#antithrombotic treatment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
0 notes
Text
Global Bovine Heparin Sodium Market [2024-2030] | Market Size, Growth, Dynamics and Trends
Global Info Research’s report offers key insights into the recent developments in the global Bovine Heparin Sodium market that would help strategic decisions. It also provides a complete analysis of the market size, share, and potential growth prospects. Additionally, an overview of recent major trends, technological advancements, and innovations within the market are also included.Our report further provides readers with comprehensive insights and actionable analysis on the market to help them make informed decisions. Furthermore, the research report includes qualitative and quantitative analysis of the market to facilitate a comprehensive market understanding.This Bovine Heparin Sodium research report will help market players to gain an edge over their competitors and expand their presence in the market.
According to our (Global Info Research) latest study, the global Bovine Heparin Sodium market size was valued at USD 41 million in 2023 and is forecast to a readjusted size of USD 60 million by 2030 with a CAGR of 5.6% during review period.
Bovine intestinal enoxaparin sodium and its injections can be used in anticoagulant, antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and halal drugs, that is, it has the halal property that porcine enoxaparin sodium does not have, and is widely used in Muslims, countries and countries. The region has a huge market. Global 5 largest manufacturers of Bovine Heparin Sodium are Bacto Chem, Syntex, Kin Master Produtos Químicos Ltda, Alliance Brasil and Ralington Pharma, which make up over 70%. Among them, Bacto Chem dominates with over 20% production value share, followed by Syntex (17%) and Kin Master Produtos Químicos Ltda (14%). Top manufacturers are based in South America, India and China.
Asia Pacific is the largest market, holding a share over 30%, followed by Europe and South America, with shares 30% and 20% separately.
Based on the product type, the Bovine Heparin Sodium is split into Type A and Type B.
Based on the product Application, the Bovine Heparin Sodium is primarily split into Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism, Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter and Complications of Pregnancy. The largest segment is Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism, accounting for nearly 70%.
The Global Info Research report includes an overview of the development of the Bovine Heparin Sodium industry chain, the market status of Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (Type A, Type B), Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter (Type A, Type B), and key enterprises in developed and developing market, and analysed the cutting-edge technology, patent, hot applications and market trends of Bovine Heparin Sodium.
Regionally, the report analyzes the Bovine Heparin Sodium markets in key regions. North America and Europe are experiencing steady growth, driven by government initiatives and increasing consumer awareness. Asia-Pacific, particularly China, leads the global Bovine Heparin Sodium market, with robust domestic demand, supportive policies, and a strong manufacturing base.
We have conducted an analysis of the following leading players/manufacturers in the Bovine Heparin Sodium industry: Kin Master Produtos Químicos Ltda、Syntex、Bacto Chem、Wegmed - Caminhos Medicinais Ltda、Alliance Brasil、Ralington Pharma、Hebei Changshan Biochemical Pharmaceutical、Suzhou Ronnsi Pharma Market segment by Type: Type A、Type B Market segment by Application:Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism、Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter、Complications of Pregnancy、Others Report analysis: The Bovine Heparin Sodium report encompasses a diverse array of critical facets, comprising feasibility analysis, financial standing, merger and acquisition insights, detailed company profiles, and much more. It offers a comprehensive repository of data regarding marketing channels, raw material expenses, manufacturing facilities, and an exhaustive industry chain analysis. This treasure trove of information equips stakeholders with profound insights into the feasibility and fiscal sustainability of various facets within the market. Illuminates the strategic maneuvers executed by companies, elucidates their corporate profiles, and unravels the intricate dynamics of the industry value chain. In sum, the Bovine Heparin Sodium report delivers a comprehensive and holistic understanding of the markets multifaceted dynamics, empowering stakeholders with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions and navigate the market landscape effectively. Conducts a simultaneous analysis of production capacity, market value, product categories, and diverse applications within the Bovine Heparin Sodium market. It places a spotlight on prime regions while also performing a thorough examination of potential threats and opportunities, coupled with an all-encompassing SWOT analysis. This approach empowers stakeholders with insights into production capabilities, market worth, product diversity, and the markets application prospects. Assesses strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, offering stakeholders a comprehensive understanding of the Bovine Heparin Sodium markets landscape and the essential information needed to make well-informed decisions. Market Size Estimation & Method Of Prediction
Estimation of historical data based on secondary and primary data.
Anticipating market recast by assigning weightage to market forces (drivers, restraints, opportunities)
Freezing historical and forecast market size estimations based on evolution, trends, outlook, and strategies
Consideration of geography, region-specific product/service demand for region segments
Consideration of product utilization rates, product demand outlook for segments by application or end-user.
Request Customization of Report@ https://www.globalinforesearch.com/contact-us About Us: Global Info Research is a company that digs deep into Global industry information to Bovine Heparin Sodium enterprises with market strategies and in-depth market development analysis reports. We provide market information consulting services in the Global region to Bovine Heparin Sodium enterprise strategic planning and official information reporting, and focuses on customized research, management consulting, IPO consulting, industry chain research, database and top industry services. At the same time, Global Info Research is also a report publisher, a customer and an interest-based suppliers, and is trusted by more than 30,000 companies around the world. We will always carry out all aspects of our business with excellent expertise and experience.
0 notes
Text
Amazing Health Benefits of Reishi Mushroom Extract Powder

Reishi mushroom extract powder is a nutrient-rich health supplement made from ground reishi mushrooms. It contains several Ganoderma benefits compounds such as polysaccharides, triterpenes and sterols that give it numerous therapeutic effects including strengthened immunity, reduced inflammation, improved sleep quality and enhanced energy levels. Additionally, Reishi mushroom extract powder boosts cognitive function providing mental clarity and focus while supporting the liver in cleansing toxins from our bodies. Reishi Mushroom Extract Powder Taken regularly as part of an overall healthy lifestyle routine, Reishi mushroom extract can help protect against illnesses and enhance physical performance naturally without any adverse side effects.
Ganoderma is a mushroom that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine. It is known to have many Ganoderma benefits, including helping support the immune system, promoting cardiovascular health, supporting brain function and cognitive performance, reducing inflammation and improving digestion. Recent studies suggest Reishi Mushroom may also be beneficial for people suffering from cancer as it can help reduce tumour size and improve survival rates when combined with other treatments. Additionally, Reishi contains compounds which act as antioxidants to protect against oxidative stress in the body.
Top 4 Health Benefits Reishi Mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum) benefits:
Anti Stress
Reishi mushrooms (Ganoderma lucidum) have long been used in traditional Chinese medicine for their range of healing properties to calming stress. Reishi Mushroom Extract Powder has proven highly effective when taken daily as it helps decrease cortisol levels and promote relaxation while improving overall well-being.
Cardio Health
Reishi mushroom extract powder is increasingly being touted as a natural way to improve cardio health. Studies have shown that reishi contains numerous compounds which possess anti-inflammatory and blood pressure-lowering effects, both of which can help reduce your risk for heart disease and stroke. Reishi has also been linked to lower cholesterol levels, improved exercise capacity (in some cases), better circulation, reduced fatigue after activity, and enhanced immune system response. It is also rich in antioxidants which can protect the body from oxidative stress and free radical damage caused by everyday activities such as exercising or smoking. For best results, it’s recommended to take around 2 grams per day of reishi mushroom extract or supplement form for at least 8 weeks for optimal benefits on overall cardio health.
Support Blood Pressure
Reishi mushroom extract powder has potential health benefits for people with high blood pressure. Studies show that compounds in reishi can reduce systolic and diastolic BP while exerting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects on the cardiovascular system. Other studies also suggest reishi may help lower total cholesterol levels. To get the most out of Ganoderma Benefits, experts recommend taking 300 –600 milligrams of a dried extract form daily over an 8 weeks or longer to achieve optimal results.
Liver Health
Reishi mushroom extract powder has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries due to its ability to improve liver health. Specifically, reishi is believed to be beneficial for supporting the body’s detoxification process and helping the liver regenerate itself, as well as protecting it from damage by free radicals. Studies have indicated that consuming reishi may help reduce inflammation of the liver cells, increasing immunity against diseases such as hepatitis B and C, while also promoting healthy cholesterol levels in those at risk of fatty liver disease.
Conclusions:
After researching Reishi mushrooms it is clear that they have been around for centuries and are highly valued in herbal medicine. They can be consumed raw, cooked or even brewed into tea to take advantage of their many health benefits such as increasing energy levels, boosting immunity and reducing stress. Additionally, due to the range of powerful antioxidants found in these mushrooms, regular consumption may support longevity and improve overall well-being.
Original Source: https://www.rootedactives.com/blogs/news/amazing-health-benefits-of-reishi-mushroom-extract-powder
#reishi mushroom capsules#reishi mushroom extract#reishi mushroom powder#reishi mushroom#mushroom supplements
0 notes
Text
Management of Cerebrovascular Steno-Occlusive Disease
Patients with steno-occlusive cerebrovascular disease are at risk of ischemic symptoms from haemodynamic insufficiency in the presence of reversible hypoperfusion, exhausted autoregulation and impaired vasodilatory reserve. Multidisciplinary management approach includes blood pressure management, antithrombotic therapy, treatment of underlying brain-body interactions targeted at optimising cerebral blood flow and oxygen delivery, and revascularisation procedures.
