diabetic conditions.
Conclusion: A New Era in Diabetic Foot Management
The innovative approach taken by Dr. Gaurav Gangwani in treating diabetic foot through peripheral angioplasty marks a significant advancement in medical treatment options available to diabetic patients in India. His focus on minimally invasive techniques to enhance recovery and prevent amputation is transforming diabetic foot care, offering new hope and improved outcomes for those suffering from this challenging complication of diabetes.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Heart Health: Understanding Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty
In the realm of cardiac interventions, coronary angiography and angioplasty stand as pillars of hope, offering individuals a pathway to improved heart health and vitality. These procedures, often used in conjunction, play a pivotal role in diagnosing and treating coronary artery disease, a condition that affects millions worldwide. Let’s delve into the intricacies of coronary angiography and angioplasty, exploring how they work hand-in-hand to restore blood flow to the heart and enhance overall well-being.
Coronary Angiography: Peering into the Heart’s Arteries
Coronary angiography in Delhi, serves as a window into the heart’s intricate vascular network, allowing cardiologists to visualize any blockages or abnormalities within the coronary arteries. During this procedure, a specialized dye is injected into the arteries, which then highlights the blood vessels on X-ray images. These images provide detailed insights into the presence, location, and severity of arterial blockages, enabling cardiologists to formulate an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
The Diagnostic Journey:
For individuals experiencing symptoms of coronary artery disease, such as chest pain or shortness of breath, coronary angiography serves as a critical diagnostic tool. By accurately identifying the extent and severity of arterial blockages, cardiologists can determine the most suitable course of action, whether it involves medication, lifestyle modifications, or invasive interventions like angioplasty.
Angioplasty: Restoring Blood Flow and Vitality
Coronary Angioplasty in Delhi, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure designed to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries and restore blood flow to the heart muscle. During angioplasty, a small balloon-tipped catheter is threaded through the arteries to the site of the blockage. Once in position, the balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque against the artery walls and widening the vessel’s diameter, thereby improving blood flow.
The Role of Stents:
In many cases, angioplasty is accompanied by the placement of a stent, a small mesh-like device that acts as a scaffold to support the artery and prevent it from collapsing or becoming blocked again. Stents may be made of metal (bare-metal stents) or coated with medication (drug-eluting stents) to reduce the risk of restenosis, or re-narrowing, of the artery. By effectively keeping the artery open, stents help maintain optimal blood flow to the heart, alleviating symptoms and reducing the risk of future cardiac events.
A Multifaceted Approach to Cardiovascular Health:
Coronary angiography and angioplasty represent integral components of a comprehensive approach to managing coronary artery disease. By combining diagnostic precision with therapeutic efficacy, these procedures empower cardiologists to address arterial blockages and optimize cardiac function, thereby improving quality of life and reducing the risk of adverse cardiac events.
Advancements in Technology and Technique:
In recent years, significant advancements in technology and technique have transformed the landscape of coronary angiography and angioplasty. From the development of more flexible and navigable catheters to the advent of advanced imaging modalities such as intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography, these innovations have enhanced procedural accuracy, safety, and outcomes, ushering in a new era of precision-driven cardiac interventions. Empowering Patients Through Knowledge: In the journey towards heart health, education and awareness are powerful allies. By understanding the role of coronary angiography and angioplasty in managing coronary artery disease, individuals can take proactive steps to prioritize their cardiovascular well-being. Whether it involves adopting heart-healthy lifestyle habits, seeking timely medical evaluation, or adhering to prescribed treatment regimens, informed decision-making empowers individuals to take control of their heart health and embark on a path towards longevity and vitality.
Conclusion:
Coronary angiography and angioplasty represent transformative interventions in the realm of cardiac care, offering individuals a lifeline in the face of coronary artery disease. Through their combined efficacy in diagnosis and treatment, these procedures embody the essence of precision medicine, tailored to the unique needs of each patient. As advancements in technology and technique continue to evolve, coronary angiography and angioplasty stand poised to shape the future of cardiovascular health, unlocking new possibilities for healing, hope, and vitality.
0 notes
Text
Inside the Abdomen: Innovations in Pressure Measurement Devices.
Introduction to Intra-Abdominal Hypertension
Intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) occurs when pressure inside the abdominal cavity increases above normal physiologic levels. The abdominal cavity houses many vital organs and any excess pressure can compromise blood flow to these organs, leading to organ dysfunction or failure. IAH is commonly seen in critically ill patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who have undergone major surgery, experienced severe trauma, or have conditions that cause widespread inflammation and edema. Left unrecognized and untreated, IAH can progress to abdominal compartment syndrome, a serious medical condition where severe pressure prevents organs from functioning properly. It is crucial for clinicians to be able to reliably measure intra-abdominal pressure so that IAH and abdominal compartment syndrome can be timely diagnosed and managed.
Advantages of Bladder Pressure Measurements
The traditional method of measuring intra-abdominal pressure involves placing a pressure transducer via a Foley catheter inserted into the bladder. The bladder lies in the abdominal cavity and closely reflects changes in IAP. Bladder pressure measurements offer several advantages - they are minimally invasive, can be easily performed at the bedside, and allow for serial measurements over time to monitor a patient's condition and response to treatments. Catheterization of the bladder is standard practice in critically ill patients so an additional measurement does not substantially increase invasiveness. As the bladder filling volume is standardized at 25 mL, bladder pressure reflects true IAP and is not impacted by variable bladder volumes.