Patients with symptomatic stenoocclusive disease have a risk of recurrent stroke of at least 10-15 per cent within 5 years. Progressive atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery (ICA) or middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the most common cause of impaired distal cerebral perfusion with cerebral misery hypoperfusion
Cerebral Hypoperfusion & Collateral Circulation In the setting of cerebral hypoperfusion, recurrent ischaemic events occur depending on the following factors: (1) amount of collateral cerebral circulation; (2) extent of haemodynamic impairment; (3) age; (4) cardiac status; (5) presence of metabolic syndrome of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance; (6) factors affecting coagulation, blood oxygen carrying capacity and delivery (such as anaemia and other haematology disorders, systemic infections and sepsis, renal and hepatic disorders).
In addition to the traditional cerebral ischaemic symptomatology pertaining to the affected vascular territory (Table 2), orthostatic symptoms, syncope, transient global amnesia, episodic limb shaking and watershed infarction are possible.
In states of misery perfusion, compensatory cerebral vasodilation is not possible as the cerebral autoregulatory capacity is exhausted and, as a result, cerebral blood flow decreases proportionally with cerebral perfusion pressure (Figure 1). Possible cerebral collateral circulation routes include: (1) contralateral internal carotid artery (ICA) through anterior communicating artery; (2) posterior circulation via posterior communicating artery; (3) leptomeningeal or pial collaterals; (4) collateral circulation from external carotid artery (ECA) with retrograde flow and connections with ophthalmic artery, extracranial connections between ECA or vertebral artery (VA) branches and distal ICA; (5) collaterals through dural meningeal arteries to cortical arteries; (6) anterior cerebral artery (ACA)-posterior cerebral artery (PCA) connections via the limbic loop; and (7) anterior spinal artery collaterals with the vertebrobasilar circulation.
Medical management principles Medical management strategies are essential to treatment of cerebral ischaemic events and prevention of recurrent strokes in face of cerebral hypoperfusion. These include: (1) cautious individualised blood pressure management (usually systolic blood pressure targets of 130-160 mmHg for those with severe bilateral carotid stenoses); (2) maintenance of fluid status to maintain appropriate plasma oncotic pressures for adequate cerebral perfusion; (3) anti-platelet and anticoagulant therapies (single anti-platelet agent and anticoagulant for those with embolic strokes or in the setting of cardiac arrthymias; dual anti-platelet therapy, with laboratory evidence of responsiveness to these agents, for those with atherosclerotic disease or perforator events), (4) statin, and (5) glycaemic control.
Treatment of underlying brainbody interactions are also essential, including attention to haemodynamic stability, cardiac status, optimising cerebral oxygen delivery with avoidance of anaemia, goal-directed therapy for sepsis, optimisation of renal perfusion and avoidance of coagulopathy and encephalopathy due to underlying multi-systemic involvement, particularly renal or hepatic impairment.
Identification of surgical candidate For patients with symptomatic severe (> 70 per cent) carotid stenosis, carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty/stenting is considered. Thrombectomy is considered for patients with embolic strokes to large size cerebral vessels. For patients who have been medically optimised but are still at risk of ischaemic symptoms of haemodynamic insufficiency due to ICA/MCA stenosis/occlusion in the setting of hypotension or orthostasis, one can identify candidates with reversible hypoperfusion, exhausted autoregulation and impaired vasodilatory reserve. Consideration of extracranialintracranial bypass procedure can be reliably made to identify patients who have reasonable chances of augmentable flow-induced long-term cerebral blood flow re-organisation (collateral shift) while preventing future hypoperfusion events. Identification of these candidates is made after blood pressure management, antithrombotic therapy and treatment of underlying brainbody interactions targeted at optimising cerebral blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Investigational adjuncts In addition to clinical findings on presentation and with monitoring (Table 2), other adjunctive investigations are useful in identifying such surgical candidates. CT perfusion scans demonstrate ischaemic penumbra of increased time-to-peak (TTP, time between first arrival of CT contrast intracranially and its peak concentration), increased mean transit time (MTT, average time for blood to travel through a volume of brain), with relatively preserved cerebral blood volume (CBV) due to vasodilation and recruitment of collateral flow, and decreased cerebral blood flow (CBF). As reference, an infarcted core shows increased TTP, increased MTT, decreased CBV and decreased CBF. SPECT (single photon emission computerised tomography) scan with acetazolamide (DiamoxTM) is used to identify patients with haemodynamic insufficiency who exhibit reversible hypoperfusion and decreased cerebrovascular reactivity when challenged with acetazolamide (Figure 3a-c). In those who are in the misery perfusion stage of haemodynamic insufficiency, they are already maximally vasodilated and dysautoregulated. In this regard, they cannot further vasodilate in response to increased carbon dioxide tension from diuretic acetazolamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
Quantitative MR angiography (q-MRA)’s non-invasive optimal vessel analysis (NOVA) is also essential to quantify and measure blood flow through large vessels of the Circle of Willis (Figure 3b). Together with formal cerebral angiography, it can be used to estimate pial and collateral flow. It gives reasonable estimates of augmentable flow to ensure appropriate blood velocity ranges after bypass, and also in anticipation of longer term collateral shift, cerebral blood flow re-organisation.
Surgical procedure Direct superficial temporal artery (STA) [donor] and middle cerebral artery (MCA) M4 cortical branch [recipient] bypass is generally preferred. Meticulous attention to blood pressure control, maintenance of intravascular volume and depth of anaesthesia are essential to avoid cerebral hypoperfusion during these cases with underlying steno-occlusive disease. Intraoperative end-to-side anastomoses are performed using 10-0 nylon sutures with indocyanine green (ICG) and intra-operative angiographic confirmation of anastomotic patency. Individualised blood pressure goals with gradual liberalisation of these parameters are done post-operatively with continuation of antithrombotic agents to maintain anastomotic patency and to avoid reperfusion-related injury.
Read More: https://www.europeanhhm.com/medical-sciences/management-of-cerebrovascular-steno-occlusive-disease
#healthcare#hospitals#health#medical care#doctors#healthy lifestyle#health and wellness#medical equipment#technologies#cerebrovascular#steno
0 notes
Text
Treatment of polycystic ovaries with herbs
Fennel
Fennel, with the scientific name of Foeniculum vulgare, is an herbaceous plant from the Apiaceae family. Fennel is known as an estrogenic compound and is used in traditional medicine to treat many digestive, endocrine, reproductive, and menstrual disorders. Fennel and its compounds have antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, antithrombotic, anti-diabetic, and anti-tumor activity ). The most important and abundant compound in fennel is a substance called Trans anethole, which has been introduced as an estrogenic active agent. Other aromatic compounds in fennel such as dianethole, photoanethole, estrogole, fenchine, and p-anisaldehyde act as estrogenic biologically active molecules .
Contact the team of doctors in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the best hospital in Sharjah to find out all the information about Treatment of polycystic ovaries with herbs.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
CRP3/MLP as a New Target to Prevent Vein Graft Failure_Crimson Publishers
CRP3/MLP as a New Target to Prevent Vein Graft Failure by Valério Garrone Barauna in Crimson Publishers

Coronary artery bypass graft surgery is the most frequently performed surgical intervention for relieving consequences associated with myocardial infarction. Despite its efficiency and advances in the methodology of collection, preservation and early onset antithrombotic treatment, vein graft failure is estimated between 15 and 30% during the first year. After 10 years of surgery, only 50% of these grafts are free of significant stenosis. Thrombosis, intimalhyperplasia, and accelerated atherosclerosis are the primary events pathophysiological of vein graft.
#crimsonpublishers#Crimson Publishers LLC#crimson publishers#surgical intervention#antithrombotic treatment
0 notes
Text
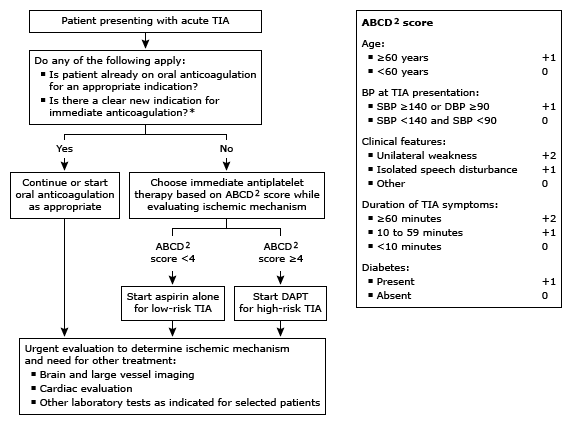
ABCD2: age, blood pressure, clinical features, duration of symptoms, and diabetes; DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (eg, aspirin and clopidogrel, or aspirin and ticagrelor); BP: blood pressure; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure. * Indications for long-term oral anticoagulation include embolism prevention for patients with atrial fibrillation, ventricular thrombus, mechanical heart valve, and treatment of venous thromboembolism.
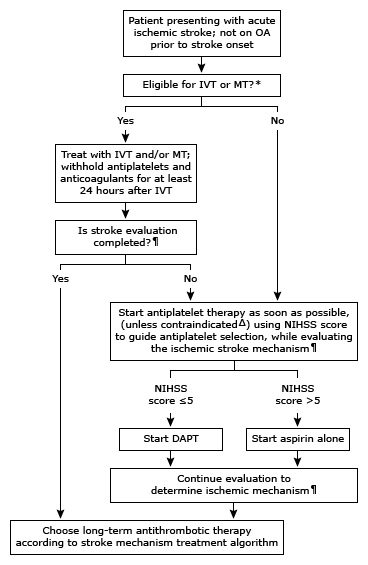
OA: oral anticoagulants; IVT: intravenous thrombolysis; MT: mechanical thrombectomy; NIHSS: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (eg, aspirin and clopidogrel, or aspirin and ticagrelor). * Refer to text and associated algorithm for details. ¶ Brain and large vessel imaging, cardiac evaluation, and (for select patients) other laboratory tests. Δ For severe systemic or symptomatic intracranial bleeding, withhold all anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy for one to two weeks or until the patient is stable.
Tx of Acute Ischemic CVA from UpToDate:
Immediate treatment– All patients with acute ischemic stroke should be evaluated to determine eligibility for reperfusion therapy with intravenous thrombolysis and/or mechanical thrombectomy, and aspirin and other antithrombotic agents should not be given alone or in combination for the first 24 hours following treatment with intravenous thrombolysis.
Otherwise, antiplatelet agents should be started as soon as possible after the diagnosis of transient ischemic attack (TIA) or ischemic stroke is confirmed, even before the evaluation for ischemic mechanism is complete. For most patients with no indication for long-term oral anticoagulation who have TIA (algorithm 2 [first algorithm above]) or ischemic stroke (algorithm 3 [second algorithm above]), we start antiplatelet therapy as follows:
•Aspirin alone – For patients with a low-risk TIA, defined by an ABCD2 score <4 (table 2), or moderate to major ischemic stroke, defined by a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score >5 (table 3), we start treatment with aspirin (162 to 325 mg daily) alone.
•DAPT – For patients with a high-risk TIA, defined by an ABCD2 score ≥4 (table 2), or minor ischemic stroke, defined by a NIHSS score ≤5 (table 3), we begin with dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) for 21 days using aspirin (160 to 325 mg loading dose, followed by 50 to 100 mg daily) plus clopidogrel (300 to 600 mg loading dose, followed by 75 mg daily) rather than aspirin alone.
●Treatment by ischemic mechanism – Once the evaluation for TIA or stroke is complete, early antithrombotic therapy can be modified if necessary (algorithm 4 and algorithm 5) according to the ischemic mechanism:
•Atrial fibrillation – For patients with TIA or ischemic stroke who have atrial fibrillation, oral anticoagulation with warfarin or a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) is recommended for secondary stroke prevention. Oral anticoagulation can be started immediately for patients with TIA, and soon after stroke onset for medically stable patients with a small- or moderate-sized infarct and no bleeding complications or uncontrolled hypertension. For patients with large infarctions, symptomatic hemorrhagic transformation, or poorly controlled hypertension, withholding oral anticoagulation for one to two weeks is generally recommended.
•Intracardiac thrombus – For patients with acute cardioembolic TIA or ischemic stroke who have intracardiac thrombus in the left ventricle or associated with mechanical or native heart valves, we suggest early parenteral anticoagulation rather than aspirin (Grade 2C). This approach is controversial.
•No indication for anticoagulation – For most patients without atrial fibrillation or another indication for long-term oral anticoagulation, the initial antiplatelet regimen can be continued; for patients with low-risk TIA or moderate to severe stroke, we recommend aspirin monotherapy (160 to 325 mg daily) (Grade 1A). For patients with high-risk TIA or minor ischemic stroke, we recommend DAPT using aspirin and clopidogrel for 21 days rather than aspirin alone (Grade 1A).
However, certain additional modifications may apply:
-Carotid revascularization – Aspirin monotherapy is preferred by some experts prior to carotid endarterectomy, while DAPT is preferred by others. DAPT is recommended prior to and continuing for 30 days after carotid artery stenting.
-Intracranial large artery atherosclerosis – For patients with TIA or ischemic stroke attributed to intracranial large artery atherosclerosis stenosis of 70 to 99 percent, we suggest DAPT for 90 days.
-Dissection – The antithrombotic treatment of TIA or ischemic stroke caused by large artery dissection is discussed in detail separately.
●Long-term antiplatelet therapy – Beyond the acute phase of TIA and ischemic stroke, and in the absence of an indication for oral anticoagulation, long-term single-agent antiplatelet therapy for secondary stroke prevention should be continued with aspirin, clopidogrel, or aspirin-extended-release dipyridamole. Long-term DAPT with aspirin and clopidogrel is not recommended.
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Guide to Outpatient COVID Treatment: Step-By-Step Doctors’ Plan That Could Save Your Life
Recently, Dr. Peter McCullough, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas testified to Texas Senate HHS Committee about how mass media and even some government agencies are silencing clinical outpatient evidence for effective treatment of COVID19 and instead push vaccines only (video shown below).
Treatments like those mentioned by Dr. McCullough can be found in sites like https://c19early.com/ but specifically, McCullough refers to the following Appendix to a document published by Association of American Physicians and Surgeons (AAPSonline.org) as an educational resource. It is based on a paper published in American Journal of Medicine (link), by Dr. Peter McCullough and 22 other clinicians (MDs) and researchers (PhDs).
“Seek early treatment and be your own advocate. All of the physicians contributing to this booklet are on the frontlines treating outpatients at the first signs of COVID illness. Studies in the US and many other countries clearly show that patients who are treated within the first 5 days of symptoms have better outcomes using the combination of medications in the algorithm below.”

COVID-19 hospitalizations and death can be reduced with outpatient treatment.
Principles of COVID-19 outpatient care include: 1) reduction of reinoculation, 2) combination antiviral therapy, 3) immunomodulation, 4) antiplatelet/antithrombotic therapy 5) administration of oxygen, monitoring, and telemedicine.
“For the ambulatory patient with recognized early signs and symptoms of COVID-19, often with nasal real-time reverse transcription or oral antigen testing pending, the following 4 principles could be deployed in a layered and escalating manner depending on clinical manifestations of COVID-19-like illness and confirmed infection: 1) reduction of reinoculation, 2) combination antiviral therapy, 3) immunomodulation, and 4) antiplatelet/antithrombotic therapy. Because the results of testing could take up to a week to return, treatment can be started before the results are known. For patients with cardinal features of the syndrome (ie, fever, body aches, nasal congestion, loss of taste and smell, etc.) and suspected false-negative testing, treatment can be the same as those with confirmed COVID-19. Future randomized trials are expected to confirm, reject, refine, and expand these principles. In this article, they are set forth in emergency response to the growing pandemic as shown in Figure 1 .
Treatment algorithm for COVID-19-like and confirmed COVID-19 illness in ambulatory patients at home in self-quarantine. BMI = body mass index; CKD = chronic kidney disease; CVD = cardiovascular disease; DM = diabetes mellitus; Dz = disease; HCQ = hydroxychloroquine; Mgt = management; O2 = oxygen; Ox = oximetry; Yr = year.
The basic groups of prescription medicines and other therapies used in COVID-19:
▪ Combination anti-viral medicines started as soon as symptoms occur ▪ Medicines to decrease inflammation, such as corticosteroids (called immunomodulators)
▪ Anticoagulant therapy to prevent blood-clots that can cause strokes, heart attacks, kidney shut-down, and death.
▪ Non-prescription supportive treatments with zinc, vitamin D, vitamin C, electrolyte drinks such as Pedialyte, and others.
▪ Home-based oxygen support, such as with an oxygen concentrator. These machines are available by physician prescription from home health medical supply businesses and are covered on most medical insurance plans.
I. Antiviral Agents:
These must be started quickly at STAGE I (Days 1-5):
Symptoms include sore throat, nasal stuffiness, fatigue, headaches, body aches, loss of taste and/or smell, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, fever.
These medicines stop the virus from (1) entering the cells and (2) from multiplying once inside the cells, and they reduce bacterial invasion in the sinuses and lung:
▪ *Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) with azithromycin (AZM) or doxycycline
OR
▪ Ivermectin with azithromycin (AZM) or doxycycline
Either combination above must also include zinc sulfate or gluconate, plus supplemental vitamin D, and vitamin C. Some doctors also recommend adding a B complex vitamin.
Zinc is critical. It helps block the virus from multiplying.
Hydroxychloroquine is the carrier taking zinc INTO the cells to do its job.
An educational resource from The Association of American Physicians and Surgeons (AAPSonline.org) 16
II. Anti-inflammatory Agents - Corticosteroids (“steroids”): Oral and Nebulized.
These are started at STAGE II (Days 3-14) to reduce inflammation, the cause of added damage to the lungs and critical organs. Symptoms include worsening cough, difficulty breathing, chest heaviness/tightness or chest pain.
As inflammation damages the airways interfering with normal oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange, blood oxygen levels drop and people experience loss of focus, drowsiness, confusion, difficulty concentrating, low energy and severe fatigue.
The exaggerated Inflammation response in COVID further increases the risk of blood clots.
Prescription medicines and other support added now to Stage I medicines are: ▪ nebulized budesonide to help penetrate the lungs and reduce inflammation ▪ oral prednisone, methylprednisolone, dexamethasone
▪ colchicine – may also be added to reduce inflammation
▪ full strength adult aspirin 325 mg to reduce inflammation and risk of blood clots ▪ home oxygen concentrator may be needed to improve oxygen levels (requires physician prescription)
III. Prescription Anticoagulants (“blood thinners”):
STAGE III (Day 7 and beyond): Symptoms seen in Stage II intensify. Difficulty breathing becomes extreme, oxygen levels drop sharply, risk of heart attack or stroke increases. At this point, people are critically ill.
The medicines to be added to Stage I and II medicines now include:
▪ Aspirin 325 mg unless told not to take by your doctors
▪ And/or low molecular weight heparin injections (e.g. enoxaparin [Lovenox]) OR
▪ apixaban (Eliquis), or rivaroxaban (Xarelto), or dabigatran (Pradaxa) or
edoxaban (Savaysa) in standard doses for 5 to 30 days
If these added steps do not lead to improvement, or the patient becomes unstable, a 911 call is warranted for ER evaluation and hospital admission so that more aggressive IV medications (such as remdesivir, Regeneron, and others) may be considered, and more intensive ventilation regimens are possible in ICU settings.