Limitations of the Bladder Method
However, bladder pressure measurements do have some limitations. Placement of the Foley catheter requires disinfection and sterile technique to prevent introducing infection. The low compliant Foley balloon material may not accurately reflect abrupt IAP swings. There is also a risk of over-distending the bladder and inflicting damage. Patients with prior pelvic surgery or trauma may have anatomical variations hindering accurate catheter placement. In certain situations such as pelvic or abdominal bleeding, a Foley catheter may not be suitable and alternative techniques are needed. Overall, while bladder pressure monitoring remains the clinical gold standard, novel devices offer options to overcome some of the constraints.
Esophageal Manometry for IAP Measurement
One alternative method is esophageal manometry which involves placement of an esophageal probe with a pressure sensor transducer. When the patient is in supine position and at end-expiration, the applied pressure is transmitted equally from the abdominal cavity to the esophagus, allowing esophageal pressure readings to substitute for direct IAP measurements. This technique is non-invasive and avoids the need for bladder instrumentation. Esophageal manometry correlates well with simultaneous bladder pressure readings. However, it requires specialized equipment and technical expertise in probe placement that may not be readily available everywhere. Positioning of the patient in strict supine posture with the head of the bed flat is important but not always practical in ICU settings.
Direct Abdominal Pressure Catheters
For overcoming the detractions of bladder and esophageal techniques, direct abdominal pressure monitoring devices have been developed. These involve percutaneous placement of a small flexible catheter with a pressure sensor tip directly into the abdominal cavity under ultrasound guidance. The most widely evaluated device is the AbViser catheter which has an 18-gauge diameter and ease of insertion. Direct IAP readings obtained through abdominal catheters demonstrate superior correlation with 'true' IAP measured during surgical abdominal decompression procedures compared to indirect bladder or esophageal readings. Besides higher accuracy, abdominal catheters allow continuous real-time monitoring of pressure trends without interference from bladder volumes or patient positioning. This is useful when titrating therapies aimed at reducing Intra Abdominal Pressure Increased Usage of Novel Devices
With enhanced technological capabilities and streamlined designs, usage of direct abdominal catheters and other novel IAP monitoring systems is growing. Their advantages include direct access to the pressure milieu, ability to track pressure waveforms and fluctuations, removal of urinary obstruction issues, and facilitation of IAP-guided clinical management protocols. This represents a shift from intermittent to continuous surveillance of an important hemodynamic parameter in high-risk critically ill populations. Wider availability of minimally invasive IAP monitors may help expand usage from specialized surgical/trauma ICUs to general medical/surgical units as well. Efforts are ongoing to further simplify device construction, reduce costs, and automate data transfer for improved real-time clinical decision making support.
Infection Prevention Strategies
Though offering distinct advantages, abdominal catheters pose their own risks including introduction of infection during placement. All percutaneous access devices, regardless of insertion site, mandate strict adherence to maxillary barrier precautions. Thorough patient skin antisepsis and use of sterile technique during device insertion are fundamental to limit bacterial ingress. Once deployed, the catheter exit site should remain clean and dry under an occlusive dressing changed as per institutional policy. Close monitoring for signs of local or systemic infection enables prompt corrective measures including catheter replacement if needed. Anti-microbial impregnation of catheters represents another strategy under investigation to stave off biofilm formation and lower infection rates with prolonged indwelling times. With diligent aseptic practices, the benefits of
0 notes
Text
Silicon Folleys Catheter Online – Urinary Drainage Made Convenient
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the convenience and accessibility of medical supplies play a crucial role in ensuring prompt and effective care.
For those seeking Silicon Folleys Catheter Online, the marketplace offers a convenient avenue to procure these essential medical devices.
Understanding the need - Silicon Folleys Catheters are medical devices commonly used for urinary drainage. They feature a balloon at the tip that is inflated once the catheter is inserted, securing it in place. These catheters are often prescribed for patients dealing with urinary retention, surgery recovery, or other medical conditions.
A critical component of respiratory care–The Phlegm suction machine in Bangalore, also known as aspirators, are indispensable in respiratory care. These devices aid in the removal of mucus and other secretions from the airways, facilitating easier breathing for patients with respiratory issues such as COPD, pneumonia, or those recovering from surgery.
The convenience of online purchases - The online marketplace has revolutionized the way we shop for medical supplies, offering a wide range of products and the convenience of doorstep delivery.
Online platforms provide a diverse range of brands and models, allowing buyers to choose the most suitable product for their specific needs. The ability to browse, compare, and purchase medical supplies from the comfort of your home or office is a significant advantage, particularly for those with limited mobility or busy schedules.
Online platforms often feature customer reviews for Phlegm Suction Machine in Bangalore, offering valuable insights into the performance and reliability of the products, aiding in informed decision-making.

Considerations before making a purchase
Supplier reputation - Choose reputable online suppliers with positive customer reviews and a track record of delivering quality medical products.
Product specifications - Ensure that these meets the specific requirements and standards recommended by healthcare professionals.
Warranty and customer support - Look for products with warranties and reliable customer support to address any concerns or issues that may arise post-purchase.
Bangalore's online marketplace for medical supplies is diverse and dynamic. Research thoroughly, explore local and trusted online platforms, and make an informed decision based on your unique healthcare needs.
Conclusion The ability to purchase Silicon Folleys Catheter Online brings a new level of convenience and accessibility to healthcare. By understanding the specific needs of the patient, researching product options, and choosing reputable online suppliers, individuals and caregivers can ensure a smooth and reliable procurement process, ultimately contributing to enhanced patient care and well-being.
#urometer in bangalore#suction catheter for sale in bangalore#buy electric wheelchair in bangalore#commode chair in bangalore
0 notes