IV. Vitamins, Supplements, and Oxygen.
▪ Zinc sulfate, gluconate or citrate. These forms are available in pharmacies, health food stores, and sold online. Zinc sulfate 220 mg provides 50 mg elemental zinc, the recommended anti-viral dose. Zinc in the form of zinc picolinate form is not recommended following reports of liver damage and tumors from studies about 20 years ago. Following these reports, the German Commission E that regulates supplements used in medical practice in Germany banned this form of zinc.
An educational resource from The Association of American Physicians and Surgeons (AAPSonline.org) 17
▪ Vitamin D3, preferable in oil in capsules for better absorption. Recommended doses for anti-viral benefit vary from 5000 IU or more for 5-30 days
▪ Vitamin C with bioflavonoids for antioxidant, anti-inflammatory effects. Dose
recommendations from our contributors vary from 1000 mg (1 gram) once or twice a day up to 4 or more times a day.
▪ A word about quercetin. Some physicians are recommending this supplement to reduce viral illnesses because quercetin acts as a zinc ionophore to improve zinc
uptake into cells. It is much less potent than HCQ as a zinc transporter, and it does
not reach high concentrations in lung cells that HCQ does. Quercetin may help
reduce risk of viral illness if you are basically healthy. But it is not potent enough to replace HCQ for treatment of COVID once you have symptoms, and it does not
adequately get into lung tissue unless you take massive doses (3-5 grams a day),
which cause significant GI side effects such as diarrhea.
Control of Contagion
A major goal of self-quarantine is the control of contagion. Many sources of information suggest the main place of viral transmission occurs in the home. Facial covering for all contacts within the home as well as frequent use of hand sanitizer and hand washing is mandatory. Sterilizing surfaces such as countertops, door handles, phones, and other devices is advised. When possible, other close contacts can move out of the domicile and temporarily stay with others not ill with SARS-CoV-2. Findings from multiple studies indicate that policies concerning control of the spread of SARS-CoV-2 are effective and extension into the home as the most frequent site of viral transfer is paramount.
Reduction of Self-Reinoculation
It is well-recognized that COVID-19 exists outside the human body in a bioaerosol of airborne particles and droplets. Because exhaled air in an infected person is considered to be “loaded” with inoculum, each exhalation and inhalation is effectively reinoculation. In patients who are hospitalized, negative pressure is applied to the room air largely to reduce spread outside of the room. We propose that fresh air could reduce reinoculation and potentially reduce the severity of illness and possibly reduce household spread during quarantine. This calls for open windows, fans for aeration, or spending long periods of time outdoors away from others with no face covering to disperse and not reinhale the viral bioaerosol.
Combination Antiviral Therapy
Rapid and amplified viral replication is the hallmark of most acute viral infections. By reducing the rate, quantity, or duration of viral replication, the degree of direct viral injury to the respiratory epithelium, vasculature, and organs may be lessened. Additionally, secondary processes that depend on viral stimulation, including the activation of inflammatory cells, cytokines, and coagulation, could potentially be lessened if viral replication is attenuated. Because no form of readily available medication has been designed specifically to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication, 2 or more of the nonspecific agents listed here can be entertained. None of the approaches listed have specific regulatory approved advertising labels for their manufacturers; thus all would be appropriately considered acceptable “off-label” use.
Zinc Lozenges and Zinc Sulfate
Zinc is a known inhibitor of coronavirus replication. Clinical trials of zinc lozenges in the common cold have demonstrated modest reductions in the duration and or severity of symptoms. By extension, this readily available nontoxic therapy could be deployed at the first signs of COVID-19. Zinc lozenges can be administered 5 times a day for up to 5 days and extended if needed if symptoms persist. The amount of elemental zinc lozenges is <25% of that in a single 220-mg zinc sulfate daily tablet. This dose of zinc sulfate has been effectively used in combination with antimalarials in early treatment of high-risk outpatients with COVID-19.
Antimalarials
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is an antimalarial/anti-inflammatory drug that impairs endosomal transfer of virions within human cells. HCQ is also a zinc ionophore that conveys zinc intracellularly to block the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which is the core enzyme of the virus replication. The currently completed retrospective studies and randomized trials have generally shown these findings: 1) when started late in the hospital course and for short durations of time, antimalarials appear to be ineffective, 2) when started earlier in the hospital course, for progressively longer durations and in outpatients, antimalarials may reduce the progression of disease, prevent hospitalization, and are associated with reduced mortality. In a retrospective inpatient study of 2541 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, therapy associated with an adjusted reduction in mortality was HCQ alone (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.34, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.25-0.46, P <0.001) and HCQ with azithromycin (HR = 0.29, 95% CI 0.22-0.40, P <0.001). HCQ was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 1955, has been used by hundreds of millions of people worldwide since then, is sold over the counter in many countries, and has a well-characterized safety profile that should not raise undue alarm. Although asymptomatic QT prolongation is a well-recognized and infrequent (<1%) complication of HCQ, it is possible that in the setting of acute illness symptomatic arrhythmias could develop. Data safety and monitoring boards have not declared safety concerns in any clinical trial published to date. Rare patients with a personal or family history of prolonged QT syndrome and those on additional QT prolonging, contraindicated drugs (eg, dofetilide, sotalol) should be treated with caution and a plan to monitor the QTc in the ambulatory setting. A typical HCQ regimen is 200 mg bid for 5 days and extended to 30 days for continued symptoms. A minimal sufficient dose of HCQ should be used, because in excessive doses the drug can interfere with early immune response to the virus.
Azithromycin
Azithromycin is a commonly used macrolide antibiotic that has antiviral properties mainly attributed to reduced endosomal transfer of virions as well as established anti-inflammatory effects. It has been commonly used in COVID-19 studies initially based on French reports demonstrating markedly reduced durations of viral shedding, fewer hospitalizations, and reduced mortality combination with HCQ as compared to those untreated. In the large inpatient study (n = 2451) discussed previously, those who received azithromycin alone had an adjusted HR for mortality of 1.05, 95% CI 0.68-1.62, and P = 0.83.23 The combination of HCQ and azithromycin has been used as standard of care in other contexts as a standard of care in more than 300,000 older adults with multiple comorbidities. This agent is well-tolerated and like HCQ can prolong the QTc in <1% of patients. The same safety precautions for HCQ listed previously could be extended to azithromycin with or without HCQ. Azithromycin provides additional coverage of bacterial upper respiratory pathogens that could potentially play a role in concurrent or secondary infection. Thus, this agent can serve as a safety net for patients with COVID-19 against clinical failure of the bacterial component of community-acquired pneumonia. The same safety precautions for HCQ could be extended to azithromycin with or without HCQ. Because both HCQ and azithromycin have small but potentially additive risks of QTc prolongation, patients with known or suspected arrhythmias or taking contraindicated medications or should have more thorough workup (eg, review of baseline electrocardiogram, imaging studies, etc.) before receiving these 2 together. One of many dosing schemes is 250 mg po bid for 5 days and may extend to 30 days for persistent symptoms or evidence of bacterial superinfection.
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is another common antibiotic with multiple intracellular effects that may reduce viral replication, cellular damage, and expression of inflammatory factors. This drug has no effect on cardiac conduction and has the main caveat of gastrointestinal upset and esophagitis. As with azithromycin, doxycycline has the advantage of offering antibacterial coverage for superimposed bacterial infection in the upper respiratory tract. Doxycycline has a high degree of activity against many common respiratory pathogens including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, anaerobes such as Bacteroides and anaerobic/microaerophilic streptococci and atypical agents like Legionella, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Chlamydia pneumoniae. One of many dosing schemes is 200 mg po followed by 100 mg po bid for 5 days and may extend to 30 days for persistent symptoms or evidence of bacterial superinfection. Doxycycline may be useful with HCQ for patients in whom the HCQ-azithromycin combination is not desired.
Favipiravir
Favipiravir, an oral selective inhibitor of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, is approved for ambulatory use in COVID-19 in Russia, India, and other countries outside of the United States.35 It has been previously used for treatment of some life-threatening infections such as Ebola virus, Lassa virus, and rabies. Its therapeutic efficacy has been proven in these diseases. Like, the antimalarials and antibiotics, favipiravir has no large-scale randomized trials completed at this time, given the short time frame of the pandemic. A dose administration could be 1600 mg po bid on day 1, following by 600 mg po bid for 14 days.
Immunomodulators
The manifestations of COVID-19 that prompt hospitalization and that may well lead to multiorgan system failure are attributed to a cytokine storm. The characteristic profile of a patient acutely ill with COVID-19 includes leukocytosis with a relative neutropenia. These patients have higher serum level of cytokines (ie, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10) and C-reactive protein than control individuals. Among patients with COVID-19, serum IL-6 and IL-10 levels appear even more elevated in the critically ill. As with any acute inflammatory state, early treatment with immunomodulators is expected to impart greater benefit. In COVID-19, some of the first respiratory findings are nasal congestion, cough, and wheezing. These features are due to excess inflammation and cytokine activation. Early use of corticosteroids is a rational intervention for patients with COVID-19 with these features as they would be in acute asthma or reactive airways disease. The RECOVERY trial randomized 6425 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in a 2:1 ratio to dexamethasone 6 mg po/IV daily for up to 10 days and found dexamethasone reduced mortality (HR = 0.65, 95% CI 0.51-0.82, P <0.001). One potential dosing scheme for outpatients starting on day 5 or the onset of respiratory symptoms is prednisone 1 mg/kg given daily for 5 days with or without a subsequent taper.
Colchicine
Colchicine is a nonsteroidal antimitotic drug that blocks metaphase by binding to the ends of microtubules to prevent the elongation of the microtubule polymer. This agent has proven useful in gout and idiopathic recurrent pericarditis. The GRECCO-19 randomized open-label trial in 105 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 found that colchicine was associated with a reduction in D-dimer levels and improved clinical outcomes. The clinical primary end point (2-point change in World Health Organization ordinal scale) occurred in 14.0% in the control group (7 of 50 patients) and 1.8% in the colchicine group (1 of 55 patients) (odds ratio, 0.11; 95% CI, 0.01-0.96; P = 0.02). Because the short-term safety profile is well understood, it is reasonable to consider this agent along with corticosteroids in an attempt to reduce the effects of cytokine storm. A dosing scheme of 1.2 mg po, followed by 0.6 mg po bid for 3 weeks can be considered.
Antiplatelet Agents and Antithrombotics
Multiple studies have described increased rates of pathological macro- and micro-thrombosis. Patients with COVID-19 have described chest heaviness associated with desaturation that suggests the possibility of pulmonary thrombosis. Multiple reports have described elevated D-dimer levels in acutely ill patients with COVID-19, which has been consistently associated with increased risk of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Necropsy studies have described pulmonary microthrombosis in COVID-19. These observations support the notion that endothelial injury and thrombosis play a role oxygen desaturation, a cardinal reason for hospitalization and supportive care. Based on this pathophysiologic rationale, aspirin 81 mg daily can be administered as an initial antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory agent. Ambulatory patients can be additionally treated with subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin or with short-acting novel anticoagulant drugs in dosing schemes similar to those use in outpatient thromboprophylaxis. In a retrospective study of 2773 inpatients with COVID-19, 28% received anticoagulant therapy within 2 days of admission, and despite being used in more severe cases, anticoagulant administration was associated with a reduction in mortality (HR = 0.86 per day of therapy, 95% CI: 0.82-0.89; P <0.001). Additional supportive data on the use anticoagulants reducing mortality has been reported in hospitalized patients with elevated D-dimer levels and higher comorbidity scores.53 Many acutely ill outpatients also have general indications for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis applicable to COVID-19.
Delivery of Oxygen and Monitoring
Because ambulatory centers and clinics have been reticent to have face-to-face visits with patients with COVID-19, telemedicine is a reasonable platform for monitoring. Clinical impressions can be gained with audio and video interviews by the physician with the patient. Supplemental information, including vital signs and symptoms, will be important to guide the physician. A significant component of safe outpatient management is maintenance of arterial oxygen saturation on room air or prescribed home oxygen under direct supervision by daily telemedicine with escalation to hospitalization for assisted ventilation if needed. Self-proning could be entertained for confident patients with good at-home monitoring.
Many of the measures discussed in this article could be extended to seniors in COVID-19 treatment units in nursing homes and other nonhospital settings. This would leave the purposes of hospitalization to the administration of intravenous fluid and parenteral medication, assisted pressure or mechanical ventilation, and advanced mechanical circulatory support.”
youtube
This is the group’s statement on vaccines:
“Vaccines in Development:
Several vaccine models are being investigated for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) including DNA and RNA vaccines. These vaccines take genetic information from other sources that is introduced into the cells. This information includes instructions to produce a SARS2-like viral antigen itself, and the immune system then reacts to it to develop immunity to the virus.
The most important consideration before approving a vaccine for human use is to make sure that the vaccine is safe and effective. Developing safe and controlled infection models for humans normally takes many years of phased testing in the lab and then in humans. Many physicians and scientists have been concerned that vaccine manufacturers, with government support, are speeding up this process in ways that are not allowing adequate time for the usual phased testing leading up to human clinical trials. Two vaccine manufacturers already have voluntarily paused their clinical trials in people due to serious adverse events.
Currently, there are no RNA-based vaccines approved for human use so it would seem prudent to take the time needed to ensure safety. Vaccines for RNA viruses are notoriously challenging and difficult to develop. We still, after all these years since AIDS emerged in the 1980s, do not have a vaccine for the AIDS virus, or the SARS-1 coronavirus that emerged in 2002-2003, and both are RNA viruses.
Several attempts have been made to create vaccines for coronavirus and other respiratory viruses but none of the vaccines have survived the testing phases. The vaccine trials for SARS-1 from 2003, for example, was shut down because it produced autoimmune hypersensitivity reactions when exposed to the natural virus after immunization in animal studies.
Another problem is that the SARS-2 virus has already shown many mutations. Viruses adapt to the environment to survive. Like the flu virus, it is difficult to predict what mutations will occur and circulate around the world each season. A new vaccine must be reformulated to adjust to the changing genetic makeup of the SARS-2 virus.
Even the best vaccines for flu are only about 30-60% effective. Compare that with an effectiveness for improvement ranging from 64% to more than 90% in more than 100 new studies showing early, outpatient treatment with our existing medications described in chapters.
As research on the vaccine continues, safety and effectiveness are of primary concern. The good news is there are very safe and effective early treatments already available as we described in Chapter 3. Clearly, early, home-based treatment has now been so successful and offers so much hope, there is less urgency to have a vaccine.”
You can sign up to receive the full protocol here: https://aapsonline.org/covidpatientguide/ or find the research paper here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7410805/
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hematuria Treatment Market 2021-2027 High Key Players For Market, Application, Product Sort, Statement
Hematuria Treatment Market Overview :
The hematuria treatment market is accruing rapidly mainly due to the increasing number of bladder or kidney stones; kidney disease; urinary tract infection, cystitis (bladder infection), or pyelonephritis (kidney infection); cancers of the urinary tract (kidney, bladder, prostate); trauma, injury, or urinary tract instrumentation; rigorous exercise; benign prostatic hyperplasia; and blood thinners for such as Antithrombotic medications.
In addition to the chronic diseases, infection or diseases are too impacting the market growth positively. At the same time, there are various treatments and novel medications available for hematuria management which are pushing up the market on the global platform.
Acknowledging the colossal growth, the market is witnessing currently, Market Research Future (MRFR) in its recently published study report asserts that the global hematuria treatment market will grow exponentially by 2023 accruing at a striking CAGR during the forecast period (2018 – 2023).
Furthermore, technological advancements transpired in the field of hematuria management and advent treatment materials are fostering the market growth of hematuria treatment to an extent.
On the other hand, factors such as the complications in the treatment, high cost of product developments, and stringent regulations for approvals are expected to obstruct the market growth during the assessment period. Also, the pending or imminent patent expiries of many blockbuster hematuria management drugs are some hampering the market growth.
Nevertheless, factors like the instigation of a large number of regulatory healthcare reforms, developments of methods for the improved diagnosis and treatments for hematuria are expected to support the market growth bringing about the hematuria management therapeutics and treading along a promising increase in the next few years.
Hematuria Treatment Market – Segments :
The MRFR analysis is segmented into five key dynamics for the convenience of understanding;
By Type : Gross/ Macroscopic Hematuria, Microscopic Hematuria, Idiopathic Hematuria, and Jogger’s Hematuria.
By Causes : Kidney Stones, Urinary Tract Infections (UTI), Urethritis, Blood Cancer, Bladder Stones, Prostate Cancer, Cystitis, Trauma, Vigorous Exercise, Polycystic Kidney Disease, Endometriosis, and Menstruation.
By Treatment : Drugs and Therapeutics, among others.
By End-user : Hospitals, Clinics, and Labs among others.
By Regions : North America, Europe, APAC, and the Rest-of-the-World.
Get Free Sample of This Report at : https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/sample_request/1732
Hematuria Treatment Market – Regional Analysis :
The North American region dominates the global hematuria treatments market. The growing prevalence of kidney diseases, bladder cancer, and others along with the high per capita healthcare expenses drive the growth in the regional market.
Some of the factors such as the increasing technological innovations in medical science and the growing investments into R&D to develop new techniques to treat hematuria are substantiating market growth.
Besides the high consumption of antibiotics in the treatment of various chronic diseases, the presence of a well-established healthcare system, and rising cases of trauma & accidents foster the growth of the hematuria management market in the region.
Europe hematuria treatment market stands at the second position in terms of the size. The market in this region exhibits a phenomenal growth prospect throughout the review period.
Furthermore, factors like financial support from the government for R&D activities, and the increasing demand for hematuria treatments & devices drive the market growth in the region. Besides, the rising incidences of accidental injuries are contributing to the market growth in this region, generating a massive demand for the management of hematuria.
The Asia Pacific hematuria treatment market is emerging as a profitable market. Factors such as the increasing healthcare expenditure and increasing prevalence of hematuria led by the growing incidences of infections related to the urinary tract, bladder, and kidney drive the growth of the hematuria treatment market in the region.
The increasing governmental funding alongside a large unmet needs presages towards the growth opportunities for the market players. Spreading awareness about the availability of different hematuria management procedures is accelerating the market growth in the region. Besides, the availability of low-cost, quality hematuria management methods drives the regional market.
Hematuria Treatment Market – Competitive Analysis :
The highly competitive hematuria treatment market appears fragmented owing to a number of players and the increasing investments made by them in R&D activities in the hematuria management. Through the strategic partnership, acquisition, expansion, product & technology launch, and collaboration, these players try to gain a competitive edge.
Hematuria Treatment Market Key Players :
Some of the leaders of the market include Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca Plc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline Inc., Merck & Co., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Limited, Novartis International AG, Pfizer, Inc., and The Medicines Company among others.
Industry/Innovation/Related News :
January 22, 2018 – Researchers at the Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre’s Division of Urology (Canada) published the result of their study to investigate or manage hematuria in the Journal of the American Medical Association. Researchers examined the rate of hematuria-related complications in over 800,000 elderly patients. And, found that Antithrombotic medications, commonly known as blood thinners are associated with significant adverse events such as blood in the urine (hematuria) or the bleeding within the skull and stomach/ intestines as these drugs allow blood to flow easier throughout the cardiovascular system.
Browse Full Report with TOC at : https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/hematuria-treatment-market-1732
#HematuriaTreatmentresearchreports#HematuriaTreatmentmarketsize#HematuriaTreatmentindustryanalysis#HematuriaTreatmentmarketanalysis#HematuriaTreatmentmarketresearch#HematuriaTreatmentmarket
1 note
·
View note
Text
Management of Cerebrovascular Steno-Occlusive Disease

Patients with steno-occlusive cerebrovascular disease are at risk of ischemic symptoms from haemodynamic insufficiency in the presence of reversible hypoperfusion, exhausted autoregulation and impaired vasodilatory reserve. Multidisciplinary management approach includes blood pressure management, antithrombotic therapy, treatment of underlying brain-body interactions targeted at optimising cerebral blood flow and oxygen delivery, and revascularisation procedures.
Patients with symptomatic stenoocclusive disease have a risk of recurrent stroke of at least 10-15 per cent within 5 years. Progressive atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery (ICA) or middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the most common cause of impaired distal cerebral perfusion with cerebral misery hypoperfusion
Cerebral Hypoperfusion & Collateral Circulation In the setting of cerebral hypoperfusion, recurrent ischaemic events occur depending on the following factors: (1) amount of collateral cerebral circulation; (2) extent of haemodynamic impairment; (3) age; (4) cardiac status; (5) presence of metabolic syndrome of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance; (6) factors affecting coagulation, blood oxygen carrying capacity and delivery (such as anaemia and other haematology disorders, systemic infections and sepsis, renal and hepatic disorders).
In addition to the traditional cerebral ischaemic symptomatology pertaining to the affected vascular territory (Table 2), orthostatic symptoms, syncope, transient global amnesia, episodic limb shaking and watershed infarction are possible.
In states of misery perfusion, compensatory cerebral vasodilation is not possible as the cerebral autoregulatory capacity is exhausted and, as a result, cerebral blood flow decreases proportionally with cerebral perfusion pressure (Figure 1). Possible cerebral collateral circulation routes include: (1) contralateral internal carotid artery (ICA) through anterior communicating artery; (2) posterior circulation via posterior communicating artery; (3) leptomeningeal or pial collaterals; (4) collateral circulation from external carotid artery (ECA) with retrograde flow and connections with ophthalmic artery, extracranial connections between ECA or vertebral artery (VA) branches and distal ICA; (5) collaterals through dural meningeal arteries to cortical arteries; (6) anterior cerebral artery (ACA)-posterior cerebral artery (PCA) connections via the limbic loop; and (7) anterior spinal artery collaterals with the vertebrobasilar circulation.
Medical management principles Medical management strategies are essential to treatment of cerebral ischaemic events and prevention of recurrent strokes in face of cerebral hypoperfusion. These include: (1) cautious individualised blood pressure management (usually systolic blood pressure targets of 130-160 mmHg for those with severe bilateral carotid stenoses); (2) maintenance of fluid status to maintain appropriate plasma oncotic pressures for adequate cerebral perfusion; (3) anti-platelet and anticoagulant therapies (single anti-platelet agent and anticoagulant for those with embolic strokes or in the setting of cardiac arrthymias; dual anti-platelet therapy, with laboratory evidence of responsiveness to these agents, for those with atherosclerotic disease or perforator events), (4) statin, and (5) glycaemic control.
Treatment of underlying brainbody interactions are also essential, including attention to haemodynamic stability, cardiac status, optimising cerebral oxygen delivery with avoidance of anaemia, goal-directed therapy for sepsis, optimisation of renal perfusion and avoidance of coagulopathy and encephalopathy due to underlying multi-systemic involvement, particularly renal or hepatic impairment.
Identification of surgical candidate For patients with symptomatic severe (> 70 per cent) carotid stenosis, carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty/stenting is considered. Thrombectomy is considered for patients with embolic strokes to large size cerebral vessels. For patients who have been medically optimised but are still at risk of ischaemic symptoms of haemodynamic insufficiency due to ICA/MCA stenosis/occlusion in the setting of hypotension or orthostasis, one can identify candidates with reversible hypoperfusion, exhausted autoregulation and impaired vasodilatory reserve. Consideration of extracranialintracranial bypass procedure can be reliably made to identify patients who have reasonable chances of augmentable flow-induced long-term cerebral blood flow re-organisation (collateral shift) while preventing future hypoperfusion events. Identification of these candidates is made after blood pressure management, antithrombotic therapy and treatment of underlying brainbody interactions targeted at optimising cerebral blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Investigational adjuncts In addition to clinical findings on presentation and with monitoring (Table 2), other adjunctive investigations are useful in identifying such surgical candidates. CT perfusion scans demonstrate ischaemic penumbra of increased time-to-peak (TTP, time between first arrival of CT contrast intracranially and its peak concentration), increased mean transit time (MTT, average time for blood to travel through a volume of brain), with relatively preserved cerebral blood volume (CBV) due to vasodilation and recruitment of collateral flow, and decreased cerebral blood flow (CBF). As reference, an infarcted core shows increased TTP, increased MTT, decreased CBV and decreased CBF. SPECT (single photon emission computerised tomography) scan with acetazolamide (DiamoxTM) is used to identify patients with haemodynamic insufficiency who exhibit reversible hypoperfusion and decreased cerebrovascular reactivity when challenged with acetazolamide (Figure 3a-c). In those who are in the misery perfusion stage of haemodynamic insufficiency, they are already maximally vasodilated and dysautoregulated. In this regard, they cannot further vasodilate in response to increased carbon dioxide tension from diuretic acetazolamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
Quantitative MR angiography (q-MRA)’s non-invasive optimal vessel analysis (NOVA) is also essential to quantify and measure blood flow through large vessels of the Circle of Willis (Figure 3b). Together with formal cerebral angiography, it can be used to estimate pial and collateral flow. It gives reasonable estimates of augmentable flow to ensure appropriate blood velocity ranges after bypass, and also in anticipation of longer term collateral shift, cerebral blood flow re-organisation.
Surgical procedure Direct superficial temporal artery (STA) [donor] and middle cerebral artery (MCA) M4 cortical branch [recipient] bypass is generally preferred. Meticulous attention to blood pressure control, maintenance of intravascular volume and depth of anaesthesia are essential to avoid cerebral hypoperfusion during these cases with underlying steno-occlusive disease. Intraoperative end-to-side anastomoses are performed using 10-0 nylon sutures with indocyanine green (ICG) and intra-operative angiographic confirmation of anastomotic patency. Individualised blood pressure goals with gradual liberalisation of these parameters are done post-operatively with continuation of antithrombotic agents to maintain anastomotic patency and to avoid reperfusion-related injury.
Conclusion For patients who have been medically optimised but still at risk of ischemic symptoms of haemodynamic insufficiency due to steno-occlusive cerebrovascular disease, one can identify candidates with reversible hypoperfusion, exhausted autoregulation and impaired vasodilatory reserve. Consideration of extracranial-intracranial bypass procedure can be reliably made to identify patients who have reasonable chances of augmentable flow-induced long-term cerebral flow re-organisation while preventing future hypoperfusion events. Identification of these candidates are made after medical optimisation, including blood pressure management, antithrombotic therapy and treatment of underlying brain-body interactions targeted at optimising cerebral blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Read More: https://www.europeanhhm.com/medical-sciences/management-of-cerebrovascular-steno-occlusive-disease
#doctors#health and wellness#healthy lifestyle#medical equipment#medical care#technologies#health#healthcare#hospitals#medical science#healthcare management#cerebrovascular#disease
0 notes
Link
2020 Yale-G’s Monthly Clinical Updates According to www.uptodate.com
(As of 2020-11-12, updated in Yale-G’s 6th-Ed Kindle Version; will be emailed to buyers of Ed6 paper books)
Chapter 1: Infectious Diseases
Special Viruses: Coronaviruses
Coronaviruses are important human and animal pathogens, accounting for 5-10% community-acquired URIs in adults and probably also playing a role in severe LRIs, particularly in immunocompromised patients and primarily in the winter. Virology: Medium-sized enveloped positive-stranded RNA viruses as a family within the Nidovirales order, further classified into four genera (alpha, beta, gamma, delta), encoding 4-5 structural proteins, S, M, N, HE, and E; severe types: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV, which causes COVID-19). Routes of transmission: Similar to that of rhinoviruses, via direct contact with infected secretions or large aerosol droplets. Immunity develops soon after infection but wanes gradually over time. Reinfection is common. Clinical manifestations: 1. Coronaviruses mostly cause respiratory symptoms (nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, and cough) and influenza-like symptoms (fever, headache). 2. Severe types (2019-nCoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV): Typically with pneumonia–fever, cough, dyspnea, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, and sometimes enterocolitis (diarrhea), particularly in immunocompromised hosts (HIV+, elders, children). 3. Most community-acquired coronavirus infections are diagnosed clinically, although RT-PCR applied to respiratory secretions is the diagnostic test of choice.
Treatment: 1. Mainly consists of ensuring appropriate infection control and supportive care for sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome. 2. In study: Chloroquine showed activity against the SARS-CoV, HCoV-229E, and HCoV-OC43 and remdesivir against 2019-nCoV. Dexamethasone may have clinical benefit.
Prevention: 1. For most coronaviruses: The same as for rhinovirus infections, which consist of handwashing and the careful disposal of materials infected with nasal sec retions. 2. For novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV: (1) Preventing exposure by diligent hand washing, respiratory hygiene, and avoiding close contact with live or dead animals and ill individuals. (2) Infection control for suspected or confirmed cases: Wear a medical mask to contain their respiratory secretions and seek medical attention; standard contact and airborne precautions, with eye protection.
Hepatitis A: HAV vaccine is newly recommended to adults at increased risk for HAV infection (substance use treatment centers, group homes, and day care facilities for disabled persons), and to all children and adolescents aged 2 to 18 years who have not previously received HAV vaccine.
Hepatitis C: 8-week glecaprevir-pibrentasvir is recommended for chronic HCV infection in treatment-naive patients. In addition to the new broad one-time HCV screening (17-79 y/a), a repeated screening in individuals with ongoing risk factors is suggested.
New: Lefamulin is active against many common community-acquired pneumonia pathogens, including S. pneumoniae, Hib, M. catarrhalis, S. aureus, and atypical pathogens.
New: Cefiderocol is a novel parenteral cephalosporin that has activity against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria, including carbapenemase-producing organisms and Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to other beta-lactams. It’s reserved for infections for which there are no alternative options.
New: Novel macrolide fidaxomicin is reserved for treating the second or greater recurrence of C. difficile infection in children. Vitamin C is not beneficial in adults with sepsis and ARDS.
Chapter 2: CVD
AF: Catheter ablation is recommended to some drug-refractory, paroxysmal AF to decrease symptom burden. In study: Renal nerve denervation has been proposed as an adjunctive therapy to catheter ablation in hypertensive patients with AF. Alcohol abstinence lowers the risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation among regular drinkers.
VF: For nonshockable rhythms, epinephrine is given as soon as feasible during CPR, while for shockable rhythms epinephrine is given after initial defibrillation attempts are unsuccessful. Avoid vasopressin use.
All patients with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) should receive a P2Y12 inhibitor. For patients undergoing an invasive approach, either prasugrel or ticagrelor has been preferred to clopidogrel. Long-term antithrombotic therapy in patients with stable CAD and AF has newly been modified as either anticoagulant (AC) monotherapy or AC plus a single antiplatelet agent.
Long-term antithrombotic therapy (rivaroxaban +/- aspirin) is recommended for patients with AF and stable CAD. Ticagrelor plus aspirin is recommended for some patients with CAD and diabetes.
VTE (venous thromboembolism): LMW heparin or oral anticoagulant edoxaban is the first-line anticoagulants in patients with cancer-associated VTE.
Dosing of warfarin for VTE prophylaxis in patients undergoing total hip or total knee arthroplasty should continue to target an INR of 2.5.
Chapter 3: Resp. Disorders
Asthma: Benralizumab is an IL-5 receptor antibody that is used as add-on therapy for patients with severe asthma and high blood eosinophil counts.
Recombinant GM-CSF is still reserved for patients who cannot undergo, or who have failed, whole lung lavage.
Pulmonary embolism (PE): PE response teams (PERT, with specialists from vascular surgery, critical care, interventional radiology, emergency medicine, cardiac surgery, and cardiology) are being increasingly used in management of patients with intermediate and high-risk PE.
Although high-sensitivity D-dimer testing is preferred, protocols that use D-dimer levels adjusted for pretest probability may be an alternative to unadjusted D-dimer in patients with a low pretest probability for PE.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Newly approved capmatinib is for advanced NSCLC associated with a MET mutation, and selpercatinib for those with advanced RET fusion-positive. Atezolizumab was newly approved for PD-L1 high NSCLC.
Circulating tumor DNA tests for cancers such as NSCLC are increasingly used as “liquid biopsy”. Due to its limited sensitivity, NSCLC patients who test (-) for the biomarkers should undergo tissue biopsy.
Cystic Fibrosis (CF): Tx: CFTR modulator therapy (elexacaftor-tezacaftor-ivacaftor) is recommended for patients ≥12 years with the F508del variant.
Vitamin E acetate has been implicated in the development of electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use associated lung injury.
Chapter 4: Digestive and Nutritional Disorders
Comparison of Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC):
Common: They are two major types of chronic cholestatic liver disease, with fatigue, pruritus, obstructive jaundice, similar biochemical tests of copper metabolism, overlapped histology (which is not diagnostic), destructive cholangitis, and both ultimately result in cirrhosis and hepatic failure. (1) PBC: Mainly in middle-aged women, with keratoconjunctivitis sicca, hyperpigmentation, and high titer of antimitochondrial Ab (which is negative for PSC). (2) PSC: Primarily in middle-aged men, with chronic ulcerative colitis (80%), irregular intra- and extra-hepatic bile ducts, and anti-centromere Ab (+).
CRC: Patients with colorectal adenomas at high risk for subsequent colorectal cancer (CRC) (≥3 adenomas, villous type with high-grade dysplasia, or ≥10 mm in diameter) are advised short follow-up intervals for CRC surveillance. Pembrolizumab was approved for the first-line treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic DNA mismatch repair (dMMR) CRC.
UC and CRC: Patients with extensive colitis (not proctitis or left-sided colitis) have increased CRC risk.
Eradication of H. pylori: adding bismuth to clarithromycin-based triple therapy for patients with risk factors for macrolide resistance.
Thromboelastography and rotational thromboelastometry are bedside tests recommended for patients with cirrhosis and bleeding.
Pancreatic cancer: Screening for patients at risk for hereditary pancreatic cancer (PC): Individuals with mutations in the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated gene and one first-degree relative with PC can be screened with endoscopic ultrasound and/or MRI/magnetic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Olaparib is recommended for BRCA-mutated advanced pancreatic cancer after 16 weeks of initial platinum-containing therapy.
HCC (unresectable): New first-line therapy is a TKI (sorafenib or sunitinib) or immune checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, +/- doxorubicin. Monitor kidney toxicity for these drugs.
UC: Ustekinumab (-umab) anti-interleukin 12/23 antibody, is newly approved for the treatment of UC.
Crohn disease: The combination of partial enteral nutrition with the specific Crohn disease exclusion diet is a valuable alternative to exclusive enteral nutrition for induction of remission.
Obesity: Lorcaserin, a 5HT2C agonist that can reduce food intake, has been discontinued in the treatment of obesity due to increased malignancies (including colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancers).
Diet and cancer deaths: A low-fat diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and grains experienced fewer deaths resulted from many types of cancer.
Note that H2-blockers (-tidines) are no longer recommended due to the associated carcinogenic N-nitrosodimethylamine.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST):
GIST is a rare type of tumor that occurs in the GI tract, mostly in the stomach (50%) or small intestine. As a sarcoma, it’s the #1 common in the GI tract. It is considered to grow from specialized cells in the GI tract called interstitial cells of Cajal, associated with high rates of malignant transformation.
Clinical features and diagnosis: Most GISTs are asymptomatic. Nausea, early satiety, bloating, weight loss, and signs of anemia may develop, depending on the location, size, and pattern of growth of the tumor. They are best diagnosed by CT scan and mostly positive staining for CD117 (C-Kit), CD34, and/or DOG-1.
Treatment: Approaches include resection of primary low-risk tumors, resection of high-risk primary or metastatic tumors with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) imatinib for 12 months, or if the tumor is unresectable, neoadjuvant imatinib followed by resection. Radiofrequency ablation has shown to be effective when surgery is not suitable. Newer therapies of ipilimumab, nivolumab, and endoscopic ultrasound alcohol ablation have shown promising results. Avapritinib or ripretinib (new TKI) is recommended for advanced unresectable or metastatic GIST with PDGFRA mutations.
Anal Cancer:
Anal cancer is uncommon and more similar to a genital cancer than it is to a GI malignancy by etiology. By histology, it is divided into SCC (#1 common) and adenocarcinoma. Anal cancer (particularly SCC among women) has increased fast over the last 30 years and may surpass cervical cancer to become the leading HPV-linked cancer in older women. A higher incidence has been associated with HPV/HIV infection, multiple sexual partners, genital warts, receptive anal intercourse, and cigarette smoking. SCCs that arise in the rectum are treated as anal canal SCCs.
Clinical features and diagnosis: 1. Bleeding (#1) and itching (often mistaken as hemorrhoids). Later on, patients may develop focal pain or pressure, unusual discharges, and lump near the anus, and changes in bowel habits. 2. Diagnosis is made by a routine digital rectal exam, anoscopy/proctoscopy plus biopsy, +/- endorectal ultrasound.
Treatment: Anal cancer is primarily treated with a combination of radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery—especially for patients failing the above therapy or for true perianal skin cancers.
Chapter 5: Endocrinology
Diabetes (DM): Liraglutide can be added as a second agent for type-2 DM patients who fail monotherapy with metformin or as a third agent for those who fail combination therapy with metformin and insulin. Metformin is suggested to prevent type 2 DM in high-risk patients in whom lifestyle interventions fail to improve glycemic indices. Metabolic (bariatric) surgery improves glucose control in obese patients with type 2 DM and also reduce diabetes-related complications, such as CVD. Teprotumumab, an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor, can be used for Graves’ orbitopathy if corticosteroids are not effective. Subclinical hypothyroidism should not be routinely treated (with T4) in older adults with TSH <10 mU/L.
Chapter 6: Hematology & Immunology
Anticoagulants: Apixaban is preferred to warfarin for atrial fibrillation with osteoporosis because it lowers the risk of fracture. Rivaroxaban is inferior to warfarin for antiphospholipid syndrome.
Cancer-associated VTE: LMW heparin or oral edoxaban is the first-line anticoagulant prophylaxis.
NH-Lymphoma Tx: New suggestion is four cycles of R(rituximab)-CHOP for limited stage (stage I or II) diffuse large B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (DLBCL) without adverse features. New suggestions: selinexor is for patients with ≥2 relapses of DLBCL, and tafasitamab plus lenalidomide is for patients with r/r DLBCL who are not eligible for autologous HCT.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T (NK) immunotherapy is newly suggested for refractory lymphoid malignancies, with less toxicity than CAR-T therapy. Polatuzumab + bendamustine + rituximab (PBR) is an alternative to CAR-T, allogeneic HCT, etc. for multiply relapsed diffuse large B-C NHL.
Refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma (r/r cHL) is responsive to immune checkpoint inhibition with pembrolizumab or nivolumab, including those previously treated with brentuximab vedotin or autologous transplantation.
Mantle cell lymphoma: Induction therapy is bendamustine + rituximab or other conventional chemoimmunotherapy rather than more intensive approaches. CAR-T cell therapy is for refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
AML: Gilteritinib is a new alternative to intensive chemotherapy for patients with FLT3-mutated r/r AML.
Oral decitabine plus cedazuridine is suggested for MDS and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
Multiple myeloma (MM): Levofloxacin prophylaxis is suggested for patients with newly diagnosed MM during the first three months of treatment. For relapsed MM: Three-drug regimens (daratumumab, carfilzomib, and dexamethasone) are newly recommended.
Transplantation: As the transplant waitlist continues to grow, there may be an increasing need of HIV-positive to HIV-positive transplants.
Porphyria: Porphyria is a group of disorders (mostly inherited) caused by an overaccumulation of porphyrin, which results in hemoglobin and neurovisceral dysfunctions, and skin lesions. Clinical types, features, and diagnosis: I. Acute porphyrias: 1. Acute intermittent porphyria: Increased porphobilinogen (PBG) causes attacks of abdominal pain (90%), neurologic dysfunction (tetraparesis, limb pain and weakness), psychosis, and constipation, but no rash. Discolored urine is common. 2. ALA (aminolevulinic acid) dehydratase deficiency porphyria (Doss porphyria): Sensorimotor neuropathy and cutaneous photosensitivity. 3. Hereditary coproporphyria: Abdominal pain, constipation, neuropathies, and skin rash. 4. Variegate porphyria: Cutaneous photosensitivity and neuropathies. II. Chronic porphyrias: 1. Erythropoietic porphyria: Deficient uroporphyrinogen III synthase leads to cutaneous photosensitivity characterized by blisters, erosions, and scarring of light-exposed skin. Hemolytic anemia, splenomegaly, and osseous fragility may occur. 2. Cutaneous porphyrias–porphyria cutanea tarda: Skin fragility, photosensitivity, and blistering; the liver and nervous system may or may not be involved. III. Lab diagnosis: Significantly increased ALA and PBG levels in urine have 100% specificity for most acute porphyrias. Normal PBG levels in urine can exclude acute porphyria. Treatment: 1. Acute episodes: Parenteral narcotics are indicated for pain relief. Hemin (plasma-derived intravenous heme) is the definitive treatment and mainstay of management. 2. Avoidance of sunlight is the key in treating cutaneous porphyrias. Afamelanotide may permit increased duration of sun exposure in patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria.
Chapter 7: Renal & UG
Membranous nephropathy (MN): Rituximab is a first-line therapy in patients with high or moderate risk of progressive disease and requiring immunosuppressive therapy.
Diabetes Insipidus (DI): Arginine-stimulated plasma copeptin assays are newly used to diagnose central DI and primary polydipsia, often alleviating the need for water restriction, hypertonic saline, and exogenous desmopressin.
Prostate cancer: Enzalutamide (new androgen blocker) is available for metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer. Cabazitaxel, despite its great toxicity, is suggested as third-line agent for metastatic prostate cancer. Either early salvage RT or adjuvant RT is acceptable after radical prostatectomy for high-risk disease.
UG cancers: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab is suggested in metastatic renal cell carcinoma for long-term survival.
Enfortumab vedotin is suggested in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Maintenance avelumab is recommended with other chemotherapy in advanced urothelial bladder cancer. Pyelocalyceal mitomycin is suggested for low-grade upper tract urothelial carcinomas.
Chapter 8: Rheumatology
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors (upadacitinib, filgotinib) are new options for active, resistant RA and ankylosing spondylitis.
Graves’ orbitopathy: new therapy–teprotumumab, an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor.
Chapter 9: Neurology & Special Senses
Epilepsy: Cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative that inhibits Na-channels, provides a new treatment option for patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy. A benzodiazepine plus either fosphenytoin, valproate, or levetiracetam is recommended as the initial treatment of generalized convulsive status epilepticus.
Migraine: Lasmiditan is a selective 5H1F receptor agonist that lacks vasoconstrictor activity, new therapy for patients with relative contraindications to triptans due to cardiovascular risk factors.
Stroke: New recommendation for cerebellar hemorrhages >3 cm in diameter is surgical evacuation. TBI: Antifibrolytic agent tranexamic acid is newly recommended for moderate and severe acute traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Ofatumumab is a new agent that may delay progression of MS.
Chapter 10: Dermatology
Minocycline foam is a new topical drug option for moderate to severe acne vulgaris.
Melanloma: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in metastatic melanoma has confirmed long-term survival. With sun-protective behavior, melanoma incidence is decreasing.
New: Tazemetostat is suggested in patients with locally advanced or metastatic epithelioid sarcoma (rare and aggressive) ineligible for complete surgical resection.
Psoriasis: New therapies for severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a TNF-alpha inhibitor (infliximab or adalimumab, golimumab) or IL-inhibitor (etanercept or ustekinumab) is effective. Ixekizumab is a newly approved monoclonal antibody against IL-17A. Clinical data support vigilance for signs of symptoms of malignancy in patients with psoriasis.
Chapter 11: GYH
Breast cancer: Although combined CDK 4/6 and aromatase inhibition is an effective strategy in older adults with advanced receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, toxicities (myelosuppression, diarrhea, and increased creatinine) should be carefully monitored. SC trastuzumab and pertuzumab is newly recommended for HER2-positive breast cancer.
Whole breast irradiation is suggested for most early-stage breast cancers treated with lumpectomy. Accelerated partial breast irradiation can be an alternative for women ≥50 years old with small (≤2 cm), hormone receptor-positive, node-negative tumors.
Endocrine therapy is recommended for breast cancer prevention in high-risk postmenopausal women.
Uterine fibroids: Elagolix (oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist) in combination with estradiol and norethindrone is for treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) due to uterine fibroids.
Chapter 12: OB
Table 12-6: Active labor can start after OS > 4cm, and 6cm is relatively more acceptable but not a strict number.
Table 12-7: Preeclampsia is a multisystem progressive disorder characterized by the new onset of hypertension and proteinuria, or of hypertension and significant end-organ dysfunction with or without proteinuria, in the last half of pregnancy or postpartum. Once a diagnosis of preeclampsia is established, testing for proteinuria is no longerdiagnostic or prognostic. “proteinuria>5g/24hours” may only indicate the severity.
Mole: For partial moles, obtain a confirmatory hCG level one month after normalization; for complete moles, reduce monitoring from 6 to 3 months post-normalization.
Chapter 14: EM
SHOCK RESUSCITATION
Emergency treatment—critical care!
“A-B-C”: Breathing: …In mechanically ventilated adults with critical illness in ICU, intermittent sedative-analgesic medications (morphine, propofol, midazolam) are recommended.
Chapter 15: Surgery
Surgery and Geriatrics: Hemiarthroplasty is a suitable option for patients who sustain a displaced femoral neck fracture.
Chapter 16: Psychiatry
Depression: Both short-term and maintenance therapies with esketamine are beneficial for treatment-resistant depression.
Schizophrenia: Long-term antipsychotics may decrease long-term suicide mortality.
Narcolepsy: Pitolisant is a novel oral histamine H3 receptor inverse agonist used in narcolepsy patients with poor response or tolerate to other medications. Oxybate salts, a lower sodium mixed-salt formulation of gamma hydroxybutyrate is for treatment of narcolepsy with cataplexy.
Chapter 17: Last Chapter
PEARLS—Table 17-9: Important Immunization Schedules for All (2020, USA)
Vaccine Birth 2M 4M 6M 12-15M 2Y 4-6Y 11-12Y Sum
HAV 1st 2nd (2-18Y) 2 doses
HBV 1st 2nd 3rd (6-12M) 3 doses
DTaP 1st 2nd 3rd 4th (15-18M) 5th + Td per 10Y
IPV 1st 2nd 3rd (6-18M) 4th 4 doses
Rotavirus 1st 2nd 2 doses
Hib 1st 2nd (3rd) (3-4th) 3-4 doses
MMR 1st 2nd 2 doses
Varicella 1st 2nd + Shingles at 60Y
Influenza 1st (IIV: 6-12Y; LAIV: >2Y (2nd dose) 1-2 doses annually
PCV 1st 2nd 3rd 4th PCV13+PPSV at 65Y
MCV (Men A, B) 1st Booster at 16Y
HPV 9-12Y starting: <15Y: 2 doses (0, 6-12M); >15Y or immunosuppression: 3 doses (0, 2, 6M).
Chapter 17 HYQ answer 22: No routine prostate cancer screening (including PSA) is recommended and answer “G” is still correct–PSA
screening among healthy men is not routinely done but should be indicated in a patient with two risk factors.
9 notes
·
View notes